
Modeling Post-level Sentiment Evolution in Online Forum Threads
Dumitru-Clementin Cercel
1
and Stefan Trausan-Matu
1,2
1
Faculty of Automatic Control and Computers, University POLITEHNICA of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania
2
Romanian Academy Research Institute for Artificial Intelligence, Bucharest, Romania
Keywords: Opinion Propagation, Post-Level Sentiment Analysis, Graph Theory, Forum Threads.
Abstract: Opinion propagation analysis in online forum threads is a relatively new research field emerging in the
context of the increasing popularity of forums. Many changes occur over time in online forum threads since
new users intervene in the discussion and express their opinions. In this paper, we propose a novel task in
the analysis of opinion propagation in online forum threads, i.e. the modeling of post-level sentiment
evolution in online forum threads. This task consists in the analysis of post-level sentiment evolution in an
online forum thread in order to obtain a simplified model of this evolution. Based on opinion mining, graph
theory, and post-level sentiment analysis, our method comprises five steps: removal of posts containing only
facts, post-level sentiment identification, removal of posts with neutral sentiment, aggregation of parent-
child vertices, and aggregation of sibling vertices. We evaluate the proposed method on real-world forum
threads, and the results of our experiments are presented in the visualization interfaces.
1 INTRODUCTION
Contemporary societies are experiencing the
prominent phenomenon of online interaction through
social media, which has huge implications for both
individuals and companies. The propagation of
opinions in social media is a dynamic phenomenon
involving a considerable number of people who
establish or end different types of relationships
between them and also produce vast quantities of
data by giving or changing their opinions. The
propagation of opinions has significantly different
characteristics compared to all previous periods: it is
rapid, less costly, and therefore more widespread
than ever.
Several studies have addressed opinion
propagation in social media. Ku et al. (Ku et al.,
2006) analyzed the opinion tracking in a news
corpus for four candidates during Taiwan’s 2000
presidential election. Recently, a method for
studying the problem of opinion propagation in
online forum threads has been proposed at user
level (Cercel and Trausan-Matu, 2014c). For more
details about the analysis of opinion propagation in
online social networks, see (Cercel and Trausan-
Matu, 2014b).
Being a type of social media, a forum thread can
be modeled as a post-reply graph, where vertices are
posts, and edges are replies between posts. The
post-reply graph associated with an online forum
thread is increasing by adding both new vertices and
edges as new posts appear over time. In this paper
we address the modeling of post-level sentiment
evolution in online forum threads as a new task of
opinion propagation analysis in online forum
threads.
2 THE ARCHITECTURE OF THE
PROPOSED METHOD
We divided our method for the post-level sentiment
evolution task in an online forum thread into the
following steps:
Preprocessing of each post in the initial post-
reply graph at time step t
τ
, τ
*. The initial
post-reply graph at time step t
τ
, τ
*, is
denoted by G
0
DT
(t
τ
)(V
0
DT
(t
τ
), E
0
DT
(t
τ
)).
Filtration of the post-reply graph
G
0
DT
(t
τ
)(V
0
DT
(t
τ
), E
0
DT
(t
τ
)) in order to remove the
posts that contain only facts and do not contain
opinions about the subject of the forum thread.
The post-reply graph obtained at the end of this
step is denoted by G
1
DT
(t
τ
)(V
1
DT
(t
τ
), E
1
DT
(t
τ
)).
Identification of the sentiment of each post from
588
Cercel D. and Trausan-Matu S..
Modeling Post-level Sentiment Evolution in Online Forum Threads.
DOI: 10.5220/0005286605880593
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2015), pages 588-593
ISBN: 978-989-758-074-1
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

the previously filtered graph G
1
DT
(t
τ
)(V
1
DT
(t
τ
),
E
1
DT
(t
τ
)).
Filtration of the post-reply graph
G
1
DT
(t
τ
)(V
1
DT
(t
τ
), E
1
DT
(t
τ
)) in order to remove the
posts with neutral sentiment. The post-reply
graph obtained at the end of this step is denoted
by G
2
DT
(t
τ
)(V
2
DT
(t
τ
), E
2
DT
(t
τ
)).
Aggregation of the parent-child vertices from the
previously filtered graph G
2
DT
(t
τ
)(V
2
DT
(t
τ
),
E
2
DT
(t
τ
)). The multipost-reply graph obtained at
the end of this step is denoted by
G
3
DT
(t
τ
)(V
3
DT
(t
τ
), E
3
DT
(t
τ
)).
Aggregation of the sibling vertices from the
previously aggregated graph G
3
DT
(t
τ
)(V
3
DT
(t
τ
),
E
3
DT
(t
τ
)). The aggregated multipost-reply graph
obtained at the end of this step is denoted by
G
4
DT
(t
τ
)(V
4
DT
(t
τ
), E
4
DT
(t
τ
)).
In the preprocessing step, we apply specific
techniques of natural language processing such as
tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, syntactic
parsing, and coreference resolution (Manning and
Schütze, 1999) to each post in the post-reply graph
G
0
DT
(t
τ
) (V
0
DT
(t
τ
), E
0
DT
(t
τ
)). In the next subsections,
we describe the remaining step of the method
proposed by us for the post-level sentiment
evolution task.
2.1 Removing Posts That Contain Only
Facts
In this step, we remove the vertices that do not
contain opinions about the subject of the forum
thread. The other vertices of the post-reply graph
G
0
DT
(t
τ
)(V
0
DT
(t
τ
), E
0
DT
(t
τ
)) will not be changed. The
outline of the algorithm for this step is given in
Algorithm 1. We perform the initialization of the
post-reply graph G
1
DT
(t
τ
)(V
1
DT
(t
τ
), E
1
DT
(t
τ
)) by using
the post-reply graph G
0
DT
(t
τ
)(V
0
DT
(t
τ
), E
0
DT
(t
τ
)) (A1 :
1-2). Then, we apply the Breadth First Search
algorithm (Cormen et al., 2009) from the root vertex
v
1
and save its output in a list (A1 : 3).
For each current vertex in the list, different from
the root vertex v
1
, we follow the next steps. First, we
obtain pairs in the form of (noun term, opinion
word) from the current vertex, where the noun term
is semantically related to a word that appears in the
subject of the forum thread (A1 : 8) For more details
about this substep, see (Cercel and Trausan-Matu,
2014c). If there are no pairs (noun term, opinion
word) in the current vertex, we eliminate this vertex
(A1 : 9-17). To this end, we obtain the parent vertex
of the current vertex (A1 : 10). As regards each child
vertex of the current vertex, we create an edge
between each child vertex and the current vertex’s
parent vertex (A1 : 14). Finally, we eliminate the
current vertex from the set V
1
DT
(t
τ
) (A1 : 15).
Algorithm 1 (A1): Removing Posts that Contain only Facts
Input: G
0
DT
(t
τ
)(V
0
DT
(t
τ
), E
0
DT
(t
τ
))
Output: G
1
DT
(t
τ
)(V
1
DT
(t
τ
), E
1
DT
(t
τ
))
1: V
1
DT
(t
τ
) ← V
0
DT
(t
τ
)
2: E
1
DT
(t
τ
) ← E
0
DT
(t
τ
)
3: M ← BreadthFirstSearch(v
1
)
4: for each node crtNode
in M do
5: if crtNode = v
1
then
6: continue
7: endif
8: Ω ← FilteringDependencyRelationsfromPost(crtNode)
9: if Ω = ∅ then
10: parentNode ← GetParentNode(crtNode)
11: N ← GetChildrenNodes(crtNode)
12: for each node childNode
in N do
13: E
1
DT
(t
τ
) ← E
1
DT
(t
τ
) \ (childNode, crtNode)
14: E
1
DT
(t
τ
) ← E
1
DT
(t
τ
) ∪ (childNode, parentNode)
15: V
1
DT
(t
τ
) ← V
1
DT
(t
τ
) \ {crtNode}
16: end for
17: endif
18: endfor
2.2 Post-level Sentiment Identification
We determine the sentiment of a post by taking into
account the sentiment strength of the opinion words
from this post. Let p
P
DT
(t
τ
) be a post in the forum
thread. The sentiment score for the post p is given by
the following formula:
4
1
44
11
()
()
|| ||||
i
ii
iwSwS
JR
ii
JRV
ii
score w
sentimentScore p
SSS
4
44
11
()
|| ||||
wS
V
ii
JRV
ii
score w
SSS
(1)
where: score(w) is the sentiment score for the
opinion word w; S
1
J
is the set of superlative
adjectives; S
2
J
is the set of comparative adjectives of
superiority; S
3
J
is the set of comparative adjectives of
inferiority; S
4
J
is the set of adjectives of other
degree; S
1
R
is the set of superlative adverbs; S
2
R
is
the set of comparative adverbs of superiority; S
3
R
is
the set of comparative adverbs of inferiority; S
4
R
is
the set of adverbs of other degree; S
V
is the set of
verbs; |S| denotes the power set of S.
To identify the sentiment score of an opinion
word, we used SentiWordNet (Baccianella and
Sebastiani, 2010). The corresponding algorithm is
described in (Cercel and Trausan-Matu, 2014a). The
variables
,
,
, and
take the values 0.9, 0.6,
-0.6, and 0.3, respectively. The post p
P
DT
(t
τ
) is
considered to express a positive sentiment if
sentimentScore(p)
(0, 1], a negative sentiment if
ModelingPost-levelSentimentEvolutioninOnlineForumThreads
589

sentimentScore(p)
[-1, 0), or a neutral sentiment if
sentimentScore(p) = 0.
2.3 Removing Posts with Neutral
Sentiment
In this step, the removed vertices do not contain
opinions with positive or negative sentiments about
the subject of the forum thread, but only opinions
with neutral sentiment. The outline of this algorithm
is given in Algorithm 2. We apply the Breadth First
Search algorithm from the root vertex v
1
and save its
output in a list (A2 : 3). For each current vertex in
the list, different from the root vertex v
1
, we follow
the next steps. First, we calculate the sentiment score
of the current vertex by using Formula 1 (A2 : 8). If
this sentiment score is non-zero, we obtain the
parent vertex of the current vertex (A2 : 10) and
create an edge between the current vertex’s each
child vertex and the current vertex’s parent vertex
(A2 : 14). Finally, we eliminate the current vertex
from the set V
2
DT
(t
τ
) (A2 : 15).
Algorithm 2 (A2): Removing Posts with Neutral
Sentiment
Input: G
1
DT
(t
τ
)(V
1
DT
(t
τ
), E
1
DT
(t
τ
))
Output: G
2
DT
(t
τ
)(V
2
DT
(t
τ
), E
2
DT
(t
τ
))
1: V
2
DT
(t
τ
)← V
1
DT
(t
τ
)
2: E
2
DT
(t
τ
) ← E
1
DT
(t
τ
)
3: M ← BreadthFirstSearch(v
1
)
4: for each node crtNode
in M do
5: if crtNode = v
1
then
6: continue
7: endif
8: crtNodeScore ← sentimentScore(crtNode)
9: if crtNodeScore = 0 then
10: parentNode ← GetParentNode(crtNode)
11: N ← GetChildrenNodes(crtNode)
12: for each node childNode
in N do
13: E
1
DT
(t
τ
) ← E
2
DT
(t
τ
) \ (childNode, crtNode)
14: E
2
DT
(t
τ
) ← E
2
DT
(t
τ
) ∪ (childNode, parentNode)
15: V
2
DT
(t
τ
) ← V
2
DT
(t
τ
) \ {crtNode}
16: end for
17: endif
18: endfor
2.4 Aggregation of Parent-Child
Vertices
The aggregation of parent-child vertices occurs
according to the following definition:
Definition 1 (Aggregation of Parent-Child
Vertices). Given at time step t
τ
, τ
*, the forum
thread (T
DT
, S
DT
, U
DT
(t
τ
), P
DT
(t
τ
), R
DT
(t
τ
)) from an
online forum and its corresponding post-reply graph
G
2
DT
(t
τ
)(V
2
DT
(t
τ
), E
2
DT
(t
τ
)), then two vertices v
i
,
v
k
V
2
DT
(t
τ
), v
i
= (v
i
p
, v
i
u
, v
i
tm
, v
i
op
), v
k
= (v
k
p
, v
k
u
, v
k
tm
,
v
k
op
), (v
i
,
v
k
)
E
2
DT
(t
τ
) will be merged if these two
vertices v
i
,
v
k
V
2
DT
(t
τ
) have the same sentiment
(positive or negative). The result of the aggregation
of the vertices v
i
,
v
k
V
2
DT
(t
τ
) is a single vertex
v
r
= (v
r
p
, v
r
u
, v
r
tm
, v
r
op
)
V
2
DT
(t
τ
) characterized
by: v
r
p
= v
i
p
∪
v
k
p
, v
r
u
= v
i
u
∪
v
k
u
, v
r
tm
= v
i
tm
∪
v
k
tm
,
and v
r
op
= v
i
op
∪
v
k
op
.
Let us consider an example for illustrating this
definition. In Figure 1(a), the vertex v
l
is a reply to
the vertex v
k
, the vertex v
k
is a reply to the vertex v
j
,
and the vertex v
j
is a reply to the vertex v
i.
The
vertices v
i
, v
j
and v
k
have the same positive sentiment
and will be aggregated according to Definition 1.
The result is the vertex v
r
with positive sentiment.
The vertex v
l
is a reply to the vertex v
r
.
In contrast,
in Figure 1(b), on the path from the vertex v
l
to
the vertex v
i
there is an alternation between vertices
with positive and negative sentiments. Therefore,
Definition 1 cannot be applied to this second
example.
Figure 1: (a) Example of aggregation of parent-child
vertices; (b) Example of a non-possible aggregation of
parent-child vertices.
The outline of the algorithm that transforms the
post-reply graph G
2
DT
(t
τ
)(V
2
DT
(t
τ
), E
2
DT
(t
τ
)) into the
post-reply graph G
3
DT
(t
τ
)(V
3
DT
(t
τ
), E
3
DT
(t
τ
)) is given
in Algorithm 3. We apply the Breadth First Search
algorithm from the root vertex v
1
and save its output
in a list (A3 : 3). For each current vertex in the list,
we obtain its parent vertex (A3 : 5).
If the current vertex in the list is different from
the root vertex v
1
or the current vertex’s parent
vertex is different from the root vertex v
1
, we follow
the next steps (A3 : 6-8). First, we calculate the
sentiment score for the current vertex and its parent
vertex by using Formula 1 (A3 : 9-10). If the current
vertex and its parent vertex have the same sentiment
(negative or positive), we obtain the child vertices of
the current vertex (A3 : 12). Then, we create an edge
between the current vertex’s each child and the
current vertex’s parent vertex (A3 : 15). Moreover,
we update the components (the contents of the
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
590

post(s), the time step(s), the user(s), and the opinions
expressed in the post(s)) of the current vertex’s
parent vertex (A3 : 16). Finally, we eliminate the
current vertex from the set V
3
DT
(t
τ
) (A3 : 17).
Algorithm 3 (A3): Aggregation of Parent-Child Vertices
Input: G
2
DT
(t
τ
)(V
2
DT
(t
τ
), E
2
DT
(t
τ
))
Output: G
3
DT
(t
τ
)(V
3
DT
(t
τ
), E
3
DT
(t
τ
))
1: V
3
DT
(t
τ
)← V
2
DT
(t
τ
)
2: E
3
DT
(t
τ
)← E
2
DT
(t
τ
)
3: M ← BreadthFirstSearch(v
1
)
4: for each node crtNode
in M do
5: parentNode ← GetParentNode(crtNode)
6: if crtNode = v
1
or parentNode = v
1
then
7: continue
8: end if
9: crtNodeScore ← sentimentScore (crtNode)
10: parentNodeScore ← sentimentScore (parentNode)
11: if crtNodeScore * parentNodeScore > 0 then
12: N ← GetChildrenNodes(crtNode)
13: for each node childNode
in N do
14: E
3
DT
(t
τ
) ← E
3
DT
(t
τ
) \ (childNode, crtNode)
15: E
3
DT
(t
τ
) ← E
3
DT
(t
τ
) ∪ (childNode, parentNode)
16: InformationUpdate(parentNode, crtNode)
17: V
3
DT
(t
τ
) ← V
3
DT
(t
τ
) \ {crtNode}
18: end for
19: end if
20: end for
2.5 Aggregation of Sibling Vertices
The aggregation of sibling vertices occurs according
to the following definition:
Definition 2 (Aggregation of Sibling Vertices).
Given at time step t
τ
, τ
*, the forum thread
(T
DT
, S
DT
, U
DT
(t
τ
), P
DT
(t
τ
), R
DT
(t
τ
)) from an online
forum and its corresponding graph G
3
DT
(t
τ
)(V
3
DT
(t
τ
),
E
3
DT
(t
τ
)), then two vertices v
i
, v
k
V
3
DT
(t
τ
), v
i
= (v
i
p
,
v
i
u
, v
i
tm
, v
i
op
), v
k
= (v
k
p
, v
k
u
, v
k
tm
, v
k
op
), will be merged
if there is v
j
V
3
DT
(t
τ
) so that (v
i,
v
j
)
E
3
DT
(t
τ
), (v
k,
v
j
)
E
3
DT
(t
τ
), and the vertices v
i
,
v
k
V
3
DT
(t
τ
) have
the same sentiment (positive or negative). The
aggregation result of the sibling vertices v
i
,
v
k
V
3
DT
(t
τ
) is a single vertex v
r
= (v
r
p
, v
r
u
, v
r
tm
, v
r
op
)
V
4
DT
(t
τ
) characterized by v
r
p
= v
i
p
∪
v
k
p
, v
r
u
= v
i
u
∪
v
k
u
, v
r
tm
= v
i
tm
∪
v
k
tm
, and v
r
op
= v
i
op
∪
v
k
op
.
Let us consider an example for illustrating this
definition. In Figure 2, the vertex v
l
is a reply to the
vertex v
j
, and the vertex v
j
is a reply to the vertex v
i
.
Both vertices v
i
and v
k
have the same sentiment, and
their parent vertex v
s
is common. Applying the
definition of the aggregation of sibling vertices for
the two vertices v
i
and v
k
, we obtain the vertex v
r
of
positive sentiment, where the vertex v
r
is a reply to
the vertex v
s
.
Figure 2: Example of aggregation of sibling vertices.
The outline of the algorithm that transforms the
graph G
3
DT
(t
τ
)(V
3
DT
(t
τ
), E
3
DT
(t
τ
)) into the graph
G
4
DT
(t
τ
)(V
4
DT
(t
τ
), E
4
DT
(t
τ
)) is given in Algorithm 4.
Algorithm 4 (A4): Aggregation of Sibling Vertices
Input: G
3
DT
(t
τ
)(V
3
DT
(t
τ
), E
3
DT
(t
τ
))
Output: G
4
DT
(t
τ
)(V
4
DT
(t
τ
), E
4
DT
(t
τ
))
1: V
4
DT
(t
τ
) ← V
3
DT
(t
τ
)
2: E
4
DT
(t
τ
) ← E
3
DT
(t
τ
)
3: M ← {v
1
}
4: while M != ∅
5: positiveNodesList ← ∅
6: negativeNodesList ← ∅
7: crtNode ← RemoveNode(M)
8: N← GetChildrenNodes(crtNode)
9: for each node childNode
in N do
10: childNodeScore ← sentimentScore(childNode)
11: if childNodeScore > 0 then
12: if positiveNodesList = ∅ then
13: positiveNode ← childNode
14: else
15: positiveNode ← positiveNode ∪ {childNode}
16: V
4
DT
(t
τ
) ← V
4
DT
(t
τ
) \ {crtNode}
17: end if
18: end if
19: if childNodeScore < 0 then
20: if negativeNode = ∅ then
21: negativeNode ← childNode
22: else
23: negativeNode ← negativeNode ∪ {childNode}
24: V
4
DT
(t
τ
) ← V
4
DT
(t
τ
) \ {crtNode}
25: end if
26: end if
27: end for
28: if positiveNodesList != ∅ then
29: for each node childNode
in positiveNodesList do
30: AddNode(M, childNode)
31: end for
32: end if
33: if negativeNodesList != ∅ then
34: for each node childNode
in negativeNodesList do
35: AddNode(M, childNode)
36: end for
37: end if
38: end while
We can define the aggregated multipost-reply graph
G
4
DT
(t
τ
)(V
4
DT
(t
τ
), E
4
DT
(t
τ
)), as follows:
Definition 3 (Aggregated Multipost-Reply
Graph). Given at time step t
τ
, τ
*, a forum thread
ModelingPost-levelSentimentEvolutioninOnlineForumThreads
591
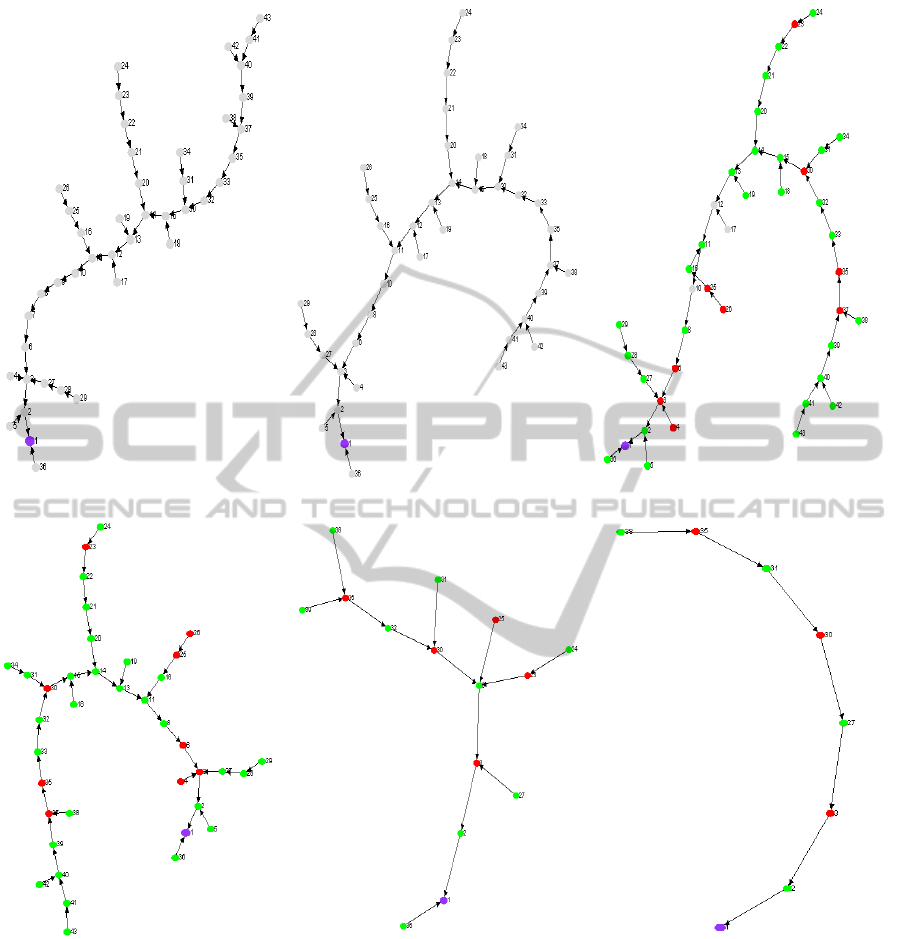
(a) Graph G
0
DT
(t
τ
)(V
0
DT
(t
τ
), E
0
DT
(t
τ
)) (b) Graph G
1
DT
(t
τ
)(V
1
DT
(t
τ
), E
1
DT
(t
τ
))
(c) Graph G
1
DT
(t
τ
)(V
1
DT
(t
τ
), E
1
DT
(t
τ
))
with post-level sentiment analysis
(d) Graph G
2
DT
(t
τ
)(V
2
DT
(t
τ
), E
2
DT
(t
τ
)) (e) Graph G
3
DT
(t
τ
)(V
3
DT
(t
τ
), E
3
DT
(t
τ
))
(f) Graph G
4
DT
(t
τ
)(V
4
DT
(t
τ
), E
4
DT
(t
τ
))
Figure 3: Modeling of post-level sentiment evolution in the forum thread at time step t
τ
= t
43
.
(T
DT
, S
DT
, U
DT
(t
τ
), P
DT
(t
τ
), R
DT
(t
τ
)) from an online
forum and its corresponding graph G
3
DT
(t
τ
)(V
3
DT
(t
τ
),
E
3
DT
(t
τ
)) obtained according to Algorithm 3, then the
forum thread is associated with an oriented graph
G
4
DT
(t
τ
)(V
4
DT
(t
τ
), E
4
DT
(t
τ
)) by applying Algorithm 4,
where:
V
4
DT
(t
τ
) = {v’’
j
| v’’
j
= (
⋃
,
⋃
,
⋃
,
⋃
),
P
DT
(t
τ
),
U
DT
(t
τ
),
,
OS
d
DT
} is the set of vertices in the graph
G
4
DT
(t
τ
) so that, if v’’
i
, v’’
j
, v’’
k
V
4
DT
(t
τ
),
(v’’
i
, v’’
k
) E
4
DT
(t
τ
), and (v’’
j
, v’’
k
) E
4
DT
(t
τ
),
the vertices v’’
i
and v’’
j
have opposite polarities
( v’’
i
has a positive sentiment, and v’’
j
has a
negative sentiment, and vice versa). A vertex v’’
j
in the set V
4
DT
(t
τ
) is a set of posts
⋃
written
by a set of users
⋃
at time steps
⋃
.
E
4
DT
(t
τ
) = {e’’
1
, e’’
2
, ..., e’’
s
} is the set of edges
in the graph G
4
DT
(t
τ
) so that, if e’ = (v’’
i
, v’’
j
)
ICAART2015-InternationalConferenceonAgentsandArtificialIntelligence
592

E
4
DT
(t
τ
), the set of posts corresponding to the
vertex v’’
i
is a reply to the set of posts
corresponding to the vertex v’’
j
,
and the vertices
v’’
i
and v’’
j
have opposite polarities.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
In this section, we present an example of applying
the proposed method on a real-world forum thread.
More concretely, we perform experiments on a
forum thread selected from the Internet Argument
Corpus (Walker et al., 2012). This forum thread has
the subject “What is God?” and comprises 43 posts
(i.e. t
τ
= t
43
). The corresponding post-reply graph
G
0
DT
(t
43
) at time step t
43
is represented in Figure 3(a).
In Figure 3, the vertices in the graphs are
represented by certain colors: the root vertex by the
purple color, the vertices with positive sentiment by
the green color, the vertices with negative sentiment
by the red color, and the vertices with neutral
sentiment by the gray color. Figure 3(b) shows the
experimental results for the post-reply graph
G
0
DT
(t
43
)(V
0
DT
(t
43
), E
0
DT
(t
43
)) after removing the
posts that contain only facts. All the vertices in the
resulted graph G
1
DT
(t
43
)(V
1
DT
(t
43
), E
1
DT
(t
43
)) contain
opinions about the subject of the forum thread.
In Figure 3(c), we represent the sentiment of
each post in the post-reply graph G
1
DT
(t
43
)(V
1
DT
(t
43
),
E
1
DT
(t
43
)) identified in the previous step. Figure 3(d)
shows the experimental results at the end of the step
of filtrating the post-reply graph G
1
DT
(t
43
)(V
1
DT
(t
43
),
E
1
DT
(t
43
)) to remove the posts with neutral sentiment.
Figure 3(e) shows the experimental results after
applying the step of aggregating the parent-child
vertices in the post-reply graph G
2
DT
(t
43
)(V
2
DT
(t
43
),
E
2
DT
(t
43
)). Figure 3(f) shows the experimental results
after applying the step of aggregating the sibling
vertices in the multipost-reply graph G
3
DT
(t
43
)
(V
3
DT
(t
43
), E
3
DT
(t
43
)) obtained in the previous step.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we address the task of modeling post-
level sentiment evolution in online forum threads.
Our method has five steps. The successive
application of these steps to the initial post-reply
graph G
0
DT
(t
τ
) (V
0
DT
(t
τ
), E
0
DT
(t
τ
)) will generate a
series of intermediate graphs. The aggregated
multipost-reply graph G
4
DT
(t
τ
)(V
4
DT
(t
τ
), E
4
DT
(t
τ
)) is
used to visualize in a simplified way the post-level
evolution of sentiments in the initial post-reply
graph G
0
DT
(t
τ
) (V
0
DT
(t
τ
), E
0
DT
(t
τ
)) at time step t
τ
, τ
*. In the future, our research on opinion
propagation will continue in other types of social
media than online forum threads.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been partially supported by the
FP7 ICT STREP project LTfLL (http://www.ltfll-
project.org/).
REFERENCES
Baccianella, A. E. S. and Sebastiani, F. (2010).
SentiWordNet 3.0: An Enhanced Lexical Resource for
Sentiment Analysis and Opinion Mining. In
Proceedings of the 7th conference on International
Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC).
European Language Resources Association (ELRA).
Cercel, D.-C. and Trausan-Matu, S. (2014a). Opinion
Influence Analysis in Discussion Forum Threads. In
Proceeding of 16th International Symposium on
Symbolic and Numeric Algorithms for Scientific
Computing (SYNASC). IEEE.
Cercel, D.-C. and Trausan-Matu, S. (2014b). Opinion
Propagation in Online Social Networks: A Survey. In
Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on
Web Intelligence, Mining and Semantics (WIMS).
ACM.
Cercel, D.-C. and Trausan-Matu, S. (2014c). User-Level
Opinion Propagation Analysis in Discussion Forum
Threads. In 16th International Conference on
Artificial Intelligence: Methodology, Systems,
Applications (AIMSA), pages 25–36, Springer
International Publishing.
Cormen, T. H., Leiserson, C. E., Rivest, R. L. and Stein,
C. (2009). Introduction to Algorithms, Third Edition,
The MIT Press.
Ku, L.-W., Lee, L.-Y. and Chen, H.-H. (2006). Opinion
extraction, summarization and tracking in news and
blog corpora. Proceedings of AAAI Spring
Symposium: Computational Approaches to Analyzing
Weblogs, pages 100–107.
Manning, C. D. and Schütze, H. (1999). Foundations of
statistical natural language processing, MIT Press.
Walker, M. A., Tree, J. E. F., Anand, P., Abbott, R. and
King, J. A. (2012). Corpus for Research on
Deliberation and Debate. In Proceedings of the 8th
conference on International Language Resources and
Evaluation (LREC). European Language Resources
Association (ELRA), pages 812–817.
ModelingPost-levelSentimentEvolutioninOnlineForumThreads
593
