
Selective Encryption of Medical Images
Aissa Belmeguenai, Lakhdar Grouche and Rafik Djemili
Laboratoire de Recherche en Electronique de Skikda, Universit´e 20 Aoˆut 1955- Skikda,
BP 26 Route d’El-hadaeik, Skikda, Algeria
Keywords:
Encryption by Region, Grain-128, Medical Images.
Abstract:
The transfer of image in the digital world plays a very important role, their security is an important issue,
and encryption is one of the ways to ensure security. Few applications like medical image security needs to
secure only selected region of the image. This work proposes a selective encryption approach for medical
images. The approach based on Grain-128 which provides the facilities of implementation of selective image
encryption and decryption. Several tests are done in order to prove the approach performance including visual
tests, key sensitivity, entropy analysis and correlation coefficient analysis.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sometimes the secure information is isolated in a one
region or few regions of the image then encrypt only
these regions, this allows us to gain considerabletime.
In this way, the encryption does not delay the pro-
cess; instead it can be inserted as an integral part of
the processing chain. In an application, when the se-
lective encryption is adopted, the choice of regions to
encrypt can be done in three ways which are: Man-
ual: The regions are defined using the mouse as an
electronic pen. Semi-automatic: In this case the re-
gions are determinedby programand always leave the
user the possibility of a manual correction (Malet and
al, 1988). For example, edge detection followed by a
correction or improperly closed contours that overlap.
Automatic: When data parts are in the same co-
ordinates location of the regions, these are prede-
fined and the choice is made consistently. Sometimes
the determinations of regions are programmed in first
then the result of processing will be used to encrypt
pilot regions. For example, for the following interest
area that carries a particularity in the image. During
an operation of Prenatal chromosome analysis and if
the presence of a chromosomal abnormality of num-
ber, this is in the form of a trisomy 13 or trisomy 21
(Geneix and al, 1988), (Malet and al, 1989). How-
ever, when establishing the caryotype of the patient,
the interest area (trisomy 13 or trisomy 21) from se-
cret information and that they should be within the
specialist doctor who has the sole authority to access
and pronounce these results to the patient.
To keep this information secret, this paper de-
scribes an implementation of Grain-128 for selective
encryption medical images. Several tests are done
for proving the system performance including visual
tests, correlation coefficient analysis, entropy analysis
and key sensitivity.
2 GRAIN-128
In this section we give a brief description of Grain-
128. The Grain-128 Keystream Generator was pro-
posed by Hell, Johansson, Maximov, and Meier
(M.Hell and W.Meier, 2006) as a variant of Grain-
v1 (Canniere and Preneel, 2005), (C. Cid and Kuri-
hara, 2009). The cipher consists of two 128-bit shift
registers, one linear feedback (LFSR), one nonlinear
feedback (NLFSR) and nonlinear Boolean functions
h.
The feedback polynomial of the NLFSR has alge-
braic degree of two, and h has degree of three. The
content of the LFSR is denoted by u
i
, u
i+1
, ...u
i+127
and the content of the NLFSR is denoted by
v
i
, v
i+1
, ...v
i+127
.
The LFSR is governed by the linear recurrence:
u
i+128
= u
i
⊕ u
i+7
⊕ u
i+38
⊕u
i+70
⊕ u
i+81
⊕ u
i+96
. (1)
The NLFSR is governed by the nonlinear recurrence:
93
Belmeguenai A., Grouche L. and Djemili R..
Selective Encryption of Medical Images.
DOI: 10.5220/0005301200930099
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2015), pages 93-99
ISBN: 978-989-758-091-8
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
v
i+128
= u
i
⊕ v
i
⊕ v
i+26
⊕ v
i+56
⊕ v
i+91
⊕ v
i+96
⊕
v
i+3
v
i+67
⊕ v
i+11
b
i+13
⊕ v
i+17
v
i+18
oplusv
i+27
v
i+59
(2)
⊕v
i+40
v
i+48
⊕ v
i+61
v
i+65
⊕ v
i+68
v
i+84
.
The contents of the LFSR and NLFSR represent the
state of the Grain-128.
The combining function h of Grain-128 produces
its output value based of the selected bits from the
NLFSR and the LFSR as:
h(i) = u
i+8
v
i+1
⊕ u
i+13
u
i+20
⊕v
i+95
u
i+42
⊕ u
i+60
u
i+79
(3)
⊕v
i+12
v
i+95
u
i+95
.
The output stream of the Grain-128 generates
from the selected bits from the LFSR and NLFSR
states and the output of h. it is computed as:
y(i) = ⊕
j∈A
v
i+ j
⊕ h(i) ⊕ u
i+93
. (4)
Where A = {2, 15, 36, 45, 64, 73, 89}.
3 SELECTIVE IMAGE
ENCRYPTION
In this section, one is interested in the selective im-
age encryption. In the selective image encryption,
the encryption is not applied to entire data but it is
applied to selected data only. Here the encryption
process is applied only to the selected regions of in-
terest leading to reduce the time for encryption see
(N. S. Kulkarni and Gupta, 2008), (Z. Brahimi, 2008)
and (Panduranga and al, 2013). Selection of interest-
ing regions are done manually or automatically based
on the application. To do this, we apply at the input
of cryptosystem both informations (encrypted image
and keystream generator) except that the keystream
generator is controlled by encrypted areas.
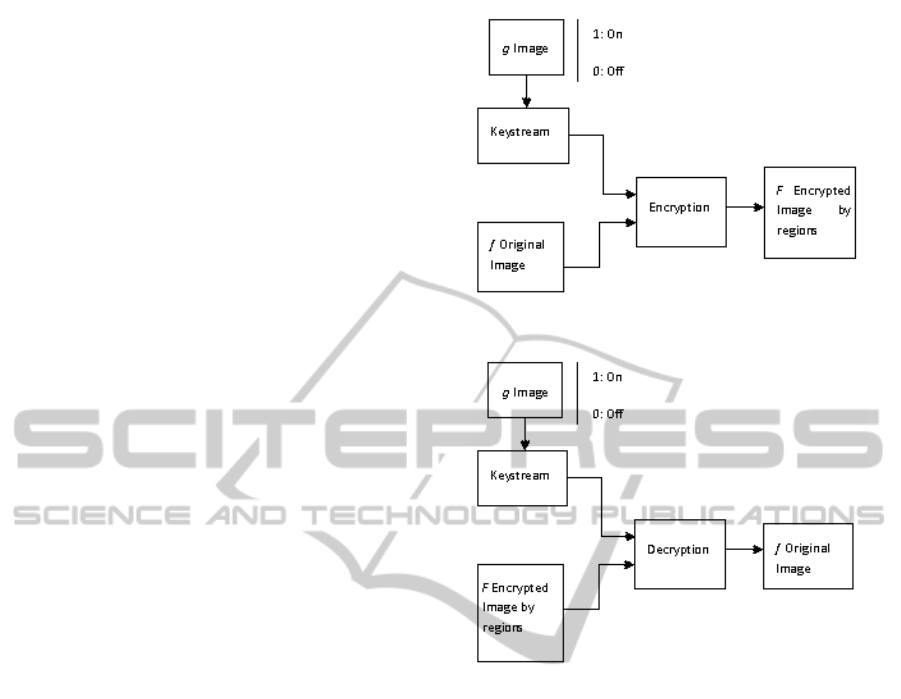
Let f be the original image and g be binary image
representing the regions to be encrypted, such that
g(i, j) =
1 if f(i, j) = to encrypt
0 if otherwise
(5)
At the reception the reverse operation is applied
to extract the hidden information. Figure 1 shows the
block diagram of selective image encryption process
and figure 2 shows the block diagram of selective im-
age decryption process.
Figure 1: Block diagram of selective image encryption pro-
cess.
Figure 2: Block diagram of selective image decryption pro-
cess.
4 PROPOSED SELECTIVE
IMAGE ALGORITHM
The proposed selective image algorithm is using the
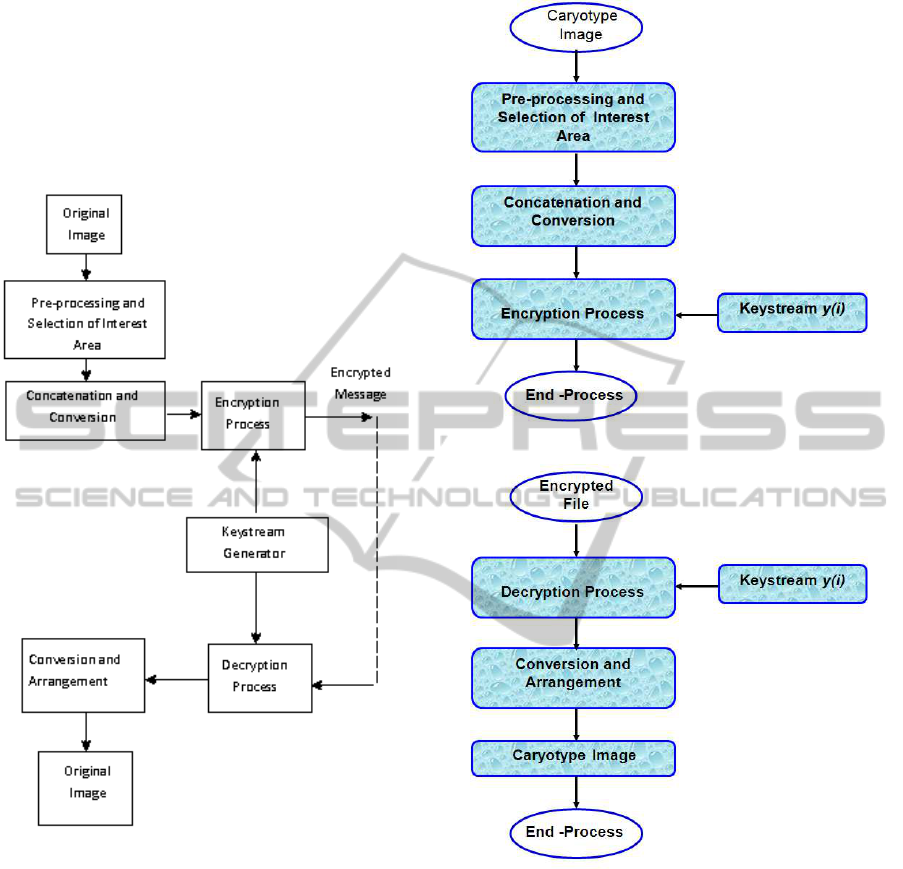
Grain-128 keystream generator. Figure 3 depict the
block diagram of the proposed approach. The flow
charts of the encryption and decryption process are
presented respectively in figures 4 and 5.
In a human Caryotype, the numbers of defects are
usually trisomy 13 and trisomy 21 thereforeobserving
three chromosomes in these boxes means that there is
an anomaly of number, which means that the contents
of these boxes must be within reach only of the doctor
in charge. In addition, the doctor in charge wrote his
final diagnosis in the observation part.
Since these three areas, boxes 13, 21 and the ob-
servation text constitute a confidential medical re-
port then they are automatically hidden and accessible
only by the doctor in charge. Thus, medical confiden-
tiality is respected.
The individual steps of encryption and decryption
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
94
process are discussed in the following sub-sections.
Let Caryotype (i.e. original image) of 391 × 300 pix-
els. Let R
1
, R
2
and R
3
three regions of interest in
Caryotype, respectively corresponding to boxes 13,
21 and the observation text. We denote by ⊕ the sum
modulo 2. By p, q and y we note respectively the dig-
ital selected regions, cipher digital selected regions
and digital keystream.
Figure 3: Block diagram of the proposed approach.
4.1 Pre-processing and Selection of
Interest Area
At first, the Caryotype gray scale image is converted
into a matrix of pixel values. Second, select R
1
, R
2
and R
3
regions.
4.2 Concatenation and Conversion
Convert the region R
1
, R
2
and R
3
into a one dimen-
sional of decimal pixel values. This is then converted
into a one dimensional binary sequence and stored it
in p used for encryption process.
Figure 4: Flow chart of the encryption process.
Figure 5: Flow chart of the decryption process.
4.3 Encryption Process
The encryption process work as follow:
• Load the digital selected regions p;
• N ← the length of p ;
• for i = 1 to N to make :
Generate the digital keystream y
i
as it shows
the keystream algorithm in section 4.6;
• End to make;
• for i = 1 to N to make:
Encrypt the digital selected regions p using
relation
SelectiveEncryptionofMedicalImages
95

q(i) = p(i) ⊕ y(i) ,
• End to make ;
• Sent the cipher digital selected regions q.
4.4 Decryption Process
The decryption process work as follow:
• Load the cipher digital selected regions q
• N ← the length of q ;
• for i = 1 to N to make :
Generate the digital keystream y
i
as it shows
the keystream algorithm in section 4.6;
• End to make ;
• for i = 1 to N to make :
Decrypt the cipher digital selected regions
using relation
p(i) = q(i) ⊕ y(i)
• End to make ;
4.5 Conversion and Arrangement
Convert the decrypted digital selected regions p into
a one dimensional of decimal pixel values, then put
each pixel in its place in the Caryotype image.
4.6 Keystream Algorithm
• Read N, length of the digital selected regions p ;
• Introduce the values of initialization of LFSR and
NLFSR ;
• for i = 1 to N + 127 to make:
Generate binary sequences u(i) and v(i) re-
spectively produced by LFSR and NLFSR as
shown the equations 1 and 2;
• End to make.
• for i = 1 to N to make:
Generate the binary sequence h(i) produced
by the combining function h ;
Generate the output of keystream using the
relation:
y(i) = ⊕
j∈A
v
i+ j
⊕ h(i) ⊕ u
i+93
.
• End to make.
5 SIMULATION AND RESULTS
In the simulation, three selected regions automatically
R
1
, R
2
and R
3
indicated in figures 6, 7 and 8 are used
to validate the approach. Simulation was carried out
using MATLAB V 7.5. By comparing the original
regions and their corresponding encrypted regions in
figures 6, 7 and 8, there is no visual information ob-
served in the encrypted regions. Figure 9 show the
visual testing of encryption and decryption for Cary-
otype.
In the experiments, the original regions and their
corresponding encrypted regions and their histograms
are shown in figures 6, 7 and 8. It is clear that the en-
crypted regions histograms are nearly uniformly dis-
tributed, and significantly different from the original
regions histograms. So, the encrypted regions do not
provide any clue to employ any statistical attack on
Figure 6: Experimental results for selected region R
1
: show
the original region R
1
and its corresponding encrypted re-
gion and their histograms.
Figure 7: Experimental results for selected region R
2
: show
the original region R
2
and its corresponding encrypted re-
gion and their histograms.
Figure 8: Experimental results for selected region R
3
: show
the original region R
3
and its corresponding encrypted re-
gion and their histograms.
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
96
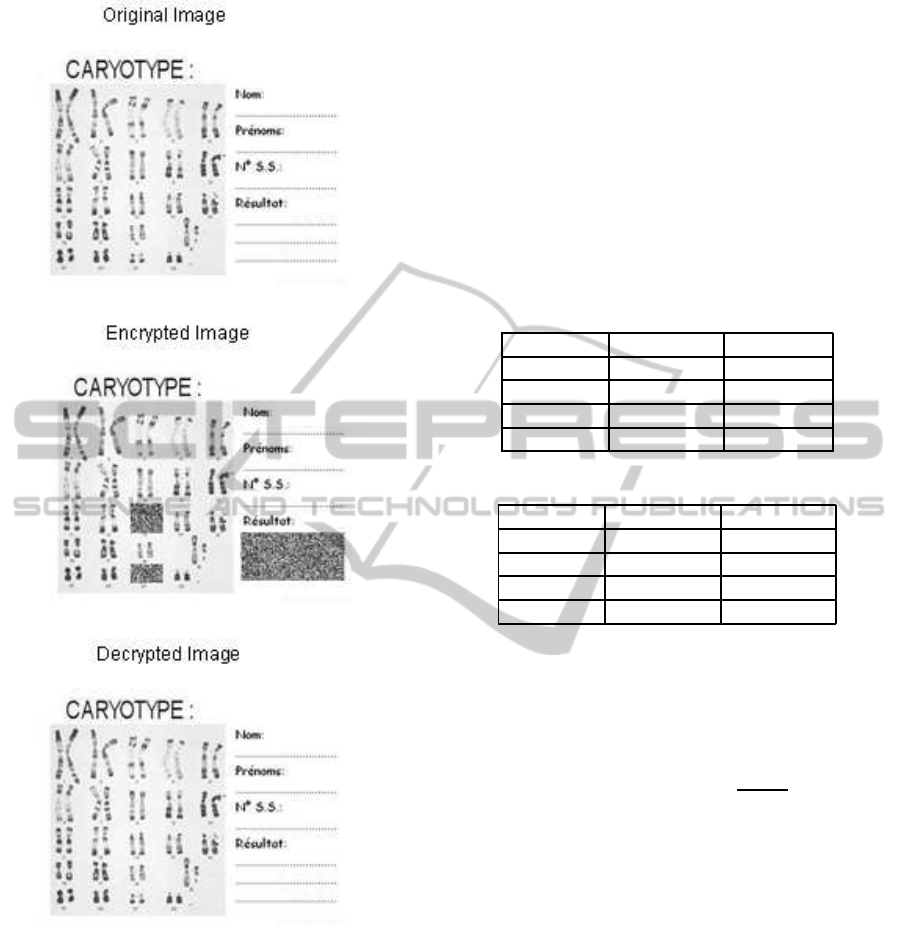
Figure 9: Visual testing of encryption and decryption for
caryotype.
the proposed design, which makes statistical attacks
difficult.
5.1 Correlation Coefficient Analysis
Table 1 and Table 2 show the correlation coefficient
results. By Cor
1
, Cor
2
, Cor
3
, and Cor
4
we denote
respectively correlation coefficient between original
image and encrypted image, correlation coefficient
between original image and decrypted image, corre-
lation coefficient between encrypted image and de-
crypted image with wrong key and correlation coef-
ficient between original image and decrypted image
with wrong key.
It is observed that the values of Cor
1
, Cor
3
, and
Cor
4
shown in the table 1 and table 2 are quite close to
the value of zero, which implies that the original im-
ages and their encrypted images are totally different
i.e. the encrypted image has no features and highly
independent on the original image. It is also clear that
the values of Cor
2
shown in the table 1 are equal to
the value 1, which implies the encrypted images are
the same as the original images.
Table 1: Correlation Coefficients Analysis.
Cases Cor
1
Cor
2
Region 1 0.0100438 1.0000000
Region 2 0.0554183 1.0000000
Region 3 -0.0062774 1.0000000
Caryotype 0.0059980 1.0000000
Table 2: Correlation Coefficients Analysis.
Cases Cor
3
Cor
4
Region 1 -0.0305526 0.0159771
Region 2 0.0688412 0.0102282
Region 3 -0.0058162 -0.0093714
Caryotype -0.0024934 -0.0018975
5.2 Entropy Analysis
It is well known that the entropy E(M) of a message
source M can be calculated as:
E(M) =
T−1
∑
i=0
P(M
i
)log2
1
P(M
i
)
. (6)
Where T Gray value of an input image (0-255), P(M
i
)
represents the probability of symbol M
i
and the en-
tropy is expressed in bits. Let us suppose that the
source emits 2
8
symbols with equal probability, i.e.,
M = {M
1
, M
2
, ..., M
2
8
}. Truly random source entropy
is equal to 8.
Table 3 and table 4 show the entropy results. By
E
1
, E
2
, E
3
, and E
4
we denote respectivelyentropy val-
ues: of original image, encrypted image, decrypted
image and decrypted image with wrong key. The val-
ues of E
2
and E
4
presented in the table 3 and table
4 are very close to the theoretical value of 8. This
means that information leakage in the encryption pro-
cess is negligible and the encryption system is secure
upon the entropy attack.
5.3 Key Sensitivity
A good cryptosystem should be sensitive to the secret
SelectiveEncryptionofMedicalImages
97
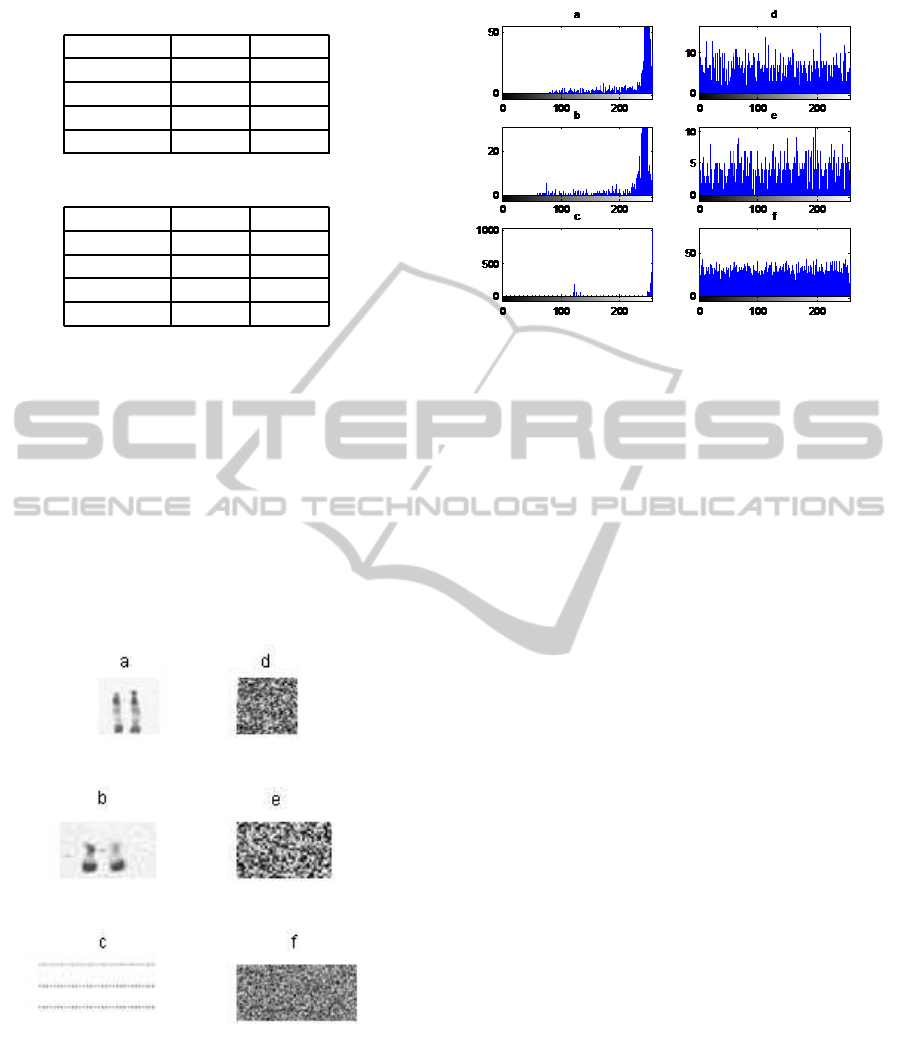
Table 3: Image Entropy.
Cases E
1
E
2
Region 1 5.3746 7.8923
Region 2 5.3398 7.8101
Region 3 1.2416 7.9755
Caryotype 2.9176 7.9812
Table 4: Image Entropy.
Cases E
3
E
4
Region 1 5.3746 7.8668
Region 2 5.3398 7.8128
Region 3 1.2416 7.9790
Caryotype 2.9176 7.9847
keys, which means change of a single bit in the secret
key should produce a completely different encrypted
image. The Grain-128 was tested to the keys sensi-
tivity, we decrypt the encrypted regions illustrated by
figures 6,7 and 8 with true key and, we decrypt the
encrypted regions illustrated by figures 6,7 and 8 with
wrong key (slightly different key). The results are
given by figures 10 and 11. The values of Cor
3
and
Cor
4
given in the table 2 are quite close to the value
of zero, and the values of E
4
given in the table 4 are
very close to the theoretical value of 8, which implies
that the proposed cryptosystem is highly sensitive to
the key.
Figure 10: Sensitivity analysis: Frame (a), (b) and (c) re-
spectively, show the decrypted regions with true key of the
encrypted regions shown in figures 6,7 and 8. Frame (d), (e)
and (f) respectively; show the decrypted regions with wrong
key of the encrypted regions shown in figures 6,7 and 8.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this Work, a selective image encryption algorithm
Figure 11: Sensitivity analysis: Frame (a), (b) and (c) re-
spectively, show the histograms of decrypted selected re-
gions with true key of the encrypted regions shown in fig-
ures 6,7 and 8. Frame (d), (e) and (f) respectively; show
the histograms of decrypted regions with wrong key of the
encrypted regions shown in figures 6,7 and 8.
for medical image using Grain-128 keystream genera-
tor was introduced. Simulations were carried out with
three different selected regions. The visual test indi-
cates that the encryptedregions was very different and
no visual information can be deduced about the orig-
inal region for all tested regions. This method is very
simple, fast and easy to implement, as encryption and
decryption selective image algorithm.
REFERENCES
C. Cid, S. K. and Kurihara, J. (2009). The rakaposhi stream
cipher. In in Proceedings of the 11th international
conference on Information and Communications Se-
curity, ICICS’09, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag,
pp. 32-46.
Canniere, C. D. and Preneel, B. (2005). Trivium a
stream cipher construction inspired by block ci-
pher design principles. In eSTREAM, ECRYPT
Stream Cipher Project, Report 2005/030 (2005-04-
29). http://www.ecrypt.eu.org/stream.
Geneix, A. and al (1988). Image processing in human cy-
togenetics new steps toward quantification. In Karyo-
gram (U.S.A.). vol 14, p45-49,1988.
Malet, P. and al (1988). New cytogenetic techniques and
medical applications. In Sem Hop Paris. 64, n23,
1576-1586,1988.
Malet, P. and al (1989). L’analyse chromosomique par
traitement d’images aspects r´ecents et perspectives. In
Annales de G´en´etiques. vol 32, n3, p.164-16,1989.
M.Hell, T. and W.Meier (2006). A stream cipher proposal:
Grain-128. In In IEEE International Symposium on
Information Theory. ISIT 2006.
N. S. Kulkarni, B. R. and Gupta, I. (2008). Selective encryp-
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
98

tion of multimedia images. In NSC 2008. December
17-19.
Panduranga, H. T. and al (2013). Selective image encryp-
tion for medical and satellite images. In International
Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET). vol 5
No 1, 2013.
Z. Brahimi, H. Bessalah, A. T. M. K. K. (2008). Selec-
tive encryption techniques of jpeg2000 codestream for
medical images transmission. In WSEAS Transactions
on Circuits and Systems. vol 7, July 2008.
SelectiveEncryptionofMedicalImages
99
