
Estimating Human Actions Affinities Across Views
Nicoletta Noceti
1
, Alessandra Sciutti
2
, Francesco Rea
2
, Francesca Odone
1
and Giulio Sandini
2
1
DIBRIS, Universit`a di Genova, via Dodecaneso 35, 16146, Genova, Italy
2
RBCS, Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, via Morego 30, 16163, Genova, Italy
Keywords:
Human Actions Understanding, View-invariant Representation, Trajectory Curvature.
Abstract:
This paper deals with the problem of estimating the affinity level between different types of human actions
observed from different viewpoints. We analyse simple repetitive upper body human actions with the goal
of producing a view-invariant model from simple motion cues, that have been inspired by studies on the
human perception. We adopt a simple descriptor that summarizes the evolution of spatio-temporal curvature
of the trajectories, which we use for evaluating the similarity between actions pair on a multi-level matching.
We experimentally verified the presence of semantic connections between actions across views, inferring a
relations graph that shows such affinities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since birth human neonates present a preference for
biological motion (Simion et al., 2008) and this is an
important trigger for social interaction. This inclina-
tion – a key element in human development research
– is also inspiring computer vision researchers to find-
ing computational models able to replicate it on arti-
ficial systems.
The contamination between the two research commu-
nities may also guide the choice of the most appropri-
ate tools for a given computer vision task: if neonates
have this capability of “understanding” motion while
their visual perception is still rudimental, it is likely
that the analysis is based on very simple motion cues –
such as sensitivity to local apparent motion, and sim-
ple features as velocity, acceleration or curvature (see
e.g. (Kuhlmeier et al., 2010; Simion et al., 2008)).
The goal of our research is to build computational
models for the iCub humanoid robot (Metta et al.,
2008) to simulate this phase of human development.
Our long term objective is to understand how much
we can infer on the nature of motion from such sim-
ple observations, as this skill seems to be at the ba-
sis of human ability in interacting with others. Also
we would like to preserve some abilities typical of
a developing human being, such as a degree of tol-
erance to view-point changes (Troje and Westhoff,
2006; Goren et al., 1975; Farah et al., 1995)
On a shorter term, our research is focusing on the
identification of biological motion (some preliminary
results can be found in (Sciutti et al., 2014)) and on
the analysis of different types of biological motion.
The latter is the goal of this paper, in which we ana-
lyze simple repetitive upper body human actions with
the goal of producing a view-invariant model from
simple motion cues. We apply this model to the es-
timate of the affinity level between different types of
actions, focusing in particular on two main categories:
transitive – which involve object manipulation – and
intransitive actions.
Since we are primarily interested in capturing abilities
typical of the early months of human development we
do not address classical action recognition tasks, abil-
ities which are likely to be gained in later stages of
development (Camaioni, 2004; Kanakogi and Itakura,
2011), also thanks to the infants prior motor experi-
ence .
Our model takes inspiration from the seminal
work (Rao et al., 2002), where the authors discuss on
the use of dynamic instants, i.e. meaningful action
units whose properties are highly characterizing the
evolution of structured activities (e.g. Pick up an ob-
ject from the floor and put it on the desk) and that have
been proved to be of substantial relevance for the hu-
man motion perception. Such points – consequence
of a variation in the force applied during an activity –
correspond to the local maxima of the curvature of the
trajectory describing the activity evolution on the im-
age plane. The authors formally prove that they also
have view-invariant properties.
In this paper we focus instead on intervals, mean-
130
Noceti N., Sciutti A., Rea F., Odone F. and Sandini G..
Estimating Human Actions Affinities Across Views.
DOI: 10.5220/0005307801300137
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2015), pages 130-137
ISBN: 978-989-758-090-1
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

ing portions of trajectories between two dynamic in-
stants, and investigate on their potentially informa-
tive content to be exploited for cross-view recogni-
tion. For our investigation, we collected a data set
of videos, each one including repetitions of a given
atomic action. Indeed, in our case dynamic instants
mainly refer to points partitioning one action instance
from the next one. After an initial low-level analysis,
that aims at segmenting the moving arm of the user,
we extract corner points from the arm region and track
them over time to collect a set of trajectories. Then,
we measure the curvature and find its local maxima.
Finally, we describe the intervals with histograms of
curvature, that we adopt in a multi-level matching to
evaluate the level of affinity between two observed
events. We experimentally provide the evidence of
the presence of actions classes inferred by estimating
the pairwise similarities of action sequences from the
same view and across different views.
Works related to the computational model we con-
sider can be found in fields as video surveillance,
video retrieval and robotics, where tasks as gesture
and action recognition or behavior modeling have
been for many years very fertile disciplines, and still
are (Fanello et al., 2013; Malgireddy et al., 2012;
Mahbub et al., 2011; Noceti and Odone, 2012; Wang
et al., 2009) We refer the interested reader to a recent
survey (Aggarwal and Ryoo, 2011) for a complete ac-
count on the topic.
From the view-invariance standpoint, the prob-
lem has been addressed considering two different set-
tings, i.e. observing the same dynamic event simul-
taneously from two (or more) cameras (Zheng et al.,
2012; Wu and Jia, 2012; Li and Zickler, 2012; Huang
et al., 2012a; Zheng and Jiang, 2013) or consider-
ing different instances of a same concept of dynamic
event (Lewandowski et al., 2010; Gong and Medioni,
2011; Junejo et al., 2011; Li et al., 2012; Huang
et al., 2012b). The latter are more related to our set-
ting. In general, view-invariance may be addressed
at a descriptor level (Junejo et al., 2011; Li et al.,
2012; Huang et al., 2012b) or at the similarity esti-
mate level. In this case machine learning (Wu and Jia,
2012; Huang et al., 2012a; Zheng and Jiang, 2013)
and, more recently, transfer learning (Zheng et al.,
2012; Li and Zickler, 2012) may be beneficial.
The approach we follow shares computational
tools and models with many of the above mentioned
works, but significantly differs in the intentions, in
that we are not interested in recognizing specific ges-
tures, actions or activities, but instead we consider a
more abstract task: to what extent are we able to infer
properties (if any) on the observed motion that per-
sist across views, even from a very coarse representa-
tion?.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Sec.
2 is devoted to the description of the approach we
follow, from the low-level analysis to the matching,
while Sec. 3 describes our experimental analysis. The
final section is left to conclusions.
2 CURVATURE-BASED MOTION
REPRESENTATION
In this section we discuss our approach to motion
modeling, that builds on top of a sparse representa-
tion and then relies on the computation of histograms
of the spatio-temporal curvature. Then, we describe
the strategy we adopt to match image sequences.
2.1 Low-level Video Analysis
The very first step of our method relies on a widely ac-
cepted video analysis pipeline, that aims at segment-
ing each image of a sequence with respect to both
motion and appearance information. Instantiated to
our case study, this corresponds to detecting the im-
age region with the moving arm of a subject while
performing a given action. The intermediate steps of
the pipeline are reported in Fig. 1. We first perform
background subtraction (Zivkovic, 2004), then refine
the obtained binary map by applying skin detection in
the HSV color space to only the foreground. Finally,
assuming only the subject of interest is moving in the
observed scene, we keep the largest connected com-
ponent of the final binary map as region of interest
(ROI).
The second stage of our method relies on de-
scribing the visual dynamic of the moving region by
means of points trajectories (Fig. 2). To this pur-
pose, we extract from the ROI the Harris corners (Shi
and Tomasi, 1994), which we describe using SIFT de-
scriptors (Lowe, 2004). Then, we track SIFTs with
a Kalman filter (Welch and Bishop, 1995) and us-
ing histogram intersection as a similarity measure be-
tween observations. To improve the quality of the
obtained spatio-temporal trajectories, we finally filter
them with anisotropic diffusion (Perona and Malik,
1990). We collect spatio-temporal trajectories for
each video, and thus set the basis for the next step of
motion representation, based on the concept of curva-
ture.
2.2 Spatio-temporal Curvature
The projection of the dynamic evolution of a 3D
point in the image plane is composed as a spatio-
EstimatingHumanActionsAffinitiesAcrossViews
131
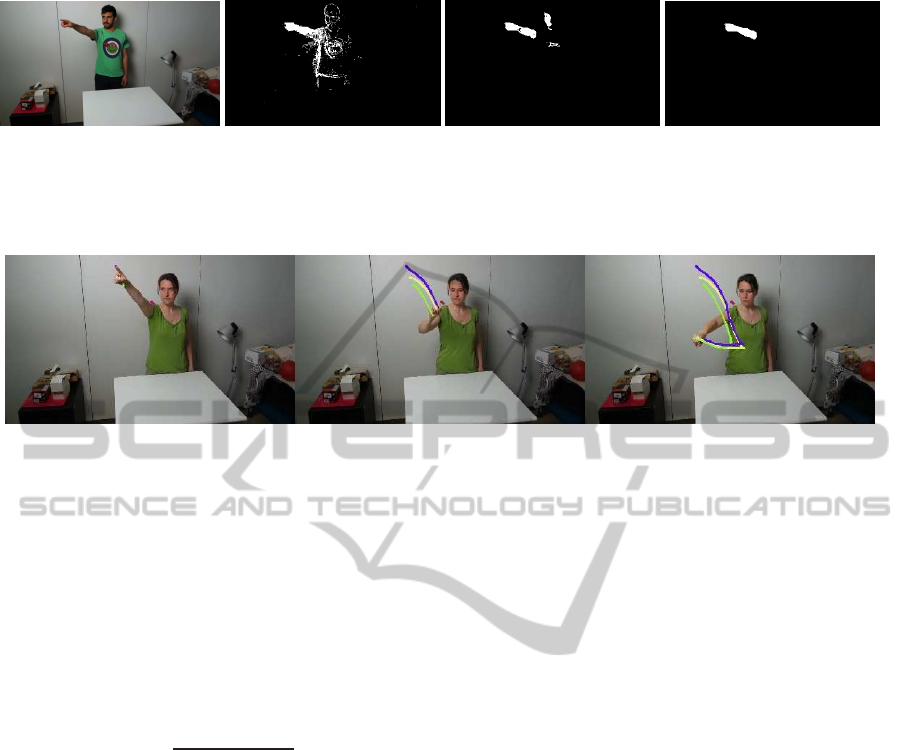

(a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 1: A visual sketch of the initial video analysis: starting from an image of the sequence (Fig. 1(a)), we first apply
background subtraction (Fig.1(b)), then detect skin on the foreground (Fig. 1(c)), and finally keep only the largest connected
component (Fig. 1(d)) as the region of interest.
Figure 2: Examples of trajectories of corner points, which we subsampled for the sake of clarity of the figure.
temporal trajectory of observations T = { P(t
i
)}
n
i=1
,
where P(t
i
) = (x(t
i
), y(t
i
),t
i
) is an image point ob-
served at time t
i
with coordinates (x(t
i
), y(t
i
)), which
are functions of time. The velocity of the points
can be expressed as the derivative of the positions,
i.e. V(t
i
) = (x
′
(t
i
), y
′
(t
i
), ∆
t
) where ∆
t
is the tempo-
ral gap between adjacent images. Similarly, the ac-
celeration is the derivative of the velocity, A(t
i
) =
(x
′′
(t
i
), y
′′
(t
i
), 0). At this point, we can compute the
trajectory curvature as
C(t
i
) =
||V(t
i
) × A(t
i
)||
||V(t
i
)||
3
. (1)
Consider the corner trajectories of Fig. 2, one of
which is reported in the 3D space-time reference sys-
tem of Fig. 3, left. On the right, we show the trend of
velocity magnitude (above) and of the curvature (be-
low) over time, enhancing their local maxima in red
and green, respectively. The corresponding space-
time points are coherently marked on the 3D visu-
alization on the left. As it can be easily observed,
while the first type of points indicates time instants in
the middle of a segment of the space-time trajectories
(points in which the user starts to decelerate to finally
stop the movement), the latter refers to instantaneous
changes in motion direction and/or dynamic.
The dynamic instants are the units on top of which
we build the representation of a trajectory. Follow-
ing the notation of the previous section, an observed
spatio-temporal sequence T = {(x(t
i
), y(t
i
),t
i
)}
n
i=1
is
now associated with a sequence DI = [
ˆ
t
1
. . .
ˆ
t
m
] of
dynamic instants, where
ˆ
t
i
∈ {t
1
, . . . , t
n
} and m < n.
According to (Rao et al., 2002), we define an
interval as a trajectory segment laying in the mid-
dle of two dynamic instants. We chose to repre-
sent the distribution of the curvature in it by means
of histograms. Therefore, at the end of the repre-
sentation, each observed trajectory is associated with
a sequence of curvature histograms, i.e. H(T) =
[H(
ˆ
t
1
,
ˆ
t
2
), . . . , H(
ˆ
t
m−1
,
ˆ
t
m
)], where H(
ˆ
t
i
,
ˆ
t
i+1
) refers to
the fact that the histograms are computed between
each pair of adjacent dynamic instants.
2.3 Multi-level Matching between
Image Sequences
Once we have detected the dynamic instants as the lo-
cal extrema of the curvature and represented the inter-
vals curvature as histograms, we may set up a multi-
level procedure to match image sequences. Hence,
let us consider two videos and the two corresponding
sets of observed trajectories, T
1
= {T
1
1
, . . . , T
1
N
} and
T
2
= {T
2
1
, . . . , T
2
M
}, described with the curvature his-
tograms to collect the sets H
1
= {H(T
1
1
), . . . , H(T
1
N
)}
and H
2
= {H(T
2
1
), . . . , H(T
2
M
)}.
To match two image sequences, we start by com-
paring pairs of trajectories of type (T
1
i
, T
2
j
), with
1 ≤ i ≤ N and 1 ≤ j ≤ M. For the sake of clarity,
we express the sequence of histograms with a more
compact style as H(T
1
i
) = [H
1
i,1
, H
1
i,2
, . . . , H
1
i,m
i
−1
] and
H(T
2
j
) = [H
2
j,1
, H
2
j,2
, . . . , H
2
j,m
j
−1
. Since the videos we
consider refer to repetitions of a given atomic actions,
we consider the average similarity between all pairs
of histograms describing portions of the two trajecto-
ries. The similarity between two trajectories is thus
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
132

Figure 3: Left: a space-time representation of a trajectory. Right: velocity magnitude (above) and curvature (below) as
functions of time. We denote local maxima of the velocity magnitude (red) and of the curvature (green). The latter correspond
to dynamic instants, relevant for the human perception of motion.
formalized as
S(T
1
i
, T
2
j
) =
1
(m
i
− 1)(m
j
− 1)
m
i
−1
∑
k=1
m
j
−1
∑
h=1
HI(H
1
i,k
, H
2
j,h
)
(2)
where HI denotes the intersection between his-
tograms. Given a video, the observed trajectories de-
scribe the evolution of 3D points all related to the
same physical event, i.e. the motion of the user arm.
Thus, it is convenient to summarize the contribution
of all the trajectories to end up with a single value
quantifying the global similarity between two videos,
i.e. two physical events. To this purpose, we select
the maximum similarities between all pairs of trajec-
tories. More formally
S(T
1
, T
2
) = max
i=1...N, j=1...M
S(T
1
i
, T
2
j
). (3)
3 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS
In the following we report on the experiments we per-
formed in order to evaluate the level of view-invariant
information included in the intervals between dy-
namic instants, which we describe and compare ac-
cording to the previous section. Our main objective
is to extract knowledge about properties of (classes
of) actions that might be captured across views with
this somehow primitive representation. To this end
we performed a qualitative evaluation on a dataset we
collected in-house.
3.1 Experimental Setup
We acquired a set of image sequences of two subjects
observed from two different viewpoints. The acqui-
sitions have been made on an indoor environment to
favor the low-level analysis and thus allow a higher
focus on the second step of motion representation and
matching. The variation of the viewpoint reflects the
application we have in mind, i.e. human robot inter-
action, where we can assume the interacting subject
to be located in a limited radial spatial range in front
of the camera (i.e. the robot). Similarly, the actions
included in the data set (shown in Fig. 4) are sug-
gested by the application. We considered 6 actions:
Pointing a finger towards a certain 3D location; Wav-
ing the hand from left to right and vice-versa; Lifting
and object from the table to a box placed on it; Throw-
ing an object away (action that we only simulated for
practical reasons); Transporting an object from and to
different positions on the table. The latter is instanti-
ated in two versions, with left-right and random object
repositioning.
Each video consists of 20 repetitions of the same
atomic action (e.g. move the object from left to right);
for each subject we acquired two videos in each view
for each action.
3.2 Proof of Concepts
Spatio-temporal Curvature. After having ex-
tracted corners trajectories from each video, we
first detect the dynamic instants. Let us start our
analysis by providing an experimental evidence of
the information carried by the dynamic instants in
the setting we consider. In Fig. 5 we show examples
EstimatingHumanActionsAffinitiesAcrossViews
133

(a) Lifting
(b) Pointing
(c) Throwing
(d) Transporting left-right
(e) Transporting from and to random positions
(f) Waving
Figure 4: Samples from the acquisitions of a subject from a
single viewpoint.
Table 1: Ranking from the comparison of videos of the
same subject and acquired from the same viewpoint.
Test Ranking
1
st
2
nd
3
rd
4
th
5
th
6
th
Lift Li T.LR T.Rnd Wa Po Th
Point
T.Rnd Po Th Li T.LR Wa
Throw
Th Po T.Rnd T.LR Li Wa
T. LR
T.LR Li T.Rnd Wa Th Po
T. Rnd
T.Rnd Po T.LR Li Wa Th
Wav
Wa T.Rnd T.LR Li Po Th
Table 2: Ranking from the comparison of videos of different
subjects, acquired from the same viewpoint.
Test Ranking
1
st
2
nd
3
rd
4
th
5
th
6
th
Lift. T.Rnd T.LR Li Th Po Wa
Point.
Th Po T.LR Li T.Rnd Wa
Throw.
Po Th Li T.Rnd T.LR Wa
T. LR
T.Rnd T.LR Li Po Th Wa
T. Rnd
Li T.Rnd T.LR Th Po Wa
Wav.
Wa Th Po T.LR T.Rnd Li
Table 3: Ranking from the comparison of videos acquired
acquired from different viewpoints.
Test Ranking
1
st
2
nd
3
rd
4
th
5
th
6
th
Lift. T.Rnd T.LR Li Th Po Wa
Point.
Th Li T.LR Wa T.Rnd Po
Throw.
Po Th T.Rnd Wa T.LR Li
T. LR
T.Rnd T.LR Li Po Th Wa
T. Rnd
T.LR T.Rnd Li Th Po Wa
Wav.
Wa Th Po T.LR T.Rnd Li
of trajectories related to different actions observed
from the two viewpoints. On the same plot, we also
report the local maxima of velocity magnitude and
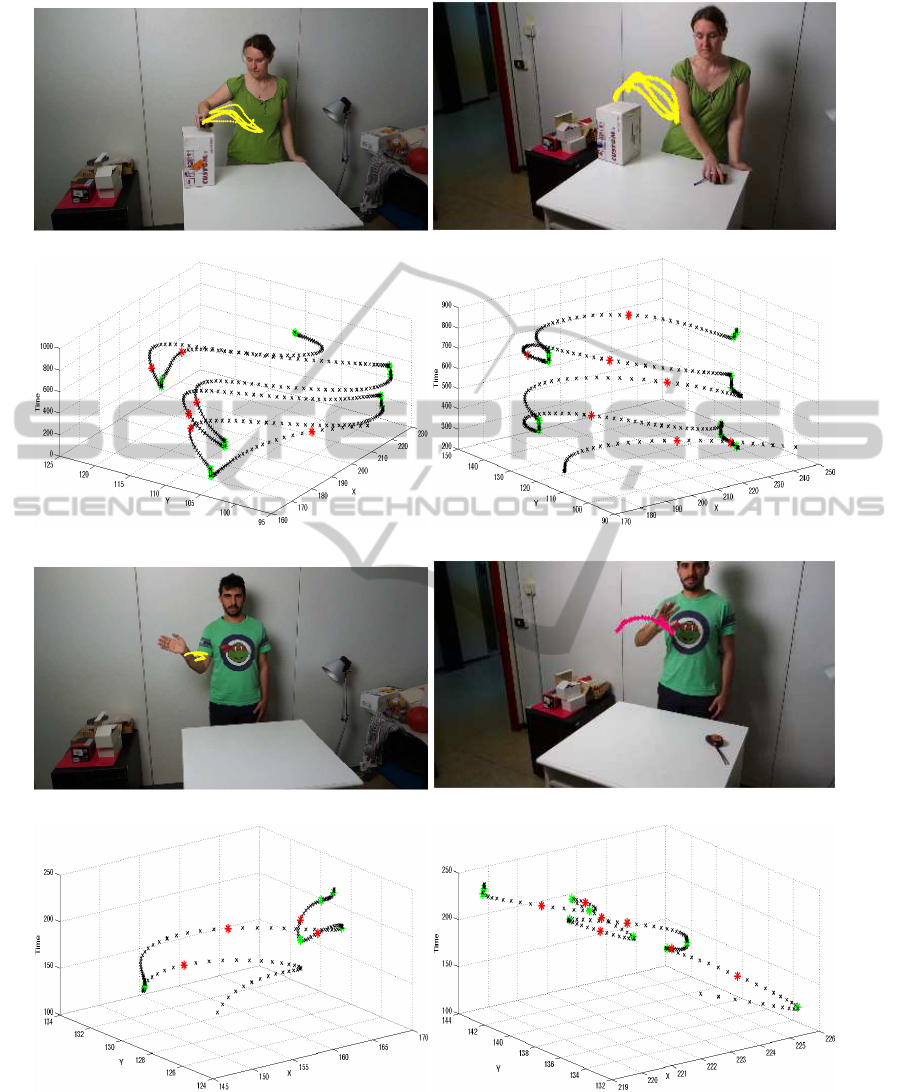
curvature. As a first thing, we may observe that the
dynamic instants are tolerant to view-point changes.
Furthermore, trajectories with diverse appearances in
the image plane (e.g. with different lengths or spatial
extents) present similar representations, showing that
the dynamic instants are also tolerant to variations
among the input data.
Action Recognition. We consider different experi-
mental configurations of increasing complexity:
• Same subject same view
• Different subject same view
• Matching across different views.
For each configuration, we consider each time a video
of test and match it with videos of all the available ac-
tions, then rank the similarities we obtained. Such
rankings are reported in Tab. 1, 2 and 3, where ac-
tions are referred to as Li (Lifting), Po (Pointing),
Th (Throwing), T.LR (Transporting left-right), T.Rnd
(Transporting random), and Wa (Waving).
It is apparent how the increasing complexity of the
configurations are reflected on the ranking results.
If the matching performs accurately when consider-
ing videos of the same subject and from the same
viewpoint, the results degrade already when the com-
parisons involve different subjects, even if observed
from the same viewpoints. This is consequence of
the movements subjectivity, that cause the presence of
maybe subtle properties in the motion that fail to be
captured from the basic representation we adopted.
Actions Type Affinity. What is interesting to be ob-
served is that the comparison of the rankings of Tab.
2 and 3 suggests the presence of some equivalence
classes between actions. To clarify this point, we per-
form an analysis of the overall similarities between
actions and visualize the results in the similarity ma-
trix of Fig. 6. Some remarks are in order. The first
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
134
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Figure 5: Examples of dynamic instants extracted from two views and considering different actions: Lifting (Fig.5(a) and
5(b)) and Waving (Fig.5(c) and 5(d)). Local extrema of velocity magnitude (red) and curvature (green) are marked.
is that the computed similarities are high on average
(all above 0.9) speaking in favor of the complexity of
the problem. Second, some affinities between actions
can be inferred. Waving appears as the most distinc-
EstimatingHumanActionsAffinitiesAcrossViews
135

tive action among the considered set. The Transport-
ing actions (both versions) are highly similar to each
other. Moreover, they show affinities with Lifting.
Pointing seems to share propertieswith Transport ran-
dom (probably because of the variability in the move-
ments direction), but also with Throwing. The latter,
not influenced by the forces caused by the manipula-
tion of objects, is thus more related to an intransitive
action type. We further go on with the analysis by
thresholding the similarity matrix with respect to the
lowest value on the diagonal (i.e. the lowest simi-
larity between two actions that must be similar). Af-
ter that, we inferred the graph-like structure in Fig.
7, where the survived elements – that can be inter-
preted as affinities between the involved actions – are
represented as arrows. It is easy to observe how the
transitive actions (in green) formed a cluster, which is
connected to an intransitive action (red) probably due
to the affinities between the two dynamics. Pointing
is also related to Throwing, that as above mentioned
can be considered (in our instance) as an intransitive
action.
Figure 6: Average mutual similarity.
Figure 7: A visual sketch of the actions affinities inferred
by mean of the analysis (in green transitive actions, in red
intransitive actions). Throwing has both colors since in our
instance we did not actually manipulate any object.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This work considered the problem of extracting
knowledge about affinities between (classes of) ac-
tions across different views, with specific reference
to the context of human-robot interaction. Starting
from investigations about human motion perception
and inspired from the seminal work (Rao et al., 2002),
we considered a coarse motion description based on
the use of histograms of curvature, which we used to
match pairs of videos with a multi-level approach. We
experimentally inferred a set of semantic connections
that characterize actions groups across views.
Our observations, made with computational tools,
confirm what observed directly in infants: they de-
velop rather early the ability of grasping some aspects
of the actions meaning, while it is likely that the capa-
bility of interpreting more specific actions properties
is developed later. This sets the scene for the repli-
cability on an artificial system – a robot in our case –
of the early stages of the human developmental evolu-
tion, in which the interpretation of the observed mo-
tion refines more and more while strengthening the
perceptual capabilities. In general an interactive robot
needs to be able to autonomously understand where to
focus its attention, for instance by perceiving the pres-
ence of motion, and biological motion in particular
as an effect of a potential interacting agent. Starting
from that, already by recognizing the class of actions
of the partner (e.g. some kind of object manipulation)
the robot could focus on the most relevant properties
of the event (e.g. the manipulated object or the ef-
fects on the context). Finally, the understanding of
the specific action and of its goal may guide the robot
to the selection of an appropriate reaction (e.g. be-
ing prepared to receive an object from the user). Fol-
lowing this mainstream, our future investigations will
be devoted to the development of a multi-level sys-
tem for action recognition, in which the complexity
of the computational model reflects the complexity of
the task.
From the point of view of the vision task, future
investigations will be also devoted to the design of
models able to cope with different complexity of the
scene (e.g. the presence of more than one moving
agents).
REFERENCES
Aggarwal, J. and Ryoo, M. (2011). Human activity analy-
sis: A review. ACM Computing Surveys.
Camaioni, L. (2004). The role of declarative pointing in
developing a theory of mind. Infancy, 5:291–308.
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
136

Fanello, S. R., Gori, I., Metta, G., and Odone, F. (2013).
Keep it simple and sparse: Real-time action recogni-
tion. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 14(1):2617–2640.
Farah, M. J., Wilson, K. D., Drain, H. M., and Tanaka, J. R.
(1995). The inverted face inversion effect in prosopag-
nosia: Evidence for mandatory, face-specific percep-
tual mechanisms. Vision Research, 35(14):2089 –
2093.
Gong, D. and Medioni, G. (2011). Dynamic manifold warp-
ing for view invariant action recognition. ICCV, pages
571–578.
Goren, C. C., Sarty, M., and Wu, P. Y. K. (1975). Visual fol-
lowing and pattern discrimination of face-like stimuli
by newborn infants. Pediatrics, 56(4):544–549.
Huang, C.-H., Yeh, Y.-R., and Wang, Y.-C. (2012a). Rec-
ognizing actions across cameras by exploring the cor-
related subspace. In ECCV, volume 7583 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 342–351.
Huang, K., Zhang, Y., and Tan, T. (2012b). A discrimina-
tive model of motion and cross ratio for view-invariant
action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Pro-
cessing, 21(4):2187–2197.
Junejo, I. N., Dexter, E., Laptev, I., and Prez, P. (2011).
View-independent action recognition from temporal
self-similarities. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. In-
tell., 33(1):172–185.
Kanakogi, Y. and Itakura, S. (2011). Developmental corre-
spondence between action prediction and motor abil-
ity in early infancy. Nat.Commun., 2:341–.
Kuhlmeier, V. A., Troje, N. F., and Lee, V. (2010). Young
infants detect the direction of biological motion in
point-light displays. Infancy, 15(1):83–93.
Lewandowski, M., Makris, D., and Nebel, J.-C. (2010).
View and style-independent action manifolds for hu-
man activity recognition. In ECCV, volume 6316 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 547–560.
Li, B., Camps, O. I., and Sznaier, M. (2012). Cross-view
activity recognition using hankelets. In CVPR, pages
1362–1369.
Li, R. and Zickler, T. (2012). Discriminative virtual views
for cross-view action recognition. In CVPR, pages
2855–2862.
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-
invariant keypoints. IJCV, 60:91–110.
Mahbub, U., Imtiaz, H., Roy, T., Rahman, S., and Ahad, A.
(2011). Action recognition from one example. Pattern
Recognition Letters.
Malgireddy, M. R., Inwogu, I., and Govindaraju, V. (2012).
A temporal bayesian model for classifying, detect-
ing and localizing activities in video sequences. In
CVPRW.
Metta, G., Sandini, G., Vernon, D., Natale, L., and Nori, F.
(2008). The icub humanoid robot: An open platform
for research in embodied cognition. In Proceedings of
the 8th Workshop on Performance Metrics for Intelli-
gent Systems, PerMIS ’08, pages 50–56.
Noceti, N. and Odone, F. (2012). Learning common be-
haviors from large sets of unlabeled temporal series.
Image and Vision Computing, 30(11):875 – 895.
Perona, P. and Malik, J. (1990). Scale-space and edge de-
tection using anisotropic diffusion. PAMI, 12(7):629–
639.
Rao, C., Yilmaz, A., and Shah, M. (2002). View-invariant
representation and recognition of actions. IJCV,
50(2):203–226.
Sciutti, A., Noceti, N., Rea, F., Odone, F., Verri, A., and
Sandini, G. (2014). The informative content of optical
flow features of biological motion. In ECVP.
Shi, J. and Tomasi, C. (1994). Good features to track. In
CVPR, pages 593 – 600.
Simion, F., Regolin, L., and Bulf, H. (2008). A predis-
position for biological motion in the newborn baby.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
105(2):809–813.
Troje, N. F. and Westhoff, C. (2006). The inversion effect
in biological motion perception: Evidence for a life
detector? Current Biology, 16(8):821 – 824.
Wang, X., Ma, X., and Grimson, W. (2009). Unsupervised
activity perception in crowded and complicated scenes
using hierarchical bayesian models. IEEE transac-
tions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence,
31(3):539–555.
Welch, G. and Bishop, G. (1995). An introduction to the
kalman filter. Technical report.
Wu, X. and Jia, Y. (2012). View-invariant action recognition
using latent kernelized structural svm. In ECCV 2012,
volume 7576 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 411–424.
Zheng, J. and Jiang, Z. (2013). Learning view-invariant
sparse representations for cross-view action recogni-
tion. In ICCV, pages 3176–3183.
Zheng, J., Jiang, Z., Phillips, P. J., and Chellappa, R. (2012).
Cross-view action recognition via a transferable dic-
tionary pair. In British Machine Vision Conference,
pages 1–11.
Zivkovic, Z. (2004). Improved adaptive gaussian mixture
model for background subtraction. In ICPR, volume 2,
pages 28–31.
EstimatingHumanActionsAffinitiesAcrossViews
137
