
Real-time Accurate Pedestrian Detection and Tracking in Challenging
Surveillance Videos
Kristof Van Beeck
1
and Toon Goedem´e
1,2
1
EAVISE, Campus De Nayer - KU Leuven, J. De Nayerlaan 5, 2860 Sint-Katelijne-Waver, Belgium
2
ESAT-PSI, KU Leuven, Kasteel Arenbergpark 10, 3100 Heverlee, Belgium
Keywords:
Pedestrian Detection, Tracking, Surveillance, Computer Vision, Real-time.
Abstract:
This paper proposes a novel approach for real-time robust pedestrian tracking in surveillance images. Such
images are challenging to analyse since the overall image quality is low (e.g. low resolution and high compres-
sion). Furthermore often birds-eye viewpoint wide-angle lenses are used to achieve maximum coverage with a
minimal amount of cameras. These specific viewpoints make it difficult - or even unfeasible - to directly apply
existing pedestrian detection techniques. Moreover, real-time processing speeds are required. To overcome
these problems we introduce a pedestrian detection and tracking framework which exploits and integrates these
scene constraints to achieve excellent accuracy results. We performed extensive experiments on challenging
real-life video sequences concerning both speed and accuracy. We show that our approach achieves excellent
accuracy results while still meeting the stringent real-time demands needed for these surveillance applications,
using only a single-core CPU implementation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Reliable pedestrian detection and tracking in surveil-
lance images opens up a wide variety of applica-
tions (e.g. abnormal behaviour detection, path pre-
diction, intruder detection, people safety on e.g. mov-
able bridges and crowd counting). In recent years,
tremendous advances concerning pedestrian detec-
tion were published. Current state-of-the-art detec-
tors achieve excellent accuracy results on publicly
available datasets (see section 2). Unfortunately, di-
rectly applying these existing techniques on challeng-
ing surveillance images is not a trivial task. This
is due to the inherent nature of these surveillance
applications; often a large number of cameras are
utilised since large areas need to be covered com-
pletely. Such scenarios impose severe constraints on
the hardware: low-cost cameras are employed with
wide-angle lenses, mounted high in a partly down-
looking birds-eye view. Consequently image process-
ing and analysis on these images is challenging.
Indeed, typical surveillance images are often cap-
tured at low-resolution and use high compression.
Classic background subtraction based object detec-
tion methods yield very noisy results at these high
compression ratios. Moreover, these techniques do
not differentiate between people and other objects.
Due to their specific viewpoint (and wide-angle lens)
standard pedestrian detectors - which are trained and
evaluated on forward-lookingimages - are also unable
to give accurate detection results on these images.
Additionally, due to perspective effects some pedes-
trians to be detected appear very small in the image,
which remains one of the most challenging tasks for
current pedestrian detectors (Doll´ar et al., 2012). Fur-
thermore, real-time processing speeds are required. In
this paper we propose a flexible and fast pedestrian
detection and tracking framework specifically ad-
dressing these challenging surveillance images. See
figure 1 for a typical example frame of the pub-
licly available surveillance dataset we used (CAVIAR
project, 2005). Our approach achieves excellent accu-
Figure 1: Example frame of one of the sequences of the
CAVIAR dataset (CAVIAR project, 2005).
325
Van Beeck K. and Goedemé T..
Real-time Accurate Pedestrian Detection and Tracking in Challenging Surveillance Videos.
DOI: 10.5220/0005308703250334
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2015), pages 325-334
ISBN: 978-989-758-091-8
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

racy results at real-time processing speeds. We over-
come the above mentioned challenges by the integra-
tion of three modalities: foreground segmentation ap-
proaches, the exploitation of scene constraints and an
accurate pedestrian detector. This is done as follows.
First, candidate regions in the image are generated.
Using a calibrated scene distortion model, an early
rejection of false patches is achieved. Next the can-
didate regions are warped to a standard viewing an-
gle and used as input for a state-of-the-art pedestrian
detector. As explained in section 3 our approach al-
lows for the use of a highly accurate pedestrian de-
tector which would otherwise be too computationally
intensive for real-time applications. Finally, the de-
tections are employed in a tracking-by-detection ap-
proach to further increase the accuracy. Note that, us-
ing our approach the actual scene calibration is triv-
ial and easily performed. We demonstrate the effec-
tiveness of our approach on challenging surveillance
video sequences, and present extensive accuracy and
speed results. Our approach is generalisable to other
object classes. The remainder of this paper is struc-
tured as follows. In section 2 we discuss related work
on this topic, and distinguish our approach from exist-
ing work. Section 3 presents our framework in detail.
Next we propose experimental results on challenging
sequences in section 4. Finally, in section 5 we con-
clude our work and give final remarks on future work.
2 RELATED WORK
Pedestrian detection and tracking in general is a very
active research topic. (Dalal and Triggs, 2005) ini-
tially proposed the use of Histograms of Oriented
Gradients (HOG) for pedestrian detection. Their
insights paved the way for numerous derived ap-
proaches; even today most state-of-the-art pedestrian
detectors still rely on HOG features albeit in a more
subtle manner (e.g. in combination with other fea-
tures). A well-known example is the work of (Felzen-
szwalb et al., 2008). As opposed to the rigid model
introduced by Dalal and Triggs they propose the in-
clusion of parts (representing e.g. the limbs or head
of a pedestrian) to increase detection accuracy, coined
the Deformable Part Models (DPM). In later work the
authors tackled the inevitable increase in computa-
tional complexity by introducing a cascaded approach
in which a fast rejection of negative detection win-
dows is possible (Felzenszwalb et al., 2010). An ex-
tension was proposed using grammar models to cope
with partial occlusion (Girshick et al., 2012). (Gir-
shick and Malik, 2013) published a new and fast train-
ing methodology for DPM models. As opposed to
enriching the model with parts, (Doll´ar et al., 2009a)
introduced the use of a rigid model with additional
features, called Channel Features (ChnFtrs).
All previously mentioned approaches employ a
sliding window paradigm: to cope with scale varia-
tions a scale-space feature pyramid is calculated and
each layer is evaluated at each location. To speedup
detection (Doll´ar et al., 2010) proposed an approach
which approximates features nearby to avoid a full
feature pyramid calculation. Several other techniques
have been proposed to speedup detection: using
model scaling in stead of image scaling, GPU imple-
mentations (Benenson et al., 2012b) and search space
minimisation techniques (Benenson et al., 2012a; Cho
et al., 2012; Pedersoli et al., 2013). For several years,
the DPM approaches remained among the top per-
forming methods (Doll´ar et al., 2009b; Doll´ar et al.,
2012). However, the need of parts for pedestrian de-
tection remains unclear (Benenson et al., 2014). In-
deed, recent work on optimised rigid models - e.g.
Roerei (Benenson et al., 2013) and ACF (Doll´ar et al.,
2014) - in fact outperform the DPM detectors.
In (Girshick et al., 2014a) the authors present the
use of convolutional neural networks (R-CNN) for
object detection, achieving unprecedented state-of-
the-art accuracy results. This methodology existed for
a long time, but its applicability to image classifica-
tion tasks was highlighted by the work of (Krizhevsky
et al., 2012). Interestingly, their method steps away
from the traditional sliding window approach, and
utilises region proposals as input for the deep learn-
ing classifiers. Although currently not real-time,
their framework is able to classify a large variety of
classes simultaneously, making it ideal for large im-
age database retrieval applications such as ImageNe-
timage (Russakovsky et al., 2014). Recently (Gir-
shick et al., 2014b) presented a hybrid approach com-
bining DPMs with CNNs, called DeepPyramid DPM.
Several pedestrian tracking algorithms exist. Due
to recent advances in object detection techniques,
tracking-by-detection has become increasingly popu-
lar. There, an object detector is combined with a re-
liable tracking algorithm (e.g. particle filtering); see
for example (Breitenstein et al., 2011). Concerning
existing work on pedestrian tracking in surveillance
images many either operate on standard viewpoint
and/or high-resolution images (Benfold and Reid,
2011; Singh et al., 2008), or employ thermal cam-
eras to facilitate segmentation to reduce the search
area (Leykin and Hammoud, 2010).
In previous work we presented a real-time pedes-
trian detection framework for similar viewpoint im-
ages which are captured with a blind-spot camera
mounted on a real truck (Van Beeck et al., 2012).
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
326

Figure 2: Overview of our detection pipeline. After a first foreground segmentation step we extract region proposals which
potentially contain pedestrians. Each region is warped to an upright fixed-height patch. Next, a highly accurate pedestrian
detector is evaluated at a single scale. Finally, the detections are retransformed and tracked.
These images are - apart from the viewpoint - chal-
lenging since the camera is moving. However, in this
work we can fully exploit and integrate foreground
segmentation methods to increase both accuracy and
speed. Furthermore, we work with images captured
from genuine surveillance cameras. These images are
of low-resolution, low-quality and, due to the use of
wide-angle lenses show large amounts of distortion
and contain non-trivial viewpoints. Existing work on
the same dataset either employs clustering algorithms
with GPU optimisation (Orts-Escolano et al., 2014),
or focusses on motion analysis by matching trained
silhouette models (Rogez et al., 2014a). We differ
significantly from these previous works: we devel-
oped an accurate tracking framework in which we can
employ a highly accurate pedestrian detector on these
challenging images, and thus perform much better
than existing methods. We achieve real-time process-
ing speeds on a single-core CPU implementation. Our
approach easily lends itself for multi-threaded imple-
mentation if higher computational speeds are needed.
3 ALGORITHM OVERVIEW
Running standard pedestrian detectors such as the
Deformable Part Models on surveillance images as
shown in figure 1 is unfeasible. Current pedestrian
detectors are only trained on upright pedestrians at
a fixed height. Scale invariance is achieved using a
scale-space pyramid. Thus in order to achieve de-
cent detections on these surveillance images the de-
tectors ought to run on multiple rotations and scales
of the same surveillance image, using both dense rota-
tion and scale steps. Evaluating the total 4D rotation-
scale search space in real-time evidently is impos-
sible. Nonetheless, the use of a pedestrian detec-
tor could significantly increase the accuracy, as op-
posed to standard techniques which only rely on e.g.
backgroundsubtraction with blob analysis due to time
constraints. Therefore, to overcome these challenges
we propose the integration of a foreground segmen-
tation approach with a scene model and a highly ac-
curate pedestrian detector. Our approach allows for
the detection of pedestrians in challenging viewpoints
(e.g. rotated) under large lens distortion at low com-
putational complexity, with very high accuracy. To
retrieve the scene model, a simple one-time calibra-
tion procedure is performed, no explicit lens or cam-
era calibration is needed. Our algorithm briefly works
as follows. As seen in figure 1, pedestrians appear
rotated and scaled based on their position in the im-
age. We exploit this scene knowledge throughout our
detection and tracking pipeline. For each input im-
age, after a preliminary segmentation, we generate
region proposals which potentially contain pedestri-
ans. The scene model is used to reduce the number
of region proposals. Next, based on the position in
the image we warp each valid potential region to an
upright and fixed-height image patch. These patches
are given as input to a state-of-the-art pedestrian de-
tector, which evaluates a pedestrian model on a single
scale only. This is the key advantage of our work:
since only one scale and position needs to be evalu-
ated we can use a highly accurate pedestrian detector
which would otherwise be too time-consuming. Fur-
thermore this approach allows for the detection of ex-
tremely small pedestrians, if the detection model is
powerful enough. The detections are retransformed to
the original input image, and employed in a tracking-
by-detection framework to associate pedestrian tracks
and handle missing detections. Since each region
can be evaluated independently, a fast multi-threaded
Real-timeAccuratePedestrianDetectionandTrackinginChallengingSurveillanceVideos
327

implementation of this approach is trivial. Figure 2
shows an overview of our approach. In the next sub-
sections we describe further details of each step in our
pipeline, and motivate important design choices.
3.1 Foreground Segmentation
First we perform a foreground segmentation step to
identify moving regions in the static camera images.
Several segmentation approaches are applicable rang-
ing from basic background subtraction methods to
more advanced motion estimation methods. Since
we employ scene constraints further on to reduce the
number of region proposals, our approach allows for
the use of a coarse segmentation. For this step we
thus prefer low computational complexity over high
accuracy, excluding time-consuming techniques (e.g.
optical flow). Hence, we rely on background esti-
mation techniques, which generate a statistical model
of the scene. Several popular methods exist. Since
a comprehensive comparison of these techniques is
out of the scope of this work, we refer to (Benezeth
et al., 2008) and (Parks and Fels, 2008) for a de-
tailed overview. Concerning background subtraction,
the main challenges in typical surveillance images
arise from changing lightning conditions and cam-
era shake. Based on these comparative works we
opted for the method of (Zivkovic and van der Heij-
den, 2006), which employs Gaussian Mixture Models
(GMM). These methods haven proven to cope well
with (limited) background motion. Their proposed
method is an extension of the original GMM where
the number of Gaussian components per pixel is auto-
matically selected. This effectively reduces memory
requirements and increases the computation speed,
making it ideal for this application. A qualitative seg-
mentation output example is shown in the overview
figure (fig. 2).
3.2 Modelling Scene Constraints
As previously mentioned, the pedestrians in the
surveillance images appear rotated and scaled. Since
the position of the surveillance camera is fixed with
respect to the ground plane both parameters only de-
pend on the position in the image. If we know the
rotation and average pedestrian height for each pixel
position x = [x, y] we can exploit this scene knowl-
edge to achieve fast and accurate pedestrian detec-
tion, similar to (Van Beeck et al., 2012). During the
generation of the region proposals this information
can be used to reject regions which diverge too much
from the expected region properties, thus limiting the
search regions. For each valid proposed region, we
use the transformation parameters to warp each patch
to an upright, fixed-scale image patch, allowing the
use of an accurate pedestrian detector whilst being
real-time. To retrieve these transformation parameters
a one-time offline calibration needs to be performed
(see figure 3). However, the scene calibration as pro-
posed here is easy to perform and trivial. For this,
we extracted the rotation and height of each annotated
pedestrian from the dataset, giving the scale and rota-
tion for that specific point. Next we interpolated the
datapoints using a second order 2D polynomial func-
tion f
i
(x) for both parameters:
f
i
(x) = p
0
+ p
1
x+ p
2
y+ p
3
x
2
+ p
4
xy+ p
5
y
2
(1)
Both f
scale
(x) and f
rotation
(x) are used as Lookup
functions (LUFs): at each position in the image they
define the expected region properties and transforma-
tion parameters.
3.3 Generation of Region Proposals
In a next step we refine the segmentation and generate
region proposals which need to be warped and evalu-
ated using our single-scale pedestrian detector. Since
we employ a pedestrian detector in the next stage
to validate each region we are allowed to propose
more regions than needed, i.e. regions without
pedestrians. An accurate detector should indeed
negatively classify such patches. However, it is
important to early reject false patches, since they lead
to useless computations and lower processing speeds.
This stage thus tries to balance between optimal
accuracy and speed, generating an optimal amount of
search locations. Figure 4 gives an overview of our
region proposal calculation. Let us now discuss each
consecutive step in this pipeline.
First Elimination. As a preprocessing step, we
first eliminate noise in the segmentation which
remained after the background subtraction step (due
to e.g. changing lightning conditions). This is
simply done using morphological opening. Next,
Figure 3: A one-time calibration step is needed. The trans-
formation parameters are extracted from the annotations.
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
328
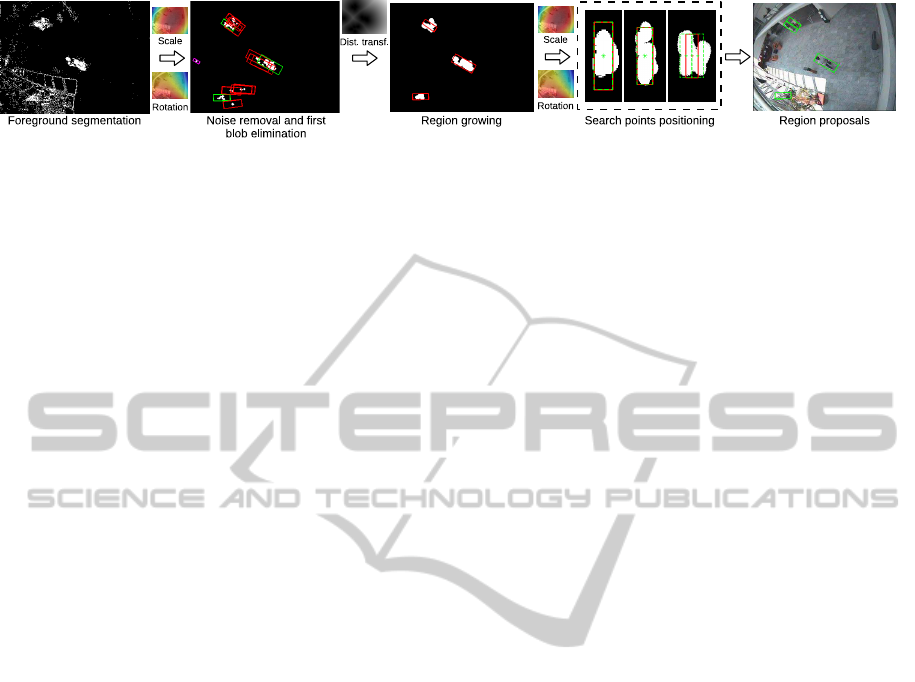
Figure 4: Our region proposals pipeline. After foreground segmentation and noise removal a first blob elimination is per-
formed. Next we perform region growing using a distance transform. Finally, we determine the optimal search points.
we perform a connected component analysis (using
8-connectivity), and test the local scene model for
each blob. That is, we construct a bounding box of
the expected scale and rotation around the centroid of
each blob. We reject two types of regions: extremely
small ones (25 pixels or less) due to the high SNR
there (drawn in magenta in the second step of fig-
ure 4), and those that diverge from an area constraint
(drawn in red). For this constraint, we require that
the area of the connected component should be
larger than a minimal percentage of the expected
area (15%). This step eliminates most invalid regions.
Region Growing. In the case of insufficient contrast,
the foreground segmentation performs suboptimal
(i.e. tends to split a valid pedestrian in multiple blobs,
as seen for the largest pedestrian in figure 4). For
each remaining valid region we therefore perform
region growing based on the Euclidean distance
transform, joining regions nearby. This has a second
advantage: multiple pedestrians which are nearby are
joined into a single detection region, even if one of
them was removed after the first elimination. This is
also illustrated in figure 4: after the first elimination
only one of both small pedestrians is maintained.
However, after region growing both are connected.
Defining Search Points. Finally, we define exact
search locations where the pedestrian detector will
be applied. This is done as follows. Each remaining
region is again verified against the scene constraints
since, due to the previous step, these regions could
have grown significantly. This is the case when
multiple (possibly previously invalid) regions are
joined. Note that we do not reject regions at this
stage. We locally evaluate each region and use the
expected height and rotation to estimate the number
of possible pedestrians. Based on the size of the
region we first evaluate if multiple search points
are necessary for this region. If so, we define a
linear grid over the entire region of which the step
size depends on the ratio of the expected and actual
region parameters, and eliminate grid points which
are located outside the segmented region.
The final region proposals are visualised as the
green rectangles shown in the rightmost image in fig-
ure 4. As seen, our regions accurately predict pos-
sible pedestrians in the image. This is the power of
this approach: by combining foreground segmenta-
tion and scene model constraints the search space for
the computationally expensivepedestriandetector can
be enormously restricted. Slight deviations from the
exact pedestrian position are allowed since we employ
a sliding-window approach in the final warped patch.
3.4 Warping Patches
Our scene model has another advantage: for each
image location we know how a pedestrian is locally
distorted. Each region proposal is warped to an up-
right pedestrian at a fixed-scale. Using this approach
we are able to accurately detect even rotated and ex-
tremely small pedestrians, using a single-scale pedes-
trian detector only. The region proposals I are warped
such that I
warp
= TI where transformation matrix
T simply consists of a Euclidean transformation of
which the parameters are extracted from the LUFs:
T =
scosθ −ssinθ t
x
ssinθ scosθ t
y
0 0 1
(2)
Note that the optimal scale to which the patches
are warped highly depends on which pedestrian de-
tector is used. This is dicussed in the next section,
where we motivate the choice of pedestrian detector
and determine the optimal scale.
3.5 Pedestrian Detector
The warped image patches are now classified by a
pedestrian detector. In fact, the method described
in the previous sections is generic and can be com-
bined with each existing pedestrian detection algo-
rithm. As discussed in section 2, recent R-CNN based
detection methods currently achieve top accuracy re-
sults concerning object detection in general. How-
ever, their performance is far from real-time, and they
are more suited for multi-class large database retrieval
tasks. Rigid pedestrian detectors (such as ChnFtrs)
Real-timeAccuratePedestrianDetectionandTrackinginChallengingSurveillanceVideos
329
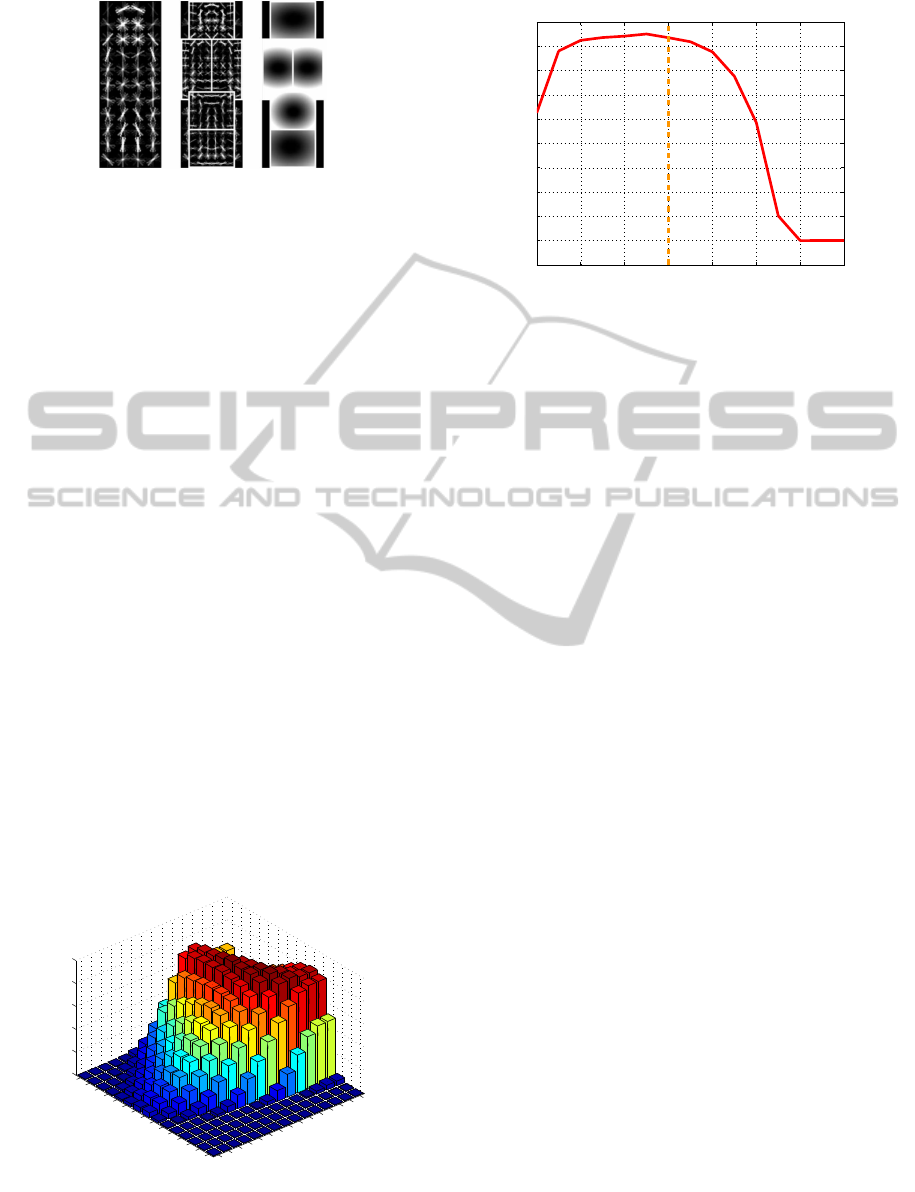
Figure 5: Pedestrian model used in our implementation. (L)
Root model. (M) Different parts. (R) Deformation costs.
currently offer the best trade-off between speed and
accuracy when a full-scale space pyramid needs to
be constructed. However, since we need to evaluate
a single scale only, no scale-space pyramid needs to
be constructed. Therefore we are able to use an accu-
rate pedestrian detector which would otherwise be too
time-consuming, such as the Deformable Part Mod-
els. Moreover, since a rigid model does not allow
for any deformation, using it in our single-scale ap-
proach is even unfeasible in a direct manner. Since
natural slight height variations exist between pedes-
trians (and due to small calibration errors), the de-
tection accuracy significantly drops when using these
models on a single-scale. Given this information, we
opted to use the cascaded DPM model (Felzenszwalb
et al., 2010). When used out-of-the-box this detec-
tor works as follows. First a scale-space pyramid is
constructed in which for each layer HOG features are
calculated resulting in a feature pyramid. Next, this
pyramid is evaluated using a sliding window with the
pedestrian model shown in figure 5. A pedestrian is
represented as a root model (left), several parts rep-
resenting e.g. the limbs and head which are calcu-
lated at twice the resolution of the root model (mid-
dle), and a deformation cost which penalises large
deviations from the expected part locations (right).
−2.5
−2
−1.6
−1.1
−0.6
−0.2
0.3
0.8
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
200
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Det. threshold
Detection accuracy versus height and threshold
Pedestrian height (pixels)
Accuracy
Figure 6: The accuracy versus the pedestrian height and de-
tection threshold for the single-scale cascaded DPM detec-
tor.
6080100120140160180200
0.45
0.5
0.55
0.6
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
Detection accuracy versus pedestrian height
Pedestrian height (pixels)
Accuracy
Figure 7: The optimal threshold slice displaying the accu-
racy versus the pedestrian height.
The responses of both root filter and part filters are
summed to give a final detection score. We altered
this detector into a single-scale only implementation,
and performed experiments to simultaneously deter-
mine the optimal scale factor to which the region pro-
posals need to be warped, and the optimal detection
threshold. This is done as follows. We extracted
about 6000 annotated pedestrians from the CAVIAR
dataset and warped them to different scales (heights).
Combined with 6000 negative patches we calculated
the accuracy in function of the height and detection
score threshold. The results are shown in figure 6.
As can be seen, at low resolutions the accuracy drops
significantly, since only very limited spatial informa-
tion is available. At high resolution similar behaviour
is seen, since the pedestrians mismatch the detec-
tion model. Concerning the detection threshold, the
detection accuracy is low at both high values (high
false negative rate) and low values (high false pos-
itive rate). Figure 7 displays the optimal threshold
slice extracted from figure 6. The accuracy is almost
constant between 130-170 pixels. However, at larger
pedestrian heights the detection time significantly in-
creases. We therefore used 140 pixels as our optimal
rescale height to which the region proposals will be
warped such that a one-scale pedestrian model can be
directly applied.
3.6 Tracking
The resulting detections are then retransformed to the
input image coordinates. Next a non-maxima sup-
pression step is performed, in which overlapping de-
tections are filtered; only the highest scoring detection
is kept. To link detections over multiple frames and
to cope with occasional missing detections we inte-
grate our approach in a tracking-by-detection frame-
work. For this we employ the well-know Kalman
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
330

Figure 8: Qualitative tracking example on two of the evaluation sequences (top and bottom row). See
http://youtu.be/kWoKBPQoeQI for a video.
filter (Kalman, 1960). For each new detection, a
Kalman filter is initialised. We employ a constant ve-
locity motion model. The state vector x
k
thus consists
of the centre of mass of each detection, the velocity
and the scale: x
k
=
x y v
x
v
y
T
. Our process
matrix A thus equals:
A =
1 0 1 0
0 1 0 1
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1
(3)
Using this motion model we predict the position of the
pedestrians in the next frame. When a new frame is
processed, we try to match each running tracker with
a new detection as follows. We construct a circular
region - based on the scale of that tracked detection -
around the estimated new centroid. If the centroid of
a new detection is found within that region, the detec-
tion is associated with this track, and the Kalman filter
is updated. If multiple detections are found, we take
the closest one based on the Euclidean distance. If no
detection can be associated with a running track, we
update the Kalman filter with its estimated position.
If this occurs for multiple frames in a row, the track is
discarded. For detections without an associated track,
evidently a new Kalman filter is instantiated. Further-
more the exact size of the bounding boxes are aver-
aged over multiple frames. See figure 8 for two qual-
itative tracking sequences of our proposed algorithm.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
We performed extensive experiments concerning
both speed and accuracy on the publicly available
CAVIAR dataset (CAVIAR project, 2005). This
dataset was recorded at the entrance lobby of the IN-
RIA labs with a wide-angle camera lens. The images
are taken with a resolution of 384× 288 at 25 frames
per second, and are compressed using MPEG2. See
figure 1 for an example frame. The dataset is di-
vided into six different scenarios: walk, browse, meet,
leave bags, rest and fight. Each scenario is again
subdivided into multiple sequences, making a total
of 28 sequences. We used all sequences of the first
four scenarios (20 sequences in total) for evaluation,
thus excluding the less common rest and fight sce-
narios. In total, our evaluation set consists of about
19650 frames, containing about 29450 annotations.
Our algorithm is implemented in Matlab, with time-
consuming parts (e.g. the detection and transforma-
tion) in C and OpenCV (using mexopencv as inter-
face). Our test hardware consists of an Intel Xeon
E5 CPU which runs at 3.1 GHz. All speed test are
performed on a single CPU core. However, a multi-
threaded CPU implementation to further increase the
processing speed is trivial.
4.1 Accuracy
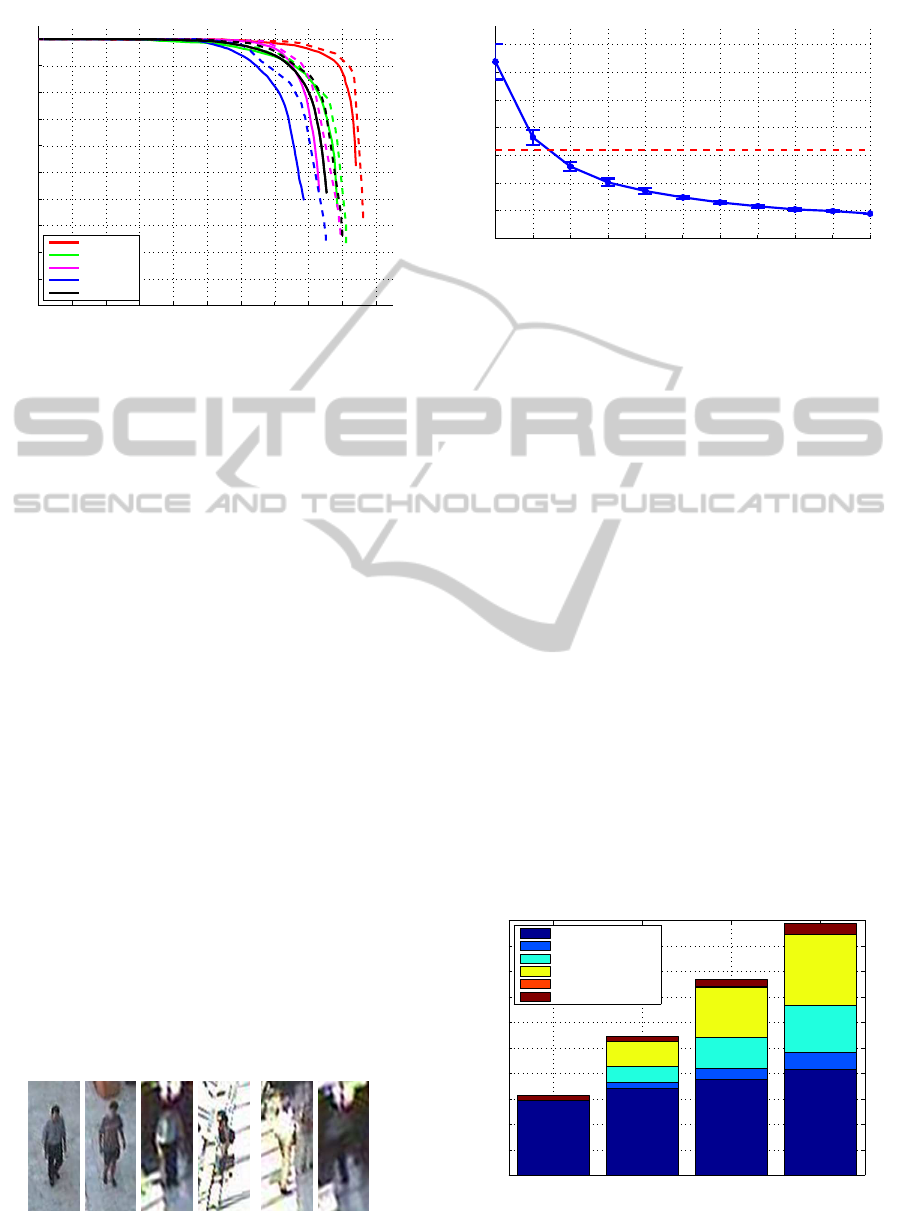
Figure 9 displays the accuracy results of our algo-
rithm, using a precision-recall curve. We give re-
sults for the four scenarios mentioned above, rang-
ing from easy (e.g. walk - limited number of per-
sons) through difficult (e.g. meet - multiple persons
with occlusions). We exclude small pedestrians from
the annotations (20 pixels), and remove annotations
in the top left corner of the image (on the balcony)
and the bottom left corner of the image (people be-
hind the covered reception desk). Furthermore we
discard annotations close to the image border, since
the pedestrians are not completely visible there (the
annotation is strict and already starts when part of a
pedestrian enters the frame). The solid lines in fig-
ure 9 indicate the accuracy without tracking, whereas
Real-timeAccuratePedestrianDetectionandTrackinginChallengingSurveillanceVideos
331
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Accuracy
Recall
Precision
Walk
Browse
Leave bags
Meet
All sets
Figure 9: The accuracy of our algorithm over the CAVIAR
dataset. Solid lines indicate the results without tracking,
dotted lines include tracking.
the dotted lines show the accuracy with tracking. The
black curves indicate the total average accuracy over
the entire evaluation set. To indicate the difficulty,
in figure 10 we display some extracted annotations
which are warped to an upright position. As can be
seen, these low-resolution output images contain se-
vere compression artifacts. Even for humans they
are sometimes difficult to recognize as a pedestrian.
However, we achieve excellent accuracy results given
these strict dataset annotations and challenging nature
of these images. Since our tracker handles missing
detections, the accuracy significantly improves.
4.2 Speed
The exact calculation time depends on the number of
region proposals per image. Figure 11 therefore dis-
plays the speed of our algorithm (in frames per sec-
ond), versus the number of region proposals. Evi-
dently, the processing speed decreases when multiple
region proposals need to be evaluated. However, even
at e.g. four region proposals we still achieve 17 fps.
Over the entire evaluation set we achieve an average
of 32 frames per second, indicated with the dotted red
line. Note that all experimental results are performed
on a single CPU core. In fact, each region proposal
can be evaluated independently, thus allowing for an
Figure 10: Example of warped annotations. Low-resolution
and high-compression artifacts are noticeable.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Processing speed
Number of region proposals
FPS
Figure 11: The processing speed of our algorithm versus
the number of regions proposals.
easy multi-threaded implementation. Figure 12 visu-
alises the individual calculation times for each impor-
tant step in the entire algorithm pipeline, for a vary-
ing number of region proposals. As visualised, gen-
eration of the region proposals takes about 15-20ms.
The warping operation is very fast: on average 1ms
per region proposal is needed. Concerning the pedes-
trian evaluation step, the average feature calculation
time per region is about 3ms whereas the model eval-
uation takes 4ms. The time needed to retransform the
coordinates is negligible.
4.3 Comparative Evaluation
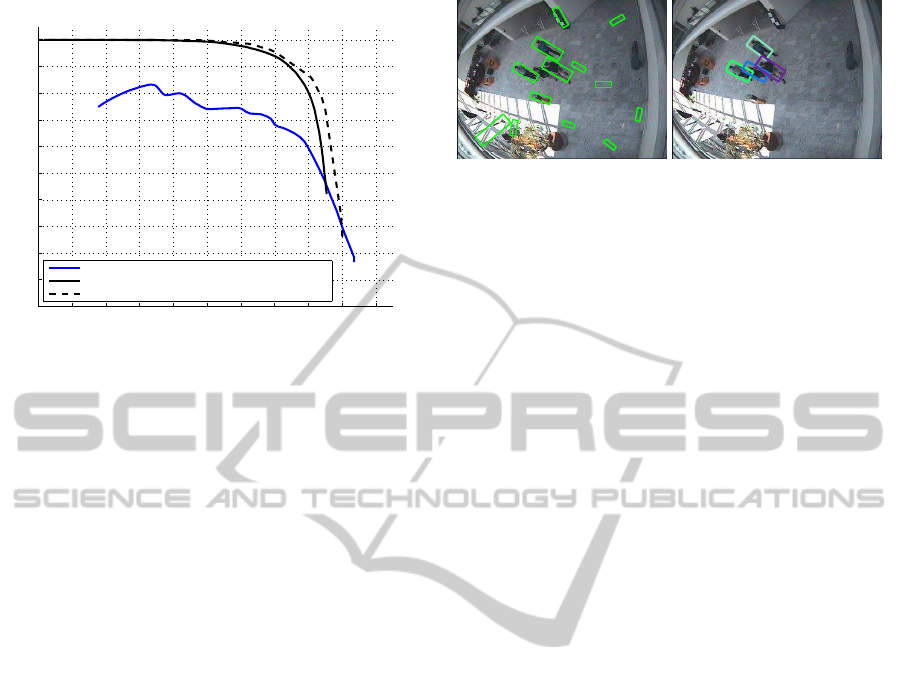
Figure 13 illustrates the accuracy improvement we
achieved as compared to a basic background subtrac-
tion technique, i.e. interpreting the foreground blobs
that are large enough as pedestrians. As seen, on
these challenging images these naive methods yield
poor results. The inclusion of our scene model and
the application of a state-of-the-art pedestrian detec-
tor raises the accuracy enormously.
A quantitative comparison with other work us-
0 (15.7 ms) 1 (27.4 ms) 2 (38.5 ms) 3 (49.4 ms)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
Detailed calculation time
Time in ms
Number of region proposals
Region propsals
Warping
Calc. features
Model evaluation
Retransform coord.
Tracking and overhead
Figure 12: An overview of the calculation time for each step
in the algorithm versus the number of region proposals.
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
332
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Accuracy improvement
Recall
Precision
Background subtraction
Region prop. + pedestrian det. (Ours)
Region prop. + pedestrian det. + tracking (Ours − final)
Figure 13: The obtained accuracy improvement compared
to a naive background subtraction approach.
ing precision-recall curves on this dataset is difficult,
since to the best of our knowledge no such accuracy
results similar to our work exist. Existing work on
these specific sequences of the CAVIAR dataset of-
ten focusses on activity recognition (e.g. fight) and
anomaly detection. However, (Rogez et al., 2014b)
present accuracy experiments using tracking failure
measurements on 11 tracks of the CAVIAR dataset.
For this, the authors consider a track lost if the track-
ing failed for 20 frames or more. In their work
a multi-hypothesis tracking approach (particle filter)
is used. They achieve a tracking failure percentage
of 33.64% with N = 20 particles and 16.82% when
N = 50. Using our approach we achieve a tracking
failure of 9.1% on the same sequences relying only
on a single hypothesis tracker (Kalman filter).
As a final qualitative analysis, we compare our ap-
proach with a naive detection approach; that is run-
ning the standard deformable part model detector on
all scales and all rotations. For this, we need to up-
scale the image five times (the smallest pedestrian to
be detected is only 25 pixels high, and the height of
the detection model equals 120 pixels), and use a rota-
tion step size of 10 degrees. Using this approach, the
calculation time for a single frame increases to about
13 minutes. Figure 14 displays the detections found
using this naive approach (left), and the output of our
algorithm (right). As seen, the naive approach yields
several false positives and fails to detect all pedestri-
ans. Our algorithm achieves excellent accuracy re-
sults with minimal computational cost (89ms for this
frame).
Figure 14: Qualitative comparison between running a de-
tector on all scales and rotations (left) versus the output of
our algorithm (right).
5 CONCLUSIONS
We presented a fast and accurate pedestrian detection
and tracking framework targeting challenging surveil-
lance videos. Our proposed algorithm integrates
foreground segmentation methods with scene con-
straints to generate region proposals, which are then
warped and evaluated by a single-scale pedestrian de-
tector. Using this approach we can employ a highly
accurate pedestrian detector for non-trivial camera-
viewpoint images where existing pedestrian detectors
fail, while still achieving real-time performance. We
performed extensive evaluation experiments concern-
ing both accuracy and speed on the publicly avail-
able CAVIAR dataset. This dataset consists of typi-
cal low-resolution high-compression surveillance im-
ages taken with a wide-angle lens from a challeng-
ing viewpoint. We show that our approach achieves
both excellent accuracy and processing speeds using a
single-core CPU implementation only. Furthermore,
our proposed method easily lends itself for a multi-
threaded implementation. Currently, the scene cali-
bration is based on annotation data. In the future we
plan to investigate if an automated calibration method
can be implemented (using e.g. an offline exhaustive
search over all scales and rotations).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge that the
dataset used here is from the EC Funded CAVIAR
project/IST 2001 37540 (CAVIAR project, 2005).
REFERENCES
Benenson, R., Mathias, M., Timofte, R., and Van Gool, L.
(2012a). Fast stixels computation for fast pedestrian
detection. In ECCV, CVVT workshop, pages 11–20.
Benenson, R., Mathias, M., Timofte, R., and Van Gool, L.
Real-timeAccuratePedestrianDetectionandTrackinginChallengingSurveillanceVideos
333

(2012b). Pedestrian detection at 100 frames per sec-
ond. In Proceedings of CVPR, pages 2903–2910.
Benenson, R., Mathias, M., Tuytelaars, T., and Van Gool, L.
(2013). Seeking the strongest rigid detector. In Proc.
of CVPR, pages 3666–3673, Portland, Oregon.
Benenson, R., Omran, M., Hosang, J., and Schiele, B.
(2014). Ten years of pedestrian detection, what have
we learned? In ECCV, CVRSUAD workshop.
Benezeth, Y., Jodoin, P.-M., Emile, B., Laurent, H., and
Rosenberger, C. (2008). Review and evaluation of
commonly-implemented background subtraction al-
gorithms. In Pattern Recognition, 2008. ICPR 2008.
19th International Conference on, pages 1–4. IEEE.
Benfold, B. and Reid, I. (2011). Stable multi-target tracking
in real-time surveillance video. In CVPR, pages 3457–
3464.
Breitenstein, M. D., Reichlin, F., Leibe, B., Koller-Meier,
E., and Van Gool, L. (2011). Online multiper-
son tracking-by-detection from a single, uncalibrated
camera. IEEE PAMI, 33(9):1820–1833.
CAVIAR project (2005). The CAVIAR project: Context
aware vision using image-based active recognition.
http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CAVIAR/.
Cho, H., Rybski, P., Bar-Hillel, A., and Zhang, W. (2012).
Real-time pedestrian detection with deformable part
models. In IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium,
pages 1035–1042.
Dalal, N. and Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of oriented gra-
dients for human detection. In Proceedings of CVPR,
volume 2, pages 886–893.
Doll´ar, P., Appel, R., Belongie, S., and Perona, P. (2014).
Fast feature pyramids for object detection.
Doll´ar, P., Belongie, S., and Perona, P. (2010). The fastest
pedestrian detector in the west. In Proceedings of
BMVC, pages 68.1–68.11.
Doll´ar, P., Tu, Z., Perona, P., and Belongie, S. (2009a). Inte-
gral channel features. In Proc. of BMVC, pages 91.1–
91.11.
Doll´ar, P., Wojek, C., Schiele, B., and Perona, P. (2009b).
Pedestrian detection: A benchmark. In Proceedings
of CVPR, pages 304–311.
Doll´ar, P., Wojek, C., Schiele, B., and Perona, P. (2012).
Pedestrian detection: An evaluation of the state of the
art. In IEEE PAMI, 34:743–761.
Felzenszwalb, P., Girschick, R., and McAllester, D. (2010).
Cascade object detection with deformable part mod-
els. In Proceedings of CVPR, pages 2241–2248.
Felzenszwalb, P., McAllester, D., and Ramanan, D. (2008).
A discriminatively trained, multiscale, deformable
part model. In Proceedings of CVPR.
Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., and Malik, J. (2014a).
Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection
and semantic segmentation. In Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition.
Girshick, R., Felzenszwalb, P., and McAllester, D. (2012).
Discriminatively trained deformable part models, re-
lease 5. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence.
Girshick, R. B., Iandola, F. N., Darrell, T., and Malik, J.
(2014b). Deformable part models are convolutional
neural networks. CoRR, abs/1409.5403.
Girshick, R. B. and Malik, J. (2013). Training deformable
part models with decorrelated features. In IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2013,
Sydney, Australia, December 1-8, 2013.
Kalman, R. (1960). A new approach to linear filtering
and prediction problems. In Transaction of the ASME
Journal of Basic Engineering, volume 82.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012). Im-
agenet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. In Advances in Neural Information Pro-
cessing Systems 25, pages 1097–1105. Curran Asso-
ciates, Inc.
Leykin, A. and Hammoud, R. (2010). Pedestrian tracking
by fusion of thermal-visible surveillance videos. Ma-
chine Vision and Applications, 21(4):587–595.
Orts-Escolano, S., Garcia-Rodriguez, J., Morell, V., Ca-
zorla, M., Azorin, J., and Garcia-Chamizo, J. M.
(2014). Parallel computational intelligence-based
multi-camera surveillance system. Journal of Sensor
and Actuator Networks, 3(2):95–112.
Parks, D. H. and Fels, S. S. (2008). Evaluation of back-
ground subtraction algorithms with post-processing.
In Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance,
2008. AVSS’08. IEEE Fifth International Conference
on, pages 192–199. IEEE.
Pedersoli, M., Gonzalez, J., Hu, X., and Roca, X. (2013).
Toward real-time pedestrian detection based on a de-
formable template model. In IEEE ITS.
Rogez, G., Orrite, C., Guerrero, J. J., and Torr, P. H. S.
(2014a). Exploiting projective geometry for view-
invariant monocular human motion analysis in man-
made environments. Computer Vision and Image Un-
derstanding, 120:126–140.
Rogez, G., Rihan, J., Guerrero, J. J., and Orrite, C. (2014b).
Monocular 3D gait tracking in surveillance scenes.
IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics
Part B (Cybernetics), 44(6):894–909.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S.,
Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A., Bern-
stein, M., Berg, A. C., and Fei-Fei, L. (2014). Ima-
genet large scale visual recognition challenge.
Singh, V. K., Wu, B., and Nevatia, R. (2008). Pedestrian
tracking by associating tracklets using detection resid-
uals. In Motion and video Computing, 2008. WMVC
2008. IEEE Workshop on, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Van Beeck, K., Tuytelaars, T., and Goedem´e, T. (2012). A
warping window approach to real-time vision-based
pedestrian detection in a truck’s blind spot zone. In
Proceedings of ICINCO.
Zivkovic, Z. and van der Heijden, F. (2006). Efficient adap-
tive density estimation per image pixel for the task of
background subtraction. Pattern recognition letters,
27(7):773–780.
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
334
