
An Agent Architecture for Adaptive Supervision and Control of Smart
Environments
Stefano Ferilli, Berardina De Carolis, Andrea Pazienza, Floriana Esposito
and Domenico Redavid
Dip. di Informatica, University of Bari, via E. Orabona 4, Bari, Italy
Keywords:
Ambient Intelligence, Workflow Management, Service Composition.
Abstract:
This paper describes the architecture and functionality of a generic agent that is in charge of handling a given
environment in an Ambient Intelligence context, ensuring suitable contextualized and personalized support to
the user’s actions, adaptivity to the user’s peculiarities and to changes over time, and automated management
of the environment itself. The architecture is implemented in a multi-agent system, where different types of
agents are endowed with different levels of reasoning and learning capabilities. In addition to controlling
normal operations of the environment, the system may identify user’s needs and goals and activate suitable
workflows to satisfy them. Some actions in these workflow involve the execution of semantic services. When
a single service is not available for fulfilling a given need, an automatic service composer is used to obtain a
suitable combination of services. The architecture has been implemented in a prototypical agent-based system
that works in a Smart Home Environment.
1 INTRODUCTION
Users of a smart environment often have contextual
needs depending on the situation. According to (Yau
and Liu, 2006), a situation-aware environment should
understand both the status of the environment, and
the status and the needs of users in order to proac-
tively support them with the most appropriate config-
uration of actions of various devices and resources in
the smart environment. This capability of the environ-
ment is even more important in the context of Ambi-
ent Assisted Living (AAL), where the aim is support-
ing elder people in their daily life by assisting them
with intelligent solutions for providing the services
they need (Sun et al., 2009).
Developing a situation aware environment re-
quires efficient, flexible and scalable solutions. We
propose an approach based on software agents able to
recognize the user’s situational goal, to provide smart
(i.e., integrated, interoperable and personalized) ser-
vices for satisfying this goal and to provide suitable
interfaces using the possibilities offered by the vari-
ous devices that are present in the environment. The
environment must be able to reason on the situation
of the users so as to understand their needs and goals
for composing the most appropriate services.
The following approaches for composing services
are most commonly used:
Manual Composition: the user must tell the system
how to compose services. In general, this process
is quite complex and requires knowledge about
existing available services and about how to com-
pose and integrate them. In order to help the
users in manual composition of services, some
interesting interaction metaphors have been pro-
posed (Humble et al., 2003).
Automatic Composition: service composition is
planned without human intervention by using
methods and techniques typical of planning in Ar-
tificial Intelligence (Paik and Maruyama, 2007).
The user has no workload for finding, filtering
and integrating services. The system, starting
from the high-level goal of the user, automatically
generates the workflow of services that satisfy her
needs. Planning however is a complex task and
requires the correct formalization of the problem,
of the actions and of the constraints. Moreover,
problems might arise in understanding the user’s
goals and in matching them semantically against
existing services.
Semi-automatic Composition: the system, accord-
ing to the recognized needs and situation, se-
lects the most appropriate composition of services
160
Ferilli S., De Carolis B., Pazienza A., Esposito F. and Redavid D..
An Agent Architecture for Adaptive Supervision and Control of Smart Environments.
DOI: 10.5220/0005326301600167
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems (PECCS-2015), pages
160-167
ISBN: 978-989-758-084-0
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

among those that are available in a repository or
that can be planned. When this is not possible, the
system interactively guides the user in finding, fil-
tering and composing services (Kim et al., 2004).
We work in this latter direction and propose a
Multi Agent System (MAS) architecture. The key
feature of our proposal is the design and development
of the architecture and functionalities of a generic
agent class that can be specialized for several specific
roles. These roles are in charge of handling the differ-
ent features and capabilities of a situation-aware en-
vironment, ensuring suitable contextualized and per-
sonalized support to the user’s actions, adaptivity to
the user’s status and needs and to changes over time,
and automated management of the environment itself.
The architecture has been implemented in a prototyp-
ical agent-based system that works in a Smart Home
Environment (SHE) scenario, where it is necessary
to combine services of the physical environment with
net-centric ones according to the recognized situation.
The paper is structured as follows. The proposed
architecture, and its most relevant components, are
described in Section 3. Then, Section 4 proposes sev-
eral kinds of roles to be implemented by agents that
work in the smart environment. A sample scenario
is proposed in Section 5, before concluding the paper
and outlining future work issues in Section 6.
2 RELATED WORK
A smart environment is able to acquire and apply
knowledge about its inhabitants and their surround-
ings in order to adapt to the situational goals (Cook,
2009). Then developing a smart environment requires
software components that, at different levels of ab-
straction, may perceive the environment and, more or
less autonomously,act on it by providing the response
that is appropriate to the situation. An agent is an
entity that matches these requirements (Wooldridge
and Jennings, 1995). In particular, BDI (Belief De-
sire Intention) agents are endowedwith this capability
and act on the basis of practical reasoning (Rao and
Georgeff, 1991). Their reasoning is based on their in-
tentions, that originate from the intersection between
beliefs about the state of the world, and desires (the
agents’ goals).
Moreover, agents can be organized in order to
solve complex and distributed problems in a Multi
Agent System (MAS). Typically MAS meet the re-
quirements on modularity, flexibility and scalability
needed to handle the complexity of a smart environ-
ment (Ayala et al., 2012). When endowed with appro-
priate knowledge and reasoning capabilities a MAS
represents a way to design and implement a proactive
and adaptive environment in relation to individual and
changing needs (Cook, 2009; Wolf et al., 2010).
Early research projects concerned with applying
intelligent agents to the realization of a Smart Home
focused on the development of a home that programs
itself by observing the lifestyle and desires of the
inhabitants, and learns to anticipate and accommo-
date their needs (Mozer, 2005; Rao and Cook, 2004;
De Carolis et al., 2005). More recently, research has
focused on how smart environments can be used to
provide assistance and support to elderly people dur-
ing their life at home (Sun et al., 2009).
Applying agent-based approaches on this domain
seems to be a promising direction for research (Cook
et al., 2009; O’Grady et al., 2010). In particular, (Mc-
Naull et al., 2011) presented a context-aware MAS
that may help to assist an individual in an AAL sce-
nario. (Sernani et al., 2013) adopt the metaphor of
the Virtual Carer for implementing a MAS for mon-
itoring the health conditions of assisted persons and
facilitating their daily activities.
Recently the agent based approach has been com-
bined to the service oriented one (Wu et al., 2007).
In (Mars´a-Maestre et al., 2008) the problem of ser-
vice personalization in smart environments is ad-
dressed by a Service Oriented Architecture imple-
mentation based on multiagent systems. In particular
they take advantage of the mobility features of soft-
ware agents. In particular, they have developed a hi-
erarchical, agent-based solution intended to be appli-
cable to different smart space scenarios, ranging from
small environments to large smart spaces like cities.
The proactive nature of a smart environment has
been investigated by several research works that pro-
pose the processing of contextual data for carrying
out analysis for erroneous events in order to pro-
vide “relevant information and/or services to the user,
where relevancy depends on the user’s task.” (Dey,
2001). Many research projects touch upon context
aware computing and ambient assisted living. Exam-
ples include the research conducted by (Chun-dong
et al., 2009), that propose a framework providing
adaptive service in an intelligent home environment.
(D’Andrea et al., 2009) propose a system that in-
terprets user’s spoken dialogue and exploits writing
recognition to control a home environment. A frame-
work for developing multi-model interfaces for re-
minding meals to elderly people is described in (Blu-
mendorf and Albayrak, 2009) and a framework for
adapting interactive systems based on user behavior
is discussed by (Bezold, 2010).
Therefore, developing a smart environment re-
quires designing a complex intelligent system able to
AnAgentArchitectureforAdaptiveSupervisionandControlofSmartEnvironments
161
acquire and apply knowledge about the environment
and its residents in order to improve their quality of
life in that environment by providing situation-aware
services through natural and effective interfaces. To
achieve this aim, we recognized the need of develop-
ing an architecture of a MAS that combines the prac-
tical reasoning capabilities of BDI agents, the learn-
ing capabilities of intelligent learning agents and the
service oriented approach in order to implement an
Ambient Intelligence (AmI) system that is able to un-
obtrusively and proactively adapt to the individual sit-
uational needs.
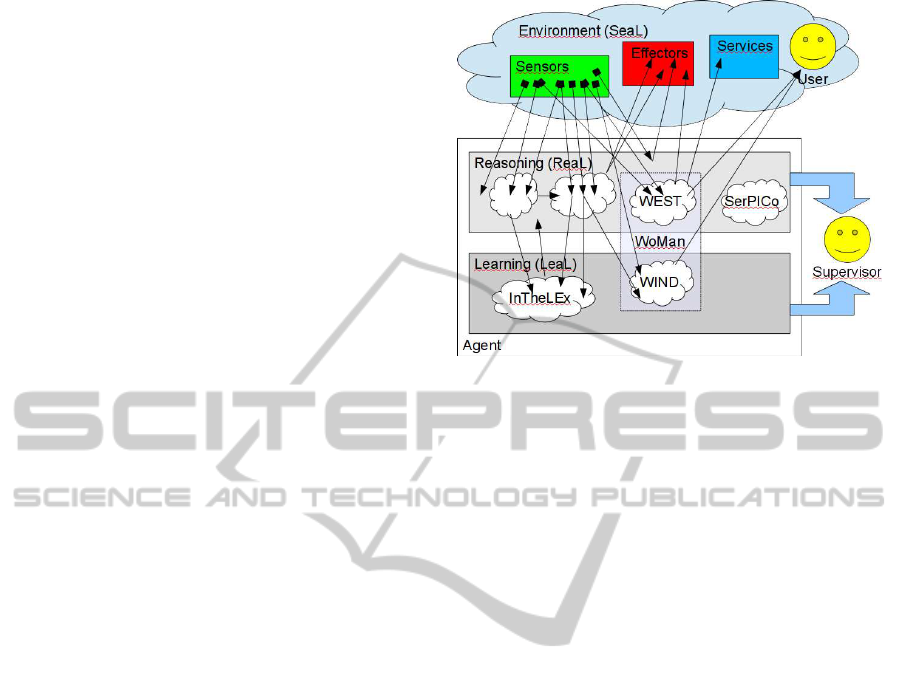
3 ARCHITECTURE
The general architecture implemented by our agents,
which is an extended version of that introduced
in (Ferilli et al., 2011), is reported in Figure 1. Ac-
cording to this architecture, each agent is endowed
with a multi-strategy reasoning engine involving two
functional levels: the Reasoning Layer (ReaL) and the
Learning Layer (LeaL). The environment in which the
agent operates represents the Sensors, Effectors and
Applications Layer (SeaL). Both ReaL and LeaL are
able to apply several types of inference, including:
Abstraction used to simplify the available informa-
tion by removing irrelevant details;
Deduction used to apply the user and context models
in order to understand what is going on in the en-
vironment and what actions should be taken con-
sequently;
Abduction used to deal with cases of incomplete
knowledge, hypothesizing sensible values for
missing information;
Induction used to adapt the user and context mod-
els based on the feedback obtained during the sys-
tem’s interaction.
The initial knowledge base used by ReaL, organized
in several cooperating modules referred to specific
topics, is built using information provided by experts,
but can be refined and improved automatically as long
as the system works by exploiting the functionality of
LeaL. Among other kinds of knowledge, it includes
user models, context models and process models to
be used for adapting/personalizing the interaction and
controlling the flow of events.
A user model includes knowledge that allows to
infer his mental and physical status, his goals and ob-
jectives, his preferences and interests, and his needs
and requirements. Personalized models may be avail-
able for specific users, typically learned by monitor-
Figure 1: Agent’s architecture.
ing their behavior. A context model includes knowl-
edge that allows to infer what kind of situation is
faced by the system, what is going on in the environ-
ment, and how to act in order to properly handle the
situations that are occurring. A process model spec-
ifies which combinations of activities are allowed to
accomplish a given goal. Many models may be avail-
able for reaching the same goal. Process models can
be combined (e.g., one process may involve a com-
plex activity, for which one or more process models
may be available). Based on the user profile and the
current context, the system identifies possible goals of
the user, and extracts from its workflow repository the
items that specify how to satisfy those goals.
The two levels currently include the following op-
erational modules: AmICo (Ambient Intelligence Co-
ordinator) applies the knowledge base; InTheLEx (In-
cremental Theory Learner from Examples) refines it
according to the feedback obtained by the user and
the environment; WoMan (Workflow Manager) con-
trols process executions and SerPICo (Service Plan-
ner Identifier and Composer) provides service com-
position facilities.
3.1 Workflow Management
WoMan (Ferilli, 2014) includes two submodules:
WEST (Workflow Enactment Supervisor and Trainer)
can supervise a process execution and foresee the next
activities of the user according to a given process
model; WIND (Workflow INDucer) can learn and/or
refine the process model based on cases that are pro-
vided as successful examples of process execution.
Given a goal, the system selects the process mod-
els that allow to reach that goal. While receiving the
events coming from the environment, the system acts
PECCS2015-5thInternationalConferenceonPervasiveandEmbeddedComputingandCommunicationSystems
162

in supervision mode, checking whether it is compli-
ant with the current model(s) that have been activated.
The outcome for each activity can be:
ok the activity is compliant with the model;
warning the event does not match the model because
the activity is not allowed by the model in the cur-
rent status of the execution;
error termination of an activity that had never be-
gun; termination of the process execution with
still pending activities.
As long as the process execution proceeds, these out-
comes are collected. If several candidate workflow
models are considered, they are used by the system to
hypothesize which models are more likely to be tak-
ing place and which ones are less likely, using its sub-
module WoGue (acronym for WOrkflow GUEsser).
For each model WoMan can also, based on the
current status and context of the execution, foresee
which will be the next actions of the user. This al-
lows the agent to carry out suitable interventions that
support or facilitate the execution of these actions, by
just communicating useful information to the user or
to an external interested person or by directly acting
on suitable effectors to modify the environment. In
other cases, the desired effect is provided by existing
services that the agent may call. While atomic ser-
vices can be directly activated by the agent, there are
complex tasks for which a single service is not avail-
able, and there is no know composition of elementary
services that solves the problem. In these cases, the
system may call SerPICo to find service compositions
that may reach the objective and are compliant with
the given constraints, preferences or requirements.
When the process execution terminates, if no error
was raised, and the system is notified that the execu-
tion was correct, the learning component is called to
refine the process model as follows:
• adding new tasks to the activity flow model;
• adding new paths between available activities in
the activity flow model;
• changing the weights of the componentsof the ac-
tivity flow model;
• refining the pre- and/or post-conditions for the ac-
tivities and/or paths in the activity flow model.
Correct cases just change the weights of the model.
3.2 Service Composition
Let us explain how to obtain OWL-S (OWL for Ser-
vices
1
) composed services using Semantic Web lan-
guages and tools, in particular the Semantic Web Rule
1
http://www.w3.org/Submission/OWL-S/
Language (SWRL)
2
. OWL-S is an ontology that en-
ables semantic descriptions of Web services by means
of three perspectives: ServiceProfile, with advertise-
ment aims; ServiceGrounding, used to link a concrete
service description (i.e., WSDL); and ServiceModel,
that defines the OWL-S process model. In particular,
each process is based on an IOPR (Inputs, Outputs,
Preconditions, and Results) model. The Inputs repre-
sent the information that is required for the execution
of the process. The Outputs represent the information
that the process returns to the requester. Precondi-
tions are conditions imposed over the Inputs that must
hold for successfully invoking the process. Since an
OWL-S process may yield several results with cor-
responding outputs, the Results entity of the IOPR
model provides a means to specify this situation.
Each result can be associated to a result condition,
called inCondition, that specifies when that particular
result can occur. It is assumed that such conditions
are mutually exclusive, so that only one result can be
obtained for each possible situation. When an inCon-
dition is satisfied, there are properties associated to
this event that specify the corresponding output (with-
Output property) and, possibly, the Effects (hasEffect
properties) produced by the execution of the process.
Effects are changes in the state of the world. The
OWL-S conditions (Preconditions, inConditions and
Effects) are represented as logical formulas. Since
OWL offers limited support to formulate constructs
like property compositions without becoming unde-
cidable, a more powerful language is required for the
representation of OWL-S conditions.
One of the proposed languages is SWRL. Al-
though SWRL is undecidable, a solution has been
proposed in (Motik et al., 2005) where decidability
is achieved by restricting the application of SWRL
rules only to the individuals explicitly introduced in
the ABox. This kind of SWRL rules, called DL-safe,
makes this language the best candidate for represent-
ing OWL-S conditions (Redavid et al., 2013). Let us
now briefly mention the characteristics of SWRL that
are relevant to our scope. SWRL extends the set of
OWL axioms (classes, properties, built-ins) to include
Horn-like rules in the form of implicationsbetween an
antecedent (body) and a consequent (head), both con-
sisting of conjunctions of zero or more atoms. The
intended meaning can be read as: whenever the con-
ditions specified in the antecedent hold, then the con-
ditions specified in the consequent must also hold. A
rule with conjunctive consequent can be transformed
into multiple rules each with an atomic consequent by
means of Lloyd-Topor transformations.
We encode an atomic OWL-S service with the fol-
2
http://www.w3.org/Submission/SWRL/
AnAgentArchitectureforAdaptiveSupervisionandControlofSmartEnvironments
163

lowing abstract rule (Redavid et al., 2013):
Preconditions ∧ inCondition → {output} ∧ E f fect
If the service has many Results, multiple rules having
different inCondition, output and/or Effect are used.
With this encoding we can apply the SWRL composer
proposed in the same work. It implements a backward
search algorithm for the composition task that works
as follows: it takes as input a set of SWRL rules and
a goal specified as a SWRL atom, and returns every
possible path built by combining the available SWRL
rules in order to achieve such a goal. These rules ful-
fill the SWRL safety condition. Specifically, the algo-
rithm performs backward chaining starting from the
goal in the same way as Prolog-like reasoners work
for query answering. The difference is that this algo-
rithm works on SWRL DL-safe rules instead of Horn
clauses. This means that, besides the rule base, it
takes into account also the Description Logic ontol-
ogy the rules refer to.
The SWRL rule path found, and consequently the
resulting OWL-S service composition, will be valid
(in the sense that it will produce results for the se-
lected goal) only if the SWRL rules in the path are
DL-safe. In other words, DL-safety means that rules
are true for individuals that are known, i.e. that ap-
pear in the knowledge base. The implemented proto-
type performs DL-safety check. This guarantees that
the application of rules is grounded in the ABox and,
consequently, that the services embodying those rules
can be executed.
4 TYPES OF AGENTS
The types of agents that implement the above archi-
tecture extend those in (Cavone et al., 2012):
Sensor Agents (SA): provide information about sen-
sor parameters and values (e.g., temperature, light
level, humidity, etc.).
Context Agents (CA): determinethe current context
from sensor events; they are able to reason at a
higher level than sensor agents, for instance start-
ing from temperature and humidity data they may
determine whether the user is in a comfortable sit-
uation (De Carolis et al., 2005).
User Profile Agent (UPA): is responsible for deter-
mining the preferencesprofile to be used, and may
serve personalization purposes.
Butler Agent (BA): combines intelligent reasoning,
machine learning, service-oriented computing
and semantic Web technologies for flexibly coor-
dinating and adaptively providing smart services
in dynamically changing contexts.
Effector Agents (EA): each appliance and device is
controlled by an EA that reasons on the opportu-
nity of performing an action instead of another in
the current context.
Interactor Agents (IA): handle interaction with the
user. They are responsible for choosing the best
interaction metaphor according to the situation
and to the user’s needs and preferences, and for
executing suitable communicative tasks by per-
forming communicative actions.
Housekeeper Agent (HA): acts as a facilitator since
it knows all the agents that are active in the house
and also the goals they are able to fulfill.
The underlying metaphor is that of a butler in a grand-
house that is in charge of perceiving the situation of
the house and of coordinating the housestaff in order
to satisfy the needs of the house inhabitants. In par-
ticular, it reasons on the user’s goals and devises the
workflow to satisfy them.
These agents coordinate themselves as follows.
Cyclically, or as an answer to a user action, the but-
ler runs its reasoning model about the user. Based on
the information provided by the appropriate CAs, it
infers the possible goals and needs of the user and
ranks them by urgency or certainty by consulting
the UPA. Given a specific goal, it selects an appro-
priate workflow by matching semantically the goal
with all the Input, Output, Pre-Condition and Ef-
fect (IOPE) descriptions of the workflows stored in
a workflow repository. During workflow enactment,
semantic matchmaking is also used to select the ser-
vices/actions to be invoked among those available in
the environment.
The available semantic Web services are listed in
a Semantic Web Services Register (SWSR) according
to the IOPE standard representation (Meyer, 2007).
Hence, the workflow services are invoked dynami-
cally, matching the user’s needs in the most effec-
tive way. As regards predicates of Web Services,
both simple and complex Web Services will be im-
plemented according to the standard OWL-S.
5 SAMPLE SCENARIO
As a sample scenario, consider a SHE in which Steve
usually lives alone, but is occasionally visited by his
relatives, friends and girlfriend (Tina). It is Friday
evening, and based on the user’s profile and cur-
rent context the system has inferred the need for
pursuing the goal ‘relaxing
amusement’. The cor-
responding workflow extracted from the repository
is ‘evening
at home’. The system loads the corre-
PECCS2015-5thInternationalConferenceonPervasiveandEmbeddedComputingandCommunicationSystems
164

(a) (b)
Figure 2: Choose Pizza service sequences (a) and Order Pizza service sequences (b).
sponding model and starts checking complianceof the
user’s actions with this model (in addition to carrying
out normal control activities over the environment).
Tina is also present.
At some point during workflow enactment, the
system foresees that the user will almost certainly per-
form task ‘dinner’ and, concurrently, ‘watch
movie’
or ‘watch football’.
• Dinner, is a complex activity that may be carried
out according to different sub-workflows: ‘for-
mal
dinner’, ‘informal dinner’, or ‘fast dinner’.
Since a precondition for ‘formal dinner’ is that
the user has dressed elegant clothes, and that
the ‘relax
amusement’ goal is not active, the
system discards the ‘formal
dinner’ option, and
starts checking compliance of the user’s actions
with the remaining two models. These actions
cause more warnings on ‘informal
dinner’ than
on ‘fast
dinner’ (e.g., activities ‘set table’ and
‘use kitchen’, required by the former, are not exe-
cuted), for which reason the latter is deemed as
more likely to be running. While tracking this
process, at some point the system foresees that the
user will carry out activities ‘pizza’ and ‘beer’. As
to the latter, it immediately activates suitable ef-
fectors to start cooling a beer. As to the former, no
pizza is available at home, so it must be ordered.
• As to the ‘watch
movie’ vs. ‘watch football’ op-
tion, the precondition for the latter requires,
among other features, that it must be Wednes-
day and that Steve’s girlfriend must not be present
(because, according to her profile, she doesn’t
like football). Due to these requirements be-
ing not fulfilled, the option is discarded, and the
‘watch movie’ action is pursued.
Both actions ‘pizza’ and ‘watch
movie’ can be carried
out by the system by calling corresponding (compo-
sitions of) Web Services. E.g., suppose that no single
Web service is available to order a pizza, nor a com-
posite service is known to the system to do this. In
this case, the system activates the Service Composer
to find one.
For instance, the set of available services, anno-
tated in OWL-S, might be as reported in Table 1. Us-
ing the OWL-S composer, the agent obtains the com-
positions in Figure 2. Note that different services use
different ontologies. These ontologies have been pre-
viously aligned, to know which classes of the former
are equivalent to which ones of the latter. Given the
compositions, the agent executes the following steps:
1. it uses the composition in Figure 2(a) to evalu-
ate what sequence of services best matches its
requirement (examples of evaluation conditions
might be a lower price or the possibility to change
the order);
2. it uses the composition in Figure 2(b) to evaluate
whether the sequence of services for the dealer se-
lected in the previous step can be used (i.e., it has
all the required input parameter values); if needed
or appropriate, it may consider the other services
offered by the provider (e.g., SpizzicoRegistration
or SpizzicoRechargeService for Spizzico);
3. in case the selected sequence is not applicable, it
goes back to step 1 to select another sequence, not
considering anymore the evaluated sequence;
4. it executes the chosen service sequence and ob-
tains the order receipt.
The agent might apply the same procedure to order
the movie.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper describes the architecture and functional-
AnAgentArchitectureforAdaptiveSupervisionandControlofSmartEnvironments
165
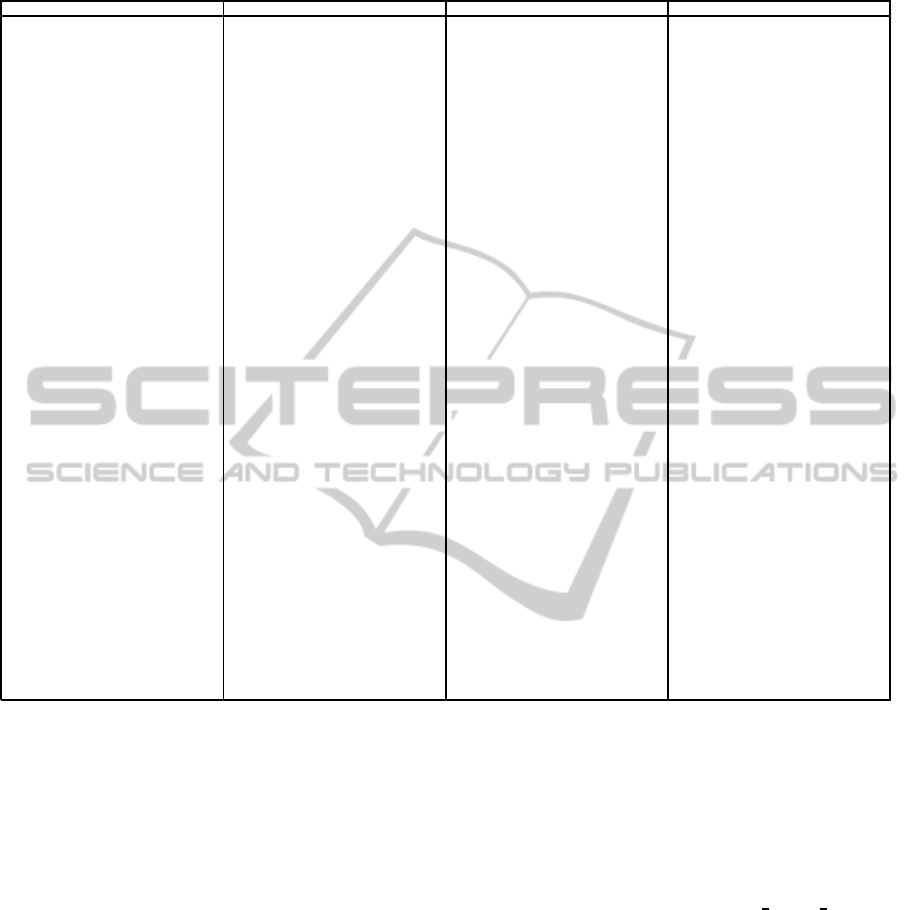
Table 1: Set of services annotated in OWL-S.
Spizzico PizzaHut RossoPomodoro GenericServices
SpizzicoMenu: given the requester’s
address and the name of the desired
Pizza, returns the internal Spizzico
Pizza code and the price, or an
unavailability message in case no
Dealer exists within acceptable dis-
tance.
• Input: Address, PizzaName
• Output: SpPizzaCode, Price
• Precondition: Ex-
ist(PizzaName) and Avail-
ableDealer(Address, Piz-
zaName)
SpizzicoOrder: given a Spizzico code,
a date and time, an optional address
and a userCode, returns a receipt
(with no more than half an hour
later than the time required) or an
unavailability message in case the
required pizza cannot be ordered or
the credit is insufficient.
• Input: PizzaCode, DateAnd-
Time, Address, userCode
• Output: receipt or NotAvail-
ableMSG
• Precondition:
Valid(PizzaCode) and Ex-
ist(userCode) and ValidTime
(DateAndTime)
SpizzicoRegistration: the registration
is needed to use the home delivery
service.
• Input: userName, password,
address, city
• Output: userCode
SpizzicoRechargeService: allows to
charge the amount associated to
user code.
• Input: userCode, creditCard-
Number, amount
• Output: userCode
HutMenu: given the requester’s ad-
dress and the name of the desired
Pizza, returns its price.
• Input: Address, PizzaName
• Output: Price
• Precondition: Ex-
ist(PizzaName) and Avail-
ableDealer(Address, Piz-
zaName)
HutOrder: given a pizza name, a date
and time, the requester’s GPS co-
ordinates, a phone number for the
delivery and a credit card number,
returns a receipt with date and time
or an unavailability messagein case
the required pizza cannot be or-
dered or the distance is too long.
• Input: pizzaName, dateAnd-
Time, GPS, phoneNum, Cred-
itCardNum
• Output: receipt or NotAvail-
ableMSG
• Precondition: Ex-
ist(PizzaName) and Ex-
ist(userCode) and Valid (Date-
AndTime) and Valid(GPS)
RossoMenu: given theGPS coordinates
of requester and the name of the
desired Pizza, returns a Pizza code
with a grade of Semantic Match-
ing (0 the required pizza, 1 a pizza
with less ingredients, 2 a similar
pizza with some different ingredi-
ents) and the price or unavailability
message in case a Dealer does not
exists within acceptable distance.
• Input: GPS, PizzaName
• Output: PizzaCode, grade,
Price
• Precondition: Avail-
ableDealer(GPS, PizzaName)
RossoOrder: given a pizza code, a date
and time, an address, a doorphone
number and a credit card number,
returns an order code (allowing to
change the order until 3 hours be-
fore) or an unavailability message
in case the required pizza cannot be
ordered or the credit is insufficient.
• Input: PizzaCode, DateAnd-
Time, Address, doorPho-
neNum, CreditCardNum
• Output: orderCode or No-
tAvailableMSG
• Precondition: Valid-
Code(PizzaCode) and
Valid(Address) and Valid-
Time (DateAndTime) and
Valid(CreditCardNum)
RossoChangeOrder:
• Input: orderCode, DateAnd-
Time
• Output: orderCode or No-
tAvailableMSG
AddressTranslator: given an address,
returns the corresponding GPS Co-
ordinates.
• Input: address
• Output: GPS
PizzaTranslator: given a listof ingredi-
ents, returns the PizzaName having
those ingredients.
• Input: IngredientList
• Output: PizzaName
ity of a generic agent that is in charge of handling a
given environment in an AmI context, ensuring suit-
able contextualized and personalized support to the
user’s actions, adaptivity to the user’s peculiarities
and to changes over time, and automated management
of the environment itself.
The architecture is implemented in a multi-agent
system, where different types of agents are in charge
of performing different tasks. At different levels, they
are endowed with reasoning and learning capabili-
ties, and are coordinated by a ‘butler’. In addition to
controlling normal operations of the environment, the
butler may identify user’s needs and goals and acti-
vate suitable workflows to satisfy them. Some actions
in these workflow involve the execution of semantic
services. When a single service is not available for
fulfilling a given need, an automatic service composer
is used to obtain a suitable combination of services.
The architecture has been implemented in a pro-
totypical agent-based system that works in a smart
home environment. It is currently undergoing exten-
sion and refinement in order to make it able to deal
with more varied and complex situations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially funded by the Ital-
ian PON 2007-2013 project PON02
00563 3489339
‘Puglia@Service’.
REFERENCES
Ayala, I., Amor, M., and Fuentes, L. (2012). Self-
configuring agents for ambient assisted living appli-
cations. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, pages
1–11.
Bezold, M. (2010). A framework for adapting interactive
systems to user behavior. Journal of Ambient Intelli-
gence and Smart Environments, 2:369–387.
Blumendorf, M. and Albayrak, S. (2009). Towards a frame-
work for the development of adaptive multimodal user
PECCS2015-5thInternationalConferenceonPervasiveandEmbeddedComputingandCommunicationSystems
166

interfaces for ambient assisted living environments.
In Proceedings of the 5th International on Confer-
enceUniversal Access in Human-Computer Interac-
tion (UAHCI ’09) – Part II, pages 150–159. Springer.
Cavone, D., De Carolis, B., Ferilli, S., and Novielli, N.
(2012). A multiagent system supporting situation
aware interaction with a smart environment. In 2nd
Int. Conf. on Pervasive Embedded Computing and
Communication Systems (PECCS-2012), pages 67–
72. SciTePress.
Chun-dong, W., Xiu-liang, M., and Huai-bin, W. (2009). An
intelligent home middleware system based on context-
awareness. In Fifth International Conference on Nat-
ural Computation, pages 165–169. IEEE.
Cook, D. (2009). Multi-agent smart environments. Jour-
nal of Ambient Intelligence and Smart Environments,
1:47–51.
Cook, D., Augusto, J., and Jakkula, V. (2009). Ambient
intelligence: Technologies, applications, and opportu-
nities. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 5:277–298.
D’Andrea, A., D’Ulizia, A., Ferri, F., and Grifoni, P. (2009).
A multimodal pervasive framework for ambient as-
sisted living. In Proceedings of the 2nd International
Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to As-
sistive Environments, PETRA ’09, pages 39:1–39:8.
ACM.
De Carolis, B., Cozzolongo, G., Pizzutilo, S., and Planta-
mura, V. (2005). Agent-based home simulation and
control. In International Symposium on Methodolo-
gies for Intelligent Systems (ISMIS), pages 404–412.
Dey, A. (2001). Understanding and using context. Personal
and Ubiquitous Computing, 5:4–7.
Ferilli, S. (2014). WoMan: Logic-based Workflow Learn-
ing and Management. IEEE Transaction on Systems,
Man and Cybernetics: Systems, 44:744–756.
Ferilli, S., Cavone, D., Carolis, B. D., and Novielli, N.
(2011). A layered architecture for situation-aware
home environments. In 6th Int. Workshop on Artifi-
cial Intelligence Techniques for Ambient Intelligence
(AITAmI 2011), page 12.
Humble, J., Crabtree, A., Hemmings, T.,
˚
Akesson, K.-P.,
Koleva, B., Rodden, T., and Hansson, P. (2003). Play-
ing with the bits - user-configuration of ubiquitous do-
mestic environments. volume 2864 of Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 256–263.
Kim, J., Spraragen, M., and Gil, Y. (2004). An intelligent
assistant for interactive workflow composition. In 9th
Int. Conf. on Intelligent User Interfaces, pages 125–
131. ACM Press.
Mars´a-Maestre, I., L´opez-Carmona, M. A., Velasco, J. R.,
and Navarro, A. (2008). Mobile agents for service per-
sonalization in smart environments. Journal of Net-
works, 3:30–41.
McNaull, J., Augusto, J., Mulvenna, M., and McCullagh, P.
(2011). Multi-agent interactions for ambient assisted
living. In Intelligent Environments, pages 310–313.
Meyer, H. (2007). On the semantics of service composi-
tions. volume 4524 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 31–42.
Motik, B., Sattler, U., and Studer, R. (2005). Query An-
swering for OWL-DL with rules. Journal of Web Se-
mantics: Science, Services and Agents on the World
Wide Web, 3(1):41–60.
Mozer, M. C. (2005). Lessons from an adaptive house. In
Cook, D. and Das, R., editors, Smart environments:
Technologies, protocols, and applications, pages 273–
294. J. Wiley & Sons.
O’Grady, M., Muldoon, C., Dragone, M., Tynan, R., and
O’Hare, G. (2010). Towards evolutionary ambient as-
sisted living systems. Journal of Ambient Intelligence
and Humanized Computing, 1:15–29.
Paik, I. and Maruyama, D. (2007). Automatic web services
composition using combining HTN and CSP. In Conf.
on Computer and Information Technology (CIT 2007).
Rao, A. and Georgeff, M. (1991). Modeling rational agents
within a bdi-architecture. In Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on
Principles of Knowledge Representation and Reason-
ing, pages 473–484.
Rao, S. and Cook, D. J. (2004). Predicting inhabitant ac-
tions using action and task models with application to
smart homes. International Journal of Artificial Intel-
ligence Tools, 13:81–100.
Redavid, D., Ferilli, S., and Esposito, F. (2013). To-
wards dynamic orchestration of semantic web ser-
vices. Transactions on Computational Collective In-
telligence, 10:16–30.
Sernani, P., Claudi, A., Palazzo, L., Dolcini, G., and Drag-
oni, A. (2013). Home care expert systems for ambient
assisted living: A multi-agent approach. In Workshop
on The Challenge of Ageing Society: Technological
Roles and Opportunities for Articial Intelligence, vol-
ume 1122, pages 1–16. CEUR Workshops.
Sun, H., Florio, V. D., Gui, N., and Blondia, C. (2009).
Promises and challenges of ambient assisted living
systems. In 6th Int. Conf. on Information Technology:
New Generations (ITNG ’09), pages 1201–1207.
Wolf, P., Schmidt, A., Otte, J., Klein, M., Rollwage,
S., Konig-Ries, B., and Gabdulkhakova, A. (2010).
Openaal - the open source middleware for ambient-
assisted living (AAL). In AALIANCE conf., pages 1–
5.
Wooldridge, M. and Jennings, N. (1995). Intelligent agents:
Theory and practice. Knowledge engineering review,
10:115–152.
Wu, C.-L., Liao, C.-F., and Fu, L.-C. (2007). Service-
oriented smart-home architecture based on osgi and
mobile-agent technology. IEEE Transactions on Sys-
tems, Man, And Cybernetics – Part C: Applications
and Reviews, 37.
Yau, S. and Liu, J. (2006). Incorporating situation aware-
ness in service specifications. In 9th IEEE Int. Symp.
on Object and Component-oriented Real-time Dis-
tributed Computing (ISORC), pages 287–294.
AnAgentArchitectureforAdaptiveSupervisionandControlofSmartEnvironments
167
