
Automatic Detection of High-voltage Spindles for Parkinson’s Disease
V. Vigneron
1,
*
, T. Syed
2
and Hsin Chen
3
1
Electrical Department, Universit
´
e d’Evry, 91020 Evry, France
2
Informatics Department, National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Karachi, Pakistan
3
Electrical Department, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan
Keywords:
Parkinson, Animal Experiment, HVS, Eigen Decomposition, Detection, Sensor Grid.
Abstract:
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder which can be characterized by several symp-
toms such as tremor, slowness of movements, bradykinesia/akinesia and absence of postural reflexes . . . and
affects 10 million people worldwide. This paper develops a novel strategy for treating patients with PD: si-
lence High-Voltage-Spindle that resemble the pathophysiological β-waves and contribute to the development
of β-waves. Silencing HVSs is expected to delay or even prevent the development of β-waves and thus the
progression of PD motor symptoms. High-voltage spindles (HVSs) are observed during waking immobility of
patients. In this study, the local field potentials collected from the lesioned and control rats on multiple chan-
nels were analyzed with an online detection algorithm to identify the characteristic oscillations of HVSs from
the second-order statistical properties of the signals and the detection performance is investigated to obtain the
optimal choices. These results provide further motivation for the real−time implementation of the automatic
HVS detection systems with improved performance for pathophysiological and therapeutic applications to the
thalamocortical network dysfunctions.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper develops a novel strategy for treating pa-
tients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). Hemi-PD rats
will be used as a model here. We will focus on
implementing a closed-loop Deep-Brain-Stimulation
(DBS) system that will delay the development of
the excessive beta oscillations (called β-waves hence-
forth). Their are found to be associated with spa-
tial memory impairments (Radek et al., 1994), sud-
den arrest of ongoing behaviour and PD and to the
movement abnormalities found in PD model rats. The
HVSs are different from the epileptic spike-wave dis-
charges whose dominant frequency lies in the 30−50
Hz band (Sitnikova et al., 2009) and from normal
sleep spindles in both physiology aspects and signal
dynamics. Indeed HVSs (i) are synchronous spike-
and-wave patterns of local field potentials (LFPs) (ii)
are oscillating in the 5−13 Hz frequency band (iii)
are initiated in cortex whereas the sleep spindles are
*
Corresponding author.
This project was funded by a PhD grant from universit
´
e
d’
´
Evry number 4552013 and PHC ORCHID. The authors
express their sincere thanks to the French embassy collabo-
rators for their interest and kind permission to publish.
prevalent in sleep states (iv) can occur frequently dur-
ing passive wakefulness. More, the onset and end
of HVSs episodes could occasionally vary across the
cortical-basal ganglia structures and thus leads to dif-
ferent morphological features.
Such uniqueness of HVSs demands an appropriate
spindle detection algorithm with a suitable threshold-
ing mechanism.
Although HVSs exhibit larger amplitudes than
normal LFPs, the motion artifacts of an awake rat also
induce large transients in LFPs. In addition, LFPs are
non-stationary and coupled with non-negligible noise.
These properties make it difficult to detect HVSs
by simple threshold or envelope detection. More-
over, although the prominent frequency components
of HVSs are around 5−13Hz, the duration of each
HVS episode is only 1−4 s. Such a short duration
makes it challenging to detect HVS episode at the on-
set by conventional frequency analysis (e.g. the Fast-
Fourier Transform), which suffers from the trade-off
between time and frequency resolutions. Based on
our pilot studies, time-frequency (TF) analysis pre-
serving the energy distribution over both time and fre-
quency spaces is useful to extract the distinctive fea-
tures of HVSs, see e.g. (Perumal and Chen, 2014)
372
Vigneron V., Syed T. and Chen H..
Automatic Detection of High-voltage Spindles for Parkinson’s Disease.
DOI: 10.5220/0005328503720378
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (MPBS-2015), pages 372-378
ISBN: 978-989-758-069-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
who use a continuous wavelet transform (CWT) to
detect the characteristic oscillations of HVSs. But the
detection performance are related to a suitable choice
of the wavelet parameters and the thresholding mech-
anism that are critical to determine the detection per-
formance. Therefore, we will compare the features
extracted by TF analysis and our proposed algorithm
for detecting the distinctive features of HVSs auto-
matically and reliably.
Finally, as this algorithm is based mainly on
second-order statistics the proposed algorithm can be
extended further to the FPGA-based real time systems
for pathophysiological and therapeutic applications.
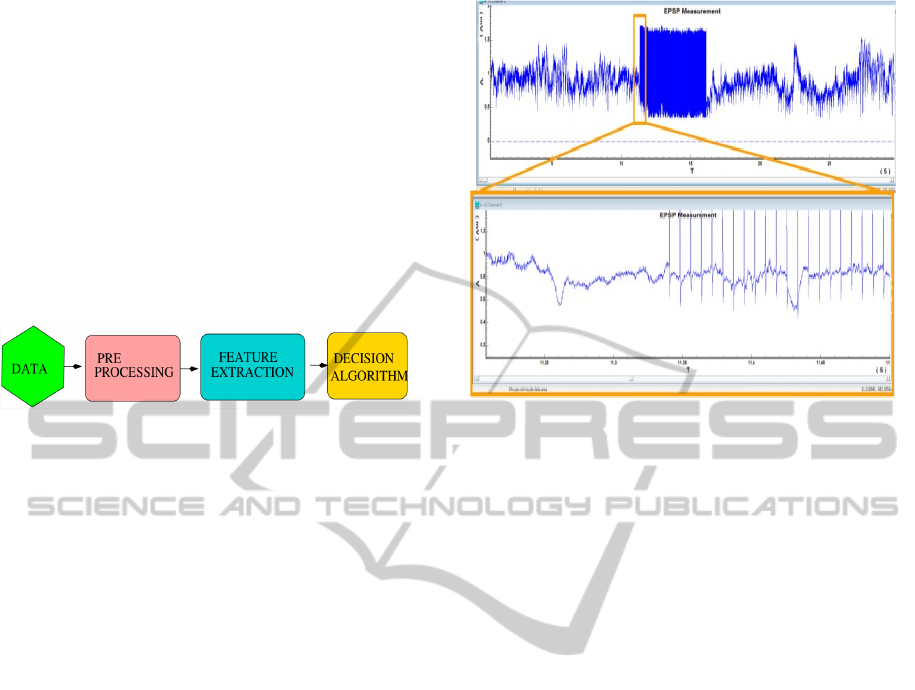
Figure 1: An overview of the HVSs detection process.
A simplified scheme in Fig. 1 gives an overview
of the work.
2 DATA ACQUISITION
The PD rat models were induced in 3-4 months old
Sprague-Dawley rats by unilateral injection (coordi-
nates: AP -4.4 mm, ML +1.2 mm, V -7.8 mm rel-
atively to bregma) of 6-OHDA in the medial fore-
brain bundle (MFB) at the rate of µl/min using an
integrated electrophysiology instrument suitable for
deep brain stimulation (DBS) procedure. Four weeks
following the unilateral injection of 6-OHDA, the le-
sioned group of rats were determined as successful
PD models through amphetamine-induced rotational
behaviour (Amp, 3mg/kg, ip) by measuring the rota-
tional speed of the lesioned rats as 6 turns per minute.
The rats were unilaterally implanted bipolar stimula-
tion electrode into the ipsilateral STN with their initial
coordinates at AP -3.6 mm and L +2.5 mm. The elec-
trode was lowered slowly along the dorsal ventral axis
of brain and then advanced ventrally to the STN to ob-
tain the electrophysiological signal with a strikingly
silent structure. The EEG recordings were collected
from a group of 34 lesioned rats and 20 control rats.
The LFPs of the lesioned rats were recorded in both
sleeping and waking immobile states in order to study
the behaviour of spindling and non-spindling charac-
teristics. The EEG patterns without artifacts and with
the duration of sixty seconds were considered in the
following sections to evaluate the performance of the
spindle detection algorithm (see Fig. 2).
Figure 2: The LFP recorded by the micro-system during
electrical stimulation (130Hz, 100 µA). The lower panel is
the magnified view of the region shown in the top trace dur-
ing the period when stimulation is just turned on.
3 ELIMINATION OF THE
BACKGROUND NOISE
The raw artifact-free EEG recordings from lesioned
(PD) and control rats (CR) are used as direct inputs to
the HVS detection algorithm with a noise cancellation
stage.
In the case of HVSs, there are several different
causes for the noise. We can mention the defects in
the sensors, the environment in which the recording
is done or also the decay of the recording medium.
Among all the type of noises encountered in practice,
the following 2 types occur in practice:
• the background noise which can be represented
by a stationary process, often originated from the
electronic circuits of the amplification devices.
• the impulse noise represented as a sequence of
very brief impulses, with random amplitudes and
locations.
To reduce these noises and restore the signal as best as
possible, we are considering them and deal with them
separately. The elimination of background noise is a
particular difficult problem since we have to find what
characterizes the difference between the useful part
of the signal and the unwanted part. We can mention
(DeFreitas et al., 2012; Miyano et al., 1980; Clancy
and Farry, 2000) among the different denoising meth-
ods in a stationary background noise for which the
methods gives satisfactory results. They usually re-
quire for the spectral properties of the noise to be
AutomaticDetectionofHigh-voltageSpindlesforParkinson'sDisease
373
known. They can do this by using a portion of the
signal that contains nothing but noise. This portion is
selected either by a direct observation of the signal or
by automatically detecting the active areas of the use-
ful signal.
We suggest here a simple spectral substraction lead-
ing to an acceptable result that we implemented. If we
assume that the noise is white with a power σ
2
esti-
mated from a portion of the signal containing nothing
but noise, the short term amplitude spectrum of the
denoised signal σ
2
is estimated by the expression:
ˆ
X(k) = G(k)X(k) (1)
where
X(k) =
N−1
∑
n=0
x(n)e
−2 jπnk/N
, (2)
refers to the Discrete Fourier Transform of a length N
window of the noisy signal x(n) and where
G(k) =
(
1 −λ
σ
√
N
|X(k)|
if λ
σ
√
N
|X(k)|
< 1
µ otherwise.
(3)
where the parameters λ and µ are adjusted experimen-
tally so as to obtain the best result. The results show
that the background noise is rather well eliminated but
the method introduces HF noises that get louder as µ
decreases. In particular, µ = 0 leads to the plain and
simple elimination of the spectral components below
the threshold, causing certain components of the noise
to behave as isolated “peaks”. HF noise can be re-
duced by decreasing λ and increasing µ but at the cost
of a lower noise reduction.
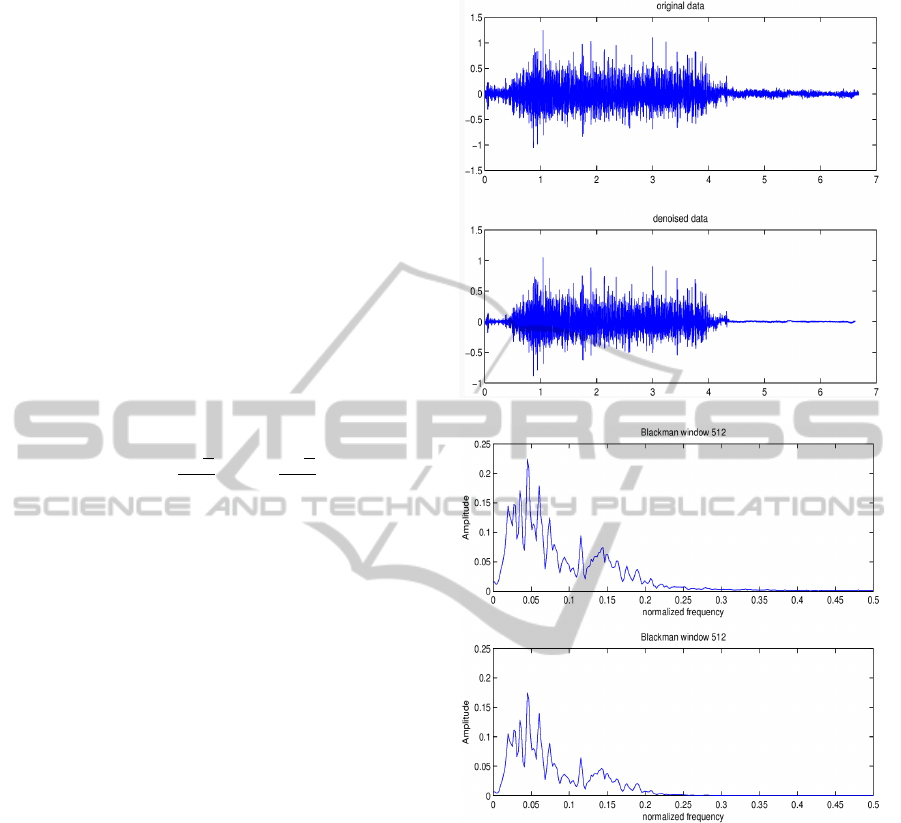
The figure 3 shows the effect of the frequency do-
main denoising operation. λ and µ have been adjusted
experimentally so as to archive the best result. This
method can effectively be applied to processes that do
have to be conducted in real-time. Detecting a “silent”
segment automatically is not an easy task, not to say
impossible to solve.
4 ALGORITHMS
Collaborative signal and information processing over
a network is a new area of research and is related
to distributed information fusion. Processing data
from many sensors generally results in better per-
formance e.g. in distributed robotics (Denzler and
Brown, 2002), environment monitoring, medical as-
sistance (Vrins et al., 2004; Vigneron and Jutten,
2004), etc. but it also requires more communication
resources (and thus, more energy); the reasons for this
are that (i) 2 sensors don’t record exactly the same
(a) Signals before and after the denoising operation
(b) Spectra of the corresponding signals
Figure 3: Noise removal demo. The frequency is expressed
in normalized frequency.
signal, (ii) all sources must be involved in the record-
ing with a non-zero variance, (iii) electrodes provid-
ing irrelevant signals can be rejected, (vi) the low
power of the signal of interest can be improved, (v)
there doesn’t exist an optimal location of the sensors,
constant in time as the “target” moves. These con-
siderations in mind, in addition to the low power of
the signal, may explain why the locations of the elec-
trodes can improve the signal extraction, while others
can decrease its efficiency. Therefore, one needs to
consider the trade-offs between performance and re-
source utilization in using networked sensors. Numer-
ous articles have dealt with this topic, but usually in
the area of digital communications (Yao et al., 1998).
BIOSIGNALS2015-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
374

4.1 The Karhunen-loeve Expansion for
Random Processes
We consider the situation in which n sensors are ran-
domly distributed in a spatial region, which is 3 di-
mensional (the cortex) but could be less. The sen-
sors relative positions are unknown. The sources may
be narrow-band or broadband and they may be in
the far or near field with respect to the sensor ar-
ray. The sources do not have specific characteristics
that can be used to our advantages. Due to these
limitations, our initial goal is limited to the detec-
tion. We assume the existence of n source signals
{s
i
(t), 1 ≤ i ≤ q} (with n < q), statistically indepen-
dent and zero-mean and the observation of at most as
many mixtures {x
i
(t), 1 ≤i ≤ n}, formed by (suppos-
edly) linear combinations of the unknown sources, i.e.
x
i
(t) =
q
∑
j=1
a
i j
s
j
(t) + n
i
(t), (4)
for each i = 1,...,n. This is compactly represented
by the mixing equation x(t) = As(t), where the ma-
trix A
(n×q)
collects the mixing coefficients, s(t) =
(s
1
(t), ...,s
n
(t))
T
is a column vector collecting the
unobserved source signals
*
, x(t) collects the n ob-
served signals. n
i
(t) is a spatially white noise with
zero mean and variance σ
2
. Denote the n ×1 sensor
data vector by
x
t
= (x
1
(t), ...,x
i
(t), ...,x
n
(t))
T
.
x
t
denotes a random process.
X
0
x
T
T +1
X
Figure 4: Augmented table.
Let X
0
be the table collecting the samples x
t
,t =
1,..., T (see figure 4) and C
0
be the covariance ma-
trix of x estimated by
ˆ
C
0
=
1
T
∑
T
t=1
x
t
x
T
t
,
ˆ
φ
i
and
ˆ
λ
i
,i =
1,..., n the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of
ˆ
C
0
. Note
that
ˆ
λ
i
and
ˆ
φ
i
are estimates of λ
i
and φ
i
, and that they
*
T
denotes usually the transpose operator.
are resp. random variables and vectors. In section 4.2,
we shall show approximate formulas for the expected
values and variances of these estimates. The array
covariance matrix C = E[x(t)x
T
(t)] = ASA
T
+ σ
2
I
n
,
where S = E[s(t)s
T
(t)], I
n
is the n ×n identity matrix.
Consistent estimates of eigenvectors and eigenvalues
of C are given by the eigen decomposition of the sam-
ple covariance matrix (Cover and Thomas, 1991)
ˆ
C =
1
T
T +1
∑
i=t
x
t
x
T
t
=
ˆ
U
S
ˆ
Λ
S
ˆ
U
T
S
+
ˆ
U
N
ˆ
Λ
N
ˆ
U
T
N
, (5)
where the ˆq × ˆq and (n − ˆq) ×(n − ˆq) diagonal matri-
ces
ˆ
Λ
S
and
ˆ
Λ
N
contain the ˆq and n− ˆq signal and noise
subspace eigenvalues respectively. The columns of
the n ×q and n ×(n − ˆq) matrices
ˆ
U
S
and
ˆ
U
N
contain
the signal and noise subspace eigenvectors, and ˆq is
any consistent estimate of q.
We wish to obtain a first-order approximation of the
eigenvectors and eigenvalues of C in terms of the φ
i
’s
and λ
i
’s, where C = C
0
+ ∆C. Suppose that X is aug-
mented by a bloc of values x
T +1
(see figure 4), then
ˆ
C = X
T
X =
X
T
0
x
T
T +1
X
0
x
T +1
=
ˆ
C
0
+x
T
T +1
x
T +1
(6)
where ∆C = x
T
T +1
x
T +1
can be seen as a (real sym-
metric) perturbation matrix. Suppose that the λ
i
’s are
distinct. These may be obtained by retaining the terms
of first order of the equation:
(C
0
+ ∆C)(φ
i
+ ∆φ
i
) = (λ
i
+ ∆λ
i
)(φ
i
+ ∆φ
i
), (7)
where C
0
φ
i
= λ
i
φ
i
. The resulting equation is:
C
0
∆φ
i
+ ∆Cφ
i
u λ
i
∆φ
i
+ ∆λ
i
φ
i
. (8)
To calculate ∆λ
i
, we premultiply (8) by φ
T
i
and, since
φ
T
i
C
0
= λ
i
φ
T
i
, we have:
∆λ
i
u φ
T
i
∆Cφ
i
. (9)
The {φ
1
,..., φ
n
} form a complete set of basis vectors
i.e. φ
T
i
φ
j
= δ
i j
,∀i, j, where δ
i j
is the Kronecker oper-
ator (δ
i j
= 1 iff i = j). Hence ∆φ
i
can be expanded as
a linear combination of the φ
j
’s as follows
∆φ
i
=
n
∑
j=1
b
i j
φ
j
, (10)
where b
i
are vectors of unknown parameters. From
(10), b
i j
= φ
j
T
∆φ
i
.
If we premultiply (8) by φ
T
j
and rearrange, we have
for i , j:
b
i j
u
φ
T
j
∆Cφ
i
λ
j
−λ
i
(i , j) (11)
To determine b
ii
, we impose a first-order normaliza-
tion condition on φ
i
+ ∆φ
i
, that is, we require
kφ
i
+ ∆φ
i
k
2
≈ kφ
i
k
2
+ 2φ
T
i
∆φ
i
, (12)
AutomaticDetectionofHigh-voltageSpindlesforParkinson'sDisease
375

and it follows that φ
i
T
∆φ
i
= b
ii
≈ 0.
Noting that φ
T
i
C
0
φ
i
= λ
i
and φ
T
i
C
0
φ
j
= 0 for i , j, we
summarize this section as follows:
λ
i
+ ∆λ
i
u φ
T
i
Cφ
i
(13)
b
i j
u
φ
T
i
Cφ
j
λ
i
−λ
j
, for i , j,
0, for i = j.
(14)
Notice that most of the approach is implicitly based
on a model where the sequence x
t
is i.i.d., i.e. noth-
ing is assumed concerning temporal evolution. The
algorithm detailed in (13) and (14) examine the non-
stationary case, i.e. falling the ’id’ in i.i.d.
4.2 Estimation of Eigenvalues and
Eigenvectors
Our next task is to estimate the eigenvalues and eigen-
vectors λ
i
and φ
i
(i = 1, . ..,n) of the autocorrelation
matrix C. For this, we calculate the sample autocorre-
lation matrix
ˆ
C =
1
T
∑
T
t=1
x
t
x
T
t
and calculate the eigen-
values and eigenvectors
ˆ
λ
i
and
ˆ
φ
i
of
ˆ
C. We can deter-
mine a value of T such that the estimates are suffi-
ciently accurate. Since
ˆ
C u C for T sufficiently large,
we may use the approximations (13) and (14) to ex-
press
ˆ
λ
i
and
ˆ
φ
i
(i = 1,..., n):
ˆ
λ
i
u φ
T
i
ˆ
Cφ
i
(15)
ˆ
φ
i
u φ
i
+
∑
j=1
j,i
φ
T
j
ˆ
Cφ
i
λ
i
−
˙
λ
j
φ
j
. (16)
Consider the expected value of the estimate: since the
expected value of
ˆ
C E[
ˆ
C] = C, therefore E[φ
T
j
ˆ
Cφ
i
] =
φ
T
i
E[
ˆ
C]φ
j
= φ
T
i
Cφ
j
= λ
i
δ
i j
. It follows from (15) and
(16) that
E[
ˆ
φ
i
] u φ
i
, E[
ˆ
λ
i
] = λ
i
. (17)
The estimates are unbiased only when the first or-
der approximation are used, i.e. the bias come usu-
ally from the second order term of the approximation
(Cover and Thomas, 1991) and the the variance comes
from the first order, thus
E[
ˆ
φ
i
] u φ
i
+
1
T
f
i
, E[
ˆ
λ
i
] = λ
i
+
1
T
g
i
(18)
where f
i
and g
i
are functions of C, with a functional
form too complex to determine.
The variances can be obtained from the first order ap-
proximation and their approximated values may be
computed as follows:
var(
ˆ
λ
i
) = E[(
ˆ
λ
i
−λ
i
)
2
] = E[
ˆ
λ
2
i
] −λ
2
i
u E[φ
T
i
ˆ
Cφ
i
] −λ
2
i
(19)
and
cov(
ˆ
φ
i
) = E[(
ˆ
φ
i
−φ
i
)(
ˆ
φ
i
−φ
i
)
T
]
u
n
∑
j=1
j,i
n
∑
k=1
k,i
E[φ
T
i
ˆ
Cφ
j
φ
T
i
ˆ
Cφ
k
]
(λ
i
−λ
j
)(λ
i
−
˙
λ
k
)
φ
j
φ
T
k
(20)
u
n
∑
k=1
k,i
E[(φ
T
i
ˆ
Cφ
j
)
2
]
(λ
i
−λ
j
)
2
(21)
Note that both equations (19) and (21) are expressed
as function of E[(φ
T
i
ˆ
Cφ
j
)
2
].
Suppose now that the X is normally distributed,
E[(φ
T
i
ˆ
Cφ
j
)
2
] can be computed as follows. Let
φ
T
i
ˆ
Cφ
j
=
1
T
N
∑
k=1
y
ik
y
jk
where y
ik
= φ
T
i
x
k
(22)
and
E[(φ
T
i
ˆ
Cφ
j
)
2
] =
1
T
2
T
∑
k=1
T
∑
`=1
E[y
ik
y
jk
y
i`
y
j`
] (23)
u
T −1
T
λ
2
i
δ
i j
+
1
T
E[(y
T
i
y
j
)
2
]. (24)
The second subscript on y is dropped since the x
t
’s
are identically distributed. When X is normally dis-
tributed with zero mean, the y
i
’s are also normal with
E[y
i
] = 0. Therefore
E[y
2
i
y
2
j
] =
(
3λ
2
i
for i = j
λ
i
λ
j
for i , j
. (25)
Finally
E[(φ
T
i
ˆ
Cφ
j
)
2
] = λ
2
i
δ
i j
+
1
T
(λ
2
i
δ
i j
+ λ
i
λ
j
). (26)
and var(
ˆ
λ
i
) ≈
2
T
λ
2
i
and cov(
ˆ
φ
i
) ≈
1
T
∑
T
`=1
j,i
λ
i
λ
j
(λ
i
−λ
j
)
2
.
4.3 HVSs Detection
The HVS detection problem can be modeled as an hy-
pothesis testing problem (Vigneron et al., 2010) and
formulated into a maximum likelihood test we de-
scribe in the following (Johnson et al., 2011).
The observations provided by the sample process are
supposed independent. The input to the detector is de-
noted by z = (z
1
,..., z
n
)
T
where z
i
, (1 ≤ i ≤ n) will
consist of either noise alone, z
i
= v
i
either signal plus
noise z
i
=
ˆ
λ
i
+v
i
computed with (15). The noise alone
possibility is called the null hypothesis and is denoted
by H
0
. The signal plus noise possibility is called the
alternative and is denoted by H
1
. The detection prob-
lem may be written as testing H
0
versus H
1
:
(
H
0
: z
i
∼ N(0,σ
2
i
= σ
2
0
)
H
1
: z
i
∼ N(
ˆ
λ
i
,σ
2
i
= σ
2
0
)
, (i = 1, . ..,n) (27)
BIOSIGNALS2015-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
376

Two assumptions are made on the noise probability
distributions (i) the noise components are indepen-
dent, (ii) their distributions are Gaussian. The inde-
pendence assumption is solely a practical requirement
for the purpose of solving the equations involved.
The gaussianity assumption comes from signal-space
analysis of considering n-dimensional space. The
choice of the Gaussian probability density function
(pdf) is more interesting when computing the likeli-
hood ratio and lead to interesting graphical interpreta-
tion. The conditional probability density of the obser-
vations p(z|H
0
) and p(z|H
1
) are unknown. Hence we
shall rewrite the conditional density as p(z|H
k
,θ
k
),
where θ
k
is a vector of unknown parameter values for
which the we have no prior on the pdf and which are
selected from a set Ω
k
. We shall select θ
k
so as to
maximize p(z|H
k
,θ
k
). Then our likelihood ratio test
takes the following form:
Λ(z) =
max
θ
1
∈Ω
1
p(z|H
1
,θ
1
)
max
θ
0
∈Ω
0
p(z|H
0
,θ
0
)
d
1
≶
d
2
η. (28)
Suppose that we take a set of n independent identi-
cally distributed observations of the preceding form.
Then we must select θ
1
= (s; Σ) which maximizes the
joint distribution
p({z
i
}|H
1
,θ
1
) =
T
∏
i=1
p(z
i
|H
1
,θ
1
) (29)
= (2π)
−nT /2
|Σ|
−n/2
exp
h
−
n
2
trΣ
−1
S
i
,
(30)
where Σ = diag(var(
ˆ
λ
i
)) computed with (15) and (16)
is the covariance matrix of z, S is the scatter matrix
S =
1
n
∑
n
i=1
(z
i
−s)(z
i
−s)
T
. The value of θ
1
which
maximizes p(z|H
1
,θ
1
) is s =
∑
n
i=1
z
2
i
/n.
We suppose that the noise variance estimate is the
same for both hypothesis. Substituting these values
back into the conditional probabilities of the likeli-
hood ratio in Eq. (28) yields
(2π)
−nT /2
|Σ|
−n/2
exp
−
n
2
trΣ
−1
S
(2π)
−T p/2
|S|
−n/2
exp
−
1
2
z
T
S
−1
z
d
1
≶
d
2
η (31)
Taking the logarithm of both side and recombining
yields
`(z) = z
T
S
−1
z
d
1
≶
d
2
2lnη + n(log|Σ|+ trΣ
−1
S −|S|).
(32)
The statistic that has been identified as `(z) is obvi-
ously a sufficient statistic for this problem: it will
tell in which decision region z lies. We need the
means and the variance of `(z) to find the densities
p(`|H
0
) and p(`|H
1
). z
T
S
−1
z is a stochastic quadratic
form. If we assume that all coordinates n
i
are inde-
pendent, have the same central moments σ
2
,µ
4
and
denote a = diag(S
−1
), then
E[`(z)|H
1
] = n + s
T
S
−1
s
var[`(z)|H
1
] = 2σ
2
tr(S
−1
)+(µ
4
−3σ
2
)a
T
a+4s
T
S
−1
s.
and
E[`(z)|H
0
] = E[n
T
S
−1
n] = tr(S
−1
Σ) = n
var[`(z)|H
0
] = var(n
T
S
−1
n) = 2σ
2
tr(S
−1
)+(µ
4
−3σ
2
)a
T
a
The probability density p(`|H
0
) is therefore given by:
p(`|H
0
) = K exp
−
1
2
(` −n)
2
2σ
2
tr(S
−1
) + (µ
4
−3σ
2
)a
T
a
(33)
so that p(d
2
|H
0
) becomes p(d
2
|H
0
) =
R
∞
β
p(`|H
0
)d`
and β = 2 lnλ + n(log|Σ|+ trΣ
−1
S −|S|)
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We can define by Z
0
= {z|`(z) < β} and Z
1
=
{z|`(z) ≥ β} two subsets of the n-dimensional space.
Therefore the conditional probability that z ∈ Z
1
(resp. Z
2
) is just the conditional probability that `(z)
is less (resp. greater) than β, i.e. HVS burst vs only
noise. Detected HVS patterns are shown in Fig. 5,
with η = 1 (no prior).
Figure 5: Illustration of the detection of PD of HVS burst.
Table 1: Main results number of burst detected with respect
to signal on noise ratio (SNR).
# sensors Signal on noise ratio
3 7 21 20
5 12 24 41
6 21 29 65
8 39 50 88
For short, the performances, as expected, increase
with the number of sensors and a high SNR.
AutomaticDetectionofHigh-voltageSpindlesforParkinson'sDisease
377

6 CONCLUSION
The proposed plan enable us to detect most HVS
episodes at its onset from the local field potentials
recorded from awake, freely moving rats and to trig-
ger the delivery of stimulations with arbitrary wave-
forms onto particular brain regions upon detecting
HVSs automatically. More generally, it could help to
improve the existing biometrics methods through bet-
ter event detection and apparently it is well adapted
for multidimensional signal. Previous results show
that the proposed filter detects about 90% of the
events and commits few errors, ensuring that most
HVS episodes identified are in agreement with real-
ity.
This corpus of methods relies on a running time
window whose window length (0.5−1s) is too long
to efficiently stop individual HVSs episodes (1−4 s).
Under this concern we will investigate in the future
the feasibility of using dynamical models to predict
the occurrence of a HVS before its onset and study if
β-waves can be induced by artificially evoked HVSs
REFERENCES
Clancy, E. and Farry, K. (2000). Adaptive whitening of
the electromyogram to improve amplitude estimation.
IEEE Trans Biomed Eng., 47(6).
Cover, T. and Thomas, J. (1991). Elements of Information
Theory. John Wiley and Sons.
DeFreitas, J., Beck, T., and Stock, M. (2012). Compar-
ison of methods for removing electromagnetic noise
from electromyographic signals. Physiological Mea-
surement, 33(2):147.
Denzler, J. and Brown, C. (2002). Information theoretic
sensor data selection for active object recognition and
state estimation. IEEE trans. on Pat. Anal. and Mach.
Intel., 24(2):145–156.
Johnson, B. A., Abramovich, Y. I., and Scharf, L. L. (2011).
Detectionestimation of multi-rank gaussian sources
using expected likelihood. Digital Signal Processing,
21(5):568 – 575.
Miyano, H., Masuda, T., and Sadoyama, T. (1980). A note
on the time constant in low-pass filtering of rectified
surface emg. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng., 27(5):274–8.
Perumal, R. and Chen, H. (2014). Performance analysis in
a wavelet-based algorithm for automatic detection of
high-voltage spindles in parkinson’s disease rat mod-
els. In 9th Asian-Pacific Conference on Medical and
Biological Engineering, Tainan, Taiwan.
Radek, R. J., Curzon, P., and Decker, M. W. (1994). Charac-
terization of high voltage spindles and spatial memory
in young, mature and aged rats. Brain Research Bul-
letin, 33:183188.
Sitnikova, E., Hramov, A. E., Koronovsky, A. A., and van
Luijtelaar, G. (2009). Sleep spindles and spike-wave
discharges in eeg: their generic features, similarities
and distinctions disclosed with fourier transform and
continuous wavelet analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods,
180:304316.
Vigneron, V. and Jutten, C. (2004). Independent Component
Analysis and Blind Signal Separation, volume LNCS
3195 of Lectures Notes in Computer Science, chap-
ter Fisher Information in Source Separation Problems,
pages 168–176. Springer.
Vigneron, V., Syed, T., Montagne, C., Barlovatz-Me imon,
G., and Lelandais, S. (2010). Template matching and
test detection. Application to cell l ocalization in cells
imagery. Pattern Recognition Letters, 31(14):2214–
2224.
Vrins, F., Jutten, C., and Verleysen, M. (2004). Fifth Inter-
national Conference, ICA 2004, volume LNCS 3195,
proceedings Sensor array and electrode selection for
non invasive fetal electrocardiogram extraction by In-
dependent Component Ananlysis. Springer-Verlag,
Granada, Spain.
Yao, K., Hudson, R., D., C., and Lorenzelli, F. (1998). Blind
beamforming on a randomly distributed sensor array
system. IEEE Journal on selected areas in communi-
cation, 16(8):1555–1566.
BIOSIGNALS2015-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
378
