
Addressing Subject-dependency for Affective Signal Processing
Modeling Subjects’ Idiosyncracies
François Courtemanche
1,2
, Emma Campbell
1,3
, Pierre-Majorique Léger
1,2
and Franco Lepore
3
1
Tech
3
lab, HEC Montréal, Louis Colin Blvd, Montréal, Canada
2
Department of Information Technologies, HEC Montréal, Côte-Sainte-Catherine Rd, Montréal, Canada
3
Department of Psychology, University of Montréal, Vincent-d’Indy Ave, Montréal, Canada
Keywords: Affective Signal Processing, Subject-dependency, Psychophysiological Inference, Personality.
Abstract: Most works on Affective Signal Processing (ASP) focus on user-dependent emotion recognition models
which are personalized to a specific subject. As these types of approach have good accuracy rates, they
cannot easily be reused with other subjects for industrial or research purposes. On the other hand, the
reported accuracy rates of user-independent models are substantially lower. This performance decrease is
mostly due to the greater variance in the physiological training data set drawn from multiple users. In this
paper, we propose an approach to address this problem and enhance the performance of user-independent
models by explicitly modeling subjects’ idiosyncrasies. As a first exemplification, we describe how
personality traits can be used to improve the accuracy of user-independent emotion recognition models. We
also present the experiment that will be carried on to validate the proposed approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper focuses on the subfield of physiological
computing that aims to infer subjects’ psychological
states based on their physiological signals
(Fairclough, 2009). When the psychological states
are related to emotions, the literature often refers to
this process as Affective Signal Processing (ASP)
(van den Broek et al., 2009a). At a theoretical level,
ASP is based on the principle of
psychophysiological inference (Cacioppo and
Tassinary, 1990), which can be defined as follows:
let ψ be the set of psychological constructs (e.g.
emotional arousal, cognitive load) and Φ be the set
of physiological variables (e.g. heart rate, pupil
dilation). The psychophysiological inference is then
described according to the following equation:
Ψ = f (Φ) (1)
Most works aiming at implementing the
physiological inference process are using a machine
learning framework (Picard et al., 2001; Christie and
Friedman, 2004; Haag et al., 2004; Bamidis et al.,
2009; Chanel et al., 2009; Verhoef et al., 2009;
Kolodyazhniy et al., 2011). Despite interesting
results, reported prediction accuracy rates are still
below the level of other machine learning problems
and cannot feed real-world applications (van den
Broek et al., 2010a). Among the different challenges
that have been identified to further develop ASP,
this paper addresses the problem of subject-
dependency (van den Broek et al., 2010b).
In machine learning, a model’s generalizability
represents its capacity to perform a valid inference
on a new and unseen data point (Bishop, 2006). The
generalization error, empirically estimated on a large
data set, therefore represents the model’s
performance. Specifically to the context of ASP, a
model’s genericity represents its capacity to perform
a valid inference on a previously unseen subject.
Genericity is then used to describe the range of
subjects onto which a model applies. Two types of
emotion recognition models are defined in regards to
their genericity (Villon and Lisetti, 2007).
1. User-dependent: the training set contains data
from one participant and the test set contains new
data from the same participant.
2. User-independent: the training set contains data
from many subjects and the test set contains data
from new subjects.
A recent review by Novak et al., (2012) reports that
most works on psychophysiological inference have
focused on subject dependent approaches.
72
Courtemanche F., Campbell E., Léger P. and Lepore F..
Addressing Subject-dependency for Affective Signal Processing - Modeling Subjects’ Idiosyncracies.
DOI: 10.5220/0005330700720077
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Physiological Computing Systems (PhyCS-2015), pages 72-77
ISBN: 978-989-758-085-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Furthermore, as shown in Table 1, a “genericity vs
generalizability” dilemma appears to be present at
the heart of ASP, as user-dependent models have
better results than non-dependent.
Schuster et al., (2012) investigated the difference
between the two types of model. They used a
recognition model based on Support Vector
Machines to differentiate three emotional valence
levels (negative, neutral and positive) using
electroencephalographic signals. The model was
trained twice on the same dataset (n = 18 subjects)
according to the type 1 and 2 protocols. Their results
showed a significant difference of the generalization
error between the two protocols, the subject
dependent approach obtaining a better performance.
Bailenson et al., (2008) also obtained better accuracy
results for user-dependent models when comparing
the two types of approach using facial and
physiological data. In another study, Bock et al.,
(2012) showed that the performance difference
between user-dependent and user-independent
models is greater for recognition models based on
physiological signals than for models based on voice
analysis. The principal reason explaining the poorer
performance of subject independent approaches is
the great variability of physiological signals
observed between different subjects. Training a
model to recognize emotional reactions of a single
subject thus allows avoiding this problem. The
subject’s psychophysiological specificities are, in
some way, learned by the model.
Table 1: Emotion recognition models comparison. UD
stands for user-dependent models and UI stands for user-
independent models.
However, even though subject dependent models
are currently more performant, they have many
pragmatic drawbacks. The most important being that
user-dependent models require a time-consuming
training phase before being operational. For
industrial or scientific applications, it implies that
every new subject must go through the complete
training process (i.e. training stimuli presentation,
physiological recordings, etc.). This requirement
represents a significant burden, as most training
procedures take an important amount of time and
sometimes include strong emotional cues (e.g. IAPS
images, movie clips). On the other hand, after the
initial training phase, subject-independent models
don’t need to be specifically adapted to new
subjects.
The current literature on psychophysiological
inference calls out for the development of more
efficient subject-independent approaches (AlZoubi
et al., 2012; Schuster et al., 2012; van den Broek et
al., 2010b). This paper therefore aims to bring a
contribution to the development of such generic
approaches. The remainder of the paper is as follow:
In section 2, we present the general framework of
the proposed approach that aims at explicitly
modeling subjects’ idiosyncrasies. In section 3, we
describe how the theory of individual response
specificity can be used to fulfill such a goal. In
section 4, we briefly describe the experiment that
will be carried on to validate the proposed approach.
Concluding remarks are given is section 5.
2 MODELING IDIOSYNCRASY
The main cause of the “genericity vs
generalizability” dilemma in ASP is related to the
idiosyncrasy of emotional reactions. Simply stated,
each person reacts differently to a same stimulus, at
both the physiological and subjective level. A same
situation can therefore generate different emotions,
and a same emotion can generate different
physiological signals. Both outcomes have been
shown to be deleterious to user-independent
recognition models (Villon and Lisetti, 2007). On
the other hand, user-dependent recognition models
do not need to model the idiosyncratic factors at play
in the f relationship (see equation 1) as they remain
constant for a same subject. Let equation 2 represent
a simple emotion prediction model based on linear
regression and two physiological signals (Φ
1
and
Φ
2
).
Ψ = β
1
Φ
1
+ β
2
Φ
2
(2)
Chanel et al. (2009) Recollection
UD
67
Hristova et al. (2009) IAPS
UD
96,9
Benovoy et al. (2007) Acting
UD
90
Picard et al. (2001) Acting
UD
81
Rani et al. (2006)
Cognitive,
games
UD
85,81
Cheng (2012) Songs
UD
95,97
Kulkolja et al. (2014) IAPS
UD
60,3
Wu et al. (2010) Simulator
UD + UI
95,5 (UD) - 36,9 (UI)
Kim et al. (2004)
audio, visual,
cognitive
UI
61,8
Kolodyazhniy et al. (2011) Film
UI
77,9
Verma et al. (2014) Music videos
UI
85
Chang et al. (2013) Movies
UI
89,2
Authors Elicitor Genericity Generalizability (%)
AddressingSubject-dependencyforAffectiveSignalProcessing-ModelingSubjects'Idiosyncracies
73
The model’s parameters (β) are simply optimized
to best fit the targets for a given subject (e.g.
subject’s arousal level). The subject’s idiosyncrasies
are therefore learned implicitly within β
1
and β
2
. For
example, the specific way in which Φ
1
reflects
emotion intensity for a subject is model by β
1
. It can
explain, in part, why when applied to a different
subject (with different idiosyncrasies), the model’s
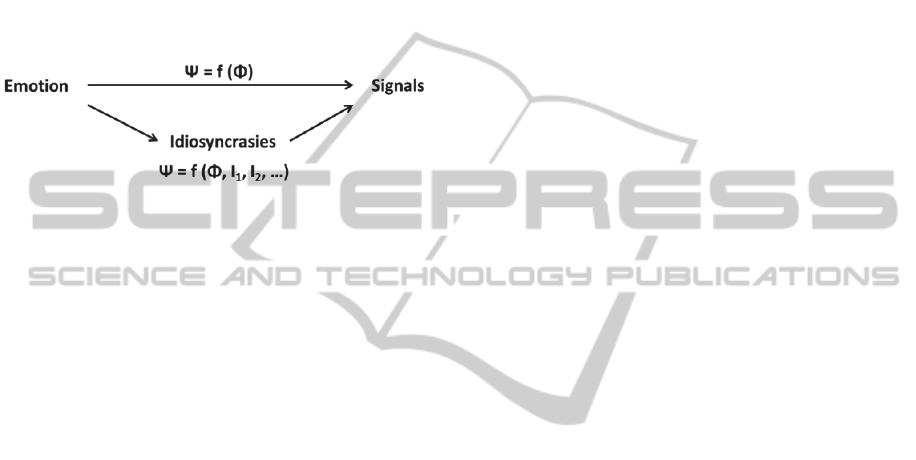
performance decreases. As illustrated in Figure 1,
we suggest to explicitly model subjects’
idiosyncrasies in order for user-independent models
to better adapts to different subjects.
Figure 1: Modeling idiosyncracies.
As modeled in equation 3, the implicit
idiosyncratic factors would be extracted from β
1
and
β
2
to explicit parameters β
i
.
Ψ = β
1
Φ
1
+ β
2
Φ
2
+ β
3
I
1
+ β
4
I
2
… (3)
There are different ways in which idiosyncratic
factors can be modeled and taken into account in
ASP. Following the previous example, β
3
could
model the way in which an idiosyncratic factor I
1
(e.g. a phobia or anxiety trait) mediate the way in
which Φ
1
reflects emotion intensity for a given
subject. This specific effect of I
1
, that was initially
implicit in β
1
, would now be explicit in β
3
. Some
research have explored this avenue by using
subjects’ characteristics. For example, Frantzidis et
al., (2010) have integrated the subjects’ gender in an
emotional arousal recognition model based on
decision trees and electroenphalographic (EEG)
data. Zhou et al., (2011) have used subjects’ culture
and gender in order to compare the generalisation
error of different training protocols. They used three
different models (decision tress, k-nearest neighbors,
and decomposition trees) to classify seven discrete
emotions using electrodermal activity,
electromyography, respiration, and EEG data.
Results showed that training on gender based
subgroups "male’’ (n = 21) and ‘’female’’ (n= 21),
lead to better performance. They obtained similar
results using models trained on culture based
subgroups ‘’Chinese’’ (n = 14), ‘’Indian’’ (n = 14)
and ‘’Western’’ (n = 14). These results show that a
subject-independent model can achieve better results
when the training set is narrowed using subjects’
characteristics.
3 INDIVIDUAL RESPONSE
SPECIFICITY
We used the Individual Response Specificity theory
(IRS) (Marwitz and Stemmler, 1998) as a
framework to model the subjects’ idiosyncrasies.
The IRS can be defined as ‘’the tendency of subjects
to present similar physiological patterns throughout
different condition during one testing session’’
(Marwitz and Stemmler, 1998). Its goal is to identify
the factors influencing the constancy in which a
same situation induces the same physiological
response in a subject. The IRS therefore refers to the
stability of the psychophysiological relation
(equation 1) for a given subject, and can explain in
part why user-dependent recognition models have
better results. Within the IRS framework, the
specificity of the physiological reactions depends on
the interaction of three components.
1. The biological component represents the
subject’s constitutional proprieties such as his/her
morphology and his/her biochemical attributes (e.g.
hypertension or glandular reactivity). This
component is very stable and characterizes a great
part of individual differences.
2. The situational factors are related to
physiological responses according to many
dimensions such as the familiarity of the situation,
the range of possible reactions or the different
situational constraints.
3. The psychological component explains how
emotional reactions of a subject facing a situation
are mediated by many psychological and evaluation
factors such as personality, general attitude,
cognitive styles and personal life experience.
From a pragmatic standpoint, obtaining information
on biological factors is either intrusive or simply
arduous to implement. For example, the
measurement of the cortisol concentration, albeit
correlated with different emotional responses
(Nejtek, 2002), requires the sampling of saliva in the
participants’ mouth. Most works on ASP therefore
address the biological component by using
baselining methods. In this line of research,
Johannes and Gaillard (2014) developed an
approach based on cluster analysis that enable a
better comparison of physiological signals between
groups of subjects.
Addressing the situational component would
require real-time information on the current context,
and therefore would limit the general applicability of
a recognition approach. Studies interested to this
aspect of the relation are still too embryonic and do
PhyCS2015-2ndInternationalConferenceonPhysiologicalComputingSystems
74

not permit the elaboration of useful and
implementable conclusions in a machine learning
context.
We therefore chose, as a first step, to work on the
psychological component. From a pragmatic point of
view, the justification of the integration of
personality parameters stands on the fact that they
are easy to collect, via questionnaires, and produce
numerical data according to multiple dimensions
easily modeled. The IRS states that for the same
situation, a similarity of perception leads to a greater
similarity in physiological reactions (Stemmler,
1997). As one’s personality is strongly related the
way he or she evaluate a situation, we choose to first
model psychological idiosyncrasies using
personality traits. The literature already contains
some results pointing in the same direction. For
instance, van den Broek et al., (2009b) note that the
relation between cardiac activity and emotional
arousal is influenced by the extraversion personality
trait. Crider (2008) reports many studies showing
that electrodermal lability is linked to the subjects’
expressivity and disposition (antagonist or
agreeableness). In a more general manner, a meta-
analysis done by Myrtek (1998) presents
correlations between 34 physiological variables and
certain personality traits. The effect size of these
correlations are ranging from small (r < |0.10|) to
moderate (r < |0.30|).
4 EXPERIMENT
An experiment will be conducted to validate the
proposed approach. Based on the Circumplex Model
of Affect (Russell, 1980), users’ emotions will be
modeled using the two psychological constructs of
valence and arousal. Valence is used to contrast
states of pleasure (e.g. happy) and displeasure (e.g.
angry), and arousal to contrast states of low arousal
(e.g. calm) and high arousal (e.g. surprise). Different
levels of emotional valence and arousal will be
induced using standardized images from the
International Affective Picture System (IAPS) (Lang
et al., 2008) (see Figure 2 for examples).
Figure 2: IAPS images (2352, 1304).
The recorded physiological signals will consist
of electrodermal activity, cardiovascular activity,
respiration, pupil diameter, and
electroencephalographic activity. Personality will be
assessed using the HEXACO Personality Inventory
(Lee and Ashton, 2004). In line with the trait theory
of personality, the HEXACO-PI defines six
personality factors: Honesty-Humility, Emotionality,
Extraversion, Agreeableness, Conscientiousness,
and Openness to Experience. Analyses will consist
in 1) testing if personality factors can act as
moderator variables between each physiological
feature and emotional target, and 2) assessing the
improvement in accuracy brought by adding
personality variables to a regular physiological
prediction model. The latter will be implemented by
instantiating the idiosyncratic parameters of equation
3 with the HEXACO personality factors (e.g. I
1
=
Openness, I
2
= Extraversion).
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we proposed an approach to address
the “genericity vs generalizability” dilemma at the
hearth of the physiological emotion recognition
problem in ASP. Our approach is based on the
modeling of the idiosyncratic factors that underlie
user-dependent recognition models’ higher accuracy.
As a first exemplification, we described how
personality traits can be used to improve the
accuracy of user-independent emotion recognition
models.
REFERENCES
Alzoubi, O., D'mello, S. K. & Calvo, R. A. 2012.
Detecting Naturalistic Expressions of Nonbasic Affect
Using Physiological Signals. IEEE Transactions on
Affective Computing, 3, 298-310.
Bailenson, J. N., Pontikakis, E. D., Mauss, I. B., Gross, J.
J., Jabon, M. E., Hutcherson, C. a. C., Nass, C. &
John, O. 2008. Real-time classification of evoked
emotions using facial feature tracking and
physiological responses. International Journal of
Human-Computer Studies, 66, 303-317.
Bamidis, P., Frantzidis, C., Konstantinidis, E., Luneski,
A., Lithari, C., Klados, M., Bratsas, C., Papadelis, C.
& Pappas, C. 2009. An Integrated Approach to
Emotion Recognition for Advanced Emotional
Intelligence. In: JACKO, J. (ed.) Human-Computer
Interaction. Ambient, Ubiquitous and Intelligent
Interaction. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Bishop, C. M. 2006. Pattern Recognition and Machine
AddressingSubject-dependencyforAffectiveSignalProcessing-ModelingSubjects'Idiosyncracies
75

Learning, New York, Springer.
Bock, R., Gluge, S., Wendemuth, A., Limbrecht, K.,
Walter, S., Hrabal, D. & Traue, H. C. Intraindividual
and interindividual multimodal emotion analyses in
Human-Machine-Interaction. Cognitive Methods in
Situation Awareness and Decision Support
(CogSIMA), 2012 IEEE International Multi-
Disciplinary Conference on, 6-8 March 2012 2012.
59-64.
Cacioppo, J. T. & Tassinary, L. G. 1990. Inferring
psychological significance from physiological signals.
American Psychologist, 45, 16-28.
Chanel, G., Kierkels, J. J. M., Soleymani, M. & Pun, T.
2009. Short-term emotion assessment in a recall
paradigm. International Journal of Human-Computer
Studies, 67, 607-627.
Chang, C.-Y., Chang, C.-W., Zheng, J.-Y. & Chung, P.-C.
2013. Physiological emotion analysis using support
vector regression. Neurocomputing, 122, 79-87.
Cheng, B. 2012. Emotion recognition from physiological
signals using support vector machine. Software
Engineering and Knowledge Engineering: Theory and
Practice. Springer.
Christie, I. C. & Friedman, B. H. 2004. Autonomic
specificity of discrete emotion and dimensions of
affective space: a multivariate approach. International
Journal of Psychophysiology, 51, 143-153.
Crider, A. 2008. Personality and Electrodermal Response
Lability: An Interpretation. Applied Psychophysiology
and Biofeedback, 33, 141-148.
Dongrui, W., Christopher, G. C., Brent, J. L., Shrikanth, S.
N., Michael, E. D., Kelvin, S. O. & Thomas, D. P.
2010. Optimal Arousal Identification and
Classification for Affective Computing Using
Physiological Signals: Virtual Reality Stroop Task.
IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 1, 109-
118.
Fairclough, S. H. 2009. Fundamentals of physiological
computing. Interacting with Computers, 21, 133-145.
Frantzidis, C. A., Bratsas, C., Klados, M. A.,
Konstantinidis, E., Lithari, C. D., Vivas, A. B.,
Papadelis, C. L., Kaldoudi, E., Pappas, C. & Bamidis,
P. D. 2010. On the Classification of Emotional
Biosignals Evoked While Viewing Affective Pictures:
An Integrated Data-Mining-Based Approach for
Healthcare Applications. IEEE Transactions on
Information Technology in Biomedicine, 14, 309-318.
Haag, A., Goronzy, S., Schaich, P. & Williams, J. 2004.
Emotion Recognition Using Bio-sensors: First Steps
towards an Automatic System. In: ANDRÉ, E.,
DYBKJAE R, L., MINKER, W. & HEISTERKAMP,
P. (eds.) Affective dialogue systems. Springer Berlin /
Heidelberg.
Hristova, E., Grinberg, M. & Lalev, E. 2009. Biosignal
Based Emotion Analysis of Human-Agent
Interactions. In: ESPOSITO, A. & VÍCH, R. (eds.)
Cross-Modal Analysis of Speech, Gestures, Gaze and
Facial Expressions. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Johannes, B. & Gaillard, A. W. 2014. A methodology to
compensate for individual differences in
psychophysiological assessment. Biological
psychology, 96, 77-85.
Kim, K., Bang, S. & Kim, S. 2004. Emotion recognition
system using short-term monitoring of physiological
signals. Medical & biological engineering &
computing, 42, 419-427.
Kolodyazhniy, V., Kreibig, S. D., Gross, J. J., Roth, W. T.
& Wilhelm, F. H. 2011. An affective computing
approach to physiological emotion specificity: Toward
subject-independent and stimulus-independent
classification of film-induced emotions.
Psychophysiology, 48, 908-922.
Kukolja, D., Popović, S., Horvat, M., Kovač, B. & Ćosić,
K. 2014. Comparative analysis of emotion estimation
methods based on physiological measurements for
real-time applications. International Journal of
Human-Computer Studies.
Lang, P. J., Bradley, M. M. & Cuthbert, B. N. 2008.
International affective picture system (IAPS):
Affective ratings of pictures and instruction manual.
Technical report B-3. University of Florida,
Gainesville, FI.
Lee, K. & Ashton, M. C. 2004. Psychometric Properties of
the HEXACO Personality Inventory. Multivariate
Behavioral Research, 39, 329-358.
Marwitz, M. & Stemmler, G. 1998. On the status of
individual response specificity. Psychophysiology, 35,
1-15.
Myrtek, M. 1998. Metaanalysen zur
psychophysiologischen persönlichkeitsforschyung
[Meta-analysis for psychophysiological personality
research]. In: RÖSLER, F. (ed.) Ergebnisse und
Anwendungen der Psychophysiologie. Göttingen:
Hogrefe Verlag für Psychologie.
Nejtek, V. A. 2002. High and low emotion events
influence emotional stress perceptions and are
associated with salivary cortisol response changes in a
consecutive stress paradigm.
Psychoneuroendocrinology, 27, 337-352.
Novak, D., Mihelj, M. & Munih, M. 2012. A survey of
methods for data fusion and system adaptation using
autonomic nervous system responses in physiological
computing. Interacting with Computers, 24, 154-172.
Picard, R. W., Vyzas, E. & Healey, J. 2001. Toward
Machine Emotional Intelligence: Analysis of Affective
Physiological State. IEEE Transactions on Pattern
Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 23, 1175.
Rani, P., Liu, C., Sarkar, N. & Vanman, E. 2006. An
empirical study of machine learning techniques for
affect recognition in human–robot interaction. Pattern
Analysis & Applications, 9, 58-69.
Russell, J. A. 1980. A circumplex model of affect. Journal
of Personality and Social Psychology, 39, 1161-1178.
Schuster, T., Gruss, S., Rukavina, S., Walter, S. & Traue,
H. C. EEG-based Valence Recognition: What do we
Know About the influence of Individual Specificity?
The Fourth International Conference on Advanced
Cognitive Technologies and Applications
(COGNITIVE 2012), 2012 Nice, France. 71-76.
Stemmler, G. 1997. Selective activation of traits:
PhyCS2015-2ndInternationalConferenceonPhysiologicalComputingSystems
76

Boundary conditions for the activation of anger.
Personality and Individual Differences, 22, 213-233.
Van Den Broek, E., Janssen, J., Westerink, J. & Healey, J.
Prerequisites for Affective Signal Processing (ASP).
In: ENCARNAÇÃO, P. & VELOSO, A., eds.
International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and
Signal Processing, 2009a Porto, Portugal. INSTICC
Press, 426-433.
Van Den Broek, E., Janssen, J. H., Zwaag Van Der, M. D.
& Healey, J. A. Prerequisites for Affective Signal
Processing (ASP) - Part III. Third International
Conference on Bio-Inspired Systems and Signal
Processing, Biosignals 2010, 2010a Valencia, Spain.
Van Den Broek, E., Janssen, J. H. A., Healey, J. A. &
Zwaag Van Der, M. 2010b. Prerequisites for Affective
Signal Processing (ASP) - Part II. Third International
Conference on Bio-Inspired Systems and Signal
Processing, Biosignals 2010. Valencia, Spain.
Van Den Broek, E., Schut, M. H., Westerink, J. H. D. M.
& Tuinenbreijer, K. 2009b. Unobtrusive Sensing of
Emotions (USE). J. Ambient Intell. Smart Environ., 1,
287-299.
Verhoef, T., Lisetti, C., Barreto, A., Ortega, F., Van Der
Zant, T. & Cnossen, F. 2009. Bio-sensing for
Emotional Characterization without Word Labels. In:
JACKO, J. (ed.) Human-Computer Interaction.
Ambient, Ubiquitous and Intelligent Interaction.
Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Verma, G. K. & Tiwary, U. S. 2013. Multimodal fusion
framework: A multiresolution approach for emotion
classification and recognition from physiological
signals. NeuroImage.
Villon, O. & Lisetti, C. Toward Recognizing Individual's
Subjective Emotion from Physiological Signals in
Practical Application. Twentieth IEEE International
Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems,
2007. CBMS '07., 20-22 June 2007 2007. 357-362.
Zhou, F., Qu, X., Helander, M. G. & Jiao, J. 2011. Affect
prediction from physiological measures via visual
stimuli. International Journal of Human-Computer
Studies, 69, 801-819.
AddressingSubject-dependencyforAffectiveSignalProcessing-ModelingSubjects'Idiosyncracies
77
