
Deadlock Avoidance in Interorganizational Business Processes using a
Possibilistic WorkFlow Net
Leiliane Pereira de Rezende and St
´
ephane Julia
Computing Faculty, Federal University of Uberl
ˆ
andia, UFU - Uberl
ˆ
andia,
2160, Av. Jo
˜
ao Naves de
´
Avila, 38400-902 Uberl
ˆ
andia, MG, Brazil
Keywords:
Interorganizational WorkFlow Net, Possibilistic Petri Net, Deadlocks, Siphon, Soundness, Process Monitor-
ing.
Abstract:
In this paper, an approach based on Siphon structures, possibilistic Petri nets and interorganizational Work-
Flow nets is proposed to deal with deadlock situations in interorganizational business processes. A deadlock
situation is characterized by an insufficiently marked Siphon. Possibilistic Petri nets with uncertainty on the
marking and on the transition firing are used to ensure the existence of at least one transition firing sequence
enabling the completion of the process without encountering the deadlock situation. Routing patterns and
communication protocols that exist in business processes are modeled by interorganizational WorkFlow nets.
Combining both formalisms, a kind of possibilistic WorkFlow net is obtained.
1 INTRODUCTION
An organization produces value for its customers by
executing various business processes. Business pro-
cesses represent the sequences of activities that have
to be executed within an organization to treat specific
cases and to reach well defined goals (Aalst and Hee,
2004). Due to complexity and variety of business pro-
cesses, contemporary organizations use information
technology to support activities which may include
automate their processes.
A workflow process corresponds to the automa-
tion of a business process, in whole or part, during
which documents, information or tasks are passed
from one participant to another for action, accord-
ing to a set of procedural rules (Members, 1994). A
Workflow Management Systems (WFMS) is a sys-
tem that completely defines, manages and executes
workflow processes through the execution of software
whose sequence of activities is driven by a computer
representation of the workflow process logic (Mem-
bers, 1994). They are a key technology for improving
the effectiveness and efficiency of business processes
within an organization (van der Aalst, 1998b).
Considering that modern organizations have to
cope with complex administrative processes, WFMS
have to deal with workflow processes shared among
multiple organizations. These systems are critical to
the functioning of many organizations. Most busi-
ness information applications are large-scale software
systems that provide essential support to companies
in their business processes. Each business partner
has to define private workflow processes that are con-
nected to other workflow processes belonging to the
other partners of the same organization (Silva et al.,
2013). An interorganizational workflow model corre-
sponds then to a finite set of WorkFlow nets loosely
coupled through asynchronous communication mech-
anisms (van der Aalst, 1998b).
Many papers have already considered Petri net
theory as an efficient tool for the modeling and analy-
sis of WFMS (van der Aalst, 1998a) (Aalst and Hee,
2004) (Soares Passos and Julia, 2009). The Work-
Flow nets, acyclic Petri net models used to represent
business processes, are defined in (Aalst and Hee,
2004).
Soundness property is an important criterion
which needs to be satisfied when treating workflow
processes. In fact, good properties of well-defined
formal models such as WorkFlow nets can easily be
proven, thus showing when business processes are
following a rigid structure that does not allow devi-
ations from the process description during real time
execution. However, in (Fahland et al., 2011), a case
study revealed that, on average, only 46% of 735 in-
dustrial business process models checked were in fact
sound. In addition, as the synchronization of par-
allel processes can easily lead to a potential source
429
Rezende L. and Julia S..
Deadlock Avoidance in Interorganizational Business Processes using a Possibilistic WorkFlow Net.
DOI: 10.5220/0005347004290439
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 429-439
ISBN: 978-989-758-096-3
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

of deadlock (van der Aalst, 2000), it can be difficult
to establish the soundness correctness of complex in-
terorganizational workflow processes. As a matter of
fact, even proving the soundness correctness of local
workflow processes is not a guarantee of the sound-
ness correctness of the whole system (the interorga-
nizational workflow model) as was shown in (van der
Aalst, 1998b). Deadlock in this case comes gener-
ally from message ordering mismatches as shown in
(Xiong et al., 2009).
There exist many research papers devoted to the
deadlock problem. Over the last two decades, a great
deal of research has been focused on solving dead-
lock problems in resource allocation systems such as
computer communication systems (Tang et al., 2012),
(Mohanty and Kumara, 2013), WorkFlow systems
(Park and Reveliotis, 2001), (Kohler and Schaad,
2008), and flexible manufacturing systems (Gang and
Ming, 2004), (Mohanty and Kumara, 2013), resulting
in a wide variety of approaches. In addition, a va-
riety of deadlock control policies based on Petri nets
have been proposed for automated manufacturing sys-
tem (Ezpeleta et al., 1995), (Huang et al., 2001), (Li
and Zhou, 2004), (Uzam and Zhou, 2007), (Ahmad
et al., 2011), (Chen and Li, 2011), (Chen et al., 2012),
(Huang et al., 2012), (Li et al., 2012). From a tech-
nical perspective, most of the control policies resolv-
ing deadlocks are developed via state space analysis
or structural analysis of Petri nets. Deadlock con-
trol policies based on structural analysis can avoid the
state explosion problem successfully, but always for-
bid some legal states (Liu et al., 2013).
Considering that a deadlock situation within the
Petri net theory (Murata, 1989) is characterized as
a zero marking for some structural objects called
Siphons (Boer and Murata, 1994), several algorithms
to detect the Siphons and efficient methods for the
synthesis of supervisors enforcing that the marking of
the Siphons never become completely empty and en-
suring the Petri nets are free from deadlock, have been
proposed in (Barkaoui and Abdallah, 1995), (Chu and
Xie, 1997), (Maruta et al., 1998), (Sadiq et al., 2000),
(Iordache et al., 2002), (Awad and Puhlmann, 2008),
(Silva et al., 2013). All these works are based on a
kind of transformation of the process model and can-
not be used at a monitoring level when a deadlock sit-
uation still exists in the control structure of the model.
In this paper, an approach based on Siphon struc-
tures, as well as possibilistic Petri nets and interor-
ganizational WorkFlow nets is proposed to deal with
deadlock situations in business processes. In particu-
lar, a kind of possibilistic WorkFlow net will be de-
fined to treat in real time the deadlock situations that
occur from message ordering mismatches between
the local WorkFlow nets.
The remainder of this paper is as follow: in sec-
tion 2, the definition of interorganizational WorkFlow
nets and soundness correctness criterion are provided.
In section 3, an overview of possibilistic Petri nets is
given. In section 4, the Siphon structure is defined.
In section 5, the possibilistic WorkFlow net is pre-
sented and an example based on a process that pre-
cedes the presentation of a paper at a conference il-
lustrates the approach. Finally, section 6 concludes
this work with a short summary, an assessment based
on the approach presented and an outlook on future
work proposals.
2 INTERORGANIZATIONAL
WORKFLOW NET
Before introducing the interorganizational WorkFlow
nets (IOWF-net) and the soundness property for these
nets, it is necessary to introduce the WorkFlow nets
(WF-nets) and soundness in the single organizational
context.
2.1 WorkFlow Net and Soundness
A Petri net that models a workflow process is called
a WorkFlow net (Aalst and Hee, 2004). A WorkFlow
net satisfies the following properties (van der Aalst,
1998a):
• It has only one source place, named Start and only
one sink place, named End. These are special
places such that the place Start has only outgoing
arcs and the place End has only incoming arcs.
• A token in Start represents a case that needs to be
handled and a token in End represents a case that
has been handled.
• Every task t (transition) and condition p (place)
should be on a path from place Start to place End.
Following, the formal definition of WorkFlow nets
is presented.
Definition 1 (WF-net). (Aalst and Hee, 2004) A Petri
net PN = (P, T, F) is a WorkFlow net if and only if:
1. There is one source place i ∈ P such that •i = φ;
2. There is one sink place o ∈ P such that o• = φ;
3. Every node x ∈ P ∪ T is on a path from i to o.
A WorkFlow net has one input place (i) and one
output place (o) because any case handled by the pro-
cedure represented by the WF-net is created when it
enters the WFMS and is deleted once it is completely
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
430

handled by the WFMS, i.e., the WF-net specifies the
life-cycle of a case. The third requirement in Defini-
tion 1 has been added to avoid “dangling tasks and/or
conditions”, i.e., tasks and conditions which do not
contribute to the processing of cases (Aalst and Hee,
2004).
Soundness is a correctness criterion defined for
WF-nets and is related to its dynamics. A WF-net is
sound if, and only if, the following three requirements
are satisfied (Aalst and Hee, 2004):
• For each token put in the place Start, one and only
one token appears in the place End.
• When the token appears in the place End, all the
other places are empty for this case.
• For each transition (task), it is possible to move
from the initial state to a state in which that tran-
sition is enabled, i.e. there are no dead transitions.
Following, the formal definition of Soundness
property in WF-nets context is presented.
Definition 2 (Soundness). (Aalst and Hee, 2004) A
procedure modeled by a WF-net PN = (P, T, F) is
Sound if and only if:
1. For every state M reachable from state i, there ex-
ists a firing sequence leading from state M to state
o. Formally:
∀
M
h
(i
∗
→ M) ⇒ (M
∗
→ o)
i
2. State o is the only state reachable from state i with
at least one token in place o. Formally:
∀
M
h
(i
∗
→ M ∧M ≥ o) ⇒ (M = o)
i
3. There are no dead transitions in (PN, i). Formally:
∀
t∈T
∃
M,M
0
h
i
∗
→ M
t
→ M
0
i
A method for the qualitative analysis of WF-nets
(soundness verification) based on the proof trees of
linear logic is presented in (Soares Passos and Julia,
2009) and another based on a reachability graph is
presented in (van der Aalst et al., 2011).
The weak soundness property corresponds to the
first requirement of the soundness property. Since the
second requirement is implied by the first one, the
only difference is the third requirement, i.e., for weak
soundness property it is not required that there are no
dead transitions, i.e. a WorkFlow net is weak sound
if, and only if, for each token put in the place Start (i),
one and only one token appears in the place End (o).
This property states that starting from the initial state
(just a token in place Start), it is always possible to
reach the final state with one token in the place End
(van der Aalst et al., 2011).
2.2 Interorganizational WorkFlow Net
and Soundness
An interorganizational WorkFlow net (IOWF-net) is
essentially a set of loosely coupled workflow pro-
cesses modeled by Petri nets. Typically, there exist n
business partners which are involved in one “global”
workflow process (Aalst, 1999). Each of these part-
ners has its own “local” workflow process, that is pri-
vate, and where full control exists over it. Therefore,
an IOWF-net is composed of at least two local work-
flow processes.
The local workflows interact at certain points ac-
cording to a communication structure. There exists
two types of communication: asynchronous commu-
nication (corresponding to the exchange of messages
between workflows) and synchronous communication
(which forces the local workflows to execute specific
tasks at the same time). Synchronous communication
corresponds to the melting of some transitions (Aalst,
1999).
In this paper, the synchronous case is not consid-
ered since we consider that each organization controls
its own process. Only asynchronous communication
protocols will be considered. Definition 3 formalizes
the concept of an IOWF-net.
Definition 3 (IOWF-net). (van der Aalst, 1998b) An
interorganizational WorkFlow net(IOWF-net) is a tu-
ple IOW F = (PN
1
, PN
2
, ..., PN
n
, P
AC
, AC), where:
1. n ∈ N is the number of local WorkFlow nets
(LWF-nets);
2. For each k ∈ {1, ..., n} : PN
k
is a WF-net with
source place i
k
and sink place o
k
;
3. For all k, l ∈ {1, ..., n} : i f k 6= l, then (P
k
∪ T
k
) ∩
(P
l
∪ T
l
) =
/
0;
4. T
∗
=
S
k∈{1,...,n}
T
k
, P
∗
=
S
k∈{1,...,n}
P
k
, F
∗
=
S
k∈{1,...,n}
F
k
(relations between the elements of
the LWF-nets);
5. P
AC
is the set of asynchronous communication el-
ements (communication places);
6. AC ⊆ P
AC
× P(T
∗
) × P(T
∗
) corresponds to asyn-
chronous communication relations
1
.
Each asynchronous communication element cor-
responds to a place named in P
AC
. The relation AC
specifies a set of input transitions and a set of output
transitions for each asynchronous communication el-
ement.
The workflow which precedes the presentation of
a paper at a conference, presented in (van der Aalst,
1998b), will be used to understand the definition of
1
P(T
∗
) is the set of all non-empty subsets of T
∗
DeadlockAvoidanceinInterorganizationalBusinessProcessesusingaPossibilisticWorkFlowNet
431

IOWF-net shown below. “This workflow can be con-
sidered to be an interorganizational workflow with
two loosely coupled workflow processes: (1) the pro-
cess of an author preparing, submitting and revising
a paper, and (2) the process of evaluating and mon-
itoring submissions by the program committee. In
this case, there exists two ‘organizations’ involved
in the interorganizational workflow: the author (AU)
and the program committee (PC). The author sends a
draft version of the paper to the program committee.
The program committee acknowledges the receipt and
evaluates the submission. The paper is accepted or re-
jected by the program committee. In both cases the
author is notified. If the paper is rejected, the work-
flow terminates, otherwise the author can start prepar-
ing the final version. After completing the final ver-
sion, a copy is sent to the program committee and the
program committee acknowledges the receipt of the
final version. If the final version is not received by
the program committee before a specific due date, the
author is notified that the paper is too late. A paper
which is too late will not be published in the proceed-
ings”.
Figure 1: An interorganizational workflow.
Figure 1 shows the IOWF-net that models the
process described above. This IOWF-net has two
LWF-nets: AU, on the left, models the local work-
flow of the author and PC, on the right, models the
workflow procedure followed by the program com-
mittee. Each of them has only one source and one
sink place. In the LWF-net AU case, the source
place is start f low author and the sink place is
end f low author. In the LWF-net PC, the source
and sink place are start f low PC and end f low PC,
respectively. The places dra ft, ack dra f t, accept,
re ject, too late, f inal version and ack f inal are the
communication places.
An IOWF-net which is composed of a number of
sound local workflows may be subject to synchroniza-
tion errors. In addition, it is also possible to have an
interorganizational workflow which is globally sound
but not locally sound (van der Aalst, 1998b). To de-
fine a notion of soundness suitable for IOWF-nets,
Aalst in (van der Aalst, 1998b) defined the unfolding
of an IOWF-net into a WF-net.
In the unfolded net, i.e. the U(IOWF-net), all the
local WF-nets are connected to each other by a start
transition t
i
and a termination transition t
o
. Moreover,
a global source place i and a global sink place o have
been added in order to respect the basic structure of
a simple WF-net. Asynchronous communication el-
ements are mapped into ordinary places(P
AC
). The
result of the unfolding is a new WF-net.
The soundness property definition for interorgani-
zational workflows is given below:
Definition 4 (Soundness). An interorganizational
WorkFlow net (IOWF-net) is sound iff it is locally
sound and globally sound. IOWF-net is locally sound
iff each of its local WorkFlow nets PN
k
is sound.
IOWF-net is globally sound iff U(IOWF-net) is sound.
The IOWF-net shown in Figure 1 is locally sound
but is not globally sound. One promptly notes that
if the transition too late of the LWF-net PC and
the transition send final version of the LWF-net AU
are fired, the messages too late and final version
cross each other leading to a state of deadlock with
a token in place a5 and the two messages are never
received (a token in place too late and a token in
place final version). Therefore, the IOWF-net does
not satisfy the soundness property but satisfies the
weak soundness property due to the fact that there
exists at least one firing sequence, for example
send draft, receive draft, send ack draft, receive
ack draft, evaluate, send accept, receive accept, pre-
pare final version, send final version, receive final
version, send ack final, receive ack final, that
reaches the final state.
3 POSSIBILISTIC PETRI NET
Possibilistic Petri nets are derived from Object Petri
nets (Sibertin-Blanc, 2001). In particular, in the ap-
proach presented in (Cardoso, 1999), a possibilistic
Petri net is a model where a marked place corresponds
to a possible partial state, a transition to a possible
state change, and a firing sequence to a possible be-
havior. The main advantage in working with possi-
bilistic Petri nets is that they allow for the updating
of a system state at a supervisory level with ill-known
information without necessarily reaching inconsistent
states.
A possibilistic Petri net model associates a possi-
bility distribution Π
o
(p) to the location of an object o,
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
432

p being a place of the net. Π
o
(p) = 1 represents the
fact that p is a possible location of o, and Π
o
(p) = 0
expresses the certainty that o is not present in place p.
Formally, a marking in a possibilistic Petri net is then
a mapping:
M : O × P −→ {0, 1}
where O is a set of objects and P a set of places. If
M(o, p) = 1, there exists a possibility of there being
the object o in place p. On the contrary, if M(o, p) =
0, there exists no possibility of there being o in p. A
marking M of the net allows one to represent:
• A Certain Marking: each token is located in only
one place (well-known state). Then M(o, p) = 1
and ∀p
i
6= p, M(o, p
i
) = 0.
• An Uncertain Marking: each token location has
a possibility distribution over a set of places. It
cannot be asserted that a token is in a given place,
but only that it is in a place among a given set
of places. For example, if there exists a pos-
sibility at a certain time to have the same ob-
ject o in two different places, p
1
and p
2
, then
M(o, p
1
) = M(o, p
2
) = 1.
A possibilistic marking will correspond in practice
to knowledge concerning a situation at a given time.
In a possibilistic Petri net, the firing (certain or
uncertain) of a transition t is decomposed into two
steps:
• Beginning of a Firing: objects are put into out-
put places of t but are not removed from its input
places.
• End of a Firing: that can be a firing cancellation
(tokens are removed from the output places of t)
or a firing achievement (tokens are removed from
the input places of t).
A certain firing consists of a beginning of a firing
and an immediate firing achievement. An uncertain
firing (or a pseudo-firing) that will increase the un-
certainty of the marking can be considered only as
the beginning of a firing (there is no information to
confirm whether the normal event associated with the
transition has actually occurred or not). To a certain
extent, pseudo-firing is a way of realizing abduction
in a knowledge base system.
The interpretation of a possibilistic Petri net is de-
fined by attaching to each transition an authorization
function η
x
1
,...,x
n
defined as follows:
η
x
1
,...,x
n
: T −→ {False,Uncertain, True}
where x
1
, ..., x
n
are the variables associated with the
incoming arcs of transition t (when considering the
underlying Object Petri net).
If o
1
, ..., o
n
is a possible substitution for x
1
, ..., x
n
for firing t, then several situations can be considered:
• t is not enabled by the marking but the associated
interpretation is true; an inconsistent situation oc-
curs and special treatment process of the net is ac-
tivated;
• t is enabled by a certain marking and the inter-
pretation is true; then a classical firing (with cer-
tainty) of an object Petri net occurs;
• t is enabled by a certain marking and the interpre-
tation is uncertain; then the transition is pseudo-
fired and the imprecision is increased;
• t is enabled by an uncertain marking; if the inter-
pretation is uncertain, t is pseudo-fired;
• t is enabled by an uncertain marking and the inter-
pretation is true: a recovery algorithm, presented
in (Cardoso et al., 1989), is called and a new com-
putation of the possibility distribution of the ob-
jects involved in the uncertain marking is realized
in order to go back to a certain marking.
The pseudo-firing (or uncertain marking) is de-
tailed through the example illustrated in Fig. 2. The
place p
1
belongs to Class
1
, p
2
to Class
2
and p
3
to
the composite class (Class
1
,Class
2
). The object in-
stances of Class
1
have an attribute date. The inter-
pretation, given by possibilistic distributions η
xy
is:
∀
y
uncertain i f (τ < x.date) ∧(signal(x))
true i f (τ ≥ x.date) ∧(signal(x))
f alse otherwise
where signal(x) is true when the associated sensor is
active on a specific shop floor.
(a) (b)
Figure 2: Marking (a) Before firing; and (b) After pseudo-
firing.
This function has the following semantics. Before
the time date, the arrival of a message from the shop
floor signaling that the object < x > was involved in
the event associated with the transition t, is possible
but does not correspond to a normal behavior. Either
the message is erroneous, or the representation of the
shop floor state (the Petri net marking) is not consis-
tent with the actual state. The imprecision concerning
DeadlockAvoidanceinInterorganizationalBusinessProcessesusingaPossibilisticWorkFlowNet
433

object < x > will increase and the transition t asso-
ciated with the corresponding event will be pseudo-
fired.
On the other hand, receiving the message after a
time date corresponds to normal behavior. So the fir-
ing of t should be a normal firing and the update of
the shop floor state should be realized with certainty.
Let us consider the initial marking of Fig. 2(a);
two substitution are possible for t: S
1
=< o
1
, o
3
>
and S
2
=< o
2
, o
3
>. Let us assume that o
1
.date = 20
and o
2
.date = 40.
Figure 3: Possibility distribution of locations of o
1
, o
2
and
o
3
.
At time τ
1
= 25 let us suppose that signal(o
2
) =
true and at time τ
2
= 35, signal(o
1
) = true. Fig. 3
depicts the possibility distributions of instances o
1
, o
2
and o
3
as a function of time (the black lines represent
a possibility equal to 1 and the bright lines a possibil-
ity equal to 0):
• at time τ = 10, the firing of transition t is possible
in the future for y = o
3
and for either x = o
1
or x =
o
2
(transition is enabled and can be fired normally
since signal(o
i
) is received);
• at time τ = 25, signal(o
2
) = true is received
but it does not correspond to a normal behav-
ior (o
2
.date > 25); η
o
2
o
3
(t) = uncertain, and t is
pseudo-fired with substitution S
2
(Fig. 2(b));
• after date τ > 25 the marking is imprecise and
cover two alternatives:
– the event corresponding to the firing of t for tu-
ple < o
2
, o
3
> has actually occurred; the infor-
mation given by signal(o
2
) was right;
– the event corresponding to the firing of t for tu-
ple < o
2
, o
3
> has not actually occurred. This
transition can still be fired, either by < o
2
, o
3
>
or by < o
1
, o
3
>;
• at time τ = 35 the receipt of signal(o
1
) = true cor-
responds to a normal behavior (o
1
.date ≤ 35) and
η
o
1
o
3
(t) = true. As explained before, this case
corresponds to the one in which the recovery algo-
rithm is called. The application of the algorithm
cancels the pseudo-firing of t for < o
2
, o
3
>. As
the marking is now precise and η
o
1
o
3
(t) = true,
transition t is fired (with certainty) with the tuple
< o
1
, o
3
>. It assume that signal(o
2
) = true was
due to noise.
4 DEADLOCK SITUATIONS
BASED ON EMPTY SIPHON
The presence of deadlock situations in Petri nets is
due to the existence of particular structures called
Siphons (Barkaoui and Abdallah, 1995). As special
structures, Siphons are related to the liveness of a
Petri net model and have been widely used in the char-
acterization and prevention/avoidance of deadlock sit-
uations (Zhong and Li, 2011). The definition of a
Siphon is the following:
Definition 5 (Siphon). Let P
0
be a non empty subset
of P (set of places). P
0
is a Siphon iff •P
0
⊆ P
0
•.
The set of the input transitions of P
0
is included in
the set of the output transitions of P
0
. Siphon P
0
is
said to be minimal iff it contains no other Siphons as
its proper subset.
As there exists more output transitions than input
transitions in the subnet, the subset of places P
0
can
be emptied of its tokens, which leads to a deadlock
situation (no transitions enabled in the Petri net). In
order that a Siphon is not completely emptied of its
token, it needs to contain at least a trap. The definition
of a trap is the following:
Definition 6. [Trap] Let P
00
be a non empty subset of
P(set of places). P
00
is a trap iff P
00
• ⊆ •P
00
. The set
of the output transitions of P
00
is included in the set
of the input transitions of P
00
.
The necessary and sufficient condition for the live-
ness in a marked Petri net is that every Siphon in a net
must contain at least a marked trap (Hack, 1972). In
addition, a necessary condition for the existence of
a deadlock situation in a Petri net is for there to be
at least an empty Siphon when considering the set of
reachable markings (Iordache et al., 2002).
Several algorithms have been presented by dif-
ferent authors for the automatic detection of Siphon
structures in Petri nets, such as the procedures based
on Incidence Matrix (Murata, 1989), inequalities
(Murata, 1989), linear algebra (Chu and Xie, 1997),
logic equations (Karatkevich, 2007), and linear equa-
tions with slack variables (Ezpeleta et al., 1993).
An example of deadlock is presented in Fig-
ure 4(a). The corresponding siphon is repre-
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
434
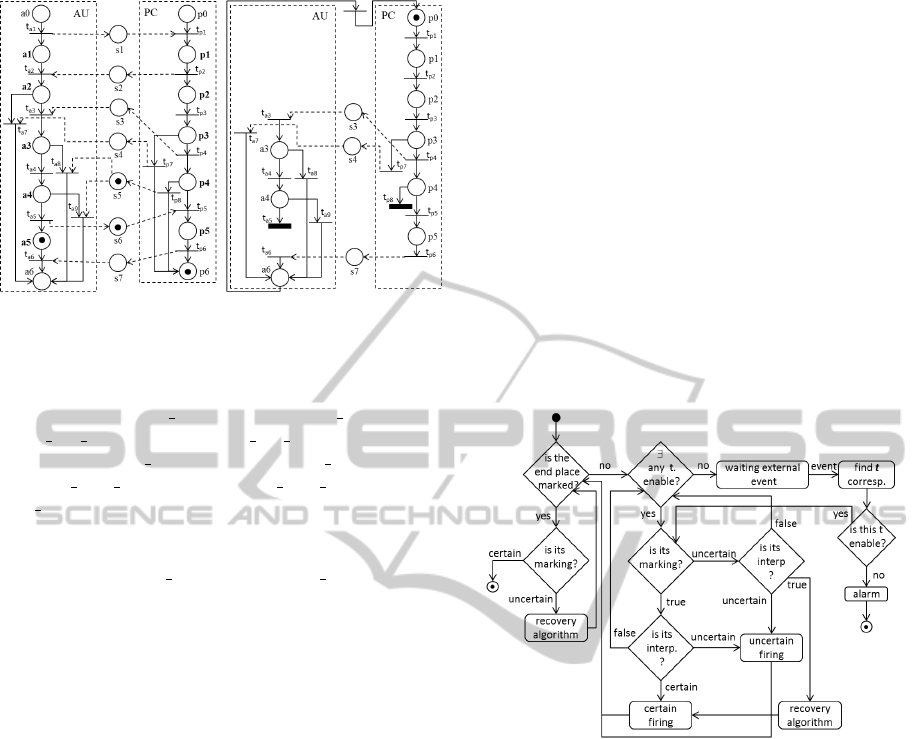
(a) Deadlock situation (b) Empty Siphon
Figure 4.
sented in Figure 4(b). It is clear that if the fir-
ing sequence send draft (t
a1
), receive draft (t
p1
),
send ack draft (t
p2
), receive ack draft (t
a2
), eval-
uate (t
p3
), send accept (t
p4
), receive accept (t
a3
),
prepare final version (t
a4
), send final version (t
a5
),
too
late (t
p8
) is fired, the Siphon in Figure 4(b) be-
comes empty through the firing of transitions t
a5
and
t
p8
and a deadlock situation (Figure 4(a)) occurs for
the marking a5, too late (p
s5
) and final version (p
s6
).
5 POSSIBILISTIC WORKFLOW
NET
As pointed out in the introduction, the synchroniza-
tion of parallel processes can easily lead to a po-
tential source of deadlock. In addition, most of the
deadlocks in a business process have structural causes
that will not allow the process to reach its final state
(Kohler and Schaad, 2008). Another important point
to be considered, is the fact that if a deadlock situa-
tion exists in a workflow process, the only solution to
avoid the deadlock situation if the model of the pro-
cess cannot be explicitly modified will be to avoid the
sequence of transition firing leading to the deadlock
situation and to follow with another firing sequence
allowing the final marking corresponding to the goal
to be reached.
A model of the process that considers the exist-
ing Siphons of the global business model and based
on the firing rules of a kind of possibilistic WorkFlow
net will eventually allow one to deviate from firing se-
quences that empty Siphon. Such a model will then be
able to deal with deadlock situations when the work-
flow model respects the weak soundness property.
This approach is divided into three consecutive
phases. The first phase is a kind of static analysis
phase and determines which transitions are responsi-
ble by emptying of the Siphon structures. In partic-
ular, it specifies the transitions that will have an un-
certain interpretation. Such transitions will have to be
pseudo-fired to explore in a kind of forward reasoning
of their effect on the Siphon marking. In the second
phase, the workflow process will be transformed into
a possibilistic WorkFlow net and uncertain interpre-
tations will be attached to the transitions encountered
in the previous phase. Finally, in the third phase, the
possibilistic WorkFlow net will be executed follow-
ing the behavior of the possibilistic token player algo-
rithm given in Figure 5. Such an inference mechanism
will ensure that deadlock situations will be avoided
during the execution of the process in the weak sound
case, guaranteeing the existence of at least one firing
sequence that will be able to reach the final marking
of the process.
Figure 5: Possibilistic token player algorithm associated
with autonomous local processes.
To illustrate the approach, the process that pre-
cedes the presentation of a paper at a conference, de-
scribed in subsection 2.2 and represented in Figure
1, will be considered. This interorganizational Work-
Flow net, as pointed out in the subsection 2.2, is not
globally sound; soon it may be subject to some syn-
chronization errors that can generate some structural
deadlocks during its execution.
The first step to make the process free of dead-
lock during its execution is to determine the Siphon
structures which can be emptied. As the focus of this
paper is not to present a new algorithm for finding
Siphon structures, the authors used the Petri net tool
PIPE (Platform Independent Petri Net Editor) (Din-
gle et al., 2009). Through the use of the PIPE tool, 24
Siphon structures were found, from which 10 can be
emptied (14 structures have trap and 10 do not). The
Table 1 shows the 10 Siphon structures.
Not all the Siphons without traps will necessar-
ily be emptied of theirs tokens. It will also depend
DeadlockAvoidanceinInterorganizationalBusinessProcessesusingaPossibilisticWorkFlowNet
435

Table 1: Siphon structures referring to Figure 1.
ID Siphon
01 a3, a4, a6, s3, s4, s7, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5
02 a2, a3, a4, a6, s2, s7, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5
03 a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a6, s7, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5
04 a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a6, s1, s7, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5
05 a0, a2, a3, a4, a6, s1, s2, s7, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5
06 a0, a3, a4, a6, s1, s3, s4, s7, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5
07 a2, a6, s2, s5, s7, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5
08 a0, a1, a2, a6, s5, s7, p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5
09 a0, a1, a2, a6, s1, s5, s7, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5
10 a0, a2, a6, s1, s2, s5, s7, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5
on the global Petri net model behavior. By produc-
ing a reachable marking graph, it is possible to check
that there exists only one deadlock state that occurs
when the transitions too late of the LWF-net PC and
send f inal version of the LWF-net AU are fired in se-
quence. Considering this, the set of empty Siphons
which lead to a deadlock situation in the Petri net
model of Figure 1 will be composed of the Siphons
01, 02, 03, 04, 05 and 06.
Considering the set of empty Siphons defined
above, the interpretation of the transitions will be
classified as true or uncertain. As the transitions send
final version and too late are directly responsible for
the emptying of the Siphon, they will have their inter-
pretation classified as uncertain. The other transitions
are not directly involved in the deadlock and will have
their interpretation classified as true.
After defining the transitions that will be eventu-
ally pseudo-fired, in order to avoid a possible dead-
lock situation, the PC and AU processes can be trans-
formed into possibilistic WorkFlow nets as illustrated
in the Figures 6(a) and 6(b), respectively. From the
point of view of a local process, the communica-
tion places of the interorganizacional WorkFlow net
will be considered as simple external events associ-
ated with transitions. In particular, an interpretation
will be attached with such transitions to indicate re-
ceived messages. For example, the interpretation as-
sociated with the transition t
p1
of the Figure 6(b) is
true if a message is received from the model of Figure
1 through the communication place dra ft.
< a > and < p > are objects belonging to the
class “Paper”, as well as variables x and y and all the
model’s places. Each transition has an interpretation
and an action attached to it defined by the designer.
The interpretation is used to manage the occurrence
of each event in the system by imposing conditions
on the firing of transitions. An action corresponds to
an application that involves the attributes of formal
variables associated with incoming arcs, allowing for
the modification of some specific attributes through
the execution of some specific methods. In order to
(a) AU process
(b) PC process
Figure 6: AU and PC process using possibilistic WorkFlow
net.
focus on the deadlock resolution problem, actions are
not represented in this paper.
The conditions correspond to the following in-
terpretations: the draft is ready to send to the
PC (sDra f t); the PC receives the draft (rDra f t);
the PC notifies the receipt of the draft to the au-
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
436

thor (sADra ft); the PC acknowledges the receipt
of the draft (rADra ft); the evaluation was com-
pleted (evaluate); the PC decides to accept the paper
(sAccept); the PC accepts the paper (rAccept); the PC
decides to reject the paper (sRe ject); the PC rejects
the paper (rRe ject); the author begins the preparation
of the final version (pFVersion); the final version is
ready to send to the PC (sFVersion); the PC receives
the final version (rFVersion); the deadline for sub-
mission of the paper is reached (tLate); the paper is
received after the deadline (rT Late); the PC notifies
the receipt of the final version to the author (sAFinal)
and the PC acknowledges the receipt of the final ver-
sion (rAFinal).
Finally, in the third phase, the communicating pro-
cesses PC and AU are executed considering the pos-
sibilistic token player algorithm given in Figure 5.
For this, let us assume that the transitions t
a1
, t
a2
,
t
a3
and t
a4
of the LWF-net AU and the transitions t
p1
,
t
p2
, t
p3
and t
p4
of the LWF-net PC have already been
fired(Figure 7(a) and 7(b)). If the transition t
a5
of the
LWF-net AU and the transition t
p5
of the LWF-net PC
are fired in sequence, the following scenario will oc-
cur:
• the transition t
p5
of LWF-net PC is enabled by a
certain marking and its interpretation is uncertain.
Then, t
p5
is pseudo-fired (Figure 7(c));
• the transition t
a5
of LWF-net AU is enabled by a
certain marking and its interpretation is uncertain.
Then, t
a5
is pseudo-fired (Figure 7(d));
• the end place (p6) of the LWF-net PC is marked
by an uncertain marking. This means that through
a pseudo firing sequence, the final marking of the
process PC was reached without encountering a
deadlock situation. Consequently, a recovery al-
gorithm, presented in (Cardoso et al., 1989), is
called to validate the sequence pseudo fired and
to go back to a certain marking. In particular, this
algorithm archives the pseudo-firing of the tran-
sition t
p5
(Figure 7(e)) finalizing the execution of
the process;
• the transition t
a9
of the LWF-net AU is enabled
by an uncertain marking and its interpretation is
true. This means that through a pseudo firing se-
quence the process AU reached a transition that
is not responsible for the emptying of the Siphon
and, consequently, for the deadlock situation in
the Petri net model of Figure 1. Consequently, the
recovery algorithm, presented in (Cardoso et al.,
1989), is called to go back to a certain marking.
In particular, this algorithm cancels the pseudo-
firing of the transition t
a5
(Figure 7(f)) and fires
with certainty the transition t
a9
(Figure 7(g)).
(a) PC (b) AU
(c) PC (d) AU
(e) PC (f) AU (g) AU
Figure 7: Simulation results of the scenario.
DeadlockAvoidanceinInterorganizationalBusinessProcessesusingaPossibilisticWorkFlowNet
437

6 CONCLUSIONS
In this article, a possibilistic WorkFlow net model
was presented with the purpose of dealing with dead-
lock situations in business processes not necessarily
sound. Combining the routing structure of WorkFlow
nets, communication mechanisms of interorganiza-
tional processes, uncertain reasoning of possibilistic
Petri nets and theoretical results on siphon theory,
the authors presented an approach that can deal with
deadlock situations that can be reached during the
real time execution of weak sound interorganizational
workflow processes. Such an approach was applied to
an example of a process that precedes the presentation
of a paper at a conference.
The other works that deal with the problem of
deadlock in interorganizational workflow processes
alter the design of the non sound model during the
analysis phase. Normally, the process’s model is al-
tered through the analysis of a reachable marking
graph as in (van der Aalst, 1998b) or by adding a
control place that forces the number of tokens in
the Siphon to remain strictly positive as in (Silva
et al., 2013). Comparing these works with the ap-
proach presented in this paper, the main advantage
is that it ensures the existence of at least one transi-
tion firing sequence during the real time execution of
weak sound interorganizational workflow processes,
enabling the completion of the process without en-
countering a deadlock situation and without modify-
ing the control structure of the model. In addition, the
presented method works for the weak sound interor-
ganizational workflow processes, given that most pro-
cesses in practice do not satisfy the soundness prop-
erty as was shown in (Fahland et al., 2011).
As a future work proposal, in order to validate ex-
perimentally such an approach, the model of the pos-
sibilistic WorkFlow net will have to be implemented
on a Petri net software tool allowing for the program-
ming of transition pseudo firing. It would seem that
the CPN Tools software resources, permitting in par-
ticular the use of complex function calculus associ-
ated with the model’s arcs, should be able to imple-
ment in a simple way some of the basic behaviors of
a possibilistic token player. It will be interesting then
to model and test a larger business process using the
CPN Tools software through Monte Carlo simulation
(Rubinstein and Kroese, 2008).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors would like to thank FAPEMIG
(Fundac¸
˜
ao de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de
Minas Gerais), CNPq (National Counsel of Tech-
nological and Scientific Development) and CAPES
(Coordenac¸
˜
ao de Aperfeic¸oamento de Pessoal de
N
´
ıvel Superior) for financial support.
REFERENCES
Aalst, W. (1999). Interorganizational workflows: An ap-
proach based on message sequence charts and petri
nets. Systems Analysis - Modelling - Simulation,
34:335 – 367.
Aalst, W. v. d. and Hee, K. v. (2004). Workflow Manage-
ment: Models, Methods, and Systems. MIT Press.
Ahmad, F., Huang, H., and Wang, X. (2011). Analysis
of the petri net model of parallel manufacturing pro-
cesses with shared resources. Information Sciences,
181:5249–5266.
Awad, A. and Puhlmann, F. (2008). Structural detection
of deadlocks in business process models. In Busi-
ness Information Systems, volume 7, pages 239–250.
Springer.
Barkaoui, K. and Abdallah, I. (1995). Deadlock avoidance
in fms based on structural theory of petri nets. In
IEEE Symposium on Emerging Technologies and Fac-
tory Automation, volume 2, pages 499–510.
Boer, E. and Murata, T. (1994). Generating basis siphons
and traps of petri nets using the sign incidence matrix.
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Funda-
mental Theory and Applications, 41:266–271.
Cardoso, J. (1999). Time fuzzy petri nets. In Fuzziness in
Petri Nets, pages 115 – 145. Springer.
Cardoso, J., Valette, R., and Dubois, D. (1989). Petri nets
with uncertain markings. In Applications and Theory
of Petri Nets, volume 483, pages 64 – 78.
Chen, Y. and Li, Z. (2011). Design of a maximally permis-
sive liveness-enforcing supervisor with a compressed
supervisory structure for flexible manufacturing sys-
tems. Automatica, 47:1028–1034.
Chen, Y., Li, Z., and Zhou, M. (2012). Behaviorally optimal
and structurally simple liveness-enforcing supervisors
of flexible manufacturing systems. IEEE Transactions
on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 42:615–629.
Chu, F. and Xie, X.-L. (1997). Deadlock analysis of
petri nets using siphons and mathematical program-
ming. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automa-
tion, 13:793–804.
Dingle, N. J., Knottenbelt, W. J., and Suto, T. (2009).
Pipe2: A tool for the performance evaluation of gen-
eralised stochastic petri nets. SIGMETRICS Perfor-
mance Evaluation Review, 36:34–39.
Ezpeleta, J., Colom, J. M., and Martnez, J. (1995). A petri
net based deadlock prevention policy for flexible man-
ufacturing systems. IEEE Transactions on Robotics
and Automation, 11:173–184.
Ezpeleta, J., Couvreur, J., and Silva, M. (1993). A new
technique for finding a generating family of siphons,
traps and st-components. application to colored petri
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
438

nets. In Advances in Petri Nets 1993, volume 674,
pages 126–147. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Fahland, D., Favre, C., Koehler, J., Lohmann, N., V
¨
olzer,
H., and Wolf, K. (2011). Analysis on demand: In-
stantaneous soundness checking of industrial business
process models. Data and Knowledge Engineering,
70:448–466.
Gang, X. and Ming, W. Z. (2004). Systemic solutions to
deadlock in fms. In American Control Conference,
volume 6, pages 5740–5745.
Hack, M. (1972). Analysis production schemata by petri
nets. Master’s thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Tech-
nology.
Huang, Y., Jeng, M., Xie, X., and Chung, S. (2001).
Deadlock prevention policy based on petri nets and
siphons. International Journal of Production Re-
search, 39:283–305.
Huang, Y.-S., Pan, Y.-L., and Zhou, M. (2012). Computa-
tionally improved optimal deadlock control policy for
flexible manufacturing systems. IEEE Transactions
on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 42:404–415.
Iordache, M., Moody, J., and Antsaklis, P. (2002). Syn-
thesis of deadlock prevention supervisors using petri
nets. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation,
18:59–68.
Karatkevich, A. (2007). Analysis by solving logical equa-
tions calculation of siphons and traps. In Dynamic
Analysis of Petri Net-Based Discrete Systems, volume
356, pages 87–93. Springer.
Kohler, M. and Schaad, A. (2008). Avoiding policy-based
deadlocks in business processes. In International
Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security,
pages 709–716.
Li, Z., Liu, G., Hanisch, H.-M., and Zhou, M. (2012).
Deadlock prevention based on structure reuse of petri
net supervisors for flexible manufacturing systems.
IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernet-
ics, 42:178–191.
Li, Z. and Zhou, M. (2004). Elementary siphons of petri
nets and their application to deadlock prevention in
flexible manufacturing systems. IEEE Transactions
on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 34:38–51.
Liu, G., Li, Z., Barkaoui, K., and Al-Ahmari, A. (2013).
Robustness of deadlock control for a class of petri
nets with unreliable resources. Information Sciences,
235:259–279.
Maruta, T., Onoda, S., Ikkai, Y., Kobayashi, T., and Ko-
moda, N. (1998). A deadlock detection algorithm for
business processes workflow models. In IEEE Inter-
nationalConference on Systems Man and Cybernetics,
volume 1, pages 611–616.
Members, W. M. C. (1994). Glossary – a workflow manage-
ment coalition specification. Technical report, Coali-
tion, Workflow Management.
Mohanty, M. and Kumara, P. (2013). Deadlock preven-
tion in process control computer system. Interna-
tional Conferenceon DistributedComputingandInter-
netTechnology, pages 12–16.
Murata, T. (1989). Petri nets: Properties, analysis and ap-
plications. Proceedings of the IEEE, 77:541–580.
Park, J. and Reveliotis, S. (2001). Deadlock avoidance in se-
quential resource allocation systems with multiple re-
source acquisitions and flexible routings. IEEE Trans-
actions on Automatic Control, 46:1572–1583.
Rubinstein, R. and Kroese, D. (2008). Simulation and the
Monte Carlo Method. Wiley, 2 edition.
Sadiq, W., Maria, and Orlowska, E. (2000). Analyzing pro-
cess models using graph reduction techniques. Infor-
mation Systems, 25:117–134.
Sibertin-Blanc, C. (2001). Cooperative objects: Princi-
ples, use and implementation. In Concurrent Object-
Oriented Programming and Petri Nets, volume 2001,
pages 216–246.
Silva, L. d. F., Soares Passos, L. M., Soares, M. d. S.,
and Julia, S. (2013). Siphon-based deadlock preven-
tion policy for interorganizational workflow net de-
sign. In IEEEInternationalConferenceonInformation-
ReuseandIntegration, pages 293–300.
Soares Passos, L. and Julia, S. (2009). Qualitative analysis
of workflow nets using linear logic: Soundness verifi-
cation. In Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 2009. SMC
2009. IEEE International Conference on, pages 2843
–2847.
Tang, F., You, I., Yu, S., Wang, C.-L., Guo, M., and Liu, W.
(2012). An efficient deadlock prevention approach for
service oriented transaction processing. Computers &
Mathematics with Applications, 63:458–468.
Uzam, M. and Zhou, M. (2007). An iterative synthesis ap-
proach to petri net-based deadlock prevention policy
for flexible manufacturing systems. IEEE Transac-
tions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 37:362–371.
van der Aalst, W. M. P. (1998a). The application of petri
nets to workflow management. Journal of Circuits
Systems and Computers, 8:21–66.
van der Aalst, W. M. P. (1998b). Modeling and analyzing
interorganizational workflows. In International Con-
ference on Application of Concurrency to System De-
sign, pages 262–272.
van der Aalst, W. M. P. (2000). Loosely coupled interorga-
nizational workflows: modeling and analyzing work-
flows crossing organizational boundaries. Information
& Management, 37:67–75.
van der Aalst, W. M. P., van Hee, K. M., ter Hofstede, A.
H. M., Sidorova, N., Verbeek, H. M. W., Voorhoeve,
M., and Wynn, M. T. (2011). Soundness of workflow
nets: Classification, decidability, and analysis. Form.
Asp. Comput., 23:333–363.
Xiong, P., Zhou, M., and Pu, C. (2009). A petri net siphon
based solution to protocol-level service composition
mismatches. In IEEE International Conference on-
Web Services, pages 952–958.
Zhong, C. and Li, Z. (2011). Petri Net Based Deadlock
Prevention Approach for Flexible Manufacturing Sys-
tems, chapter 15, pages 416–433. Information Science
Reference.
DeadlockAvoidanceinInterorganizationalBusinessProcessesusingaPossibilisticWorkFlowNet
439
