
TIDAQL
A Query Language Enabling on-Line Analytical Processing of Time Interval Data
Philipp Meisen
1
, Diane Keng
2
, Tobias Meisen
1
, Marco Recchioni
3
and Sabina Jeschke
1
1
Institute of Information Management in Mechanical Engineering, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany
2
School of Engineering, Santa Clara University, Santa Clara, U.S.A.
3
Airport Devision, Inform GmbH Aachen, Aachen, Germany
Keywords: Time Interval Data, Query Language, on-Line Analytical Processing, Distributed Query Processing.
Abstract: Nowadays, time interval data is ubiquitous. The requirement of analyzing such data using known techniques
like on-line analytical processing arises more and more frequently. Nevertheless, the usage of approved mul-
tidimensional models and established systems is not sufficient, because of modeling, querying and processing
limitations. Even though recent research and requests from various types of industry indicate that the handling
and analyzing of time interval data is an important task, a definition of a query language to enable on-line
analytical processing and a suitable implementation are, to the best of our knowledge, neither introduced nor
realized. In this paper, we present a query language based on requirements stated by business analysts from
different domains that enables the analysis of time interval data in an on-line analytical manner. In addition,
we introduce our query processing, established using a bitmap-based implementation. Finally, we present a
performance analysis and discuss the language, the processing as well as the results critically.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, time interval data is recorded, collected
and generated in various situations and different ar-
eas. Some examples are the resource utilization in
production environments, deployment of personnel in
service sectors, or courses of diseases in healthcare.
Thereby, time interval data is used to represent obser-
vations, utilizations or measures over a period of
time. Put in simple terms, time interval data is defined
by two time values (i.e. start and end), as well as de-
scriptive values associated to the interval: like labels,
numbers, or more complex data structures. Figure 1
illustrates a sample database of five records.
Figure 1: A sample time interval database with intervals de-
fined by [start, end), an id, and three descriptive values.
For several years, business intelligence and ana-
lytical tools have been used by managers and business
analysts, inter alia, for data-driven decision support
on a tactical and strategic level. An important tech-
nology used within this field, is on-line analytical pro-
cessing (OLAP). OLAP enables the user to interact
with the stored data by querying for answers. This is
achieved by selecting dimensions, applying different
operations to selections (e.g. roll-up, drill-down, or
drill-across), or comparing results. The heart of every
OLAP system is a multidimensional data model
(MDM), which defines the different dimensions, hi-
erarchies, levels, and members (Codd, 1993).
The need of handling and analyzing time interval
data using established, reliable, and proven technolo-
gies like OLAP is desirable in this respect and an es-
sential acceptance factor. Nevertheless, the MDM
needed to model time interval data has to be based on
many-to-many relationships which have been shown
to lead to summarizability problems. Several solu-
tions solving these problems on different modeling
levels have been introduced over the last years, lead-
ing to increased integration effort, enormous storage
needs, almost always inacceptable query perfor-
mances, memory issues, and often complex multidi-
mensional expressions (Mazón et al., 2008; Kimball
and Rose, 2013). Additionally, these solutions are,
54
Meisen P., Keng D., Meisen T., Recchioni M. and Jeschke S..
TIDAQL - A Query Language Enabling on-Line Analytical Processing of Time Interval Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0005348400540066
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 54-66
ISBN: 978-989-758-096-3
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

considering real-world scenarios, only applicable to
many-to-many relationships having a small cardinal-
ity which is mostly not the case when dealing with
time interval data. As a result, the usage of MDM and
available OLAP systems is not sufficient, even
though the operations (e.g. roll-up, drill-down, slice,
or dice) available through such systems are desired.
Enabling such OLAP like operations in the con-
text of time interval data, requires the provision of ex-
tended filtering and grouping capabilities. The former
is achieved by matching descriptive values against
known filter criteria logically connected using opera-
tors like and, or, or not, as well as a support of tem-
poral relations like starts-with, during, overlapping,
or within (Allen, 1983). The latter is applied by
known aggregation operators like max, min, sum, or
count, as well as temporal aggregation operators like
count started or count finished (Meisen et al., 2015).
The application of the count aggregation operator
for time interval data is exemplified in Figure 2. The
color code identifies the different types of a time in-
terval (e.g. cleaning, maintenance, room service, mis-
cellaneous). Furthermore, the swim-lanes show the
location. The figure illustrates the count of intervals
for each type over one day across all locations (e.g.
POS F5 and POS F6) using a granularity of minutes
(i.e. 1,440 aggregations are calculated).
Figure 2: On top the time interval data (10 records) shown
in a Gantt-Chart, on the bottom the aggregated time-series.
In this paper, we present a query language allow-
ing to analyze time interval data in an OLAP manner.
Our query language includes a data definition (DDL),
a data control (DCL), and a data manipulation lan-
guage (DML). The former is based on the time inter-
val data model introduced by Meisen et al., (2014),
whereby the latter supports the two-step aggregation
technique mentioned in Meisen et al., (2015). Fur-
thermore, we outline our query processing which is
based on a bitmap-based implementation and sup-
ports distributed computing.
This paper is organized as follows: In section 2,
we discuss related work done in the field of time in-
terval data, in particular this section provides a conci-
se overview of research dealing with the analyses of
time interval data. We provide an overview of time
interval models, discuss related work done in the field
of OLAP, and present query languages. In section 3,
we introduce our query language and processing. The
section presents among other things how a model is
defined and loaded, how temporal operators are ap-
plied, how the two-step aggregation is supported, how
groups are defined, and how filters are used. We in-
troduce implementation issues and empirically evalu-
ate the performance regarding the query processing in
section 4. We conclude with a summary and direc-
tions for future work in section 5.
2 RELATED WORK
When defining a query language, it is important to
have an underlying model, defining the foundation
for the language (e.g. the relational model for SQL,
different interval-based models for e.g. IXSQL or
TSQL2, the multidimensional model for MDX, or the
graph model for Cypher). Over the last years several
models have been introduced in the field of time in-
tervals, e.g. for temporal databases (Böhlen et al.,
1998), sequential pattern mining (Papapetrou et al.,
2009, Mörchen, 2009), association rule mining
(Höppner and Klawonn, 2001), or matching
(Kotsifakos et al., 2013).
Chen et al., (2003) introduced the problem of min-
ing time interval sequential patterns. The defined
model is based on events used to derive time inter-
vals, whereby a time interval is determined by the
time between two successive time-points of events.
The definition is based on the sequential pattern min-
ing problem introduced by Agrawal and Srikant
(1995). The model does not include any dimensional
definitions, nor does it address the labeling of time
intervals with descriptive values.
Papapetrou et al., (2005) presented a solution for
the problem of “discovering frequent arrangements of
temporal intervals”. An e-sequence is an ordered set
of events. An event is defined by a start value, an end
value and a label. Additionally, an e-sequence data-
base is defined as a set of e-sequences. The definition
of an event given by Papapetrou et al., is close to the
underlying definition within this paper (cf. Figure 1).
Nevertheless, facts, descriptive values, and dimen-
sions are not considered.
Mörchen (2006) introduced the TSKR model de-
fining tones, chords, and phrases for time intervals.
Roughly speaking, the tones represent the duration of
intervals, the chords the temporal coincidence of
tones, and the phrases represent the partial order of
TIDAQL-AQueryLanguageEnablingon-LineAnalyticalProcessingofTimeIntervalData
55

chords. The main purpose of the model presented by
Mörchen is to overcome limitations of Allen’s (1983)
temporal model considering robustness and ambigu-
ousness when performing sequential pattern mining.
The model neither defines dimensions, considers
multiple labels, nor recognizes facts.
Summarized, models presented in the field of se-
quential pattern mining, association rule mining or
matching do generally not define dimensions and are
focused on generalized interval data, or support only
non-labelled data. Thus, these models are not suitable
considering OLAP of time interval data, but are a
guidance to the right direction.
Within the research community of temporal data-
bases different interval-based models have been de-
fined (cf. Böhlen et al., 1998). The provided defini-
tions can be categorized in weak and strong models.
A weak model is one, in which the intervals are used
to group time-points, whereas the intervals of the lat-
ter carry semantic meaning. Thus, a weak interval-
based model is not of further interest from an analyt-
ical point of view, because it can be easily trans-
formed into a point-based model. Nevertheless, a
strong model and the involved meaning of the differ-
ent operators – especially aggregation operators – are
of high interest from an analytical view. Strong inter-
val-based models presented in the field of temporal
databases lack to define dimensions, but present im-
portant preliminary work.
In the field of OLAP, several systems capable of
analyzing sequences of data have been introduced
over the last years. Chui et al. (2010) introduced S-
OLAP for analyzing sequence data. Liu and Runden-
steiner (2011) analyzed event sequences using hierar-
chical patterns, enabling OLAP on data streams of
time point events. Bebel et al., (2012) presented an
OLAP like system enabling time point-based sequen-
tial data to be analyzed. Nevertheless, the system nei-
ther support time intervals, nor temporal operators.
Recently, Koncilia et al., (2014) presented I-OLAP,
an OLAP system to analyze interval data. They claim
to be the first proposing a model for processing inter-
val data. The definition is based on the interval defi-
nition of Chen et al., (2003) which defines the inter-
vals as the gap between sequential events. However,
Koncilia et al., assume that the intervals of a specific
event-type (e.g. temperature) for a set of specific de-
scriptive values (e.g. POS G2) are non-overlapping
and consecutive. Considering the sample data shown
in Figure 1, the assumption of non-overlapping inter-
vals is not valid in general (cf. record 2,285,965 and
2,285,971). Figure 3 illustrates the model of Koncilia
et al. showing five temperature events for POS G2
and the intervals determined for the events. Koncillia
et al. mention the support of dimensions, hierarchies,
levels, and members, but lack to specify what types
of hierarchies are supported and how e.g. non-strict
relations are handled.
Figure 3: Illustration of the model introduced by Koncilia
et al., (2014). The intervals (rectangles) are created for each
two consecutive events (dots). The facts are calculated us-
ing the average function as the compute value function.
Also recently, Meisen et al., (2014) introduced the
T
IDA
M
ODEL
“enabling the usage of time interval data
for data-driven decision support”. The presented
model is defined by a 5-tuple ,,,, in which
denotes the time interval database, the set of de-
scriptors, the time axis, the set of measures, and
the set of dimensions. The time interval database
contains the raw time interval data records and a
schema definition of the contained data. The schema
associates each field of the record (which might con-
tain complex data structures) to one of the following
categories: temporal, descriptive, or bulk. Each de-
scriptor of the set is defined by its values (more spe-
cific its value type), a mapping- and a fact-function.
The mapping-function is used to map the descriptive
values of the raw record to one or multiple descriptor
values. The mapping to multiple descriptor values al-
lows the definition of non-strict fact-dimension rela-
tionships. Additionally, the model defines the time
axis to be finite and discrete, i.e. it has a start, an end,
and a specified granularity (e.g. minutes). The set of
dimensions can contain a time dimension (using a
rooted plane tree for the definition of each hierarchy)
and a dimension for each descriptor (using a directed
acyclic graph for a hierarchy’s definition). Figure 4
illustrates the modeled sample database of Figure 1
using the T
IDA
M
ODEL
.
Figure 4: Data of the sample database shown in Figure 1
modeled using the T
IDA
M
ODEL
(Meisen et al., 2014).
The figure shows the five intervals, as well as the
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
56

values of the descriptors location (cf. swim-lane) and
type (cf. legend). Dimensions are not shown. The
used mapping function for all descriptors is the iden-
tity function. The used granularity for the time dimen-
sion is minutes.
Another important aspect when dealing with time
interval data in the context of OLAP, is the aggrega-
tion of data and the provision of temporal aggregation
operators. Kline and Snodgrass (1995) introduced
temporal aggregates, for which several enhanced al-
gorithms were presented over the past years. Never-
theless, the solutions are focused on one specific ag-
gregation operator (e.g. SUM), do not support multi-
ple filter criteria, or do not consider data gaps. Kon-
cilia et al., (2014) address shortly how aggregations
are performed using the introduced compute value
functions and fact creating functions. Temporal oper-
ators are neither defined nor mentioned. Koncilia et
al., point out that some queries need special attention
when aggregating the values along time, but a more
precise problem statement is not given. Meisen et al.,
(2015) introduce a two-step aggregation technique for
time interval data. The first one aggregates the facts
along the intervals of a time granule and the second
one aggregates the values of the first step depending
on the selected hierarchy level of the time dimension.
Figure 5 illustrates the two-step aggregation tech-
nique. In the illustration, the technique is used to de-
termine the needed resources within the interval
[16:30, 16:34]. Within the first step, the sum of the
resources for each granule is determined and within
the second step the maximum of the determined val-
ues is calculated, i.e. 14. Additionally, they introduce
temporal aggregation operators like started or fin-
ished count.
Figure 5: Two-step aggregation technique presented by
Meisen et al., (2015).
The definition of a query language based on a
model and operators (i.e. like aggregations), is com-
mon practice. Regarding time-series, multiple query
languages and enhancements of those have been in-
troduced (cf. Rafiei and Mendelzon, 2000). In the
field of temporal databases time interval-based query
languages like IXSQL, TSQL2, or ATSQL have been
defined (Böhlen et al., 1998) and within the analytical
field, MDX (Spofford et al., 2006) is a widely used
language to query MDMs. Considering models deal-
ing with time interval data in the context of analytics,
Koncilia et al., (2014) published the only work the
authors are aware of that mentions a query language.
Nevertheless, the query language is neither formally
defined nor further introduced.
Summarized, it can be stated that recent research
and requests from industry indicate that the handling
of time interval data in an analytical context is an im-
portant task. Thus, a query language is required capa-
ble of covering the arising requirements. Koncilia et
al., (2014) and Meisen et al., (2014, 2015) introduced
two different models useful for OLAP of time interval
data. Different temporal aggregation operators, as
well as standard aggregation operators, are also pre-
sented by Meisen (2015). Nevertheless, a definition
of a query language useful for OLAP and an imple-
mentation of the processing are, to the best of our
knowledge, not formally introduced.
3 THE TIDA QUERY LANGUAGE
In this section, we introduce our time interval data
analysis query language (T
IDA
QL). The language was
designed for a specific purpose; to query time interval
data from an analytical point of view. The language
is based on aspects of the previously discussed
T
IDA
M
ODEL
. Nevertheless, the language should be
applicable to any time interval database system which
is capable of analyzing time interval data. Neverthe-
less, some adaptions might be necessary or some fea-
tures might not be supported by any system.
3.1 Requirements
The requirements concerning the query language and
its processing were specified during several work-
shops with over 70 international business analysts
from different domains (i.e. aviation industry, logis-
tics providers, service providers, as well as language
and gesture research). We aligned the results of the
workshop with an extended literature research. Table
1 summarizes selected results.
Table 1: Summary of the requirements concerning the time
interval analysis query language (selected results).
Requirement Description
Data Control Language (DCL)
[DCL1]: authorization
aspects
It is expected that the language encom-
passes authorization features, e.g. user
deletion, role creation, granting and re-
voking permissions.
TIDAQL-AQueryLanguageEnablingon-LineAnalyticalProcessingofTimeIntervalData
57

Table 1: Summary of the requirements concerning the time
interval analysis query language (selected results). (cont.)
[DCL2]: permissions
grantable on global and
model level
Permissions must be grantable on a
model and a global level. It is expected
that the user can have the permission to
add data to one model but not to an-
other. For simplicity, it should be pos-
sible to grant or revoke several permis-
sions at once.
Data Definition Language (DDL)
[DDL1]: loading and
unloading
The language has to offer a construct to
load new and unload models. The
newly loaded model has to be available
without any restart of the system. An
unloaded model has to be unavailable
after the query is processed. However,
queries currently in process must still
be executed.
[DDL2]: non-onto,
non-covering, non-
strict hierarchies
Each descriptor dimension must sup-
port hierarchies which might be non-
onto, non-covering, and / or non-strict
(cf. Pedersen, 2000).
[DDL3]: raster levels A raster level is a level of the time di-
mension. For example: the 5-minute
raster-level defines members like
[00:00, 00:05) … [23:55, 00:00). Sev-
eral raster levels can form a hierarchy
(e.g. 5-min 30-min 60-min
half-day day).
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
[DML1]: raw data
records
The language must provide a construct
to select the raw time interval data rec-
ords.
[DML2]: time-series by
time-windows
The language must support the specifi-
cation of a time-window for which
time-series of different measures can be
retrieved.
[DML3]: temporal
operators
It must be possible to use temporal op-
erators for filtering as e.g. defined by
Allen (1983). Depending on the type of
selection (i.e. raw records or time-se-
ries) the available temporal operators
may differ.
[DML4]: The two-step
aggregation technique
Meisen et al., (2015) present a two-step
aggregation technique which has to be
supported by the language. Both aggre-
gation operators (see Figure 5) must be
specified by a query selecting time-se-
ries, no pre-defined measure should be
necessary.
[DML5]: complete
time-series
A time-series is selected by specifying
a time-window (e.g. [01.01.2015,
02.01.2015) and a level (e.g. minutes).
The resulting time-series must contain
a value for each member of the selected
level, even if no time interval covers the
specified member. The value might be
N/A or null to indicate missing infor-
mation.
[DML6]: insert, update
and delete
The language must offer constructs to
insert, update and delete time interval
data records.
[DML7]: open, half-
open, or closed
intervals
The system should be capable of inter-
preting intervals defined as open, e.g.
(0, 5), closed, e.g. [0, 5], or half-
opened, e.g. (0, 5].
Table 1: Summary of the requirements concerning the time
interval analysis query language (selected results). (cont.)
[DML8]: meta-
information
It is desired that the language supports
a construct to receive meta-information
from the system, e.g. actual version,
available users, or loaded models.
[DML9]: bulk load It is desired, that the language provides
a construct to enable a type of bulk
load, i.e. increased insert performance.
3.2 Data Control Language
The definition of the DCL is straight forward to the
DCL known from other query languages e.g. SQL. As
defined by requirement [DCL1], the language must
encompass authorization features. Hence, the lan-
guage contains commands like ADD, DROP, MODIFY,
GRANT, REVOKE, ASSIGN and REMOVE. In our imple-
mentation, the execution of a DCL command always
issues a direct commit, i.e. a roll back is not sup-
ported. Figure 6 shows the syntax diagram of the
commands. Because of simplicity, a value is not fur-
ther specified and might be a permission, a username,
a password, or a role.
Figure 6: Commands of the DCL query language.
To fulfill the [DCL2] requirement, we define a
permission that consists of a scope-prefix and the per-
mission itself. We define two permission-scopes
GLOBAL and MODEL. Thus, a permission of the
GLOBAL scope is defined by
GLOBAL.<permission>
(e.g. GLOBAL.manageUser). Instead, a permission
of the MODEL scope is defined by
MODEL.<model>.<permission>
(e.g. MODEL.myModel.query).
For query processing, we use the Apache Shiro au-
thentication framework (http://shiro.apache.org/).
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
58

Shiro offers annotation driven access control. Thus,
the permission to e.g. execute a DML query is per-
formed by annotating the processing query method.
3.3 Data Definition Language
The DDL is used to define, add, or remove the models
known by the system. [DDL1] requires a command
within the DDL which enables the user to load or un-
load a model. The syntax diagram of the LOAD and
UNLOAD command is shown in Figure 7. A model can
be loaded by using a model identifier already known
to the system (e.g. if the model was unloaded), or by
specifying a location from which the system can re-
trieve a model definition to be loaded. Additionally,
properties can be defined (e.g. the autoload property
can be set, to automatically load a model when the
system is started). In the following subsection, we
present an XML used to define a T
IDA
M
ODEL
.
Figure 7: Commands of the DDL query language.
3.3.1 The XML T
IDA
M
ODEL
Definition
As mentioned in section 2, the T
IDA
M
ODEL
is defined
by a 5-tuple ,,,,. The time interval database
contains the raw record inserted using the API or
the INSERT command introduced later in section
3.4.1. From a modelling perspective it is important for
the system to retrieve the descriptive and temporal
values from the raw record. Thus, it is essential to de-
fine the descriptors and the time axis within the
XML definition. Below, an excerpt of an XML file
defining the descriptors of our sample database
shown in Figure 1 is presented:
<model id="myModel">
<descriptors>
<string id="LOC" name="location" />
<string id="TYPE" name="type" />
<int id="RES" null="true" />
</descriptors>
</model>
The excerpts shows that a descriptor is defined by a
tag specifying the type (i.e. the descriptor implemen-
tation to be used), an id-attribute, and an optional
name-attribute. Additionally, it is possible to define if
the descriptor allows null values (default) or not. To
support more complex data structures (and one’s own
mapping functions), it is possible to specify one’s
own descriptor-implementations:
<descriptors>
<ownImpl:list id="D4" />
</descriptors>
Our implementation scans the class-path automati-
cally, looking for descriptor implementations. An
added implementation must provide an XSLT file,
placed into the same package and named as the con-
crete implementation of the descriptor-class. The
XSLT file is used to create the instance of the own
implementation using a Spring Bean configuration
(http://spring.io/).
<!-- File: my/own/desc/List.xslt -->
<xsl:template match="ownImpl:list">
<xsl:call-template name="beanDesc">
<xsl:with-param name="class">
my.own.desc.List
</xsl:with-param>
</xsl:call-template>
</xsl:template>
The time axis of the T
IDA
M
ODEL
is defined by:
<model id="myModel">
<time>
<timeline start="20.01.1981"
end="20.01.2061"
granularity="MINUTE" />
</time>
</model>
The time axis may also be defined using integers, i.e.
[0, 1000]. Our implementation includes two default
mappers applicable to map different types of temporal
raw record value to a defined time axis. Nevertheless,
sometimes it is necessary to use different time-map-
pers (e.g. if the raw data contains proprietary tem-
poral values) which can be achieved using the same
mechanism as described previously for descriptors.
Due to the explicit time semantics, the measures
defined within the T
IDA
M
ODEL
are different than
the ones typically known from an OLAP definition.
The model defines three categories for measures, i.e.
implicit time measures, descriptor bound measures,
and complex measures. The categories determine
when which data is provided during the calculation
process of the measures. Our implementation offers
several aggregation operators useful to specify a
measure, i.e. count, average, min, max, sum, mean,
median, or mode. In addition, we implemented two
temporal aggregation operators started count and
finished count, as suggested by Meisen et al., (2015).
TIDAQL-AQueryLanguageEnablingon-LineAnalyticalProcessingofTimeIntervalData
59

We introduce the definition and usage of measures in
section 3.4.2.
The T
IDA
M
ODEL
also defines the set of dimen-
sions . The definition differs between descriptor di-
mensions and a time dimension, whereby every di-
mension consists of hierarchies, levels, and members.
It should be mentioned that, from a modelling point
of view, each descriptor dimension fulfills the re-
quirements formalized in [DDL2] and that the time
dimension supports raster-levels as requested in
[DDL3]. The definition of a dimension for a specific
descriptor or the time dimension can be placed within
the XML definition of a model using:
<model id="myModel">
<dimensions>
<dimension id="DIMLOC" descId="LOC">
<hierarchy id="LOC">
<level id="HOTEL">
<member id="DREAM" rollUp="*" />
<member id="STAR" rollUp="*" />
<member id="ADV" reg="TENT"
rollUp="*" />
</level>
<level id="ROOMS">
<member id="POSF" reg="POS F\d"
rollUp="DREAM" />
<member id="POSG" reg="POS G\d"
rollUp="DREAM" />
</level>
<level id="STARROOMS">
<member id="POSA" reg="POS A\d"
rollUp="STAR" />
</level>
</hierarchy>
</dimension>
</dimensions>
</model>
Figure 8 illustrates the descriptor dimension defined
by the previously shown XML excerpt. The circled
nodes are leaves which are associated with descriptor
values known by the model (using regular expres-
sions). Additionally, it is possible to add dimensions
for analytical processes to an already defined model,
i.e. to use it only for a specific session or query. The
used mechanism to achieve that is similar to the load-
ing of a model and will not further be introduced.
Figure 8: Illustration of the dimension created with our
web-based dimension-modeler as defined by the XML ex-
cerpt.
The definition of a time dimension is straight for-
ward to the one of a descriptor dimension. Neverthe-
less, we added some features in order to ease the def-
inition. Thus, it is possible to define a hierarchy by
using pre-defined levels (e.g. templates like
5-min-raster, day, or year) and by defining the level
to roll up to, regarding the hierarchy. The following
XML excerpt exemplifies the definition:
<model id="myModel">
<dimensions>
<timedimension id="DIMTIME">
<hierarchy id="TIME5TOYEAR">
<level id="YEAR" template="YEAR"
rollUp="*" />
<level id="DAY" template="DAY"
rollUp="YEAR" />
<level id="60R" template="60RASTER"
rollUp="DAY" />
<level id="5R" template="5RASTER"
rollUp="60R" />
<level id="LG" template="LOWGRAN"
rollUp="5R" />
</hierarchy>
</timedimension>
</dimensions>
</model>
A defined model is published to the server using the
LOAD command. The following subsection introduces
the command, focusing on the loading of a model
from a specified location.
3.3.2 Processing the LOAD Command
The loading of a model can be triggered from differ-
ent applications, drivers, or platforms. Thus, it is nec-
essary to support different loaders to resolve a speci-
fied location. In the following, some examples illus-
trate the issue. When firing a LOAD query from a web-
application, it is necessary that the model definition
was uploaded to the server, prior to executing the
query. While running on an application server, it
might be required to load the model from a database
instead of loading it from the file-system. Thus, we
added a resource-loader which can be specified for
each context of a query. Within a servlet, the loader
resolves the specified location against the upload-di-
rectory, whereby our JDBC driver implementation is
capable of sending a client’s file to the server using
the data stream of the active connection. After retriev-
ing and validating the resource, the implementation
uses a model-handler to bind and instantiate the de-
fined model. As already mentioned, the bitmap-based
implementation presented by Meisen et al., (2015) is
used. The implementation instantiates several indexes
and bitmaps for the defined model. After the
instantiation, the model is marked to be up and run-
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
60
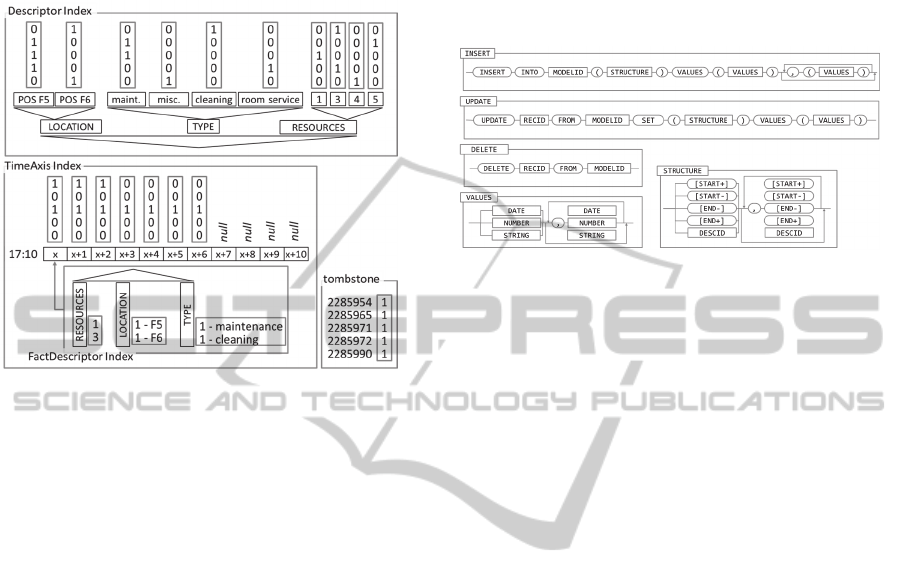
ning by the model-handler and accepts DML queries.
Figure 9 exemplifies the initialized bitmap-based in-
dexes filled with the data from the database of Figure
1.
Figure 9: Example of a loaded model (cf. Meisen et al.,
2015) filled with the data shown in Figure 1.
3.4 Data Manipulation Language
Considering the requirements, it can be stated that the
DML must contain commands to INSERT, UPDATE,
and DELETE records. In addition, it is necessary to
provide SELECT commands to retrieve the time inter-
val data records, as well as results retrieved from ag-
gregation (i.e. time-series). Furthermore, a GET com-
mand to retrieve meta-information of the system is
needed.
3.4.1 INSERT,UPDATE and DELETE
Figure 10 illustrated the three commands INSERT,
UPDATE, and DELETE using syntax diagrams which
fulfill the requirement [DML6]. The INSERT com-
mand adds one or several time interval data records
to the system. First, it parses the structure of the data
to be inserted. The query-parser validates the correct-
ness of the structure, i.e. the structure must contain
exactly one field marked as start and exactly one field
marked as end even though the syntax diagram sug-
gest differently. Additionally, the parser verifies if a
descriptor (referred by its id) really exists within the
model. Finally, it reads the values and invokes the
processor by passing the structure, as well as the val-
ues. The processor iterates over the defined values,
validates those against the defined structure, uses the
mapping functions of the descriptors to receive the
descriptor values, and calls the mapping function of
the time-axis. The result is a so-called processed rec-
ord which is used to update the indexes. The persis-
tence layer of the implementation ensures that the raw
record and the indexes get persisted. Finally, the
tombstone bitmap is updated which ensures that the
data is available within the system.
Figure 10: Syntax diagrams of the commands INSERT,
UPDATE and DELETE.
A deletion is performed by setting the tombstone
bitmap for the specified id to 0. This indicates that the
data of the record is not valid and thus the data will
not be considered by any query processors anymore.
The internally scheduled clean-up process removes
the deleted records and releases the space.
An update is performed by deleting the record
with the specified identifier and inserting the record
as described above.
To support bulk load, as desired by [DML9], an
additional statement is introduced. The statement
SET BULK TRUE is used to enable the bulk load,
whereby SET BULK FALSE stops the bulk loading
process. When enabling the bulk load, the system
waits until all currently running INSERT, UPDATE, or
DELETE queries of other sessions are performed. New
queries of that type are rejected across all sessions
during the waiting and processing phase. When all
queries are handled, the system responds to the bulk-
enabling query and expects an insert-like statement,
whereby the system directly starts to parse the incom-
ing data stream. As soon as the structure is known, all
incoming values are inserted. The indexes are only
updated in memory. If and only if the memory capac-
ity reaches a specified threshold, the persistence-layer
is triggered. In this case, the current data in memory
is flushed and persisted using the configured persis-
tence-layer (e.g. using the file-system, a relational da-
tabase, or any other NoSQL database). The memory
is also flushed and persisted whenever a bulk load is
finished.
TIDAQL-AQueryLanguageEnablingon-LineAnalyticalProcessingofTimeIntervalData
61

3.4.2 SELECTRaw Records and
Time-series
The SELECT command is addressed by the require-
ments [DML1], [DML2], [DML3], [DML4],
[DML5], and [DML7]. Figure 11 illustrates the select
statements to select records and time-series. Because
of space limitations, we removed more detailed syn-
tax diagrams for the LOGICAL and GROUP
EXPRESSION. The non-terminal MEASURES is speci-
fied later in this subsection when introducing the
SELECTTIMESERIES in detail.
Figure 11: Syntax diagrams of the SELECT RECORDS and
SELECTTIMESERIES commands.
As illustrated, the intervals can be defined as
open, half-open or closed (cf. [DML7]). The pro-
cessing of the intervals is possible, thanks to the dis-
crete time-axis used by the model. Using a discrete
time-axis with a specific granularity makes it easy to
determine the previous or following granule. Thus,
every half-open or open interval can be transformed
into a closed interval using the previous or following
granule. Hence, the result of the parsing always con-
tains a closed interval which is used during further
query processing.
As illustrated in Figure 11, the SELECTRECORDS
statement allows to retrieve records satisfying a logi-
cal expression based on descriptor values (e.g.
LOC="POS F5" OR (TYPE="cleaning" AND
DIMLOC.LOC.HOTEL="DREAM")) and/or fulfilling a
temporal relation (cf. [DML3]). Our query language
supports ten different temporal relations following
Allen (1983): EQUALTO, BEFORE, AFTER, MEETING,
DURING, CONTAINING, STARTINGWITH, FINISH‐
INGWITH, OVERLAPPING, and WITHIN. The inter-
ested reader may notice that Allen introduced thirteen
temporal relationships. We removed some inverse re-
lationships (i.e. inverse of meet, overlaps, starts, and
finishes). When using a temporal relationship within
a query, the user is capable of defining one of the in-
tervals used for comparison. Thus, the removed in-
verse relationships are not needed, instead the user
just modifies the self-defined interval. In addition, we
added the WITHIN relationship which is a combina-
tion of several relationships and allows an easy selec-
tion of all records within the user-defined interval (i.e.
at least one time-granule is contained within the user-
defined interval).
When processing a SELECT RECORD query, the
processor initially evaluates the filter expression and
retrieves a single bitmap specifying all records ful-
filling the filter’s logic (cf. Meisen et al., 2015). In a
second phase, the implementation determines a
bitmap of records satisfying the specified temporal re-
lationship. The two bitmaps are combined using the
and-operator to retrieve the resulting records. De-
pending on the requested information (i.e. count,
identifiers, or raw records (cf. [DML1])), the imple-
mentation creates the response using bitmap-based
operations (i.e. count and identifiers) or retrieving the
raw records from the persistence layer. Figure 12 de-
picts the evaluation of selected temporal relationships
using bitmaps and the database shown in Figure 1.
Figure 12: Examples of the processing of temporal relation-
ships using bitmaps (and the sample database of Figure 1).
Figure 13: Syntax diagrams of the MEASURES definition.
The SELECTTIMESERIES statement specifies a
logical expression equal to the one exemplified in the
SELECT RECORDS statement. In addition, the state-
ment specifies a GROUP EXPRESSION which de-
fines the groups to create the time-series for (e.g.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
62

GROUPBYDIMLOC.LOC.ROOMS). Furthermore, the
measures to be calculated for the time-series and the
time-window (cf. [DML2]) are specified. It is also
possible to specify several comma-separated mea-
sures. Figure 13 shows the syntax used to specify
measures (cf. MEASURES in Figure 11).
A simple (considering the measures) example of a
SELECTTIMESERIES query is as follows:
SELECT TRANSPOSE(TIMESERIES)
OF MAX(SUM(RESOURCES)) AS "needed Res"
ON DIMTIME.TIME5TOYEAR.5RASTER
FROM myModel
IN [01.01.2015, 02.01.2015)
WHERE DIMLOC.LOC.HOTEL="DREAM"
GROUP BY TYPE
As required by [DML4], a measure can be defined us-
ing the two-step aggregation technique. The first ag-
gregation (in the example SUM) is specified for a spe-
cific descriptor and the second optional aggregation
function (in the example MAX) aggregates the values
across the stated level of the time-dimension.
When processing the query, the system retrieves
the bitmaps for the filtering and the grouping condi-
tions. The system iterates over the bitmaps of the
specified groups and the bitmaps of the granules of
the selected time-window. For each iteration, the im-
plementation combines the filter-bitmap, group-bit-
map, and the time-granule-bitmap and applies the
first aggregation function. The second aggregation
function is applied whenever all values of a member
of the specified time-level are determined by the first
step (cf. Figure 6). This processing technique ensures
that for each time-granule a value is calculated, even
if no interval covers the granule (cf. [DML5]).
3.4.3 GET Meta-information
[DML8] demands the existence of a command which
enables the user to retrieve meta-information, like the
version of the system. This requirement is fulfilled by
adding a GET command to the query language. A
statement like GET VERSION, GET USERS, or GET
MODELS enables the user to retrieve information pro-
vided from the system. Filtering is currently not re-
quired and thus, not supported.
4 IMPLEMENTATION ISSUES
This section introduces selected implementation as-
pects of the language and its query processing. First,
we introduce processing implementations for the
most frequently used query-type SELECT
TIMESERIES and show performance results for the
different algorithms. In addition, we present consid-
erations of analysts using the language to analyze
time interval data and address possible enhancements.
4.1 SELECTTIMESERIES Processing
In section 3, we outlined the query processing based
on the TIDAMODEL and its bitmap-based
implementation (cf. section 3.3.2 and 3.4.2). For a de-
tailed description of the bitmap-based implementa-
tion we refer to Meisen et al., (2015). In this section,
we introduce three additional algorithms which are
capable to process the most frequently used SELECT
TIMESERIES queries, introduced in section 3.4.2.
Prior to explaining the algorithms, it should be
stated, that we did not implement any algorithm based
on A
GGREGATIONTREEs (Kline and Snodgrass,
1995), M
ERGESORT, or other related aggregation al-
gorithms defined within the research field of temporal
databases. Such algorithms are optimized to handle
single aggregation operators (e.g. count, sum, min, or
max). Thus, the implementation would not be a ge-
neric solution usable for any query. Nevertheless,
such algorithms might be useful to increase query
performance for specific, often used measures. It
might be reasonable to add a language feature, which
allows to define a special handling (e.g. using an
A
GGREGATIONTREE) for a specific measure.
Next, we introduce our naive implementation. All
three presented algorithm do not support queries us-
ing group by, multiple measures, nor multi-threading
scenarios. To support these features, commonly used
techniques (e.g. iterations and locks) could be used.
The algorithm filters the records of the database,
which fulfill the defined criteria of the IN (row 04)
and WHERE clause (row 06). Next, it calculates the
measure for each defined range (row 10). The calcu-
lation of each measure depends mainly on its type (i.e.
measure of lowest granularity (e.g. query #1 in Table
2), measure of a level (e.g. query #2), or two-step
measure (e.g. query #3)). Because of space limita-
tions, we state the complexity of the calc-method in-
stead of presenting it. The complexity is O(k∙n),
with k being the number of granules covered by the
TimeRange and n being the number of records.
The other algorithms we implemented are based on
I
NTERVALTREEs (INTTREE) as introduced by Kriegel
(2001). The first one (A) - of the two I
NTTREE - based
implementations - uses the tree to retrieve the relevant
records considering the IN-clause (row 05 of the na-
ive algorithm). Further, the algorithm proceeds as the
naive algorithm.
TIDAQL-AQueryLanguageEnablingon-LineAnalyticalProcessingofTimeIntervalData
63

01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
TimeSeries naive(Query q, Set r) {
TimeSeries ts = new TimeSeries(q);
// filter time def. by IN [a, b]
r = filter(r, q.time());
// filter records def. by WHERE
r = filter(r, q.where());
// it. ranges def. by IN and ON
for (TimeRange i : q.time()) {
// filter records for the range
r’ = filter(r, i);
// det. measures def. by OF
ts.set(i, calc(i, r’, q.meas());
}
return ts;
}
The second implementation (B) differs from the first
one, by created a new INTTREE for every query.
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
TimeSeries iTreeB(Query q, Set r) {
TimeSeries ts = new TimeSeries(q);
// filter records def. by WHERE
IntervalTree iTree =
createAndFilter(r, q.in(),
q.where());
// it. ranges def. by IN and ON
for (TimeRange i : q.time()) {
// use iTree to filter by i
r’ = filter(iTree, i);
// det. measures def. by OF
ts.set(i, calc(i, r’, q.meas());
}
return ts;
}
As shown, the algorithm filters the records according
to the IN- and WHERE-clause and creates an I
NTTREE
for the filtered records (row 04). When iterating over
the defined ranges, the created iTree is used to re-
trieve the relevant records for each range (row 08).
4.2 Performance
We ran several tests on an Intel Core i7-4810MQ with
a CPU clock rate of 2.80 GHz, 32 GB of main
memory, an SSD, and running 64-bit Windows 8.1
Pro. As Java implementation, we used a 64-bit JRE
1.6.45, with XMX 4,096 MB and XMS 512 MB. We
tested the parser (implemented using ANTLR v4) and
processing considering correctness. In addition, we
measured the runtime performance of the processor
for the three introduced algorithms (cf. section 4.2),
whereby the data and structures of all algorithms were
held in memory to obtain CPU time comparability.
We used a real-world data set containing 1,122,097
records collected over one year. The records have an
average interval length of 48 minutes and three de-
scriptive values: person (cardinality: 713), task-type
(cardinality: 4), and work area (cardinality: 31). The
used time-granule was minutes (i.e. time cardinality:
525,600). We tested the performance using the
SELECT TIMESERIES queries shown in Table 2.
Each query specifies a different type of query (i.e. dif-
ferent measure, usage of groups, or filters) and was
fired 100 times against differently sized sub-sets of
the real-world data set (i.e. 10, 100, 1,000, 10,000,
100,000, and 1,000,000 records).
Table 2: The shortened queries used for testing.
# Query
1
OF COUNT(TASKTYPE) IN [01.JAN, 01.FEB)
WHERE WA.LOC.TYPE='Gate'
2
OF SUM(TASKTYPE) ON TIME.DEF.DAY
IN [01.JAN, 01.FEB) WHERE WORKAREA='SEN13'
3
OF MAX(COUNT(WORKAREA)) ON TIME.DEF.DAY
IN [01.JAN, 01.FEB) WHERE TASKTYPE='short'
The results of the runtime performance tests are
shown in Figure 14. As illustrated, the bitmap-based
implementation performs better than the naive and
I
NTTREE algorithms when processing query #1 and
#3. Regarding query #2 the I
NTTREE-based imple-
mentations perform best. As stated in Table 3, the
most important criterion to determine the perfor-
mance is the selectivity. Regarding a low selectivity
the I
NTTREE-based algorithm (B) performs best.
Table 3: Statistics of the test results.
number of records selectivity
in DB
selected by query selected / in DB
#1 #2 #3 #1 #2 #3
10
1
1 0 0 0.1000 0.0000 0.0000
10
2
5 0 7 0.0500 0.0000 0.0700
10
3
12 2 46 0.0120 0.0020 0.0460
10
4
147 9 480 0.0147 0.0009 0.0480
10
5
1.489 121 5.148 0.0149 0.0012 0.0515
10
6
15.378 1.261 51.584 0.0154 0.0013 0.0516
Nevertheless, considering persistency and reading
of records from disc the algorithm might perform
worse. We would also like to state briefly, that other
factors (e.g. kind of aggregation operators used) in-
fluence the performance of the bitmap algorithm, so
that it outperforms the I
NTTREE-based implementa-
tion, even if a low selectivity is given.
4.3 Considerations
The query language and processing introduced in this
paper, is currently used within different projects by
analysts and non-experts of different domains to ana-
lyze time-interval data. In the majority of cases, the
introduced language and the processing is capable of
satisfying the user’s needs. Nevertheless, there are
limitations, issues, and preferable enhancements. In
the following, we introduce selected requests/impro-
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
64

Figure 14: The measured average CPU-time performance (out of 100 runs per query).
vements:
1. The presented query language and its processing
do not support any type of transactions. A record
inserted, updated, or deleted is processed by the
system as an atomic operation. Nevertheless, roll-
backs needed after several operations have to be
performed manually. This generally increases im-
plementation effort on the client-side.
2. The presented XML definition of dimensions (cf.
3.3.1) uses regular expressions to associate a
member of a level to a descriptor value. Regular
expressions are sometimes difficult to be formal-
ized (especially for number ranges). An alterna-
tive, more user-friendly expression language is
desired.
3. The UPDATE and DELETE commands (cf. 3.4.1)
need the user to specify a record identifier. The
identifier can be retrieved from the result-set of an
INSERT-statement or using the SELECT REC‐
ORDS command. Nevertheless, users requested to
update or delete records by specifying criteria
based on the records’ descriptive values.
4. When a model is modified, it has to be loaded to
the system as new, the data of the old model has
to be inserted and the old model has to be deleted.
Users desire a language extension, allowing to up-
date models. Nevertheless, the implications of
such a model update could be enormous.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we presented a query language useful to
analyze time interval data in an on-line analytical
manner. The language covers the requirements
formalized by several business analyst from different
domains, dealing with time interval data on a daily
basis. We also introduced four different implementa-
tions useful to process the most frequently used type
of query (i.e. SELECT TIMESERIES). An important
task for future studies is to confirm, or define new
models and present novel implementations solving
the problem of analyzing time interval data. In addi-
tion, future work should focus on distributed and in-
cremental query processing (e.g. when rolling-up a
level). The mentioned considerations (cf. section 4.3)
of our introduced language and its implementation
should be investigated. Another interesting area con-
sidering time-interval data is on-line analytical min-
ing (OLAM). Future work should study the possibili-
ties of analyzing aggregated time series to discover
knowledge about the underlying intervals. Finally, an
enhancement of the processing of the two-step aggre-
gation technique should be considered. Depending on
the selected aggregations an optimized processing
strategy might be reasonable.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The approaches presented in this paper are supported
by the German Research Foundation (DFG) within
the Cluster of Excellence “Integrative Production
Technologies for High-Wage Countries” and the pro-
ject “ELLI – Excellent Teaching and Learning in En-
gineering Sciences” as part of the Excellence Initia-
tive at the RWTH Aachen University.
REFERENCES
Agrawal, R. and Srikant, R., 1995. Mining sequential
Patterns, Int. Conf. Data Engineering, Taipei, Taiwan,
pp. 3-14.
Allen, J. F., 1983. Maintaining knowledge about Temporal
Intervals, Communication ACM 26, 11, pp. 832-843.
Böhlen, M. H., Busatto R., Jensen C. S., 1998. Point-versus
interval-based temporal data models, 14th Int. Conf. on
Data Engineering, Orlando, Florida, USA, 23.-27.
Feburary, pp. 192-200.
Chen, Y.-L., Chiang, M.-C., and Ko, M.-T., 2003. Disco-
TIDAQL-AQueryLanguageEnablingon-LineAnalyticalProcessingofTimeIntervalData
65

vering time-interval sequential patterns in sequence
databases, Expert Systems with Applications 25(3), pp.
343-354.
Codd, E. F., Codd, S. B., and C. T. Salley, 1993. Providing
OLAP (On-Line Analytical Processing) to User-
Analysts: An IT Mandate, E. F. Codd and Associates
(sponsored by Arbor Software Corp.).
Höppner, F., Klawonn, F., 2001. Finding informative rules
in interval sequences. Hoffmann, F., Adams, N., Fisher,
D., Guimarães, G., Hand, D.J. (eds.) IDA2001. LNCS,
vol. 2189, Springer, Heidelberg, pp. 123-132.
Kimball, R. and Ross, M., 2013. The data warehouse
toolkit: The definitive guide to dimensional modeling,
3rd Edition, Wiley Computer Publishing.
Kline, N. and Snodgrass, R. T., 1995. Computing temporal
aggregates, 11th Int. Conf. on Data Engineering (ICDE
1995), Taipei, China, 06.-10. March, pp. 222-231.
Koncilia, C., Morzy, T., Wrembel, R., and Eder J., 2014.
Interval OLAP: Analyzing Interval Data, Data
Warehousing and Knowledge Discovery (DaWaK
2014), Volume 8646, Springer Int., pp. 233-244
Kotsifakos, A., Papapetrou, and P., Athitsos, V., 2013.
IBSM: Interval-based Sequence Matching, 13th SIAM
Int. Conf. on Data Mining (SDM13), Austin, Texas,
USA, 02.-04. May.
Kriegel, H.-P., Pötke, M., and Seidl, T. (2001). Object-
Relational Indexing for General Interval Relationships,
7th Int. Symposium on Spatial and Temporal Databases
(SSTD 2001), Los Angeles, California, 12.-15. July, pp.
522-542.
Mazón, J.-N., Lichtenbörger, J., and Trujillo J., 2008.
Solving summarizability problems in fact-dimension
relationships for multidimensional models, 11th Int.
Workshop on Data Warehousing and OLAP (DOLAP
'08). Napa Valley, California, USA, 26.-30. October.
pp. 57-64.
Meisen, P., Meisen, T., Recchioni, M., Schilberg, D.,
Jeschke, S., 2014. Modeling and Processing of Time
Interval Data for Data-Driven Decision Support, IEEE
Int. Conf. on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, San
Diego, California, USA, 04.-08. October.
Meisen, P., Keng, D., Meisen, T., Recchioni, M., Jeschke,
S., 2015. Bitmap-Based On-Line Analytical Processing
of Time Interval Data, 12th Int. Conf. on Information
Technology. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, 13.-15. April.
Mörchen, F., 2006. A better tool than Allen’s relations for
expressing temporal knowledge in interval data, 12th
ACM SIGKDD Int. Conf. on Knowledge Discovery and
Data Mining, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA.
Mörchen, F., 2009. Temporal pattern mining in symbolic
time point and time interval data, IEEE Symp. on Com-
putational Intelligence and Data Mining (CIDM 2009),
Nashville, Tennessee, USA, 30. March-2. April.
Pedersen, T. B. 2000, Aspects of data modeling and query
processing for complex multidimensional data, Ph.D.
thesis, Aalborg Universitetsforlag, Aalborg.
Publication: Department of Computer Science,
Aalborg Univ., no. 4.
Papapetrou, P., Kollios, G., Sclaroff S., and Gunopulos, D.,
2005. Discovering Frequent Arrangements of Temporal
Intervals, 5th IEEE Int. Conf. on Data Mining
(ICDM’05), IEEE Press, pp. 354-361.
Papapetrou, P., Kollios, G., Sclaroff S., and Gunopulos D.,
2009. Mining Frequent Arrangements of Temporal
Intervals, Knowledge and Information Systems, vol. 21,
no. 2, pp. 133-171.
Rafiei, D. and Mendelzon, A. O., 2000. Querying Time
Series Data Based on Similarity, IEEE Transactions on
Knowledge and Data Engineering, 12(5).
Spofford, G., Harinath, S., Webb, C., Huang, D. H., and
Civardi, F., 2006. MDX-Solutions: With Microsoft
SQL Server Analysis Services 2005 and Hyperion
Essbase, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0471748080.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
66
