
Modelling the Resistance of Enterprise Architecture Adoption
Linking Strategic Level of Enterprise Architecture to Organisational Changes and
Change Resistance
Nestori Syynimaa
1,2,3,4
1
Informatics Research Centre, Henley Business School, University of Reading, Reading, U.K.
2
School of Information Sciences, University of Tampere, Tampere, Finland
3
Enterprise Architect, CSC - IT Center for Science, Espoo, Finland
4
Founder, Gerenios Ltd, Tampere, Finland
Keywords: Enterprise Architecture, Adoption, Change Resistance, Strategic Level.
Abstract: During the last few years Enterprise Architecture (EA) has received increasing attention among industry and
academia. By adopting EA, organisations may gain a number of benefits such as better decision making,
increased revenues and cost reduction, and alignment of business and IT. However, EA adoption has been
found to be difficult. In this paper a model to explain resistance during EA adoption process (REAP) is
introduced and validated. The model reveals relationships between strategic level of EA, resulting
organisational changes, and sources of resistance. By utilising REAP model, organisations may anticipate and
prepare for the organisational change resistance during EA adoption.
1 INTRODUCTION
During the last few years Enterprise Architecture
(EA) has received increasing attention among
industry and academia. An effective EA is critical to
business survival and success (TOGAF, 2009).
Indeed, in 21
st
century EA will be determining factor
that separates the successful from the failures, the
survivors from the others (Zachman, 1997). EA has
some important strategic outcomes, such as better
operational excellence and strategic agility (Ross et
al., 2006). Despite the benefits to be gained, EA is not
widely adopted in organisations (Schekkerman, 2005;
Ambler, 2010; Computer Economics, 2014). This
might be caused by the fact that EA has been found
difficult to adopt. From theoretical point of view, EA
adoption is an instance of organisational change
aiming for realisation of EA benefits. However, about
70 per cent of organisational change initiatives fail
(Hammer and Champy, 1993; Beer and Nohria, 2000;
Kotter, 2008).
This study aims for increase the understanding of
the dynamics of EA adoption. To be more specific,
we are seeking an answer to the question: Why is
Enterprise Architecture difficult to adopt?
1.1 Definition of Enterprise
Architecture
Enterprise Architecture (EA) has multiple definitions
in the current literature. The concept of Enterprise
Architecture consists of two distinct terms, enterprise
and architecture.
Definition of enterprise seems to be quite constant
in the EA literature. Enterprise can be anything from
a local team to a multi-level organisation of a global
corporation (TOGAF, 2009; ISO/IEC/IEEE, 2011;
Dietz et al., 2013; PEAF, 2013). It is a social system
with an assumed purpose (Proper, 2013; Dietz et al.,
2013) having a common set of goals (TOGAF, 2009).
As the term enterprise is usually used as a synonym
of a business or company, later in this paper we will
use the term organisation instead of it. Organisation
covers both businesses and public sector and thus
suits better to be used in this paper.
Similarly, definitions of architecture and
architecture description are more or less constant.
Architecture is a structure of the enterprise and an
architecture description its representation
(ISO/IEC/IEEE, 2011). To be more specific,
architecture is seen as a formal description of an
enterprise at a certain time (Zachman, 1997; TOGAF,
143
Syynimaa N..
Modelling the Resistance of Enterprise Architecture Adoption - Linking Strategic Level of Enterprise Architecture to Organisational Changes and Change
Resistance.
DOI: 10.5220/0005349901430153
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 143-153
ISBN: 978-989-758-098-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2009; ISO/IEC/IEEE, 2011), either from the current
state or from one or more future states (CIO Council,
2001; Gartner, 2013).
Definitions of Enterprise Architecture are more
diverse, but they also have some similarities. What is
shared among most of the definitions is the concept
of managed change of the enterprise between the
current and future states for a purpose (GERAM,
1999; CIO Council, 2001; Pulkkinen, 2008; Gartner,
2013). According to EA specialists, this purpose is to
meet goals of stakeholders and to create value to the
enterprise (Syynimaa, 2010, see also PEAF, 2010).
Aforementioned definitions can be summarised to
the following definition used in this paper. Enterprise
Architecture is; (i) a formal description of the current
and future state(s) of an organisation, and (ii) a
managed change between these states to meet
organisation’s stakeholders’ goals and to create value
to the organisation.
1.2 Enterprise Architecture Adoption
The word adoption can be defined as “the action or
fact of adopting or being adopted” where adopt refers
to "choose to take up or follow (an idea, method, or
course of action)" (Oxford Dictionaries, 2010).
Similar concepts are implementation, “the process of
putting a decision or plan into effect; execution”
(ibid.) and institutionalisation, which is to “establish
(something, typically a practice or activity) as a
convention or norm in an organization or culture”
(ibid.). Following these definitions, in the EA context
adoption can be defined as the process where
organisation starts using EA methods and tools for the
very first time.
As a consequence, EA adoption is causing
changes to the organisation. The organisation is
adopting a new way to communicate (to describe) its
current and future states, and a new formal way to
develop the organisation to achieve its stakeholders’
goals. Thus, we will adopt organisational change as
the underpinning theory to explain EA adoption.
As noted earlier, organisations can be categorised
as systems. Lee (2010) states that systems may evolve
from one state to another deliberately by design, or in
a natural uninformed way (the default). Van de Ven
and Poole (1995) have recognised four ideal-types
organisational development theories to explain
organisational change processes (Figure 1). These are
Life Cycle, Evolution, Dialectic, and Teleology. Life
Cycle theory sees change being imminent;
organisation is moving from a start-up towards its
termination through certain phases. Each of these
phases is necessary, so the change is following always
the same steps. Environment may influence this
change, but it is not a driving force. Teleological
theory sees that the change takes place because the
organisation is trying to achieve a certain goal or
purpose. Although this theory is also cyclical,
fundamental difference is that there is no certain
sequence of events to be followed. Moreover, the or-
Figure 1: Process Theories of Organisational Development and Change (Van de Ven and Poole, 1995).
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
144

ganisations do not “terminate”, but are changing
indefinitely. Dialectical theory assumes that
organisation exist in world of continuous conflicts.
The change takes place when two or more opposing
forces gain power enough to confront the status quo.
Evolutionary theory sees change as a method to
survive; competing from the same resources causes
elimination of some of the organisations.
The most used theories in the current change
management literature are life cycle and teleological
theory (Van de Ven and Poole, 1995; Kezar, 2001). It
can be argued that the latter one, teleological theory,
explains the best EA adoption. First of all, EA is
adopted in a single entity: an organisation. Secondly,
EA adoption is constructive, as it is aiming to a
specific goal e.g. EA adoption.
According to Csribra and Gergely (2007) there are
two ways to predict future events in teleological
change via goal attribution. These are an action-to-
goal and goal-to-action. The former can be
interpreted as a question: What is the function of EA
adoption? In the same way the latter can be
interpreted as a question: What action should be taken
to achieve EA being adopted? A summary of
differences of these two interpretation action can be
seen in Table 1.
Table 1: The Functions of Teleological Interpretation of
Actions (Csibra and Gergely, 2007).
Primary
function
Type of inference
‘Action-to-Goal’ ‘Goal-to-Action’
On-line
Prediction
Goal prediction:
Predicting the likely
effect of an on-
going action
Action anticipation:
Predictive tracking of
dynamic actions in
real time
Social
Learning
Discovering novel
goals and artefact
functions
Acquiring novel
means actions by
evaluating their causal
efficacy in bringing
about the goal
EA adoption can be of both types. If the
organisation has a problem it tries to solve with EA
adoption, it would be action-to-goal type; function of
EA adoption is to solve the problem. If, on the other
hand, organisation’s goal is to adopt EA, it would be
goal-to-action type. In this research we are interested
in which actions are taken while adopting EA so the
type of inference is goal-to-action.
Another dimension of predicting future events in
teleological change is the primary function of the
prediction (Csibra and Gergely, 2007). There are two
functions, on-line prediction and social learning. The
former is aiming for prediction of either the goal or
action based on ongoing actions. The latter aims to
learning and finding of novel goals or means actions.
In this paper, we are interested in increasing the
understanding of the EA adoption so the primary
function is social learning.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In order to model Enterprise Architecture adoption,
the literature related to EA and organisational change
was reviewed. Based on the literature review, an EA
adoption model was formed to explain the resistance
during EA adoption.
Model’s validity is a primary measure of its utility
and effectiveness (Groesser and Schwaninger, 2012).
Therefore its validity needs to be tested using an
appropriate validation method. Our model contains
merely causal relationships and can therefore be
validated using structure verification tests (Barlas,
1996). For instance in a major behaviour patterns
test, the model’s accuracy to reproduce real-life
behaviour is tested (Barlas, 1996).
Our model is validated against empirical data
acquired from a real-life EA-pilot. The validation is
performed by analysing the empirical data using a
directed content analysis approach. This approach is
similar to the Grounded Theory approach by Strauss
and Corbin (1990). The major difference is that the
codes and keywords are derived from theory or from
relevant research findings instead of data (Hsieh and
Shannon, 2005). Therefore the validity of our model
can be tested by analysing data by using the model as
a source for codes and keywords.
3 ENTERPRISE ARCHITECTURE
ADOPTION MODEL
In this section we will describe the formulation of our
conceptual model of EA adoption. First the three
individual components of the model are introduced.
The first component, the strategic level of Enterprise
Architecture, is based on a selected Enterprise
Architecture literature. Second and third components,
organisational change and change resistance,
respectively, are adopted from general organisational
change literature. After introduction of the
components, the conceptual model of EA adoption is
presented.
3.1 Strategic Level of Enterprise
Architecture
Enterprise Architecture is a relatively new phenome-
ModellingtheResistanceofEnterpriseArchitectureAdoption-LinkingStrategicLevelofEnterpriseArchitectureto
OrganisationalChangesandChangeResistance
145
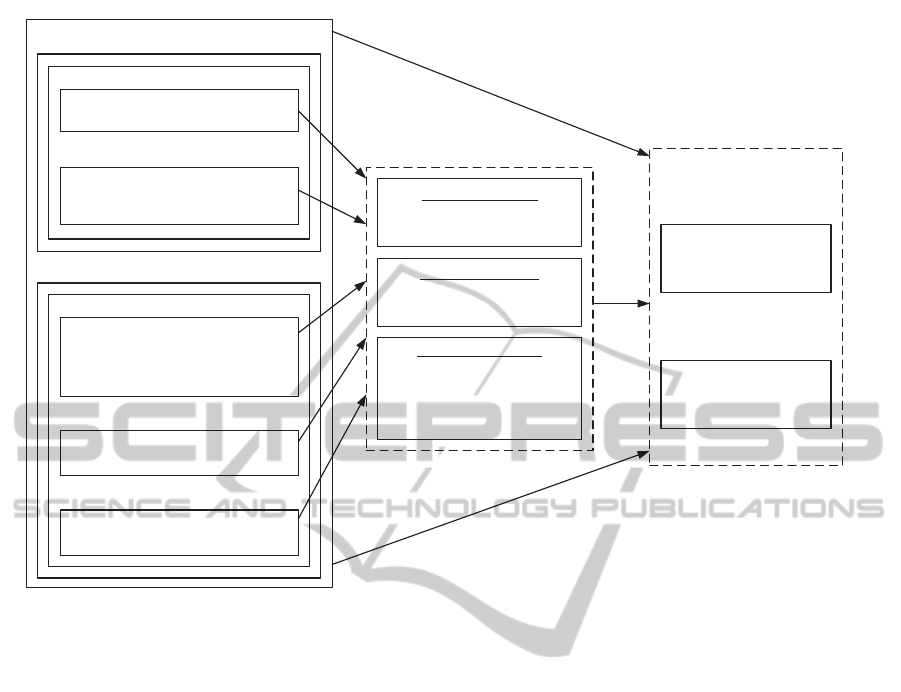
Figure 2: Antecedents, Explicit Reactions, and Change Consequences of Organisational Change (Oreg et al., 2011).
non, having a multiple schools of thought. Lapalme
(2011, 2012) has recognised three ideal schools from
the current EA literature; Enterprise IT Architecting,
Enterprise Integrating, and Enterprise Ecological
Adaption.
Enterprise IT Architecting school is aiming to
alignment of organisation’s IT assets and business
activities. The school often describes EA as “the glue
between business and IT” (Lapalme, 2012, p. 38).
From a strategic point of view, EA is merely a tool to
fulfil business objectives without questioning them in
any way.
The goal of Enterprise Integrating school is to
execute organisation’s strategy by maximising
organisation’s coherency. Thus the school views EA
as “the link between strategy and execution” (ibid.,
2012, p. 40).
For Enterprise Ecological Adaptation school EA
means designing all organisational facets, including
bidirectional relationship to its environment. This
school is interested also in what is happening outside
of organisation’s borders, and is actively trying to
change also the surrounding environment. Thus EA is
described to be “the means for organisational
innovation and sustainability” (ibid., 2012, p. 41).
Each of the three EA schools of thought can be
seen being on a different strategic level. At the lowest
level, EA is used merely as the glue between business
and IT. On higher levels, EA is seen more as a means
to executing organisation’s strategy, but also as way
to systemically change the environment of the
organisation.
Strategic level decisions and choises are affecting
the whole organisation. Organisations may take
different tactical stance to achieve their strategy
(Casadesus-Masanell and Ricart, 2010). This means
that strategic decisions likely causes more changes
than the tactical ones. As such, it can be argued that
the higher the strategic level of EA, the more changes
the organisation will face during the EA adoption.
3.2 Organisational Changes
Oreg et al., (2011) have formed a model of change
recipient actions (Figure 2) based on a literature
review of 79 quantitative organisational change
studies between 1948 and 2007. Their model suggests
that change and pre-change antecedents are linked to
individual’s explicit reactions and change
consequences. Also explicit reactions are linked to
change consequences. This model gives us a good
starting point for our model of EA adoption. As noted
Traits; Coping styles; Needs;
Demographics
Antecedent
s
Pre-Change Antecedents
Change Recipient Characteristics
Supportive environment and trust;
Commitment; Culture; Job
characteristics
Internal Context
Participation; Communication and
info; Interactional and procedural
justice; Principal Support;
Management competence
Change Antecedents
Change Process
Anticipated outcomes; Job
insecurity; Distributive justice
Perceived Benefit/Harm
Compensation; Job design; Office
layout; Shift schedule
Change Content
Affective reaction
Negative, e.g., Stress
Positive, e.g., Pleasantness
Explicit Reactions
Cognitive reaction
Change evaluation
Change beliefs
Behavioral reaction
Change recipient
involvement
Behavioral intentions
Coping behaviors
Change consequences
Job satisfacetion
Org. Commitment
Performance
Work-Related
Consequences
Well-being
Health
Withdrawal
Personal Consequences
Traits; Coping styles; Needs;
Demographics
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
146

earlier, EA adoption is an instance of teleological
organisational change. Therefore it can be assumed
that pre-change and change antecedents will result in
organisational and personal consequences, either
directly or indirectly by explicit reactions, also in EA
adoption.
Organisational changes can be categorised to four
types (Cao et al., 2000; 2003). These types of
organisational change are; (i) changes in processes,
(ii) changes in functions (structural change), (iii)
changes in power within the organisation (political
change), and (iv) changes in values (cultural change).
This categorisation gives us a tool for classifying
anticipated consequences and results caused by EA
adoption.
3.3 Change Resistance
Every change, no matter how big or small, will face
resistance. However, the higher the impact of the
change the higher is the resistance (Bovey and Hede,
2001). Change resistance can be defined as “any
phenomenon that hinders the process at its beginning
or its development, aiming to keep the current
situation” (Pardo del Val and Martinez Fuentes, 2003,
p. 152). Following this definition, resistance during
EA adoption refers to any phenomenon hindering the
adoption. Resistance can be intentional or
unintentional, can be recognised by target, or can be
recognised by observer (Hollander and Einwohner,
2004). Another concept closely related to resistance
is inertia, which can be defined as “a tendency to do
nothing or to remain unchanged” (Oxford
Dictionaries, 2010). In other words, for some reason,
organisation resists changing the status quo of the
organisation. One example of inertia is a structural
inertia, which “refers to a correspondence between
the behavioural capabilities of a class of organizations
and their environments” (Hannan and Freeman, 1984,
p. 151). In the other words, the organisation has high
structural inertia when the speed of reorganisation is
lower than the speed of environmental conditions
change. In our EA adoption model, conceptually we
do not make difference between change resistance
and inertia.
Pardo del Val and Martinez Fuentes (2003) have
recognised two types of resistance related to
organisational change; inertia during the planning
stage, and inertia in the execution stage. Reasons
behind the former type of inertia are (i) distorted
perception, interpretation barriers and vague strategic
priorities, (ii) low motivation, and (iii) lack of
creative response. Reasons behind the latter type of
inertia are (iv) political and cultural deadlocks, and
(v) other reasons. In the context of EA adoption,
resistance can occur during the planning stage of the
adoption and during its execution. Complete list of
sources of resistance in the planning and execution
stages can be seen in Table 3 and Table 2,
respectively.
Table 2: Sources of Change Resistance During the
Execution (adapted from Pardo del Val and Martinez
Fuentes, 2003).
Category Source of Resistance
Political and
Cultural
Deadlocks
Implementation climate and relation between
change values and organisational values,
Departmental politics,
Incommensurable beliefs,
Deep rooted values,
Forgetfulness of the social dimension of
changes.
Other
Sources
Leadership inaction,
Embedded routines,
Collective action problems,
Capabilities gap,
Cynicism.
Table 3: Sources of Change Resistance During the Planning
(adapted from Pardo del Val and Martinez Fuentes, 2003).
Category Source of Resistance
Distorted
Perception
Myopia,
Denial,
Perpetuation of ideas,
Implicit assumptions,
Communication barriers,
Organisational silence.
Low
Motivation
Direct costs of charge,
Cannibalisation costs,
Cross subsidy comforts,
Past failures,
Different interests among employees and
management.
Lack of
Creative
Response
Fast and complex environmental changes,
Resignation,
Inadequate strategic vision.
3.4 EA Adoption Model
The conceptual model of Resistance in EA adoption
Process (REAP) can be seen in Figure 3. The model
is based on the EA and organisational change
literature. Logical reasoning of the model is as
follows. Enterprise Architecture can be used on
different strategic levels (Lapalme, 2012). The
selected strategic level sets boundaries to EA
adoption, e.g. what kind of objectives are set for the
adoption and thus what kind of organisational
changes may result (Cao et al., 2003). In other words,
the strategic level of EA influences the objectives of
the adoption. These objectives (change antecedents)
are influencing the resulting changes directly and
indirectly via explicit reactions of people (Oreg et al.,
ModellingtheResistanceofEnterpriseArchitectureAdoption-LinkingStrategicLevelofEnterpriseArchitectureto
OrganisationalChangesandChangeResistance
147

Figure 3: Conceptual Model of Resistance in EA Adoption Process (REAP).
2011). During the planning and execution phases of
the adoption, organisational resistance (reactions of
people) may distort adoption and thus influences the
outcomes of the adoption (Pardo del Val and
Martinez Fuentes, 2003).
3.5 Validation
3.5.1 Enterprise Architecture Pilot
In this sub-section our model is validated using
empirical data collected from a real-life EA pilot (see
CSC, 2011). The EA pilot was conducted in 2010
among 12 Finnish Higher Education Institutions
(HEIs), which of two merged in the beginning of the
pilot. During the pilot, EA was adopted by
participating HEIs.
Demographic data collected from the public
websites of the participating institutions can be seen
in Table 4. Pilot participants represented 29 % of
Finnish HEIs. Nine of the participating institutions
were Universities of Applied Sciences (formerly
known as Polytechnics) and two Universities.
Table 4: Pilot Institutions.
HEI Students Employees Location
1 8 100 800 Southern Finland
2 2 000 200 Northern Finland
3 2 900 300 Northern Finland
4 5 200 400 Southern Finland
5 4 800 600 Northern Finland
6 7 500 600 Southern Finland
7 16 000 1 200 Southern Finland
8 4 800 400 Western Finland
9 3 000 300 Northern Finland
10 15 900 2 900 Northern Finland
11 10 000 800 Southern Finland
HEIs were organised to six groups each focusing
to a certain problem domain. These groups were
Education, Adult Education, Merger, Consortium,
Quality Assurance, and Network. Quality Assurance
(QA) and Adult Education (AE) sub-projects were
merged during the pilot.
Table 5: Pilot Groups.
Group Institution(s)
Network 1, 4, 6
Education 7
Consortium 3, 5, 9
Merger 11 (12)
QA & AE 2, 8, 10
3.5.2 Data Collection
The data was collected using semi-structured
interviews as a part of a PhD research. Themes for the
interviews were derived from the factors affecting EA
adoption. These factors were identified from the
literature during a Systematic Literature Review
conducted following the instructions by Kitchenham
(2007). The review included 35 studies on EA
adoption. Identified factors were categorised under
three categories; Organisational factors, such as
organisational capabilities, EA related factors, such
as EA specific skills, and environmental (contextual)
factors, such as possible external pressure. Following
instructions by Kvale (1996), questions seen in Table
were formed for interviews.
Interviews were performed between June and
October 2010 by phone and were recorded for
transcribing. Total number of 22 individuals were
interviewed from three different roles; CIOs, rectors
(principals), and Quality Assurance staff.
Strategic level of
Enterprise Architecture
Objectives
(desired changes)
Resistance during
planning
Enterprise Ecological
Adaptation
Enterprise Integrating
Enterprise IT
Architecting
Cultural
Political
Structural
Process
Outcomes
(r es u ltin g c han g e s)
Cultural
Political
Structural
Process
Distorted Perception
Low Motivation
Lack of creative
response
Resistance during
execution
Political and Cultural
Deadlocks
Other Reasons
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
148

Figure 4: Group Level Analysis.
3.5.3 Data Coding
Coding was performed using NVivo software
package; Version 9.2.81.0 (64-bit). Transcriptions of
the interviews were automatically organised as nodes
using NVivo’s Auto code feature so that each
question formed a node. Each of these nodes
contained all answers for the particular question from
all interviews.
Table 6: Interview Questions.
Think about some major change(s) your organisation have
faced during the past few years. Describe such a change and
how it was conducted. Which challenges, if any, the change
faced.
Describe the process how new information systems are
defined, acquired or implemented, and introduced in your
organisation.
Describe how new development initiatives are introduced in
your organisation. Who or which party is driving such
initiatives? How important this is for the success of the
initiative?
Describe on what basis are development initiatives given
resources in your organisation.
Describe how EA is organised in your organisation.
Describe how communication is organised in your
organisation. How about between external stakeholders?
About EA pilot, explain what are your or your organisation's
expectations for the pilot. How are they related to your
organisation's strategy?
Which kind of expectations from other stakeholders have you
faced/know?
Explain how EA pilot or similar initiatives are related to the
government level programs. How are such programs
coordinated? What are the power relationships in such
coordination?
Table 6: Interview Questions (cont.).
Tell me about EA pilot, explain how was the used framework
selected? Does the framework require any modification to suit
your purposes? Explain. On which kind of principles is the EA
pilot based on? Explain in your own words EA and related
terms.
Explain your and your organisation's EA experience. Has there
been any training during the pilot? Which parts of EA, if any,
you think your organisation has most challenges? Have you
used contracted specialists/consultants during the pilot?
Table 7: Categories Used in Analysis.
Main category and source Sub-categories
Strategic level of EA
(Lapalme, 2012)
Enterprise IT Architecting,
Enterprise Integrating,
Enterprise Ecological
Adaptation.
Objectives
(Cao et al., 2003)
Processes, Structural,
Cultural,
Political.
Resistance during planning
(Pardo del Val and Martinez
Fuentes, 2003)
Distorted perception, Vague
strategic priorities,
Low motivation,
Lack of creative response.
Resistance during execution
(Pardo del Val and Martinez
Fuentes, 2003)
Political and cultural
deadlocks,
Other reasons.
The actual coding of each node followed the same
process. Each answer were coded by searching for
occurences of the codes listed in Table 7 First each
answer was analysed from the strategic level of EA
point-of-view, next from changes point-of-view, and
finally from the resistance point-of-view.
AD
Network
IN
AR
CU
PO
ST
PR
DI
LO
LA
DE
OT
AD
Education
IN
AR
CU
PO
ST
PR
DI
LO
LA
DE
OT
AD
Consortium
IN
AR
CU
PO
ST
PR
DI
LO
LA
DE
OT
AD
Merger
IN
AR
CU
PO
ST
PR
DI
LO
LA
DE
OT
AD
QA & AE
IN
AR
CU
PO
ST
PR
DI
LO
LA
DE
OT
Legend:
This pilot with link
This pilot without a link
Previous change(s) with a link
Previous change(s) with a link
Interpreted from capabilities
Link
ModellingtheResistanceofEnterpriseArchitectureAdoption-LinkingStrategicLevelofEnterpriseArchitectureto
OrganisationalChangesandChangeResistance
149

4 RESULTS
Illustrated summary of analysis on the group level can
be seen in Figure 4, where the analysis of each group
(see Table 5) are combined to a single diagram. Boxes
on the left represents strategic levels of EA, boxes in
the middle the types of organisational change, and
boxes on the right categories of sources of resistance.
The legend for used abbreviations can be seen in
Table 8.
Black and white circles represents findings from
the analysis of the questions related to the goals and
objectives of the EA pilot. A white circle indicates that
the particular concept is found from the data. Solid
black dot indicates that it is found from the data and
linked to another finding. For instance in the Network
group it can be seen that there is evidence in the data
suggesting that the level of EA is seen as Enterprise
Integrating. However, the same respondent has not
mentioned any particular change, so there is nothing
it could be linked to. It can also be noted that there is
a link between Enterprise IT Architecting and
Process change. In this case, the respondent has
expressed both the strategic level of EA, and the
actual change to be achieved. In some cases, such as
in the Network group, there is also a link between the
change and a source of resistance, supported by the
data. Black and white squares represents findings
from the analysis of the questions related to past
changes and challenges, and diamonds to possible
sources of resistance interpreted from answers.
Table 8: Abbreviations of Categories Used in Analysis.
Strategic level Change type Resistance
AD
Enterprise
Ecological
Adaptation
CU Cultural DI
Distorted
Perception
IN
Enterprise
Integrating
PO Political LO
Low
Motivation
AR
Enterprise IT
Architecting
ST Structural LA
Lack of
Creative
response
PR Process DE
Political and
Cultural
Deadlocks
OT
Other
Reasons
The summary of the findings is illustrated in
Figure 5. Dotted arrows indicates logically deduced
influence, as described in the REAP. Solid arrows, in
turn, indicate empirically validated influence.
Next we will briefly explain and discuss results in
textual form. As suggested by REAP model, all
strategic levels of EA were present in the data.
However, there were no evidence of the adoption
aiming for cultural changes of the organisation.
Therefore Cultural change was removed from the
results. One possible explanation for this is that as EA
is used for the very first time, it is “safer” to focus on
easier changes first. After all, as it can be seen in
Figure 4, previous cultural changes in organisations
have caused resistance in four out of five resistance
categories, as has political changes.
Sources of resistance were found in all five
categories, as suggested by the REAP model.
However, only 10 out of 24 sources were found from
the data. This leaves 14 sources of resistance (see
Table 3 and Table 2) which were not faced in the EA
pilot. One explanation for this is that such sources of
resistance might not been faced in Finnish HEIs at all.
More likely explanation is that those sources of
resistance were not met in this particular pilot but
would likely be faced in other settings. For instance
during the executing of cultural changes, political and
cultural deadlocks are most likely faced. As noted
earlier, there were no cultural changes executed nor
planned during the EA-pilot.
The REAP model is a qualitative model, e.g. it
captures the resistance emerging from the data, but
does not judge any source of resistance being more
important than other. However, it should be noted that
most of the resistance faced during the planning phase
of the EA-pilot were related to understanding of EA
concepts (Distorted Perception). Other studies have
also noticed the lack of EA knowledge in the Finnish
public sector. For instance Lemmetti and Pekkola
(2012) argues that current definitions of EA are
inconsistent and thus confusing both researchers and
practitioners. This is also supported by Hiekkanen et
al., (2013); EA is underutilised due to lack of
understanding it properly. In general, poor
communication have been found to be one of the
factors contributing to EA adoption failures
(Mezzanotte et al., 2010). Moreover, value of EA is
directly influenced by how EA is understood in the
organisation (Nassiff, 2012).
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we formed a model to explain the
process of Enterprise Architecture (EA) adoption. A
teleological organisational change was adopted as an
underpinning theoretical view to EA adoption. The
model of resistance during EA adoption process
(REAP) was formed based on the literature. Our
model revealed previously unexplored relationships
between the strategic level of EA and objectives of
EA adoption. Also relationships between these
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
150
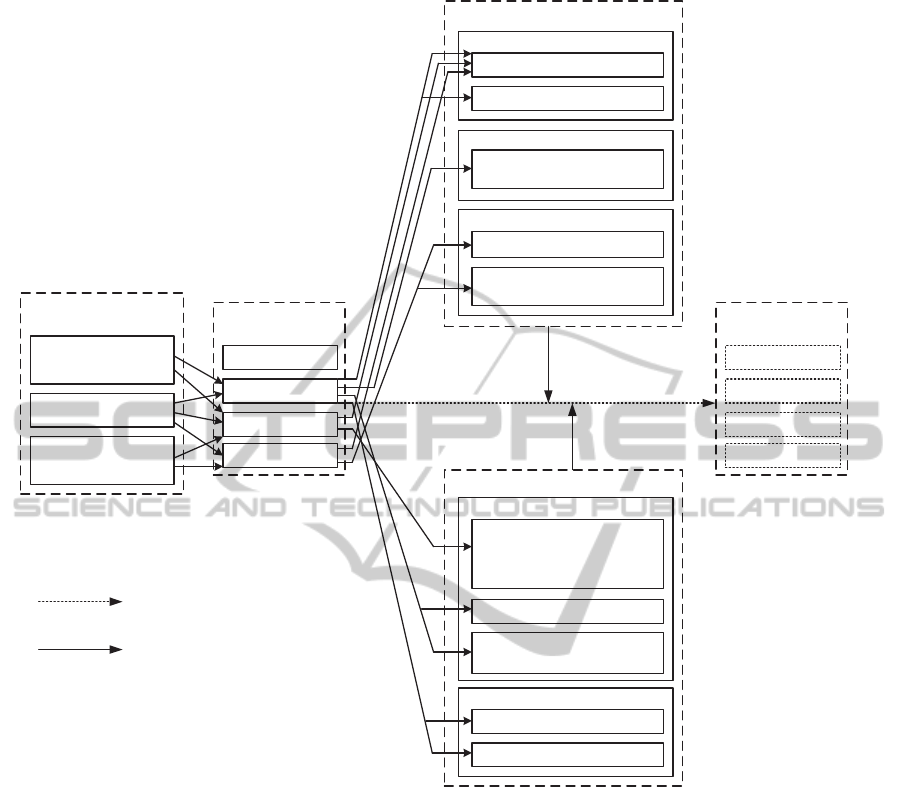
Figure 5: Results of Data Analysis.
objectives and various sources of organisational
resistance were identified.
As it can be interpreted from the analysis, the
REAP model can be used to categorise the adoption
process. Moreover, as stated by Barlas and Carpenter
(1990) a valid model can be assumed to be one of the
many possible ways to describe a real world. Thus it
can be argued that the model is valid in this context,
e.g. it does reproduce real life behaviour found from
the EA-pilot.
5.1 Implications
The results of this study have implications to both
science and practice. For science, REAP model
provides a model to explain the organisational
resistance during the EA adoption. We have
demonstrated that the resistance depends on the
changes the EA adoption is causing. As such, it
contributes to the organisational science.
For the practice, the REAP model provides a tool
which can be used to anticipate possible sources of
resistance. When the relationships between the
strategic level of EA, resulting changes, and sources
of resistance are known, one can prepare for and
minimise the resistance during the adoption.
5.2 Limitations and Future Work
The empirical data used to validate the model was
gathered from an EA pilot conducted among 12
Finnish Higher Education Institutions. This limits the
generalisability of the results as such a qualitative
data is contextually-bound. However, similar
Objectives
(desired changes)
Cultural
Poli tical
Structural
Process
Strategic level of
Enterprise Architecture
Resistance during planning
Enterprise Ecological
Adaptation
Enterprise Integrating
Enterprise IT
Architecting
Outc omes
(resulting changes)
Cultural
Political
Structural
Process
Distorted Perception
Low Motivation
Resistance during execution
Communication barriers
Perpetuation of ideas
Different interests among
employees and management
Lack of creative response
Inadequate strategic vision
Fast and complex
environmental change
Political and Cultural Deadlocks
Implementation climate and
relation between change
values and organisational
values
Forgetfulness of the social
dimension of changes
Other
Capabilities gap
Cynicism
Departmental politics
Logically deduced
influence
Empirically validated
influence
ModellingtheResistanceofEnterpriseArchitectureAdoption-LinkingStrategicLevelofEnterpriseArchitectureto
OrganisationalChangesandChangeResistance
151

challenges have been found also from other settings
(Kaisler et al., 2005; Pehkonen, 2013; Seppänen,
2014) which supports our findings. REAP is based on
general non-HEI-specific literature, and therefore it is
likely explaining resistance during EA adoption also
in a wider context. Therefore we are encouraging
researchers and practitioners to apply REAP model in
other settings to increase its validity and
generalisability.
Author acknowledges that the REAP model is one
possible way to describe EA adoption. This means
that REAP is not necessarily comprehensive, i.e.
there may be sources of resistance that are not
captured by the model. Therefore we are encouraging
researchers also to improve the model.
Analysing the empirical data with the REAP
model revealed that most of the planning phase
resistance was caused by the lack understanding EA
knowledge. Thus one direction for the future research
could be finding ways to overcome this type of
resistance.
REFERENCES
Ambler, S. 2010. Enterprise Architecture Survey Results:
State of the IT Union Survey [Online]. Available:
http://www.ambysoft.com/surveys/stateOfITUnion201
001.html [Accessed Jan 21
st
2015].
Barlas, Y. 1996. Formal aspects of model validity and
validation in system dynamics. System Dynamics
Review, 12, 183-210.
Barlas, Y. & Carpenter, S. 1990. Philosophical roots of
model validation: two paradigms. System Dynamics
Review, 6, 148-166.
Beer, M. & Nohria, N. 2000. Cracking the code of change.
Harvard Business Review, 78, 133-141.
Bovey, W. H. & Hede, A. 2001. Resistance to
organizational change: the role of cognitive and
affective processes. Leadership & Organization
Development Journal, 22, 372-382.
Cao, G., Clarke, S. & Lehaney, B. 2000. A systemic view
of organisational change and TQM. The TQM
Magazine, 12, 186-193.
Cao, G., Clarke, S. & Lehaney, B. 2003. Diversity
management in organizational change: towards a
systemic framework. Systems Research and Behavioral
Science, 20, 231-242.
Casadesus-Masanell, R. & Ricart, J. E. 2010. From strategy
to business models and onto tactics. Long range
planning, 43, 195-215.
CIO Council 2001. A Practical Guide to Federal Enterprise
Architecture. Available at
http://www.cio.gov/documents/bpeaguide.pdf.
Computer Economics. 2014. Enterprise Architecture
Adoption and Best Practices. April 2014. [Online].
Available:
http://www.computereconomics.com/article.cfm?id=1
947 [Accessed Jan 21
st
2015].
CSC. 2011. Kokonaisarkkitehtuuri eli KA-pilotti [Online].
Available: http://raketti.csc.fi/kokoa/pilotti [Accessed
May 30
th
2011].
Csibra, G. & Gergely, G. 2007. ‘Obsessed with goals’:
Functions and mechanisms of teleological
interpretation of actions in humans. Acta Psychologica,
124, 60-78.
Dietz, J. L. G., Hoogervorst, J. A. P., Albani, A., Aveiro,
D., Babkin, E., Barjis, J., Caetano, A., Huysmans, P.,
Iijima, J., van Kervel, S. J. H., Mulder, H., Op ‘t Land,
M., Proper, H. A., Sanz, J., Terlouw, L., Tribolet, J.,
Verelst, J. & Winter, R. 2013. The discipline of
enterprise engineering. Int. J. Organisational Design
and Engineering, 3, 86-114.
Gartner. 2013. IT Glossary: Enterprise Architecture (EA)
[Online]. Available: http://www.gartner.com/it-
glossary/enterprise-architecture-ea/ [Accessed Feb 21
st
2013].
GERAM 1999. GERAM: Generalised Enterprise
Reference Architecture and Methodology. Version
1.6.3. IFIP-IFAC Task Force on Architectures for
Enterprise Integration. IFIP-IFAC Task Force.
Groesser, S. N. & Schwaninger, M. 2012. Contributions to
model validation: hierarchy, process, and cessation.
System dynamics review, 28, 157-181.
Hammer, M. & Champy, J. 1993. Reengineering the
corporation: a manifesto for business revolution,
London, Nicholas Brearly.
Hannan, M. T. & Freeman, J. 1984. Structural inertia and
organizational change. American sociological review,
149-164.
Hiekkanen, K., Korhonen, J. J., Collin, J., Patricio, E.,
Helenius, M. & Mykkanen, J. 2013. Architects'
Perceptions on EA Use -- An Empirical Study. In:
Business Informatics (CBI), 2013 IEEE 15th
Conference on, Jul 15
th
-18
th
2013. 292-297.
Hollander, J. A. & Einwohner, R. L. 2004. Conceptualizing
Resistance. Sociological Forum, 19, 533-554.
Hsieh, H.-F. & Shannon, S. E. 2005. Three Approaches to
Qualitative Content Analysis. Qualitative Health
Research, 15, 1277-1288.
ISO/IEC/IEEE 2011. Systems and software engineering --
Architecture description. ISO/IEC/IEEE
42010:2011(E) (Revision of ISO/IEC 42010:2007 and
IEEE Std 1471-2000).
Kaisler, H., Armour, F. & Valivullah, M. 2005. Enterprise
Architecting: Critical Problems. In: HICSS-38.
Proceedings of the 38th Annual Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences, 2005 Waikoloa,
Hawaii, USA.
Kezar, A. 2001. Understanding and facilitating
organizational change in the 21st century. ASHE-ERIC
Higher Education Report. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Kitchenham, B. 2007. Guidelines for performing
Systematic Literature Reviews in Software
Engineering, Keele, Keele University.
Kotter, J. P. 2008. A sense of urgency, Harvard Business
Press.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
152

Kvale, S. 1996. Interviews: An introduction to qualitative
research interviewing, Thousand Oaks, California,
Sage Publications, Inc.
Lapalme, J. 2011. 3 Schools of Enterprise Architecture. IT
Professional, PP, 1-1.
Lapalme, J. 2012. Three Schools of Thought on Enterprise
Architecture. IT Professional, 14, 37-43.
Lee, A. S. 2010. Retrospect and prospect: information
systems research in the last and next 25 years. Journal
of Information Technology, 25, 336-348.
Lemmetti, J. & Pekkola, S. 2012. Understanding Enterprise
Architecture: Perceptions by the Finnish Public Sector.
In: SCHOLL, H., JANSSEN, M., WIMMER, M.,
MOE, C. & FLAK, L. (eds.) Electronic Government.
Berlin: Springer.
Mezzanotte, D. M., Dehlinger, J. & Chakraborty, S. 2010.
On Applying the Theory of Structuration in Enterprise
Architecture Design. In: Computer and Information
Science (ICIS), 2010 IEEE/ACIS 9th International
Conference on, 18-20 Aug. 2010 2010. 859-863.
Nassiff, E. 2012. Understanding the Value of Enterprise
Architecture for Organizations: A Grounded Theory
Approach. PhD Thesis, Nova Southeastern University.
Oreg, S., Vakola, M. & Armenakis, A. 2011. Change
Recipients’ Reactions to Organizational Change: A 60-
Year Review of Quantitative Studies. The Journal of
Applied Behavioral Science, 47, 461-524.
Oxford Dictionaries. 2010. Oxford Dictionaries. April 2010
[Online]. Oxford University Press. Available:
http://oxforddictionaries.com/ [Accessed Nov 18
th
2014].
Pardo del Val, M. & Martinez Fuentes, C. 2003. Resistance
to change: a literature review and empirical study.
Management Decision, 41, 148-155.
PEAF. 2010. 160 Character Challenge. What is the
Purpose of EA? [Online]. Pragmatic EA Ltd. Available:
http://www.pragmaticea.com/docs/160-char-
challenge-analysis.pdf [Accessed Sep 24
th
2014].
PEAF. 2013. Definition of "Enterprise" [Online]. Essex,
UK: Pragmatic EA Ltd. Available:
http://www.pragmaticef.com/frameworks.htm
[Accessed Feb 21
st
2013].
Pehkonen, J. 2013. Early Phase Challenges and Solutions
in Enterprise Architecture of Public Sector. Master's
Thesis, Tampere University of Technology.
Proper, H. A. 2013. Enterprise Architecture. Informed
steering of enterprises in motion. ICEIS 2013. Angers,
France.
Pulkkinen, M. 2008. Enterprise Architecture as a
Collaboration Tool. PhD Thesis, University of
Jyväskylä.
Ross, J. W., Weill, P. & Robertson, D. C. 2006. Enterprise
architecture as strategy: Creating a foundation for
business execution, Boston, Massachusetts, USA,
Harvard Business School Press.
Schekkerman, J. 2005. Trends in Enterprise Architecture
2005: How are Organizations Progressing? Amersfoort,
Netherlands: Institute for Enterprise Architecture
Developments.
Seppänen, V. 2014. From problems to critical success
factors of enterprise architecture adoption, Jyväskylä,
University of Jyväskylä.
Strauss, A. & Corbin, J. 1990. Basics of Qualitative
Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing
Grounded Theory, Sage Publ.
Syynimaa, N. 2010. Taxonomy of purpose of Enterprise
Architecture. 12th International Conference on
Informatics and Semiotics in Organisations, ICISO
2010. Reading, UK.
TOGAF 2009. TOGAF Version 9, Van Haren Publishing.
Van de Ven, A. H. & Poole, M. S. 1995. Explaining
Development and Change in Organizations. The
Academy of Management Review, 20, 510-540.
Zachman, J. A. 1997. Enterprise architecture: The issue of
the century. Database Programming and Design, 10,
44-53.
ModellingtheResistanceofEnterpriseArchitectureAdoption-LinkingStrategicLevelofEnterpriseArchitectureto
OrganisationalChangesandChangeResistance
153
