
Proactive Domain Data Querying based on Context Information in
Ambient Assisted Living Environments
Vinícius Maran
1,4
, Alencar Machado
1,2
, Iara Augustin
3
,
Leandro Krug Wives
1
and José Palazzo M. de Oliveira
1
1
Institute of Informatics, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil
2
Polytechnic School, Federal University of Santa Maria, Santa Maria, RS, Brazil
3
Technology Center, Federal University of Santa Maria, Santa Maria, RS, Brazil
4
Academic Coordination Office, Federal University of Santa Maria, Cachoeira do Sul, RS, Brazil
Keywords: Situation, Prediction, Context-awareness, Data Query, Ambient Assisted Living, Ubiquitous Computing.
Abstract: Ubiquitous computing defines a set of technologies to make computing omnipresent in real life environ-
ments. In the area of ambient assisted living, ubiquitous technologies have been used to improve the life
quality and expectancy for elderly people. Recently, researches have shown that the use of context-
awareness combined with proactive actions can cause systems to act more appropriately in assistance to the
user. In this paper, we present a new persistent and proactive data retrieval model for ambient assisted living
systems. This model provides an architecture that is able to integrate information that is gathered from the
user environment and considers the current user context to act in a proactive manner. The model was im-
plemented on a service integrated in a Situation as a Service middleware and it was applied in a case study
for evaluation and validation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Presently, we perceive an increased demand of tech-
nology for domestic environments, either as the
world population is aging (WorldMeters, 2013), and
by the fact that companies often prefer to keep em-
ployees at home working remotely. This context
emphasizes the possibility of expanding Smart
Homes and Ambient Assisted Living’s (AAL) appli-
cation domain. The vision presented in this article is
focused on Smart Homes. The home infrastructure
and AAL layer provides services dedicated to home
care for people who need help in daily activities.
People and devices interact to perform specific
activities, which are oriented to develop daily activi-
ties in these environments. In this sense, different
situations arise and are often related to the user pro-
file and also related with the activity being executed.
For example, people with impaired cognitive abili-
ties due to aging may unintentionally place them-
selves in dangerous or uncomfortable situations in
simple activities such as cooking, or leave a room
without checking if important actions such as turn-
ing off the shower were taken. Software and hard-
ware solutions related to ubiquitous computing are
being proposed to support this demand. For instance,
in a previous paper the Situation as a Service Mid-
dleware (SIaaS) was presented (Machado et al.,
2014). In the current paper, a solution to store in-
formation and make contextualized selection of
information using SIaaS middleware is presented.
This solution is supported by a set of require-
ments established in other works (Maran et al.,
2014) (Makris et al., 2013). Current solutions do not
clearly address how an information query can be
constructed with contextual information in high
level to generate the most appropriate decision based
in the acquired data to manipulate current or future
situations. The definition of a model to integrate
ontologies and JavaScript Object Notation for
Linked Data (JSON-LD) language (Lanthaler and
Gutl, 2012) is presented in this work. Thus, a signif-
icantly decrease in the overhead information pre-
sented by other tools is expected. Furthermore, we
also developed a model to integrate ontological
representation of context information, serialized in
JSON-LD, and domain information, which are often
used in ubiquitous systems to allow querying this
information based on context. A model to query
domain information based on context information
610
Maran V., Machado A., Augustin I., Krug Wives L. and Palazzo M. de Oliveira J..
Proactive Domain Data Querying based on Context Information in Ambient Assisted Living Environments.
DOI: 10.5220/0005365006100617
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 610-617
ISBN: 978-989-758-097-0
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

was also defined. With these models, a service to
persist and retrieve data related to reactive and pro-
active situations in the SIaaS was created.
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2 dis-
cusses the main concepts related to this work; Sec-
tion 3 presents the models and service to query do-
main data based on context information; Section 4
presents a case study and discusses the application
of the models on it; Section 5 presents the conclu-
sions and future works in this area.
2 BACKGROUND
In the future, Ambient Intelligence (AmI) will ena-
ble environments to support people to inhabiting
them, being sensitive to their needs and capable of
anticipating behaviors (Sadri, 2011). Ambient As-
sisted Living (AAL) and Smart Homes are emerging
as AmI focused on specific characteristics of users.
For instance, existing researches present conceptual
models to transform homes into AAL environments,
modeling their context and services (Klein et al.,
2007). AAL characterize a domestic and automated
environment as one in which different users interact
personally and with physical objects.
These physical objects can be managed by spe-
cific systems developed for AAL. As the user behav-
ior change over the time, situations that involve
users also change over time. In our case, AAL’s
situations are related to health and, for this reason
experts’ knowledge for detection and handling these
situations is necessary. Besides, AAL systems need
knowledge about the world around users they moni-
tor and, in order to perform actions, they need to
interact with users through interaction devices (Au-
gusto et al., 2009). Moreover, services have to cope
with medical guidelines in a context-aware way in
order to provide users with instructions that are
appropriate to the patient’s situation. Systems for
AAL can choose most appropriate actions when they
are supported by mechanisms to query historic con-
text, current and futures situations involving the
user. With this information, the system may act in
advance, which characterizes a proactive system.
The implementation of context awareness in compu-
ting systems is a key requirement for it to occur.
2.1 Context-awareness
According to Dey et al. (2001) context may be de-
fined as "any information that might be used to
characterize the situation of entities (person, place
or object) that are considered relevant to the inter-
action between a user and an application". Recent
works proposed variations on definition of context
(Makris et al., 2013), where context is defined as the
flow of information, measured and inferred about
the general state of the related entities.
Consequently, a system considered context-
sensitive should be able to deal with various levels
of abstraction involved in sensitivity to context (Ma-
ran et al., 2014). It should start in the lowest level of
abstraction, collecting and aggregating information
from sensors, passing through intermediate levels,
making inferences about data and information gen-
erated from sensors with semantic annotations that
define contexts themselves, until the highest level of
abstraction, where situations define semantic rela-
tionships between contexts of interest. In ubiquitous
architectures, sensitivity to context directly inter-
feres in many operations.
Integration between ontologies and databases has
been presented in several researches, and some of
them are described in next section. Due to the large
amount of data collected from the environment and
the necessity of subsequent queries to these data, it
is necessary to integrate ontologies with databases.
2.2 Related Work
Comparative analyses between tools to integrate
ontologies and databases were presented in recent
works (Klein et al, 2007). Integration tools can be
classified into: (i) integration with relational data-
bases, (ii) integration with NoSQL databases, and
(iii) integration with distributed file systems.
Regarding integration with purely relational da-
tabases, it was observed a significant increase in
amount of information created for maintaining set-
tings of converted OWL-DL files to relational sche-
ma (Batzios and Mitkas, 2009). Furthermore, there
has been a decrease in performance of queries and
operations in database, primarily due to necessity for
constant conversion of query languages. More recent
approaches have worded with the integration of
ontologies with distributed file systems, primarily to
allow better distribution of information. These ap-
proaches contribute to the scalability of systems, but
suffer since they need external agents to work with
the original file system to perform queries and infer-
ences (Neumann et al., 2010).
NoSQL databases have been used in various ap-
plications, including integration with ontologies.
Recent works (Neumann et al., 2010) describe the
integration of XML databases with ontologies serial-
ized in XML or RDF files. The main problem with
this approach is that XML databases often need too
ProactiveDomainDataQueryingbasedonContextInformationinAmbientAssistedLivingEnvironments
611
much memory. This is a big problem when systems
use large ontologies. In DB4OWL, Batzios and
Mitkas (2009) present an object-oriented representa-
tion of OWL-DL ontologies, integrating ontologies
with object-oriented databases.
There are a number of important requirements
that must be considered in the management of in-
formation in AAL environments that are not met by
the studied solutions: (a) Context information is
often represented in ontologies, and domain-specific
information is often represented in relational data-
bases. Therefore, it is necessary to provide ways to
integrate this information and to query them in an
integrated manner (Bolchini et al., 2013); (b) Usage
of proactive methodologies together with reactive
action to manipulate situations of interest demon-
strated good results to execute services (Klein et al.,
2007). However, the focus of these solutions is the
implementation and execution of services, not data
retrieval about the domain and context information
itself. As result of this analysis, we developed a
proactive data retrieval model for AAL.
3 PROACTIVE APPROACH FOR
DATA QUERYING BASED ON
CONTEXT INFORMATION
The proactive approach here presented for data que-
rying based on contextual information is applied in
the SIaaS Middleware showed in (Machado et al.,
2014). In a home care system for smart homes, the
main issue is to identify the essential characteristics
that an AAL system needs to manipulate situations
of interest involving users in their living environ-
ment. Thereafter, the system must: identify different
situations along time in an extensible manner, reac-
tively manipulate the current situation and proactive-
ly manipulate future situations.
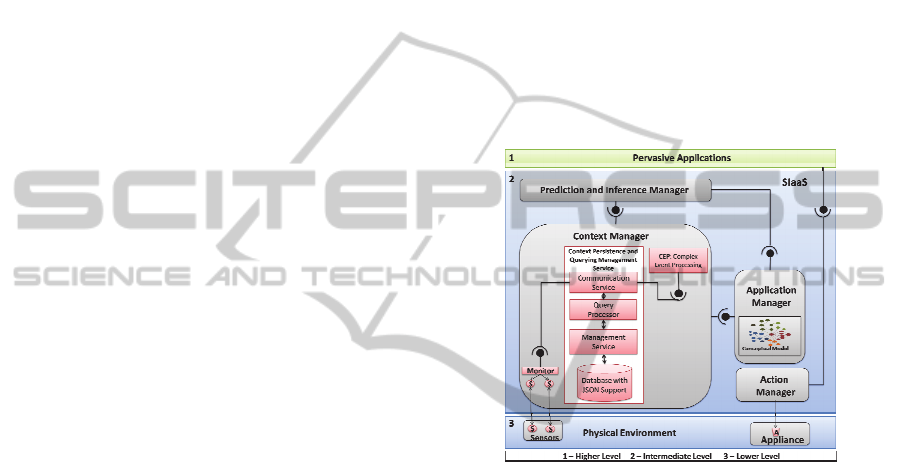
In this sense, SIaaS (Figure 1) is responsible for
the management of environmental resources and for
the detection of current and future situations of in-
terest for pervasive applications. In this context,
pervasive applications are software developed by
specialized companies in specific fields, such as
health, surveillance and energy, and they run in the
SIaaS. In fact, they are deployed in the SIaaS, and
these applications contain knowledge regarding
decision-making processes necessary to manipulate
situations of interest. In fact, applications can state
the situations they are interested in and the system
will activate these applications when one situation is
detected. The middleware architecture has three
levels. The lowest level comprises the physical envi-
ronment, where sensors and appliances are located.
The intermediate level is the SIaaS itself, a system
that manages the environment and provides situa-
tions for pervasive applications (the highest level).
As depicted in Figure 1, the SIaaS is composed
of four modules. Besides, it uses a conceptual model
(inside the application manager), which is based on
Ontology Web Language (OWL). The Applications
Manager module allows the installation (i.e., de-
ployment) of a pervasive application and obtains its
context and situations of interest. After one applica-
tion is deployed, this module informs these situa-
tions of interest to the Prediction and Inference
Manager module and notifies the application’s con-
text of interest to the Context Manager module.
Figure 1: SIaaS Middleware.
The Context Manager has tree subsystems: the Con-
text Persistence and Querying Management Service,
the Monitor, which manages sensor produced raw
data, and the Complex Event Processing system.
The Context Persistence and Querying Manage-
ment Service is a new component in the SIaaS archi-
tecture, and generates event instances according to
what is described in the application´s context of
interest. Thus, each time an event occurs, it is sent to
the Complex Event Processing, which uses a pattern
presented in (Machado et al., 2014) to describe
events, and processes event flows to determine if an
event is of interest for an application already de-
ployed in the SIaaS. If a pattern is detected, it noti-
fies the Prediction and Inference Manager module.
The Prediction and Inference Manager is responsi-
ble for performing inference and predictions, and
has two subsystems. The Inference subsystem con-
tains rules to detect the current situation, and the
Prediction tries to determine the probability of a
situation to happen in the future. If a situation hap-
pens now or is predicted to happen in the future, its
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
612

corresponding application is started. In this moment,
the pervasive application chooses the most relevant
actions to manipulate the situation detected and
requests the Action Manager component to execute
these actions.
The Action Manager component then selects the
services that result in the most appropriated func-
tionalities to execute the actions specified by the
application. This selection process takes into account
the user context, comprising user disabilities, for
instance. In this paper, we will focus on the Context
Manager module, more specifically in the Context
Persistence and Querying Management Service. We
will present a solution for data querying based on
contextual information to generate high-level infor-
mation that results in situations of interest.
3.1 Context Persistence and Querying
Management Service
To allow persistence and retrieval of context and
domain information, a set of services that can be
accessed through an API provided by the SIaaS
middleware was defined. Contextual information is
considered dynamic, inferred on raw data from read-
ings taken on environment (Makris et al., 2013).
Domain information is usually more static compared
contextual information and represents information
that describes specific domain of application. This
type of information is usually represented and stored
in relational databases (Klein et al., 2007).
The Context Persistence and Querying Manage-
ment Service consists of four functionalities, which
allows context information to be stored and retrieved
according to the occurrence of specific events that
determine situations of interest. The subsystem con-
sists on the following components: (i) Database
with native JSON support: a database that supports
JSON serialization to store ontologies implemented
in OWL-DL that describes contextual information
was used. In addition, this database must support the
relational model, which allows domain information
to be stored in the same database; (ii) Management
Service: a service that performs the management of
databases used by the Context Persistence and Que-
rying Management Service. It implements routines
that manage the communication between persistence
of information and OWL-API (Horridge and Bech-
hofer, 2011), and Pellet (Parsia and Sirin, 2004); (iii)
Query Processor: Implements the control of que-
ries. This module receives requests made by the
SIaaS and translates the queries to a form compati-
ble with the database used by the subsystem. Thus, it
is possible to perform the integration between con-
textual and domain data, a problem researched by
other works (Bolchini et al., 2013); (iv) Communi-
cation Service: Provides a communication interface
to external modules, and is able to perform query
operations like insert, update and delete data in the
service.
3.2 Context Modeling and
Serializations of Ontologies
For context modeling, we have used the model pre-
viously presented by Machado et al. (2014) and
Silva et al. (2014) (see Figure 2). The conceptual
model begins with Entity. Entities are concrete or
abstract concepts used to reason about a domain of
interest, for instance, person, space, time, and sen-
sor. So, the environment is represented by a set of
entities and their semantic relations, which charac-
terize the context of the environment. Then, seman-
tic relations are a very important concept, and are
represented by triples in the form
<Es, p, Eo>. In
this triple, Es represents the subject of the relation,
and Eo represents the object of the relation. Subjects
and objects are linked by a contextual predicate.
The contextual predicate was first described by Ye
et al. (2012), and it links two contextual entities
through a relation. Using this kind of semantic rela-
tion, pervasive applications can define contexts of
interest.
Thus, pervasive applications can use this kind of
statement to define a set of semantic relations of
interest. Therefore, the context of interest is a subset
of instances with their corresponding semantic rela-
tions. When these relations are evaluated, it is possi-
ble to determine which actions the applications will
use. Figure 2 shows the core of the model, including
domotic, user and proactive domains. Initially, when
users are involved with his daily activities, they
perform (human) actions. These actions result in
external events collected by the AAL system.
Events start and finish the current situation and
influence predictive situations that involve the user
at the current time. The events that influence a pre-
dictive situation (future situation) that will involve
the user are always processed by the Pervasive Ap-
plication. In this contextual model, Semantic Web
Rule Language (SWRL) rules can be used to specify
a current situation to be detected by the system. In
addition, probabilistic values can be modeled using
PR-OWL in order to determine if a situation is hap-
pening now (isSituationOf) or will happen in the
future (willBeSituationOf). Using information about
the current or future situations, the system can select
Automated Actions to manipulate situations.
ProactiveDomainDataQueryingbasedonContextInformationinAmbientAssistedLivingEnvironments
613

Figure 2: Ambient Assisted Living Ontology Network.
For instance, if an interaction with a Person is neces-
sary to manipulate a situation, the system may
choose an Automated Action of the type Regarding
a Person to be executed by a Functionality provided
by the Device of type InteractionWithPerson. This
Functionality needs to be sensitive to Disability of
Person. The Automated Action produces an Internal
Event and using it, the system can detect if the cur-
rent or future situation change or will change in
relation to a Person. In AAL, information related to
the domain refers to resources, people and services,
and may be used by systems (Sadri et al., 2011).
We modeled personal information about patients
according to a list of information considered confi-
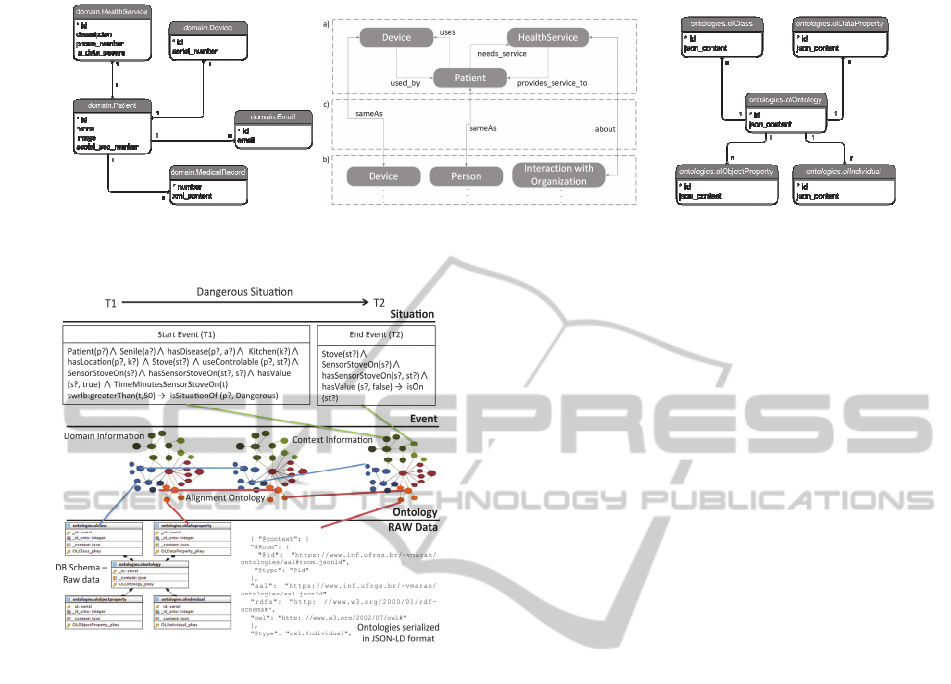
dential for patient according to CDT (2014). Figure
3(a) shows an ER diagram of data structure of per-
sonal information about patients in AAL. The dia-
gram (presented in Figure 3(a)) includes information
related Patients and their medical information, rep-
resented by PhoneNumber, MedicalRecord and
Email. In addition, people can use devices that are
registered in the Device table and can use health
services of external companies, defined in
HealthService table. Thus, implemented service can
provide confidential health information only if the
health service is considered safe, or it can filter this
information according to the service used by the
patient. To integrate context with domain-specific
data, we defined an alignment between context in-
formation ontology and a specific domain ontology,
which describes structure and individuals; this
alignment is persisted in the relational database. To
represent the domain structure, we exported the
schema of relational database for a simple ontology,
where Device, Patient and HealthService tables
were defined as classes in ontology (Figure 3(b)).
Furthermore, normal and reverse relationships were
modeled between classes. To align the ontologies
that describe the application domain (a) and the
context definitions (b), a third ontology was imple-
mented (c).
It imports other ontologies and implements
sameAs relationships between context.Device and
domain.Device, and between context.Person and
domain.Patient in addition to the relation between
domain.HealthService and context.InteractionWith-
Organization. Thus, we make connection between
definitions of context and domain information, both
used in data querying. Figure 4 shows the different
levels of abstraction used in SIaaS. The Situation
level presents a situation of interest for pervasive
applications. Situations are represented on a time
interval (T1 and T2) where a situation is valid, and
start and end Events are described using SWRL.
The definition of contexts, and rules that describe
the starting and ending events of situations, as well
as the definition of temporal questions regarding
situations are modeled in a context Ontology.
A form of serialization of OWL-DL ontologies
was implemented using JSON-LD. Based on this
modeling, we extended the model to a scheme de-
scribed in JSON-LD, where each axiom defined in
OWL-DL was converted to JSON-LD in a segment-
ed manner. This file segmentation allows the data-
base to be easily replicated thus increasing scalabil-
ity. In addition, segmentation of axioms allows them
to be shared through REST requests. To perform the
persistence of instances and ontologies, we defined a
set of database schemas, one for domain data persis-
tence (shown in Figure 3(c)), and another for storage
of ontologies that represent context, domain infor-
mation and the alignment between them (Figure
3(b)). Each table in this schema represents a set of
individuals in ontologies separated by their structur-
al type (according to the OWL-DL definitions). All
tables have an attribute used as a unique identifier
(_id), and content (_content), which represent the
definition of axiom in JSON.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
614
a
)
b)
c
)
Figure 3: (a) Relational diagram with information about patients and health plans in AAL Systems; (b) Alignment between
context and domain data; (c) Database schema used in ontology serialization.
Figure 4: Abstraction levels of SIaaS.
To manage the model, a set of algorithms to deal
with database schema integration were implemented.
The schema was implemented with PostgreSQL,
which supports the relational model and deals with
JSON. We also implemented an integration with
OWL-API and Pellet. Thus, both axioms of ontology
as information relating to application domain could
be persisted and retrieved in the same database.
3.3 Management of Persistence and
Retrieval of Information
To allow the recovery of information in the service
that implements the model developed in this paper,
we consider the following situations: (i) The Moni-
tor module performs constant monitoring of infor-
mation from sensors. This information should be
grouped according to a set of rules and stored as
inferred context for analysis and subsequent use by
other services and applications. (ii) Based on an
analysis made by Monitor service, it informs Com-
plex Event Processing certain context information,
in conjunction with domain information, which
needs to be used by the Prediction and Inference
Manager to detect situations of interest for the per-
vasive applications deployed on the middleware.
The models presented earlier, of context, domain
and alignment, are implemented in OWL-DL, and
later converted to JSON-LD in the Management
Service of Context Persistence and Query. After,
these settings are inserted into the database. Thus,
ontological representations, implemented in OWL-
DL, of domain and context are persisted and inte-
grated into the OWL API by loading the same in-
formation for inferences in memory.
To insert new context information, the Monitor
performs insertions using the Communication Ser-
vice. When a new context is entered, the service
stores and updates the model in memory, because
this new context can directly affect inferences. To
retrieve domain information based on contextual
information, the management service queries the
database and relates the definitions present in the
ontology with the definitions used in the database.
To validate the model we considered a case study
based on an AAL environment. This case study is
detailed in the next section.
4 CASE STUDY
A case study that represents a set of conditions in an
environment was defined for evaluation purposes.
The case study is based on the union of two applica-
tion domains: Intelligent Environments for health
care (Ambient Assisted Living - AAL), and ubiqui-
tous hospital systems (e-HealthCare Systems).
Let’s consider John, an elderly patient about 70
years old that has a history of cardiovascular disease.
Let’s imagine he is at home, more specifically in his
living room (his current localization). In addition,
his house has a set of sensors, which collect data and
transmit them to the SIaaS middleware, which con-
stantly monitors the environment. John also has a
ProactiveDomainDataQueryingbasedonContextInformationinAmbientAssistedLivingEnvironments
615

caregiver, i.e., a person to help him if something
wrong happens. Suddenly, the sensors start produc-
ing a stream of data and the middleware interpret it
as someone falling and infer that John has just felt.
Immediately, the middleware reacts by notifying
John’s caregiver through his smartphone. In parallel,
as John is in his living room, and his TV (device) is
turned on and is capable of providing alerts, an alert
is sent to it. Since John manages to get up by himself
and the middleware recognizes he is ok, people
registered as next to him are informed.
As John has a history of cardiovascular disease
(e.g., this information is in his profile), the SIaaS,
through an analysis of his past situations, infers a
recurrent pattern, i.e., John frequently falls. In this
behavior pattern, John needs hospitalization. Thus, it
is necessary to inform to a hospital service previous-
ly hired by him to deal with this situation. At the
time a call to the health service is made, the middle-
ware sends a semantic description of his recent his-
tory of activities and of the contexts of interest
(heartbeat and temperature) involved in recent simi-
lar situations. This semantic description is shared
with the system of the hospital, which appends this
information to the hospital record of John (along
with other sensitive medical information). Infor-
mation actions and contexts, as well as a summary
of medical records are transmitted by some ubiqui-
tous system of the hospital to an ambulance, which
performs a call to John. When an ambulance arrives
at John’s residence, the SIaaS confirms the arrival of
the ambulance to the pervasive application and to
the hospital’s system.
4.1 Reactivity
Let’s say that John hired a monitoring service that
works with the SIaaS middleware. In addition, he
acquired a pervasive application that deals with
Falling and notRaised situations. All models are
loaded in SIaaS and inferences can be performed on
these representations because they are integrated to
OWL-API and to Pellet by the service described in
this work. The situation “John’s Fall” is defined by
a starting event, at time T1, and a final event at T2.
Table 1(a) presents this situation and its associated
SWRL rules defining the starting and finishing
events. As John takes a long time to rise, notRaised
situation is inferred by the system. Table 1 (b) pre-
sents rules that define the events of that situation.
These rules are persisted in the service and loaded to
reasoner, so it is possible to infer when events occur
in the environment. When John falls, the service
triggers the corresponding event, converting models
to JSON, and inserting it in the database. When a
situation is inserted in the database, another trigger
sends a message to module CEP to warn the corre-
sponding pervasive application that a situation of
interest has just happened.
Table 1: (a) Initial and final events of the falling situation;
(b) Initial and final events of the notRaised situation.
Starting
Event (a)
Patient(?p) ∧ SensorFalling(?s)∧
hasDevice(?p, ?s) ∧ SensorFallingOn
(true)∧ TimeMinutesSensorFallingOn
(?t) ∧ LivingRoom(?l) ∧ hasLocation
(?p, ?l) ∧ swrlb:greaterThan(t,10) →
isSituationOf (?p, Fall_i)
Finishing
Event (a)
Patient(?p)
∧ SensorFalling(?s)∧
hasDevice(?p, ?s)
∧
SensorFallingOn(false) → isSituation-
Of(?p, Fall_f)
Initial
Event (b)
Patient(?p) ∧ isSituationOf(?p,
Fall_i)∧TimeMinutesSensorFallingOn
(?t) ∧ (not) isSituationOf(?p, Fall_f)
∧ swrlb:greaterThan(t,20) → isSitua-
tionOf (?p, notRaised_i)
Final
Event (b)
(?p, notRaised_i) → isSituationOf (?p,
notRaised_f)
4.2 Proactivity
To query proactively, we used a proactive method-
ology (Machado et al., 2014). There, rules are com-
bined with Bayesian networks to determine the
probability that undesired situations may occur.
Constantly, the module consults the database to
verify if, according to current context, situations of
interest occurred previously. This is done with a
query about situations occurring in similar contexts
in a given time, using concept of time windows
(Machado et al., 2014). In this concept, situations of
interest have a limited time frame and occur in a
limited amount of time before or after the current
situation. The code snippet below shows a query of
situations arising in contexts similar to the current
one. In this case, time entities are taken into consid-
eration, with an interval of 2 hours from the current
time.
SELECT count(*) as situationOccourrenceNum, ontol-
ogies."olindividual"._id,ontologies."olindividual"
._content as SemanticDescription FROM do-
main."Patient", ontologies."olindividual" WHERE
CAST(domain."Patient"._id as text) like ontolo-
gies."olindividual"._content->> 'isSituationOf'
AND ontologies."olindividual" ._content ->> 'has-
StartTime' BETWEEN '10:00' AND '12:00' GROUP BY
ontologies."olindividual"._id
The query result is informed by the CEP service
with a number of occurrences of unwanted situations
that occurred in the given time window and a seman-
tic description (presented below) of the information
regarding the patient if they need to be sent to the
hospital system.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
616

{ "@context": { "#situation1":{"@id":
"https://www.inf.university.br/~main/ontologies/aa
l#situation1.jsonld","@type":"@id"},"aal":
"https://www.inf.university.br/~main/ontologies/aa
l.jsonld",
"rdfs": "http: //www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#",
"owl":"http: //www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#", "#Pa-
tient":"https://www.inf.university.br/~main/ontolo
gies/aal#Situation.jsonld"},
"@type": "owl:Individual","rdfs:label":[
{ "@value": "situation 1", "@language": "en"},
{ "@value": "situacao 1","@language":"pt-br"}],
"owl:individualOf":[ {"owl:Class":"#Situation"}],
"isSituationOf": "1", "hasStartTime": "10:30",
"hasEndTime": "10:45" }
CEP, in turn, analyzes information sent by the
service, and infers that there are positive probabili-
ties of the unwanted situation CardiacAttack to
happen. Thus, CEP informs the application the in-
formation about situations and medical patient in-
formation, which should be sent to the hospital sys-
tem, with a request for an ambulance.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The combination of actions taken reactively and
proactively increases the efficiency of control sys-
tems in assisted living environments. SIaaS middle-
ware was implemented and offered a model for
making reactive and proactive decisions. In this
paper, we extended the SIaaS middleware adding
new models to perform the integration of contextual
definitions stored in ontologies and domain-specific
information stored in relational databases; and re-
trieves this information in an integrated and proac-
tive manner. These contributions were implemented
in SIaaS middleware in form of a new Context Per-
sistence and Querying Management Service, which
allows SIaaS to query about domain and context
data proactively.
As future work, we intend to expand the integra-
tion between tools of inference of ontologies and the
persistence solution allowing the developers to use
the approach transparently, using the API as ontolo-
gy management interface and to compare this solu-
tion against solutions based on triple stores that are
often used for the persistence of ontologies.
REFERENCES
Augusto, J. C., Nakashima, H., Aghajan, H. 2009. “Ambi-
ent Intelligence and Smart Environments: a State of
the Art”. In: Handbook of ambient intelligence and
smart environments. p. 3–31. Springer New York.
Batzios, A., Mitkas, P. A. 2009. "db4OWL: An Alterna-
tive Approach to Organizing and Storing Semantic
Data." In: Internet Computing, IEEE. v.13, n.6, p.48-
55.
Bolchini, C., Quintarelli, E., Tanca, L. 2013.“CARVE:
Context-aware Automatic View Definition over Rela-
tional Databases”.In:Information Systems,v.38,i.1.
Center for Democracy & Technology Website. Available
at: https://www.cdt.org/files/healthprivacy/20090625
_deidentify.pdf.
Dey A. K., Abowd G. D., Salber D. 2001. “A Conceptual
Framework and a Toolkit for Supporting the Rapid
Prototyping of Context-aware Applications” In: Hum.-
Comput. Interact. n. 16, p. 97–166.
Horridge, M., Bechhofer, S. 2011. "The OWL API: A Java
API for OWL Ontologies." In: Semantic Web. p. 11-
21.
Klein, M., Schmidt, A., Lauer. R. 2007. "Ontology-
centered Design of an Ambient Middleware for As-
sisted Living: The Case of Soprano.". In: 30th Annual
German Conference on Artificial Intelligence.
Lanthaler, M., Gutl, C. 2012. "On Using JSON-LD to
Create Evolvable RESTful Services" In: Proceedings
of the Third International Workshop on RESTful De-
sign. p. 25-32.
Machado. A , Lichtnow, D., Pernas, A. M., Wives, L. K.,
Palazzo Moreira de Oliveira, J. 2014. “A Reactive and
Proactive Approach for Ambient Intelligence”. In:
16th International Conference on Enterprise Infor-
mation Systems, Lisbon. v. 2. p. 501-512.
Makris, P., Member, S., Skoutas, D. N. 2013. "A Survey
on Context-Aware Mobile and Wireless Networking:
On Networking and Computing Environments' Inte-
gration." In: Communications Surveys & Tutorials,
IEEE. v. 15.1. p. 362-386.
Maran, V., de Oliveira, J., Augustin, I. 2014. "Are The
Integrations Between Ontologies and Databases Really
Opening the Closed World in Ubiquitous Compu-
ting?" In: International Conference on Software Engi-
neering & Knowledge Engineering. Vancouver, CA.
Neumann, C. P., Fischer, T., Lenz, R. 2010. “OXDBS –
Extension of a Native XML Database System with
Validation by Consistency Checking of OWL-DL On-
tologies” In: Proceedings of the 14th International
Database Engineering & Applications Symposium.
Parsia, B., Sirin, E. 2004. "Pellet: An OWL DL Reasoner."
In: Third International Semantic Web Conference-
Poster. no. 18. Pp. 51-53.
Sadri, F. 2011. “Ambient Intelligence: A survey”. In:
ACM Computer. v. 43, n. 4, p. 36-70.
Silva Kambara. J, Machado Medeiros, G, Thom, L. H.,
Krug Wives, L. 2014. “Business Process Modeling
and Instantiation in Home Care Environments” In:
16th International Conference on Enterprise Infor-
mation Systems, Lisbon. v. 2. p. 513-525.
Ye, J., Dobson, S., McKeever, S. 2012.“Situation Identifi-
cation Techniques in Pervasive Computing: A Re-
view”.In: Pervasive and mobile computing,v.8,n1.
WorldMeters. Current World Population. Website. Avai-
lable: http://www.worldometers.info/world-
population/
ProactiveDomainDataQueryingbasedonContextInformationinAmbientAssistedLivingEnvironments
617
