
A User-centered Approach for Modeling Web Interactions Using Colored
Petri Nets
Taffarel Brant-Ribeiro
1
, Rafael Ara
´
ujo
1
, Igor Mendonc¸a
1
, Michel S. Soares
2
and Renan G. Cattelan
1
1
Faculty of Computing, Federal University of Uberl
ˆ
andia, Uberl
ˆ
andia, MG, Brazil
2
Department of Computing, Federal University of Sergipe, S
˜
ao Crist
´
ov
˜
ao, SE, Brazil
Keywords:
Web Interaction Modeling, Formal Methods, Colored Petri Nets, Human-Computer Interaction.
Abstract:
Interactions are communication acts which take place between at least two agents and result in information
interchange. To represent these activities, formal methods can be used to model interaction flows and Colored
Petri Nets (CPNs) are a handy formal language with graphical notation for modeling systems. This paper
introduces wiCPN (Web Interaction Modeling Using Colored Petri Nets), a language based on CPNs for rep-
resenting Web interactions with improved notation. Our proposal is first presented with its proper refinements
over traditional CPNs. Next, we have applied the approach for modeling the interaction of Classroom eXperi-
ence’s (CX) Web front-end, a real u-learning environment. As CX is an educational system developed to assist
instructors and students during academic activities, we verified the developed model’s reachability to ensure
it was able to represent users different access levels. We also validated our proposal with user experiments,
comparing it with UML. Our designed model represented CX’s interaction correctly, considering user access
levels and maintaining an understandable notation. Results indicate advantages of wiCPN over UML for mod-
eling interactive interfaces. By gathering strengths of Petri Nets with a higher level graphical notation, wiCPN
propitiated better understanding of the model, representing interaction in a structured and intuitive way.
1 INTRODUCTION
Interactive issues tend to go far beyond creating nice
layouts, addressing relevant aspects such as usability
features, ways of presenting information correctly and
cultural characteristics of users (Clemmensen, 2012).
To perceive such requirements and to develop prod-
ucts that work properly when in touch with users, in-
teraction modeling is a software engineering activity
able to assist software production process, being sig-
nificant during specification phases and over devel-
opment and verification steps of systems deployment
processes (Sommerville, 2010).
Application of formal methods for modeling in-
teractions can provide benefits, including the guaran-
tee of consistency across platform designs and the in-
corporation of a user interface design phase into the
formally-based procedure of software development
(Bowen and Reeves, 2007). In this scope, a Petri Net
is a formal and mathematical graphic language, ap-
propriate for modeling distributed and concurrent sys-
tems (Jensen, 1994). Colored Petri Nets (CPNs) are
high level Petri Nets whose tokens have colors and
can represent data values. This extension increases
the descriptive power of modeling, since the trigger-
ing of transitions is made depending on the availabil-
ity of these colored tokens (Jensen et al., 2007).
A CPN model describes the possible states a mod-
eled system can reach and the transitions which may
occur among these states. Therefore, they are an
effective formalism for describing concurrency, syn-
chronization and causality, being suitable for model-
ing, analyzing and prototyping dynamic issues of in-
teractions (Jensen, 1994). CPNs have been studied in
a wide range of application areas and many projects
have been documented in the literature while imple-
mented in industry, e.g., hardware and software de-
signs (Kim et al., 2012), security analysis of network
protocols (Choosang and Gordon, 2014), parallel file
systems (Nguyen and Apon, 2012) and distributed
computing systems (Weidlich et al., 2013).
In this work, we applied CPNs as a conceptual ba-
sis, since they have relevant characteristics for mod-
eling interactions, such as: (i) well-defined seman-
tics, (ii) graphical portrayal, (iii) possibility of formal
analysis and (iv) hierarchical modeling. Thereby, we
introduce wiCPN (Web Interaction Modeling Using
Colored Petri Nets), a language for representing in-
37
Brant-Ribeiro T., Araújo R., Mendonça I., S. Soares M. and Cattelan R..
A User-centered Approach for Modeling Web Interactions Using Colored Petri Nets.
DOI: 10.5220/0005365100370048
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 37-48
ISBN: 978-989-758-097-0
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

teractions between users and Web interfaces which
extends traditional CPNs to better depict Web inter-
actions in a dynamic and uncomplicated way.
As a practical example of wiCPN’s use, we mod-
eled the Web interface of a real U-Learning Envi-
ronment (ULE) system. To validate our proposal,
we compared wiCPN with UML by running user ex-
periments and, according to results, wiCPN evinced
to be a concise notation, without losing expressive-
ness. With wiCPN, only a single diagram is required
to represent the same interactive flow that, in UML,
would require multiple diagrams, overwhelming the
design team and potentially generating inconsisten-
cies in case of changes in one diagram that would
need to be propagated to other ones. Within this sit-
uation, wiCPN notation enables a mapping between
an interactive element (e.g., a given screen or a Web
page) and its functionality, allowing users to identify
their exact location, context and interaction options.
The remaining of this article is structured as fol-
lows: in Section 2, we detail CPNs components and
usage; in Section 3, we present wiCPN, a language
developed for representing Web interactions; in Sec-
tion 4, we first introduce Classroom eXperience (CX),
our educational platform, and then we utilize it as
a case study for demonstrating wiCPN proposal; in
Section 5, we present user experiments and results,
comparing our technique with UML; in Section 6, we
discuss related work; and, finally, in Section 7, we
present our conclusions and final remarks.
2 COLORED PETRI NETS
CPNs provide a full abstraction to design, specify and
validate systems (Jensen, 1994). Like ordinary Petri
Nets, they are represented as graphs with places, tran-
sitions, arcs and tokens. However, in CPNs tokens
are not blank markers, but have data attached to them.
A token’s color is a type’s specification. Places are
assigned with one or more colors (called sets or mul-
tisets) and arcs are either specified with schemas or
associated to boolean conditions. Also, as arcs simul-
taneously enter and exit places, they have functions
to determine which set or multiset elements shall be
removed or put into places they are bound. Besides,
there are boolean expressions, named guards, which
are associated with transitions and enforce conditions
over CPN elements.
Figure 1 shows a model’s slice in which it is pos-
sible to observe two places (Login and LoginScreen),
a transition (inLog) and some arcs with schemas.
Places Login and LoginScreen are, respectively, as-
signed with a set Active and a multiset LoginScreen.
The former holds act, a token which belongs to color
Active. The latter possesses three tokens, being two
of them (dUserTrue and dUserFalse) parts of set
dUser – which pertains to color UserData –, while
the other one (newUser) is related to set nUser – and
is associated to color newUserData. As place Login-
Screen can be filled with tokens of different colors,
it is assigned with a homonym multiset composed
by the union of colors UserData, newUserData and
Active. Also, transition inLog is connected to both
places through arcs that can only transport a single
token, act, in accordance with their schemas.
Figure 1: A model’s slice with places, arcs and a transition.
CPNs also can be organized into hierarchic mod-
ules (Jensen et al., 2007). This concept is settled on
a many-level structural mechanism, which sustains
both a top-down as well as a bottom-up working man-
ner. New associated modules can be created from
prevalent ones and reused in other parts of models.
Figure 2 shows a hierarchy where two slices of a
model can be spotted: (a) an upper part where tran-
sition LanguageScreen is highlighted and (b) a lower
module containing the whole activity that takes place
inside of LanguageScreen.
Figure 2: Two hierarchic modules.
The formal definition of a Colored Petri Net
(Jensen, 1994) is represented as a 9-tuple: CPN = ( Σ,
P, T, A, N, C, G, E, I ); where: Σ denotes a finite and
non-null set of colors or types, P retracts a finite set
of places, T represents a finite set of transitions, A
portrays a finite and disjunct set of arcs, N denotes
node functions, C retracts color sets and multisets, G
represents guards, E portrays expression functions (or
arc schemas) and I is an initialization function.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
38

CPN models can be used to verify system features
and properties, i.e., to demonstrate that desirable at-
tributes are accomplished or unwanted characteristics
are absent. Verification of system properties is sus-
tained by a set of State Space Methods, which are
automatically generated and with them it is possible
to respond a large set of verification issues related
to system behaviors, such as absence of deadlocks,
assurance of always reaching a certain state and the
guaranteed delivery of determined services.
Practical application of CPN modeling and analy-
sis leans deeply on the existence of tools which sup-
port creation and manipulation of models. In this con-
text, CPN Tools
1
is a tool suite for creating, editing,
simulating and analyzing CPN models (Gehlot and
Nigro, 2010). This suite was chosen for its possibility
of creating graphical representation of models – as it
possesses an editor that allows users to create and ar-
range CPN components – and for having tooling that
calculates state space of models and verify their prop-
erties automatically. Figures 1 and 2 – as well as all
others figures that illustrate system modeling in this
paper – were designed making use of CPN Tools.
3 wiCPN: WEB INTERACTION
MODELING USING COLORED
PETRI NETS
Our work focused on creating a method for repre-
senting interactions that take place between users and
Web front-ends. Thus, a couple of interactive issues
were considered while elaborating a model that would
support these needs, such as the way interactive flows
occur in Web interfaces (Rogers et al., 2011) and the
fact that determined screens and functions must only
be accessed by certain users (Sommerville, 2010).
To figure out these needs, we considered an orga-
nizational aspect that propitiated better understanding
of CPN modules. In this scope, models must support
both flows – presenting links among system screens –
and navigation – indicating actions associated to pos-
sible flows –, what allows the models to present inter-
action in an uncomplicated and dynamic way.
As a result, to better depict Web interactions while
making use of CPNs, we present wiCPN (Web In-
teraction Modeling Using Colored Petri Nets), a lan-
guage for representing interactions between users and
Web interfaces. wiCPN is an extension of CPNs,
maintaining several of its characteristics, but with re-
finements such as: classification of places into re-
sources, system screens and ports; differentiation be-
1
http://cpntools.org/
tween ordinary and conditional transitions and usage
of a color to represent interactive flow. Explaining our
model accurately, a Web Interaction Modeling Using
Colored Petri Nets is a 9-tuple: wiCPN = ( Σ
wi
, P
wi
,
T
wi
, A
wi
, N
wi
, C
wi
, G
wi
, S
wi
, I
wi
); where:
• Σ
wi
= < Col, Active >, a non-null set of col-
ors and types, compound by Col – a finite group
of colors or types that determines the functions
which can be used in the net – and Active – a re-
served color that must be used in the modeling;
• P
wi
= { < r
1
, r
2
, ... , r
t
> ∪ < s
1
, s
2
, ... , s
b
>
∪ < p
1
, p
2
, ... , p
r
> }, a set of places formed
by three subsets: available resources (r), system
screens (s), and input/output ports (p);
• T
wi
= { < f
1
, f
2
, ... , f
m
> ∪ < c
1
, c
2
, ... , c
n
> },
a set of transitions formed by two subsets: flow
transitions (f ) and conditional transitions (c);
• A
wi
= a finite and disjunct set of arcs, such that
P
wi
∩ T
wi
= P
wi
∩ A
wi
= A
wi
∩ T
wi
=
/
0;
• N
wi
: A
wi
→ P
wi
× T
wi
∪ T
wi
× P
wi
, a set of nodal
functions that maps every arc into a resulting pair
whose first element is the source node and the sec-
ond one is the destination node;
• C
wi
: P
wi
→ Σ
wi
, a group of color functions which
map each place into color sets or multisets;
• G
wi
: c → bool, a set of guards which map each
conditional transition into a boolean expression;
• S
wi
: A
wi
→ colSet ⊂ Σ
wi
, a set of arc schemas
that map each arc into a color set expression sub-
set of Σ
wi
;
• I
wi
= an initialization function which maps each
place into an expression whose result is a multiset
over the places’ colors.
After these descriptions, it is possible to recognize
some elements’ characteristics in nets modeled with
the wiCPN approach using CPN Tools:
• Places are specified as (a) resources, (b) sys-
tem screens or (c) (d) input/output ports – which
are depicted in Figure 3 and distinguished by
green, purple and blue colors, respectively. Re-
sources represent conditions and system require-
ments, such as security issues that enable users to
access specific system screens. Input/output ports
can be stylized in two ways: (c) with a single bor-
der – while appearing in upper parts of the model
– or (d) with a double border and an in/out tag
– in lower parts of the model, representing inter-
connectivity among modules. Input/output ports
represent paths that connect system screens, such
as interface buttons and links.
AUser-centeredApproachforModelingWebInteractionsUsingColoredPetriNets
39

Figure 3: Some places modeled using wiCPN.
• Places can depict resources and input/output ports
simultaneously (Figure 4(a)) or system screens
and input/output ports (Figure 4(b)). This hap-
pens when resources or system screens are bound
to hierarchic transitions and, in this case, they are
stylized with a double border while appearing in
lower modules of the model.
Figure 4: Places portraying a double role.
• Color Active is reserved and must be assigned
only in two cases: to input/output ports connected
to hierarchical transitions – as seen in Figures 3(c)
and 3(d) – and to a single token that controls the
interaction activity of the model. Both cases can
be observed in Figure 5, where (a) portrays Lo-
gin assigned to color Active and (b) depicts the
color’s declaration while being attributed to act.
Figure 5: Declaration and usage of color Active.
• Lastly, transitions (Figure 6) depict two kinds of
flows: ordinary ones, which are stylized in black
and called flow transitions (e.g., chkLogin), and
those that depend on conditions, which are de-
picted in red and named conditional transitions
(e.g., loginFalse and loginTrue). Flow transitions
show up in the whole modeling in order to depict
existing common fluxes, while conditional tran-
sitions appear in circumstances where system re-
sources are checked by the model.
With these refinements, it is possible to observe
that wiCPN approach proposes a new manner of rep-
resenting interactions during software modeling ac-
tivities. While using this extension, generated models
are visualized as navigation maps, able to illustrate
existing interactive flows in systems interfaces.
Figure 6: Some transitions modeled using wiCPN.
4 PUTTING wiCPN TO WORK
In order to validate wiCPN, we modeled the Web
front-end interaction of Classroom eXperience (CX),
a ubiquitous educational system that currently is used
in a real ULE. To explain how it proceeded, we first
present CX and then demonstrate how we applied
wiCPN to model CX’s interaction, verifying the de-
veloped model by making use of a state space method.
4.1 Classroom Experience
CX
2
is a ubiquitous computing platform for captur-
ing, storing and accessing content from educational
environments (Ferreira et al., 2012). CX allows in-
structors to lecture in a dynamic and unobtrusive way,
also assisting students while accessing captured con-
tent (Ara
´
ujo et al., 2013). As a typical Capture and
Access (C&A) platform, CX aims at recording live
experiences and making their information available
for later access. Currently, CX has been used in class-
rooms equipped with video cameras, microphones,
projectors and electronic whiteboards (Figure 7).
Figure 7: Classroom equipped with camera, microphone,
multimedia projectors and an electronic whiteboard.
Instructors are able to interact with the electronic
whiteboard as if they were using a traditional white-
board or a chalkboard. During a regular interaction
flow of the system, instructors could, for instance,
access CX’s Web front-end and set up some infor-
mation before the class, such as lecture title, key-
words, abstract, duration and slides file. When ar-
riving into classroom to start lecturing, they access
2
http://cx.facom.ufu.br/
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
40

the Web front-end and download the lecture content
to present it to students. At this moment, they teach
without changing their conventional style while CX
captures content being presented by means of special-
ized hardware and software components. After the
recording phase, captured media streams are synchro-
nized, stored and made available for students.
CX provides a customized access based on per-
sonal information to display lectures according to
user needs. Students can interact with captured con-
tent through tags and comments made over the lec-
ture content. Such annotations are shared with other
students, thus extending and enriching the originally
captured information. Moreover, instructors are able
to register the assignments’ dates and subjects, which
will be displayed to students and used for content rec-
ommendation and personalization.
As can be noticed, students and instructors are dis-
tinct user roles, implying in different system permis-
sions. While the former can solely get enrolled in
courses to access captured lessons and interact with
other users, the latter can also create courses, register
lectures and perform their capture, besides being able
to register metadata such as the lesson difficulty level
or the aforementioned assignments calendar.
4.2 Modeling CX’s Interface
With wiCPN ’s refinements in mind, we modeled the
interaction of CX’s Web front-end, employing our
method’s characteristics to achieve better visualiza-
tion and understanding of the model. As a result, Fig-
ure 8 depicts the high modeling level. Hierarchical
transitions (e.g., LoginScreen, MainScreen, among
others) represent screens and are composed by sub-
nets which contain the whole activity that takes place
inside of each transition. This happens because every
system screen becomes hierarchical – as each one of
them has an inherent flow with particular conditions
– and these characteristics are substantial in order to
enable the correct modeling of CX’s interactions.
It is also possible to recognize the input/output
ports in Figure 8. As they are currently in the top
level of the modeling, they are directly connected to
the module’s hierarchical transitions. Nevertheless,
when the abstraction level goes deeper, input/output
ports get stylized with double blue borders, in addi-
tion to their In, Out and In/Out markings, which can
be observed in Figure 9. Indeed, Figure 9 depicts the
whole interaction flow which happens inside of Main-
Screen. As already depicted in Figure 8, MainScreen
is connected to many other pages, so in Figure 9 it is
assigned with a homonym multiset composed by the
union of colors which lead to each one of the other
system screens presented in the module.
Exemplifying an ordinary interaction flow, the
first thing a user does during a common attempt to
login into CX is to access the interface login page –
represented in Figure 8 as the hierarchical transition
LoginScreen. When this action happens, LoginScreen
becomes active, as the token “act” sensitizes a tran-
sition named inLog – previously shown in Figure 1
(which illustrates a slice of LoginScreen module’s in-
teraction flow).
After being authenticated, the user reaches the in-
put port Initial – identifiable on Figure 8 as the place
just after LoginScreen’s transition and on Figure 9 as
the first element of MainScreen’s module. At this mo-
ment, the flow proceeds to another validation, where
the system checks whether the user is a student or an
instructor. In case the user is a student, the condi-
tional transition StuAut becomes sensitized, carrying
the token “act” to the leading screen of the system –
represented as place MainScreen in the model. How-
ever, if the user is an instructor, transition InstAut be-
comes sensitized instead and the token “act” reaches
the system’s leading screen at the same time the to-
ken “perm” arrives into place InstructorPerm, filling
it with resources and enabling instructors to access
more features than students.
In this scope, a student can never access the func-
tionality for creating a new class – since this activity is
an instructor’s duty only –, and our model fully sup-
ports this restriction, as the In/Out port inAddClass
(visible in Figure 9) is not reachable by students, be-
cause the transition inAddC never gets sensitized.
4.3 Verifying the Model
While making use of CPN Tools, it is also possible
to explore the modeled system’s behaviors using net
simulations, model checking and state space methods
(Jensen et al., 2007). In fact, a full state space can por-
tray all practicable executions of an analyzed model,
computing every reachable state and their changes,
while representing these in a directed graph. The fun-
damental concept behind a state space is to set up a
graph which has an arc for each binding element and a
node for every reachable marking. A modeling’s state
space is calculated automatically and this enables to
prove with mathematical meanings that it possesses
determined formal properties.
Figure 10 presents the graph we generated using
CPN Tools’ state space tool. The first node depicts
the marking previously shown in Figure 1 (the mo-
ment when a user accesses the login page). After this,
in node 2, user information can be inserted in order
to log into the system or introduced to register a new
AUser-centeredApproachforModelingWebInteractionsUsingColoredPetriNets
41

Figure 8: The top level of the modeling.
Figure 9: The MainScreen’s interaction flow when the user is an instructor.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
42
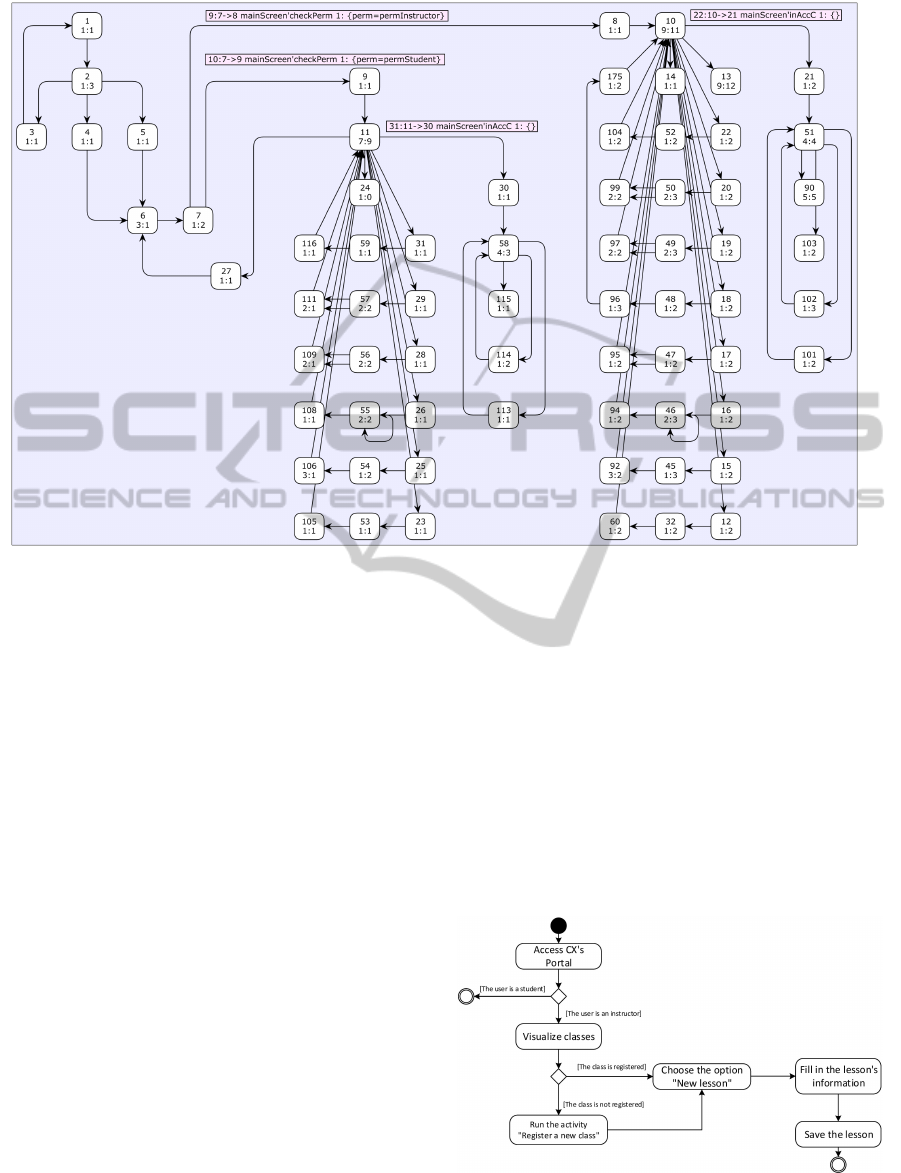
Figure 10: CX’s graph of reachability.
user – that is why the graph trifurcates. Consequently,
while nodes 4 and 5 respectively denote a successful
login and a new user registration – proceeding to node
6 –, node 3 represents an unsuccessful login and re-
turns the user to the login page (node 1).
Right ahead, node 7 represents when the system
validates whether the user is a student or an instructor,
as depicted in Figure 9. In case he/she is an instruc-
tor, the interaction proceeds to node 8, while a stu-
dent flow would advance to node 9. At this moment,
it is perfectly clear to notice that a student reachabil-
ity is inferior if compared to the states an instructor
can reach. Also, nodes 10 and 11 illustrate the sys-
tem’s main screen, but in different user perspectives.
While in node 10 an instructor can access every sys-
tem screen, node 11 shows that students reach a re-
duced amount of pages.
5 USER EXPERIMENTS
For the user-based experiments, we applied a ques-
tionnaire to 30 undergraduate Computer Science stu-
dents enrolled in a Human-Computer Interaction
(HCI) course. Students were used to work with in-
teractive flows on a regular basis, in the context of the
HCI course. A few of them have had previous expe-
rience with UML language, but no student have had
previous contact with Petri Nets.
We separated students into two groups of 15. To
the first group, we presented a 15-minute briefing
about UML language and then presented a couple of
interactive flows modeled with UML activity and use
case diagrams (some of the models that were used can
be seen in Figures 11 and 12). To the second group,
we also presented a 15-minute briefing about wiCPN
and presented the same interactive flows, but modeled
with wiCPN. Since we aimed to analyze users under-
standing capability of several interactive issues, we
did not employ swimlanes, but instead we modeled
activity flows as clear as possible in UML diagrams.
Figure 11: “Register a new class” UML activity diagram.
After studying their corresponding (either UML
AUser-centeredApproachforModelingWebInteractionsUsingColoredPetriNets
43
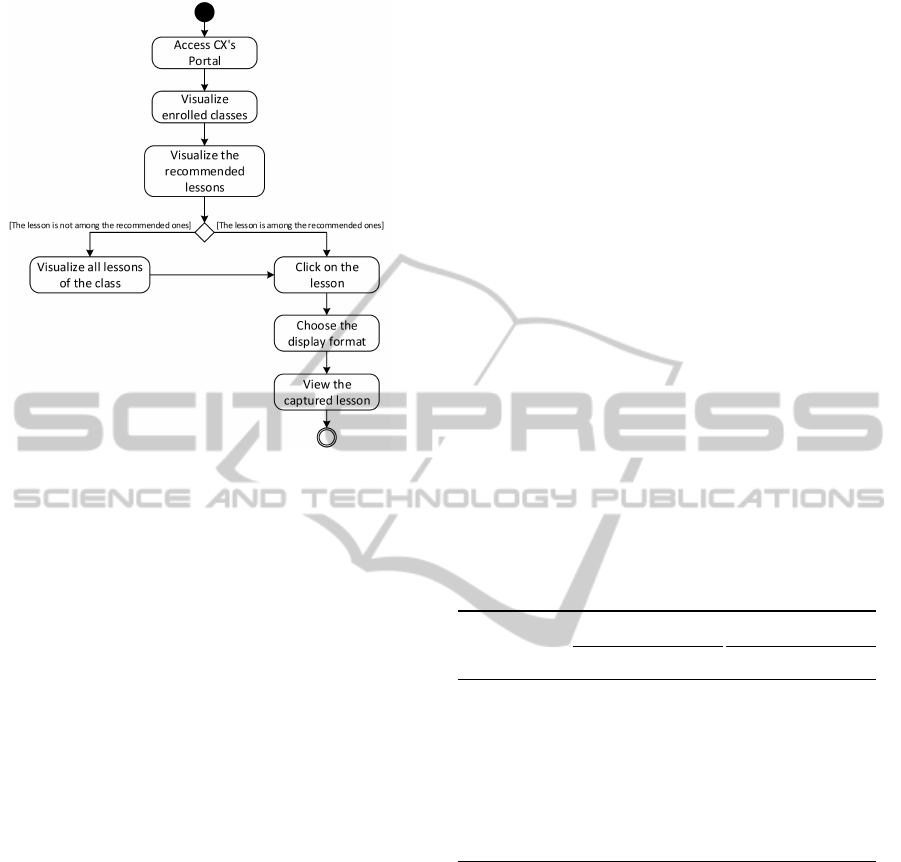
Figure 12: “Access captured lesson” UML activity diagram.
or wiCPN ) diagrams, each student answered a ques-
tionnaire to assess his/her understanding about the
modeling of the interactive flows. The questionnaire
comprised 12 affirmatives to which the student should
mark his/her agreement level in a 1-to-7 Likert scale
(being 1 - Completely disagree, 2 - Disagree, 3 - Par-
tially disagree, 4 - Neutral, 5 - Partially agree, 6 -
Agree, and 7 - Completely agree):
1. The modeling of the interactive flows is intuitive.
2. In the presented modeling, there are screens with-
out well-defined purposes.
3. I can understand which activities are available for
each type of user.
4. Information about my current screen is not always
available in the model.
5. From my current screen, I can always realize
which other screens I can access.
6. It is not possible to implement all functions pre-
sented in the model.
7. I cannot understand the interactive flow repre-
sented in the model.
8. I can understand the purpose of all screens in the
presented modeling.
9. The permissions granted for each type of user are
not clear.
10. I always know my current screen in the model.
11. I cannot figure out which screens I can access
from my current screen.
12. The modeling provides all information necessary
to implement the presented functions.
We employed a reversed and negated items
method for detecting insufficient effort in responding
our survey in order to legitimate user answers (Huang
et al., 2012). As can be noticed in our questionnaire,
pairs of different affirmatives express the same ideas
with opposite meanings: pair 1-7 examines general
understanding of the modeling, pair 2-8 verifies the
intended purpose of screens, pair 3-9 is related to the
proper identification of user options and permissions,
pair 4-10 contemplates current user location in the in-
teractive flow, pair 5-11 covers the screen reachability,
and pair 6-12 regards model completeness.
We assumed that students would respond to each
pair with opposite opinions. This way, to evaluate the
questionnaire items properly, the second affirmative
of each pair should be reversed in the Likert scale (i.e.,
a 1 becomes a 7, a 2 becomes a 6, and so on). After
invalidating contradictory answers, we then computed
the mean ( ¯x), standard deviation (s) and coefficient of
variation (CV) for each pair of answers among the two
groups of students. Results are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Mean, standard deviation and coefficient of varia-
tion of students’ responses to questionnaires.
Affirmatives
1
UML wiCPN
¯x ± s CV (%) ¯x ± s CV (%)
1 and 7 4,20±2,01 47,79 5,40±1,06 19,55
2 and 8 5,13±1,85 35,97 2,40±0,83 34,50
3 and 9 5,33±1,72 32,22 6,00±0,85 14,09
4 and 10 3,20±1,08 64,91 2,27±0,96 42,40
5 and 11 4,87±2,10 43,15 6,27±0,70 11,23
6 and 12 3,60±2,03 56,34 2,33±1,35 57,65
1
Each pair’s second affirmatives had their results inverted
and incorporated into the first ones, in order to nullify
or highlight responses given in first items; UML: Unified
Modeling Language; wiCPN : Web Interaction Modeling
Using Colored Petri Nets; ¯x ± s: Mean and standard de-
viation; CV : Coefficient of variation.
Results show that students from the second group
(wiCPN) presented mean values with higher partial-
ity and lower deviations than students from the first
group (UML). Besides that, for most pairs, CV val-
ues were lower for wiCPN – except for the last pair,
which surpassed it in 1.31%. Such results demon-
strate that wiCPN scored adjacent and uniform levels,
ensuring high homogeneity in opinions and reinforc-
ing that our approach was well-accepted and evalu-
ated among students that used it.
Figure 13 shows the frequency of answers ob-
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
44

tained in questionnaires. Since the affirmatives pre-
sented in questionnaires alternated positive and neg-
ative ideas, we expected students to express agree-
ments in pairs 1-7, 3-9 and 5-11, while pairs 2-8, 4-
10 and 6-12 were expected to be susceptible to dis-
agreements. Following the same order of pairs in both
samples, scores given by students that used wiCPN
were more tendentious than those from students that
used UML. While in the first column (UML) stu-
dent opinions appear to be divided, the second column
(wiCPN) shows strong trends (either to agreement or
disagreement) in each pair of given answers.
Figure 13: Frequency of answers obtained in student ques-
tionnaires. UML scores showed divided opinions, while
wiCPN presented clear tendencies for agreement in pairs
1-7, 3-9 and 5-11, and disagreement in 2-8, 4-10 and 6-12.
More than 30% of students from the first group
(UML) affirmed that the modeling of interactive flows
was not intuitive. In the same group, half of the stu-
dents informed that screens had no clear purpose – no
similar answer was observed among students from the
second group (wiCPN ). Furthermore, almost 20% of
the students that used UML declared they could not
understand which activities were available for each
type of user, while only 5% of students that used
wiCPN reported the same difficulty.
Among those who used UML, about 30% revealed
having trouble to identify their current screen and,
from there, to which other screens they could move
in the modeling. No student using wiCPN reported
such problems. Finally, more than 40% of students
asserted that it was not possible to implement all
the functionalities using only the provided UML di-
agrams, something pointed out by less than 5% of the
students that used wiCPN.
6 RELATED WORK
An interesting work found in literature is UITD (User
Interface Transition Diagram), a modeling notation
for representing shifts that happen in interfaces, be-
ing also able to trigger determined transitions based
on their specific conditions (G
´
omez and Cervantes,
2013). UITD notation results in pseudo-digraphs (di-
rected graphs whose transitions have a possibility of
looping), where vertexes denote user interface presen-
tations and directed edges depict transitions.
Since UITD is a variation of well-acquainted State
Transition Diagrams – also known as State Charts
(Harel, 1987) – and its notation extends State Charts’
modeling scope to an interaction range, existing tool
support (such as Yakindu
3
) is not able to fully repre-
sent UITD ’s graphs. Noticeably, the approach we in-
troduce in this work is also based on an existing mod-
eling language: CPNs. Nevertheless, wiCPN makes
use of a specific tool suite for generating, editing, sim-
ulating and making full analysis of CPN models. As
UITD does not have an exclusively CASE tool for
supporting its generated graphs, its modeling activi-
ties end up being performed on applications originally
developed for other purposes or, even, without mak-
ing any use of proper tools.
MoLIC (Modeling Language for Interaction as
Conversation) comprises a model focused on HCI
specifications (Sangiorgi and Barbosa, 2009). Pro-
posed to be incorporated into the UML family,
MoLIC represents interactions as conversation top-
ics. However, since each conversation thread is repre-
sented by scenes constructed using natural languages
and user perspectives, the model is subjugated to am-
biguity and subjectivity.
Another approach for modeling applications by
making use of UML and with focus on representing
mobile Web interfaces was also encountered (Vera
et al., 2012). Based on processes defined by OOHDM
(Object Oriented Hypermedia Design Method), their
work unified activities of interaction modeling by us-
ing two UML diagrams: a component diagram for
3
http://statecharts.org/
AUser-centeredApproachforModelingWebInteractionsUsingColoredPetriNets
45

representing interface navigation and a class diagram
for the domain modeling. Both diagrams were ex-
panded by making use of tag values and stereotypes.
As a conclusion, these extensions added further in-
formation to models and allowed their configuration,
what contributed to make code generation an easier
task during the development process. Although their
proposed methodology clearly brought formalization
gains, it is focused merely on the specification of mo-
bile Web applications. Otherwise, wiCPN method
configures a different scope, focusing on user interac-
tions which may originate from several different de-
vices, such as computers, notebooks, cellphones and
tablets – requiring only the need of a Web browser
installed in these equipments.
Being recently adopted as a new standard by
OMG (Object Management Group), IFML (Interac-
tion Flow Modeling Language) was developed to rep-
resent user interactions, application contents and con-
trol behaviors of software front-ends (Rossi, 2013).
IFML includes a set of graphical notations capable of
generating visual models which aim at depicting in-
teraction flows and interface behaviors, with a main
focus on structure and front-end activities perceivable
by users. An IFML diagram consists of view con-
tainers that represent user interface windows or Web
pages. These containers can have elements called
view components which can hold input and output
parameters. Both containers can be associated with
events, in order to express their support to user inter-
actions. However, despite being dedicated to specify
user interaction dynamics in interface applications,
IFML’s hypertext modeling is recent and lacks an
appropriate and organized base of notations, concep-
tions and design methods (Gal-Chis, 2013). Also,
IFML does not address the modeling of presentation
issues, e.g., layouts and styles of application front-
ends (Rossi, 2013). This may have occurred because
IFML is an extension of WebML (Web Modeling
Language), a Web designing notation first defined in
early 2000’s and which experienced just about ten
years of use. As IFML is currently in Beta version,
adjusts are likely to be performed for giving the lan-
guage more confidence in its field. Our approach, on
the other hand, makes use of CPNs – which are based
on Petri Nets, a language for describing systems first
documented in 1962 (Petri, 1962) and widely spread
and extended since then (Silva, 2013) –, what quite re-
inforces the strengths and breadth of usage that Petri
Nets bring to the systems modeling domain.
Another work found in the literature presented
an interaction model of a smart community cyber-
physical system called Net-in-Net (Ma et al., 2010).
As elucidated by the authors, cyber-physical systems
are environments which integrate physics with Inter-
net in order to provide efficient, confidential and op-
portune interactions between applications and users.
Since their work aims at representing interaction
flows of a complex system characterized by security,
stability and reliability issues, it should have been for-
malized by making use of a proper robust and verifi-
able language. However, Net-in-Net interactivity was
modeled by making use of simple flow charts, result-
ing eventually in subjective models.
This subjectivity also happens in another work,
where a vocabulary for web user interface design is
proposed (Tena et al., 2013). As it compiles terms
that are constantly changing and being substituted,
its reuse becomes nearly impractical (since the re-
sult is at the mercy of time misconceptions) and the
generated vocabulary has wispy usage for other re-
searches. A cognitive model for representing inter-
actions between drivers and vehicles was also found
(Ciardelli et al., 2011). Proposed to consider user be-
haviors and detect potential dangerous situations, the
work presented an approach to the analysis and mod-
eling in automotive applications and exploited a sim-
ulation platform and a sensor network assembled in
vehicles. As a conclusion, authors showed prelimi-
nary results demonstrating the method practicability
and discussed how a continued research could bring
improvements for human safety oriented applications.
With a few resemblances to our approach while
concerning to Petri Nets theory, ICOs (Interactive Co-
operative Objects) is an object Petri Nets-based inter-
face description language for engineering and devel-
opment of applications (Martinie et al., 2014). ICOs’
associated CASE tool, named Petshop (which stands
for Petri net workShop), is able to provide support for
the design, specification, prototyping, and validation
processes of interactive software.
While sharing the benefits of a concrete ba-
sis in formal language notations, ICOs also makes
use of concepts borrowed from the object-oriented
paradigm, such as dynamic instantiation, encapsu-
lation and inheritance. For a correct use of such
paradigm, an object Petri Net dialect had to be used
in order to comprehend the object-orientation’s whole
scope. Therefore, plenty of skills – not only in user
interface design, but also in object-oriented program-
ming, Java language, implementation and Petri Nets-
based modeling – are required to represent correctly
the interactive applications while using ICOs, what
inevitably induces a high learning curve for making
engineers able to work on the projects.
In another work, a Petri Net based framework to
support design, implementation and verification of
animated interfaces in a two-levels process is pre-
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
46

sented (Mirlacher et al., 2012). While the higher level
view of the approach focuses on interactive objects,
considering their properties and composition of ani-
mations, the lower level stands for temporal aspects,
caring about usage of interpolation and possible con-
nection issues with rendering hardware. This model
gets rather complex as it handles both inter-objects’
animated properties and the whole orchestration of
animation shifts that may happen when systems per-
formance is lower than expected. Designing inter-
faces that concern about potential degradation is a
heavy burden for engineers who have to be aware of
computer animation issues and numeric analysis ap-
plication, to distinguish in a quick and efficient way
which and how animations should be degraded.
Unlike these last works, wiCPN approach was
made to be visual and intuitive – while making use of
a formal modeling language capable of verification.
This way, our work comprehends a method for gen-
erating models that professionals from various fields
can understand and clearly see how their interaction
flows behave, thus being able to contribute better with
the underlying processes of systems modeling.
To synthesize the discussions held in this section,
Table 2 presents all related works concerned to inter-
action modeling that were perceived throughout the
text. A criteria-based evaluation conducted by our re-
searchers was able to show that all approaches have
positive traits and certain gaps that justify why they
are used in more specific contexts. The approaches
were judged based on six different criteria: (a) ex-
istence of a specific CASE Tool that fully supports
the method; (b) approach’s ability of modeling the
interaction of Web front-ends; (c) generated models’
ease of understanding; (d) no prior obligation to learn
other contents to properly use the technique; (e) if the
approach was based on a formal language; and (f)
method’s ability to comprise security requirements,
such as user authentication. For measuring each cri-
terion, three levels of incidence were stipulated: an
empty circle (#) for approaches that lack a specific
criterion; a circle in half (G#) to works which partially
fulfill a criterion; and a full circle ( ) to those ones
that entirely comprehend a established criterion.
As noted in Table 2, the approaches of (Ma et al.,
2010), (Tena et al., 2013) and (Ciardelli et al., 2011)
do not have exclusive CASE Tools for applying their
methods. This absence may lead to inconsistencies,
such as erroneous representations of interactive flows,
inducing problems of misunderstanding models. Fur-
thermore, most works demonstrate some ability to
represent interactions of Web interfaces, even if par-
tially. However, several details of interactivity are lost
in some studies – such as in (Sangiorgi and Barbosa,
Table 2: Evaluation of analyzed approaches.
Works (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f)
(G
´
omez and Cervantes, 2013) G# G# G#
(Sangiorgi and Barbosa, 2009) G# G# G# #
(Vera et al., 2012) G# G# #
(Rossi, 2013) G# G#
(Ma et al., 2010) # G# G# #
(Tena et al., 2013) # G# # #
(Ciardelli et al., 2011) # # G# G# # #
(Martinie et al., 2014) G# # #
(Mirlacher et al., 2012) # #
wiCPN G# G#
2009), (Vera et al., 2012) and (Ciardelli et al., 2011) –
and this occurs because not all formalization methods
were exclusively created for this purpose.
Among listed approaches, (Martinie et al., 2014)
and (Mirlacher et al., 2012) were the ones that gen-
erated models with the highest difficulty level of un-
derstanding. This is justified by the fact that these
works also involve the greatest amount of knowledge
required in different areas to be previously understood
by professionals who aim to use them. Furthermore,
half of the works did not present any grounding or
usage of formal methods in their approaches. Dur-
ing cases of complex systems specification, such as
in (Ma et al., 2010) and (Ciardelli et al., 2011), the
use of verifiable formalizations shows up as a rele-
vant practice, thanks to the possibility of perceiving
and fixing errors during early stages of software de-
velopment processes.
7 CONCLUSION
This paper introduced wiCPN (Web Interaction Mod-
eling Using Colored Petri Nets), a language for rep-
resenting Web interactions with improved notation
and semantics. Designed as an extension of CPNs,
wiCPN brings together the strengths of CPNs with a
high level graphical notation that was able to refine
the model components and represent interaction in a
structured and intuitive way. By allowing the creation
of hierarchies, wiCPN stimulates the refinement and
better organization of the generated models.
As a case study, our approach was tested in a
real ULE with modeling and verification of Class-
room eXperience’s Web front-end. Generated mod-
els were replicated in UML and, together, served as
a basis for a detailed user experiment. Results from
AUser-centeredApproachforModelingWebInteractionsUsingColoredPetriNets
47

user experiments demonstrated wiCPN to be a con-
cise and intuitive notation, capable of simplifying the
design process and, thus, avoiding redundancies and
inconsistencies. With good expressiveness, our lan-
guage was able to propitiate better understanding of
the whole interactive process, by presenting both the
connections among the system screens and the actions
associated to every possible flow.
Furthermore, wiCPN was also capable of portray-
ing the many access levels of different user types, re-
specting the roles they play in the system and the con-
tent and activities they are allowed to see and perform.
This point demonstrated the language’s capability of
comprehending issues that concern to systems secu-
rity requirements and can also serve as a basis for fu-
ture work in this scope.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the Brazilian research
agencies FAPEMIG (grant APQ-04627-10), CAPES,
CNPq (grant 445500/2014-0) and PROPP/PPGCO
for supporting this work.
REFERENCES
Ara
´
ujo, R. D., Brant-Ribeiro, T., Cattelan, R. G., Amo, S.
A. d., and Ferreira, H. N. (2013). Personalization of
Interactive Digital Media in Ubiquitous Educational
Environments. In Proc. of the IEEE SMC’13, pages
3955-3960, Manchester, UK.
Bowen, J. and Reeves, S. (2007). Using formal models to
design user interfaces: A case study. In Proc. of the
21st BCS HCI, pages 159-166.
Choosang, S. and Gordon, S. (2014). A Coloured Petri
Net Methodology and Library for Security Analysis
of Network Protocols. JCP, 9(2):243-256.
Ciardelli, L., Bixio, L., and Regazzoni, C. (2011). Inter-
action Modeling in Automotive Applications: a Cog-
nitive Approach. In Proc. of the IEEE CogSIMA’11,
pages 248-251.
Clemmensen, T. (2012). Usability Problem Identification in
Culturally Diverse Settings. Inform Syst J, 22(2):151-
175.
Ferreira, H., Ara
´
ujo, R., de Amo, S., and Cattelan, R.
(2012). Classroom Experience: A Platform for Mul-
timedia Capture and Access in Instrumented Educa-
tional Environments. In Proc. of the SBSC’12, pages
59-64.
Gal-Chis, C. (2013). Web Application Methodologies With
RE Tools Support. IJCT, 11(3):2314-2320.
Gehlot, V. and Nigro, C. (2010). An Introduction to Sys-
tems Modeling and Simulation with Colored Petri
Nets. In Proc. of the WSC’10, pages 104-118.
G
´
omez, M. and Cervantes, J. (2013). User Interface Transi-
tion Diagrams for Customer-Developer Communica-
tion Improvement in Software Development Projects.
JSS, 86(9):2394-2410.
Harel, D. (1987). Statecharts: A Visual Formalism for
Complex Systems. Sci Comput Program, 8(3):231-
274.
Huang, J., Curran, P., Keeney, J., Poposki, E., and DeShon,
R. (2012). Detecting and Deterring Insufficient Effort
Responding to Surveys. J Bus Psychol, 27(1):99-114.
Jensen, K. (1994). An Introduction to the Theoretical As-
pects of Coloured Petri Nets. In A Decade of Con-
currency, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages
230-272. Springer-Verlag.
Jensen, K., Kristensen, L., and Wells, L. (2007). Coloured
Petri Nets and CPN Tools for Modelling and Valida-
tion of Concurrent Systems. STTT, 9(3):213-254.
Kim, D., Cimren, E., Havey, R., and Zaidi, A. K. (2012).
Improving Cluster Tools Performance Using Colored
Petri Nets in Semiconductor Manifacturing. In Proc.
of the WSC’12, pages 205:1-205:12.
Ma, L., Yao, J., Xu, M., Yuan, T., and Shao, M. (2010). Net-
in-Net: Interaction Modeling for Smart Community
Cyber-Physical System. In Proc. of the 7th UIC/ATC,
pages 250-255.
Martinie, C., Navarre, D., and Palanque, P. (2014). A Multi-
Formalism Approach for Model-based Dynamic Dis-
tribution of User Interfaces of Critical Interactive Sys-
tems. Int J Hum-Comput St, 72(1):77-99.
Mirlacher, T., Palanque, P., and Bernhaupt, R. (2012). En-
gineering Animations in User Interfaces. In Proc. of
the 4th ACM SIGCHI EICS, pages 111-120.
Nguyen, H. and Apon, A. (2012). Parallel File System Mea-
surement and Modeling Using Colored Petri Nets. In
Proc. of the 3rd ACM/SPEC, pages 229-240.
Petri, C. A. (1962). Communication With Automata. PhD
thesis, Universit
¨
at Hamburg.
Rogers, Y., Sharp, H., and Preece, J. (2011). Interaction
Design: Beyond Human-Computer Interaction. Wiley
Publishing, Chichester, UK, 3rd edition.
Rossi, G. (2013). Web Modeling Languages Strike Back.
Internet Computing, IEEE, 17(4):4-6.
Sangiorgi, U. and Barbosa, S. (2009). MoLIC Designer:
Towards Computational Support to HCI Design with
MoLIC. In Proc. of the 1st ACM EICS, pages 303-308.
Silva, M. (2013). Half a Century After Carl Adam Petri’s
Ph.D. Thesis: a Perspective on the Field. Annual Re-
views in Control, 37(2):191 - 219.
Sommerville, I. (2010). Software Engineering. Addison-
Wesley Publishing Company, Boston, USA, 9th edi-
tion.
Tena, S., D
´
ıez, D., D
´
ıaz, P., and Aedo, I. (2013). Standard-
izing the Narrative of Use Cases: a Controlled Vocab-
ulary of Web User Tasks. IST, 55(9):1580-1589.
Vera, P., Giulianelli, D., Rodriguez, R., and Pons, C. (2012).
User Interface and Navigation Modeling Methodol-
ogy for Mobile Hypermedia Systems. In Proc. of the
7th CCC, pages 1-6.
Weidlich, M., Mendling, J., and Gal, A. (2013). Net-
Based Analysis of Event Processing Networks: the
Fast Flower Delivery Case. In Proc. of the Petri
Nets’13, pages 270-290.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
48
