
Software Cost Estimation for Global Software Development
A Systematic Map and Review Study
Manal El Bajta
1
, Ali Idri
1
, Jos
´
e Luis Fern
´
andez-Alem
´
an
2
, Joaquin Nicolas Ros
2
and Ambrosio Toval
2
1
Software Project Management Research Team, ENSIAS, Mohammed V University, Rabat, Morocco
2
Software Engineering Research Group, Regional Campus of International Excellence “Campus Mare Nostrum”,
University of Murcia, Murcia, Spain
Keywords:
Systematic Mapping Study, Software Cost Estimation, Global Software Development.
Abstract:
Software cost estimation plays a central role in the success of software project management in the context of
global software development (GSD). The importance of mastering software cost estimation may appear to be
obvious. However, as regards the issue of customer satisfaction, end-users are often unsatisfied with software
project management results. In this paper, a systematic mapping study (SMS) is carried out with the aim of
summarising software cost estimation in the context of GSD research by answering nine mapping questions.
A total, of 16 articles were selected and classified according to nine criteria: publication source, publication
year, research type, research approach, contribution type, software cost estimation techniques, software cost
estimation activity, cost drivers and cost estimation performances for GSD projects. The results show that the
interest in estimating software cost for GSD projects has increased in recent years and reveal that conferences
are the most frequently targeted publications. Most software cost estimation for GSD research has focused on
theory. The dominant contribution type of software cost estimation for GSD research is that of models, while
the predominant activity was identified as being software development cost. Identifying empirical solutions to
address software cost estimation for GSD is a promising direction for researchers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Global Software Development (GSD) refers to soft-
ware work starting at geographically separated areas
across national boundaries considering synchronous
and asynchronous interaction. GSD has been adopted
by numerous companies. However, these global
projects confront a number of problems, which are
particularly linked to the gap between different par-
ticipants: physical distance between the groups of
developers causing a lack of trust, time-zone differ-
ences, communication problems among teams, effort
estimation problems, cultural differences, and oth-
ers. Current research tends to characterise these prob-
lems, but if success is to be achieved in GSD, compa-
nies must minimise challenges by adjusting their pro-
cesses and rearranging their tools and organisational
structure.
GSD projects can increase requirements as re-
gards development processes, project management
practices, architecture, quality, collaboration tools
and so on. These challenges may exceed the advan-
tages of the lower labour rates in the developing coun-
try since they could lead to substantial overheads in
the day-to-day operations of a GSD project. This rea-
soning shows that it is vital to understand and estimate
the total costs of GSD in order to help evaluate the
comparison with local software development in terms
of efficiency.
A large range of software cost estimation tech-
niques had already been developed before the GSD
trend began (Jørgensen, 2004). Early research on the
topic was conducted in 2006 (Keil et al., 2006), when
researchers were able to promote analyses of project
factors in order to gain insights into the comparison
of development costs for distributed software devel-
opment projects and collocated projects. In a study
published in 2012 (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012),
researchers advance the question of cost estimation
for distributed software projects by identifying chal-
lenges and proposing solutions with which to better
drive estimates. Britto et al. (Britto et al., 2014)
present a systematic literature review on effort esti-
mation in GSD. In their study, only 5 papers were se-
lected, which allowed the extraction of only 10 esti-
mation methods. It is important to note that the study
of Britto et al. did not consider software maintenance
effort/cost estimation; it only concerned software de-
197
El Bajta M., Idri A., Fernández-Alemán J., Nicolas Ros J. and Toval A..
Software Cost Estimation for Global Software Development - A Systematic Map and Review Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0005371501970206
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE-2015), pages 197-206
ISBN: 978-989-758-100-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

velopment effort/cost estimation. What is more, the
study did not classify the techniques according to
their contribution type. Considering the importance
of the above limitations, the objective of this study is
to carry out a systematic review which: 1) includes 16
selected papers among them the 5 ones of Britto et al.,
2) considers software development as well as mainte-
nance effort estimation, and 3) discusses effort/cost
estimation performance.
The paper is structured as follows: Sect. 2
presents the research method used in the study. Sect.
3 reports the results and findings obtained from the
SMS. Sect. 4 outlines threats to validity. Sect. 5 dis-
cusses the main findings and presents implications for
researchers and practitioners, while our conclusions
and future work are presented in Sect. 6.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
2.1 Mapping Questions
The SMS was performed to obtain the current
research on software cost estimation for GSD. This
study answers nine mapping questions (MQs). These
questions are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Mapping questions.
ID Mapping question
MQ1 Which publication sources and channels are
the main targets for software cost estimation
for GSD research?
MQ2 How has the frequency of software cost esti-
mation for GSD research changed over time?
MQ3 What are the research types of software cost
estimation for GSD studies?
MQ4 Which research approaches are used in soft-
ware cost estimation for GSD studies?
MQ5 What are the contribution types of software
cost estimation for GSD research?
MQ6 Which cost estimation techniques are most
frequently used for GSD projects?
MQ7 Which software cost estimation activities have
been addressed by GSD research?
MQ8 Which cost drivers affect GSD projects?
MQ9 Which cost estimation performances have
been obtained from GSD projects?
2.2 Search Strategy and Paper Selection
Criteria
The articles were identified by consulting the follow-
ing sources: IEEE Xplore digital library, ACM digital
library, ScienceDirect and Google Scholar. The fol-
lowing search string was used in order to perform the
automatic search in the digital libraries selected:
(Software OR system* OR application*) AND
(cost OR effort OR resource) AND (estimat* OR
plan* OR predict* OR measur* OR calcul* OR
manage* OR control*) AND (Global development
OR distributed development OR outsourc* OR Off-
shor* OR Dispersed development). This search string
was applied to the title, abstract and keywords of the
papers to reduce the search results. Each paper was
retrieved by the first author and specific information
of each relevant paper was filled in an Ms Excel file.
The aim of the selection process was to identify
the most relevant studies for this mapping study. Each
paper was retrieved and evaluated by one author who
decided whether it should be included by consider-
ing its title, abstract and keywords. The final selec-
tion result was reviewed and approved by the remain-
ing authors. The first step after the articles had been
identified was to eliminate duplicate titles, and titles
which were clearly not related to the review (16 se-
lected studies out of 103 relevant studies). The inclu-
sion criteria were limited to those studies that focused
on software cost estimation for GSD projects, and any
studies that met at least one of the following exclusion
criteria (EC) were excluded:
• EC1. Papers that are not published in journals,
conferences or workshops.
• EC2. Papers that are not in English.
2.3 Quality Assessment (QA) Process
The QA in an SMS is a major focus that increases
the depth of a study. In order to enhance our study,
a questionnaire was therefore designed to assess the
quality of candidate papers. The scoring used in this
questionnaire was determined on the basis of previous
studies (Idri et al., 2015), (Ouhbi et al., 2013b) and
(Ouhbi et al., 2013a).
(a) The paper has been published in a recognized and
stable journal or conference. This question was
rated by considering the computer science confer-
ence rankings in the Computing Research and Ed-
ucation (CORE) 2013 Conference Rankings, and
the 2013 Journal Citation Reports. The possible
answers to this question were:
• For conferences: (+2) if it is ranked CORE
A*; (+1.5) if it is ranked CORE A; (+1) if it
is ranked CORE B; (+0.5) if it is ranked CORE
C; (+0) if it is not in CORE ranking.
• For journals: (+2) if it is ranked Q1; (+1,5) if it
is ranked Q2; (+1) if it is ranked Q3; (+0.5) if it
is ranked Q4; (+0) if it is not in JCR ranking.
ENASE2015-10thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
198

(b) The main focus of the paper is software cost es-
timation activities used to deal with GSD chal-
lenges. Yes (+1); Partially (+0.5); No (+0)
(c) The study is complete and discusses the results
obtained. Yes (+1); Partially (+0.5); No (+0)
(d) The study is empirical and presents relevant re-
sults for our SMS. Yes (+1); No (+0)
2.4 Data Extraction Strategy
The data extraction strategy was based on providing
the set of possible answers to the MQs. The strategy
is explained below:
MQ1. In order to answer this question, it is necessary
to identify the publication source and channel for each
paper.
MQ2. In order to discover the publication trend, the
articles should be classified per publication year.
MQ3. A research type can be classified into the fol-
lowing categories:
• Evaluation research: existing software cost esti-
mation for GSD approaches are implemented in
practice and an evaluation of them is conducted.
• Solution proposal: a solution for software cost es-
timation for GSD is proposed. This solution may
be a new software cost estimation for a GSD ap-
proach or a significant extension of an existing ap-
proach.
• Other, e.g. opinion paper, experience paper.
MQ4. The research approach can be classified as be-
ing:
• A case study: an empirical inquiry that inves-
tigates a software cost estimation approach for
GSD within its real-life context.
• A survey: a method used to collect quantitative
software cost estimation for GSD information.
• A experiment: an empirical method applied un-
der controlled conditions in order to observe its
effects on software cost estimation in the GSD
context.
• A review: an analysis of software cost estimation
for existing GSD literature.
MQ5. A contribution can be classified as being:
• A technique: a procedure used to accomplish a
software cost estimation for a GSD task. e.g. a
data mining technique.
• A model: a representation of a system that allows
software cost estimation for GSD properties to be
investigated.
• Other, e.g. process, tool.
MQ6. Several cost estimation techniques for GSD
projects have been used in the last few decades. These
techniques can be classified as (Wen et al., 2012) and
(Jorgensen and Shepperd, 2007):
• Expert judgment: this involves consulting a group
of experts in order to use their experience to pro-
pose an estimation of a given project (Hughes,
1996).
• machine learning models: Approaches that are
based on soft computing such as artificial neural
networks, fuzzy logic models and genetic algo-
rithms (Idri et al., 2006).
• non-machine learning models: these provide lin-
ear and non-linear regression models to establish
equations with which to perform software estima-
tion. (Boehm et al., 2000).
MQ7. Software cost estimation activities that were
addressed by GSD research can be categorised as:
• Software development cost: Performed by man-
agers and software system engineers for activities
such as functional design, software requirement,
development code, development tools, integration
of software and finally the test procedures.
• Software maintenance cost: Related to the con-
trol and the monitoring of the software after it has
been delivered to the final user, since there will
always be problems with the software as it gets
older
• Other, e.g. Reengineering cost
MQ8. Cost drivers that affect GSD projects are di-
vided into 4 categories, namely Product, Platform,
Personnel and Project factors (Boehm, 1981).
MQ9. In this paper, we focus on the two main criteria
that affect GSD projects: geographical and temporal
challenges and their influence on cost performance.
According to the PMBOK Cost Management knowl-
edge area, cost performance is included in three main
outputs of a GSD project:
• Cost Performance Baseline: An authorised time-
phased budget at completion used to measure,
monitor, and control overall cost performance on
the project.
• Work performance measurements: The calculated
cost variance for work packages and control ac-
counts
• Basis of estimates: The amount and type of ad-
ditional details supporting the cost estimate vary
according to the application area.
SoftwareCostEstimationforGlobalSoftwareDevelopment-ASystematicMapandReviewStudy
199

3 RESULTS
3.1 Quality Assessment
SMSs generally emphasise the quality of selected
studies. This QA is usually carried out to discover
the general view of the paper’s implication in the sub-
ject. However, Kitchenham et al. (Kitchenham and
Charters, 2007) specify that even if some researchers
use QA as a selection criterion in their systematic re-
view, this assessment is not mandatory for an SMS.
Table 2 provides information about the total score of
the selected studies. The majority of the selected pa-
pers (66.25%) have at least a medium score for qual-
ity, which shows that they contain useful information,
particularly as regards information on software cost
estimation and the impact of GSD projects on the cost
estimates. No studies were discarded from these in-
puts during the QA process.
Table 2: Quality levels of relevant studies.
Quality level Papers Percent (%)
Very high ( 4 < score 6 5) 1 6,25
High ( 3 < score 6 4) 1 6,25
Medium ( 2 < score 6 3) 7 43,75
Low ( 1 < score 6 2) 5 31,25
Very low ( 0 < score 6 1) 2 12,50
Table 3 shows the number of articles based on the
ranking of the conference or journal at/in which they
were published.
Table 3: Articles by their journal or conference rank.
Journals Number Conferences Number
Q1 1 CORE A* 1
Q2 2 CORE A 1
Q3 0 CORE B 0
Q4 1 CORE C 6
3.2 MQ.1: Source and Channel of
Publications
Table 4 provides a schematic representation of publi-
cation channels and the number of articles per publi-
cation source. Table 5 presents the journals and con-
ferences at which the papers selected for this SMS
were published. This result clearly shows that the
International Conference on Global Software Engi-
neering (ICGSE) is the main publication source for
our topic. With regard to journals, systems, software
and computer science journals are the targets of re-
searchers in the field.
Table 4: Publication channel.
Publication channels Selected papers Percent
Conference 11 68,75%
Journal 5 31,25%
Total 16 100%
Table 5: Journal (J) and Conferences (C) of selected studies.
Publication channels Type Total
International Conference on Global Soft-
ware Engineering (ICGSE)
C 4
Computer Science and Information Tech-
nology (CSIT)
C 2
Software Engineering International Con-
ference (ICSE)
C 1
SRII Global Conference (SRII) C 1
Software Engineering, Artificial In-
telligence, Networking and Paral-
lel/Distributed Computing (ACIS)
C 1
Services Computing, IEEE International
Conference (SCC)
C 1
Innovations in Information Technology
Conference
C 1
International workshop on Economics
driven software engineering research
(EDSER)
C 1
IEEE Software J 1
Advances in Software Engineering J 1
Systems and Software J 1
European Journal of Scientific Research J 1
3.3 MQ.2: Publication Distribution Per
Year
Fig. 1 shows the number of publications per year. The
amount of publications interested in software cost es-
timation for GSD projects has increased since 2006.
This year corresponds to the outset of the increasing
concern about the effect of globalization on the soft-
ware industry in general (da Silva et al., 2010) and
is also the year in which the first ICGSE conference
took place.
Figure 1: Publication per year.
3.4 MQ.3: Research Type
Sixty two percent of the selected articles are evalua-
tion research, while 25% of the selected papers are so-
ENASE2015-10thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
200

Figure 2: Research Type.
lution proposals. 12,50% are contained in the ”Other”
category, which comprises theoretical papers and ex-
perience papers. Fig. 2 divides the selected articles
by their publication date. The first column shows arti-
cles published before the year 2009, the second shows
those published between 2009 and 2011 and the last
shows those published since 2012.
According to the data shown in Fig. 2, the number
of evaluation research papers is low in comparison to
the number of solution proposals up until 2009. In
this period, estimation cost for GSD projects was a
relatively new subject that needed more investigation
and exploration. From 2012 on, the focus shifted to
the validation and evaluation of existing software cost
estimation methods for GSD projects.
3.5 MQ.4: Research Approach
Four of the selected papers are solution proposals.
Two of them were validated using experiments, while
the other two were not empirically validated. Five
out of 10 of the selected evaluation research studies
were based on theoretical approaches and 4 out of 10
were based on case studies, while not a single arti-
cle was based on an experiment. This situation may
result from the difficulty involved in observing the ef-
fects of methods on software cost estimation under
controlled conditions, particularly in the case of dis-
tributed projects in the GSD context. More details on
MQ.3 and MQ.4 are provided in Table 6.
Table 6: Research Types and Approaches.
Case
study
Experiment Survey Theory
Evaluation 4 0 1 5
Solution 1 1 0 2
Other 1 0 0 1
3.6 MQ.5: Contribution Types
Fig. 3 presents the distribution of the selected studies’
contribution types. Thirty eight percent of the cate-
gories are models. Techniques (Lotlikar et al., 2008)
Figure 3: Contribution types.
for the cost estimation of GSD represent 50% of the
selected studies’ types. These models gather data
mining techniques used to help researchers and soft-
ware companies establish data by providing a number
of algorithms and methods with which to deal with
software cost and effort challenges. Each of these data
mining techniques analyses data and provides results
with which to best match the software cost of a GSD
project. The third partition ”Other” represents only
twelve percent split between processes and tools.
3.7 MQ.6: Software Cost Estimation
Techniques
Several software estimation techniques can success-
fully be used to estimate costs. non-machine learn-
ing models (7 out of 16 selected studies) include CO-
COMO (II) (Keil et al., 2006), SLIM (Muhairat et al.,
2010), Use Case Points (Azzeh, 2013) and Function
Points (Peixoto et al., 2010). The use of expert judg-
ment (3 out of 16 selected studies) consists of asking
the opinion of multiple experts who use their experi-
ence and knowledge of the project to provide an es-
timation of the cost. An objective estimation is se-
cured by obtaining as many values as possible from
different experts. Indeed, the objective of the Delphi
technique (Peixoto et al., 2010) is to repeat the estima-
tion process until an agreement is established. Table 7
presents details of the cost estimation techniques used
for GSD projects.
3.8 MQ.7: Software Cost Estimation
Activities
About 80% of the selected studies discuss the soft-
ware development costs of GSD projects. These stud-
ies show the strong link between the software life cost
and its development phase. The second most frequent
topic after development cost is contained in the few
SoftwareCostEstimationforGlobalSoftwareDevelopment-ASystematicMapandReviewStudy
201

Table 7: Estimation techniques for GSD projects.
Type technique Estimation techniques Papers Percentage
non-machine
learning models
COCOMO(2) (Nassif et al., 2012), (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012), (Azzeh,
2013), (Muhairat et al., 2010), (Keil et al., 2006), (Lamers-
dorf et al., 2010)
85,7%
SLIM (Nassif et al., 2012), (Muhairat et al., 2010) 28,5%
Function points (Nassif et al., 2012), (Peixoto et al., 2010) 28,5%
Use case points (Nassif et al., 2012), (Azzeh, 2013), (Peixoto et al., 2010) 42,8%
Multiple Linear Re-
gression
(Nassif et al., 2012) 14,2%
Expert judgment Delphi (Nassif et al., 2012), (Peixoto et al., 2010) 28,5%
ISBSG (Nassif et al., 2012), (Muhairat et al., 2010) 28,5%
Planning Pocker (Peixoto et al., 2010) 14,2%
Epert Judgement (Peixoto et al., 2010) 14,2%
machine Artificial Intelligence (Humayun and Gang, 2012) 14,2%
learning models Case-based reasoning (Hamdan et al., 2006), (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012) 28,5%
Regression trees (Humayun and Gang, 2012) 14,2%
Neural Network (Nassif et al., 2012) 14,2%
Genetic Algorithm (Humayun and Gang, 2012) 14,2%
studies that concentrate on the maintenance phase.
This phase focuses principally on the extraction and
consideration of factors that affect software mainte-
nance. If the software maintenance cost is to be prop-
erly applied, it is essential to estimate the cost and
reduce it by controlling certain factors.
Table 8 summarises the elements that affect soft-
ware cost development and maintenance in the GSD
context. Software development and maintenance are
the major issues to affect a GSD project. The study
is based on the analysis of data collected from se-
lected papers. Software activities have been shown
to have significant costs. The development cost re-
sulting from the overall estimate and the estimation
of the benefits of strategies and the networking re-
main highly uncertain and open to improvement, as
do the costs incurred as the results of maintenance,
particularly modification, improvement or enhance-
ment along with reengineering costs. These costs
have been known to erode whatever benefits the GSD
model may provide.
3.9 MQ.8: Software Cost Drivers
There are 16 cost drivers, which are divided into the
four categories depicted in Table 9: Product, Plat-
form, Personnel, and Project Factors. As this table,
shows some cost drivers are common to all types of
software projects while others are specific to GSD
projects. The majority of cost drivers that impact
on GSD projects are related to factors in distributed
software projects: time zone, language (communica-
tion) and cultural differences (team culture). Note that
the most frequently used cost drivers are project ef-
fort (44,4%), process model (33,3%) and time zone
(22,2%).
In order to establish trust in distributed projects,
researchers recommend bringing about cultural un-
derstanding, creditability, capabilities, pilot project
performance, personal visits and investments in the
field of GSD. These studies also suggest cultural un-
derstanding, capabilities, contract conformance, qual-
ity, timely delivery, development processes, manag-
ing expectations, personal relationships and perfor-
mance as the key factors for better achievement par-
ticularly as regards good communication.
3.10 MQ.9: Software Cost
Performances
The main reason for studying cost performances in
the GSD context is to reduce costs. Five different cost
performance variables were included to quantitatively
characterise GSD projects: Distributed work, client
control and behavior, project team, project methodol-
ogy and technology variables (Ramasubbu and Balan,
2012).
Cost performance is principally evaluated in three
ways, as can be seen in Table 10 (Ramasubbu and
Balan, 2012). The direction of distributed develop-
ment as regards cost performance is decided by the
direction of the methods in a statistical test model cre-
ated using quantitative data or grounded conclusions
from qualitative data obtained from primary studies.
In summary, only 3 studies provide estimates derived
from empirical data obtained from cost performance
methods applied in different projects of different com-
panies.
4 THREATS TO VALIDITY
The results of this SMS may have been influenced by
ENASE2015-10thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
202
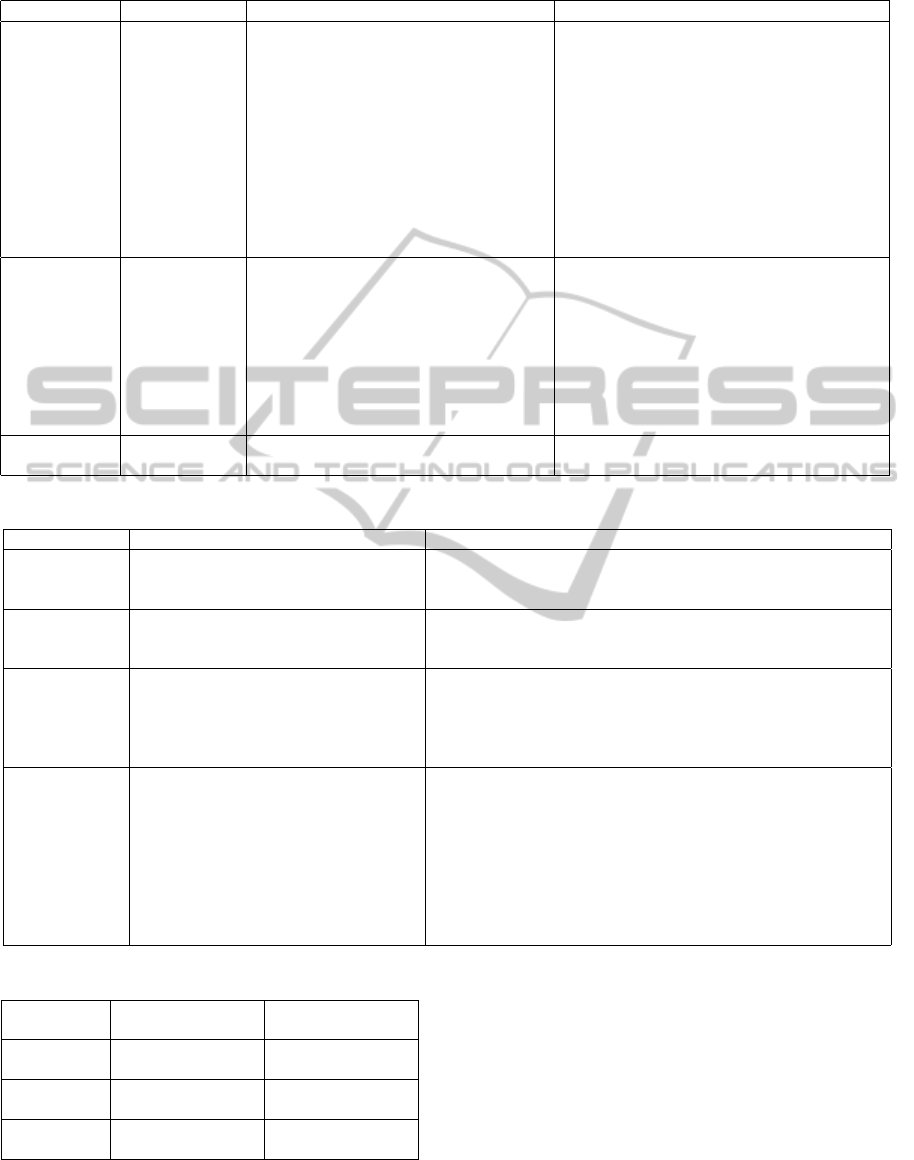
Table 8: Software cost estimation activities.
Activities Elements Descriptions Papers
Software
development
cost
Development
budget
Costs resulting from the overall estimate
to software development
(Nassif et al., 2012), (Azzeh, 2013)
Software
improvement
Costs resulting from estimating the bene-
fits of strategies such as tools, reuse, and
process maturity
(Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012)
Project plan-
ning and
control
cost of schedule and control breakdowns
by component and activity
(Lamersdorf et al., 2010), (Narendra et al.,
2012)
Project con-
straints
Costs resulting from the networking, com-
munications, delay in Response and dif-
ferent Time Zone
(Peixoto et al., 2010), (Muhairat et al., 2010)
Software
maintenance
cost
Corrective
maintenance
Costs resulting from the modification of
software into correct issues detected after
initial deployment
(Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012)
Adaptive
maintenance
Costs resulting from the modification of a
software solution to help it stay effective
in a changing business environment
(Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012)
Perfective
maintenance
Costs resulting from the improvement or
the enhancement of a software solution to
improve overall performance
(Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012)
Reengineering
cost
Enhancements Costs resulting from the sequence innova-
tions
(Forbath et al., 2008)
Table 9: Software cost drivers.
Category Cost drivers Papers
Product Code size (Muhairat et al., 2010)
Reuse (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012)
Product complexity (Keil et al., 2006)
Platform Design and technology newness (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012), (Forbath et al., 2008)
Time zone (Narendra et al., 2012), (Lamersdorf et al., 2010)
Platform volatility (Keil et al., 2006)
Personnel Team size (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012)
Team culture (Azzeh, 2013)
Team trust (Azzeh, 2013), (Muhairat et al., 2010)
Communication (Keil et al., 2006), (Narendra et al., 2012)
Development productivity (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012), (Lamersdorf et al., 2010)
Project Project effort (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012), (Peixoto et al., 2010),
(Lamersdorf et al., 2010), (Muhairat et al., 2010)
Project management effort (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012), (Peixoto et al., 2010),
(Lamersdorf et al., 2010), (Nassif et al., 2012)
Process model (Azzeh, 2013), (Muhairat et al., 2010)
Task allocation (Lamersdorf et al., 2010), (Narendra et al., 2012)
Work Pressure (Muhairat et al., 2010)
Client involvement (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012)
Work dispersion (Keil et al., 2006), (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012)
Table 10: Software cost performances.
Evaluation
type
Cost performance
method
papers
Baseline
comparison
Historical project
databases
(Muhairat et al.,
2010)
Variation re-
duction
MRE , Prediction
level
(Ramasubbu and
Balan, 2012)
sensitivity
analysis
CCNN (Nassif et al.,
2012)
the coverage of the study search, bias in study selec-
tion, and inaccuracy in study data extraction. Four
types of threats to the validity (Easterbrook et al.,
2008) of the study results are therefore discussed in
the following subsections.
Construct validity is concerned with the exacti-
tude of the interpretation of the concepts studied and
the completeness of the relevant studies collected. In
this mapping study, the key concepts under consider-
ation are contributions towards software cost estima-
tion for GSD projects. To ensure the correct interpre-
tation of these key concepts, we verified the defini-
tions of the concepts in related literature and all the
SoftwareCostEstimationforGlobalSoftwareDevelopment-ASystematicMapandReviewStudy
203

authors discussed these definitions in order to reach a
consensus as to their understanding of them.
Internal validity is concerned with the analysis of
the data extracted. The threats to internal validity
are minimal considering that only descriptive statis-
tics were used during the data analysis in this SMS.
Conclusion validity is concerned with the search
terms used in the automatic search and the search
sources are presented in order to make the results of
this mapping study reproducible.
External validity is concerned with the represen-
tativeness of the selected studies as regard the overall
goal of the mapping study. The results of this map-
ping study were considered with regard to the soft-
ware cost estimation for distributed projects. These
results and representative venues can serve as a start-
ing point for researchers and practitioners working in
this field.
5 DISCUSSION
This mapping study indicates that the application of
software cost estimation techniques for GSD projects
is a fairly immature area in both research and prac-
tice. First, about two thirds of the selected studies (11
studies out of 16) were published at conferences and
workshops, while only 31.2% (5 out of 16) of the se-
lected studies attained the maturity needed to be pub-
lished in a journal. Furthermore, only one of the se-
lected studies (Ramasubbu and Balan, 2012) attained
a very high quality level (i.e., evidence obtained from
QA).
The fact that the number of selected studies in-
creased over the last decade shows that the application
of software cost estimation knowledge is receiving in-
creasing attention from the software research commu-
nity. The selected studies were published at 12 differ-
ent venues, indicating that extensive attention is being
paid to this study topic by researchers with a broad
range of different research interests in software cost
estimation. All of the above indicates that this study
topic is likely to remain attractive. However we would
urge the research community to strive for high-level
evidence in future studies. The results of this SMS
also highlight a number of implications for further re-
search in the field:
(1) Challenges associated with software cost and ef-
fort estimation in GSD are not new. One of the main
reasons for the growth in GSD is the cost of reduc-
ing software development, and effort estimation is a
key component of this cost. Good effort estimation
is thus important for the success of any GSD project.
The results of this mapping study show the need for
more research into techniques that can be used to im-
prove software cost estimation analysis. An adapta-
tion of techniques and models that takes into account
the challenges and factors associated with GSD must
also be investigated.
(2) This mapping study also shows that the applica-
tion of the knowledge recovery approach in various
forms needs to be explored seriously. In many soft-
ware cost estimation cases, practitioners need to re-
cover the knowledge about software characteristics,
especially when developing or maintaining a global
software project that is not well described and docu-
mented. But little work has been done on the applica-
tion of knowledge recovery in software cost estima-
tion activities for GSD.
(3) The quantification of the cost drivers’ impact on
productivity implies a high degree of objectivity and
accuracy. However, concepts such as the impact of
communication or team trust and team culture on pro-
ductivity are very difficult to quantify, and the re-
sults should be treated with care. This is owing to
the complexity and unpredictability of personnel be-
haviour which has the greatest impact on estimation
costs, particularly in distributed development.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper presents the outcomes of an SMS of cost
estimation in the context of GSD projects, in order
to serve both research and practice. This SMS has
shown a wide spectrum of software estimation tech-
niques, activities and cost drivers for GSD projects.
Most of the selected studies present cost contribu-
tion as regards cultural, language and time zone dif-
ferences, which are directly related to making the
achievement of globally performed software projects
more stimulating.
Upon considering the lack of primary studies
identified in this SMS, we believe that further research
is required into the approaches used in the GSD con-
text. We are also of the opinion that the adaptation
of those techniques based on the specific aspects of
GSD, in addition to the inherent uncertainty of the
data, could provide more faithful estimates of effort.
The globally distributed environment implies many
challenges and elements. The GSD sourcing strat-
egy and cost estimation process topology could have
a great influence on cost estimates. Future research
should therefore be carried out to explore how these
challenges and factors affect cost estimation tech-
niques.
ENASE2015-10thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
204

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the Erasmus
Mundus program Action 2: EU Mare Nostrum UE-
MARE NOSTRUM (204195-EM-1-2011-1-ES-ERA
MUNDUS-EMA21) and the project ‘DataMining for
Software Project Management’ financed by the Uni-
versity Mohammed V of Rabat. This work is also par-
tially supported by the GEODAS-REQ project (Span-
ish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness and
European Fund for Regional Development, TIN2012-
37493-C03-01)
REFERENCES
Azzeh, M. (2013). Software cost estimation based on use
case points for global software development. In Com-
puter Science and Information Technology of the 5th
International Conference, pages 214–218.
Boehm, B., Abts, C., and Chulani, S. (2000). Software de-
velopment cost estimation approachesa survey. An-
nals of Software Engineering, 10(1-4):177–205.
Boehm, B. W. (1981). Software engineering economics.
Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Britto, R., Freitas, V., Mendes, E., and Usman, M. (2014).
Effort estimation in global software development: A
systematic literature review. In Proceedings of the 9th
IEEE International Conference on Global Software
Engineering (ICGSE), pages 135–144.
da Silva, F. Q., Costa, C., Franc¸a, A. C. C., and Prikla-
dinicki, R. (2010). Challenges and solutions in dis-
tributed software development project management:
A systematic literature review. In Proceedings of the
5th IEEE International Conference on Global Soft-
ware Engineering (ICGSE), pages 87–96. IEEE.
Easterbrook, S., Singer, J., Storey, M.-A., and Damian, D.
(2008). Selecting empirical methods for software en-
gineering research. In Guide to advanced empirical
software engineering, pages 285–311.
Forbath, T., Brooks, P., and Dass, A. (2008). Beyond
cost reduction: Using collaboration to increase inno-
vation in global software development projects. In
Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference
on Global Software Engineering (ICGSE), pages 205–
209.
Hamdan, K., El Khatib, H., Moses, J., and Smith, P. (2006).
A software cost ontology system for assisting estima-
tion of software project effort for use with case-based
reasoning. In Innovations in Information Technology,
2006, pages 1–5.
Hughes, R. T. (1996). Expert judgement as an estimat-
ing method. Information and Software Technology,
38(2):67–75.
Humayun, M. and Gang, C. (2012). Estimating effort in
global software development projects using machine
learning techniques. International Journal of Infor-
mation and Education Technology, 2(3):208–211.
Idri, A., Azzahra Amazal, F., and Abran, A. (2015).
Analogy-based software development effort estima-
tion: A systematic mapping and review. Information
and Software Technology, 58(0):206–230.
Idri, A., Zahi, A., and Abran, A. (2006). Software cost es-
timation by fuzzy analogy for web hypermedia appli-
cations. In Proceedings of the International Confer-
ence on Software Process and Product Measurement,
Cadiz, Spain, pages 53–62. Citeseer.
Jørgensen, M. (2004). A review of studies on expert es-
timation of software development effort. Journal of
Systems and Software, 70(1):37–60.
Jorgensen, M. and Shepperd, M. (2007). A systematic re-
view of software development cost estimation stud-
ies. Software Engineering, IEEE Transactions on,
33(1):33–53.
Keil, P., Paulish, D. J., and Sangwan, R. S. (2006).
Cost estimation for global software development. In
Proceedings of the 2006 International Workshop on
Economics Driven Software Engineering Research
(EDSER), pages 7–10.
Kitchenham, B. A. and Charters, S. (2007). Guidelines for
performing systematic literature reviews in software
engineering. Technical report, Software Engineering
Group, Keele University and Department of Computer
Science University of Durham.
Lamersdorf, A., Munch, J., Torre, A. F.-d. V., Sanchez,
C. R., and Rombach, D. (2010). Estimating the ef-
fort overhead in global software development. In Pro-
ceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference on
Global Software Engineering (ICGSE), pages 267–
276.
Lotlikar, R. M., Polavarapu, R., Sharma, S., and Srivastava,
B. (2008). Towards effective project management
across multiple projects with distributed performing
centers. In Proceedings of the IEEE International
Conference on Services Computing (SCC), volume 1,
pages 33–40.
Muhairat, M., Aldaajeh, S., and Al-Qutaish, R. E. (2010).
The impact of global software development factors on
effort estimation methods. European Journal of Sci-
entific Research, 46(2):221–232.
Narendra, N. C., Ponnalagu, K., Zhou, N., and Gifford,
W. M. (2012). Towards a formal model for opti-
mal task-site allocation and effort estimation in global
software development. In Proceedings of the Annual
SRII Global Conference, pages 470–477.
Nassif, A. B., Capretz, L. F., and Ho, D. (2012). Software
effort estimation in the early stages of the software
life cycle using a cascade correlation neural network
model. In Proceedings of the 13th International Con-
ference on Software Engineering (ACIS), Artificial In-
telligence, Networking and Parallel/Distributed Com-
puting, pages 589–594.
Ouhbi, S., Idri, A., Fern
´
andez-Alem
´
an, J. L., and Toval, A.
(2013a). Requirements engineering education: a sys-
tematic mapping study. Requirements Engineering,
pages 1–20.
Ouhbi, S., Idri, A., Fern
´
andez-Alem
´
an, J. L., and Toval, A.
(2013b). Software quality requirements: a system-
atic mapping study. In Software Engineering Con-
SoftwareCostEstimationforGlobalSoftwareDevelopment-ASystematicMapandReviewStudy
205

ference (APSEC, 2013 20th Asia-Pacific, volume 1,
pages 231–238. IEEE.
Peixoto, C. E. L., Audy, J. L. N., and Prikladnicki, R.
(2010). Effort estimation in global software develop-
ment projects: Preliminary results from a survey. In
Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference
on Global Software Engineering (ICGSE), pages 123–
127.
Ramasubbu, N. and Balan, R. K. (2012). Overcoming the
challenges in cost estimation for distributed software
projects. In Proceedings of the 34th International
Conference on Software Engineering, pages 91–101.
Wen, J., Li, S., Lin, Z., Hu, Y., and Huang, C. (2012). Sys-
tematic literature review of machine learning based
software development effort estimation models. In-
formation and Software Technology, 54(1):41–59.
ENASE2015-10thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
206
