
Costing as a Service
Andr
´
e Machado
1
, Carlos Mendes
1
, Miguel Mira da Silva
2
and Jo
˜
ao Almeida
3
1
INOV, Lisbon, Portugal
2
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, T
´
ecnico Lisboa, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
3
Card4B, Systems S.A., Lisbon, Portugal
Keywords:
Costing, TDABC, Cost Templates, Cloud Computing, Cloud Services, SaaS.
Abstract:
Cost awareness and cost efficiency have always been major concerns to organizations from all industries but
in the last few years its importance grew due to the global economic and financial crisis. Considering their
small size and market exposure, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) need cost awareness and efficiency
more than ever. However, efficient and accurate costing methodologies are out of reach for most SMEs. In this
research we propose that costing should be offered as a service to reduce the cost of cost analysis. Our research
proposal is a cloud-based costing system that offers costing as a service using Time-Driven Activity Based
Costing (TDABC) methodology and the concept of Business Process Costing Templates. When combined,
they reduce the cost of cost analysis, especially for SMEs. We used the Design Science Research Methodology
(DSRM) to conduct our research. This proposal was demonstrated in three Portuguese organizations and
evaluated with feedback gathered from interviews and results from the system instantiation in all organizations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Enterprises are becoming increasingly complex and
managing that complexity is a growing challenge.
Competition is fierce among these entities that always
tried to differentiate between themselves through a
variety of factors, one of which is efficiency. Cost ef-
ficiency has always been a major concern to organiza-
tions but in the last few years its importance grew due
to global economic and financial crisis. Due to their
small size and market exposure, Small and Medium
Enterprises (SMEs) need cost efficiency more than
ever (OCDE, 2009).
However, as organizational complexity grows, so
does the complexity of cost analysis (Wileman, 2010).
Information about how and where the money was
spent is a concern of organizations across all indus-
tries. Knowledge about costs distribution and true un-
derstanding of overhead costs allocation is essential
for an enterprise to focus on the most profitable prod-
ucts and services (Delloite, 2011).
In order to obtain detailed information about costs
and overheads distribution several cost methodolo-
gies were developed. These methodologies evolved
and differentiated themselves from traditional cost ac-
counting systems to better distribute overhead costs
that have been rising inside organizations in recent
years (Miller and Vollmann, 1985). The increasing
importance of overhead costs comes from the fact
that the industry has evolved from manufacturing to
services (
ˇ
Skoda, 2009). This development implied a
substantial growth of overhead costs (Miller and Voll-
mann, 1985;
ˇ
Skoda, 2009).
Organizations using these accurate costing
methodologies know exactly where resources are
being spent and what is the profitability of their
products or services. However, the adoption of these
costing methodologies is far behind of what would
be expected. The lack of adoption is explained by
the high costs of these methodologies for SMEs
since they require time, expertise and expensive and
complex software solutions that are out of reach for
the most of these organizations (Hall et al., 2011).
2 PROBLEM
Costing has been a major concern to all organizations
since their genesis. As a competitive advantage, cost
efficiency has been something that all organizations
tried to achieve in order to increase their profit mar-
gins or reduce the price of their products or services.
Cost efficiency is recognized as one of the most im-
portant aspects in respect to the competitive advan-
173
Machado A., Mendes C., Mira da Silva M. and Almeida J..
Costing as a Service.
DOI: 10.5220/0005373401730181
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 173-181
ISBN: 978-989-758-098-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

tages of an organization.
Normally, organizations resort to cost accounting
in order to analyse costs and achieve the desired cost
reductions. This approach has a major issue: tradi-
tional cost accounting systems give low detailed in-
formation and lack the needed granularity to prop-
erly do cost analysis and, therefore, cost reduction.
Not least, most accounting systems are focused on
mandatory state-demanded reports (Hicks and Cost-
ing, 2002) showing only large blocks of information
totally misaligned with the organization’s business
processes. Therefore, when it comes to calculate the
cost of a product or service, traditional methodolo-
gies give inaccurate values, mostly because they lack
the needed granularity and differentiation of informa-
tion (Lambert III and Chen, 1996). Often, such infor-
mation is inaccurate because of wrong distribution of
overhead costs. Correct distribution of overhead costs
is truly essential since they have grown from being a
minor share of the total costs to the major one (
ˇ
Skoda,
2009).
Presently, there are several costing methodolo-
gies to address the abovementioned problem. These
methodologies resort to the activities that occur in-
side the organization to design the flow of costs from
the inputs (e.g. material) to the outputs of an organi-
zation (products or services). This cost awareness al-
lows organizations to take measures to improve their
efficiency.
The problem with these accurate costing method-
ologies is that they require a lot of expertise and are
normally supported by very expensive and complex
software solutions (Hall et al., 2011). Whereas large
organizations can support the costs associated with
the required expertise and software solutions, SMEs
cannot (Hall et al., 2011). It is crucial that SMEs have
access to these accurate cost methodologies since they
operate in a market that is more competitive (Nandan,
2010) and they are more exposed to the effects of an
economic crisis (OCDE, 2009).
To solve this problem we propose that costing and
cost analysis should be offered as a service instead of
as an investment in a one-time project. This approach
should enable organizations to access accurate cost-
ing methodologies because costs are diluted over time
and the tools needed to perform this cost analysis are
also offered as a service. Our proposal will also give
organizations the ability to do on-demand cost anal-
ysis so that they can constantly evaluate the flow of
costs as well as take measures to improve their cost
efficiency.
3 RELATED WORK
We will provide an overview of the tools and methods
available that could contribute to solve the identified
problem.
Cost Accounting (or costing) can be defined as
the process of collecting, classifying, assigning and
analysing the costs associated with the activity of an
organization (Blocher, 2005). Cost Accounting pro-
vides the detailed cost information that management
needs to control current operations and plan for the fu-
ture. The goal of cost accounting is to gather all pos-
sible information so that it can be structured and used
by management to take decisions and measure the or-
ganization’s performance (Vanderbeck, 2012; Cooper
and Kaplan, 1987).
3.1 Costing Methodologies
3.1.1 Activity based Costing
ABC methodology defines an activity as an action ex-
ecuted inside an organization (e.g. packaging) that
has a particular cost rate based on the cost of the re-
sources allocated to that activity. Allocation of re-
sources to activities and then to products or services
is done based on interviews to those involved in the
activities as well as in some estimates provided by the
management team. This process results on splitting
the costs related to the resources used by the activities
using variables like percentage or headcount. Output
costs are calculated adding the costs of all the activ-
ities that were needed to create the final product or
service (Blocher, 2005).
Traditional costing methodologies assign over-
head costs by volume, that is, overhead costs are dis-
tributed by products using some variable (or driver)
that reflects capacity usage (e.g. number of hours)
regardless of the specificities of the product. On the
other hand, ABC uses activities which mean that dif-
ferent products may use a set of different activities
and therefore a set of different cost rates to calculate
the final cost of a product or service.
Although ABC has some advantages over tradi-
tional costing systems it also has some pitfalls. First,
costs are calculated using individual and subjective
estimates. The accuracy of these estimates may be
questionable since, in most cases, there is no evidence
of correctness. Wrong estimates may distort measure-
ments (Kaplan and Anderson, 2007). Second, ABC
requires not only the creation of an activity for ev-
ery task performed inside the organization but also its
cost specification. Thus, the complexity of the model
grows with the number of activities. Finally, since it
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
174

is common to have activities with variable costs (e.g.
special packing vs standard packing) and ABC de-
fines activities as single tasks with fixed cost rates,
models tend to have many similar activities just to
simulate variable costs.
3.1.2 Time-Driven Activity Based Costing
Time-Driven Activity Based Costing (TDABC) (Ka-
plan and Anderson, 2007; Kaplan and Anderson,
2004) is an alternative costing methodology to ABC
focused on assigning overhead costs to cost outputs.
The TDABC model simulates the actual processes
used to perform work throughout an enterprise, there-
fore capturing far more variation and complexity than
a conventional ABC model. Such variation and com-
plexity is captured without significant demand for
data estimates or processing capabilities. TDABC as-
signs resource costs directly to the cost objects requir-
ing only two sets of estimates: the cost of supplying
resource capacity and the capacity used by each trans-
action processed (Kaplan and Anderson, 2007).
Regarding flexibility and concerning the limita-
tions of ABC of each activity reflecting only one
factor/condition, TDABC introduces the concept of
time-equations to model the different resources con-
sumed by an activity (Dejnega, 2011). If we take as an
example the packaging of an order that takes longer
when gift wrapping is requested, in ABC there would
be two activities: one for standard packaging and an-
other for gift wrapping. However, in TDABC it is pos-
sible to express this variation with a time-equation.
Finally, TDABC provides mechanisms to gather
information about its own accuracy and to identify
possible wastes or inefficiencies (Kaplan and Ander-
son, 2007).
3.2 Business Process Cost Templates
Business Process Cost Templates is a method to re-
duce the costs of adopting efficient costing method-
ologies, such as TDABC, through re-utilization and
standardization of business processes for organiza-
tions inside the same field or industry. The main goal
of these templates is to dilute the costs associated with
the analysis required to implement a costing method-
ology, in particular TDABC, making the adoption of
such methodologies more affordable (Lourenc¸o and
Mira da Silva, 2013).
The method that creates a template for a particu-
lar field is composed of two distinct phases: a Mod-
elling Phase and an Application Phase. The first is
done only once and is where the field or industry is
analysed and a generic cost model is developed. The
second results of the application of the template pro-
duced. The template is instantiated and the specifici-
ties of the organization are set. These specificities
may include addition or removal of activities, chang-
ing the coefficients in time-equations, or adding some
unrepresented condition. This adjustment is crucial
since not all organizations are identical, even though
they belong to the same industry or field (Lourenc¸o
and Mira da Silva, 2013).
4 PROPOSAL
We briefly describe our proposal as a cloud-based
costing service that uses TDABC and the concept
of Business Process Cost Templates to reduce the
costs associated with cost analysis.
4.1 Costing Service Objectives
We highlight from our cloud-based costing ser-
vice the following features: Time-Driven Activity
Based Costing methodology, Business Process Cost-
ing Templates, Creation/Edition of Business Pro-
cesses and Time-Equations, What-if Analysis, Data
Integration, Data Visualization and Automatic Pre-
configuration.
Offering a costing service in a cloud environment
helped us achieve the needed technological cost re-
duction. Current solutions require local software in-
stallations that raise the costs of the service because,
in addition to compelling the purchase of the techno-
logical equipment needed, it also implies operational
costs. Those tools are also very complex and require
expertise whenever modifications to the model are
needed. These issues prevented managers from per-
forming cost analysis as an ongoing process.
As for the costing methodology, we adopted TD-
ABC for the reasons stated in the Related Work (sec-
tion 3). TDABC is an accurate costing methodol-
ogy that solves the problems identified in previous
methodologies and that is simple to understand and
implement, providing quick benefits for those who
adopt it (Pernot et al., 2007). TDABC also has clear
connections with BPM that helped us connect it with
Business Process Costing Templates.
Regarding Business Process Costing Templates,
we chose to use them within our service because they
provide a way of creating cost templates to a given
industry and distribute them for all the organizations
that operate within that industry. These templates can
be created and modified by an organization or by a
cost analysis expert and included within our tool. Pro-
viding cost templates to more than one company leads
CostingasaService
175

to cost reduction, since the cost of creating a template
can be distributed by multiple organizations. These
templates can be later improved or adapted to the re-
ality of the organization deploying the template. Even
though the organization may incur in a cost by doing
this, it will be a lower cost when compared to the cost
of a complete analysis.
Finally, What-if Analysis, Data Integration and
Data Visualization, are meant to provide means of
assessing the organization’s performance. Although
these features are not directly related to the cost re-
duction of the cost analysis they are required to com-
ply with the guidelines proposed by TDABC.
4.2 Costing Service - Analysis Process
Figure 1 shows the process of performing a cost anal-
ysis using the costing service. Users should start by
configuring resources and resource pools and import-
ing transactions. If the costing service is being used
by more than one user, each one may be account-
able for one of the activities. In the case of the re-
sources, users should define, for every resource be-
longing to the organization, the name of the resource,
its monthly capacity and the cost of providing such
capacity. On the other hand, regarding resource pools,
users should define the name of the resource pool
and its classification, whether it is a support resource
pool or a functional resource pool. Afterwards, users
should configure the resource pool structure, that is,
which support resource pools belong to which func-
tional resource pools.
Users must also associate resources to resource
pools. Resources can either be associated to support
or functional resource pools. After completing these
associations, resource pools will have their cost calcu-
lated so that users can know the costs of their resource
structure before completing the analysis.
Afterwards, users should decide if they want to
automatically configure business processes and activ-
ities or if they want to manually specify them. The
main difference is closely related to the quality of the
data available. If users know that their data matches
the processes of the organization, they can let the tool
automatically configure them. On the other hand, if
users already have some sort of ”optimized” business
process template, they should manually configure the
tool. Users may also let the costing tool infer busi-
ness processes and then fine-tune them. We encour-
age users to perform an automatic configuration since
this simplifies the process of analysis even further.
Finally, users should associate the functional re-
source pools to the business processes that those func-
tional resource pools are accountable for and then
compute the analysis. Running the analysis finishes
the process of cost analysis. However, users may
change resource cost values, fine-tune activities and
business processes or change associations and then re-
compute analysis.
4.3 Costing Service Tool
We developed our costing tool according to the guide-
lines defined by both TDABC and Business Process
Costing Templates meaning that they represented our
requirements document.
Figure 2 shows the Dashboard of our tool. We
provide information regarding the number of Trans-
actions (8682) used to make the analysis, the number
of Business Processes (77) identified and the list of
the top five most costly Resource Pools and Business
Processes.
5 DEMONSTRATION
We demonstrated our proposal by instantiating our
artefact (the costing service) in three real world Por-
tuguese organizations, namely ”Social Security IT In-
stitute”, ”Defence Data Center” and “Card4B”.
The demonstrations consisted in instantiating the
costing service, i.e., creating the cost template, within
the costing tool, to the organization being tested. This
includes the definition of resources, resource pools,
business activities, business processes and the rela-
tionships between these entities to the particular en-
vironment of the organization being tested.
5.1 Social Security IT Institute
The Social Security IT Institute is a public institute,
integrated in the indirect state administration, with ad-
ministrative and financial autonomy. It is an organi-
zation with nationwide intervention. Although sev-
eral state competences have been assigned to the In-
stitute, we focused our demonstration in the service
desk competences.
Following the process described in section 4.2, we
started by gathering relevant data to feed the transac-
tional data needed to perform the analysis. We asked
the Institute to provide us with a CSV file containing
the data to be imported as transactions. We had access
to 8682 real transactions to perform the analysis.
Regarding the resources, there are several re-
sources involved in all the business processes and de-
partments inside the organization. These resources
are diversified and include technical and management
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
176
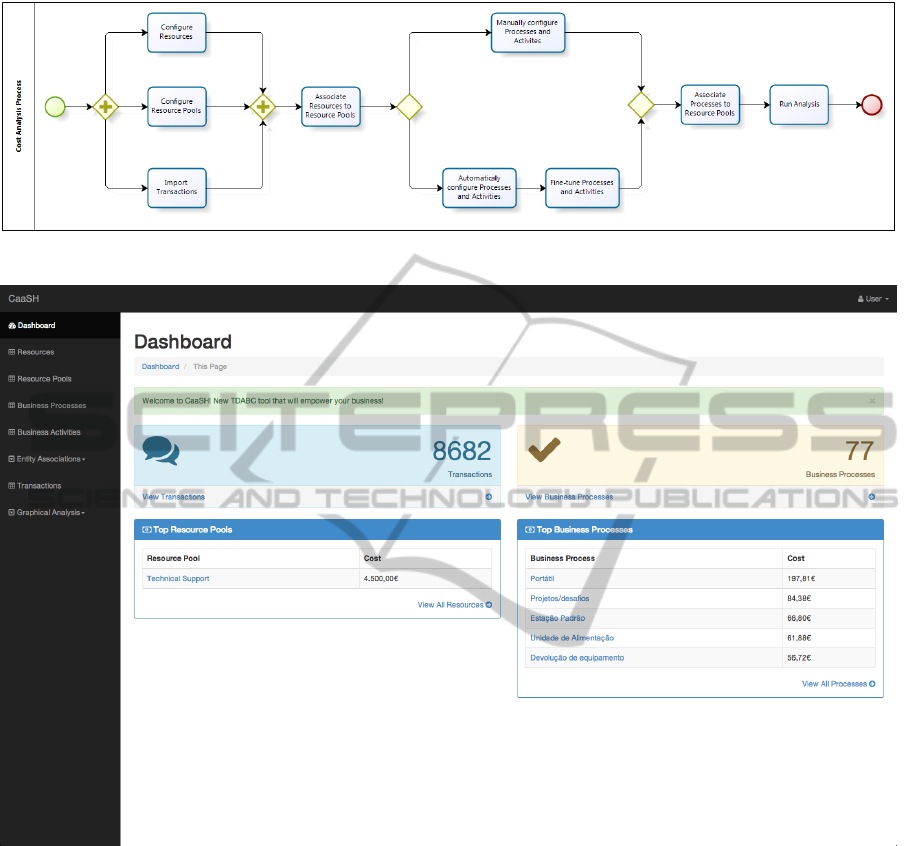
Figure 1: Costing Service - Analysis Process.
Figure 2: CaaSH - Dashboard - Costing Tool.
staff, electricity, rents, material and equipments. Al-
though all these resources and resource pools (such as
the Technical Support department) are properly iden-
tified, the organization opted to avoid gathering the
unit costs of each resource and their contribution to
the resource pools. This decision was justified since
the organization had been previously involved in a
cost analysis project. From the results of this former
project, the Institute knew the daily cost of the tech-
nical support staff. However, they were unable to link
it to the execution of the business processes, which is
the main objective of our demonstration.
Based on these limitations, we defined a resource
and a resource pool that matched the daily value sup-
plied. We knew that the monthly time capacity of this
resource was 8 hours/day and 22 days/month, which
was converted in minutes with a 10% waste on work-
ing hours, giving the final monthly time capacity of
9504 minutes for each technical support worker. If
we assume (since we cannot disclose the real value)
the cost of providing such capacity as 200e/day, the
cost of providing 9504 minutes of technical support
labour would cost 4400e. Since there is no other sup-
port resources or resource pools, this means that the
capacity cost rate (CCR) of this resource is 0,46e.
From the 8682 transactions supplied, the auto-
matic configuration of the costing tool was able to de-
tect 77 business processes with 791 unique business
processes instances. This means that the analysis was
performed using data from 791 complete executions
CostingasaService
177

of a business process (from the 77 identified). Fig-
ure 3 shows a sample of the results obtained from the
analysis. The sample shows, for each business pro-
cess identified, the average time and cost of execution
as well as the number of instances that were identified
for that business process. The red and green rectan-
gles also show another interesting result from the cost
analysis. The red rectangle shows a group of three
business processes that were identified by the costing
tool and that correspond to the same business process,
as we were able to verify with the Social Security IT
Institute management. This results from the wrong
definition of workflows inside the IT Service Man-
agement software (EasyVista) which leads to wrong
categorization of incidents/service requests in the ser-
vice desk. The green rectangle shows the same prob-
lem described earlier but this time with an even minor
difference (name pluralization).
Not only the costing tool delivered what was ex-
pected, i.e., the cost of executing the business process
that accomplishes the resolution of a service request
or incident, but it also provided valuable insights to
the organization regarding the workflows definition in
the IT Service Management software. The organiza-
tion can easily know the average time and cost of exe-
cuting a business process. Moreover, the institute can
further analyse the data and find the cost for every
execution of every business process. The Social Se-
curity IT Institute management members considered
these results very useful since they can now further
analyse the different costs that the same business pro-
cess generates. For instance, a desktop related inci-
dent has an average cost of 23,22e but the minimum
cost and the maximum cost of such incident was, re-
spectively, 2,31e and 70,83e. Having this informa-
tion, the management may now try to understand what
motivated such difference and take measures to miti-
gate the cause.
5.2 Defence Data Center
The Defence Data Center belongs to the General Sec-
retariat of the Ministry of National Defence (Portu-
gal) and among its several competences they are also
responsible for service desk activities.
The Defence Data Center service desk uses
EasyVista software for IT Service Management, i.e.,
the same software used by the Social Security IT In-
stitute. It is also configured according to the best
practices defined internally (ITIL). This means that
the demonstration was almost identical to the previ-
ous case. Again, we followed the costing service pro-
cess of analysis (section 4.2).
Results obtained from the analysis are similiar to
those shown in Figure 3. Again, we detected groups
of business processes that were identified by the cost-
ing tool and that correspond to the same business pro-
cess. As we stated before, this results from the wrong
definition of workflows inside the IT Service Manage-
ment software.
5.3 Card4B
Card4B develops and operates integrated mobility
solutions through interoperable contactless ticketing,
passenger information, embedded systems and smart-
phones, systems integration and business intelligence.
Presently, Card4B is developing a project, designated
ecoDrive - Intelligent Eco Driving and Fleet Man-
agement, which is a multidisciplinary project, target-
ing the public transportation network, in which INOV
is responsible for the identification of business pro-
cesses (BPMN) and the cost analysis of those busi-
ness processes using a TDABC approach.
The costing service described in the proposal (sec-
tion 4) was adopted as a solution for the ecoDrive
project since it delivered all the needed features to
accomplish the objectives defined. However, this
project required that the identification of business pro-
cesses and activities was done prior to the system de-
ployment, meaning that we would only have access to
real transactional data after the system enters in pro-
duction, since there is no digital data from the past.
Starting with the business processes, we were able
to identify 10 different business processes, each one
with its distinct set of activities. For example, we
identified a business process ”Occurrences” that is re-
lated to the different events that may cause changes to
the operational service of a bus. The activity list of
this business process includes ”Change Driver” and
”Change Vehicle”. Another example was the busi-
ness process ”Corrective Maintenance” that features
activities such as ”Repair of damage” and ”Damage
Report”. These 10 business processes and respective
activities are the ones that will constitute the founda-
tion for the transactional data to be exported from the
software being developed by Card4B for the public
transportation industry.
As we stated before, we didn’t have access to real
transactional data since the system is not in produc-
tion yet. In this particular case, our tool will im-
port transactional data from JSON web services rather
than from a CSV file, enabling the costing tool to get
data in real time. As a result, after configured, the
costing tool can pull data, in a given time interval, so
that it can produce updated metrics without user in-
tervention.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
178
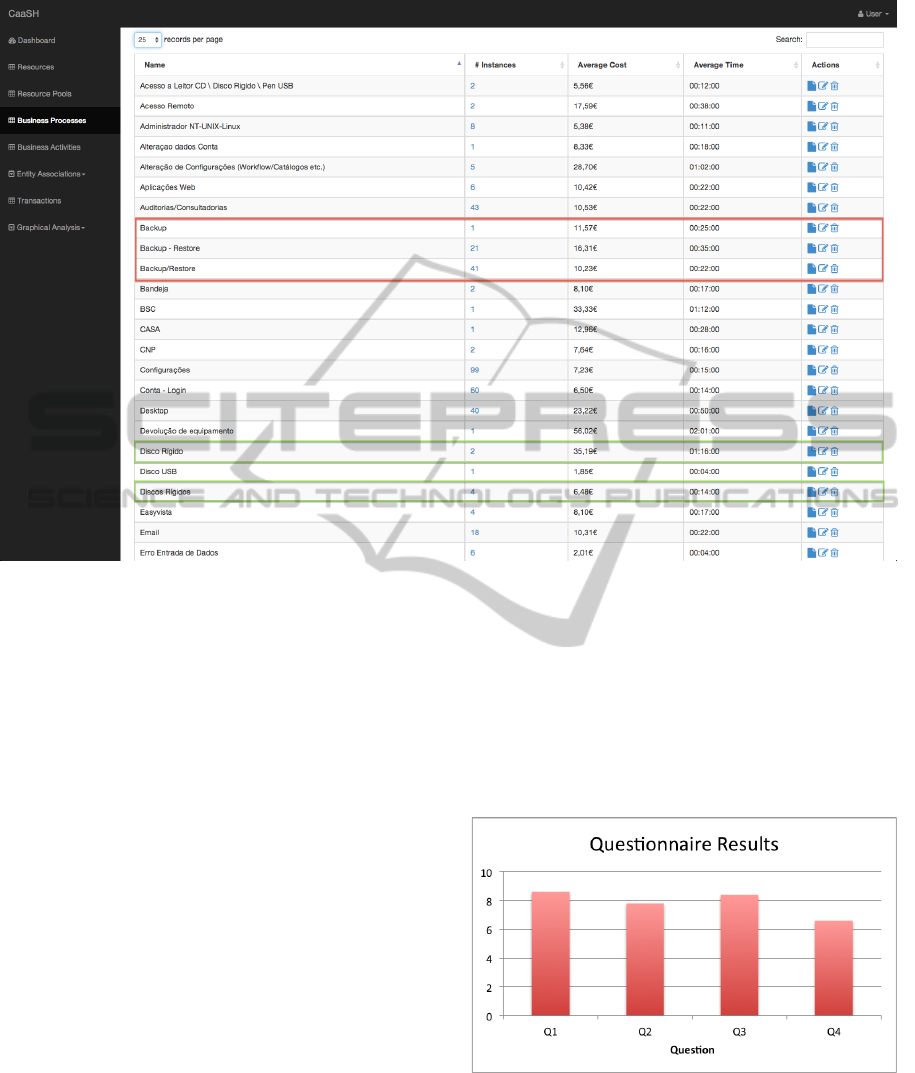
Figure 3: CaaSH - SS IT Institute - Business Processes Sample.
6 EVALUATION
The goal of this evaluation is to determine if the so-
lution proposed in the Proposal (section 4) solves the
problem stated in the Problem (section 2).
The evaluation method will consist in the follow-
ing steps:
1. Interviews and Questionnaires. Gather feed-
back from the proposal through the demonstration
and identify improvements;
2.
¨
Osterle et al. Principles. To formally evaluate
the research;
3. Demonstration’s Critical Review. To critically
evaluate the research, objectives fulfillment and
the demonstrations conducted;
6.1 Interviews and Questionnaires
After demonstrating our costing service, we con-
ducted a small questionnaire to those involved so that
we could obtain a more structured feedback. The
questionnaire was made to five interviewees with the
following business roles: Planning, Quality and Au-
dit Manager, Budget Manager, Planning and Control
Manager, Accountant for Client Support and an IT
Director.
We carried out four questions to these profession-
als that helped us assess the artefact utility and the ful-
fillment of the objectives defined earlier. These ques-
tions were also defined having in mind the needed in-
formation to formally evaluate the research.
Figure 4: Questionnaire Results.
Figure 4 shows the questionnaire results which av-
eraged 7,85 out of 10. We also gathered feedback
from the interviews that provided us insights in dif-
ferent topics needed to evaluate this research as we
will further detail in this section.
CostingasaService
179

6.2
¨
Osterle et al. Principles
¨
Osterle et al. proposes an evaluation method based
within four principles (
¨
Osterle et al., 2010). Our re-
search met the four principles of
¨
Osterle. This evalua-
tion is based on the feedback received from practition-
ers, which were described in the previous sections.
1. Abstraction. The artefact we propose can be ap-
plied to the majority of the service-oriented or
process-based organizations;
2. Originality. None of the interviewees had knowl-
edge of any research or product similar to the pro-
posed artefact. Similar research was not found re-
garding the costing service;
3. Justification. Our artefact is justified by the lack
of a similar solution and from the positive feed-
back gathered during this research;
4. Benefit. According to the interviewees, at least in
the industries consulted, there would be a valuable
benefit, since it would provide an easier and more
affordable way to perform a cost analysis.
6.3 Demonstration’s Critical Review
We consider that our research was properly evaluated
and tested with our demonstrations. We demonstrated
our proposal in three Portuguese organizations, from
two distinct industries, with the objective of providing
those organizations with new ways to conduct simple
and reliable cost analysis.
Our demonstrations targeted three organizations
that are making clear efforts to consider business pro-
cess costing a priority. Two of the three organiza-
tions (the service desks), already have their services
oriented according to best practices such as ITIL and
ISO 20000. That gave us an advantage regarding the
costing service implementation. Although our service
provides an easy way to start costing business pro-
cesses and services, we do realize that the organiza-
tions deploying such service should have a consider-
able maturity in their architecture.
We were able to deliver average cost per business
process and real cost per business process instance.
We consider the latter to be a great benefit to service-
oriented organizations since it enables organizations
to comprehend the average cost of supplying a service
or executing a business process but also the real cost
for every business process instance executed. This
helps organizations detect erroneous paths and singu-
lar problems that occurred at a moment in the organi-
zation.
Finally, every interviewee that saw the costing ser-
vice configuration and use considered the process of
conducting a cost analysis using our tool very easy
and understandable.
7 CONCLUSION
Cost efficiency has always been a major concern to
organizations from all industries around the world. In
recent years, economic crisis and increased competi-
tion in an increasingly global economy pushed even
further the need for cost efficiency and cost aware-
ness. It became crucial to assess and benchmark an
organization’s performance and to identify improve-
ment opportunities across all sectors of the organiza-
tion and over the cost stream.
Our artefact is a cloud-based costing service
meant to provide costing as a service. Our main ob-
jective was to develop a solution to reduce the costs
associated with cost analysis so that SMEs can reach
the accurate costing methodologies needed to assess
an organization’s cost efficiency and performance.
We validated our proposal in three Portuguese or-
ganizations belonging to two different industries: Ser-
vices industry (two Service Desks) and the Public
Transportation industry. We completed the demon-
strations by instantiating the proposed costing service.
7.1 Main Contributions
We believe that our proposal brings a valuable con-
tribution in the context of costing and cost analysis.
The resulting costing service allows organizations to
conduct a bigger share of the cost analysis without
demanding significant levels of expertise or capital.
The proposed costing service not only provided a
solution to the problem of high costs of cost analysis
but also delivered a costing tool capable of correctly
and completely support TDABC and Business Pro-
cess Costs Templates. These methods combined with
the capabilities of our costing tool produced well-
defined steps that act as a guideline for both analysts
and managers looking for a cost analysis solution.
The end result is a costing service capable of deliver-
ing the ability for an organization to do cost analysis
with internal resources and expertise, without needing
substantial investment.
7.2 Limitations
The limitations regarding our proposal can be divided
into two groups, technical limitations and conceptual
limitations.
Regarding the technical limitations, although we
consider our costing tool to be more than just a pro-
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
180

totype, we must state that it lacks some characteris-
tics needed to be a full cloud-based costing service.
The developed costing tool does not support integra-
tion and importing of tax and analytical accounting
data. In order to avoid data input mistakes and to
enable high volumes of data integration this would
be mandatory. We also consider that the developed
costing tool, although producing some useful metrics,
lacks the ability to produce management reports.
As for the conceptual limitations, they are related
to profitability, capital and investment characteristics
that are needed to correctly reflect all the costs within
the analysis. The research process and the interviews
revealed that although costs and cost analysis are ma-
jor concerns to organizations, they are strongly tied to
capital costs, working capitals, return on investments
and profitability. Although we excluded from the be-
ginning of this research such concepts and metrics,
we must acknowledge that the lack of such character-
istics is a limitation that must be addressed in future
research.
7.3 Future Work
Although we achieved three full demonstrations in
two distinct industries, we consider that applying
the service to more complex and different industries
would be desirable since that could further validate
the proposed costing service. Our demonstrations
were carried using a significant volume of transac-
tional data. However, high transactional volume in-
dustries would be advisable to further test the costing
service.
Another interesting aspect would be to develop
BPMN importing capabilities within our costing tool.
Since some organizations already have their business
processes modelled in BPMN it would simplify the
process of cost analysis even further.
Finally, the costing tool should also be able to im-
port business processes and activities specific drivers.
This would enable the tool to produce different met-
rics other than just the cost of business processes and
activities. Since our effort was to develop a service
to reduce the cost of cost analysis, we opted to leave
this feature as a future development because it would
require transactional data to be much more specific
than the datasets we had access to, conditioning the
costing service validation and demonstration.
REFERENCES
Blocher, E. (2005). Cost Management: A Strategic Empha-
sis. McGraw-Hill College.
Cooper, R. and Kaplan, R. S. (1987). How Cost Account-
ing Systematically Distorts Product Costs. Account-
ing and Management: Field Study Perspectives, pages
204–228.
Dejnega, O. (2011). Method: Time Driven Activity Based
Costing - Literature Review. Journal of Applied Eco-
nomic Sciences, 5(1(15)/ Spring 2011):7–15.
Delloite (2011). CIO Survey Report 2011 The Guerilla CIO
Working Smarter to Add Value. Technical report.
Hall, O. P., McPeak, C., et al. (2011). Are SMEs ready for
ABC? Journal of Accounting and Finance, 11(4):11–
22.
Hicks, D. T. and Costing, A.-B. (2002). Making It Work for
Small and Mid-Sized Companies.
Kaplan, R. S. and Anderson, S. R. (2004). Time-Driven
Activity-Based Costing. Harvard Business Review.
Kaplan, R. S. and Anderson, S. R. (2007). Time-Driven
Activity-Based Costing: A simpler and more powerful
path to higher profits. Harvard Business Press.
ˇ
Skoda, M. (2009). The Importance of ABC Models in Cost
Management. Annals of the University of Petrosani,
Economics, 9(2):263–274.
Lambert III, S. and Chen, K. H. (1996). Overhead Cost
Pools. Internal Auditor, 53(5):62.
Lourenc¸o, A. G. and Mira da Silva, M. (2013). A cloud-
based service for affordable cost analysis. 19th Amer-
icas Conference on Information Systems.
Miller, J. G. and Vollmann, T. E. (1985). The Hidden Fac-
tory. Harvard Business Review, 63(5):142–150.
Nandan, R. (2010). Management Accounting needs of
SMEs and the Role of Professional Accountants: A
Renewed Research Agenda. Journal of Applied Man-
agement Accounting Research, 8(1):65–78.
OCDE (2009). The Impact of the Global Crisis on SME and
Entrepreneurship Financing and Policy Responses.
Technical report.
¨
Osterle, H., Becker, J., Frank, U., Hess, T., Karagiannis, D.,
Krcmar, H., Loos, P., Mertens, P., Oberweis, A., and
Sinz, E. J. (2010). Memorandum on Design-Oriented
Information Systems Research. European Journal of
Information Systems, 20(1):7–10.
Pernot, E., Roodhooft, F., and Van den Abbeele, A. (2007).
Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing for Inter-library
Services: A Case Study in a University. The Journal
of Academic Librarianship, 33(5):551–560.
Vanderbeck, E. J. (2012). Principles of Cost Accounting.
Cengage Learning.
Wileman, A. (2010). Driving Down Cost: How to Manage
and Cut Costs-Intelligently. Nicholas Brealey Pub.
CostingasaService
181
