
e-Business Architecture for Web Service Composition based on
e-Contract Lifecycle
Jos
´
e Bernardo Neto and Celso Massaki Hirata
Technological Institute of Aeronautics, Department of Computer Science, S
˜
ao Jos
´
e dos Campos, SP, Brazil
Keywords:
e-Business, Composition, e-Contract, Web Service, Distributed Systems, REST.
Abstract:
Nowadays, most of the approaches for compositions of web services are focused on feasibility of implemen-
tation rather than on satisfying business concerns. Meeting business concerns also demands flexible and agile
implementations. We present an approach for service composition based on the lifecycle of e-contract. E-
contracts have clauses and rules that express business concerns on how services are offered and consumed.
We propose an architecture that enables the automation of implementation of composite services. The au-
tomation is on the configuration of web service engines. The architectural model supports the publication of
contracts that describe how services are offered from different providers in order to develop the composition
of services.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, electronic commerce transactions are be-
coming increasingly complex. They have complex re-
quirements in terms of provision, delivery, and pay-
ment. They also demand flexible and agile processes
to implement agreements. Transactions are carried
out following contracts. A contract creates legal obli-
gations between the involved parties. In this article,
e-contracts are contracts whose lifecycle activities are
supported by the computation and communication in-
frastructures provided by the Internet. Implementa-
tions of e-commerce transactions are made through
the use of concepts and software abstractions such
as Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and web ser-
vices. They make functional building blocks acces-
sible over standard Internet protocols, independent of
platforms and programming languages. There are two
major classes of web services: (i) REST-compliant
web services, in which the primary purpose of the
service is to manipulate XML representations of Web
resources using a uniform set of stateless operations;
and (ii) arbitrary web services, in which the service
expose an arbitrary set of operations (Gronvall et al.,
2011). Web services can be grouped into a composi-
tion in order to provide more value to clients. The key
to web service composition is: (i) to identify and ex-
plore the interdependencies of the services in order to
make them more desirable to clients; (ii) to optimize
resources used by providers; and (iii) to improve the
overall client experience with the service.
Currently, both tasks identifying valuable compo-
sitions and building compositions are obstacles in ser-
vice composition. The difficulty of building compo-
sition is partly due to the lack of support to deal with
contracts in an integrated manner to implement the
composed web services. In this paper, we propose
an approach to support the lifecycle activities of e-
contracts for web service composition, allowing auto-
matic configuration of the engines (Neto and Hirata,
2013). E-contract structure, such as terms, clauses
and fields, are used to bind the configuration of the
services and the client demand. Changes in the re-
sources of e-contract can produce an impact in the
configurations of services. Concerning the compo-
sition of services, we use e-contracts from different
providers to help create compositions of services of-
fered to the clients. The contribution of this paper is
a novel approach to build service compositions while
respecting the business rules supported by e-contract
lifecycle.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2 pro-
vides the related work to facilitate understanding the
proposal approach. Section 3 presents the background
used in this paper. Section 4 work introduces the pro-
posed approach, which includes formalization of the
proposal, the architectural model structure, the lifecy-
cle of the composition and presents implementation
details. Section 5 discusses benefits and obstacles and
276
Bernardo Neto J. and Hirata C..
e-Business Architecture for Web Service Composition based on e-Contract Lifecycle.
DOI: 10.5220/0005377902760283
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 276-283
ISBN: 978-989-758-098-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

finally, Section 6 concludes and briefly describes fu-
ture work.
2 RELATED WORK
In general, most studies on composition of services
are based on the SOAP/WSDL-based services and the
focus is on orchestration and choreography using the
BPEL language. Orchestration means coordination
of multiple and different services or tasks. It is a
process of combining isolated web services in order
to implement a complex driven service. In addition,
choreography needs collaboration, considering inter-
actions points that apply the collaboration among ser-
vices from different providers. In this composition
model, no service has a privileged role once each ser-
vice needs to describe its parts during the interaction
process. An e-contract is considered an agreement be-
tween a set of parties that describes how the collab-
oration should occur (Halili et al., 2013). Proposed
architectures provide tools that allow the develop-
ment of software to support service arrangements in
complex business rules (Huang et al., 2009) (Karuna-
murthy et al., 2012). In general, RESTful approaches
propose compositions based on reuse, management of
resources in HTTP methods with simple service de-
scriptions. RESTful does not require description of
services via WSDL: clients should know the URL of
the services. The composition is built from services
of the same provider (Pautasso, 2009) (Subbu, 2010).
Some e-contract studies aim to facilitate and automate
the agreement in a cross organizational business pro-
cess. They focus on enforcement of e-contract rules
through different organizations. It is worth highlight-
ing the importance of semantics of clauses and val-
idation of the e-contract template. Web services are
a major tool to manage the e-contract terms in orga-
nizational business systems (Marchione et al., 2009)
(Chiu et al., 2003). Regarding the use of contracts in
composition of Web Services, a notable work is that
one of Milanovic (Milanovic, 2005). The approach
uses contracts for managing abstract machines as a set
of service providers with particular properties and op-
erations. The goal is to provide arrangement patterns
to use in different scenarios of composition, whether
it is sequential or parallel. The author proposes the
Contract Definition Language (CDL) as an extension
of WSDL in order to compare the terms required for
the construction of an electronic contract to deploy
the services. The contract is based on mathematical
logic for constructions of clauses. A limitation of this
approach is that the behavior of each component ser-
vice is specified through WSDL and does not explore
the configuration of the services for automatic config-
uration of web service engines.
Besides configuration of services, relevant works
have as the central theme Service-Level Agreement
(SLA). The primary focus is the agreement between
client and supplier which can be described as quality
and level of service being provided. In general, the
works use the WSDL as language for description of
services and their settings. WS-BPEL is used to cre-
ate compositions (Sun et al., 2006). The SLA frame-
works are also used to define the percentage of avail-
ability of cloud computing (Baset, 2012). Consider-
ing the e-contract lifecycle approach, we understand
that SLA limits the scope of the possible agreements
once the SLA configurations are used for monitoring
the provision of IT services.
In summary, the previous work addresses the com-
position under different points of view. The novel ap-
proach presented in this paper leverages the advan-
tages of REST and manages the resources associated
with e-contracts through the clauses and rules to share
the available data. We understand that the use of e-
contract in the description, configuration and query
of the permissions to manage and use the service is
a hard basis for construction of the composition sup-
ported by web service transactions.
3 BACKGROUND
The main background work for our proposal is the
model of lifecycle of e-contract (Neto and Hirata,
2013).
The proposal of e-contract lifecycle enables the
automatic configuration of the web services en-
gines in an e-commerce solution for distributed long-
duration transactions. The lifecycle involves activ-
ities of provider and clients that use e-contract as
the agreement. Through an e-contract the provider
can adjust its service according to pre-contract fields.
Once the client signs the e-contract, it can make or-
ders based on the services agreed. As illustrated in
Figure 1, the e-contract lifecycle has six phases: draft
elaboration, configuration of the engine, publication
of service, negotiation, operation, and closure. The
execution of the phases is in general sequential.
Each phase has inputs (conditions) to start and
must produce outputs when it finishes. In Figure 1
the solid arrows represent the main path and the bro-
ken arrows indicate optional paths. Besides the ser-
vice provider, the architectural model (Neto and Hi-
rata, 2013) uses a specific agent to support activities
of the lifecycle: the broker. The broker is an agent that
stores and manages the artifacts of the e-contracts to
e-BusinessArchitectureforWebServiceCompositionbasedone-ContractLifecycle
277

Figure 1: Lifecycle phases of an e-contract.
support the lifecycle phases.
In the proposal phase, a draft contract is created
based on a stored template or on a new one proposed
by the broker. A contract template is the reference
document that forms the basis of contracts of a spec-
ified class. A contract template consists of a num-
ber of contract clauses; each one addresses a particu-
lar concern in the business interaction. The template
contains a basic structure to adapt semantically in the
e-contracts. The service provider looks for a suitable
template where it can specify information about obli-
gations of the parties with respect to the object, in this
case, its services. After modifying the template by
adding its information or appending data, the draft is
produced. The provider can change the draft until it
decides that the draft is ready to be implemented. The
work to adjust the draft for the services to be offered
represents the configuration phase. In this phase the
key issue is to verify if the services can be offered (im-
plemented) according to the contract. Time and capa-
bility issues must be considered by the provider. The
capability issue refers to the ability of the provider to
make the service available as well as to accomplish
the tasks related to the service. The configuration
phase is completed when the provider signs the con-
figured draft, generating the pre-contract. The con-
figuration phase involves implementation of the ser-
vice engine, which in general can be automated. Af-
ter publication, the pre-contract can only be read by
clients. At this point of the lifecycle, the provider is
ready to start the negotiation phase, through the bro-
ker. The broker waits for client. If the client agrees
with the clauses proposed, it signs the pre-contract
generating (accepting) the e-contract. The client can
negotiate one or more clauses of the pre-contract, by
exchanging messages with the provider, through the
broker. It forwards the information to the provider
and waits for a response. If the provider agrees with
the modification, it sends a message to the broker that
forwards it to the client. The negotiation is in general
interactive and specific to a client. After the contract
is signed, the operation phase can start.
The relationship between contract artifacts (tem-
plate, draft, pre-contract and e-contract) are presented
below in the UML class diagram in Figure 2. Each ar-
tifact is a subclass of the template, consequently a su-
per class of the all artifacts. The closed lock icon indi-
cates that the artifact is changed only with the owner
´
s
permission, whereas the draft and the new template
can be proposed or modified by the provider.
Figure 2: Artifacts produced during the lifecycle process.
4 SERVICE COMPOSITION
Compositions are mechanisms that allow the creation
of new services based on existing ones (Pautasso,
2009). Several activities are required to accomplish
compositions. In order to facilitate the understand-
ing and communication of designers of composed ser-
vices, we claim that an architectural model is useful.
The focus of our architectural model is to identify
and define elements and responsibilities for the ac-
tivities in compositions. Many concerns can be con-
sidered in an architectural model based on services.
They include business, functional, and non-functional
requirements. Ideally, an architecture should have
enough information to both build the software and
verify the requirements that derived this architecture.
In general, business requirements constantly change,
and due to this fact, a secondary concern with respect
to business requirements is the effort to comply with
the ever-changing business rules in a timely manner.
Part of the business concerns can be formally speci-
fied in contracts. Contracts can be seen as constraints
that can be translated into requirements for the parties
involved. We consider that constraints are terms that
the parties should jointly comply with while require-
ments are terms that a party both sets for itself and
must comply with. If parties comply with require-
ments that are derived from the constraints, it is ex-
pected that constraints will be met. A party has flex-
ibility to define its requirements and arrange its re-
sources to satisfy them. In what follows, we describe
the architecture and how to provide the automation
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
278

based on contracts.
The architectural model, illustrated in Figure
3, helps the composition of services based on e-
contracts. It works as an Universal Description Dis-
covery and Integration(UDDI) service in order to ex-
pose the composition capabilities for Web services.
The architectural model defines responsibilities so
that compositions of services can be designed and im-
plemented. We consider other stakeholder, brokers
who are responsible for the identification and imple-
mentation of service compositions. Due to dynamic
nature of business, we consider that the architecture
must facilitate the implementation of services. There-
fore, automation of implementation is an issue of in-
terest as much as possible.
The architecture was designed for keeping sim-
plicity of REST style combined with the concepts
and SOAP standards. The internal structure of the
agents uses concepts of orchestration model to coor-
dinate the sequencing of tasks associated with differ-
ent providers. On the other hand, the agents coop-
eration partly works in choreography model. Tags
of BPEL language such as <invoke>, <sequence>
and <flow> are replaced by CRUD methods and java
classes in order to adapt the resource management.
Figure 3: Architectural model to manage the composition
of services.
Provider brokers act on behalf of providers for
the composition. They contain information about the
provider to enable composition. The PB also works as
a Contract Repository of a composite of services, stor-
ing standard templates of contracts and standard con-
tract clauses (Goodchild et al., 2000). Composer is
responsible for building the composition of services.
The Transaction Coordinator manages the distributed
transactions of services after the e-contract is ready, in
the operational phase. The Client Broker is responsi-
ble for interaction with the clients. Table 1 describes
the responsibilities of the agents in the architecture.
The interactions among agents are governed by the
web service transaction respecting the e-contract life-
cycle rules.
In the architecture, brokers (both client and
provider brokers) are a means to allow a scalable so-
lution for the composition. Brokers perform much
of the work to accomplish composition without over-
loading the providers. Brokers make it possible for
information about providers to be promptly available
for composition. Each broker is responsible for repli-
cating information to others. After synchronizing, it
is expected that all brokers have the same published
information (Subbu, 2010).
4.1 Lifecycle of the Composition of
Services
In order to make the composition, we consider two
types of lifecycles with dependencies between them.
The first type of lifecycle consider composer and
providers as the main parties of the agreement. The
final product of the first lifecycle is e-contract type 1.
This lifecycle follows the sequence described above.
In the second type of lifecycle, clients and composer
are the main parties of the agreement. The final prod-
uct of the second lifecycle is e-contract of type 2. We
will refer the e-contracts type 1 and type 2 simply as
e-contract 1 and e-contract 2 respectively.
For e-contract 1, the first phases are represented
in Figure 4 as interactions 1 to 5. The condition to
start the proposal phase is the composers responsi-
bility; at least one template of e-contract 1 must be
available in the PBs repository. Figure 4 interaction 1
represents that the provider is looking for a template
to describe its services. After finding the template,
it requests metadata information about the possibil-
ities of service configuration. Setting the template
means to align business transactions with semantic
schema. The submission of a new template implies
the publication in a PBs repository and the semantic
compatibility with the composers framework. Once
the template is selected, the provider can change its
internal structure by appending a new resource. At
this moment, the template is called draft. The draft
contains the information of the services to be config-
ured and provided. As the draft does not carry the
provider
´
s signature, and thus, does not include ser-
vice identification, it can be changed. The config-
uration phase works on the draft and aims to align
the service rules of the e-contract with the providers
configuration. In this phase, some fields of the tem-
plate are used to set the web service engines such as
cost, response time, availability or protocol parame-
ters (Karunamurthy et al., 2012). So, the configura-
tion phase finishes when the provider signs the draft,
changing to a pre-contract. At this point, the pre-
contract 1 (one) is ready to be published. It is im-
portant to observe that it can be published in any PB
(backend of the architecture), as shown in Figure 4
e-BusinessArchitectureforWebServiceCompositionbasedone-ContractLifecycle
279

Table 1: Agents involved in the composition of service and their responsibilities.
Agent Responsibility
Provider P Provides service. It has services and resources available and requires a specific site to
publish its pre-contract. It elaborates the contract proposal
Provider Broker PB Works as UDDI (metadata servers). It contains a template repository. It is responsible
for both sending to composer the pre-contract published and updating the other PBs
with its publication
Composer CP Is responsible for building the composition of services using different pre-contracts
available in the Provider Brokers. It publishes the composite pre-contracts in CBs
Transaction
Coordinator TC
During the transactions in the operation phase, the TC manages operations and coor-
dinates the Client calls to Provider. It returns results and exceptions that control the
order of operations during the transaction
Client Broker CB Works as a UDDI of pre-contracts of the composition and makes the composite pre-
contracts public
Client C Requests a composite service
interaction 3.
The output of the publication phase is the pre-
contract, which is ready to be accessed, once it is
published in a PB. It is not necessary to publish the
pre-contract in the same PB where the template was
found. In any event, the architecture provides syn-
chronization of the publications among the available
provide brokers (PB), as it is shown in Figure 4 inter-
action 5. The synchronization also works in order to
update the new templates in all available PBs.
Figure 4: First phases of the lifecycle (e-contract 1).
The PB is also responsible for sending the pre-
contract address to the composer, when the provider
publishes its pre-contract, in order to start the compo-
sition process, as shown in Figure 4 interaction 4.
If there are two or more pre-contracts ready to be
used (published in PB), the composer can start the
composition process. It can add some data to the
pre-contracts 1 or can propose some changes to the
pre-contracts, such as the definitions of deadlines to
satisfy the composed service or timeouts for resource
reservations. These actions create a link among the
pre-contracts and stay active during the whole life-
cycle. When the composer tries to change the pre-
contract data, the negotiation phase starts as shown
in Figure 5 interaction 1. The composer updates the
e-contract resource in the PBs URI and waits for the
provider authorization, as indicated in interaction 2.
If the provider agrees with the updates, then it sends
a confirmation, changing their pre-contract, as indi-
cated in interaction 3. Then the PB updates other PBs
with new information, as shown in interaction 4.
Figure 5: Negotiation phase of e-contract 1.
During the negotiation phase, we handle with the
lifecycle of the composition, shown in Figure 6. Fig-
ure 6 illustrates two simple lifecycles of services, in
white color, and the lifecycle of the composition, in
gray color. The proposal phase of the composition
starts with the negotiation phase of the simple life-
cycles. The composer makes the composition based
on the negotiation with the providers. When build-
ing the composition with dependencies between the
pre-contracts 1 by adding data, it means a proposal
to a pre-contract of the composition. The configura-
tion phase is represented by adjustments of provider’
engines in order to prepare the publication of com-
posed services agreed. The publication phase ends
when the pre-contract of the composition is published
in a CB. The e-contract produced by the composition
is e-contract 2 (two). In the lifecycle of e-contract 1,
providers can notify the composer that it is possible to
publish services or products according to e-contract
1 rules, whereas, e-contract 2 (two) is an agreement
among providers and clients managed by the com-
poser.
E-contract 2 (two) can be seen as a virtual agree-
ment where the composer stores the URIs of e-
contracts type 1 (one) to construct e-contract 2. If
all providers agree with the conditions, as a result of
negotiation phases of e-contract 1, the composition is
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
280
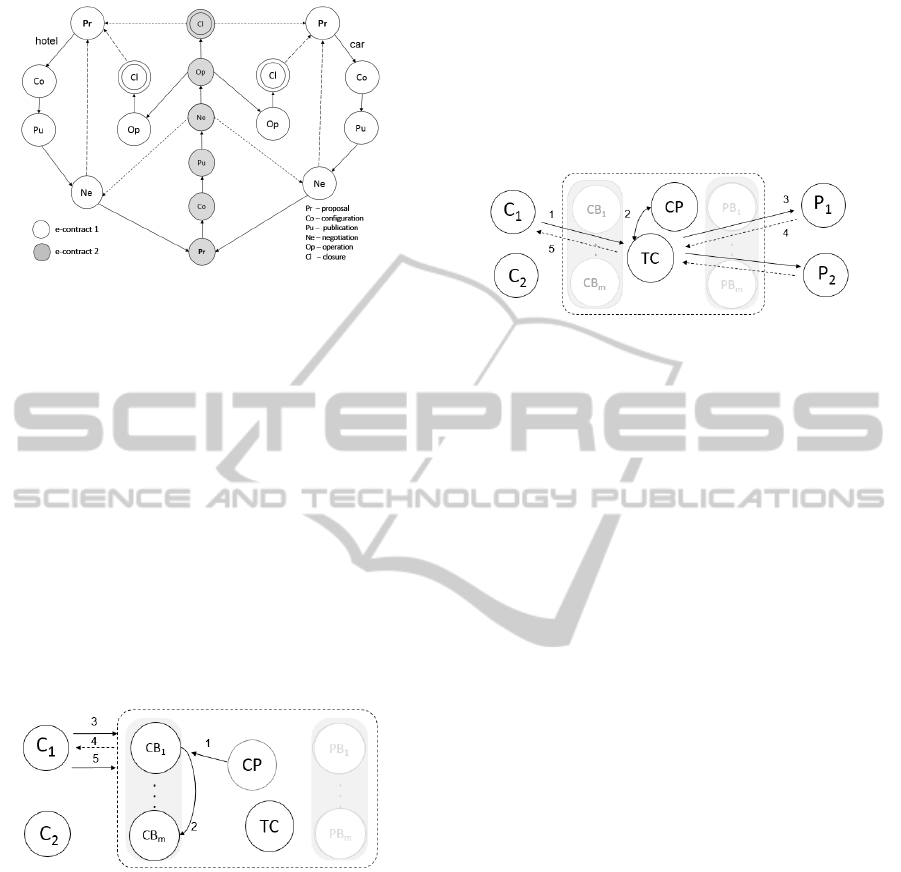
Figure 6: Interactions between the lifecycles used in the
composition process.
prepared to clients. The composition characterizes the
proposal phase of e-contract 2. This phase ends with
the draft of the e-contract of the second lifecycle. The
construction of the e-contract 2 (two) can add depen-
dencies in the published pre-contracts 1. PBs forward
composer’s messages to the providers in order to ad-
just and configure services. After that, the composer
can publish the composition as pre-contract 2 (two),
as shown in Figure 7, interaction 1. The Client Bro-
ker is responsible for updating other Client Brokers
about the publication, as shown in interaction 2. The
composer also sets the parameters in pre-contract 2
(two) in order to use them in the operational phase.
At this point, the client can search for the packages of
service, as shown in interactions 3 and 4.
Figure 7: Some interactions of the of e-contract 2.
The condition for the next phase is the clients sig-
nature. The operation phase depends on the clients in-
teraction, as indicated in Figure 7 interaction 5. If the
client signs the pre-contract, then the operation phase
can start. Alternatively, the client can ask to change
the published pre-contract. In this case, the Client
Broker requests the authorization from composer that
uses the Provider Broker to forward it to the providers
involved. If the providers agree with the modifica-
tion, then the Client Broker and the Provider Broker
are responsible to replicate the modification data. The
negotiation phase finishes when the client signs the
agreement, confirming that it accepts the terms of the
offered package. The package is a set of services of-
fered by providers, through the Client Brokers, Com-
poser, and Provider Brokers, according to the descrip-
tion of pre-contracts used in the composition. The e-
contract is stored in the composer database and the
client can access the packages. The signature of the
contract creates a resource reservation, depending on
the type of service offered.
Figure 8: Operation phase of the composition.
In the operation phase, the client can order the
packages as indicated in Figure 8 interaction 1. The
Transaction Coordinator is responsible for managing
and updating the distributed transactions during this
phase. TC retrieves the e-contract information in
the Composer as shown in interaction 2. The oper-
ation phase may use any transaction protocol for web
services, such as the Timestamp-based Two Phase
Commit Protocol for RESTful Services (TS2PC4RS)
(da Silva Maciel and Hirata, 2010). In TS2PC4RS,
the clients can read, prewrite, write and update opera-
tions. It initially records resources that can be busi-
ness components in the List of buffered PreWrites
(LPW) using timestamp order. Each provider has its
own LPW handled during this phase. TS2PC4RS pro-
vides not only support for long-term transactions, re-
laxing the isolation and atomicity properties, but also
support the control of concurrency. The client can up-
date its preWrites in the course of transaction without
having to start a new transaction if there is one already
stored through the Transaction Coordinator, interac-
tion 1 to 5. When the client aborts the transaction or
changes it, it loses its priority and other clients can
have their prewrites accepted. All agreed parameters
have been adjusted during the configuration phase.
The operation phase is long enough to implement all
transactions and include the related warranties of the
agreed services.
4.2 The Mechanism to Manage the
Lifecycle Artifacts
Since the objective of the architecture is to enable
simple compositions of services in a efficient manner,
we design the agents as RESTful web services. The
standard hypermedia is eXML Schema handled by
HTTP methods (Fielding, 2000)(Subbu, 2010). The
data are resources and they are also handled by REST
e-BusinessArchitectureforWebServiceCompositionbasedone-ContractLifecycle
281

as representational states, i.e., an artifact is an actual
set of representational states (Gronvall et al., 2011).
REST was defined as the principal mechanism for
production and management of the artifacts. REST
style uses the simplicity and reuse of HTTP resources
over the Internet. It is used by agents to manage the
artifacts produced during the lifecycle.
The role of each agent and permissions depends
directly on the phase of the artifact. We adapted the
role-based access control (RBAC) concepts to create,
manage and handle the artifacts (Ferraiolo and Kuhn,
2009). Considering the management of the files, the
agents have different permissions per phase. In gen-
eral, the agent’s permission is restricted until a spe-
cific timeout per phase. Once the e-contract is pro-
duced, there are read-only permission for all agents.
The production of the artifacts is similar to the
production line. The input of the production line is
the template and output is the the e-contract. Inside
the production line, between proposal and operation
phase, the architecture implementation handles and
modifies the artifact by operations. The operations
in the files are native HTTP methods. We defined
the agents’ permissions for each phase. For example,
the provider has Write permission during the proposal
phase and Read permission in the operation phase.
It is important to highlight some characteristics.
First, the file stores all information about the artifact
during the whole process and then all operations in it
are of type Read or Write. Second, transactions are
serialized to avoid any inconsistency. Two operations
Read type do not generate conflict, however, other
pairs involving a Write operation can generate incon-
sistency if they are operations from different transac-
tions in the same phase(George Coulorius and Kind-
berg, 2009).
We can divide the production line into different
stages, phases of the lifecycle. The artifacts han-
dled by agents are input or output requirements of
the lifecycle phases. All of them start from a stan-
dard, which is a template with unique address. Each
artifact is accessed by its root address. The path of
the artifact is defined in the proposal phase. The ar-
chitecture keeps the address static in order to find,
manage and modify it during the lifecycle. The
agents use the GET method to retrieve the actual
state of the artifact by giving a root address such as
http://localhost:8080/eContract/002. The result de-
pends on the artifact phase. All data that make up
and characterize the artifacts are appended to the root
address. If the configuration fields of the artifact are
empty then it is on the proposal phase, otherwise it is
on the configuration phase. It is important to consider
that the architecture’s implementation stores the pre-
vious versions. The related versions are obtained only
from the e-contracts 1 artifacts.
Finally, we should emphasize that the signature,
a requirement to create the e-contract, has preceded
the transaction that involves negotiation. This REST
transaction is atomic, i.e., or either all events occur
or nothing (Pardon and Pautasso, 2014). If, in the
negotiation phase, the internal agents do not receive
all confirmations, the pre-contracts involved can be
discarded by the timeout.
In the next section, we present a simple example
implemented in Netbeans platform 8.0.1 for architec-
ture agents and providers access. The client can use
any REST client available for download.
5 APPROACH ANALYSIS
This section is divided into two parts considering
the practical example described. (i) Benefits: The
main benefit of our approach is providing support
for the automatic configuration of the Web Service
engines via e-contract. The lifecycle model of e-
contract and the architecture allows that adjustments
of the e-contract were implemented automatically ac-
cording to the parties interests. The configurations
were made with little effort, with simple adjustments
of parameters. The e-contract, result of the interac-
tion among the parties, could be used during oper-
ation phase to order services and keeps the config-
uration parameters for web service interoperability.
The client who used the application based on an ar-
chitectural model obtained more flexibility to order
its packages, i.e., it had priority to update its orders
in providers’ LPWs during the operation phase. An-
other advantage is the role of automation definition
process adapted to the standard of the transactional
structure of web services. The characterization of
the e-contract by standard template is built by terms,
representational states, with specific permissions per
agent. This mechanism made the control easy for
the description, search and manipulation of e-contract
clauses via HTTP methods. This characterization al-
lowed not only the reuse of the agent architecture and
the update of the states, but also the modification of
the terms of the e-contract, with low processor capac-
ity and reduced latency. In summary, the time spent
in standard web service transactions was used to build
the e-contract concurrently.
(ii) Limitations: There are limitations in our ap-
proach. First, the negotiation phase required human
interaction to choose the best parameters. The sec-
ond limitation is potential and can occur when pre-
contracts 2 are too restrictive and cannot express the
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
282

clients’ desires. We argue that it is job of the broker to
build attractive compositions, even if they are some-
how restrictive. It is important to consider that the
architecture was not implemented in a large scale ex-
ample, and there are some gaps about settings, about
how to cancel the contract during the lifecycle and
what are the practical implications. Finally, two im-
portant aspects were not addressed in this work: se-
curity and fault-tolerance. They were not the focus of
this work, but certainly they require further investiga-
tion.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
The adaptation of the e-contract lifecycle for the com-
position context allows the visualization of the flexi-
bility of approach and suitability to different business
scenarios. Also, the distributed architecture allows
the approach to become scalable by addition of bro-
kers that replicate the data published. Accordingly,
the same pre-contract may be published by different
brokers to improve the fault tolerance. The greatest
benefit of the approach is to reduce the complexity of
building the composition, which is created from ex-
tracts of e-contracts previously signed, maintaining a
reasonable flexibility. This article does not discuss
the methodology to choose the parameters from dif-
ferent services in order to create the dependency in the
composition, in fact, it proposes an innovative way to
merge services by e-contract support.
Future work includes fault tolerance analysis and
security analysis. A complementary work approach
allows the client to propose a new composition in-
stead of the composer (broker).
REFERENCES
Baset, S. A. (2012). Cloud slas: Present and future. SIGOPS
Oper. Syst. Rev., 46(2):57–66.
Chiu, D., Cheung, S., and Till, S. (2003). A three-layer
architecture for e-contract enforcement in an e-service
environment. In System Sciences, 2003. Proceedings
of the 36th Annual Hawaii International Conference
on, pages 10 pp.–.
da Silva Maciel, L. A. H. and Hirata, C. M. (2010). A
timestamp-based two phase commit protocol for web
services using rest architectural style. J. Web Eng.,
9(3):266–282.
Ferraiolo, D. F. and Kuhn, D. R. (2009). Role-based access
controls. CoRR, abs/0903.2171.
Fielding, R. T. (2000). Architectural styles and the design
of network-based software architectures. PhD thesis,
University of California, Irvine.
George Coulorius, J. D. and Kindberg, T. (2009). Dis-
tributed Systems Concepts and Design. Addilson
Wesley.
Goodchild, A., Herring, C., and Milosevic, Z. (2000).
Business contracts for b2b. In Proceedings of the
CAISE*00 Workshop on Infrastructure for Dynamic
Business-to-Business Service Outsourcing, pages 5–6.
Gronvall, E., Ingstrup, M., Ploger, M., and Rasmussen,
M. (2011). Rest based service composition: Exem-
plified in a care network scenario. In Visual Lan-
guages and Human-Centric Computing (VL/HCC),
2011 IEEE Symposium on, pages 251–252.
Halili, F., Rufati, E., and Ninka, I. (2013). Styles of ser-
vice composition – analysis and comparison meth-
ods. In Computational Intelligence, Communication
Systems and Networks (CICSyN), 2013 Fifth Interna-
tional Conference on, pages 302–307.
Huang, Y., Li, J., Dun, H., and Wang, H. (2009). Analyzing
service composition patterns in bpel. In Proceedings
of the 2009 International Joint Conference on Artifi-
cial Intelligence, JCAI ’09, pages 623–627, Washing-
ton, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Karunamurthy, R., Khendek, F., and Glitho, R. H. (2012).
A novel architecture for web service composition. J.
Netw. Comput. Appl., 35(2):787–802.
Marchione, F. G., Fantinato, M., de Toledo, M. B. F., and
Gimenes, I. M. S. (2009). Price definition in the estab-
lishment of electronic contracts for web services. In
Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on
Information Integration and Web-based Applications
& Services, iiWAS ’09, pages 217–224, New York,
NY, USA. ACM.
Milanovic, N. (2005). Contract-based web service compo-
sition framework with correctness guarantees. In Pro-
ceedings of the Second international conference on
Service Availability, ISAS’05, pages 52–67, Berlin,
Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Neto, J. B. and Hirata, C. M. (2013). Lifecycle for man-
agement of e-contracts based on web service. In Pro-
ceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and
Computer Science, volume 1.
Pardon, G. and Pautasso, C. (2014). Atomic distributed
transactions: A restful design. WWW Companion
’14, pages 943–948, Republic and Canton of Geneva,
Switzerland. International World Wide Web Confer-
ences Steering Committee.
Pautasso, C. (2009). Restful web service composition with
bpel for rest. Data Knowl. Eng., 68(9):851–866.
Subbu, A. (2010). RESTful Web Services Cookbook.
O’Reilly, third edition.
Sun, W., Zhang, J., and Liu, F. (2006). Ws-sla: A frame-
work for web services oriented service level agree-
ments. In CSCWD, pages 714–717. IEEE.
e-BusinessArchitectureforWebServiceCompositionbasedone-ContractLifecycle
283
