
How Can Semantics and Context Awareness Enhance the Composition of
Context-aware Services?
Tarik Fissaa
1
, Hatim Guermah
1
, Hatim Hafiddi
1,2
and Mahmoud Nassar
1
1
IMS TEAM, SIME Lab, ENSIAS, Mohammed V Rabat University, BP 713, Agdal Rabat, Morocco
2
ISL TEAM, STRS Lab, INPT, Rabat, Morocco
Keywords:
Ubiquitous Computing, Semantic Context aware service, Ontology, Service Composition, AI Planning.
Abstract:
The context-aware services refers to applications that use so-called contextual information to provide appro-
priate services or relevant information to the user or other applications to perform a specific task. An important
challenge in context-aware service oriented systems is the creation of a new service on demand to carry out
more complex tasks through the composition of existing services. In this work, we aim to propose a seman-
tic based architecture for the development of context aware services composition using Artificial Intelligence
(AI) planning. The straightforward translation between AI planning through PDDL and Semantic web services
via OWL-S allows to automate the composition process. Thus planning based service composition launches a
goal-oriented composition procedure to generate a plan of composite service corresponding to the user request.
1 INTRODUCTION
The pervasive computing vision introduced by Mark
Weiser in the early 90’s, results from the conver-
gence of powerful, small, affordable computing de-
vices with networking technologies that tie them all
together. Thus, it has brought about a new gener-
ation of service oriented architectures, based on the
Context-Aware Service (CAS) paradigm. Context
driven development of service oriented systems en-
ables them to be context-aware and consequently to
provide users with customized and personalized be-
haviors depending on their contexts.
One of the core principles of Service oriented
computing (SOC) is the idea of assembling services
to form a chain by discovering and dynamically
composing those multiple existing services to sat-
isfy a user task rather than building new applica-
tions from ’scratch’. Automation of this process is
emerging as one of the most interesting challenges
facing SOC today. In order to be context-aware,
composite services need to follow some requirements
in order to resolve the challenges brought by the
context-awareness paradigm, thus the composed ser-
vice should be built in automatic and dynamic way
depending on the context of use.
The manual composition of services is complex
and susceptible to errors because of the dynamic be-
havior and flexibility of the context aware services.
AI planning technologies has proven to be useful for
the automation of services composition. By treat-
ing services as an action, planners do various sorts of
reasoning about how to combine services into a plan
responding to the user goal. AI planning based al-
gorithms try to find a feasible composition solution
through search of possible services to accomplish a
specific task.
For the above reasons, CAS development can
benefit from semantic web services, Model Driven
Engineering (MDE) via ODM (Object Management
Group, 2009) and AI planning techniques. Model-
Driven Engineering is a software design and devel-
opment approach that strongly focuses on models
and pretends that these models can be refined and
finally transformed into a technical implementation.
The purpose of Semantic Web Services(Martin et al.,
2007) is to use semantic specification to automate the
discovery, invocation, and composition Web services.
The Ontology Web Language for services (OWL-S) is
the most direct outcome for describing Web services
in the semantic web.
In this work, we aim to propose in first stage an
overview of an architecture for the automation of con-
text aware services composition. Our major contribu-
tion in this paper is the proposition of an extension
to OWL-S with context elements to take advantage
of the context awareness, and especially we propose
a tool for automatic services composition using AI
640
Fissaa T., Guermah H., Hafiddi H. and Nassar M..
How Can Semantics and Context Awareness Enhance the Composition of Context-aware Services?.
DOI: 10.5220/0005381706400647
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 640-647
ISBN: 978-989-758-097-0
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

planning as recommanded in semantic web services
OWL-S specifications (Martin et al., 2007).
The remainder of this paper is structured as fol-
lows. Next we present a motivation scenario that con-
cerns context-aware E-health system. In section 3 we
present some definitions and background. In section
4, we give an overview of the proposed architecture,
section 5 presents a brief descriptions of our Context
Modeler. In section 6 we present our proposal for se-
mantic CAS by extending OWL-S. Section 7 presents
some related work in context aware service compos-
tion approachs. The final section gives rise to some
concluding remarks and plans for future works.
2 E-HEALTH MOTIVATING
SCENARIO
In this scenario, the underlying idea is to allow elderly
people, chronic patients to stay at home and to bene-
fit from a remote and automated medical supervision.
Let’s take the case of a patient with a cardiac arrhyth-
mia. The patient’s situation requires monitoring to
detect crises or problems that may be caused by the
increase or decrease in his heart rate. Thus in the case
of a problem the patient should be informed of a criti-
cal condition, and take the necessary precautions. The
role of the context-aware system is to find the near-
est caregiver (nurse or available physician) to help the
patient depending on the severity of his condition. In
parallel, depending on the current situation of the pa-
tient, the system must find an ambulance to transport
the patient to the hospital. The aim is to provide the
patient with both higher levels of security and inde-
pendence that allows him to live a normal life despite
his illness. This e-health scenario highlights the fun-
damental challenges for the composition of context-
aware services. Having regard to the need to use the
patient context, the e-health system should be context
aware. Therefore, different types of services can be
defined (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: E-health Scenario.
3 BACKGROUND
3.1 Context
The notion of ’context’ is vague to define, many re-
searchers working on context had given a variety
of different definitions. However, a universally ac-
cepted definition is yet to be agreed. Schilit (Schilit
et al., 1994) defined context to be: location, identi-
ties of nearby people, objects and changes to these
objects. Other definitions had been proposed, Brezil-
lon (Br
´
ezillon, 2003) define context as an information
that characterizes the interactions between humans,
applications and the environment. Dey et al.(Dey and
Abowd, 2000) discuss that the important aspects of
context cannot be enumerated, as they differ from sit-
uation to situation and depend on the purpose of the
application, furthermore they formally defined con-
text as:”... any information that can be used to char-
acterize the situation of an entity. An entity is a per-
son, place or object that is considered relevant to the
interaction between a user and an application, in-
cluding the user and applications themselves.” In our
work we will adopt this definition because it remains
the most generic.
3.2 Context Awareness
Having defined the concept of context, we still need
to define the usage of context through context aware-
ness, context awareness refers to the ability of an ap-
plication to discover and take advantage of contextual
information, such as user location and nearby devices.
Shilit (Schilit et al., 1994) was the first to introduce
the concept of context-awareness and have defined it
as the ability of an application to discover and react to
changes according to the user’s environment. Brown
(Brown et al., 1997) defines it as applications whose
behavior can change depending on the user’s context.
Dey(Dey and Abowd, 2000) considers an application
as context aware if it uses contextual information to
provide relevant information and services to the user,
where relevance depends on the user’s task.
3.3 AI Planning and PDDL
Planning is a problem solving technique, where
knowledge about available actions and their conse-
quences is used to identify a sequence of actions,
which, when applied in a given initial state, satisfy
a desired goal. In general, a planning problem has the
following components:
• A description of the possible actions which may
HowCanSemanticsandContextAwarenessEnhancetheCompositionofContext-awareServices?
641

be executed (a domain theory) in some formal lan-
guage.
• A description of the initial state of the world
• A description of the desired goal
Thus Service composition can be modeled as a AI
planning problem. Based on the initial state, the de-
sired goal and context information, planning-based
service composition launches a goal-oriented compo-
sition procedure to generate a plan with respect to
users context.
PDDL: The Planning Domain Definition Lan-
guage (PDDL) proposed by (Mcdermott et al., 1998)
is a standard encoding language for planning tasks.
The PDDL is inspired by well-known STRIPS (Stan-
ford Research Institute Planning System) (Fikes and
Nilsson, 1972) and it is an action-centered language
as well as STRIPS. It uses precondition and post-
condition to describe the applicability and effects of
actions. Despite some argument in the some features
of PDDL, the language has been wildly accepted in
AI community, since it standardizes the domain de-
scription and the problem description in planning re-
search. Then we can compare the AI planner and
share planning resources. The introduction of PDDL
has facilitated the scientific development of planning.
Planning tasks specified in PDDL are separated
into two files:
• A domain file: composed of the predicates which
are used to describe the knowledge in the world
and the actions which can change the world states.
• A problem file: The problem file includes objects
in the world, initial state and goal specification.
4 ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW
Our approach for context-aware service Composition
is based on an integrated environment based on the
synergie between Semantic Web Ontology and Con-
text Awareness. Figure 2 presents an architectural
overview of all the system’s component aimed at pro-
viding personalized services according to the user
context. There are the main components that we dis-
tinguish in the architecture:
• Context Ontology Modeler: it defines the capture
phase and representation of context. It is com-
posed of two components.
– A model of context in specific domain (e-health
in our case), conformity with the proposed
metamodel. This metamodel is defined in a
generic and abstract way to be used indepen-
dently from the application area.
– OWL context ontology generated from a model
of context using models transformation based
on ODM the new OMG standard dedicated to
ontology.
• Discovery and Reasoning: allows reasoning and
deducing new situations from OWL ontology of
context and inference rules that well help in defin-
ing the necessary adaptations in the final compos-
ite service. The discovery is the process of finding
appropriate services semantically to avoid prob-
lems occured in syntactical matching. Let’s men-
tion that we don’t deal in this work with discov-
ery and reasoning our focus is on the composition
phase.
• Composition Planner: To build context aware ser-
vices, we need to define mechanisms for the com-
position of appropriate services and to adapt their
behavior according to the current context. Such
mechanisms will favorite loosely coupling be-
tween the core service and its adaptations seen as
transversal preoccupations. The adaptations are
eventually conditioned by the existence of rele-
vant situations to the current context. Therefore
following a users request, and a set of services
described as actions, a planner would find a col-
lection of services automatically that achieves the
request to build an adapted composite service.
5 CONTEXT ONTOLOGY
MODELER
To model the context in generic and abstract way, we
propose a metamodel that defines the context and its
sub context, context property, validity, and specifica-
tions of each context property (see Figure 3). This
metamodel is based on the following specifications:
• A context decomposes into sub contexts.
• A sub context can be, recursively, decomposed
into categories for its structuring.
• A context, a sub context and a category are con-
stituted of context properties.
• A context property is gathered by sensors:
SensedCtxProperty, or derived from other context
properties: DerivedCtxProperty, or stored in the
database: StoredCtxProperty.
• Each property has a context validity.
• A derivedCtxProperty is obtained by derivation
from a set of properties based on derivationFunc-
tion.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
642
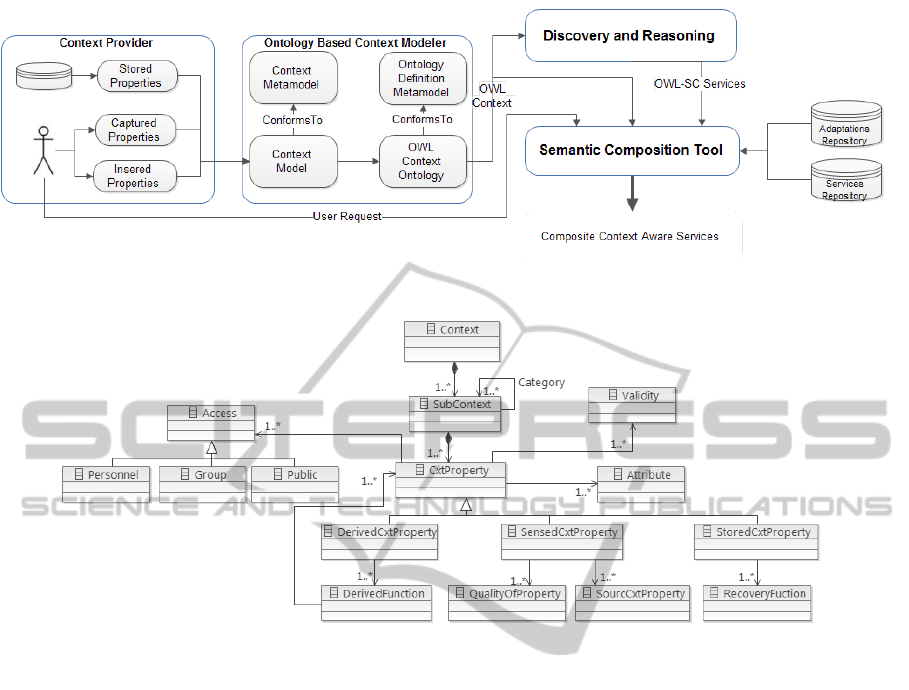
Figure 2: Overview of the proposed architecture.
Figure 3: Context metamodel.
• A StoredCtxProperty is obtained through the re-
covery features of stored properties (e.g. Recov-
eryFunction).
• A sensedCxtProperty is obtained and character-
ized by the context source SourceCxtProperty and
the acceptance value of context property Quality-
ofProperty.
• Each sub context has a specific type of access.
To illustrate our metamodel, let’s project it on the case
of figure of the E-health system. The context for this
system in particular and context-aware computing in
general is composed mainly of the following sub con-
texts:
• environment: represent user’s location,time...etc.
• Medical Information: contains user’s health prop-
erties (in our case Blood Sugar, HRV, and Blood
pressure).
• User: contains properties describing the user
(Blood groupe, age, preference).
• Device: contains parameters that describe the en-
tity Device (e.g. medicals device, mobile phones,
PDA...etc).
5.1 Context Metamodel Transformation
to OWL
Models transformations provide a mechanism for au-
tomatically creating or updating target models based
on information contained in existing source models.
Formally, a simple model transformation has to de-
fine the way for generating a model Mb, conforming
to a metamodel MMb, from a model Ma conforming
to a metamodel MMa.In our case, the source meta-
model corresponds to a view from our context meta-
model and the target metamodel corresponds to the
OWL metamodel.
As a result we obtain an OWL ontology based on
our context model, the resulting ontology consists of
a set of classes, individuals, properties and relations
that describe the various context properties (see Fig-
ure 4). This OWL ontology can be used for reasoning,
discovering and composing.
HowCanSemanticsandContextAwarenessEnhancetheCompositionofContext-awareServices?
643

Figure 4: excerpt of the E-health ontology.
6 CONTEXT AWARE SEMANTIC
COMPOSER
6.1 Context Aware Semantic Services
OWL-S is an ontology for the description of seman-
tic Web services expressed in the Web Ontology Lan-
guage (OWL). OWL-S defines an upper ontology
for semantically describing Web services along three
main aspects: The Service Profile describes what the
service does in terms of inputs, outputs, preconditions
and effects (IOPEs). The Service Model describes
how a service works in terms of a process model
that may describe a complex behaviour over under-
lying services. The Service Grounding describes how
the service can be accessed, usually by grounding to
WSDL. But to take advantage of context-awareness,
it’s important to have an efficient mechanism to adapt
services (composite or single ones) according to the
context which is not supported by the current OWL-S.
Therefore we propose an extension to OWL-S called
OWL-SC (C stand for context) based on context ele-
ments to detect the necessary adaptations. Figure 5 il-
lustrate our Semantic Context Aware Service (SCAS).
The SCAS is based on the following specifications:
• The SCAS has a ServiceModele, ServiceProfile
and ServiceGrounding.
• The service model can be viewed as a process.
• The Process containts AtomicProcess or Compos-
iteProcess.
• The ServiceProfile is related to a context Property.
• Each ContextProperty contains Contextual At-
tributes: Attribute.
• Each AtomicProcess contains an Adaptation.
• For a given AtomicProcess a set of Adaptation-
Rule is associated.
• An AdaptationRule can involve the execution of
an ordered set of Adaptations.
• An Adaptation is related to a relevent context
property.
6.2 The Composition Phase
To automate the composition of context-aware ser-
vices, we have to resort a strategy for composing
and adapting context aware services. Figure 6 shows
the process of composing our semantic context aware
services using AI planning. The relevant extended
OWL-S services description is acquired by semantic
services discovery. The key features of the composer
are:
• Translate the Web services description of domain
and problem written in OWL-S to the planning
problems described in PDDL.
• Input the result generated by the converting pro-
cess into AI planner.
• Translate back the actions sequence that AI plan-
ner got in the precedent step into a composite Web
service.
6.2.1 Translation OWL-SC to PDDL
The purpose of the OWLS2PDDL converter is to
translate a given OWL-DL expression in OWL-S ser-
vice descriptions and a given service composition
problem into an equivalent PDDL planning problem
which can be understood by AI planners. Due to
space limitations, we only describe the essential trans-
lation process: an operator of the planning domain
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
644
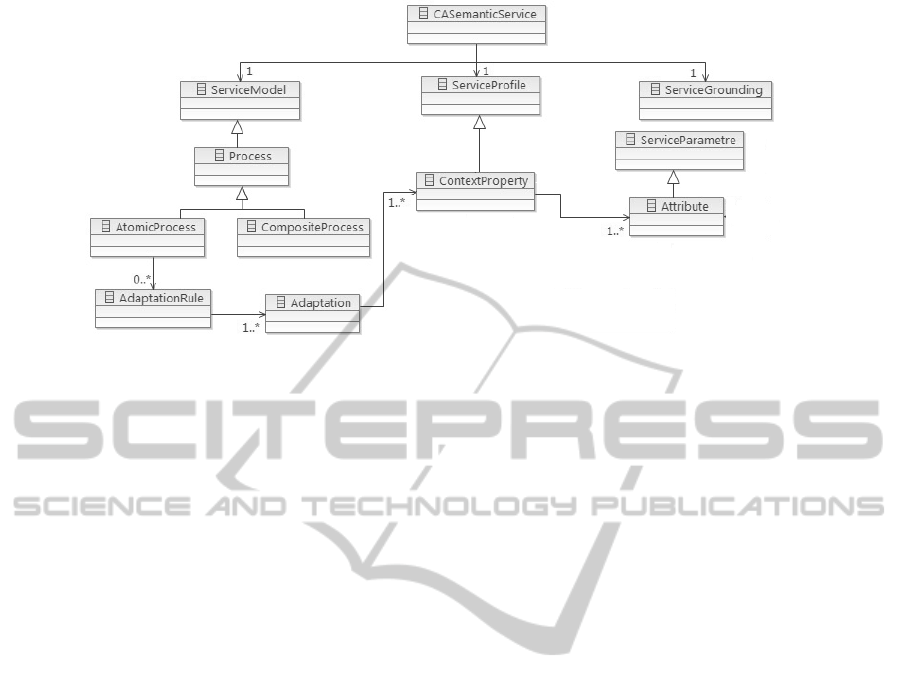
Figure 5: Semantic context aware service by extending OWL-S.
.
corresponds to a service profile in OWL-S: both oper-
ator and profile describe a pattern of how an action or
web service as an instance should look like. A method
is a special type of operator, that allows the user to
describe composed web services. Any OWL-S ser-
vice profile input parameter correlates with an equally
named one of an PDDL action, and the hasPrecondi-
tion service parameter can directly be transformed to
the precondition of the action by use of predicates.
The same holds for the hasEffect condition parame-
ter. If the service exist then it’s translation is part of
the planning domain generation and if the service is
requested (goal) then it’s part of the problem descrip-
tion.
6.2.2 Planning
Planning focuses on selecting suitable actions and
ordering them in an appropriate sequence so as to
achieve some goal automatically. In general a clas-
sical AI planning problem can be described as a quin-
tuple < S, S
0
, G, A, Γ >, where:
• S is the set of all possible states of the world.
• S
0
⊂ S denotes the initial state of the world.
• G ⊂ S denotes the goal state of the world the plan-
ning system attempts to reach.
• A is the set of actions the planner can perform in
attempt to reach a desire goal.
• The translation relation Γ ⊆ SxAxS defines the
precondition and effects for the execution of each
action.
In terms of Web services S
0
and G represent the initial
state and the goal state respectively, specified by the
service requestors. A is a set of available services and
Γ denotes the current states of each service.
So far we have presented available Web Services
and initial and goal state of the problem domain in
PDDL. The domain and problem files can be sent to
any PDDL based planner to generate a valid compo-
sition plan. The generated plan provides the sequence
of the context aware service composition.
6.2.3 Translation PDDL to OWL-SC
After the acquisition of solutions, a reverse transla-
tion process has to take place, in order to provide the
resulting composite web service to the original OWL-
S standard and the initial web services domain. This
reverse translation accommodates composite service
deployment and execution monitoring.
6.2.4 Adaptation Tool
The adaptations are eventually conditioned by the ex-
istence of relevant situations to the current context.
Thus, the composite service must be able in our case
to dynamically adapt its behavior to different context
changes. It consists in weaving the required Adapta-
tion Aspects, following a set of AdaptationRules into
the core service to produce the corresponding Context
aware service.
6.3 Running Example
Let’s take the case when the system detect a critical
condition that require a medical intervention. The pa-
tient receives an alarm service and recommendations
provided by the system and the physician and a trans-
portation service is triggred taken into account the lo-
calisation and the nearest hospital. This case require
a context driven composition. Figure 7 depicts an ex-
ample of a plan generated in this cas.
HowCanSemanticsandContextAwarenessEnhancetheCompositionofContext-awareServices?
645
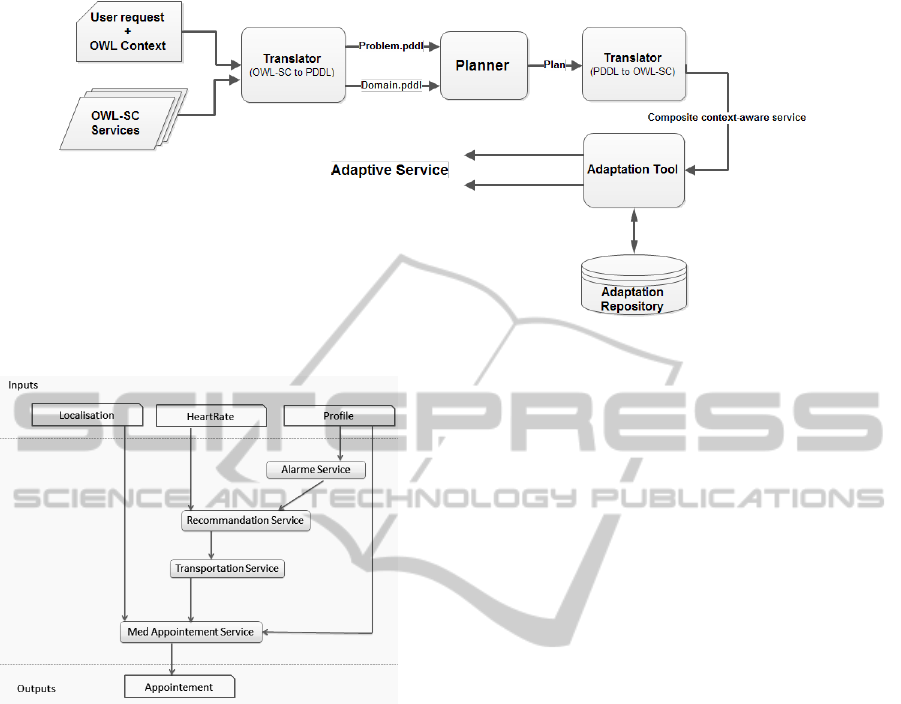
Figure 6: Semantic Composition Tool.
Figure 7: Generated plan.
7 RELATED WORK
Context modeling is of vital importance for Context-
aware applications developers and architects, since
it provides dynamic service behaviors, content adap-
tation and pertinent usage for end-users. For the
above reasons, Strang and Linnhoff-Popien (Strang
and Linnhoff-Popien, 2004) present a survey of
six context modeling approaches: Key-value mod-
eling(Schilit et al., 1994), markup scheme model-
ing (Nilsson et al., 2000), object oriented modeling
(Schmidt and Van Laerhoven, 2001), graphical mod-
eling (Henricksen et al., 2003), logic based modeling
(Ghidini and Giunchiglia, 2001) and ontology based
modeling approaches. Their analysis favors ontology
based context modeling.
SHOP-2 (Sirin et al., 2004) uses services descrip-
tions in DAML-S, the predecessor of OWL-S, and
performs Hierarchical Task Network (HTN) planning
to solve the problem. The main disadvantage of this
approach lies in the fact that the planning process, due
to its hierarchical nature, requires the specification of
certain decomposition rules.
OWLS-XPlan (Klusch et al., 2005) uses the se-
mantic descriptions of atomic web services in OWL-
S to derive planning domains and problems, and in-
vokes a planning module called XPlan to generate
the composite services. The system is PDDL com-
pliant, as the authors have developed an XML dialect
of PDDL called PDDXML. Although the system im-
ports semantic descriptions, the planning module re-
quires exact matching for service inputs and outputs.
Authors in(Hatzi et al., 2013) presents PORSCE
II, an integrated system that performs automatic se-
mantic web service composition exploiting AI plan-
ning. The main advantages of the proposed frame-
work the extended utilization of semantic informa-
tion, in order to perform planning under semantic
awareness and relaxation. In our point of view this is
an interesting approach to deal with semantic compo-
sition however the context dimension is ignored and
not taken into account.
The presented approaches don’t take into account
the notion of context awareness.
Authors in (Li et al., 2011) present an approach
to support context-aware semantic service composi-
tion, by weaving context aspects defined by means of
ontology concepts, within plan compositions. Weav-
ing is performed statically, before starting the execu-
tion of the main service. However, they don’t deal
with context modeling and reasoning also automatic
composition is not considered. Authors in (Mrissa
et al., 2007) trie to solve IO compatibility issues be-
tween services within a composition of services by
integrating the notion of context and service media-
tor. This concept of context they use does not take
into account the underlying definitions of the context
relative to ubiquitous environments and the fact to in-
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
646

sert a mediator service within each pair of services in
the composition process may, from our point of view,
significantly increase response time and system per-
formance.
The main advantage of our approach is the use of
metamodel and a model transformation into an on-
tology to facilitate the context modeling phase, thus
we propose a synergy beetwen context awareness and
semantics in order to enhance and automate the com-
position of services in ubiquitous environment.
8 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we present a semantic based architecture
for the composition of context aware services.Thus,
following MDE specifications we propose an ontol-
ogy based context modeler in order to give support to
translation from context models into an OWL context
ontology. Next step is reasoning and discovering ser-
vices to extract high level informations. Finally, our
main proposition is a semantic context-aware service,
represented by extending OWL-S. Therefore services
will be used for composition by our AI planning based
tool in order to generate a composite context aware
service.
We project to provide an applicative layer of our
tool for service composition in order to automate the
whole process of the composition. We also plan
to evaluate more composition mechanisms such as
heuristics and other problem solving algorithms.
REFERENCES
Br
´
ezillon, P. (2003). Focusing on context in human-
centered computing. Intelligent Systems, IEEE,
18(3):62–66.
Brown, P., Bovey, J., and Chen, X. (1997). Context-aware
applications: from the laboratory to the marketplace.
Personal Communications, IEEE, 4(5):58–64.
Dey, A. and Abowd, G. (2000). Towards a better under-
standing of context and context-awareness. In CHI
2000 Workshop on The What, Who, Where, When, and
How of Context-Awareness.
Fikes, R. E. and Nilsson, N. J. (1972). Strips: A new ap-
proach to the application of theorem proving to prob-
lem solving. Artificial intelligence, 2(3):189–208.
Ghidini, C. and Giunchiglia, F. (2001). Local models se-
mantics, or contextual reasoning= locality+ compati-
bility. Artificial intelligence, 127(2):221–259.
Hatzi, O., Vrakas, D., Bassiliades, N., Anagnostopoulos,
D., and Vlahavas, I. (2013). The porsce ii framework:
Using ai planning for automated semantic web ser-
vice composition. The Knowledge Engineering Re-
view, 28(02):137–156.
Henricksen, K., Indulska, J., and Rakotonirainy, A. (2003).
Generating context management infrastructure from
high-level context models. In In 4th International
Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM)-
Industrial Track. Citeseer.
Klusch, M., Gerber, A., and Schmidt, M. (2005). Semantic
web service composition planning with owls-xplan. In
AAAI Fall Symposium on Semantic Web and Agents,
USA.
Li, L., Liu, D., and Bouguettaya, A. (2011). Semantic based
aspect-oriented programming for context-aware web
service composition. Information Systems, 36(3):551–
564.
Martin, D., Burstein, M., Mcdermott, D., Mcilraith, S.,
Paolucci, M., Sycara, K., Mcguinness, D. L., Sirin, E.,
and Srinivasan, N. (2007). Bringing semantics to web
services with owl-s. World Wide Web, 10(3):243–277.
Mcdermott, D., Ghallab, M., Howe, A., Knoblock, C., Ram,
A., Veloso, M., Weld, D., and Wilkins, D. (1998).
Pddl - the planning domain definition language. Tech-
nical Report TR-98-003, Yale Center for Computa-
tional Vision and Control,.
Mrissa, M., Ghedira, C., Benslimane, D., Maamar, Z.,
Rosenberg, F., and Dustdar, S. (2007). A context-
based mediation approach to compose semantic web
services. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology
(TOIT), 8(1):4.
Nilsson, M., Hjelm, J., and Ohto, H. (2000). Composite
capabilities/preference profiles: Requirements and ar-
chitecture. W3C Working Draft, 21.
Object Management Group (2009). Ontology definition
metamodel (omg) version 1.0. Technical Report
formal/2009-05-01, Object Management Group.
Schilit, B., Adams, N., and Want, R. (1994). Context-
aware computing applications. In Mobile Computing
Systems and Applications, 1994. WMCSA 1994. First
Workshop on, pages 85–90. IEEE.
Schmidt, A. and Van Laerhoven, K. (2001). How to build
smart appliances? Personal Communications, IEEE,
8(4):66–71.
Sirin, E., Parsia, B., Wu, D., Hendler, J., and Nau, D.
(2004). Htn planning for web service composition
using shop2. Web Semantics: Science, Services and
Agents on the World Wide Web, 1(4):377–396.
Strang, T. and Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2004). A context mod-
eling survey. In In: Workshop on Advanced Context
Modelling, Reasoning and Management, UbiComp
2004 - The Sixth International Conference on Ubiq-
uitous Computing, Nottingham/England.
HowCanSemanticsandContextAwarenessEnhancetheCompositionofContext-awareServices?
647
