
Building a Community Cloud Infrastructure for a Logistics Project
Maria Teresa Baldassarre
1
, Nicola Boffoli
1
, Danilo Caivano
1,2
,
Gennaro del Campo
2
and Giuseppe Visaggio
1,2
1
Department of Informatics, University of Bari, Bari, Italy
2
SER&Practices SPIN-OFF, Bari, Italy
Keywords: Cloud Computing, Private Cloud, SaaS, Integrated Logistics.
Abstract: Cloud computing is becoming more and more adopted as infrastructure for providing service oriented
solutions. Such a solution is especially critical when software and hardware resources are remotely
distributed. In this paper we illustrate our experience in designing the architecture of a community cloud
infrastructure in an industrial project related to integrated logistics (LOGIN) for made in Italy brand
products. The cloud infrastructure has been designed with particular attention towards aspects such as
virtualization, server consolidation and business continuity.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing is rapidly becoming a common
model adopted for delivery and utilization of
services over the internet in the sense that it provides
computer infrastructure and services on an on-
demand and on-need basis, without organizations or
users having to sustain large hardware and software
investments. Rather, the services provided are
accessed on a pay-per-use modality, i.e. users pay
for what they use of the computer infrastructure and
services provided (Marston 2011). Another benefit
of this model is the fact that services are available
over the web from any site, without the user needing
to know details concerning the software, interface or
services (Wang 2008). In spite the several
definitions of cloud computing in literature
(Armbrust 2011, Lenk et.al 1999, Mell et al.2011,
Wang et al.2008) the software engineering research
and industrial community has conformed to adopt
the definition provided by the US National Institute
of Standards and Technology (NIST) according to
which: “Cloud computing is a model for enabling
convenient on-demand network access to a shared
pool of configurable computing resources (e.g.
Networks, servers, storage, applications and
services) that can be rapidly provisioned and
released with minimal management effort or service
provider interaction. This cloud model is composed
of five essential characteristics, three service models
and four deployment models” (Mell et al. 2008).
The aim of this paper is to present our specific
experience in designing and developing a
community cloud infrastructure (Baiardi et. al 2010)
within a research project on integrated logistics
called LOGIN. The aim of the project was to build
an extended Digital Network Enterprise (DBE) able
to provide digital services for logistics. The DNE is
based on a software platform through which all
enterprises that require logistic services request the
services they need and the platform then combines
the services available to meet the demand.
The design and implementation of an IT platform
for managing real-time logistic flows with respect to
both tangible and intangible assets converges
towards the need of a digital business ecosystem
between logistic suppliers and users. The support to
such technologies requires a highly flexible cloud
infrastructure that meets the requirements and
specifications of all the partners involved in the
project. Moreover, the cloud infrastructure must be
able to provide access to remotely distributed
hardware and software resources. These resources
must be scalable entities that provide a service and
are available over the web.
This paper presents the details of the cloud
infrastructure developed to orchestrate and manage
all the services related to a logistics project. In the
next section the architecture of the cloud
infrastructure is defined with details on the quality
420
Baldassarre M., Boffoli N., Caivano D., del Campo G. and Visaggio G..
Building a Community Cloud Infrastructure for a Logistics Project.
DOI: 10.5220/0005400504200427
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 420-427
ISBN: 978-989-758-097-0
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

characteristics addressed and the three layers of the
architecture (hardware, software, virtualization). A
short description of the application of the cloud
solution to the logistics project is then provided.
Finally conclusions are drawn.
2 CLOUD SOLUTION FOR
LOGISTICS
As first step, we analysed the deployment models
among the available ones: private, public,
community, and hybrid cloud (Armbrust et al. 2011,
Baiardi et al.2010, Grossman et al.2009), and
decided upon a community cloud. This was the most
appropriate since the LOGIN project involved
several industrial partners and research organizations
having in common a set of software systems to share
in the infrastructure. The choice of a community
cloud turned out to be the most cost effective and
able to assure security and privacy at the same time
as the services are available to the all members of
the community. The service model chosen was SaaS
as it consisted of offering the services to users on a
pay-per-use basis, according to a specific
econometric model shared by all the partners
involved. Second, we identified the components of
the cloud infrastructure:
hardware components (Hardware Layer);
technologies for virtualization based on the
hardware layer (Virtualization Layer);
platforms and tools for managing the cloud
environment (Software Layer).
The cloud computing solution had to enable
access to hardware and software resources remotely
accessible via web. Furthermore, the service was to
assure provision of virtual machines (VM) suitable
to host the software components required for the
realization of the LOGIN platform. Users were to
access to a:
Portal: access point to the cloud infrastructure
from where it is possible to access and
manage VM (create, delete, power-on, reset,
power-off, …) functionalities.
Services Catalogue: a catalogue of services
(virtual machines/ software) preconfigured
with an operating system and applications (db
server, web server, etc.). From this catalogue
users are able to choose resources and services
based on their needs in real time.
2.2 Quality Characteristics
The cloud computing infrastructure was developed
pursuing the following quality characteristics:
high usage percentages of resources:
implemented with technical workloads
designed to reallocate resources automatically
and dynamically in accordance with the
priorities set;
support to virtualization;
scalability of resources both upwards (adding
resources) and downwards (reducing the
resources assigned to a service);
dynamic allocation: on-demand for resources
based on a self-service concept. The user can
autonomously access the portal and create or
eliminate a VM or change its characteristics in
terms of resource allocation;
reliability of the systems that should be able to
support a failover;
security. A network firewall is assigned to
every VM. Protection policies can be
personalized;
reduction of management costs for what
concerns energy consumption, network and
physical space occupied.
As of today, to the best of our knowledge, there
is no common adopted standard for securing the
information of a cloud infrastructure (Mell and
Grance 2009, Srinvasanm and Rodrigues 2012).
Moreover, literature provides various reference
models for cloud, each proposed by different
organizations and related to different perspectives
(Farzad 2011). Solutions can be based on the service
model used (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) or the deployment
model adopted (Public, Private, Community,
Hybrid) as well as on the technology adopted or take
into account other criteria such as physical location
of the data, ownership of the resources, architecture
of the IT solution, management of the services
provided, just to name a few. Consequently,
depending on the characteristics one refers to,
different security needs should be considered
(Humberg et al. 2013, Grobauer et al. 2010). In
Humberg (2013) for example, authors propose a
methodology that supports users in examining
models of their systems and processes for potential
risks.
In defining the cloud infrastructure of the
LOGIN project we have taken into account the
requirements of the ISO 27000 series standards (ISO
27001:2005, ISO27002:2007) with focus on IT-
security risks (ISO27005:2008). The ISO27001
standard details the requirements for defining and
information security management system taking into
account the best practices listed in the ISO27002
document, whereas the risk management process
BuildingaCommunityCloudInfrastructureforaLogisticsProject
421

phases are detailed in ISO27005. When evaluating
the risk level of the LOGIN cloud infrastructure we
integrated the process illustrated by the ISO27005
standard with the European Union Agency for
Network and Information Security risk assessment
process (ENISA 2009). Further details of the
analysis and results are reported in (LOGIN 2012).
2.3 Architecture
From an implementation perspective, the cloud
computing approach involves definition of three
layers: hardware, software and virtualization, along
with a set of guidelines for designing the
applications to bind to the cloud infrastructure.
Relevant importance is assigned to the virtualization
layer which, although physically an integrated part
of the software layer, it is positioned between the
latter and the hardware level. Figure1 shows the
description of the architecture designed and then
implemented where one can see the main
instruments for developing the sub-components:
“Hypervisor” for the VTL layer and “Cloud
Manager” for the SWL layer. Furthermore, the
network model (Figure.1) points out two
communication zones: one for managing the entire
cloud infrastructure (management network) and one
for providing the services (customer network).
In the next paragraphs the three layers of the
architecture implemented are described. The
representation of the layers is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1: Network model.
Figure 2: Implementation of the Architecture Layer.
2.3.1 Hardware Layer (HWL)
This layer is responsible for defining the physical
resources, such as: servers, routers, switch, electric
power systems, air conditioning and UPS. The cloud
infrastructure implemented follows a hybrid
approach with both central and distributed systems.
In particular we have used an IBM Mainframe
System z9 Business Class (BC) and server Intel x86.
2.3.2 Virtualization Layer (VTL)
The main focus of the virtualization layer is its
ability to abstract both software and hardware
components of machines and make them available to
other components as virtual resources. This layer
creates a pool of storage and computational
resources partitioning the physical resources through
the use of virtualization technologies. This layer is
an essential component and provides many of the
key features including dynamic resource allocation.
The VTL, as for HWL, has been implemented
with a hybrid solution made up by different
hypervisors that rely on different hardware
architectures. More precisely it is made up of a
z/VM for the System z architecture and a VMware
for the System x architecture.
The main functionalities of the solution for this
layer are:
multitasking, as it supports the contemporary
execution of multiple operating systems (guest
OS);
isolation, assures that a malfunction in a VM
and of the operating system connected to it
does not spread to other virtual machines;
resources and workload management, prevents
an operative system from absorbing all the
computing power of a CPU slowing down all
the other virtual machines;
administration: the system administrator can
start, stop, reconfigure or clone the VM
without having to stop those not involved in
the transaction.
2.3.3 Software Layer (SWL)
This layer is made up of cloud management systems
on one hand and operative systems and application
frameworks on the other. The main objective of this
layer is to assure that the characteristics of cloud
computing are respected and adequate service levels
are assured. This is possible through configuration,
management, monitoring and measurement
resources allocated and used to minimize the
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
422

workload deriving from the deployment of the
operating system and applications.
Significant features are represented by the
automation of IT environments, such as allowing
users to request new resources (provisioning) in a
self-service manner and being able to fulfil them
rapidly. The cloud computing infrastructure is
completed by a set of tools that support users, the
system administrator and the cloud administrator.
The software solution involves using the IBM Tivoli
Service Automation Manager (TSAM) suite as
backend application, and IBM Tivoli Monitoring
(ITM) as monitoring platform.
Two software applications complete the software
layer: Maximo and Simple Service Request
Manager. The Maximo platform controls the
underlying hardware infrastructure on which the
virtualization of the virtual machines (VM) is built.
The cloud administrator who defines the rules
needed to deploy each service uses it. Maximo also
manages authorizations assigned to users in the role
of TSAM Administrator. More precisely, users that
are assigned to this role can carry out administrative
tasks relating to the back-end component such as:
publish images, view reports on the service use and
on user activities; configure, enable, or cancel the
registration of software packages. On the other hand
SimpleSRM offers final users (system
administrators) functionalities for creating,
modifying, managing and monitoring each IT
context in terms of VM, resources assigned to each
VM and middleware/applications to install on each
VM. All the previous operations are carried out in a
self-service mode. A VM can be provisioned using
Service Request Manager. Also, with Service
Request Manager it’s possible to access to basic
tasks on VM like: power-on, power-off, restart, reset
password and so on.
The main interface is presented in figure 3. It is
possible to access all the operations, while on the
right side a summary view of requests and projects is
shown. An example of provisioning is depicted in
figure 4. On the bottom part of the form it is possible
Figure 3: Simple SRM access interface.
to specify the amount of resources to reserve for VM
or for various instances of VM such as: how many
CPUs, how much memory, or disk space.
Figure 4: Example of Provisioning.
2.4 Services and Applications
A set of services and applications have been
developed and installed on the cloud infrastructure
as integrated part of the LOGIN-ICT platform
(Figure 5). In the following a brief description is
provided for each sub-system.
SAPS: system for automated management of
planning and scheduling. It uses advanced
methods for process management and
modelling as well as techniques for
transforming a process model into a project
plan;
SGQ: quality management system. It includes
editing tools as well as instruments for
verifying, validating and executing a quality
model for process or product goals;
EDI: electronic data interchange. Manages
logistic, commercial and financial document
flows;
SICOR: system for creating and composing
organisms of a digital business ecosystem
(DBE). More precisely: stakeholders make a
request (e.g. an order, specific competences,
supply of goods, etc.), and the SICOR
component processes the request by
identifying possible suppliers and composing
a contract between users and suppliers;
GESCA: freight management. This service
integrates algorithms for optimizing freights
based on criteria such as packaging of goods
and containers used to transport them;
FDBMS: federated database management
system. Federates the databases, either
exogenous or endogenous, that the system
BuildingaCommunityCloudInfrastructureforaLogisticsProject
423
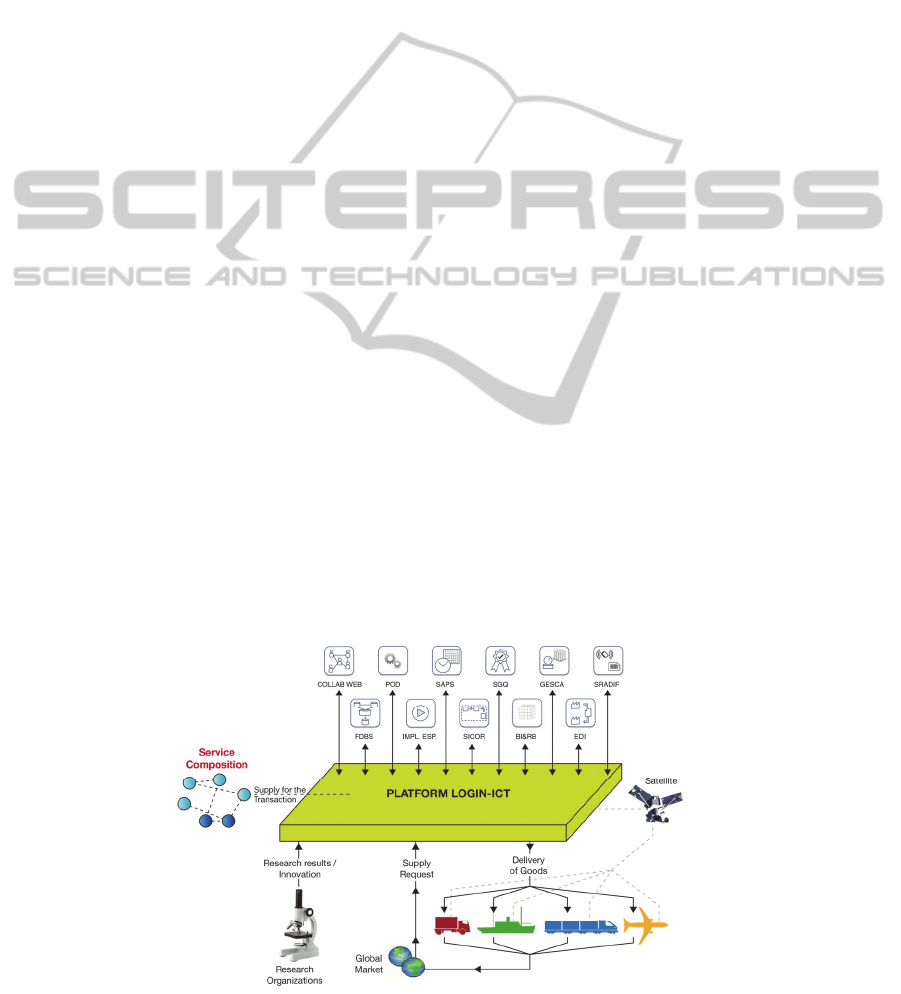
needs in a virtual database that users or
applications may access;
POD: process oriented development. Allows
to formally describe a process and transform it
into an executable workflow;
SRADIF: system for warehouse and transport
management. It organizes transportation of
goods based on RFID technology and
monitors warehouse environments where the
goods are stored;
BI&RB: business intelligence and report
building. This service guides users among the
data collected related to the business processes
and products monitored in the quality
management system (SGQ) and the
information extracted through business
intelligence features;
COLLAB-WEB: collaborative web is a set of
packages for enhancing collaboration among
stakeholders. They include features such as:
FAQ, forums, CRM and e-mail. The system
guides the user in choosing the package that
best suits his communication needs.
3 APPLICATION TO A
LOGISTICS PROJECT
The community cloud infrastructure has been
developed and applied within a research project
involving thirty small to medium enterprise partners
and three research organizations.
The focus of the project was to develop an
integrated platform for the provision of advanced
integrated logistics services (LOGIN). In detail, the
aim is to optimize the entire value chain, from
production of materials to their sale on international
markets through multimodal transport systems such
as sea, rails, tires, etc. (Figure.7). The goods the
project refers to are made in Italy brands such as
DOP wines, cheeses, clothes, local goods.
A user accesses the LOGIN HUB where the
services are listed and selects what is needed for
ordering and managing the goods. The services are
all provided through the community cloud
infrastructure described in the previous section and
are provided in SaaS mode. Services are
distinguished in services for logistics operators and
logistics users. The first category include services
such as: planning, monitoring and tracking of goods;
prevention and intervention in critical situations;
secure transportation of goods; coordination of
requests; interaction with public administrations;
coordination of goods plan and information.
Whereas services for logistic users include:
coordination of demand and supply; booking of
goods; supply chain management just to name a few.
Currently the research project is at the
experimental phase where case studies have been
designed for testing the platform and the community
cloud infrastructure in its whole. More precisely,
case studies have been designed for coordinating
logistics concerning domains such as fish market,
wineries, oil mills, agro-industry partners (local
vegetable and cheese producers). In the next section
we will describe the case study currently being
carried out in a fish market domain.
3.1 Case Study Scenario: Fish Market
The case study consists in the development of
features for tracking the catch within a commercial
Figure 5: LOGIN-ICT Platform Services and Application.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
424

fishing industry. The chain involves the following
stakeholders: fishermen, buyers (wholesale,
supermarkets), chain operators (carriers), final seller,
consumer. The fish marketing chain is made up of
the following phases:
fishermen communicate their catch
(COLLAB-WEB component);
wholesales/supermarkets make a purchase
order of the fish caught (SICOD component)
to the fishermen;
order is confirmed; traceability labels, QR-
Code, are printed and affixed on the catch
cases. This is done through an e-commerce
portal built with Joomla CMS OSS;
the catch is submitted to the carrier on the
port;
catch is sold at retail price. Each product is
identified and tracked by QR-code placed on
the merchandise either it is the entire case, a
package or single piece (components involved
are EDI, POD, FBMS, SRADIF);
In this scenario each product can by tracked by
their QR-Code.
Once modelled, the above phases were enhanced
and carried out through a solution made up of the
following parts:
A mobile application installed on a tabled
used by fishermen to register their catch in a
centralized database; confirm the purchase
order of buyers; print the QR-code labels for
tracking the catch sold;
The application can be used directly on the
fishing boat or the pier as long as there is a WiFi or
cell phone network connection.
An e-commerce web portal where authorized
buyers can make purchase orders of the catch
previously registered by the fishermen;
A web portal where chain operators (carriers,
retail sellers) can register the traceability
information, print the QR-Code labels and
show all the tracking information to a client;
A web and mobile portal that shows all the
tracking data of a sold product associated to a
specific QR-Code.
The integration of all the data managed during
the various phases of the commercial fish market
chain on behalf of all the stakeholders is supported
by the process oriented logic (SAPS and POD
components) that allow to model the process flows
and automate as many steps as possible through the
available services of the LOGIN HUB platform
components.
3.2 Benefits of the Solution
The community cloud infrastructure has proven to
be a beneficial solution in terms of scalability,
flexibility and also server consolidation. More
details are presented in the next paragraphs.
3.2.1 Scalability & Flexibility
For what concerns scalability, it is the case to
distinguish between vertical and horizontal. Vertical
scalability requires adding resources to an existing
one (a VM in our case) that hosts a single instance of
the application in order to better manage the
workload; Horizontal scalability refers to the
capability of an entity (application/service in our
case) of incrementing its resources adding servers
(VM) on which to distribute the workload.
In general SaaS applications should assure
scalability and sharing of resources, whenever
necessary, according to a multi-tenant perspective.
This requires that applications use appropriate
languages, primitives, techniques and technologies.
The LOGIN platform includes both SaaS
applications (designed and oriented towards cloud)
and traditional ones (e.g. web applications) that use
the resources made available by the underlying layer
of the cloud architecture. In this context, scalability
was addressed differently according to the software.
For SaaS applications horizontal scaling was
adopted by provisioning new VM where the
application itself could distribute the workload. In
this case the underlying cloud infrastructure
provided the necessary flexibility for producing an
appropriate execution environment (VM) quickly.
The distribution of the workload wouldn’t have been
possible if the application had not been designed to
work in the cloud. The tracking and monitoring
component of the infrastructure, which must manage
large amounts of data, represents an example.
For traditional applications (e.g, web portals that
users use to interact with the system) vertical scaling
was carried out. This implied increasing the
resources made available by the VMs hosting the
applications. In some cases, by exploiting advanced
features of the underlying middleware, (DBMS,
HTTP servers, etc.) ad hoc solutions were
implemented which achieved horizontal scalability
through clustering techniques. The underlying cloud
infrastructure also in this case provided the
necessary flexibility for quickly producing an
appropriate execution environment (VM).
BuildingaCommunityCloudInfrastructureforaLogisticsProject
425

3.2.2 Server Consolidation
Data Centre Infrastructure Management (DCIM) are
software tools used for managing a data centre. A
modern DCIM should include strategies and
functionalities for consolidating the workload on a
minimum number of physical servers, allowing
saving between 30% and 60% of energy
consumption and obtaining similar results for what
concerns CO2 emissions. In order to achieve server
consolidation we have assigned VM to physical
servers so that none of them ended up being neither
under-utilized (wasting energy since a server with
low workload still consumes 70% of the energy
consumed at full load), nor over-utilized.
Nonetheless, the consolidation problem of VMs is
an NP-Hard problem and as so, there are currently,
to the best of our knowledge, no efficient solutions
for this problem with respect to nontrivial sized data
centres (Mastroianni et al. 2013. In the consolidation
carried out tools have been integrated with the
common virtual platforms of z/VM and VMWare
and support management of heterogeneous data
centres. This has been guaranteed by using a
uniform dashboard integrated with (API) libraries of
the underlying virtualization platforms in order to
retrieve information from the servers and govern the
assignment and migration operations of the VM so
that efficiency is maximized and energy
consumption is minimized.
Before the consolidation (left part) the VM were
distributed on 8 physical servers and the resource
consumption was between 20-50%. At the end of the
consolidation process (right part) the same VM were
redistributed so that the workload was distributed
across four servers with a resource consumption
ranging between 70-90%. The other servers were
shut off of put in low consumption mode to save
energy.
In short, the scalable strategy adopted for
consolidation consisted in distributing the
intelligence instead of centralizing it in a single
point and migrating from deterministic algorithms to
solutions able to distribute the workload on the VM
based on their usage.
4 CONCLUSIONS
We have shown how a cloud computing
infrastructure has been developed for providing
services within a logistics project to all the users. In
particular we have chosen a community cloud as
deployment model and SaaS as service model for
providing the services to users. The fish market case
study scenario has illustrated how the components
(services and applications) built on the cloud
infrastructure communicate and interact in a real
context. The solution identified has assured
scalability and flexibility, as well as energy saving.
The community cloud infrastructure has allowed
users of the LOGIN project to access services on a
pay per use basis without having to purchase
software products and install them on their
computers or company servers as all applications are
accessed remotely. The project is in still in execution
as further case studies are being carried out in other
contexts such as wine distribution and furniture
market.
Figure 6: LOGIN platform: services are managed by the LOGIN HUB and then coordinated among the distributors (market,
airport, port, road transport, intermodal, warehouse, rail station) to respond to a specific demand.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
426

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work presented in this paper is the result of the
research project “LOGIN – LOGistica INTegrata”
funded by the Ministry of Industry and Economical
Development (MISE) - Industria 2015 Bando Nuove
Tecnologie per il Made in Italy
REFERENCES
M. Armbrust, A. Fox, R Griffith, AD. Joseph, R Katz, A
Konwinski, G Lee, D Patterson, A Rabkin, I Stoica,
MZaharia., 2011. “A View of Cloud Computing”,
Communications of the ACM, Vol. 53 No. 4, pp. 50-
58.
A.Lenk, M.Klems, J.Nimis, S.Tai, T.Sandholm, 1999,
“What is inside the cloud? An architectural map of the
cloud landscape”, Workshop on SE Challenges of
Cloud Computing, ICSE2009, Vancouver Canada,
May2009, pp.23-31.
P.Mell, T.Grance, 2011, “The NIST definition of cloud
computing”, Technical Report NIST Special
Pubblication 800-145, USA.
L.Wang et al., 2008 “Early definition and experience”,
Scientific cloud computing, IEEE, pp.825-830.
L.Wang et al., 2008. “Cloud computing: a perspective
study”, New generation computing – Advances of
distributed information processing, vol.28, pp.137-
146,.
F.Baiardi, D.Sgandurra, 2010. “Securing a Community
Cloud” International Conference on Distributed
Computing Systems Workshops, Computer Society,
pp.32-41.
R.Grossman, 2009. The case for cloud computing, IEEE
Computer, vol11, n.2, pp.23-27.
S. Marston, Z. Li, S.Bandyopadhyay, J.Zhang, A.
Ghalsasi, 2011, Cloud computing – the business
perspective. Decision Support Systems, 51(2011),
pp.176-189.
C. Mastroianni, M. Meo, G. Papuzzo, 2013, "Analysis of a
Self-Organizing Algorithm for Energy Saving in Data
Centers". To appear on Proc. of the 9th Workshop on
High-Performance, Power-Aware Computing, Boston
(MA), USA, May 2013.
T. Humberg, Wessel, D. Poggenpohl, S. Wenzel, T.
Ruhroth, J. Jürjens, 2013, “Ontology-based analysis
of compliance and regulatory requirements of business
processes”. Proceedings of the 3rd International
Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
- CLOSER 2013 - pp. 553-561.
P. Mell, T.Grance. 2009, The NIST Definition of Cloud
Computing, Version 15, 10-7-09 National Institute of
Standards and Technology, Information Technology
Laboratory.
S. Farzad. 2011, “Cloud computing security threats and
responses”. In International Conference on
Communication Software and Networks (ICCSN),
2011 IEEE 3rd, Xi'an, 2011.
B.Grobauer, T.Walloschek, E. Stocker, 2010,
"Understanding Cloud Computing Vulnerabilities,"
Security & Privacy, IEEE , vol.9, no.2, pp.50,57,
March-April 2010, doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.115.
M. R. P. Srinivasanm Sarukesi, P. Rodrigues. 2012,
“State-of-the-art cloud computing security
taxonomies: A classication of security challenges in
the present cloud computing environment”. In
ICACCI '12, Chennai, India.
LOGIN 2012, “Risk Mitigation for Cloud Computing
Security – an evaluation model proposal and its
experimentation in LOGIN” Technical Report TR.4-
OR2.2012.
BuildingaCommunityCloudInfrastructureforaLogisticsProject
427
