
Dynamical Diffraction Area Applicability in Case of 1D Photonic
Crystals with Sinusoidal Permittivity Profile
K. O. Romanenko
1
and A. V. Sel’kin
2
1
Saint Petersburg State University, Solid State Physics Dep., Ulyanovskaya 1, Peterhof 198504,
Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation
2
Ioffe Physical Technical Institute, 26 Polytekhnicheskaya, St Petersburg 194021, Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation
Keywords: Photonic Crystal, Bragg Reflection, Dynamical Theory of Diffraction.
Abstract: Bragg reflection and transmission spectra of the 1D photonic crystals characterized by a spatially sinusoidal
profile of permittivity are studied as a function of the crystal-plate thickness. Applicability of the dynamical
theory of diffraction in describing such spectra is considered. In the framework of the dynamical theory, we
(i) calculated and analysed the reflection and transmission spectra for oblique incidence of polarized light, (ii)
computed the spectra making use of the transfer matrix technique, and (iii) compared quantitatively the results
of the two approaches. As a result, the analytical dynamical theory of diffraction is found to be correct in
calculating the Bragg spectra in the vicinity of single photonic band-gap when the plate thickness is equal to
the integer number of the spatial periods, or the permittivity is symmetric about the middle plane of the
structure.
1 INTRODUCTION
Optical research of new artificial structures, studying
their properties and applying them to modern
technological devices is a trend in science nowadays.
Photonic crystals belong to a large class of such
structures (Joannopoulos et al., 2008; Sibilia et al.,
2008). The photonic crystal (PhC) is a spatially
periodic structure which permittivity is a spatially
periodic function with the period equal-order to
electromagnetic wavelength. In semiconductors,
electronic properties are governed by the presence of
allowed and forbidden energy bands for electrons. In
the case of PhC one can control properties and
propagation of electromagnetic waves. This unique
feature of PhC can be utilized in various applications:
photonics, lasers, optoelectronics, etc.
Propagation of light in PhC is very similar to
propagation of X-rays in ordinary crystals for which
the dynamical theory of diffraction is widely used to
study optical properties (Cowly, 1995). Therefore it
is of interest to apply the dynamical theory approach
to PhCs taking into account high spatial modulation
of the PhC dielectric function (Sel’kin, 2004).
In this work, we discuss the model of the opal-like
PhC characterized by the one-dimensional (1D)
periodicity of permittivity
s
z
. As an example, we
consider the permittivity of an opal-like PhC
averaged along all the crystallographic directions
except for [111]. In this case (Bazhenova et al., 2007;
Gajiev et al., 2005)
1,
sasbs
zfz fz
(1)
where
a
and
b
are the permittivities of spheroidal
particles that constitute the PhC and interparticle
space, respectively, and
s
f
z
is the effective filling
function (Figure 1).
It should be noted that the effective filling
function can be approximated well by the harmonic
one. It allows us to suppose that the dynamical theory
can be applicable when describing Bragg reflection
and transmission spectra of opal-like PhCs. The
model proposed is of principal interest because it is
closely associated with the previously performed
theoretical and experimental studies (Bazhenova et
al., 2007; Fedotov et al., 2011; Gajiev et al., 2005) of
the opal-like PhCs and allows one to answer the
question why the dynamical theory of diffraction is
applicable to the PhC with relatively high dielectric
contrast.
118
O. Romanenko K. and V. Sel’kin A..
Dynamical Diffraction Area Applicability in Case of 1D Photonic Crystals with Sinusoidal Permittivity Profile.
DOI: 10.5220/0005403601180121
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology (PHOTOPTICS-2015), pages 118-121
ISBN: 978-989-758-093-2
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Figure 1: Effective filling function
s
f
z of opal-like PhC
along [111] direction. Solid line is given by exact
calculation; dashed line corresponds to harmonic
approximation.
The main purpose of our study is to elucidate the
validity limits of the dynamical theory of diffraction,
in particular, to find a minimum slab thickness that
provides rather good numerical agreement between
the analytical and full-electrodynamic computations
of Bragg reflection and transmission spectra.
2 DYNAMICAL THEORY OF
DIFFRACTION APPLIED TO
PHOTONIC CRYSTALS
Let consider an infinite spatially periodic structure.
The corresponding permittivity
()r
, the electric,
Er
, and magnetic,
H
r
, fields of an
electromagnetic wave can be expanded into Fourier
series over the reciprocal-lattice vectors
G
. In the
vicinity of a Bragg resonance determined by the Laue
condition
2
2
kkG
for the wave vector k
and a
specified vector
G
, such expansions take the form
*
0
ee
iGr iGr
GG
r
,
(2)
0
ee
ir
i
kG
k
G
r
Er A A
(3)
1
00
e( ) e
i
i
kGr
rk
G
Hr
GkA Akk
(4)
where
0
2/kc
is the wavenumber of light
in vacuum with the circular frequency
(
is the
wavelength),
0
is the average dielectric constant.
The amplitudes
0
A
and
G
A
satisfy a set of equations
222
0
2
0
*
00 00
2
0
2
00
()
()()
G
G
GG
G
kk AkkA kA
kG k A
kG kGA k A
(5)
and are related to an external fields through
Maxwell’s boundary conditions. On the other hand,
the equality to zero of the determinant of equations
(5) gives us the dispersion relations
()k
for
eigenmodes. So, the problem of finding the reflection
and transmission coefficients for a PhC plate
becomes, in principle, quite clear.
3 NUMERICAL CALCULATION
AND ANALYTICAL APPROACH
Now examine interaction between a monochromatic
plane wave and 1D periodic structure of a thickness
L
, the permittivity being harmonically varied with
the spatial period
0
ee,
iGz
GG
iGz
z
(6)
where
2G
and
GG
. Let the thickness of
the slab be
12
,Ll N l
(7)
with
1
l and
2
l being fractions of Λ at the front and the
back of the structure, respectively, and N be the
integer number of spatial periods (Figure 2).
Figure 2: The structure under study: a sinusoidal profile of
permittivity includes
N periods,
, where N is integer and
21
,ll
.
We calculated reflectance and transmittance of such
structure with different parameters
1
,l
2
,l
N
solving
equations obtained from Maxwell’s boundary
conditions. Two approaches were considered based
(i) on the dynamical theory of diffraction and (ii) on
the numerical transfer matrix technique, in order to
compare them to each other and draw conclusion
NΛ
l
1
l
2
DynamicalDiffractionAreaApplicabilityinCaseof1DPhotonicCrystalswithSinusoidalPermittivityProfile
119
about validity of the analytical model when
describing the reflectance and transmittance spectra.
As a result, it was found that the dynamical theory
of diffraction describes correctly the spectra in the
vicinity of a single photonic band-gap as compared
with the computations based on the transfer matrix
technique, if
12
ll
or
12
ll
.
(8)
In all other cases, conspicuous contradiction
between analytical and numerical approaches takes
place. It was shown analytically that
12
1,,RT Fll
(9)
where R is reflectance, T is transmittance and
12 1 2
,[cos()cos()]
F
ll Gl Gl
(10)
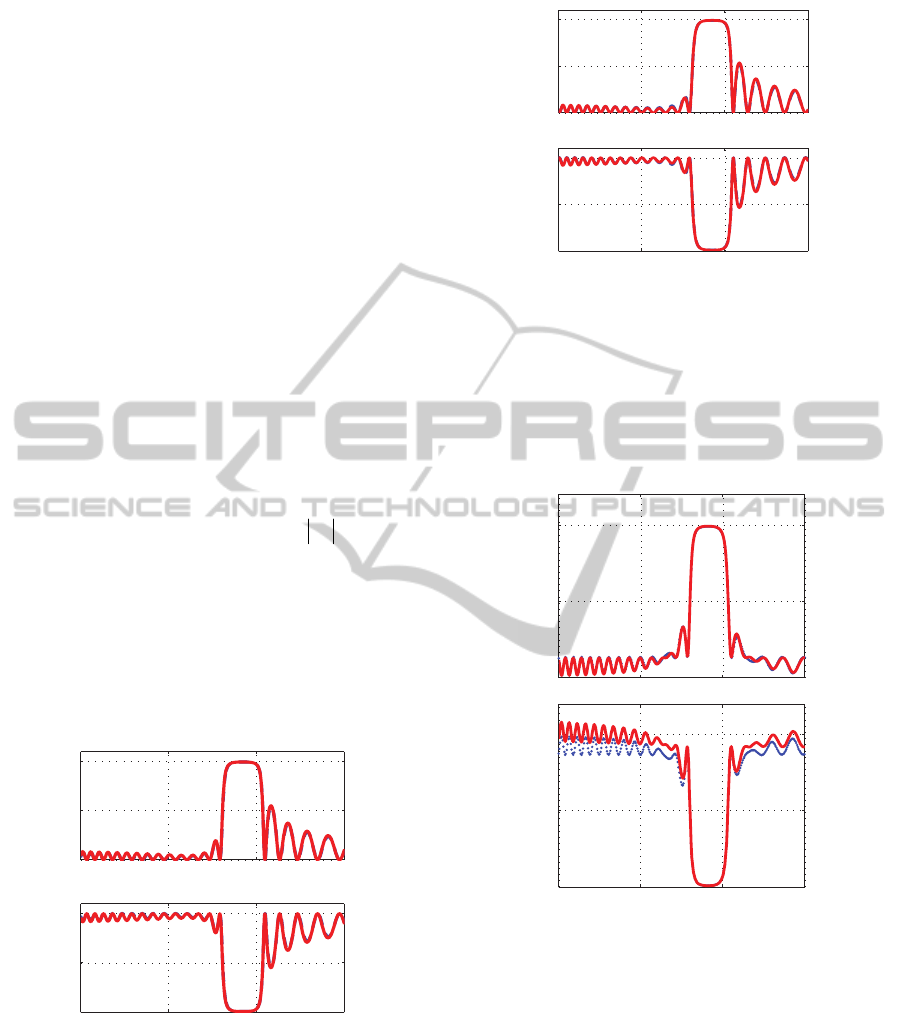
Figures 3 and 4 show, as an example, some results
of computations of the reflectance and transmittance,
respectively, when normal incidence of light on the
plane surface of the structure is considered. The
parameter values are taken close to that for an opal-
like polystyrene PhC (
0
2. ,127
0.135
G
)
(Bazhenova et al., 2007). It can be noticed that at the
conditions (8) both approaches give practically the
same results (Figure 3) independent on
N
, among
them the value
0N
. If permittivity is symmetric
with respect to the middle plane of the structure
(
12
ll
), this conclusion is valid at any thickness
L
of the slab including the limiting case
0L
.
Figure 3: Reflectance and transmittance spectra at normal
incidence of light on the PhC-plate (the number of the
spatial periods, Λ,
is N=30): (a,b)
12
ll
, (c,d)
12
ll
.
Red solid curves correspond to the dynamical model; blue
dotted curves are computed with the transfer matrix
technique.
Figure 3: Reflectance and transmittance spectra at normal
incidence of light on the PhC-plate (the number of the
spatial periods, Λ,
is N=30): (a,b)
12
ll
, (c,d)
12
ll
.
Red solid curves correspond to the dynamical model; blue
dotted curves are computed with the transfer matrix
technique (cont.).
Figure 4: Reflectance (a) and transmittance (b) spectra at
normal incidence of light on the PhC-plate (the number of
the spatial periods, Λ, is N = 30): here the conditions (8) are
not satisfied. Red solid curves correspond to the dynamical
model; blue dotted curves are computed with the transfer
matrix technique.
When the conditions (8) are not fulfilled, the
analytical approach does not agree well with the
numerical one (Figure 4), which is most pronounced
in the case of transmission spectra. Moreover, the
transmittance exceeds unity on some frequencies,
2 2
.5 3 3.5
0
0.5
1
l
1
=0.4Λ
l
2
=0.4Λ
(a)
2 2
.5 3 3.5
0
0.5
1
l
1
=0.4Λ
l
2
=0.4Λ
ReflectanceTransmittance
Wavelength, λ/Λ
(b)
2 2
.5 3 3.5
0
0.5
1
l
1
=0.4Λ
l
2
=0.6Λ
2 2
.5 3 3.5
0
0.5
1
l
1
=0.4Λ
l
2
=0.6Λ
ReflectanceTransmittance
Wavelength, λ/Λ
(c)
(d)
2 2.5 3 3.5
0
0.5
1
l
1
=0
l
2
=0.5Λ
2 2.5 3 3.5
0
0.5
1
l
1
=0
l
2
=0.5Λ
ReflectanceTransmittance
Wavelength, λ/Λ
(a)
(b)
PHOTOPTICS2015-InternationalConferenceonPhotonics,OpticsandLaserTechnology
120

which is in contradiction with the energy balance
principle.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The reflectance and transmittance spectra have been
calculated within two approaches based on the
dynamical theory of diffraction as applied to 1D
photonic crystals and on the numerical modeling
using the transfer matrix technique. The dynamical
theory is shown to be correct if a photonic crystal
plate is symmetric in its dielectric properties about
plate boundaries or the thickness of the plate is a
multiple of the spatial period of the structure. The
conditions obtained are consistent with the energy
balance and time-reversal symmetry considerations.
REFERENCES
Bazhenova A. G., Sel’kin A. V., Men’shikova A. Yu. and
Shevchenko N.N., 2007.
Solid State Physics, vol. 49, p.
2010.
Cowly J. M., 1995. Diffraction Physics, Elsevier Science B.
V. Amsterdam.
Fedotov V. G., Sel’kin A. V., Ukleev T. A., Men’shikova
A. Yu. and Shevchenko N. N., 2011.
Phys. Status Solidi
B, vol. 248, p. 2175.
Gajiev G. M., Golubev V. G., Kurdyukov D. A., Medvedev
A.V., Pevtsov A.B., Sel’kin A.V., Travnikov V.V.,
2005.
Phys. Rev. B, vol. 72, p. 205115.
Joannopoulos J. D., Johnson S. G., Winn J. N. and Meade
R.D., 2008.
Photonic Crystals. Molding the Flow of
Light
, Princeton University Press. Princeton, Oxford.
Sel’kin A. V., 2004. Proc. of 12th Int. Symp.
“Nanostructures: Physics and Technology”,
p. 111. St.
Petersburg.
Sibilia C., Benson T. M., Marciniak M. and Szopik T.,
2008.
Photonic Crystals: Physics and Technology,
Springer-Verlag. Italia.
DynamicalDiffractionAreaApplicabilityinCaseof1DPhotonicCrystalswithSinusoidalPermittivityProfile
121
