
The Basis of “Atom in the External Field” Eigenfunctions to the
Problem of High Harmonic and Terahertz Radiation Generation
Study
Sergey Yu. Stremoukhov and Anatoly V. Andreev
Faculty of Physics, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Leninskie Gory, 1, build.2, 119991, Moscow, Russia
Keywords: Quantum-mechanical Description, Non-Perturbative Theory, High Harmonic Generation, Terahertz
Radiation Generation.
Abstract: The paper is devoted to the discussion of the main principles of the non-perturbative quantum-mechanical
approach to the description of a single atom interaction with multicomponent laser fields. The main
advantage of the theory is that the authors use a basis of “an atom in the field” eigenfunctions which are the
exact solution of “an atom in the field” boundary value problem the Hamiltonain of which coincides with
the one from the Schrodinger equation written in the velocity gauge. The theory is applied to analytical and
numerical investigation of the high-order harmonic generation and the terahertz radiation generation
phenomena.
1 INTRODUCTION
High order harmonic generation (HHG) is one of the
most promising tools for generation of coherent
ultraviolet and X-ray radiation (Popmintchev, 2012).
The elementary act of harmonic generation lies in
the scale of a single atom interaction with a laser
field. There are a lot of theoretical approaches which
are used to describe the HHG (see the introduction
part of the (Andreev, 2012)). Intuitively the process
can be understood in the frame of the “simple man
model” (Krausz, 2009): an electron is ionized by an
intense laser field, accelerated inside the oscillating
laser field and gained kinetic energy, then it comes
back to a bound state emitting a burst of photons
with an attosecond pulse duration.
The terahertz (THz) radiation generation also has
a lot of potential applications in molecular
spectroscopy, imaging etc., that is why it is under an
active study now. The process of atomic or
molecular gas interaction with a multicolor laser
field is one of the most effective tools for the
generation of high intensity broadband pulsed THz
radiation (Cook, 2000). The fundamental act of
interaction with a laser field accompanied with the
THz generation lies in the atomic (Karpowicz, 2009;
Zhou, 2009; Zhang, 2012; Andreev, 2012; Andreev,
2013) or media (Kim, 2007; Couairon, 2007) scales.
That is why different physical mechanisms have
been used to describe this phenomenon: the four-
wave mixing process (Cook, 2000), the photocurrent
of free charges (Kim, 2007; Babushkin, 2011), the
plasma current oscillation (Debayle, 2014) and intra-
atomic nonlinearity mechanism (Andreev, 2013).
Here we discuss the quantum-mechanical non-
perurbative theory of a single atom interaction with
a multicomponent laser field which could
simultaneously describe the HHG and the THz
radiation generation phenomena. The main
advantage of the theory is in the absence of the
smallness parameter E/E
at
(E
at
= 5.1•10
9
V/cm being
the intra-atomic field strength value). As a result, the
theory can precisely describe the phenomena
appearing in sub- and near-atomic laser fields. The
main principles of the theory are discussed below
(for more details, please, see (Andreev, 2011)).
2 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF THE
THEORY
The process of a single atom interaction with a laser
field can be described with the Schrodinger equation
which has the form of:
128
Stremoukhov S. and Andreev A..
The Basis of “Atom in the External Field” Eigenfunctions to the Problem of High Harmonic and Terahertz Radiation Generation Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0005403901280133
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology (PHOTOPTICS-2015), pages 128-133
ISBN: 978-989-758-093-2
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2
,
1
() , ,
2
rt
q
ipAtUrrt
tmc
(1)
where
()
A
t
is the vector potential and ()Ur
is the
intra-atomic field potential.
To solve the eq. (1) we used a non-traditional
basis of “an atom in the external field” wave-
functions
,
N
rt
which is the exact solution of the
boundary value problem of an atom in the external
field:
2
1
() ,
2
,.
N
NN
q
pAt Ur rt
mc
Ert
(2)
The operator of the boundary value problem (2)
coincides with the Hamiltonian of eq. (1), so these
two equations have the same symmetry properties.
The eigenfunctions
,
N
rt
can be analytically
expressed in terms of eigenfunctions
n
ur
for the
free-atom boundary value problem:
1
ˆˆ
,, exp .
Nn
q
rt u rV V i At r
c
Similar to a set of free-atom eigenfunctions
n
ur
which form a complete basis of the orthonormal
functions, the eigenfunctions of the boundary value
problem (2) for “an atom in the external field” form
also a complete basis of orthonormal functions
,
N
rt
. There is a one-to-one correspondence
between these two bases. Note that the
eigenfunctions
,
N
rt
coincide exactly with the
eigenfunctions
n
ur
when the instant value of the
external field amplitude is equal to zero. Hence,
these two bases coincide at the time points when
I(t)=0; and what is more important they coincide
before the laser pulse arrival and after its
termination.
As we have mentioned above, the eigenfunctions
,
N
rt
have the same symmetry properties as the
wavefunction of the Schrodinger equation (1).
Therefore, it looks quite natural to use the basis of
these functions for solving the eq. (1). However, due
to the time derivative in the left-hand-side of
equation (1) the equations for the probability
amplitudes of such expansion will inevitably include
the integrals over the products of these
eigenfunctions and their time derivatives. But the
operator of the boundary value problem (2) is time
dependent; hence, the eigenfunctions of this problem
and their time derivatives are not orthogonal. To
overcome this problem we can initially expand the
wavefunction
,rt
into a series of eigenfunctions
n
ur
:
,,
,
(,) () () (,,)(,,)
nl nl
nl
rt a tu r akltuklrdk
and then make use of the one-to-one correspondence
of these two bases. Moving from eq. (1) to a set of
equations for the probability amplitudes we should
calculate the following integral:
*2
1
(())().
2
nm
e
upAtUrudV
mc
Decomposing
n
ur
through the set of
,
N
rt
we
can find this integral analytically:
*2
1
1
(())()
2
() ()
nm
np p pm
p
e
upAtUrudV
mc
VtEV t
and then write a set of differential equations for the
population amplitudes of discrete states and
continuum quasistates:
1
,
()
() () (),
n
nk k km m
mk
da t
iVtEVtat
dt
(3)
where E
k
are the energy eigenvalues.
To calculate the spectrum of atomic response we
should calculate previously the atomic current
density:
,
.
2
jrt
qq q
pA pA
mc c
(4)
In the far-field zone the spectrum of atomic response
coincides with the spectrum of atomic current
(Landau, 1981), which is:
1
,,,
n m pq np pq qm
nm pq
J
ti atat VtdVt
(5)
where
n
at
are the probability amplitudes of
atomic states,
p
q
d
are the matrix elements of the
dipole operator and
pq p q
EE
.
Notice that in all the equations above the atomic
states were designated by the one-letter symbol (n).
However, the atomic states of the three-dimensional
TheBasisof"AtomintheExternalField"EigenfunctionstotheProblemofHighHarmonicandTerahertzRadiation
GenerationStudy
129
spherically symmetric boundary value problem
depend on three quantum numbers: a principle
quantum number n, an orbital quantum number l,
and its projection m. By writing only a one-letter
symbol we mean all the three quantum numbers
from the previous formulas.
The equations (3, 5) enable to calculate the
photoemission spectrum at given parameters of the
laser field interacting with an atom and describe the
features of the HHG spectrum (the short wavelength
part of the photoemission spectrum) as well as the
THz spectrum (the long wavelength part of the
photoemission spectrum). However the set (3)
include the infinite number of equations. The infinite
set of equations (3, 5) cannot be solved neither
analytically nor numerically. On the other hand, at
any finite amplitude of the laser field only some
finite number of atomic levels makes an appreciable
input in the atomic response. The main advantage of
the “an atom in the external field” basis is the
following: the input of each state can be numerically
calculated before we solve the set of equations for
probability amplitudes. We can exactly estimate the
accuracy of calculations with the help of truncated
basis at any amplitude of the laser field. It should be
also noted that the number of states in “an atom in
the external field” basis is truncated, but each
eigenfunction of this basis is the infinite series over
the eigenfunctions of the “free atom” basis and the
coefficients of this decomposition depend on the
laser field amplitude.
2.1 Matrix Elements of the V Operator
Let us have a look at the matrix elements of the V
operator. To calculate it analytically we will write
the free-atom boundary value as a multiplication of
its radial part
,nl
Rr
and its angular part
,
(, )
lm
Y
:
,, , ,
(, )
nlm nl lm
urRrY
. The matrix element of
the transition between two states described by two
sets of quantum numbers
11 1
nlm and
22 2
nlm has
the form of
12
12
2
22 11
1
22 2 11 1
21
21
21
12
2
0
1
000
4 2 12 12 1
() ,
ll
lm
ll l
lm
nl l nl
nlm V nlm Y e t
lll
lll
mmm
ll l
Rrj tRrrdr
(6)
where
() ,
q
tAtr
c
()
l
jt
are generalised
Bessel functions,
et
is the unit polarization vector
of the laser field. Assuming that the vector-potential
can be presented by the following
2
0
00
sin ( )( ) ,
i
i
tt
iiiii
i
At Ae t t t
where
0i
A
is the amplitude of the vector potential of
the components of the laser fields,
i
are the
temporal widths of the pulses,
i
,
i
,
i
,
0i
t
are
the frequencies of the components of the laser fields,
their chirps, phases and delays, respectively; we can
set the control parameter of the theory as
00
.
ii
q
Ar
c
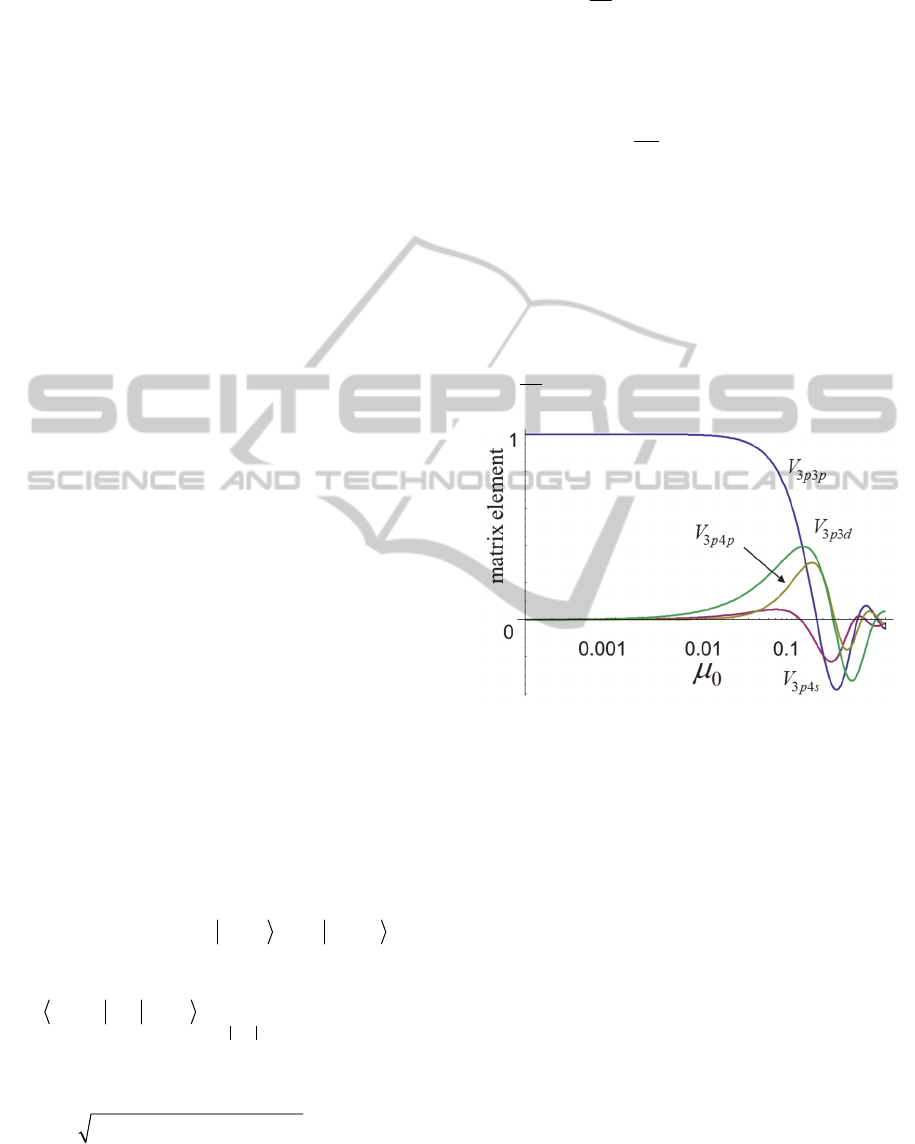
Figure 1: Matrix elements for discrete-discrete transitions
as a function of the field strength
0
Using the hydrogen-like wave-functions
,,nlm
ur
we can analytically integrate (6) and investigate the
properties of the matrix elements. Figure 1
represents the behaviour of some matrix elements
calculated between the discrete states as a function
of the control parameter value. It is clearly seen that
the matrix elements demonstrate non-linear and non-
monotonical behaviour. As a result, the atomic
response has also the non-linear dependency on the
laser field amplitude which is qualitatively different
in subatomic and near-atomic regions. The
expansion of the matrix elements into the series of
the laser field amplitudes includes all the powers of
the ratio
E/E
at
. So, any multiquantum process is
accounted in a consecutive manner.
Some matrix elements calculated between
discrete and continuum states as a function of
electron energy calculated at two values of the
control parameter are presented in figure 2. It is
PHOTOPTICS2015-InternationalConferenceonPhotonics,OpticsandLaserTechnology
130

clearly seen that the non-monotonical behaviour of
the matrix elements strongly depends on the value of
the laser field strength (the value of the control
parameter). Moreover, in the region of high electron
energy the value of the matrix elements decreases
and we can estimate the upper boundary of the of
photoelectron energy region which must be taken
into account for the calculation of the system of
equations (3) with a given accuracy.
Figure 2: Matrix elements for discrete-continuum
transitions as a function of the photoelectron energy
calculated at a given value of the control parameter
5
0
510
(a),
0
0.8
(b).
2.2 Matrix Elements of the J Operator
The mathematical formalism provides us with a
possibility to calculate the angular-frequency
spectrum (AFS) of the atomic response for the case
of an arbitrary mutual orientation of the atomic
angular momentum and the laser field polarization
vector. The polarization of the AFS components
depends on both the angular momentum direction
and the polarization of the incident field. In the non-
polarized ensemble of atoms the response field
polarization depends only on the polarization state of
the laser field.
In order to investigate the convergence of the
usage of the truncated basis of wave-function let us
have a look at the atomic current calculated for only
one level (ground state-ground state
00
j
)
transition.
11 1 2 2 2
11 1 2 2 2
00
1
,111
11 1 2 2 2 2 2 2
00
0
0.
nlm n l m
nlm n l m
Pj
iVnlm
nlm d n l m n l m V
(7)
Figure 3: Matrix elements for J operator as function of
field strength
0
.
Despite the fact that the initial and the final states of
this transition are fixed, the value of this matrix
element depend on the impact of the exited states.
Figure 3 shows the dependence of this matrix
element calculated for the case of the hydrogen atom
(1s ground state), with taking into account only one
exited state (2p – a curve with squares, 3p – a curve
with circles), two exited states (2s and 3p – a curve
with triangles), three exited states (2s, 2p, 3p – a
curve with rhombuses). Figure 3 demonstrates fast
convergence of the sum (7) since the curve
calculated with taking into account the first exited
state of the atom (the curve with squares) almost
perfectly represents the behavior of the matrix
element calculated with taking into account the
impact of three states (the curve with rhombuses).
3 APPLICATION OF THE
THEORY
Figure 4 represents the typical photoemission
spectrum calculated for the case of an Ar atom
interaction with a two-colour laser field formed by
the fundamental and the second harmonics of the
Ti:Sapphire laser, the parameters of which have the
form of
01 02
0.1,
12
26.6 ,fs
TheBasisof"AtomintheExternalField"EigenfunctionstotheProblemofHighHarmonicandTerahertzRadiation
GenerationStudy
131
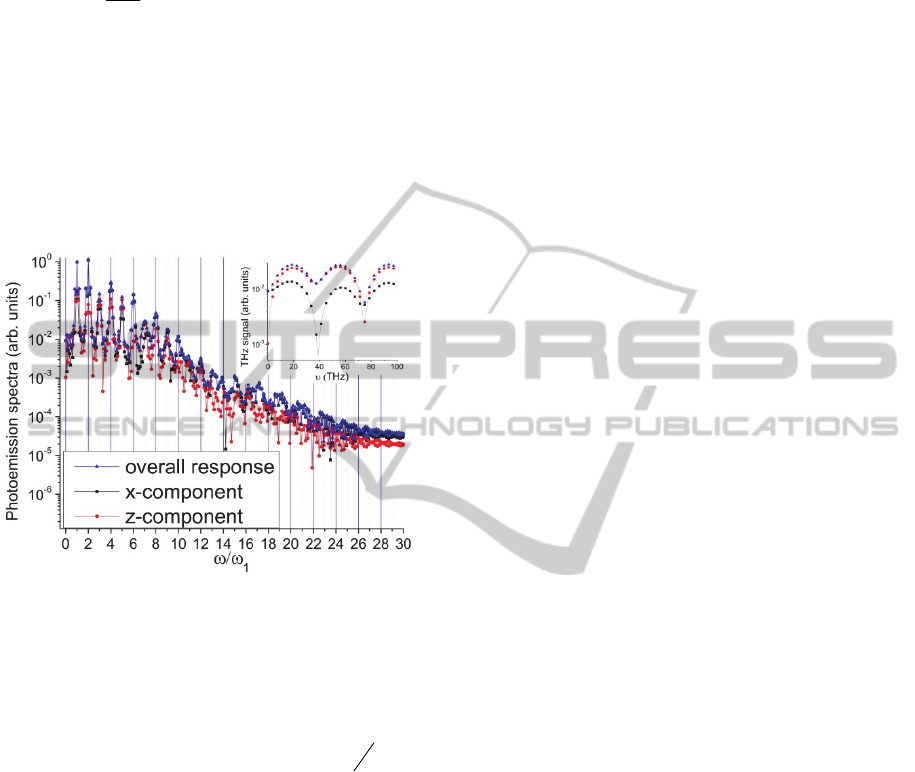
02 01
0,tt 0,
i
0,
i
the angle between the
polarization of the components of the field being
equal to
21
48
(Andreev, 2013). We assume here
that the fundamental harmonic is polarized along the
z-axis, and the second harmonic is polarized in zy-
plane. It is clearly seen that the spectrum consists of
both odd and even harmonics which have non-zero
projections on the two perpendicular axes. The
information about the polarization properties of the
generated harmonics can be directly extracted from
the photoemission spectrum with the help of the
Stokes parameters.
Figure 4: The photoemission spectrum of an Ar atom
interacting with the two-colour laser field formed by the
fundamental and the second harmonics of the Ti:Sapphire
laser: the integral intensity of response (triangles) and the
intensities of the two orthogonally polarized components
(squares and circles). The parameters of the two-colour
laser field are the following:
01 02
0.1,
12
26.6 ,
f
s
02 01
0,tt 0,
ii
21
48
.
(Inset) The THz part of the photoemission spectrum
(Andreev, 2013).
The inset in the figure 4 demonstrates the THz (long
wavelength) part of the photoemission spectrum.
The signal has also non-zero projections on the two
perpendicular axes.
The theory described above was applied for the
investigation of some features of the HHG and the
THz radiation phenomenon. We theoretically
explained the saturation of the cut-off frequency in
near-atomic laser field (Andreev, 2011; Andreev,
2013). The value of the cut-off frequency coincides
with the experimentally measured one (Andreev,
2013). We also theoretically investigated the HHG
(Andreev, 2013) and the THz radiation generation
(Andreev, 2013) in the ionization-free regime in the
case of a two-colour laser field interaction with an
atom. What is more interesting in this investigation
is that the HHG spectra are not limited to below-
threshold and near-threshold harmonics which are
effectively generated in the same region of the laser
field intensities (Sofier, 2010; Yost, 2009). The
specific features of the THz radiation emitted by the
extended gas interacting with a two-color laser field
is been investigated in (Stremoukhov, 2015). It is
shown that spatial oscillations of the THz radiation
efficiency appearing during the dispersion effects in
the gas change the conical structure of the THz
radiation. The theory was also applied for the
interpretation of the resent experiment of the
effective generation of high intensity high ellipticity
harmonics in two-colour orthogonally polarized
laser fields (Lambert, 2015)
4 CONCLUSIONS
The basic principles of the quantum-mechanical
non-perturbative theory based on the usage of the
bases of “an atom in the external field”
eigenfunctions are described and discussed in the
application to the description of the HHG and the
THz radiation generation phenomena. It is shown
that the usage of these bases of functions enables
taking into account the symmetry properties of the
problem and, thus, brings the numerical
investigation of the light-atom interaction to a new
level. What is more important, with the help of the
theory ones can calculate the atomic response for the
case of an arbitrary mutual orientation of the atomic
angular momentum and the laser field polarization
vector. The recent applications of the theory are
named and discussed shortly.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work was partially supported by the Russian
Foundation for Basic Research (RFBR Gr. № 15-02-
04352).
REFERENCES
Andreev A.V., Stremoukhov S.Yu., Shoutova O.A., 2011.
Nonlinear optical response of an atom imposed on a
laser pulse of near-atomic strength
, JETP Letters, V.
93, № 8, 476–486.
Andreev A.V., Stremoukhov S.Yu., Shoutova O.A., 2011.
Interaction of Atom With Laser Pulses of Intra-Atomic
PHOTOPTICS2015-InternationalConferenceonPhotonics,OpticsandLaserTechnology
132

Field Strength, Femtosecond-Scale Optics, InTech,
247-284.
Andreev A.V., Stremoukhov S.Yu., Shoutova O.A., 2012.
“Light-induced anisotropy of atomic response:
prospects for emission spectrum control”,
Eur. Phys.
J. D, 66:16.
Andreev A. V. and Stremoukhov S. Yu., 2013. Terahertz-
radiation generation in the ionization-free regime of
light-atom interaction,
Phys. Rev. A, 87, 053416.
Andreev A.V., Stremoukhov S.Yu., Shoutova O.A., 2013.
High-order optical harmonic generation in ionization-
free regime: origin of the process,
Journal of the
Optical Society of America B: Optical Physics, 30(7),
1794–1803.
Andreev A.V et al, 2013. High-order harmonic cut-off
frequency in atomic silver irradiated by femtosecond
laser pulses: theory and experiment,
Eur. Phys. J. D,
67: 22.
Babushkin I et al., 2011. Tailoring terahertz radiation by
controlling tunnel photoionization events in gases,
New J. Phys., 13, 123029.
Cook D. J. and Hochstrasser R. M., 2000. Intense terahertz
pulses by four-wave rectification in air,
Opt. Lett., 25,
1210.
Couairon A. and Mysyrowicz A., 2007. Femtosecond
filamentation in transparent media,
Phys. Rep., 441, 47.
Debayle A et al., 2014. Analytical model for THz
emissions induced by laser-gas interaction,
Opt.
Express, 22, 13691.
Karpowicz N. and Zhang X.-C., 2009. Coherent Terahertz
Echo of Tunnel Ionization in Gases.
Phys. Rev.
Lett.,102, 093001.
Krausz F. Ivanov M. 2009. Attosecond physics. Rev. Mod.
Phys. 81, 163–234.
Kim K.-Y., et al., 2007. Terahertz emission from ultrafast
ionizing air in symmetry-broken laser fields,
Opt.
Express, 15, 4577.
Lambert, G. et al. 2015. Towards enabling femtosecond
helicitydependant spectroscopy with high-harmonic
sources.
Nat. Commun. 6:6167.
Landau, L. D. & Lifshits, E. M. 1981. Quantum
Mechanics, 3rd ed.
, Elsevier Science.
Popmintchev T., et al., 2012. Bright coherent ultrahigh
harmonics in the keV X-ray regime form mid-infrared
femtosecond lasers,
Science, 336, 1287-1291.
Sofier H., et al., 2010. Near-threshold highorder harmonic
spectroscopy with aligned molecules
, Phys. Rev. Lett.
105, 143904
.
Stremoukhov S. Yu. and Andreev A. V., 2015. Spatial
variations of the intensity of THz radiation emitted by
extended media in two-color laser fields,
Laser Phys.
Lett., 12, 015402 .
Yost D. C., et al, 2009.Vacuum-ultraviolet frequency
combs from below-threshold harmonics,
Nat. Phys. 5,
815–820
.
Zhang D, et al., 2012. Synchronizing Terahertz Wave
Generation with Attosecond Bursts,
Phys. Rev. Lett,.
109, 243002.
Zhou Z., et al., 2009. Terahertz emission of atoms driven
by ultrashort laser pulses,
Phys. Rev. A, 79, 063413.
TheBasisof"AtomintheExternalField"EigenfunctionstotheProblemofHighHarmonicandTerahertzRadiation
GenerationStudy
133
