
Towards a Hybrid World
The Fuzzy Quality of Collaboration/Interaction (FuzzyQoC/I) Hybrid Model
in the Semantic Web 3.0
Sofia B. Dias
1
, Sofia J. Hadjileontiadou
2
, José A. Diniz
1
and Leontios J. Hadjileontiaids
3
1
Faculdade de Motricidade Humana, Universidade de Lisboa, 1499-002 Cruz Quebrada, Lisbon, Portugal
2
Hellenic Open University, Praxitelous 23, GR-10562, Athens, Greece
2
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki GR-54124 Thessaloniki, Greece
Keywords: Cloud Learning Environment, Fuzzy Logic/Ontologies, Hybrid Modelling, i-Treasures, Online Learning
Environment (OLE), Quality of Collaboration (QoC), Quality of Interaction (QoI), Semantic Web 3.0.
Abstract: As a decision support tool, a hybrid modelling can offer the ability to better understand the dynamics of a
particular ecosystem. This paper proposes a hybrid approach that may serve as a means to synthesize/represent
knowledge obtained from the data, in order to explore online learning environment (OLE) states, based on
different scenarios. The potentiality of the quality of collaboration (QoC) within an Internet-based computer-
supported collaborative learning environment and the quality of interaction (QoI) with a learning management
system (LMS), both involving fuzzy logic-based modeling, as vehicles to improve the personalization and
intelligence of an OLE is explored. In this approach, a novel framework could be established, when bridging
the fields of blended- and collaborative-learning into an enhanced educational environment. The combined
measures (i.e., QoC, QoI) can form the basis for a more realistic approach of OLEs within the concept of
semantic Web and the associated Web 3.0 features, as they effectively capture the behaviour of the
stakeholders involved in the context of Higher Education. Finally, a potential case study of the examined
hybrid modelling (FuzzyQoC/I), referring to the “i-Treasures” European FP7 Programme, is discussed, to
explore its functionality/applicability under pragmatic learning scenarios, serving as a proof of concept.
1 INTRODUCTION
The concept “Semantic Web” has been used
inconsistently by academic researchers, holding a
landscape of different fields, technologies, concepts
and applications. From one point of view, Semantic
Web technology could play an important role in the
context of Learning Management Systems (LMSs),
giving the possibility to organize information for easy
retrieval, reuse, and exchange between different
learning systems/tools. From another, combined with
the concept of intelligent LMS (iLMS), blended (b)-
learning scenarios can offer a number of learning
tools, in a wide range of interaction and collaboration
(Dias et al., 2014; Dias, 2014). Lukasiewicz and
Straccia (2008), more pragmatically, have examined
five of the most important challenges facing Semantic
Web, namely: vastness, vagueness, uncertainty,
inconsistency, and deceit. However, nowadays, the
central challenge would be to provide adapted and
personalized alternatives, where intelligent models
could contribute, involving artificial intelligence and
incertitude modeling, e.g., via Fuzzy Logic (FL). The
latter is an efficient field that is suitable for dealing
with vagueness. In addition, it is considered a form of
continuous multi-valued logic allowing “computing
with words” and modeling complex systems,
characterized by imprecise and vague behaviours by
means of a linguistic approach (Zadeh, 1965, 1971).
In general, the whole point of Web 3.0 is to provide
accessible information to people and computers at
anytime from anywhere. Furthermore, with new
technological innovations for applying intelligent
agents (Web 4.0), cloud computing services has been
coined as an umbrella term to describe a category of
sophisticated on-demand computing services,
initially offered by commercial providers (such as
Amazon, Google, and Microsoft) (Voorsluys et al.,
2011). By embedding the cloud computing within
iLMS, access to large amount of data and different
computational learning resources/environments
becomes feasible.
187
B. Dias S., J. Hadjileontiadou S., Diniz J. and J. Hadjileontiaids L..
Towards a Hybrid World - The Fuzzy Quality of Collaboration/Interaction (FuzzyQoC/I) Hybrid Model in the Semantic Web 3.0.
DOI: 10.5220/0005404901870195
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2015), pages 187-195
ISBN: 978-989-758-108-3
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Based on the aforementioned perspectives, this paper
examines the potentiality of the quality of
collaboration (QoC), within an Internet-based
computer-supported collaborative learning (CSCL)
environment, and the quality of interaction (QoI) with
a LMS, both involving FL-based modeling as a
vehicle to improve the personalization and
intelligence of an online learning environment (OLE).
Furthermore, these combined measures, i.e., QoC and
QoI, can form the basis for a more pragmatic
approach of OLEs via Web analytics and Web
controlling/monitoring, within the concept of
semantic Web and the associated Web 3.0 features. A
detailed description of this idea is explored and
described in the succeeding section, towards a hybrid
modelling approach, namely FuzzyQoC/I, where the
term hybrid implies both the modelling of the
interaction between the users (QoC) and between
them and the system (LMS QoI).
2 THE HYBRID APPROACH IN
THE SEMANTIC WEB 3.0
As underlined before, Higher Education paradigms
are shifting to incorporate more online, blended,
collaborative and hybrid learning. An essential factor,
however, in determining the efficacy of online
learning environments towards the creation and
development of sustainable learning communities is
the users’ QoI with LMSs. From this perspective, the
FuzzyQoI model (Dias and Diniz, 2013) has shown
significant potential to: a) handle a multitude of
variables and inference upon them, furnishing us with
a quantitative approach to evaluate the QoI, both in
professors’ and students’ case; and b) function as a
means for better understanding and explaining the
nature of underlying aspects and causalities, which
influence the construction of users’ interaction
behaviour under the LMS-based b-learning approach.
In addition, the collaboration/metacognition-Fuzzy
Inference System (C/M-FIS) model (Hadjileontiadou
et al., 2003) has contributed to the quantitative
evaluation of the QoC, taking into account both the
personal (metacognitive) and the social
(collaborative) contexts.
A more detailed description of the FuzzyQoI and the
C/M-FIS models can be found in Dias and Diniz
(2013) and Hadjileontiadou et al. (2003),
respectively.
The exploratory trajectory followed through the case
studies and the systemic approach adopted in both
models revealed noticeable aspects within the
CSCL/OLE, which all are influenced by the human
behaviour characteristics. OLE usability, profiles and
interaction issues holistically relate with the human
factor. This also holds for the collaborative
interactions within a CSCL environment. Combined
with the boosting of the Internet metamorphosis to an
increasingly social tool, the need for online education
that efficiently incorporates users’ characteristics,
evolving social needs and expectations becomes
apparent. This, really, could transform the perception
of the LMS to a more intelligent tool that functions in
a more “personalized” way.
Talking about personalization, the problem becomes
crucial when authors want to provide materials,
which should support different users in their different
phases of the learning process. The task, thus, is to
find a (technological and procedural) solution in order
to effectively support the learners. The knowledge
society demands competencies and skills that require
innovative educational practices based on open
sharing and the evaluation of ideas, fostering
creativity and teamwork (collaboration) among the
learners.
The vast number of tools supporting collaboration on
the Web is an indicator that social software tools are
not only a flash in the pan, but lead to a new notion of
learning and a measure for sustainable competence
development. Towards such endeavour, ideas like
semantic analysis of learning activities, tagging
opportunities with a focus on appropriateness for
learning, visualization of communities and people
with similar (learning) interests, new approaches to
content and network analysis, and a technical
integration of different LMS, should be considered.
These ideas clearly comply with the emerging
concept of semantic Web 3.0 (Lukasiewicz and
Straccia, 2008). Actually, the Web 3.0 is about
connecting data, all data, everywhere and putting
them in massive graph databases that can be read and
conceptually understood by computers. Currently,
most Web pages are designed to be read by people,
not machines. Nevertheless, because linked, graph-
based data are machine-readable, hence, computers
could be able to answer increasingly sophisticated
questions for the user-to interpret data, understand
context, infer meaning and do reasoning. In other
words, semantic databases, which sprang out of
artificial intelligence, allow computers first to
“think”, to understand big, conceptual queries, and
then find and combine exactly the information
humans need to make ever-smarter decisions.
In this context, teaching-learning process should be
seen as a complex and constantly dynamic reality
(Peters, 2001; Garrison and Kanuka, 2004; Bates,
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
188

2005) that could be supported by Information and
Communication Technologies (ICTs)-based techno-
pedagogical models that include representations,
visions, skills, resources, attitudes and practices of
their social actors, all placed under the concept of the
semantic Web 3.0. In fact, the combination of
traditional Face-to-Face (F2F) and online learning,
within the context of b-learning, offers different
delivery methodologies/modes that have the potential
to optimize the learning development, deployment
costs and time (Oliver and Trigwell, 2005). In
parallel, education paradigms shifted to incorporate
online collaborative learning environments (Johnson
et al., 2013). Actually, collaborative learning can
assist students to feel more interactive and also exerts
a positive influence in terms of motivation, behaviour
and self-determination, as well as engagement in
learning activities (Reeve and Tseng, 2011; Wijnia et
al., 2011).
It is noteworthy that nowadays, digital devices and
ICT, in general, intermediate the relationships
between two or more users, defining a kind of “social
interfacing” (de Souza e Silva, 2006). Within the
latter, not only the communication relationships are
reshaped, but also the space where these interactions
take place. The embedded mobility in the interfacing
allows the connection between physical and digital
spaces, supporting interconnectivity of
social/conceptual and technological interface under
the ubiquity perspective. In this way, interactive
activities, communicative understandings, learning
theories (especially as framed through cognitive
load), self-efficacy and self-regulation, become more
dynamic and challenging issues to be addressed
within an OLE.
Taking the aforementioned perspectives together, an
enhanced LMS-based intelligent teaching/learning
modeling approach could be formed, by suggesting
the incorporation of the hybrid and innovative
processing techniques from the fields of fuzzy
modeling and fuzzy set theory. In this fashion, a novel
research framework could be established, by
exploring the ways effective teaching could be
accomplished, when bridging the fields of b- and
collaborative (c)-learning into a hybrid and enhanced
teaching-learning environment. In this way, a holistic
approach of the fundamental channels from which the
educational process is conveyed could be adopted,
combining cognitive and social information of the
peers’ behaviour and interactions. Consequently, the
following objectives could be set:
• development of an educational and innovative
framework around the online instructional
environments, by exploring the potentialities of
b/c-learning/teaching in the context of Higher
Education and semantic Web 3.0,
• contribution to educational improvement on
teaching practice supported in the LMS Moodle
(or OLEs in general), providing new tools more
suited to users’ QoC and QoI,
• development, application and validation across
a vast number of users (students/professors) of
efficient hybrid modeling approaches of LMS
Moodle data, based on fundamentals of Fuzzy
Logic-based Inference Systems (FISs),
• introduction of extended means, new tools and
pathways for shifting from the typical form of
LMS to the iLMS (Dias et al., 2014),
incorporating issues, such as personalization
and technological adaptiveness,
• course effect analysis using the FuzzyQoI model
(Dias and Diniz, 2013), to examine how the
course content affects the users’ QoI with LMS
Moodle across the years,
• identification of possible macroscopic causal
dependencies, converged or dispersed
interaction trends, periodicities, specific
patterns dominance in the LMS Moodle
interaction/collaborative/metacognitive
attitude, all reflected at the FISs, i.e., C/M-FIS
and FuzzyQoI models response,
• comparative analysis across the forthcoming
hybrid modeling approaches, blending the
benefits of each one and identifying their pros
and cons, and
• construction of new guidelines/
recommendations about the enhancement of
OLE-based teaching/learning processes,
contributing to the enrichment of the higher
education institutions (HEIs) services and
reformulation of educational policies/practices.
Adding to the above, ontologies could be used to link
the quantitative metrics of QoC and QoI to
information coding, so it could easier be processed by
software agents, opening the door for a slew of new
semantic Web 3.0-based applications. In fact,
according to Gruber (1993), an ontology is a formal,
explicit specification of a shared conceptualization.
Pragmatically, a common ontology defines the
vocabulary with which queries and assertions are
exchanged among software entities. An ontology has
concepts that identify the data entities of interest and
these concepts are organized in a hierarchy, called a
taxonomy; concepts might have attributes and
relationships, whereas a data item that has been
marked up with a label corresponding to a concept is
called a data instance. Through this organization,
ontologies could contribute to a shared and common
TowardsaHybridWorld-TheFuzzyQualityofCollaboration/Interaction(FuzzyQoC/I)HybridModelintheSemantic
Web3.0
189

Figure 1: The architecture of the proposed FuzzyQoC/I hybrid model that connects the educational and fuzzy worlds,
integrating the C/M-FIS and FuzzyQoI models. OLE: Online Learning Environment, CLE: Cloud Learning Environment,
CSCL: Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, LMS: Learning Management System, HEI: Higher Education
Institution, QoC: Quality of Collaboration, QoI: Quality of Interaction.
understanding of QoC and QoI that can be
communicated among the educational stakeholders
and iLMSs/iOLEs. As the latter involve Web-based
educational material, ontologies can be used to
describe relationships between pages and other data
(like QoC and QoI metrics), so to contribute to a
personalized supporting system that could maximize
the QoC and QoI; hence, enhance user’s
teaching/learning experience. They can, therefore, be
used to recommend learning resources of potential
interest to the learner that potentially increase his/her
QoI; even to recommend a “study-buddy”, with
whom the learner shares common abilities and
interests and can maximize his/her QoC when
collaborates with him/her. From a technical point of
view, this could be achieved by employing, for
example, the DARPA Agent Markup
Language/Ontology Inference Layer (DAML+OIL)
ontology language (McGuinness et al., 2002), which
describes structure of the domain, combined with the
Resource Description Framework (RDF), which is
used, in the same time, to describe specific instances,
and Ontology Web Language and Information
Retrieval (OWLIR) that handles the Event Ontologies
(Connolly et al., 2001).
In one step further, using Cloud computing platforms
(e.g., Microsoft Azure) and technologies in
conjunction with semantic Web 3.0 technology and
metadata, a shift from the traditional LMS to Cloud
Learning Environments (CLEs) could be achieved, by
facilitating the autonomous or collaborative study of
user-chosen blends of content and courses from
heterogeneous sources (Mikroyannidis, 2012). In
CLE, semantic knowledge base serves as the core of
the OLE, facilitating learners in finding educational
services and collaborate on the Cloud, evoking
collaborative ontology management techniques. In
this concept, the proposed hybrid QoC/I model could
combine both LMS and CLE in the learning process,
placing the user at the centre and capturing his/her
interaction with both contexts. This could, actually,
assist HEIs to enrich their educational framework,
facilitating, at the same time, the professors’/learners’
interaction (both autonomous and collaborative) with
the OLEs.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
190

A schematic presentation of the proposed
architectural structure of the FuzzyQoC/I hybrid
model is depicted in Figure 1. Apparently, the online
communication channels considered in Fig. 1 should
not be seen as static; yet with fluidity, directed to
provide flow opportunities of communication in
human-computer interaction in an OLE. From a
common perspective, learners should be
behaviourally, intellectually, and emotionally
involved in online learning tasks. Nevertheless, the
role of educational technology is to improve
academic literacies in students, to create engaging
communities of practice, and to improve learner’s
motivation and self-empowered learners (Wankel and
Blessinger, 2013).
2.1 Fuzzy Ontologies
In the hybrid model presented in Fig. 1, the role of FL
is catalytic. One of the issues that could also be
approached from the FL concept is the ontology one.
As it was mentioned above, the Semantic Web allows
relational knowledge to be embedded as metadata in
Web pages, enabling machines to use ontologies and
inference rules in retrieving and manipulating data. In
this vein, ontologies are a key component of the
Semantic Web.
As an extension of the ontologies, the fuzzy
ontologies could also be defined (Widyantoro and
Yen, 2001), incorporating the functionality of an
ontology with the flexibility of the FL. The main
definitions and characteristics of fuzzy ontologies are
epitomized bellow, as a glimpse to the enhanced
potentialities of the hybrid modeling of Fig. 1.
In general, the definition of a fuzzy ontology structure
includes: concepts, fuzzy relations among concepts, a
concept hierarchy or taxonomy, non-hierarchical
associative relationships and a set of ontology
axioms, expressed in an appropriate logical language.
Consequently, a lexicon for a fuzzy ontology
includes: lexical entries for concepts (knowledge
about them can be given by fuzzy attributes, with
context-dependent values), lexical entries for fuzzy
relations, coupled with weights expressing the
strength of associations, and reference functions
linking lexical entries to concepts or relations they
refer to.
Apart from the structural characteristics of the fuzzy
ontology described above, the issue of fuzzy ontology
mapping should also be considered. In particular,
ontology mapping is the effective method to solve the
problems of knowledge sharing and reusing across
the heterogeneous ontologies in the Semantic Web
(Doan et al., 2002). The current ontology mapping
technologies are not sufficient for fuzzy ontologies
(Ma et al., 2014). Therefore, with the growing
number of heterogeneous fuzzy ontologies in the
Semantic Web, the fuzzy ontology mapping that can
handle fuzzy data becomes an important research
topic. The aforementioned characteristics of the fuzzy
ontologies show the potentiality of FL to handle
heterogeneous data and perform more effective
reasoning at the ontological level. Hence, provisional
embedding within the hybrid model presented in Fig.
1 enriches its ingredients, towards the successful
integration of the knowledge representation in the
Semantic Web within the educational context.
Next, a provisional case study of the proposed hybrid
model is discussed, with regard to the i-Treasures
Programme.
3 THE I-TREASURES CASE
STUDY
The i-Treasures: “Intangible Treasures - Capturing
the Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) and Learning
the Rare Know-How of Living Human Treasures” is
an Integrated Project (IP) of the European Union's 7th
Framework Programme ICT for Access to Cultural
Resources (February 1, 2013-2017). The main aim of
i-Treasure is to develop an open and extendable
platform to provide access to intangible cultural
heritage resources and, at the same time, to propose a
novel strategic framework for the safeguarding and
transmission of ICH (http://i-treasures.eu).
Considering the latter, it is apparent that the issues of
personalized learning, LMS interaction, ontologies
coding and enriched feedback (facilitated via a
sensory motor learning approach) are common
elements. Based on this mutuality in the design, direct
analogies could be considered as injection of the
hybrid model fuzziness in the evolution of the i-
Treasures Programme. In particular:
• Since the LMS is one of the main facilitator of
the user’s interaction with the i-Treasures
platform, the simultaneous measurement of
his/her QoI with the LMS via the QoC/I
modeling (see Fuzziness/Hybrid Modeling in
Fig. 1), could be an important enhancement in the
functionality of the i-Treasures platform. This
could also be used as effective feedback to the
user (see Personalized Feedback in Fig. 1), and
combined with the sensorimotor learning
concept, could evoke reflective processes
towards the intention for improvement.
TowardsaHybridWorld-TheFuzzyQualityofCollaboration/Interaction(FuzzyQoC/I)HybridModelintheSemantic
Web3.0
191

Figure 2: The i-Treasures use-cases referring to traditional and contemporary singing, traditional and contemporary dance,
traditional pottery, and contemporary music composition (http://i-treasures.eu).
• Similarly to the case of QoI, the QoC could serve
as dynamic feedback to the i-Treasures user,
reinforcing transitional changes and supporting
knowledge development. As cultural knowledge
is transmitted not only via changes in an
individual across time, but also via the groups’
behavior over time (Flynn and Siegler, 2007), the
dynamic monitoring of the FL-based estimated
QoC and QoI could facilitate the capturing of
such changes (e.g., as transitions across the
ellipses of Fig. 1, both at the individual and at the
group level), exposing attitude shifts and trends,
accompanied by cultural knowledge
development. This approach could also be
combined with the affective information of the i-
Treasures acquisition modules to correlate the
user’s emotional engagement with the evolution
of his/her QoI and QoC trends.
• The MEBNs (Laskey, 2008) used for the
ontology-based knowledge representation in i-
Treasures Programme could be accompanied by
the concept of fuzzy ontologies, described in the
previous section (see Fig. 1), in an effort to
handle uncertainty in alternative to the
probability way, employing the advantageous
characteristics of the FL.
• Since the i-Treasures Programme is multi-
layered, with a variety of acquisition modules
and different use-cases, its performance
evaluation and monitoring (as a whole system) is
quite difficult to be approached in a mono-
dimensional way. In this context, an estimation
of the general performance indices (GPIs) for
each use case, as well as for their sub-use cases
could be achieved based on nested FISs. In
addition, the GPI of the integrated platform could
be estimated, reflecting its overall quality, as
shown in Fig. 3.
From the above, it is clear that the FuzzyQoC/I hybrid
model could be used to capture micro- (localities) and
macro- (generalities) levels of the i-Treasures system
use.
4 FINAL CONSIDERATIONS
The concept of a FL-based hybrid model, which
combines QoC and QoI within the context of
semantic Web 3.0 and CLEs in a holistic perspective
of the online learning educational context, shedding
light upon the requirements for offering personalized
feedback to learners, supporting them throughout
their learning journey, and enriched recommendation
services to HEI policy/service quality managers, was
the focus of this paper. The provisional hybrid model
presented here combines the FL-based approaches in
modelling collaborative/metacognitive and LMS user
interaction data, along with the perspectives of fuzzy
ontologies and fuzzy ontology mapping techniques.
In this way, higher flexibility, more enhanced
modeling capabilities and multidimensional inference
from the fusion of information estimated at various
levels of interaction/collaboration within the co-
existing CSCL environments and CLE/OLEs under
the b-learning concept are provided. The dynamic
feedback of QoI and QoC, combined in the proposed
FuzzyQoC/I hybrid approach, can account for the
non-stationarities seen in students’ learning process,
providing more pragmatic capturing of the underlying
interaction trend-shifts and/or artefacts.
Moreover, the hybrid concept adopted in this paper is
in line with the European Union’s perspective about
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
192
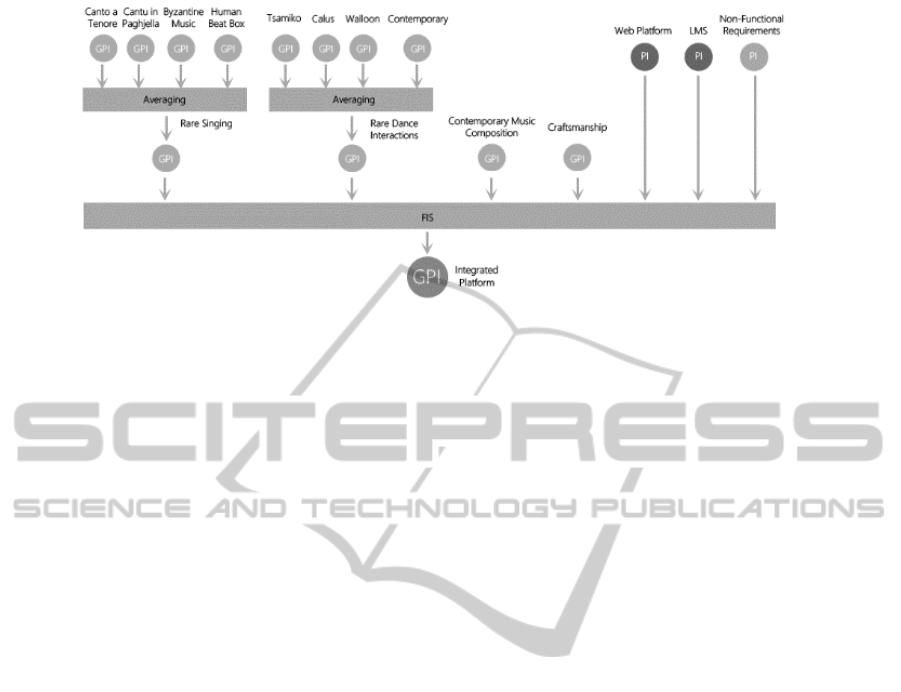
Figure 3: Fusion of the general performance indicators (GPIs) of each use-case of the i-Treasures with Web platform/LMS
performance indicators (PIs) as FIS inputs to output the integrated platform GPI of the i-Treasures.
the trends and evolution of Higher Education in the
next years (Johnson et al., 2015).
The metrics of QoC and QoI (combined in the hybrid
model) are of great importance, as they could become
key-discriminators amongst hybrid learning
environments, as emerging digital tools make it easier
for students to ask and respond to each other’s
questions and for instructors to provide feedback in
real-time. In line with this, the personalized feedback
based on the FL-based estimated QoC and QoI could
also help instructors to leverage components of online
learning and to make personalized learning scalable
in large introductory classes. Compared to the
traditional model of learning, in which space is
needed to accommodate hundreds of students, hybrid
learning can address the learning path of each
individual student. From a motivational point of view,
our approach resembles the efforts for hybrid
modelling of instructional design (ID), such as the 4-
Component/ID (4C/ID) (Van Merriënboer et al.,
2003). In the 4C/ID, a hybrid-modelling framework
for scaffolding practice and just-in-time information
presentation, aiming to control cognitive load
effectively, is presented. Taking this further, the
FuzzyQoC/I model could be seen as a flexible
nutshell, where such ID approaches could be
encapsulated and developed in a synchronized way,
towards the maximization of the learner’s learning
experience, both at the task (cognitive load) and
collaboration/interaction (QoC/QoI) levels.
In the same view of the aforementioned, the
implementation potentiality of the hybrid modeling
was examined in a real case study, i.e., the i-Treasures
programme, which is a currently EU FP7 running (up
to 2017), aiming at the development of an open and
extendable platform to provide access to ICH
resources, enable project knowledge exchange
between researchers, and contribute to the
transmission of rare know-how from Living Human
Treasures to apprentices via sensorimotor learning.
Due to the nature and design of the i-Treasures, its
structural characteristics are in direct connection with
the ones of the FuzzyQoC/I hybrid model. In this
vein, the applicability of the concept behind the
hybrid approach to the real case of the i-Treasures
was explored and possible interactions were
identified. The outcomes of the provisional adoption
of this theoretical approach in a case study will allow
to further validate the proposed hybrid methodology
and expand its database and implementation on case
studies from diverse areas (such as the i-Treasures
Programme), for its further generalization
refinement. It is our hope that this effort could
significantly add to the appreciation of the
potentialities of the newly available technological
means and networking concepts, such as semantic
Web 3.0, in the field of Higher Education. Moreover,
the ideas discussed in the present paper expectantly
could provide an intelligent framework for possible
reforms and alterations to the b- and c-learning
modeling; hence, to effectively affect the educational
processes within online teaching/learning
environments at HEIs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The first author has been supported by the Foundation
for Science and Technology (FCT, Portugal)
(Postdoctoral Grant SFRH/BPD/496004/2013).
Moreover, this work was realized within the
framework of the EU FP7-ICT-2011-9-ICT-
2011.8.2, under the grant agreement n° 600676: "i-
Treasures" Project (http://i-treasures.eu).
TowardsaHybridWorld-TheFuzzyQualityofCollaboration/Interaction(FuzzyQoC/I)HybridModelintheSemantic
Web3.0
193

REFERENCES
Bates, T., 2005. Technology, e-learning and distance
education. London, Routledge.
Coffield, F., Moseley, D., Hall, E., & Ecclestone, K., 2004.
Learning styles and pedagogy in post-16 learning: a
systematic and critical review. London, UK, Learning
and Skills Research Centre/University of Newcastle.
Connolly, D., van Harmelen, F., Horrocks, I., McGuinness,
D. L., Patel-Schneider, P. F., & Stein, L. A., 2001.
DAML+OIL (March 2001) Reference Description.
W3C Note 18 December 2001.
Davis, E., 1990. Representations of Commonsense
Knowledge. San Mateo, CA, Morgan Kaufmann.
De Souza e Silva, A., 2006. From Cyber to Hybrid Mobile
Technologies as Interfaces of Hybrid Spaces. Space
and culture, 9(3), 261-278.
Dias, S. B., 2014. Towards an intelligent online learning
environment. A systemic approach. Saarbrücken,
Germany, LAP Lambert Academic Publishing.
Dias, S. B., & Diniz, J. A., 2013. FuzzyQoI model: A fuzzy
logic-based modelling of users’ quality of interaction
with a learning management system under blended
learning. Computers & Education, 69, 38-59.
Dias, S. B., Diniz, J. A., & Hadjileontiadis, L. J., 2014.
Towards an intelligent learning management system
under blended learning: trends, profiles and modelling
perspectives. In J. Kacprzyk, & L. C. Jain (Eds.),
Intelligent Systems Reference Library, Volume 59.
Berlin/Heidelberg, Springer-Verlag,
Doan, A., Madhavan, J., Domingos, P., & Halevy, A., 2002.
Learning to map between ontologies on the semantic
Web. Proc. of the 11th International World Wide Web
conference (pp. 662-673).
Felder, R. M., & Silverman, L. K., 1988. Learning and
teaching styles in engineering education. Engineering
Education, 78(7), 674-681.
Flynn, E., & Siegler, R., 2007. Measuring change: Current
trends and future directions in microgenetic research.
Infant and Child Development, 16(1), 135-149.
Garrison, D. R., & Kanuka, H., 2004. Blended learning:
Uncovering its transformative potential in higher
education. The Internet and Higher Educ., 7, 95-105.
Graf, S., 2007. Adaptivity in learning management systems
focussing on learning styles (Unpublished PhD Thesis),
Vienna Univ. Technology, Vienna, Austria.
Gruber, T. R., 1993. A translation approach to portable
ontologies. Knowledge Acquisition, 5(2), 199-220.
Hadjileontiadou, S. J., Nikolaidou, G. N., Hadjileontiadis,
L. J., & Balafoutas, G. N., 2003. A Fuzzy Logic
Evaluating System to Support Web-based
Collaboration Using Collaborative and Metacognitive
Data, In Proc. of the 3rd IEEE International
Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies
(ICALT’03) (pp. 96-100). Athens, Greece.
Johnson, L., Adams Becker, S., Cummins, M., Estrada, V.,
Freeman, A., & Ludgate, H., 2013. NMC Horizon
Report: 2013 Higher Education Edition. Austin, Texas,
The New Media Consortium.
Johnson, L., Adams Becker, S., Estrada, V., & Freeman, A.,
2015. NMC Horizon Report: 2015 Higher Education
Edition. Austin, Texas, The New Media Consortium.
Jonassen, D. H., & Grabowski, B. L., 1993. Handbook of
individual differences, learning, and instruction.
Hillsdale, New Jersey, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Laskey, B. K., 2008. MEBN: A language for first-order
Bayesian knowledge bases. Artificial Intelligence,
172(2-3), 140-178.
Liu, Y., 2014. Meditations on the semantic net: Oriented
library information service in cloud computing era. In
S. Li, Q. Jin, X. Jiang, & J.J. Park (Eds.) Frontier and
future development of information technology in
medicine and education (pp. 1863-1870). LNEE,
Volume 269 (pp. 1863-1870). Netherlands, Springer.
Lukasiewicz, T., & Straccia, U., 2008. Managing
uncertainty and vagueness in description logics for the
Semantic Web. Web Semantics: Science, Services and
Agents on the World Wide Web, 6(4), 291-308.
Ma, Z., Zhang, F., Yan, L., & Cheng, J., 2014. Fuzzy
Semantic Web Ontology Mapping. In Fuzzy Knowledge
Management for the Semantic Web (pp. 157-180).
Berlin-Heidelberg, Springer.
McGuinness, D. L., Fikes, R., Hendler, J., & Stein, L. A.,
2002. DAML+OIL: An ontology language for the
semantic Web. IEEE Intelligent Syst., 17(5), 72-80.
Mikroyannidis, A., 2012. A semantic framework for cloud
learning environments. In C. Lee (Ed.), Cloud
computing for teaching and learning: strategies for
design and implementation (pp. 17–31). Hershey, PA,
IGI Global.
Oliver, M., & Trigwell, K., 2005. Can ‘blended learning’ be
redeemed?. E-learning and Dig. Media, 2(1), 17-26.
Paquette, G., 2014. Technology-based instructional design:
evolution and major trends. In J. M. Spector, M. D.
Merrill, J. Elen, & M. J. Bishop (Eds.), Handbook of
Research on Educational Communications and
Technology (pp. 661-671). New York, Springer.
Peters, O., 2001. Learning and teaching in distance
education: Analysis and interpretations from an
international perspective. London, Kogan Page.
Reeve, J., & Tseng, C. -M., 2011. Agency as a fourth aspect
of students’ engagement during learning activities.
Contemporary Educational Psychol., 36(4), 257-267.
Van Merriënboer, J. J., Kirschner, P. A., & Kester, L., 2003.
Taking the load off a learner's mind: Instructional
design for complex learning. Educational psychologist,
38(1), 5-13.
Voorsluys, W., Broberg, J., & Buyya, R., 2011.
Introduction to cloud computing. Cloud Comp., 1-41.
Wankel, C., & Blessinger, P., 2013. Increasing student
engagement and retention in e-learning environments
(Web 2.0 and blended learning technologies). Howard
House, Wagon Lane, Bingley, UK, Emerald Group.
Whittaker, J., 2009. Graphical models in applied
multivariate statistics. Hoboken, NJ, Wiley Pub.
Widyantoro, D. H., & Yen, J., 2001. Incorporating Fuzzy
Ontology of Term Relations in a Search Engine. Proc.
of the 1st BISC International Workshop on Fuzzy Logic
and the Internet (pp. 155-160). Berkeley, USA.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
194

Wijnia, L., Loyens, S. M. M., & Derous, E., 2011.
Investigating effects of problem-based vs. lecture-
based learning environments on student motivation.
Contemporary Educ. Psychology, 36(2), 101-113.
Zadeh, L. A., 1965. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control, 8, 338-353.
Zadeh, L. A., 1971. Toward a theory of fuzzy systems. In
R. E. Kalman, & N. De Claris (Eds.), Aspects of
Network & System Theory. NY, Rinehart & Winston.
TowardsaHybridWorld-TheFuzzyQualityofCollaboration/Interaction(FuzzyQoC/I)HybridModelintheSemantic
Web3.0
195
