
“BPELanon”
Protect Business Processes on the Cloud
Marigianna Skouradaki
1
,Vincenzo Ferme
2
, Frank Leymann
1
, Cesare Pautasso
2
, Dieter H. Roller
1
1
Institute of Architecture of Application Systems, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany
2
Faculty of Informatics, University of Lugano (USI), Lugano, Switzerland
Keywords:
Anonymization, BPEL, Workflows, Business Processes.
Abstract:
The advent of Cloud computing supports the offering of many Business Process Management applications on a
distributed, per-use basis environment through its infrastructure. Due to the fact that privacy is still an open
issue in the Cloud, many companies are reluctant to move their Business Processes on a public Cloud. Since the
Cloud environment can be beneficiary for the Business Processes, the investigation of privacy issues needs to
be further examined. In order to enforce the Business Process sharing on the Cloud we propose a methodology
(“BPELanon”) for the anonymization of Business Processes expressed in the Web Service Business Process
Execution Language (BPEL). The method transforms a process to preserve its original structure and run-time
behavior, while completely anonymizing its business semantics. In this work we set the theoretical framework
of the method and define a five management layers architecture to support its realization. We developed a tool
that implements the “BPELanon” method, validate its functionality and evaluate its performance against a
collection of real-world process models that were conducted in the scope of research projects.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the recent years the Cloud revolutionized many In-
formation Technologies, one of the affected fields is
this of Business Process Management. In this case
Cloud environments are used to deploy and execute
Business Processes (BP)(Amziani et al., 2012) and pro-
vide them as a Service (BPaaS)(Wang et al., 2010) that
is provisioned through Platform as a Service (PaaS)
(Hahn et al., 2014) solutions. The adoption of a Cloud
solution can be targeted on public, private or hybrid
Cloud solutions (RightScale, 2014). However, when
outsourcing the BP to the public Cloud consumers lose
the control of their data(Chow et al., 2009). Because of
this weakness many companies are reluctant to adopt
public Cloud solutions(Ko et al., 2011).
Cloud solutions have been proven more benefi-
ciary for the companies, in comparison to the iso-
lated business model followed by now (Accorsi, 2011).
Therefore, privacy issues on the Cloud are currently
discussed in the literature (Bentounsi et al., 2012;
Jansen, 2011; Doelitzscher et al., 2010; Anstett et al.,
2009). To reach these objectives we propose a method
and implement a tool to anonymize or pseudonymize
Business Processes expressed in the Business Pro-
cess Execution Language (BPEL). The proposed so-
lution produces an anonymized or a pseudonymized
BP for safe deployment and execution on the Cloud.
The anonymized/pseudonymized BP will maintain
its executional and timing behavior. In the case of
pseudonymization the output of the executed BP can
also be mapped back to the original, non-anonymized
version of the BP.
This work has a focus on the BP, which means
that the data and Web Services that surround the BP
will be simulated in a “dummy” way. Later on, our
solution can be extended or combined with already
existing solutions for data(Sedayao, 2012; Zhang et al.,
2014) and Web Services(Doelitzscher et al., 2010)
anonymization to protect the company’s artifacts to
the maximum possible degree. The contributions of
this work are as follows:
1.
identify the requirements of anonymizing or
pseudonymization a BP
2.
propose a method (“BPELanon”) that identifies the
critical attributes and exports the anonymized BP
containing the original BPEL BP without its busi-
ness semantics, but solely its executable structure
3.
provide and explain a tool that implements the
method introduced
4.
validate the tool’s functionality and evaluate its
241
Skouradaki M., Ferme V., Leymann F., Pautasso C. and Roller D..
“BPELanon” - Protect Business Processes on the Cloud.
DOI: 10.5220/0005427502410250
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER-2015), pages 241-250
ISBN: 978-989-758-104-5
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

performance through a collection of real-world
BPEL BP that were conducted under the scope of
research projects
This paper extends the work described in (Sk-
ouradaki et al., 2014) in terms of the realization, valida-
tion, and evaluation of a tool that supports “BPELanon”
method. It is structured as follows: Section 2 ana-
lyzes the requirements and upcoming challenges of
the method to be developed; Section 3 describes the
design of the method; Section 4 provides a concrete
realization of our approach; Section 5 validates the
functionality of the “BPELanon” through case studies,
and evaluates its performance against 24 real-world
BP; Section 6 discusses related work that has been
done for anonymization; and Section 7 summarizes
and discusses an outlook to future work.
2 APPROACHING THE
PROBLEM
2.1 Requirements
The design of “BPELanon” must address the follow-
ing initial list of requirements identified during our
work in various research projects, and especially dur-
ing our collaboration with industry partners. The main
requirement and purpose of method is to:
[R1:PSEUDONYMIZATION/ANONYMIZATION]
Support both pseudonymization and anonymization of
BP upon the user’s choice. Pseudonymization is the
technique of masking the data, while maintaining ways
to the original data (Federal Ministry of Justice, 1990).
On the contrary, anonymization changes the critical
data and makes it impossible to trace back the original
version of data (Strauch et al., 2012). Providing the
option of pseudonymization makes it possible for the
originator to trace bugs or inconsistencies found in the
anonymized file, and apply changes to the original.
In order to guarantee the satisfaction of
[R1:PSEUDONYMIZATION/ANONYMIZATION]
a number of other requirements occur. These can be
grouped to requirements that stem from the XML
nature of BPEL. XML-specific requirements:
[R2:NO SENSITIVE INFO]
Scramble the company’s sensitive information that
can be revealed in activity names, variable names,
partner link names, partnerlink type names, port
type names, message names, operation names, role
names, XSD Element names, namespaces, and XPath
expressions. The name choice for these attributes is
usually descriptive, and reflects the actual actions to
which they correspond. So they can reveal a lot of the
BP semantics.
[R3:NO NAMESPACES INFO]
The exported BP must not contain namespace
information in incoming links to external web sites
that reveal business information (backlinks).
[R4:NO BACKLINK INFO]
The exported BP must not contain names (including
activity names, variable names, partner link names,
partnerlink type names, message names, operation
names, role names, and XSD Element names) with
backlinks to business information .
[R5:NO XPATH INFO]
The exported BP must not contain XPath expressions
with backlinks to business information. If no custom
XPath functions are used, [R5:NO XPATH INFO] is
a consequence of requirement [R4:NO BACKLINK
INFO].
[R6:NO DOCUMENTATION INFO]
Remove description containers (comments and
documentation) that reveal critical information and
semantics .
BPEL-specific requirements:
[R7:KEEP STRUCTURE & EXECUTABILITY]
The exported BP must keep the structural information
and executability.
[R8:KEEP RUNTIME]
The exported BP must maintain an equivalent run-time
behavior.
[R9:KEEP TIMING]
The exported BP must maintain equivalent timing be-
havior.
The following requirements are related to the
renaming method that will be applied:
[R10:PREVENT REVERSE ENGINEERING]
It has to be ensured that the scrambled name prevents
reverse engineering to get the original names. For
example if data is encrypted with a known function
(e.g., RSA, MD5) and we know the used key, then it is
easy to obtain the original data.
[R11:AVOID CONFLICTS]
Names must be chosen in a way that conflicts are
avoided between the original and exported file. For
example an easy name choice would be to change
each name with respect to its type followed by
an ascending ID. In this case the name of activity
“Payment” would have been changed to the name
“Activity1”. Nevertheless, this way is not considered
safe. “Activity1” could also have been a possible name
choice for the original BP as it is a word frequently
met in Business Process Management. This would
lead to a sequence of conflicts. Which elements
named “Activity1” correspond to the anonymized
element and which to the one contained in the original
BP?
CLOSER2015-5thInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
242
[R12:HUMAN READABLE NAMES]
The names must lead to an human-readable exported
file. For example let’s assume that we use UUIDs for
name choice. That would lead to activity names such
as:
f81d4fae-7dec-11d0-a765-00a0c91e6bf6
.
The exported file would not be easy to read for
humans.
2.2 Challenges
This section analyzes the challenges that stem from
the need to satisfy the requirements described in
Section 2.1. Each BP specification is wrapped in
a package which is a directory containing all de-
ployment artifacts. At the minimum the directory
should contain a deployment descriptor, and one or
more process definitions BPEL, Web Service Defi-
nition Language (WSDL), and XML Schema Defi-
nition Language (XSD) files(Apache Software Foun-
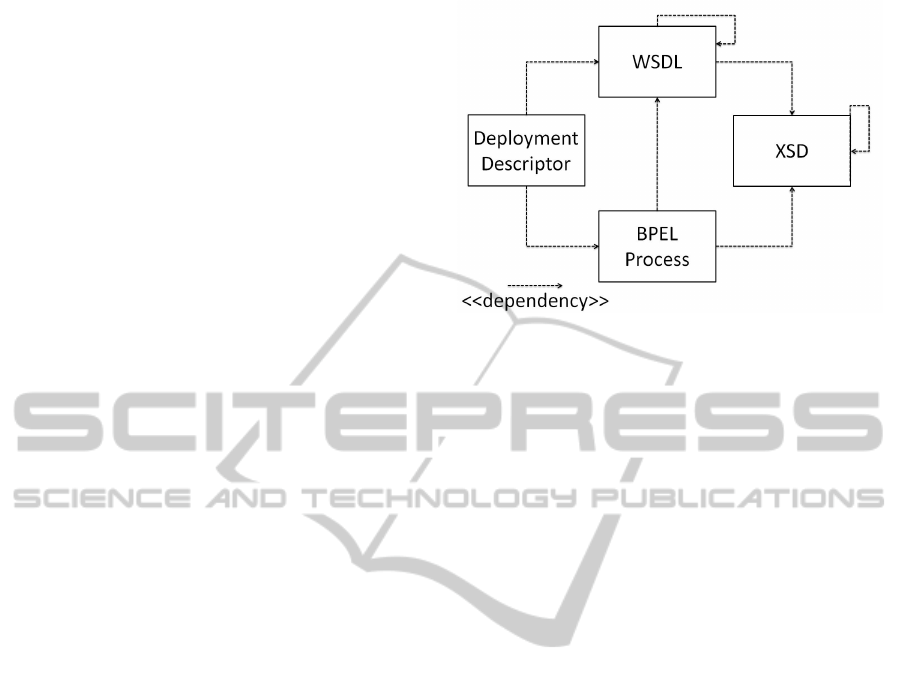
dation, 2013). Many dependency relations among
files as shown in Figure 1 increase the complexity of
anonymization as small changes in a file may lead to
numerous subsequent changes to other BP artifacts
[C1:SUBSEQUENT CHANGES]. The complexity is
also increased by the need to remove all sensitive in-
formation from the BPEL BP package [C2:NO SEN-
SITIVE INFO]. The renaming method also needs to
be carefully examined in order to keep timing, pre-
vent reverse engineering of the anonymization, avoid
conflicts between the names, and use human-readable
names.
The BPEL-specific requirements reveal a new set
of challenges that will be more complex to fulfill.
How do data and data specific decisions affect the run-
time behavior of the anonymized model? [C4:DATA
CHALLENGES]. How is BPEL life-cycle affected
by anonymization? [C5:BPEL LIFECYCLE]. To
what extend will timing behavior be maintained?
[C6:TIMING BEHAVIOUR]. We discuss these chal-
lenges in Section 5 and intend to further investigate
them in future work.
3 DESIGNING THE METHOD
This section describes the method that is used for de-
veloping “BPELanon”. Elements in a BPEL file can
be divided into three groups:
•
Free Elements Group: Elements that need to be
anonymized, but are not bound to changes that
occurred in other files.
•
Externally Bounded Group: Elements that need
to be changed because they were bounded with
Figure 1: Dependencies of the artifacts of a BPEL BP.
elements that are changed in the WSDL or XSD
files.
•
Internally Bounded Group: Elements that need
to be changed because they are bounded to other
changed elements within the same file. Internally
Bounded Groups can be found in both BPEL, XSD
and WSDL files.
The anonymization of “Free Elements Group” is trivial,
as it can be reduced to string replacement. However,
the anonymization of “External Bounded Group” and
“Internally Bounded Group” are more complex tasks.
For its implementation we need a “Registry of Alter-
ations”. This is a registry of metadata that is created
during the anonymization of a file and logs the occur-
ring changes. It must contain at least the following
information: the element’s type, and the corresponding
attributes’ new and old data.
The main idea of the anonymization is to scan each
artifact of the BPEL BP looking for element attributes
that might contain semantics (critical attributes) that
need to be scrambled. Then add to the “Registry of
Alterations” their old and new value. The informa-
tion on which attributes are critical can be stored with
metadata. Next we scan the documents looking for
references to the scrambled elements and update their
values. Below we describe the anonymization method
for the “Externally Bounded Group”.
Anonymization starts with the creation of a meta-
data schema that reflects the interconnections shown
in Figure 1. Next we construct a “Table of Refer-
ences” that shows the relations between a BPEL BP
and its WSDL files. This is done by parsing the
<bpel:import>
annotations of the BPEL file. We
then process the WSDL files, which contain the def-
initions for the artifacts that are referenced in BPEL.
We run through each one of the WSDL files in “Table
of References” and start anonymizing the attributes of
the elements step by step. In order to fulfill [R8:KEEP
"BPELanon"-ProtectBusinessProcessesontheCloud
243

Algorithm 1: Anonymization process of BPEL-WSDL for “WSDL Bounded Group”.
create TableOfReferences by parsing <bpel:import>annotations of BPEL
for all WSDL files W in tableOfReferences do
for all elements E in W do
a ← getCriticalAttributes(E)
for all a do
updateRegistryOfAlterations(E.type,a.type,a.data,“old”)
applyAnonymizationPattern(a.data)
updateRegistryOfAlterations(E.type,a.type,a.data,“new”)
end for
end for
for all element E in BPEL file do
a ← getCriticalAttributes(E)
for all a do
resultType ← findTypeOfInterconnection(E.type,a.type)
a.data ← getNewValueOfAttribute(resultType,a.data) {from registryOfAlterations}
end for
end for
end for
if anonymization then
delete tableOfReferences
delete registryOfAlterations
end if
RUNTIME] the function of anonymization will pick
random words of an English Dictionary (WinEdt,
2000) as we argue that a word of well known human
language will lead to more readable results with re-
spect of using random strings as IDs. As discussed
in Section 2.1 we only focus on the anonymization
of critical attributes as not every attribute needs to
be anonymized. By maintaining a “Registry of Alter-
ations”, we apply the subsequent changes to the BPEL.
We have created an outer loop that repeats this process
for each WSDL file. Another option would be to parse
all WSDL files and finally apply the changes to BPEL
file in one parse. However, WSDL files might have
common names and this would lead to more complex
solution. We have therefore chosen this safer although
most likely more complex in execution time solution.
At the end of the process “Table of References” and
“Registry of Alterations” are destroyed if the tool is set
to anonymize and not pseudonymize. Algorithm 1 de-
scribes the above procedure. For reasons of simplicity
it focuses to the anonymization of a BPEL-WSDL set.
However, for the anonymization of the complete set of
artifacts presented in Figure 1 a similar process needs
to be followed. The complete process of the BPEL BP
anonymization is realized through the tool described
in this paper.
4 REALIZATION
In this section we present the realization approach of
the “BPELanon” method presented in the previous
section. “BPELanon” is implemented on a Java en-
vironment. As shown in Figure 3 the architecture of
the realization can be separated in five different man-
agement layers. The layer “Interaction Management”
refers to the part of the implementation that interacts
with the user (i.e. the person that want to anonymize
their BP); the layer “File Management” is responsible
for the managements of the BP files; the “Anonymize
Management” for the execution of the BP anonymiza-
tion; the “Rename Management” to provide the new
words to be used and finally the “Registry Manage-
ment” to log the changes to a registry.
At this point we will move one step further, to
the architectural details and see how the components
of the different layers interact with each other for
“BPELanon” realization. The components of the
“Interaction Management” are realized through a
graphical interface. With this the user can navi-
gate through the files of the BPEL BP, configure
if he needs anonymization or pseudonymization
[R1:PSEUDONYMIZATION/ANONYMIZATION],
and finally trigger the selected process. This user
interface is depicted in Figure 2.
When the user selects the BP, then the buttons
“Anonymize” and “Delete originals” become enabled.
The user can choose anonymize to scramble the data
of a BP (pseudonymize) and “Delete Originals” to lead
to complete anonymization of the BPEL BP.
The “Importer” of the interaction layer is responsi-
ble for parsing the files, creating the corresponding
CLOSER2015-5thInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
244

Figure 2: User Interface of the realization of Interaction Management Layer.
Java objects, and calculates the “Table of References”
that is used to track down the existing dependencies.
With the usage of “Table of References” we are
achieving consistency in the exported file [R7:KEEP
STRUCTURE & EXECUTABILITY]. The mapping
of the dependencies as well as the parsed objects are
then given to the “Anonymizer” component, which is
basically responsible for the anonymization. In order
to calculate the critical elements, their attributes, and
their dependencies between the files, the layer has a
special anonymizer component (BPEL Anonymizer,
XPath Anonymizer, WSDL Anonymizer and XSD
Anonymizer) for each one of the BP artifacts. The
implementation of these components aims to the satis-
faction of the requirements [R3:NO NAMESPACES
INFO], [R4:NO BACKLINK INFO], [R5:NO XPATH
INFO] and [R6:NO DOCUMENTATION INFO].
The “Anonymizer” component, interacts with
the “Name Provider” component that is respon-
sible for fetching and providing random new
words to the “Anonymizer”. To accomplish its
goal the “Name Provider” interacts with an XML
database that realizes an English Dictionary retrieved
from (WinEdt, 2000). With this technique we
achieve to choose the new names in such way
that requirements [R2:NO SENSITIVE INFO],
[R10:PREVENT REVERSE ENGINEERING] and
[R12:HUMAN READABLE NAMES] are satisfied.
The “Anonymizer” interacts also with the “Registry
of Alterations” which as discussed is responsible
for logging the applied changes. By “Registry of
Alterations” we can achieve pseudonymization
[R1:PSEUDONYMIZATION/ANONYMIZATION]
as the changes have been recorded. If the registry is
deleted then we achieve anonymization. Requirement
[R11:AVOID CONFLICTS] is also satisfied through
the “Registry of Alterations” component as we track
the changes, and do the corresponding checks to avoid
conflicts. The anonymizer returns the anonymized
files to the “Exporter” component that will finally save
the anonymized project and notify the user through
the user interface.
The last step of our realization is the execution
of the anonymized BPEL BP. As expected, the
anonymized BPEL BP is searching to invoke services
that are anonymized, and thus nowhere implemented.
In order to make the anonymized BP executable we
need to create dummy services with respect to the new
values. This is implemented through the functionality
of creating mock-up services, offered by SOAP
UI
1
. If the timing information has been initially
provided from the provider of the BP, then we can add
corresponding timers to the dummy services in order
to satisfy [R9:KEEP TIMING]. The demonstration of
the executable anonymized BP and evaluation of its
time performance are discussed in Section 5.
5 VALIDATION AND
EVALUATION
This section validates realization of the “BPELanon”
method through case studies. We visualize the pre-
sented BPEL BP with the BPEL Designer of Eclipse
IDE
2
and for their execution we have used the Apache
ODE
3
.
During the validation process we had two limita-
tions: a) we are not allowed to publish our real world
processes and b) most of the real-world BP that are
collected until now are not executable. This is because
of the complexity to reproduce their runtime environ-
ment. For this reasons we make the first demonstration
through an artificial BP. The original artificial BP is
shown on the top part of Figure 5. The anonymized
version is shown at the bottom of the figure. This
BP represents a library BP through which a user can
choose to rent or return a book.
Hence, the BP starts with a “Pick” activity (cf.
“PickRentOrReturn”) in which the user chooses the
desired action. In the case of book rental the user as-
1
http://www.soapui.org/
2
https://eclipse.org/bpel/
3
http://ode.apache.org/
"BPELanon"-ProtectBusinessProcessesontheCloud
245
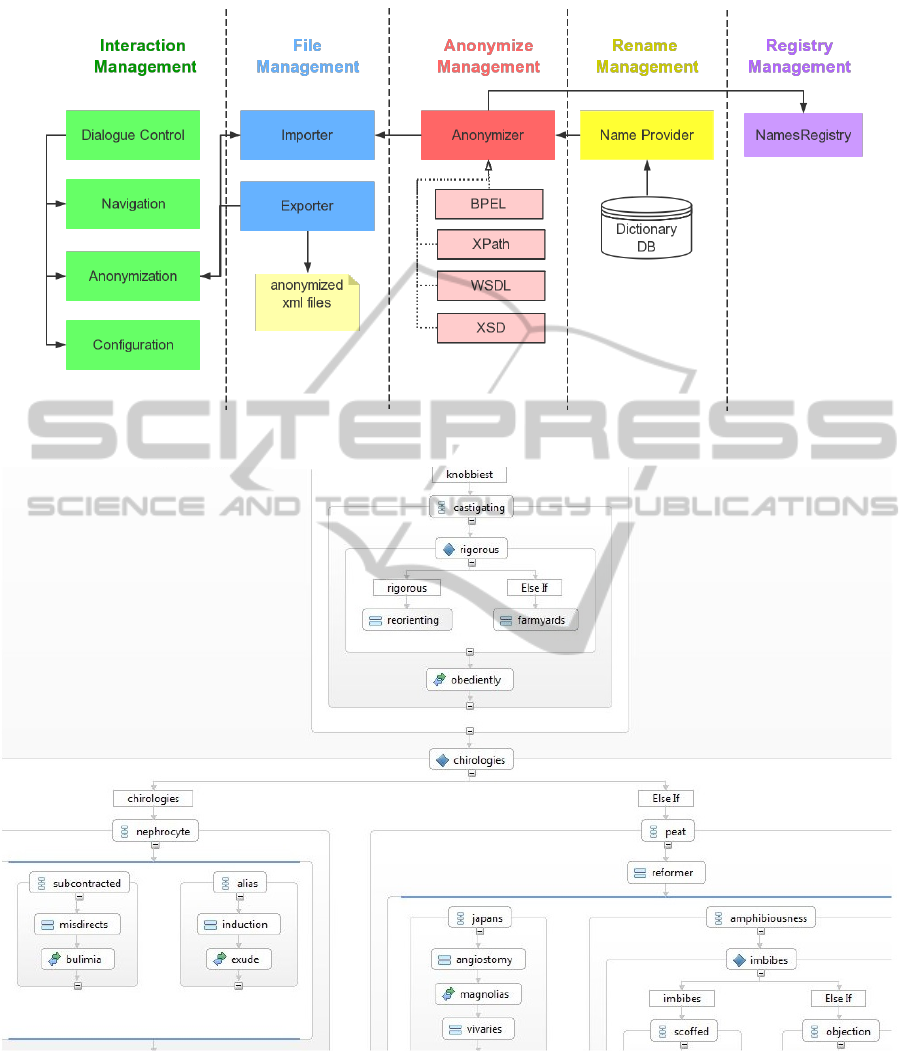
Figure 3: Architecture of “BPELanon” realization.
Figure 4: The anonymized real-world BPEL Businsess Process.
signs the ID of the book to rent and the quantity of
copies. The BP waits for some seconds. This is be-
cause the “InvokeSearchService” is asynchronously
invoked, and combined with a correlation activity. The
“Search Service” searches for the book and availabil-
ity of copies and proceeds to the “InvokeRentService”
for the book rental. In the case where the book does
not exist or there is not sufficient number of copies
an exception is thrown. The second flow of the BP
“returnBookProcess” represents the return of a book to
the library. For this the “ReturnService” is invoked (cf.
“InvokeReturnService”) and the message is returned to
CLOSER2015-5thInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
246
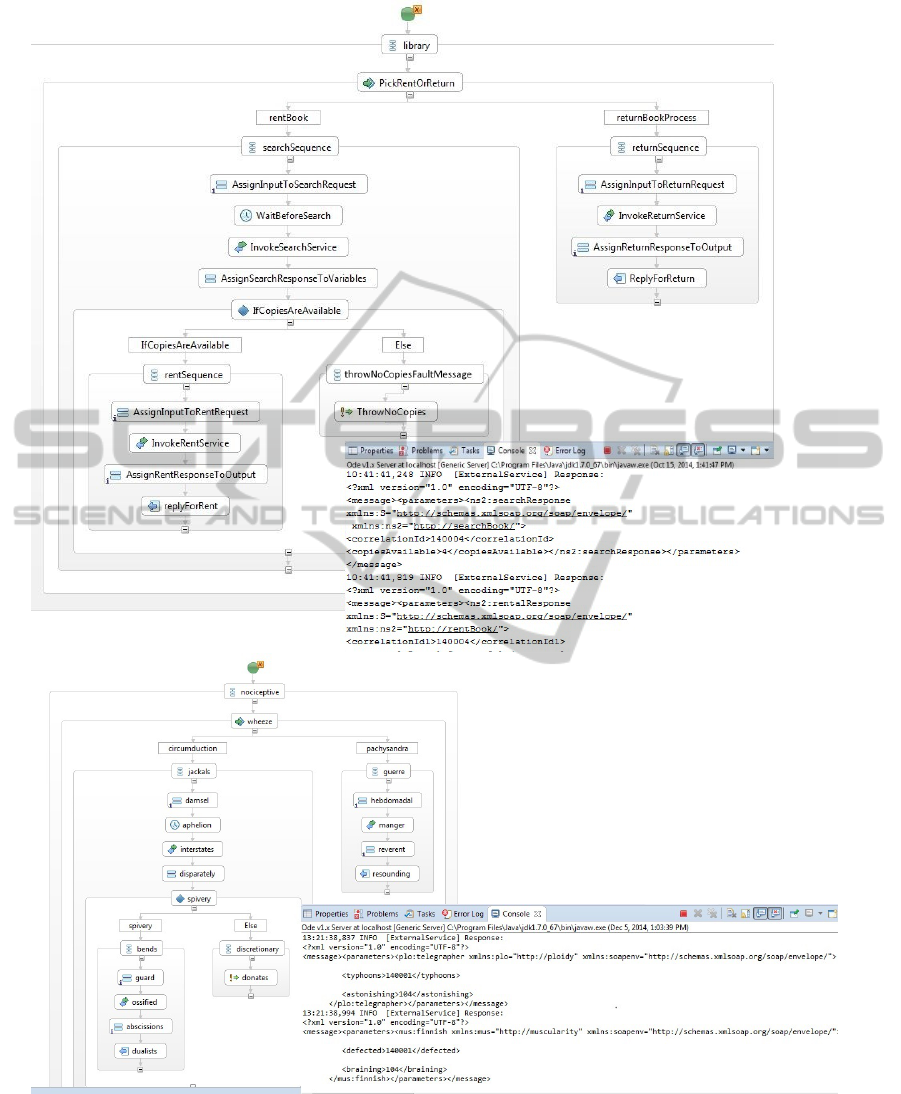
Figure 5: The original and anonymized BPEL Business Process with their execution details.
the user. The full BP package contains the BPEL file,
XSD and WSDL files as shown in Figure 6. There are
also XPath expressions used in many cases. One ex-
ample is the “IfCopiesAreAvailable” statement, where
the number of copies is compared to 0. The window
at the bottom of the BP shows an execution run where
a book rental is chosen.
Moving to the anonymized version of the BP at
the bottom part of Figure 5 we can see the scrambled
names [R2:NO SENSITIVE INFO] of the various ele-
"BPELanon"-ProtectBusinessProcessesontheCloud
247
Figure 6: The structure of artifacts of the artificial BPEL BP.
ments. These correspond to the “Free Elements” group
as discussed in Section 2.2.
As seen the names are human-readable
[R12:HUMAN READABLE NAMES] and they are
completely independent of the originals so reverse
engineering is prevented [R10:PREVENT REVERSE
ENGINEERING]. The anonymization of the other two
groups (“Externally Bounded Group” and “Internally
Bounded Group”) are basically shown through the
executability of the BP. Namely, if they are not
anonymized consistently the BP cannot be executed.
As seen in Figure 5 the structural information
of the BP and its executability (cf. console to the
bottom right corner) are preserved. Concerning exe-
cutability the user still has the option to pick which
BP flow to execute, input some data, and get a re-
sponse. The timer is also not changed, so the tim-
ing behavior [R9:KEEP TIMING] is maintained as
the rest of the activities are executed right away in
both the original and the anonymized BP. The fact
that the BP is executable proves that the files are
consistently anonymized and that conflicts between
the names in the original and anonymized files were
avoided [R11:AVOID CONFLICTS]. The anonymiza-
tion of namespaces (cf. xmlns:plo=“http://ploidy” in
Figure 5) apply to “Externally Bounded Group” as
they need to be applied consistently to all types of
files (i.e. BPEL, XSD, WSDL). The anonymization
of the name of the element in a complex type in XSD
file corresponds to the “Internally Bounded Group”
(cf.
<
defected
>
and
<
braining
>
elements in Fig-
ure 5). Finally, as we show in the console the back-
links in the namespaces are also anonymized [R3:NO
NAMESPACES INFO],[R4:NO BACKLINK INFO]
and [R5:NO XPATH INFO].
As the example shown in Figures 5 has simple
structure, we also validate our implementation with a
real-world BP shown in Figure 4. The BP is conducted
in the scope of a research project and was originally a
scientific workflow. The real-world BP are confidential
and thus it cannot be shown in original format. For
this reason we only provide the anonymized version
of the model. Figure 4 shows a selected zoomed-out
representative part of the model to demonstrate the
anonymization. Despite the structural complexity of
the BP it is also anonymized consistently. In the case of
“Else if” elements, the name has been also anonymized,
but the BPEL designer chooses to show by default the
“Else if” keyword to indicate the alternative path.
In order to check the algorithm’s performance we
ran our experiments on a notebook equipped with Intel
Core i7-3520M CPU and 16GB RAM. The machine
is running on Windows 7. As we discussed, we re-
alized the algorithm on a Java environment. For the
experiments we have used a set of 24 real-world BP
that were conducted in the scope of research projects.
Anonymization for each model was executed three
times, and the corresponding timings were collected.
Figure 7 shows how the algorithm performed for
the anonymization of the models. The vertical axis
shows the corresponding average execution times of
the anonymization runs. The horizontal axis shows the
total of XML elements of the BPEL BP artifacts and
was calculated as defined by Equation 1.
∑
{XMLElements}
e =
(
∑
i∈{BPEL}
XMLelement(i) ∈ BPEL) ∀ BPEL f ile +
(
∑
i∈{BPEL}
XMLelement(i) ∈ BPEL) ∀ BPEL f ile +
(
∑
k∈{WSDL}
XMLelement(k) ∈ W SDL) ∀W SDL f ile +
(
∑
l∈{XSD}
XMLelement(l) ∈ X SD) ∀ XSD f ile +
∑
j∈{DD}
XMLelement( j) ∈ DeploymentDescriptor
(1)
As seen in Figure 7 more than half of the models
(14) have up to 1000 XML elements while the rest span
from the values 1000 - 5000 XML elements. Concern-
ing the execution times we can see that the algorithm
Figure 7: Performance of “BPELanon”.
CLOSER2015-5thInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
248

performs in a linear
O(n)
complexity where
n
is the
total number of XML elements of the BP. For lower
times we can see more points on the execution time
trendline. This shows that the execution time is highly
related to the number of XML elements. As the BP get
more complicated we can see that the points have some
distance from the execution trendline. This indicates
that the XML elements are not the only factor affecting
the execution times. We suspect that the structure of
the BP, the total number of files to access, and the total
number of the applied replacements also play a role
to the performance. However, this assumption needs
more data and was left for future work.
6 RELATED WORK
Cloud computing has introduced even more privacy
issues, prompting researchers and companies to fo-
cus and propose ways to tackle these issues. Some
of these issues have been resolved through the use of
anonymization of data, Web Services or BP. (Sedayao,
2012) discuss data anonymization in Cloud environ-
ments and state that “data anonymization can ease
some security concerns, allowing for simpler demil-
itarized zone and security provisioning and enabling
more secure cloud computing”. (Zhang et al., 2014)
deal with the challenge of guaranteeing privacy on data
shared in public Cloud infrastructures. They have a fo-
cus on data analysis and propose a privacy-preserving
framework based on MapReduce
4
on Cloud. Most of
the approached we were able to find discuss about data
anonymization and since the BP deal also with data,
they can be seen as complementary to our approach.
In the field of Business Process Management we
were not able to find any other approach that describes
a distinct method to anonymize BP expressed in BPEL
language. Nevertheless, anonymized BP are already
used in existing projects. For example in (Kunze
et al., 2011) anonymized models are used in a large
public collection of BP, but the method followed to
anonymize the BP is not discussed, and the BP in this
collection are not in an executable format. Bentounsi
et al. (Bentounsi et al., 2012) propose a method to
publish BP on the Cloud by maintaining privacy. How-
ever, this approach is based on fragmenting the BP
and sharing some parts of it. The sensitive data of the
client are anonymized but the context of the fragment
is maintained. Adopting this approach would not serve
our goal, since we want to encourage the sharing of
the complete BP while completely hiding any business
information.
4
http://research.google.com/archive/mapreduce.html
Towards the realization of our method the tools
XMLAnonymizer(XMLanonymizer, 2010) and XM-
LAnonymizerBean(SAPTechnical.COM, 2007) were
found. XMLAnonymizer is a primary approach
to anonymization that focuses on changing the at-
tribute value of the XML file ([R4:NO BACKLINK
INFO] partially covered). The XMLAnonymizerBean
anonymizes elements and attributes by removing the
namespaces of an XML file ([R3:NO NAMESPACES
INFO] partially covered). Overall, these utilities par-
tially satisfy the requirements of “BPELanon”. The
“BPELanon” method is a more complex approach
since it deals with all the requirements and challenges
described in section 2.2.
7 CONCLUSION
In this paper we have proposed a method
(“BPELanon”) for the anonymization of BPEL
BP, that can be valuable when sharing BP on the
Cloud, where privacy of personal data, and compet-
itive assets are an open issue. The anonymization
of a BPEL BP can be complex due to the numerous
artifacts that comprise the BP, and the dependencies
that exist among these files. For anonymization of
a BP one needs to know the critical elements that
need anonymization, and the dependencies between
the participating artifacts, in order to track down
the sequences of changes that need to be applied.
We validated both the method and the tool through
case studies of an artificial BP and a real-world BP.
We evaluated the method’s performance through 24
real-world BP conducted in the scope of research
projects.
In future work we will investigate what is the
impact of anonymization to the BPEL BP life-cycle
and the ways that data and data dependent decisions
are influenced by anonymization. For the complete
anonymization of a BP we need to combine it or im-
plement also methodologies for Web Service and Data
anonymization. It is then essential that the first release
of the complete “BPELanon” will then be distributed
to companies for evaluation and usage on public Cloud
environments.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is funded by BenchFlow project (DACH
Grant Nr. 200021E-145062/1). The authors would
like to thank B. V. Tahil and N. Siddam for their con-
tribution towards the realization.
"BPELanon"-ProtectBusinessProcessesontheCloud
249

REFERENCES
Accorsi, R. (2011). Business process as a service: Chances
for remote auditing. 35th IEEE COMPSACW, pages
398–403.
Amziani, M., Melliti, T., and Tata, S. (2012). A generic
framework for service-based business process elastic-
ity in the cloud. BPM’12, pages 194–199, Berlin,
Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Anstett, T., Leymann, F., Mietzner, R., and Strauch, S.
(2009). Towards bpel in the cloud: Exploiting dif-
ferent delivery models for the execution of business
processes. ICWS’09, pages 670–677. IEEE Computer
Society.
Apache Software Foundation (2013). Creating a process.
http://ode.apache.org/creating-a-process.html.
Bentounsi, M., Benbernou, S., Deme, C. S., and Atallah,
M. J. (2012). Anonyfrag: An anonymization-based
approach for privacy-preserving bpaas. Cloud-I ’12,
pages 9:1–9:8, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Chow, R., Golle, P., Jakobsson, M., Shi, E., Staddon, J., Ma-
suoka, R., and Molina, J. (2009). Controlling data in
the cloud: Outsourcing computation without outsourc-
ing control. CCSW ’09, pages 85–90, New York, NY,
USA. ACM.
Doelitzscher, F., Reich, C., and Sulistio, A. (2010). De-
signing cloud services adhering to government privacy
laws. CIT ’10, pages 930–935.
Federal Ministry of Justice (1990). German Federal Data
Protection Law.
Hahn, M., S
´
aez, S. G., Andrikopoulos, V., Karastoyanova,
D., and Leymann, F. (2014). SCE
MT
: A Multi-tenant
Service Composition Engine. SOCA’14, pages 89–96.
IEEE Computer Society.
Jansen, W. (2011). Cloud hooks: Security and privacy issues
in cloud computing. HICSS ’11, pages 1–10.
Ko, S. Y., Jeon, K., and Morales, R. (2011). The hybrex
model for confidentiality and privacy in cloud com-
puting. HotCloud’11, pages 8–8, Berkeley, CA, USA.
USENIX Association.
Kunze, M., Luebbe, A., Weidlich, M., and Weske, M. (2011).
Towards understanding process modeling – the case
of the bpm academic initiative. volume 95 of BPMN
2011, pages 44–58. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
RightScale (2014). 2014 state of the cloud report from
rightscale. http://www.rightscale.com/lp/2014-state-of-
the-cloud-report.
SAPTechnical.COM (2007). Xml anonymizer bean in
communication channel to remove namespace pre-
fix in xml payload. http://www.saptechnical.com/
Tutorials/XI/XMLPayload/Index.htm.
Sedayao, J. (2012). Enhancing cloud security using data
anonymization. Intel IT, IT@ Intel White Paper. IT
Best Practices, Cloud Computing and Information Se-
curity.
Skouradaki, M., Roller, D., Pautasso, C., and Leymann, F.
(2014). BPELanon: Anonymizing BPEL processes.
ZEUS ’14, pages 9–15.
Strauch, S., Breitenb
¨
ucher, U., Kopp, O., Leymann, F., and
Unger, T. (2012). Cloud Data Patterns for Confiden-
tiality. CLOSER ’12, pages 387–394. SciTePress.
Wang, M., Bandara, K. Y., and Pahl, C. (2010). Process
as a service. IEEE SCC ’10, pages 578–585. IEEE
Computer Society.
WinEdt (2000). WinEdt Dictionaries. http://
www.winedt.org/Dict/.
XMLanonymizer (2010). XMLanonymizer - utility
to anonymize data of an xml file. https://code.
google.com/p/xmlanonymizer/.
Zhang, X., Liu, C., Nepal, S., Yang, C., and Chen, J. (2014).
Privacy preservation over big data in cloud systems.
Security, Privacy and Trust in Cloud Systems, pages
239–257. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
CLOSER2015-5thInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
250
