
Requirements for Relaxation Coaching
A Formalization of the Fogg Behavior Model
Rogier M. van Eijk
Department of Information and Computing Sciences, Utrecht University, Utrecht, the Netherlands
Keywords:
Relaxation Training, Persuasive Design, Coaching Systems.
Abstract:
Relaxation training consists of doing regular (e.g., daily) relaxation exercises over a longer period of time
(e.g., months). Adherence to relaxation training is for many people difficult because of time constraints, social
obligations, forgetting to practice and so on. This is a pity because relaxation training can act as a natural
antidote to health-related effects of excessive stress like poor sleep. In this paper, we present a formal model
of relaxation coaching that is rooted in the theory of persuasive design. This model supports the development
of coaching systems that can improve people’s adherence to relaxation training with its associated health
benefits.
1 THE NEED FOR RELAXATION
Ben is a fifty year old teacher of mathematics at a
secondary school. He suffers from a lot of stress in
his life. Each day he has deadlines that he cannot
finish and so he spends most of his evenings marking
assignments and exams. When lying in bed he feels
wide awake, worrying about tomorrow and unable to
fall asleep. When he gets up in the mornings he feels
exhausted.
In today’s society, many people have problems
related to excessive stress, like poor sleep (American
Psychological Association, 2014). Excessive stress
and poor sleep have negative effects on people’s
health and well-being (Everly Jr. and Lating, 2013).
Excessive stress is known to accelerate the aging pro-
cess (Liu and Mori, 1999). Poor sleep is a prevalent
problem for the elderly (Kamel and Gammack, 2006).
Ben visits his general practitioner who prescribes
him relaxation training. In eight weekly sessions
with a therapist, Ben practices relaxation and starts
to feel better. He finds himself spending less time
lying awake in bed and he feels more refreshed in the
mornings.
Relaxation training is a mind-body intervention
that counteracts the harmful effects of stress (Dusek
and Benson, 2009). It has been shown helpful for
aging people (Galvin et al., 2006; Glei et al., 2012).
Relaxation training is an integral part of insomnia
therapy (Morin and Espie, 2004) and has been shown
helpful for elder people with poor sleep (Friedman
et al., 1989; Sun et al., 2013).
After the eighth and last training session, Ben
receives from his therapist a transcript of the relax-
ation exercise to practice at home on a regular basis.
Although Ben is motivated the first couple of days,
he starts to skip doing the exercise more and more
and eventually stops practicing altogether. A few
weeks later he sleeps as badly and feels as stressed
as before.
Traditional relaxation training is provided through
individual or group sessions supervised by a therapist
(Everly Jr. and Lating, 2013). Usually, these sessions
are supplemented with home-practice assignments
(Bernstein et al., 2000). Adherence to relaxation
training is difficult (Taylor et al., 1983; Jacob et al.,
1984) due to for instance time constraints, social
obligations and simply forgetting to practice (Mur-
doch, 2000).
Ben installs a mobile coaching application. The
system assists Ben in understanding the workings
and effects of the relaxation exercises, modifying
exercises to his specific needs and circumstances and
in actually performing the exercises. With the use of
the coaching system Ben starts to practice relaxation
on a regular basis at home. He regains the benefits
from his improved relaxation skills, like less stress
and better sleep.
31
van Eijk R..
Requirements for Relaxation Coaching - A Formalization of the Fogg Behavior Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0005427600310036
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AgeingWell-
2015), pages 31-36
ISBN: 978-989-758-102-1
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Mobile coaching systems have the potential to im-
prove therapy adherence by providing additional sup-
port (Klein et al., 2013). This holds also for insomnia
therapy (Espie et al., 2013). The elderly form a di-
verse group with a variety of characteristics (Gregor
et al., 2002), which requires the tailoring of support
to specific needs and circumstances .
In this paper, we address the problem of develop-
ing coaching systems to improve adherence to relax-
ation training by providing tailored support. The main
contribution of the paper is the development of the ba-
sic requirements for relaxation coaching in the form
of a formal model that is rooted in the theory of per-
suasive design (Section 3). In Section 2 we provide
background on relaxation training and persuasive de-
sign. In section 4 we provide conclusions and outlines
for further research.
2 RELAXATION & PERSUASION
The stress response is an activation of the sympathetic
nervous system which due to the mediation of stress-
related hormones like cortisol and epinephrine leads
to physiological phenomena like an increase of oxy-
gen consumption, blood pressure and heart rate. In
this way, the body is prepared for taking action. Ex-
cessive invocation of the stress response can lead to
many kinds of health issues and diseases (Everly Jr.
and Lating, 2013).
The relaxation response is the exact opposite of
the stress response (Benson, 1993): the sympathetic
nervous system is de-activiated leading to among oth-
ers a decrease in oxygen consumption, blood pres-
sure and heart rate. In this manner, the body works
towards rest and recovery. The relaxation response
can act as a natural antidote to the stress response,
undoing (parts of) its harmful effects. Whereas the
stress response occurs involuntary and automatically,
the relaxation response needs to be consciously in-
voked and requires repeated practice in the form of
relaxation exercises. Many types of relaxation exer-
cises exist. Prominent types are (mindfulness) medi-
tation, progressive muscle relaxation and yoga.
Building new behavior like doing relaxation ex-
ercises on a regular basis at home can be supported
by technology (Oinas-Kukkonen, 2012). Such sup-
porting technology is usually referred to as persuasive
technology (Fogg, 2003). Persuasive technology aims
at changing people’s behavior and / or attitudes in
a non-forceful way without using non-ethical means
such as deception. The design of persuasive technol-
ogy is not an easy task and attempts are easy to fail.
Different models of human behavior are used
in the development of persuasive technology (Mohr
et al., 2014). Relaxation exercises are a relatively sim-
ple and well-defined type of behavior. To understand
the persuasive aspects of such behavior, the Fogg be-
havior model can be used (Mohr et al., 2014). Ac-
cording to the Fogg behavior model (Fogg, 2009), for
particular behavior to occur three factors have to come
together: A person should (i) be motivated to do the
behavior, (ii) have the ability to perform the behavior
and (iii) the behavior should be triggered. If one of (i),
(ii) and (iii) is not met, the behavior will not occur.
3 COACHING ALGORITHM
In his paper, Fogg provides a qualitative description
of his behavior model (Fogg, 2009). However, for a
coaching system to support behavior change and be
able to reason about the different components of be-
havior we need a (simple) formal model. This model
is presented in Table 1.
Motivation. Fogg defines three dimensions of mo-
tivation: ‘pleasure and pain’, ‘hope and fear’ and ‘so-
cial acceptance and rejection’. We will consider each
of these in the light of relaxation training.
First, a person’s motivation depends on the emo-
tions and sensations of pleasure and pain that he or
she experiences in the here and now. In the context of
relaxation training this dimension can be operational-
ized as the state of relaxation and/or stress a person
experiences and the immediate effects exercises have
on this state.
The relaxation effects of exercises depend on the
type of exercise and the type of person. Some breath-
ing exercises have almost immediate calming effects
like for instance ‘ocean breathing’. This is a tech-
nique from yoga in which the practitioner slows down
his or her breath by a muscle contraction in the throat.
A few minutes of ocean breathing in bed can induce
a profound state of relaxation. Additionally, different
people prefer different types of relaxation exercises.
A way to measure relaxation is in terms of so-
called subjective units of relaxation (SURS) (Everly Jr.
and Lating, 2013). On this scale, a score of 10 corre-
sponds to a dreamlike state of profound relaxation,
while a score of 5 corresponds to the state of an av-
erage person on an average day. A score of 1 corre-
sponds to a panic attack (Everly Jr. and Lating, 2013).
For instance, if a person feels very stressed (e.g., has a
SURS of 3) and wants to feel better than average (e.g.,
SURS of 6) and ocean breathing results in an increase
of 1 unit per 5 minutes practicing, then the person is
motivated to do up to 15 minutes of ocean breathing.
ICT4AgeingWell2015-InternationalConferenceonInformationandCommunicationTechnologiesforAgeingWelland
e-Health
32
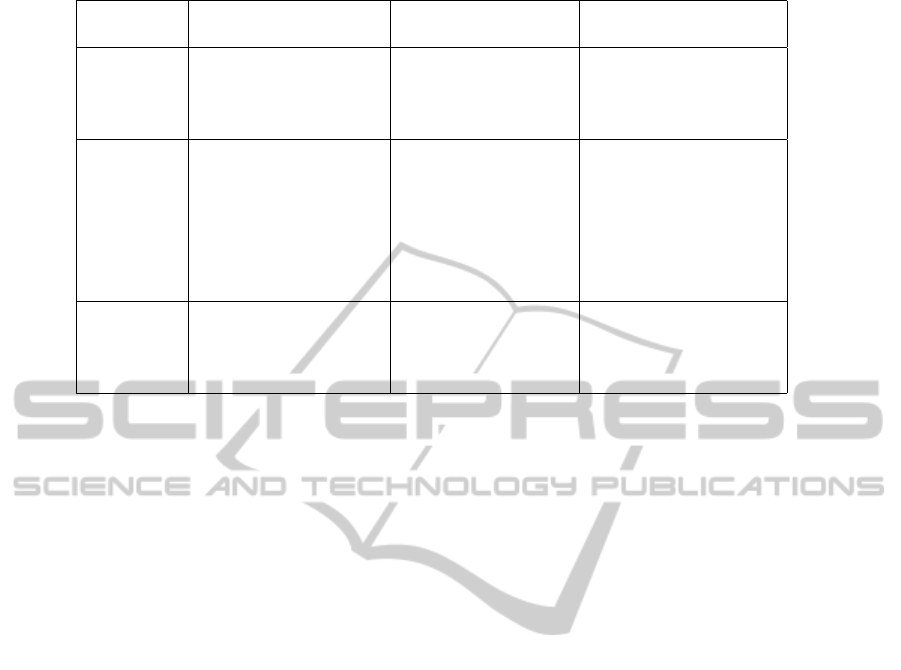
Table 1: Components of Relaxation Coaching
Fogg behavior model Relaxation training Units
Motivation Pleasure Relaxation state SURS
Hope Sleep quality sleep hours / bed hours
Social acceptance Social status social levels
Ability Time Duration minutes
Money Price euro’s
Non-routine Skill progression skill levels
Physical effort Energy kJ / hour · kg
Brain-cycles Information words / minute
Social deviation Privacy deviation privacy levels
Triggering Spark Education motivation
Facilitator Modification ability
Signal Instruction performance levels
Secondly, ‘hope and fear’ constitutes the dimen-
sion of thoughts and feelings about future states of
being. In the context of relaxation training this can
be operationalized as the anticipated longer-term ef-
fects of relaxation training, like better sleep. In in-
somnia therapy, relaxation exercises are performed on
a regular basis (e.g., once or twice daily) for weeks or
months (Morin and Espie, 2004). Different measure-
ments of quality of sleep exist (Buysse et al., 1989), a
prominent one being ‘sleep efficiency’. This measure
amounts to the time a person has slept divided by the
total time the person has spent in bed. For instance,
if a person has practiced a daily progressive muscle
relaxation for three weeks, which led to an improve-
ment in sleep efficiency from 0.5 to 0.6, and he wants
to improve his sleep efficiency to 0.7 then he will be
motivated to practice the daily relaxation exercise for
another three weeks (assuming a linear relation be-
tween duration of practice and sleep efficiency).
Finally, ‘social acceptance and rejection’ concerns
the social dimension of motivation. We can opera-
tionalize it as social status, which is a combination of
education, profession, marital status and sex (Holling-
shead, 1975). In the context of relaxation training,
we can take this to be the combination of received
relaxation training (e.g., education in the form of a
completed 8-week mindfulness training, a 500 hour
yoga teacher training and so on) and provided relax-
ation training (e.g., 3 years experience as a profes-
sional yoga teacher). We can quantify this as a social
level between 1 and 10 (e.g., 1 denotes the level of a
beginner student and 10 denotes the level of an expert
teacher). For instance, a person who has practiced
mindfulness meditation for four years (e.g., level 4)
and wants to progress one level is motivated to do a
mindfulness teacher training program (e.g., yielding a
social status of level 5).
Ability. The ability to do a relaxation exercise de-
pends on the resources one has available to practice.
According to the Fogg behavior model, ability can
be decomposed into the availability of six different
resources: time, money, non-routine, physical effort,
brain cycles and social deviance.
We start with the time it takes to perform a behav-
ior. In the context of relaxation training, the ability
to do a relaxation exercise depends on the duration of
the exercise and the time one has available to practice.
For instance, if a person is able to spend 5 minutes of
practice and the practice consists of an exercise with
a duration of 3 minutes then the person has the ability
to do it. On the other hand, if for the same person un-
der the same circumstances the practice would consist
of a 7 minute exercise, the person would be unable to
do it.
Secondly, we consider ‘money’: the monetary
costs that are associated with the behavior. Different
exercises have different costs associated with them.
There are many relaxation exercises freely available
on the Internet. Other exercises are described in books
or on DVD’s that the practitioner must buy to get ac-
cess. Yet other exercises are learned under supervi-
sion of a relaxation therapist, which are even more
expensive. So for instance, if a person is not able to
spend any money on a relaxation practice, then he will
be able to do freely available exercises, but not ones
that are supervised by a therapist.
Let us consider ‘non-routine’. A routine behav-
ior is a behavior that people are used to do, possi-
RequirementsforRelaxationCoaching-AFormalizationoftheFoggBehaviorModel
33

bly over and over again. A non-routine behavior on
the other hand, is a behavior that people are not used
to do and maybe have never done before. We can
operationalize the resource ‘non-routine’ in terms of
skill levels, quantified by natural numbers between 0
and max skill. Relaxation training programs involve a
progression through skill levels. For instance, differ-
ent yoga techniques are assigned different skill lev-
els leading practitioners to progress from one level
to a next (Iyengar, 1966). So for instance, an abso-
lute beginner (level 1) who has no ability to progress
yet has the ability to do a yoga posture like mountain
pose (level 1) but is unable to do a headstand (level 4)
(Iyengar, 1966).
Next, we consider the resource ‘physical ef-
fort’. Different relaxation exercises require dif-
ferent amounts of physical effort. For instance,
mindfulness-based stress reduction contains both
seated and walking meditation exercises (Kabat-Zinn,
1990). A walking exercise requires more physi-
cal effort than a sitting exercise (Montoye, 2008).
The resource ‘physical effort’ can be operationalized
in terms of energy expenditure, quantified by natu-
ral numbers between 0 and max
energy. Usually,
this is expressed in kilojoules per hour per kilogram
bodyweight, although other alternative measures ex-
ist (Montoye, 2008). Walking takes 3, 5 times more
energy than sitting (i.e., 3, 5 and 1, 0 kJ · h
−1
· kg
−1
,
respectively). So for instance, a person who is able
to spend 2, 0 kJ · h
−1
· kg
−1
has with respect to the re-
source ‘physical effort’ the ability to practice a sitting
meditation, but is not able to do a walking practice.
Next comes the resource ‘brain cycles’. Accord-
ing to Fogg, this concerns the thinking process that
is involved in performing the behavior. Some relax-
ation exercises require only a few instructions to per-
form. An example is a breath awareness exercise in
which a practitioner is simply asked to concentrate on
his or her breath and when attention waivers to notice
the source of distraction and then bring the attention
back to the breath (Kabat-Zinn, 1990). Other relax-
ation exercises involve many more instructions, like
for instance progressive muscle relaxation in which
the practitioner is required to tense and release spe-
cific muscles in specific ways in specific orderings
(Bernstein et al., 2000). We operationalize the re-
source ‘brain cycles’ as the information to be pro-
cessed in order to perform the behavior. This can op-
erationalized as information processing speed (Kail
and Salthouse, 1994). In the context of relaxation
training, we can quantify this as the number of words
of the instruction per minute. For instance, a person
who is not able to process more than 30 words per
minute is able to do a breath awareness exercise with
an instruction of 20 words per minute, while being
unable to do a progressive muscle relaxation exercise
involving an instruction of 60 words per minute.
Finally, we consider the resource ‘social de-
viance’. According to Fogg this amounts to going
against the norms of a social context. Some relaxation
exercises require more privacy than others. For in-
stance, progressive muscle relaxation should be done
in a quiet environment with no distractions. It re-
quires the practitioner to sit down and close his or
her eyes. Some informal mindfulness exercises on the
other hand, require the practitioner just to be aware
of sensations and thoughts and should be done in the
midst of hectic everyday life. We operationalize ‘so-
cial deviance’ as the difference between achieved pri-
vacy and desired privacy (Altman, 1976). It can be
quantified in terms of levels of privacy, ranging from 0
to max privacy. Achieved privacy corresponds to the
level of privacy of the actual context, while desired
privacy corresponds to the level of privacy that is the-
oretically required for the exercise. So for instance, if
a person is in a business environment (e.g., achieved
privacy level 1) and he is able to deviate one level of
privacy, he is able to do an informal mindfulness ex-
ercise (e.g., desired privacy level 2), but not able to do
a progressive muscle relaxation (e.g., desired privacy
level 5).
Triggering. According to Fogg, a trigger is some-
thing that tells people to do a behavior. There are three
types of triggers: sparks, facilitators and signals.
A spark is used to increase a person’s motivation
for the behavior. We operationalize this as the ed-
ucation that comes with relaxation training, explain-
ing among others the rationale, workings and effects
of the exercises. Manuals for relaxation training like
the manuals of mindfulness based stress reduction
(Kabat-Zinn, 1990) and progressive muscle relaxation
(Bernstein et al., 2000) contain a lot of educational
material. For instance, education on the nature of
stress (e.g., the harmful effects of the stress response)
and relaxation (e.g., the need to repeatedly invoke the
relaxation response as an antidote to excessive stress)
and their effects on sleep (e.g., it is easier to sleep
with a calm mind than an overactive one) can increase
a person’s motivation for doing relaxation exercises.
Education can be measured in terms of the effects it
has on a person’s motivation. For instance, by in-
forming a person about the effects of having done a
daily progressive muscle relaxation exercise for three
weeks (i.e., an improvement in sleep efficiency from
0.5 to 0.6), the person becomes motivated to do the
practice for another three weeks.
A facilitator is used to increase a person’s ability
ICT4AgeingWell2015-InternationalConferenceonInformationandCommunicationTechnologiesforAgeingWelland
e-Health
34

to do the behavior. We operationalize this as the mod-
ification of exercises to a person’s needs and circum-
stances. For instance, the tailoring of exercises to the
individual is an important aspect of yoga (Desikachar,
2010). Modification can be measured in terms of its
effects on the ability of a person to do the exercise.
For instance, if for a meditation exercise the instruc-
tion to walk (which requires 3, 5 kJ · h
−1
· kg
−1
) is
modified to an instruction to stay seated (requiring
1, 0 kJ · h
−1
· kg
−1
), then a person who can spend 1, 0
kJ · h
−1
· kg
−1
gains the ability to do the exercise.
Finally, a signal is used to let a person actually
perform the behavior. We operationalize it as the in-
struction that is needed to perform the exercise. Ex-
ercise can have different instructions. For instance,
the instruction of an exercise can vary from just men-
tioning the name of the exercise (‘do 15 minutes of
body scan now’) to a detailed, step-by-step guidance
through the exercise (‘. . . now bring your attention
to your feet . . .’). Performance can be measured as
a number between 0 and max performance. For in-
stance, for a person who does not know the body scan
exercise, the instruction ‘do 15 minutes of body scan
now’ does not lead to the performance of the exer-
cise (e.g., performance level 0), while a step-by-step
guidance through the exercise results in an actual per-
formance of the exercise (e.g., level 1).
Algorithm. Finally, we take the described com-
ponents together in a basic algorithm of relaxation
coaching. Figure 1 depicts the pseudo code of the
algorithm.
The algorithm takes as input a relaxation train-
ing program trp, which is modeled as a list of exer-
cises. In each round of the algorithm, the next exer-
cise of the list (i.e., head(trp)) is selected. The coach
assesses the person’s motivation with respect to this
exercise and while the person is not motivated to do
the exercise, the coach intervenes through education.
After that an assessment of the person’s abilities is
made and the coach modifies the exercise to fit it to
the person’s circumstances. Finally, an assessment
of the performance is made: While the exercise has
not been performed, the coach provides instruction
to do the exercise. In the last step of the algorithm,
the performed exercise is removed from the training
program, yielding tail(trp) and the new exercise to
be performed is selected. The algorithm terminates
when there are no more exercises to be done (that is,
e equals NIL).
Related Work. Stress@work is a system for stress
coaching that monitors people’s stress at work and
gives recommendations how to handle it (Bakker
COACH(rtp:relaxation training program)
e:exercise;
m:motivation;
a:ability;
p:performance;
e=head(rtp);
WHILE e!=NIL do;
WHILE NOT motivated(m,e) do
m=educate(m,e);
END-WHILE
WHILE NOT able(a,e) do
a=modify(a,e);
END-WHILE
WHILE NOT performed(p,e) do
p=instruct(p,e);
END-WHILE
trp=tail(trp);
e=head(trp);
END-WHILE
Figure 1: The coaching algorithm.
et al., 2012). The system encompasses an algorithm
for stress intervention that involves the recommenda-
tion of relaxation exercises. This model is not clearly
rooted in the theory of persuasive design.
A model of exercise support in the context of in-
somnia therapy is provided by Beun and colleagues
(Beun et al., 2014). This model identifies exercises
support as a cyclic process consisting of four stages
of exercise support: introduction, plan and commit,
task execution and evaluation. No further details on
the application to relaxation exercises are provided.
4 CONCLUSIONS
We have developed basic requirements for relaxation
coaching in the form of a formal model that is rooted
in the theory of persuasive design.
The model is to be considered as a first step to be
further refined and extended with other operational-
izations and measures. To mention one example, the
resource ‘physical effort’ can be extended with a mea-
sure for physical impairments (e.g., incapability to
stand or walk, a shoulder injury and so on).
Next steps of the requirement engineering process
are the design, prototyping and evaluation of mobile
relaxation coaching systems, which should provide
further feedback to improve the formal model.
RequirementsforRelaxationCoaching-AFormalizationoftheFoggBehaviorModel
35

REFERENCES
Altman, I. (1976). Privacy: A conceptual analysis. Envi-
ronment and behavior, 8(1):7–29.
American Psychological Association (2014). Stress in
America: Are teens adopting adults stress habits?
American Psychological Association, Washington,
DC.
Bakker, J., Holenderski, L., Kocielnik, R., Pechenizkiy, M.,
and Sidorova, N. (2012). Stress@work: from mea-
suring stress to its understanding, prediction and han-
dling with personalized coaching. In Proceedings of
the 2nd ACM SIGHIT International Health Informat-
ics Symposium, IHI ’12, pages 673–678, New York,
NY, USA. ACM.
Benson, H. (1993). The relaxation response. In Goleman,
D. and Gurin, J., editors, Mind Body Medicine: How
to Use Your Mind for Better Health, pages 125–149.
Consumers Reports Book, New York, NY.
Bernstein, D., Borkovec, T., and Hazlett-Stevens, H. (2000).
New Directions in Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Training: a Guidebook for Helping Professionals.
Praeger Publishers, Westport, CT.
Beun, R. J., Griffioen-Both, F., Ahn, R., Fitrianie, S., and
Lancee, J. (2014). Modeling interaction in automated
e-coaching: A case from insomnia therapy. In COG-
NITIVE 2014, The Sixth International Conference on
Advanced Cognitive Technologies and Applications,
pages 1–4. IARIA.
Buysse, D., Reynolds III, C., Monk, T., Berman, S., and
Kupfer, D. (1989). The pittsburgh sleep quality in-
dex: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and
research. Psychiatry Research, 28(2):193 – 213.
Desikachar, T. (2010). The heart of yoga: Developing
a personal practice. Inner Traditions International,
Rochester, Vermont.
Dusek, J. and Benson, H. (2009). Mind-body medicine: A
model of the comparative clinical impact of the acute
stress and relaxation response. Minnesota Medicine,
92(5):47–50.
Espie, C., Hames, P., and McKinstry, B. (2013). Use of
the internet and mobile media for delivery of cognitive
behavioral insomnia therapy. Sleep Medicine Clinics,
8(3):407–419.
Everly Jr., G. and Lating, J. (2013). A Clinical guide to
the treatment of the human stress response. Springer,
New York.
Fogg, B. (2003). Persuasive Technology. Morgan Kauf-
mann, San Francisco.
Fogg, B. (2009). A behavior model for persuasive design.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on
Persuasive Technology, Persuasive ’09, pages 40:1–
40:7, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Friedman, L., Bliwise, D., Yesavage, J., and Salom, S.
(1989). A preliminary study comparing sleep restric-
tions and relaxation treatments for insomnia in older
adults. Journal of Gerontology, 46(1):1–8.
Galvin, J., Benson, H., Deckro, G., Fricchione, G., and
Dusek, J. (2006). The relaxation response: Reduc-
ing stress and improving cognition in healthy aging
adults. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Prac-
tice, 12:186–191.
Glei, D., Goldman, N., Lin, Y.-H., and Weinstein, M.
(2012). Relaxation practice and physiologic regula-
tion in a national sample of older taiwanese. The
Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine,
18(7):653–661.
Gregor, P., Newell, A. F., and Zajicek, M. (2002). Design-
ing for dynamic diversity: Interfaces for older people.
In Proceedings of the Fifth International ACM Con-
ference on Assistive Technologies, Assets ’02, pages
151–156, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Hollingshead, A. (1975). Four factor index of social status.
Technical report, Yale University, New Haven, CT.
Iyengar, B. (1966). Light on Yoga. Schocken Books Inc.,
New York, NY.
Jacob, R., Beidel, D., and Shapiro, A. (1984). The relax-
ation word of the day: A simple technique to measure
adherence to relaxation. Journal of Behavioral As-
sessment, 6(2):159–165.
Kabat-Zinn, J. (1990). Full Catastroph Living: Using the
Wisdom of Your Body and Mind to Face Stress, Pain
and Illness. Bantam Dell, New York, NY.
Kail, R. and Salthouse, T. (1994). Processing speed as
a mental capacity. Acta Psychologica, 86(2–3):199–
225.
Kamel, N. and Gammack, J. (2006). Insomnia in the el-
derly: Cause, approach, and treatment. The American
Journal of Medicine, 119:463–469.
Klein, M., Mogles, N., and Wissen, A. v. (2013). An intel-
ligent coaching system for therapy adherence. IEEE
Pervasive Computing, 12(3):22–30.
Liu, J. and Mori, A. (1999). Stress, aging, and brain oxida-
tive damage. Neurochemical Research, 24(11):1479–
1497.
Mohr, D., Schueller, S., Montague, E., Burns, M., and
Rashidi, P. (2014). The behavioral intervention tech-
nology model: An integrated conceptual and techno-
logical framework for ehealth and mhealth interven-
tions. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 16(6).
Montoye, H. (2008). Energy costs of exercise and sport.
In Nutrition in Sport, pages 53–72. Blackwell Science
Ltd, Oxford, UK.
Morin, C. and Espie, C. (2004). Insomnia: a Clinical Guide
to Assessment and Treatment. Springer, New York,
NY.
Murdoch, J. (2000). A technique for assessing adherence
to relaxation training instructions
´
. Psychological Re-
ports, 87:523–524.
Oinas-Kukkonen, H. (2012). A foundation for the study of
behavior change support systems. Personal and Ubiq-
uitous Computing, 17:1223–1235.
Sun, J., Kang, J., Wang, P., and Zeng, H. (2013). Self-
relaxation training can improve sleep quality and cog-
nitive functions in the older. Journal of Clinical Nurs-
ing, 22:1270–1280.
Taylor, C., Agras, W., J.A., S., and Allen, R. (1983). Ad-
herence to instructions to practice relaxation exer-
cises. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology,
51(6):952–953.
ICT4AgeingWell2015-InternationalConferenceonInformationandCommunicationTechnologiesforAgeingWelland
e-Health
36
