
DeLi2P
A User Centric, Scalable Demand Side Management Strategy for Smart Grids
Syed Muhammad Ali
1
, Mohammad Naveed
2
, Fahad Javed
3
, Naveed Arshad
2
and Jahangir Ikram
2
1
Department of Electrical Engineering, University of British Columbia, Okanagan BC, Canada
2
Syed Babar Ali School of Science and Engineering, Lahore University of Management Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan
3
Department of Computer Science GIFT University, Gujranwala, Pakistan
Keywords:
Smart Grids, Demand Side Management, Peak Reduction, Demand Elasticity.
Abstract:
Smart grids coulpled with effiicient demand side management (DSM) is an important step for greener cities
of the future. DSM has the potential to significantly improve smart grid operations by reducing the peak to
average ratio. Current DSM schemes are able to reduce peak load by as much as 30% which can translate to
significant cost savings and reduction in green house emissions. But for realistic deployment of DSM systems
in the grid there are two very important aspects which need to be considered: scalability and user acceptability.
Since the current DSM algorithms are required to control potentially hundreds of thousands of devices, they
have to be scalable and tractable for such myriad numbers. On the other hand DSM affects the life style of
the consumer and this should be as less disruptive as possible. The various DSM techniques proposed in the
literature attempt to first reduce the cost and then attempt to resolve one of the two aforementioned aspects.
The result is that the techniques are either scalable or are only considerate of the deadlines of the consumers.
An ideal system should cater to both of these aspects. Our system Deli2P is user centric and scalable thus
catering to both of these aspects. Essentially we provide to the consumer a deadline centric interface. The
deadlines solutions are generally not scalable. But instead of solving this problem as a scheduling for deadline
problem we transform the problem to a priority-based problem thus making it scalable for large number of
devices. Our results show that with this scheme we can reduce peak power by upto 30% but without violating
consumers‘ deadlines.
1 INTRODUCTION
The continuous increase in electricity demand and
the shrinking resources of energy has resulted in a
scarcity of electricity. In such a scenario conserv-
ing and optimally consuming the existing resources
has gained paramount importance. In fact energy
efficiency is being called as ‘the most important’
fuel for the future. One of the major ways for ef-
ficient energy management is demand side manage-
ment (DSM) (Gellings, 1985). Coupling DSM with
the future smart grids technologies therefore is being
seen as the major resource for the future smart grids
(Rahimi and Ipakchi, 2010). The goal of these future
DSM systems is to manage the domestic consumer’s
load for a more environmental and economically ef-
ficient energy generation scheduling. This is usually
achieved by offloading the electric consumption from
high cost timings to other timings when the electric-
ity price is low (Liu et al., 2014). This phenomenon
is commonly known as peak shaving.
However, for a DSM strategy to be viable for do-
mestic consumer it is imperative that this load move-
ment is acceptable to the consumers‘ schedules and
practical constraints. Historically it has been ob-
served that strategies which do not consider con-
sumers preferences as first class requirement fail to
deliver due to stiff resistance or non-cooperation from
the consumers. As Kim and Shcherbakova report on
the reasons for DSM failures, the consumer needs
to be involved in the DSM activities and her re-
quirements need to be understood and catered for
(Kim and Shcherbakova, 2011). To cater to the con-
sumers‘ needs there are two strategies used by the
DSM planners and researchers: Either consumer’s ex-
act requirements are captured by eliciting the deadline
within which the task must be achieved (Arif et al.,
2013), or the devices are assigned priorities and these
priorities are used for planning (Beal et al., 2012).
The difference in the two strategies on operational
148
Muhammad Ali S., Naveed M., Javed F., Arshad N. and Ikram J..
DeLi2P - A User Centric, Scalable Demand Side Management Strategy for Smart Grids.
DOI: 10.5220/0005437301480156
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems (SMARTGREENS-2015), pages 148-156
ISBN: 978-989-758-105-2
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

level may seem insignificant initially but from a com-
putational perspective the two strategies have signifi-
cant implication in the scalability of the system. The
preference based scheduling problem is a very com-
mon problem in operations research and computer
science. Various job scheduling tasks exist in real
world and researchers have analyzed this problem in
detail. Scheduling of loads constrained by prefer-
ences is very similar to job scheduling problem. How-
ever, this problem is classified as NP-complete prob-
lem and to-date no scalable algorithm has been pro-
posed to solve this problem. The implication of this
NP-complete classification is that a problem without
necessary transformations will be intractable for large
number of devices thus making it not suitable for large
number of devices. As the number of devices increase
the algorithm will take an exponentially more time for
computation.
On the other hand priority-based systems are able
to aggregate the devices into priority classes and the
planning decision is reduced from controlling hun-
dreds of devices under constraints to just control-
ling each priority class. Since the number of priority
classes is much smaller than number of devices, plan-
ning for this system is tractable. ColorPower is an ex-
ample of such a technique (Ranade and Beal, 2010).
This reduction in size makes the problem tractable for
a micro-grid or even city level scheduling.
However, priority classes are limiting in that dead-
lines for individual devices are not part of the schedul-
ing. This is problematic as this results in lower con-
sumer satisfaction as the needs of the consumer can
be violated. From the experience of Power7 of UK
we know that the consumers‘ life styles are dynamic
and such fixed measures are not very useful. To this
end, in this paper we propose a novel transformation
of deadlines to priority-based DeLi2P model.
Deli2P collects user deadlines from devices. The
modern electronic devices are fitted with timers to
stop or start a device at a specific time. Similar to
these timers in Deli2P consumer can select the time
at which she requires the device’s process to be com-
plete by putting in the“putoff” time on the device or
device plug interface. For example, if a consumer is
putting in dishes for washing then the consumer can
feed in 6 hours for the dishes to be washed and ready.
Deli2P transforms this deadline into a priority in
the following way. The controller gathers three im-
portant parameters of a particular device. These pa-
rameters include operational time of a device, dead-
line of the operation and the time available before
deadline, the “putoff”. Based on these parameters it
assigns priority to a device, which changes as time
available approaches the deadline of operation. For
example, a device with operational time of 2 hours has
a deadline of operation 6 hours from the time the re-
quest was made. Using this information our controller
computes the time available after every decision cycle
in our algorithm as will be explained later. Priority as-
signment will be done using a mathematical function
described in section 3 of the paper. With each de-
vice assigned a priority, based on the time available
for execution we can aggregate the priority demands
and schedule the device operation in the same way as
done by Ranade and Beal (Ranade and Beal, 2010). If
the device is not activated for operation in the current
level of priority then it moves to a higher level. With
higher priority level, the device has a higher chance of
getting the activation signal. Priority level transition
is done at equal time intervals based on time available
which in this case is six hours divided into time pe-
riods of three hours (where 6 is the deadline and 3 is
the number of flexible (Rehman et al., ) priority lev-
els). This process is continued till the device is either
operated or it is at the highest level where it is guar-
anteed execution.
When sufficient supply is available the system al-
lows all the devices to execute as soon as they submit
a demand to consume. As the demand grows above
the supply, the devices with the least priority are in-
structed to ”wait” for servicing based on a probabilis-
tic model. This ensures that the demand never sur-
passes the supply. For example, in the early hours of
the day when the demand is much less than supply
and all devices are given go ahead for execution. But
as the demand is about to cross the supply our algo-
rithm puts each device in one of the flexible priority
levels and let them change their state only when the
demand-supply situation gets better or the deadline is
close enough. Deli2P in this way is able to reduce
the peak demand of the day while satisfying the con-
sumer’s preferences.
The rest of the paper discusses the related work
in this area, our proposed solution, its model and fi-
nally a discussion on evaluation, conclusion and fu-
ture work.
1.1 Related Work
Demand side management (DSM) techniques usually
have one of the two goals: the first one is to reduce
the electricity cost and the second is to reduce the
peak load (Chai et al., 2014). A range of algorithms
attempt to reduce the cost of electricity for the con-
sumers. These include algorithms which incorporate
the time of use pricing in reducing the cost of electric-
ity of the consumer (Fan, 2011)(Lee and Lee, 2011),
and DSM systems which maximizes the benefit of
DeLi2P-AUserCentric,ScalableDemandSideManagementStrategyforSmartGrids
149

renewable energy sources for home consumer (Arif
et al., 2013)(Daoxin et al., 2012). For these systems
the goal is not overall supply-demand management
but rather it is to minimize the cost of electricity to
the consumer. However, this does not guarantee that
the demand is shaped according to the global or util-
ity’s goals. To achieve this specific goals direct con-
trol systems are proposed which aim at reducing the
peak load. The difference is that in the first category
the goal is cost reduction and peak load reduction is
implicit whereas in the second the peak load reduction
is the goal and cost savings due to better load profiles
are implicit.
The direct control algorithms thus control the con-
sumer devices remotely. However, shutting down end
user device is usually not very acceptable to the end
users. This has been studied and expounded by many
researchers (Kim and Shcherbakova, 2011). To cap-
ture the needs of the consumers there are two main
processes proposed in the literature.
One stream of research for such DSMs is to gather
the preferences or constraints of the consumers. That
is, for each device the system predicts or collects from
user the range within which the device can be sched-
uled. These constraint elicitation can be implicit as is
the case Du and Lu (Du and Lu, 2011) and Molderink
(Molderink et al., 2010) where forecasting and con-
sumer profiling using sensors in the user premises are
used to determine the constraints of the consumers. In
other cases such as those proposed by Kim and Poor
(Kim and Poor, 2011) and Arif and colleagues (Arif
et al., 2013), the constraints are explicitly provided by
the consumers through some interface. The authors
of the systems argue that since we have knowledge of
the consumer’s constraints and schedule the devices
accordingly, the DSM load management will be ac-
ceptable to the consumers.
However, as has been discussed by Molderink
(Molderink et al., 2010), Arif (Arif et al., 2013)
and Javed in AdOpt (Javed and Arshad, 2009), such
scheduling is NP-complete (Ullman, 1975). To date
there has been no polynomial time algorithm to solve
the NP-complete problems. The only way to solve
such problems is to enumerate all the possible com-
binations. But all combinations are exponential and
thus planning for hundreds of thousands of devices is
not possible. Use of artificial intelligence techniques
such as genetic algorithms and ant colony optimiza-
tion decrease the computation time but still take too
long for large scale system scheduling and are known
to be inaccurate.
The other stream is to allow the users to stipulate
priority classes to devices or join the device to a con-
tractual obligation group. ColorPower1 and Color-
Power 2 allow the consumers to assign priorities to
devices (Ranade and Beal, 2010; Beal et al., 2012).
The system then manages the probability of execution
for each priority class such that the demand shaping
goals are reached while maintaining that the distri-
bution is fair and according to consumer’s priorities.
Kim and Poor also proposed similar system however
their grading of the devices was not as versatile(Kim
and Poor, 2011). Pennywise on the other hand allow
users to sign contracts with the utility. Since these
contracts are standardized the utility can bunch to-
gether devices under similar contracts for computa-
tion. Escriva and colleagues also used such contracts
for their proposed DSM strategy (Escriv-Escriv et al.,
2010).
Since in these systems there is a natural way to
combine the devices into consumption classes, the
number of decision variable reduces to the number
of consumption classes. For few hundred classes the
existing algorithms are able to solve within a reason-
able time as is shown by Javed and Arshad in AdOpt
(Javed and Arshad, 2009).
However, since the priority systems observed by
the authors are somewhat rigid. ColorPower, and
Pennywise do not allow the consumers to change
the priorities. Colorpower allows consumers to press
an emergency button to explicitly demand electricity.
However if priority of a device changes then this up-
dation will take 24 hours to come into effect. Simi-
larly re-negotiating contracts for Pennywise or in Es-
criva’s system is a cumbersome task. As has been
shown in UK’s Power7 package, the consumers do
not like to be bounded to certain priorities and con-
tracts. As a biological being, the priorities and needs
for the human consumer changes rapidly and regu-
larly. The priorities for consumers are rarely consis-
tent and fixed contracts do not do justice either.
To this end, in this paper we propose a transforma-
tion to convert a simple deadline based user feedback
into a priority based system. Since we collect explicit
preference and bound the system by it, we can reap
the benefits of better user acceptability. Since we con-
vert these preferences into priorities very similar to
the ColorPower scheme, we can compute the solution
in reasonably small time as well getting use the bene-
fit of both the systems.
1.2 Proposed Solution
In this section we will first describe how our strategy
consider consumers deadlines. Then we discuss how
we have incorporated and improved existing Color-
Power algorithm for our planning.
The goal of DSM is to control consumer devices to
SMARTGREENS2015-4thInternationalConferenceonSmartCitiesandGreenICTSystems
150
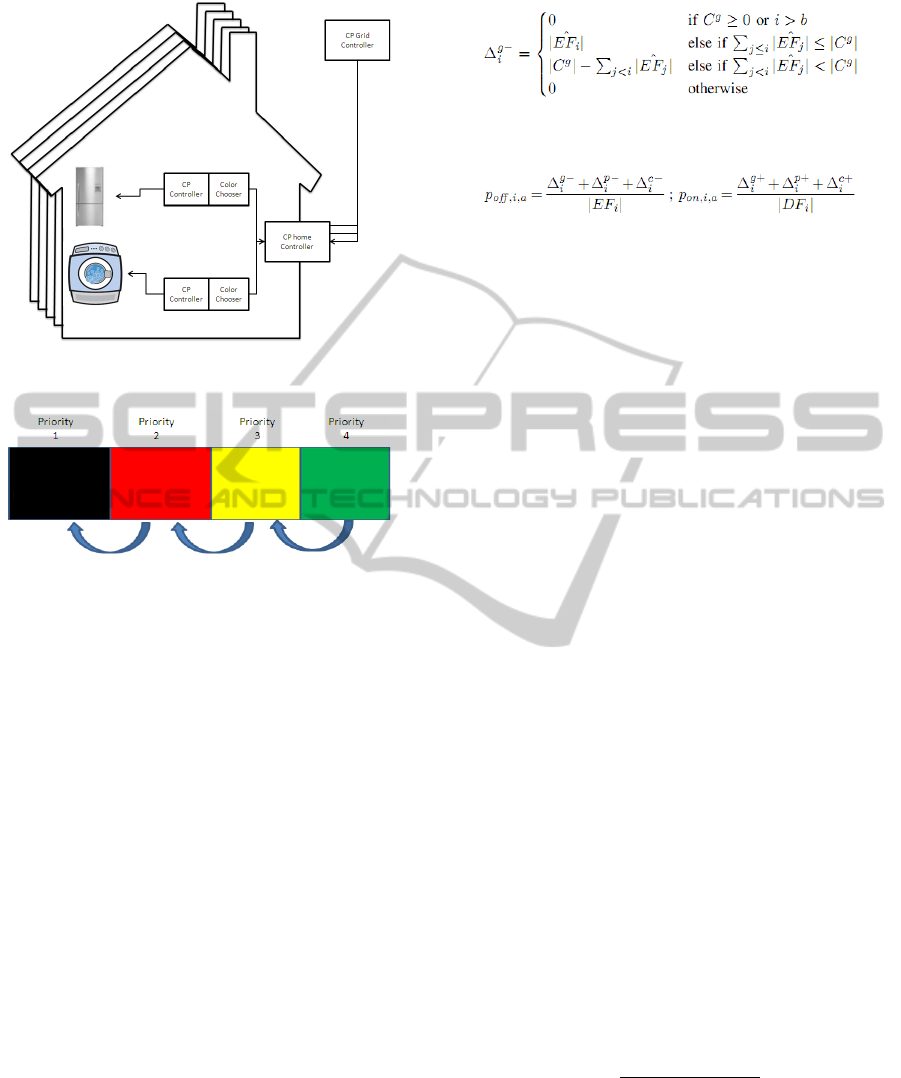
Figure 1: The architecture of the home system working with
Deli2p and its interaction with the grid controller.
Figure 2: Priority scale for DeLi2P. As the deadline time ap-
proaches the priority color transitions from green to yellow
to red and then black, the highest priority level.
reduce the electricity demand to specific thresholds.
As previously discussed, there are two non-functional
requirements of the DSM system, first is that it should
be scalable and second it should be bound by the
needs of the consumers. In this regard the priority
based algorithms provide adequate solution for the
first requirement. For instance, ColorPower is scal-
able, provides privacy preserving aggregation method
and is fair in its distribution of electricity.
This algorithm operates in the following way. The
controller assigns each device a color specifying its
priority as shown in figure 2. At every heartbeat the
home controller collects its demand from devices of
each color. If two devices are yellow then it will
add the demand of both devices as yellow. The al-
gorithm provides for a grid wise aggregation mecha-
nism whereby the grid controller has the aggregated
demands for each of the four priority colors. The grid
controller then assigns a probability to each priority
color based on the supply demand equation. The pol-
icy is that the highest priority gets to use the supply
till its demand is met. If supply is left then the lower
priority is provided the supply. If for a priority level
the supply is partial then each device in the priority is
given a probability based on the amount of electricity
available and the demand of that color. This way the
Figure 3: ColorPower (Beal et al., 2012) controller for de-
vice.
Figure 4: ColorPower (Beal et al., 2012) controller for the
grid.
lower priority devices run on a probabilistic basis.
However, this scheme does not provide provisions
for the consumer to constraint the load movement ac-
cording to consumer’s operations. If a consumer pur-
chases a washing machine then she would wish to
have the clothes washed within a specific period of
time and if the algorithm does not provide this guar-
antee then the consumer will be tempted to bump up
the device’s priority to get the required service. This
may result in spiraling up of priorities thereby leaving
no space for optimization. Essentially the CP does
not guarantee running a device even if the electricity
is available.
DeLi2P uses the same efficient, scalable and fair
ColorPower (CP) controllers to provide control of the
device to the utility planner. One of the contributions
and indeed an important contribution of our work is
that instead of consumer assigning priorities we make
these priorities adaptable in that the device controller
adapts the devices’ color according to the amount of
time it has available to complete the task.
The difference is that when a consumer attempts
to use a device, the consumer is provided with a
timer to set the time of task completion. This can
be achieved by installing a timer on the device. This
maybe an external timer for legacy machine or it
maybe an internal timer in the future smart devices
however, discussion of its deployment is beyond the
scope of this work. The consumer sets the time when
she requires the task to be completed. Based on the
time to deadline DeLi2P calculates the color of the
device at runtime using the following formula:
C
i
=
d(d
i
− o
i
) − curre
len(k)
Where d
i
is the deadline set by the user, o
i
is the op-
erational execution time or the maximum time it will
take the device to complete the task and curr is the
current time. C
i
is the priority color of the device at
time curr. len(k) is the length of interval that we give
to each color.
DeLi2P-AUserCentric,ScalableDemandSideManagementStrategyforSmartGrids
151

As the time moves forward, that is the difference
between (d
i
− o
i
) − curr reduces, the priority of the
device increase thereby increasing its chance to com-
plete the task. The operational flow is similar to Col-
orPower except for the color assignment after each
two minute period the color for the device is ascer-
tained. If the consumer has asked for the device to
operate and the operation has not yet started then the
color is propagated to the CP home controller along
with historical consumption value. The CP home con-
troller aggregates the demand for each color, adds it
to the data passed by previous house and passes it
forward to next house so that it is transmitted to the
CP Grid controller as shown in figure 1 and discussed
in (Ranade and Beal, 2010). The CP grid controller
based on its algorithm shown in figure 4 calculate the
fractional part for each color. This value is passed to
the CP Device controller and the device controller se-
lects the state of the device using formula in figure
3
To illustrate the process, let us assume that a con-
sumer attempts to use washing machine. The con-
sumer wants the operation to be completed in 8 hours
time and the operational execution time for the ma-
chine is 1 hour. Thus we have (8 - 1) hours to com-
plete the task. This puts the device in yellow or cat-
egory 3. Based on the global demand the CP grid
controller assign probabilities to the colors and these
probabilities are propagated to the CP device con-
trollers. If at this time the supply is sufficient to sup-
ply yellow priority then this device will run immedi-
ately. But if yellow is partially supplied or not sup-
plied at all then this device will use the CP controller
using formula in figure 3. If the device gets a chance
to run then it will execute otherwise it will wait till C
i
is red. With an updated color the device’s probabil-
ity of execution will chance. If the supply is so short
that even the red does not execute then 1 hour before
the deadline device will turn black. Since black is
emergency color the device will be provided with sup-
ply and the task will be achieved within the stipulated
time. Figure 5 describes the aforementioned process
as a flow chart.
1.3 Solution Model
In this section we model the demand of electricity ac-
cording to its priorities. The time in our algorithm is
divided into t time slices and we have j priorities. De-
mand of electricity for j priority class generated in a
time slice t is given as:
∀
j
d
j
t
= Demand for j
th
priority at t time
For ColorPower, this will also be net demand or
Figure 5: Flow chart describing the algorithm opertion on a
single device.
D
j
t
of the respective time slice and the priority class
since there is no concept of carrying over load which
has not been provided supply. But for DeLi2P, load
which is not provided supply is considered is carried
over thus net demand at time t for j priority class is:
∀
j
D
j
t
= d
j
t
+ (D
j
t−1
× p
j
t−1
+ ∆
j−1
t
) − ∆
j
t
Here ∆
j−1
t
is the demand for the lower priority
level which has expired and needs to elevated to the
next level and ∆
j
t
is the expired demand from j
th
level
which needs to be elevated to the j + 1
th
level.
p
j
t
is the probability of selection for the j
th
prior-
ity at time t. DeLi2P and ColorPower use the same
formulation for calculating p
j
t
gieven as:
p
j
t
= 1 if
max( j)
∑
i= j
D
i
t
≤ S
p
j
t
= 0 if
max( j)
∑
i= j+1
D
i
t
≥ S
p
j
t
=
S −
∑
max( j)
i= j+1
D
i
t
D
j
t
otherwise
Where S is the total supply to the system.
The graphs in figure 6 show this transformation
of priority level induced by the transfer of ∆ load
from load priority levels to higher levels. Initial pri-
ority levels in form of colors are shown in figure
7. Though the probability assignment in ColorPower
and DeLi2P is same, the underlying total demand D
j
t
varies in DeLi2P to incorporate the concept of dead-
line but in ColorPower, the deadline is not accommo-
dated. With this strategy a peak reduction of up to
SMARTGREENS2015-4thInternationalConferenceonSmartCitiesandGreenICTSystems
152

a b
c d
e f
Figure 6: Graphs showing demand and DSM through DeLi2P results. On the left the graphs show the demand for the day and
on the right the demand after application of DeLi2P. The peak demand ranges from 26MW on day 3 to 23MW on day 2. on
all these days DeLi2P has restricted the peak demand to 18MW without violating consumer deadlines. x-axis shows time in
minutes while y-axis shows power consumption in watts.
30% is achieved with minimum missed deadlines thus
ensuring user satisfaction.
2 EVALUATION
Our evaluation comprise of three steps: In the first
step we show the working of Deli2p as a case study
for one house consisting of four devices. The main
objective of this demonstration is to show the color
transition feature of Deli2p. In the second step we
show the evaluation of Deli2p for one hundred de-
vices under various deadline constraints and user pri-
orities. In the third step we compare Deli2p with Col-
orPower algorithm and show their comparative effec-
tiveness and peak shaving ability.
2.1 Experimental Setup
To carry out analysis, simulations for the proposed al-
gorithm and related work were developed in C# pro-
gramming language. These simulations were con-
ducted on Intel i5 Processor with 4GB of physical
memory having 2.4GHz of clock speed. Power con-
sumption data for 100 different devices was used in
simulations for extensive testing of algorithms. The
data is generated at the rate of 2 samples / minute by
the configurable simulator presented in (Arshad et al.,
2013). The aggregated consumption of each device
at a articular time window was used to compute av-
erage power for that specific appliance. The average
powers were then put to use in demand response al-
gorithms corresponding to the time window for which
they were computed to obtain results close to the ac-
tual environment.
DeLi2P-AUserCentric,ScalableDemandSideManagementStrategyforSmartGrids
153
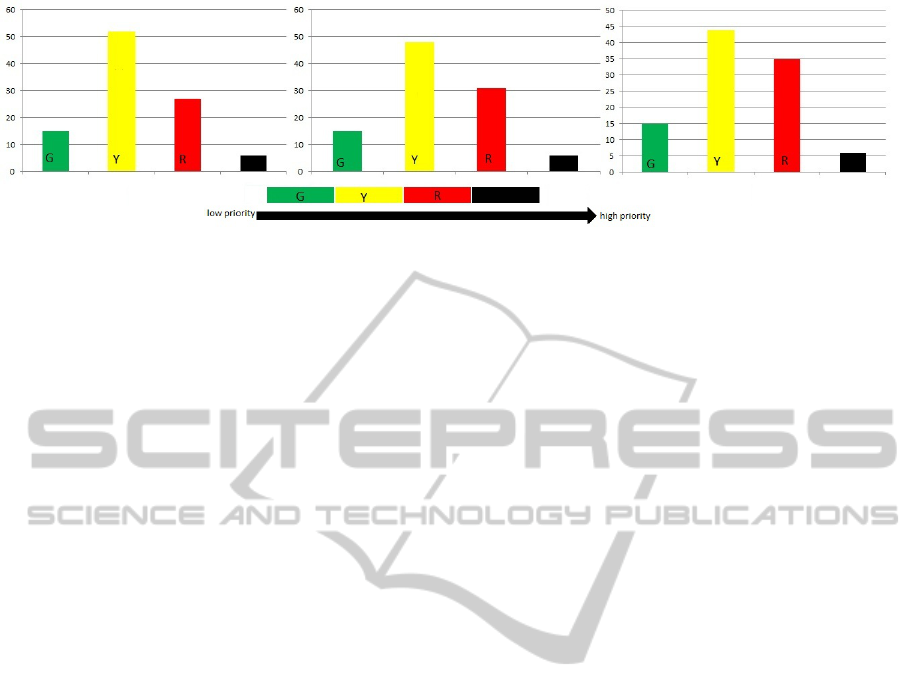
Figure 7: Initial priority levels assigned to devices on Days 1, 2 and 3 respectively from figure 6. These priority levels change
over the course of 24 hrs based on the supply demand situation.
2.2 Case Study of DeLi2P for One
House
In this case study we show the operation of 4 devices
for a single household. All four devices’ requirements
are fed to the system at the same time. As shown in
figure 8 when the device operational request is fed in
our system, the controller assigns priority based on
deadline and duration. The probabilistic model then
sends it turn ON or OFF signal. If the device turns ON
it completes its operation in a single time period, as
seen for device 4 in this case. However, failing to do
so causes device transition to a higher priority level.
As it can be seen from this table that device 1 is first
in a least prior GREEN mode. Since it does not get
activated it moves to higher priority until eventually at
time t = d
i
− o
i
(d
i
is the deadline of ith device and o
i
is the operational time of ith device) it enters BLACK
mode where it is applied turn ON signal to ensure ex-
ecution of operation for that particular device before
the deadline. After it has completed its operation the
device turns white indicating the operation has been
accomplished.
2.3 Applying DeLi2P to One Hundred
Devices
In our evaluation above, we expand our algorithm
on a pool of 100 devices which are assigned opera-
tional duration and putoff time. The figure 9 shows
one case in which devices are activated by scheduling
their deadlines into priority levels. Based on Power
demand-supply equations explained earlier our prob-
abilistic model turn on the devices without exceed-
ing total supply. The devices which are not oper-
ated eventually move into higher level of priority i.e
from Green to Yellow to Red. However, if a device
fails to activate within flexible priority levels it enters
BLACK category in which each device is given turn
on signal to make sure no device goes non-operated
in order to achieve consumers‘ satisfaction
In this section we show the results of applying
DeLi2P for one hundred devices. As described ear-
lier, when a consumer attempts to use a machine the
system asks the consumer to provide a deadline by
which time she requires the task done. Based on the
available time the algorithm assigns an initial priority
level to the device. Considering the overall supply-
demand equation, the device is run when its deadline
is near or earlier if there is enough electricity avail-
able.
The results of application of DeLi2P are shown
in figure 6. The graphs on the left show the demand
of the system without DeLi2P and on the right the
results are with DeLi2P with 18000 KW (18MW) as
the target maximum load. As can be seen, DeLi2P is
able to maintain this target even though the demand
ranged from 25 MW on day 3 to 23 MW on day 2
while satisfying the deadlines set by the consumers.
2.4 Comparison of DeLi2P with
ColorPower
To illustrate on grid let us consider the demand in
figure 10(a). This is a hypothetical but realistic de-
mand where each of the priority level is equally di-
vided. This is the demand that was assumed by Color-
Power algorithm authors for their validation (Ranade
and Beal, 2010). The second figure 10(b) shows the
response of ColorPower and similar algorithms. As
can be seen the demand is flat lined at demand of
140 units. This may result in a yellow device to be
unavailable for as much as 20 hours. To ameliorate
this situation in figure 10(c) the response of DeLi2P
is shown. As the time moves forward DeLi2P ele-
vates the priority of yellow, green and red. This el-
evation of priority means that the device has the op-
portunity to run within the deadline constrain set by
the consumer. the deadline will fail only when a part
of black is above the threshold line. This in essence
is the breaking point of the algorithm, that is, if we
require to shut down devices in black then the dead-
SMARTGREENS2015-4thInternationalConferenceonSmartCitiesandGreenICTSystems
154

Figure 8: . This figure shows how colors are changed for a 24 hours period for four devices in a house depending on their
priority and how close they are to their deadline.
Figure 9: This figure shows the working of Deli2p with one hundred devices over a 24 hours period. The algorithm starts of
by putting the devices in one of the priority and changes the priority as the deadline is close.
a b c
Figure 10: Graphs showing net demand, demand shaping through ColorPower and through DeLi2P.
lines for those consumers will be violated. In com-
parison ColorPower does not cater for this situation
hence evaluating it for deadline failure is not possi-
ble.
3 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
The need to incorporate consumer’s priorities and re-
quirements in to demand side management system is
critical to its acceptance and thereby its use. In this
paper we have considered two key requirements for
increasing the acceptability of the consumer. First
we have provided a way for the consumer to be an
active part of the DSM. This provides satisfaction to
the consumer as proposed by Breukers and colleagues
(Breukers et al., 2001). Secondly, we have provided
a way for the consumer’s deadlines to be catered for
in a scalable manner by converting those deadlines to
priority levels and thereby making the algorithm scal-
able, secure and fair as well.
We see this as a viable solution for future DSM
DeLi2P-AUserCentric,ScalableDemandSideManagementStrategyforSmartGrids
155

systems. The future of this work is to apply it to a
residential area and observe the consumer’s response
to this strategy. A second path of research is to incor-
porate machine learning to learn consumer behavior
in order to automate the timer task in order to aid the
consumer. Yet another possibility is to incorporate
time of use pricing in this system such that the con-
sumer is informed of the price savings that she can
achieve by setting the timer to a later time.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work is in part supported by grants from the De-
partment of Computer Science at LUMS, and ICT Re-
search and Development Fund of Pakistan.
REFERENCES
Arif, A., Javed, F., and Arshad, N. (2013). Integrating re-
newables economic dispatch with demand side man-
agement in micro-grids: a genetic algorithm-based ap-
proach. Energy Efficiency, pages 1–14.
Arshad, N., Ali, U., and Javed, F. (2013). A highly config-
urable simulator for assessing energy usage. Energy
Procedia, 42:308–317.
Beal, J., Berliner, J., and Hunter, K. (2012). Fast precise
distributed control for energy demand management.
In Self-Adaptive and Self-Organizing Systems (SASO),
2012 IEEE Sixth International Conference on, pages
187–192. IEEE.
Breukers, S., Keiskanen, E., Brohmann, B., Mourik, R., and
Feenstra, C. (2001). connecting research to practice
to improve energy demand-side management (dsm).
Energy, 36(4):2176–2185.
Chai, B., Costa, A., Ahipasaoglu, S., Huang, S., Yuen, C.,
and Yang, Z. (2014). Minimizing commercial build-
ing cost in smart grid: An optimal meeting schedul-
ing approach. In Smart Grid Communications (Smart-
GridComm), 2014 IEEE International Conference on,
pages 764–769.
Daoxin, L., Lingyun, L., Yingjie, C., and Ming, Z. (2012).
Market equilibrium based on renewable energy re-
sources and demand response in energy engineering.
Systems Engineering Procedia, 4(0):87 – 98. Infor-
mation Engineering and Complexity Science - Part II.
Du, P. and Lu, N. (2011). Appliance commitment for house-
hold load scheduling. Smart Grid, IEEE Transactions
on, 2(2):411 –419.
Escriv-Escriv, G., Segura-Heras, I., and Alczar-Ortega, M.
(2010). Application of an energy management and
control system to assess the potential of different con-
trol strategies in hvac systems. Energy and Buildings,
42(11):2258 – 2267.
Fan, Z. (2011). Distributed demand response and user adap-
tation in smart grids. In Integrated Network Manage-
ment (IM), 2011 IFIP/IEEE International Symposium
on, pages 726 –729. Internet traffic method for DR.
Modeling user preference as willingness to pay. Sim-
ulation based. no rebound calculations.
Gellings, C. (1985). The concept of demand-side manage-
ment for electric utilities. Proceedings of the IEEE,
73(10):1468 – 1470.
Javed, F. and Arshad, N. (2009). Adopt: An adaptive
optimization framework for large-scale power distri-
bution systems. In Proceedings of the 2009 Third
IEEE International Conference on Self-Adaptive and
Self-Organizing Systems, SASO ’09, pages 254–264,
Washington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Kim, J.-H. and Shcherbakova, A. (2011). Common failures
of demand response. Energy, 36(2):873 – 880.
Kim, T. and Poor, H. (2011). Scheduling power consump-
tion with price uncertainty. Smart Grid, IEEE Trans-
actions on, 2(3):519 –527.
Lee, J.-W. and Lee, D.-H. (2011). Residential electricity
load scheduling for multi-class appliances with time-
of-use pricing. In GLOBECOM Workshops (GC Wk-
shps), 2011 IEEE, pages 1194 –1198. Scheduling al-
gorithm using time of use to reduce cost. No rebound
in simulation.
Liu, Y., Yuen, C., Huang, S., Ul Hassan, N., Wang,
X., and Xie, S. (2014). Peak-to-average ratio con-
strained demand-side management with consumer’s
preference in residential smart grid. Selected Topics in
Signal Processing, IEEE Journal of, 8(6):1084–1097.
Molderink, A., Bakker, V., Bosman, M., Hurink, J., and
Smit, G. (2010). Management and control of domes-
tic smart grid technology. Smart Grid, IEEE Transac-
tions on, 1(2):109 –119.
Rahimi, F. and Ipakchi, A. (2010). Demand response as a
market resource under the smart grid paradigm. Smart
Grid, IEEE Transactions on, 1(1):82 –88. Introduc-
tory case building paper.
Ranade, V. V. and Beal, J. (2010). Distributed control
for small customer energy demand management. In
SASO’10, pages 11–20.
Rehman, M. M. U., Javed, F., Arshad, N., Ikram, M. J.,
Babri, A. H., and Masood, U. A cooperative de-
mand response system for small scale commercial
consumers.
Ullman, J. D. (1975). Np-complete scheduling problems.
Journal of Computer and System sciences, 10(3):384–
393.
SMARTGREENS2015-4thInternationalConferenceonSmartCitiesandGreenICTSystems
156
