
Plug and Play with a QoV Model
A Research Based Learning Approach
Carlos Vivas L´opez, Diana Hern´andez Alcantara, Juan Carlos Tud´on Mart´ınez
and Ruben Morales-Menendez
Tecnol´ogico de Monterrey, School of Engineering and Sciences,
Av. E. Garza Sada # 2501, 64.849 Monterrey NL, Mexico
Keywords:
Research Based Learning, Educational Technology, SemiActive Suspension Systems.
Abstract:
An application that allows and encourages the Research-Based Learning (RBL) was developed. This facilitates
students the interaction with a real prototype under the Plug & Play approach. Students with minimal knowl-
edge of hardware, low-level programming, signal processing or control design, intuitively could discover and
build your knowledge based on a generic guide. The system is based on instructional design for the student to:
establish a link between theory and practical solutions, internalize the knowledge, exploit critical thinking, and
high motivation by the intellectual challenge of solving a real problem. The experimental platform includes a
prototype scale (1:5) Quarter of Vehicle (QoV) model with an Electro-Rheological damper that represents a
vehicle semi-active suspension system. The QoV model is equipped with several sensors for measuring: the
positions on the motor base, the suspended mass and between the rim and the sprung mass, the acceleration
in the tire and the sprung mass, and the damper force of the system. An Human Machine Interface talks
with a DSpace data acquisition card that communicates with the sensors/actuators system and works directly
with Matlab/Simulink. Early results have been found more efficient teaching-learning for several reasons:
(1) students concentrate efforts on the learning objective (minimum programming), (2) a real scale prototype
is available, (3) students can share their designs seamlessly and reuse software accelerating , and (5) high
motivation because the research and easy use of the system.
1 MOTIVATION
M´exico ended 2014 as the largest vehicle producer in
Latin America and 7
th
worldwide. Mexican automo-
tive industry saw its consolidation as one of the top
countries in vehicle production and export, as a result
of Nissan, Honda and Mazda’s new facilities opening
in central M´exico. During 2014 the automotiveindus-
try was close to 3.5 million produced vehicles; with-
out considering the launch Daimler/Nissan, together
with the foreseeable arrival of new investment from
the existing brands in M´exico, plus a couple of com-
panies reassuring its investment this year (Elie, 2013).
Mexico will be close to 5.0 million produced vehi-
cles in 2020. This will demand more successful pro-
fessionals in this field. automotive industry. The dis-
tribution requirements in terms of total employment
are: (1) Manufacturing components: 52 %, (2) As-
sembly: 21 %, (3) Logistics and storage: 8 %, (4)
Administration: 8 %, (5) Design and development
product: 6 %, (6) Sales and Service customer: 3%
and (7) Industrial safety: 2 %. The employment in
the sector is concentrated in manufacturing and as-
sembly (73 %); but, the activity with greater value-
added is Design. The Mexican automobile sector has
the most modern and efficient installed capacity for
vehicle production worldwide. Production capacity
is highly technical and very flexible, which makes
it possible to manufacture several types of models.
Mexico must increase its focus on Design and Devel-
opment Product to enhance the value-added sector.
Higher education has a crucial role in this oppor-
tunity. Higher education seeks to develop graduates
with a wide range of intellectual and practical knowl-
edge and skills, such as critical and creative think-
ing, written and oral communication, quantitative lit-
eracy, information literacy, teamwork and problem
solving, civic knowledge and engagementlocal and
global, intercultural knowledge and competence, eth-
ical reasoning and action, and foundations and skills
for lifelong learning, (n.d., 2011). Tecnol
´
ogico de
Monterrey is working on these needs through different
initiatives in undergraduate programs such as Inter-
ship Program in Research and Innovation, (Galeano-
277
Vivas-López C., Hernández Alcantara D., Tudón Martínez J. and Morales-Menendez R..
Plug and Play with a QoV Model - A Research Based Learning Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0005440202770284
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2015), pages 277-284
ISBN: 978-989-758-107-6
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

S´anchez et al., 2011) (Galeano-S´anchez et al., 2012).
Students for the automotive sector with better cre-
dentials and skills using innovative teaching-learning
techniques such as Research Based Learning (RBL)
are been graduated every year.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2
briefly reviews the RBL approach and how is going
to be exploited in this study case. Section 3 describes
the opportunities in the control system of semi-active
suspensions to justify the development of educational
technology. Section 4 presents some preliminary re-
sults. Finally, section 5 concludes the paper.
2 RESEARCH BASED LEARNING
The term undergraduate research and its integration
into the curriculum grows out of US practice; in
particular through innovations pioneered at the Mas-
sachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) through the
leadership of Margaret MacVicar, MITs Dean of Un-
dergraduate Education. In 1969, MIT started the Un-
dergraduate Research Opportunities Program. This
developed as a cross-institutional initiative that sup-
ported selected students to work on student initiated
and faculty-supported research projects.
The Boyer Commission on Educating Undergrad-
uates in the Research University called for ten key
changes in undergraduate education, four of which
demand to strengthen the undergraduateexperience of
research: (1) Make Research-Based Learning (RBL)
the standard, (2) Construct an Inquiry-Based Fresh-
man year, (3) Build on Research-Based Strategies to
characterize the whole of a research university educa-
tion, and (4) Culminate with a capstone experience.
After this report, all types of US institutions of higher
learning were transformed based on the principle that
research-based learning should inform all levels of
undergraduate education, (n.d., 1998).
At higher education level, you cannot be a good
teacher unless you are also a good researcher. The
quality which makes higher education higher and
quiet different from training is that it is grounded
in a deep understanding of the provisional nature of
knowledge, (Baldwin, 2005). Linking research and
teaching has several advantages in enhancing student
learning. Immersing students in the relevant disci-
plinary and research cultures and the process of do-
ing research and enquiry can be of wider benefit. Re-
search strategies develop important skills. Addition-
ally, students who are actively involved in research
are more engaged.
(Healey and Jenkins, 2009) organized the ways of
engaging students in research in a two-axes map, Fig.
1. One axis classifies the ways students may be en-
gaged in research according to the extent to which stu-
dents are treated primarily as the audience or as par-
ticipants, while the other axis classifies the approach
as emphasising research content or research processes
and problems. All ways are valuable and interdepen-
dent. Effective programmes incorporate all these dif-
ferent modes.
Students are participants
Students frequently are an audience
Emphasis
on research
content
Emphasis
on research
processes
and problems
Research
Tutored
Research
based
Research
led
Research
oriented
Figure 1: The nature of undergraduate research. Research-
led: learning about current research in the discipline;
research-oriented: developing research skills and tech-
niques; research-based: undertaking research and inquiry;
and research-tutored: engaging in research discussions.
• Research-led: learning about current research in
the discipline. Students can be engaged through
lectures, academic staff-led seminars, laboratories
and course work.
• Research-oriented: developing research skills and
techniques. Course lectures, practical and labora-
tory classes and course work are common modes
of teaching in which research skills and tech-
niques are particularly developed.
• Research-based: undertaking research and in-
quiry. The most obvious way for students to en-
gage in research is to undertake research projects
(or capstone research) and inquiry projects, both
within the curriculum and outside it.
• Research-tutored: engaging in research discus-
sions. Engaging in discussion is a key way to de-
velop understanding.
In much of higher education programs relatively
too much teaching and learning is in the bottom half
of this model, and most students would benefit from
spending more time in the top half. The way the four
approaches are interlinked together is important in the
design of effective courses.
3 EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY
The primary functions of an automotive suspension
system are to (Gillespie, 1992): (1) isolate the chas-
sis motion from road irregularities, (2) keep the tire-
road contact with minimal load variations, and (3)
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
278

resist roll of the chassis. They depend on the vehi-
cle vertical force that it must transmit from the tires
to the chassis. According to the capability to adjust
the damping force, the automobile suspensions can
be classified as: passive, active or semi-active. Pas-
sive suspensions are only able to dissipate the energy
and their damping characteristics are time invariant,
while active ones are able to store, dissipate and gen-
erate energy through a variable damping coefficient
but they are very expensive to apply because require
an external power supply.
Semi-active control has recently been an area of
much interest because of its potential to provide sim-
ilar performances of active actuators; but, without a
significant external power supply (Fijalkowski, 2011).
The semi-active suspensions consist on a spring and
damping component; its continuous variable damping
coefficient adjusted by external control signals offers
much better performance .
There are 4 main technologies of semi-active
dampers: Electro-Hydraulic, Pneumatic Actuators,
Magneto-Rheological and Electro-Rheological (ER).
ER dampers are used in this application, they contain
a rheological fluid, the semi-activeness is manipulated
by adjusting an electric field.
Four topics will be considered with this edu-
cational technology: (1) Quarter of Vehicle (QoV)
model, (2) Damper modeling, (3) Control systems,
and (4) Data-based control algorithms.
QoV Model. The QoV model is the most basic
system to represent an automotive suspension, Fig.
2. Its use assumes an equivalent load distribution
among the four corners and a linear dependency with
respect to the translational and rotational chassis mo-
tions. The system considers a sprung mass (m
s
) and
an unsprung mass (m
us
). A spring with stiffness coef-
ficient k
s
and a semi-active damper represent the sus-
pension between both masses. The semi-active damp-
ing force (F
SA
) depends on a control input variable
and it is highly nonlinear with respect to the suspen-
sion motion. The stiffness coefficient k
t
models the
wheel tire. The vertical position of the mass m
s
(m
us
)
is defined by z
s
(z
us
), while z
r
corresponds to the un-
known road disturbance, Fig. 3.
Damper Modeling. To characterize all rhelogical
phenomena, an efficient experimentation is needed.
Different experiments allow to explore the damping
force in the Force-Velocity characteristic map. Each
experiment consists on a displacement sequence that
analyzes the mechanical properties and an electric se-
quence that explores the transient response between
the magnetic field and damping variation, (Lozoya-
Santos, 2013).
Control Systems. An extensive classification of
m
s
m
us
s
us
z
z
r
z
k
t
k
s
SA
F
Figure 2: Quarter of Vehicle (QoV) Model.
different control strategies for semi-active dampers
according to the type of manipulation (continuous or
on-off ), control goal (comfort, road holding or both),
type of control law to include the semi-activeness
(clipped, frequency adaptive, frequency switched,
measurement-based), type of control design (model-
based or free of model), etc. is presented in (Lozoya-
Santos, 2013).
The interest in semi-active suspensions derives
from the potential for improvements to vehicle ride
performance with no compromise in handling, with-
out considering its type of control design. It is nec-
essary to assume a balance in the controller design
goals.
Data-based Control Algorithms. Only measure-
ments and analytical estimations are used to monitor
the suspension behavior to adjust the damping force
according to the desired performances. The most rep-
resentative control approach for comfort is the Sky-
Hook (SH) controller, which has been successfully
applied on commercial vehicles. The principle of this
algorithm is to link the chassis to the sky by a vir-
tual damper and put a controlled damper among the
masses, in order to reduce the vertical oscillations of
the chassis.
Based on the acceleration measurement instead of
the velocity of the sprung mass, the named Acceler-
ation Driven Damper (ADD) control (Savaresi et al.,
2005) and its improvedversion have become new effi-
cient comfort-oriented controllers. In the sense of re-
ducing the number of measurements that are used to
control the damping force, (Spelta et al., 2011) pro-
posed the Mix-1-stroke algorithm that shows similar
performance as the SH-ADD controller, but with only
one measurement.
In a dual way to the SH, the Ground-Hook (GH)
controller has been proposed to reduce the road hold-
ing by including a virtual damping between the wheel
and road and a controllable semi-active shock ab-
sorber. This is the most representativecontrol strategy
PlugandPlaywithaQoVModel-AResearchBasedLearningApproach
279

Sprung mass
Unsprung
mass
Force sensor
(suspension)
Sprung mass
accelerometer
Deflection sensor
(suspension)
Position sensor
Sprung mass
Linear motor
Position sensor
Unsprung mass
accelerometer
Electro-Rheological damper
Figure 3: Quarter of Vehicle (QoV) Model.
fully oriented to road holding, (Valasek et al., 1997).
This ER shock absorber is adjusted using a manip-
ulation voltage between 0 and 5 kV. Below the wheel
lies an linear servomotor that mimics the desired road
profile. The servomotor have a bandwidth of 0-20
Hz with a maximum velocity of 1.5 m/s. The mo-
tor has its own servo-driver and is operated from a
computer by sending the desired road profile through
the Dspace
TM
. This platform is equipped with a wide
variety of sensors as is shown in Fig. 3. A photo is
shown Fig. 4.
Figure 4: Experimental QoV Model, manufactured by
SOBEN
TM
.
A Human Machine Interface (HMI) was devel-
oped to easily interact with the experimental QoV
model. This HMI is the fundamental platform for the
RBL proposal. Basically, this represents a Hardware-
in-the-Loop (HiL), that is used in the development and
test of complex real-time embedded systems, Fig. 5.
Figure 6 shows how a Dspace card talks with the
experimental platform and Matlab/Simulink on real
time. The HMI running on Matlab has configured a
general control system with different options for each
Figure 5: Human Machine Interface (HMI).
Figure 6: Communication system.
k
t
k
s
F
D
Control
Algorithm
Performance
goals
Zs
Zus
Zs
Zus
Zs
Zus
¨
¨
.
ms
mus
Zs
...
...
Datales
Controller-1
Controller-2
Controller-n
Road-m
Road-1
Road-2
Figure 7: Plug and play system.
block/signal, Fig. 7. Based on this flexibility, the HMI
allows:
• Design a control system as if you were drawing a
block diagram (Drag and Drop), Fig. 8.
• Reuse software such as: road profile, control al-
gorithms, etc.
• Online plotting and registering.
• Online access to the Matlab and toolboxes plat-
form.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
280
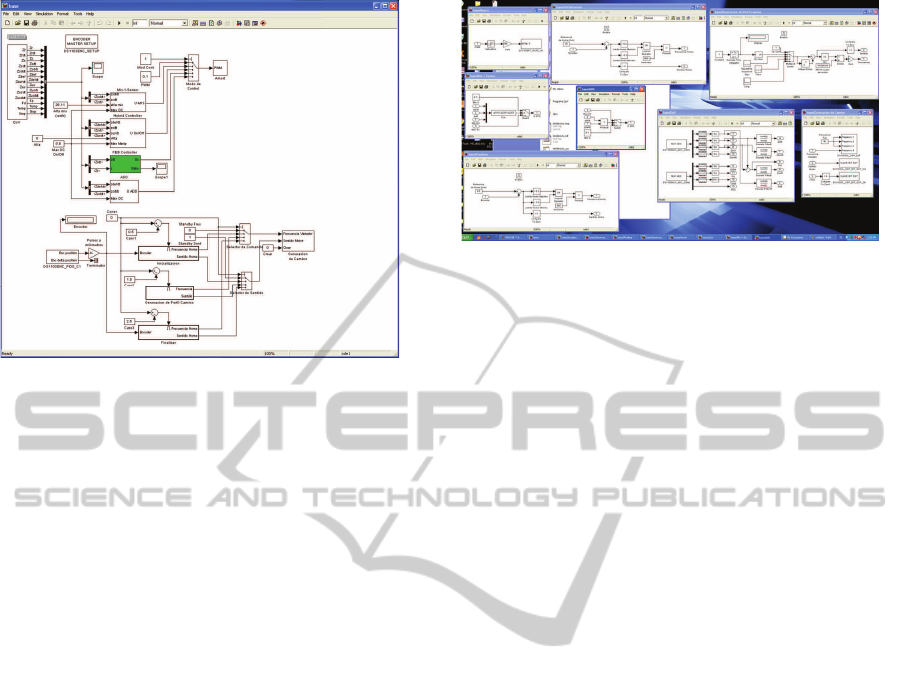
Figure 8: Simulink interface. Configure a control system is
as easy as drawing it.
4 EARLY RESULTS
Early results could be discussed in 3 great points: (a)
HMI, (b) RBL and (c) Academic results
4.1 HMI
A Vehicle Dynamics course provides a fundamental
understanding of vehicle ride and handling behaviour
and links this understanding to the practical impli-
cations for chassis and suspension design. Mechan-
ical Engineering students have a low background in
control systems, instrumentation, low-level program-
ming, etc. The main goal of the HMI is to allow stu-
dents an easy and friendly operation of the experi-
mental QoV model. To design , implement and test
in a prototype vehicle (in minutes) is a great learn-
ing experience and motivation. This HMI opens a
number of opportunities in active learning, problem-
based learning and research-based learning , allowing
students so extremely easy to live a practical experi-
ence. Practice on a prototype has some disadvantages
as some dynamic phenomena can not be reproduced
accurately; however, also has important advantages
such as time efficiency and overall safety of experi-
mentation. Additionally, students will have a reposi-
tory of several elements to design (to draw) a control
system such as different profile of the roads, type of
standard tests, data-based control algorithms, model-
based control algorithms, etc.
Students will be focus in the academic goals, with-
out consuming time on implementation details (it is
not the objective of this course). Eventually, students
will be able to design and contribute with new tool-
Figure 9: Vehicle Dynamics Repository: control algo-
rithms, road profiles, etc.
boxes to the Vehicle Dynamics repository with new
ideas and code.
4.2 RBL
The Vehicle Dynamics course was re-designed in
three teaching-learning activities: (1) Lectures, (2)
Experiments and (3) Reports, Fig. 10. The novel ac-
tivities to this course are Experiments and Reports.
Lectures were more conventional but focus in the Ex-
periments.
Three modes of inquiry were exploited in the Lec-
tures: structured providing a problem and an outline
for addressing it; guided providing questions to stim-
ulate inquiry, but students are self-directed as regards
exploring these questions; and open where students
formulate the questions themselves. Also during the
Lectures, special emphasizes was given to different
strategies for linking teaching and research, (Baldwin,
2005):
• Draw on Personal Research in Designing and
Teaching Courses. Own research was incorpo-
rated into the course to motivate students. Grad-
uate students participate and discuss their current
research results as a part of Automotive Consor-
cium Research Group.
• Place the Latest Research in the Field Within Its
Historical Context in Classroom Teaching. The
lastest damping theories and control algorithms
are included. The technological advances in the
automotive industry are discussed.
• Design Learning Activities Around Contemporary
Research Issues. Students were asked to explore
cutting-edge research problems, i.e. the tradeoff
of comfort and road-holding for semiactive sus-
pension systems (which is an open question).
• Teach Research Methods, Techniques and Skills
Explicitly Within Programs. ER damper modeling
demands both model equation and experimental
PlugandPlaywithaQoVModel-AResearchBasedLearningApproach
281

data. Representative data comes from a special
Design of Experiments. Students must learn these
research methods.
• Build Small-scale Research Activities into Under-
graduate Assignments. This is the main applica-
tion of this proposal.
• Infuse Teaching with the Values of Researchers.
Through different activities the following values
of researchers are discussed: openness, scepti-
cism to received theories, honesty with oneself as
well as others, respect for evidence, respect to oth-
ers, tolerance of ambiguity, respect for the sub-
jects of study, persistence, analytical rigour, ac-
curacy, humility, willingness to admit error, and
creativity.
Lectures
Challenge
#1
Challenge
#2
Challenge
#3
Challenge
#4
Challenge
#5
Reporting
RBL3
RBL1
RBL2RBL4
RBL6RBL5
Figure 10: Vehicle Dynamics course. Teaching design
based on RBL.
Experiments are possible because the new ex-
perimental QoV (HMI). Five experimental sessions
were designed as challenges for the students. Dif-
ferent assignments were considered through each of
the four ways of engaging students in research around
each challenge. A balanced distribution of time
and teaching-learning techniques should give bet-
ter results to different learning styles and academic
topic. Teaching new material in manageable amounts,
through five challenges, modeling, guiding student
practice, helping students when they made errors, and
providing for sufficient practice and review. Also,
with experiential and hands-on activities after the ba-
sic material was learned. A review is an important
component of instruction between each challenge.
Review can help students strengthen the connections
among the material they have learned. The review
of previous learning can help them recall words, con-
cepts, and procedures effortlessly and automatically
when they need this material to solve problems or to
understand new material. The development of exper-
tise requires thousands of hours of practice, and daily
review is one component of this practice.
An example of teaching design for Challenge #
2, based in Fig. 1, will be described. Students are
organized in collaborative teams of five members.
1. Research-led: Spent some lectures outlining a
research problem (ER Damper experimental model-
ing) and setting it in a theoretical context based on
the state-of-the-art.
2. Research-oriented: Students must read some
papers to learn about: design of experiments, damper
models and model identification. Also, students read
the QoV manual to learn how these ideas can be im-
plemented.
3. Research-based: Students undertake research
by implementing the experiments in the experimental
QoV model through the HMI.
4. Research-tutored: Students must discuss the
used methods/algorithms to solve this challenge, the
main findings and unresolved issues.
Reporting includes some activities as conse-
quences of the Experiments/Challenges. There are
several important process that students must com-
plete with the experimental results of the challenges,
the most important are: (1) analyze, (2) discuss,
(3) learn/validate concepts, (4) communicate and (5)
write a report. As a result of experimentation to solve
the challenges, analysis of the results to understand
the phenomena and/or generate knowledge. Students
must write a technical report (i.e. abstract, introduc-
tion, state of the art, experimental design, results, dis-
cussion, conclusions, and bibliography). The writ-
ing of this report is justified by several reasons. For
learning, the act of writing provides a chronology
of thoughts, they can then label, objectify, modify,
or build on; and it engages in becoming invested in
ideas and learning. Writing-to-learn forms and ex-
tends thinking and thus deepens understanding.
Learning is a complex and dynamic process in-
volving interactions between previously acquired lev-
els of understanding and the conceptualization and in-
corporation of new material. Writing a report encour-
ages a level of cognitive activities which maximizes
the potential of the students to modify and restruc-
ture knowledge. Students improve their learning by
constructing and evaluating the knowledge to acquire,
students gain ownership of knowledge by asking their
own questions about existing knowledge. Writing a
report definitely plays the key role in the process of
student knowledge-construction.
Learning through writing activities and experi-
ences that interest and stimulate students is usually in-
herently motivating. The writing a report activities in-
cluded conceptual understanding, procedural knowl-
edge and logical thinking is a means for transforming
concepts and skills. Writing engaged all students ac-
tively express and explain meaning at their own abili-
ties.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
282

4.3 Academic Results
The early results of this work should be analyzed from
two perspectives: (1) the academic outcomes and (2)
the results of the didactic proposal using the HMI. Al-
though the results are preliminary, they are motivat-
ing.
Figure 11 presents an example of experimental re-
sults that students obtained. Top plot shows the tran-
sient response of a suspension system using different
damping coefficient. Students can test manually the
ER damper for different electric current and evaluate
the results. Bottom plot shows an road profile esti-
mation system, this experiment is very easy for im-
plementation, but it is a really complex problem for
undergraduate students, (Tud´on-Mart´ınez, 2014). All
students can complete the five challenges and make
the experience.
About the didactic proposal, based in a survey
with 42 students, the main comments are:
• HMI - Use. Students with basic background in
Matlab/Simulink indicate the HMI is very ease of
use. Students without this background said it is a
good HMI.
• HMI - Academic Purpose. Some students think
they lost the implementation details because the
Plug & Play concept.
• Debugged Software. Students can design, de-
velop, debug and validate their assignments off
line. The experimental implementation was very
short.
• Motivation - QoV Model. All students showed
high motivation; however, some of them are skep-
tics to the real vehicle behavior. Even the QoV
model is an accepted framework for practical ap-
plications; but certainly there are some limita-
tions/constraints because only the vertical dynam-
ics of the vehicle is considered. The scaled proto-
type represents the main concern.
• Motivation - Academic Topic. All students
showed high motivation for being part of a real
problem with an open question.
• Software Reuse. All students appreciated the
available code; some students modify it. Stu-
dents recognized some values: advantage of col-
laboration, recognition of authorship, recognition
of standards procedure as documentation of soft-
ware.
4.4 Related Work
The Institut National Polytechnique de Grenoble
(INPG), France has a similiar QoV experimental test
Road profile, z [m]
r
Experimental data
Estimation
Time [s]
Estimation performance of the road disturbance
−5
−4
−3
−2
−1
0
1
2
3
4
5
x 10
−3
Low dampingMedium dampingHigh damping
Suspension
deflection, z [m]
def
Vehicle dynamics at different damping coefficients
−0.02
−0.015
−0.01
−0.005
0
0.005
0.01
0.015
0.02
t
1
t
2
t
3
t
4
Figure 11: Some experimental results.
bench. They are using the XP Windows HMI, but is
restricted to: (1) limited number of road profiles, (2)
General state space based controller, and (3) there are
not real time plots. They have 4 test benches for aca-
demic purposes. Given the restrictions on use, these
equipments are used in a limited way to validate re-
sults.
Also, Gipsa-Lab at INPG has a 1:5-scaled baja
style racing car, which represents a full vehicle in-
cluding wheels, engine, steering, breaking system,
and the key element a SA uspension system, Fig. 12.
This experimental platform has two computers: (1)
Host computer where the user sets the initialization
parameters, configures the desired road profile, imple-
ments the suspension control algorithms, and records
the acquired data; and (2) Target computer where the
control algorithms are compiled and executed in a RT
operating system (xPC target
TM
). This is an excel-
lent experimental system for research purposes with
a open software. Similar experiments can be done to
our proposal, but the needed time for learning the use
of experimental platform and the needed time for de-
veloping and implementing the tests is excessive high
for educational purposes.
The University of Bundesweher at Munich, Ger-
many has a similar experimental QoV model to us.
Figure 12: 1:5-scaled baja style racing car.
PlugandPlaywithaQoVModel-AResearchBasedLearningApproach
283

They are researching about chasis control systems
looking for optimal solutions in rough roads. They
developed an HMI based on C++. This platform has
an open code: (1) to interact with sensors and actu-
ators, (2) to implement non conventional controllers,
(3) to design new road profiles, (4) to plot simulta-
neously several signals, and (5) to compare real and
simulated results on real time. Similar to Gipsa-Lab
approach, the main purpose is research only.
The essential difference of these related works to
us is: (1) the HMI which was designed for academic
purposes (Plug & Play Approach) based on a teach-
ing technique and (2) the software that support the
HMI, which is the result of two PhD dissertations:
(Lozoya-Santos, 2013), (Tud´on-Mart´ınez, 2014). An
important constraint of our proposal is the cost of the
Dspace
TM
card; however, there are cheaper options.
5 CONCLUSIONS
he proposed educational technology is based on both:
Plug & Play approach and Research Based Learning
(RBL). Early results show the Plug & Play approach
simplifies the used of the experimental QoV model
allowing an efficient teaching-learning system
Preliminary results are: (1) high motivation of stu-
dents, which greatly facilitates the teaching-learning
process, (2) the HMI allowed for experimentation
very efficiently, (3) unlike the original course (i.e.
only in a classroom), practical experience taught the
students to ”see”, ”feel”, ”listen” various phenomena
of vertical vehicle dynamics, (4) although we have no
evidence to prove the results of the writing reports,
we believe that the students internalized the concepts
they learned to better understand, organize and com-
municate their ideas (orally and in writing). Our only
evidence is that test scores were substantially higher.
As future work, we will begin to statistically
measure and compare the performance of students
through the terms. Designing rubrics to validate the
benefits of HMI in terms of efficiency during the
teaching-learning process.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors thank Tecnol
´
ogico de Monterrey and CONA-
CyT because their partial support through the Auto-
motive Consorcium Research Group and the Bilateral
(M´exico-France) PCP 03/10 and 06/13.
REFERENCES
Baldwin, G. (2005). The Teaching-Research Nexus. Tech-
nical report, The University of Melbourne.
Elie, P. (2013). Driving Value 2013 Automotive M&A In-
sights .
Fijalkowski, B. (2011). Automotive Mechatronics: Opera-
tional and Practical Issues. Springer.
Galeano-S´anchez, N., Morales-Menendez, R., and Cant´u-
Ortiz, F. (2011). A Research-Based Learning Ap-
proach for Undergraduate Students: The Internship
Program in Research and Innovation Model. In 3o. Int
Conf on Computer Supported Education, pages 143–
146, Holland.
Galeano-S´anchez, N., Morales-Menendez, R., and Cant´u-
Ortiz, F. (2012). Developing Research Skills in Un-
dergraduate Students trough an Intership Program in
Reseacrh and Innovation . Int J of Eng Education,
28(1):48–56.
Gillespie, T. (1992). Fundamentals of Vehicle Dynamics.
Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc.
Healey, M. and Jenkins, A. (2009). Developing Undergrad-
uate Research and Inquiry. Technical report, The Uni-
versity of Manchester.
Lozoya-Santos, J. (2013). Control of Automotive Semiactive
Suspensions. PhD thesis, Tecnol´ogico de Monterrey,
Campus Monterrey, M´exico.
n.d. (1998). Boyer Commission on Educating Undergrad-
uates in the Research University. Reinventing under-
graduate education: a blueprint for Americas re-
search universities. .
n.d. (2011). Association of American Collegues and Uni-
versity. Liberal Education and America’s Promise
(LEAP): Essential Learning Outcomes.
Savaresi, S., Siciliani, E., and Bittanti, S. (2005). Accel-
eration Driven Damper (ADD): an Optimal Control
Algorithm for Comfort Oriented Semi-Active Suspen-
sions . ASME Trans.: J. of Dynamic Syst., Measure-
ments and Control, 127(2):218–229.
Spelta, C., Previdi, F., Savaresi, S., Bolzern, P., Cutini, M.,
Bisaglia, C., and Bertinotti, S. (2011). Performance
Analysis of Semi-Active Suspensions with Control of
Variable Damping and Stiffness . Vehicle System Dy-
namics, 49:237–256.
Tud´on-Mart´ınez, J. (2014). Fault Tolerant Control in Au-
tomotive Semi-Active Suspensions. PhD thesis, Tec-
nol´ogico de Monterrey, School of Engineering and
Sciences, M´exico.
Valasek, M., Novak, M., Sika, Z., and Vaculin, O. (1997).
Extended Ground-hook - New Concept of Semi-
Active Control of Trucks Suspension. Vehicle System
Dynamics, 27:289–303.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
284
