
Conceptualize the Domain Knowledge Space in the Light of Cognitive
Skills
Fatema Nafa and Javed Khan
Media Communications and Networking Research Laboratory
Department of Computer Sciences Kent State University, Kent, Ohio, U.S.A.
Keywords: Learning Analytics, Higher Order Thinking Skills, Domain Knowledge and Relationships Extraction.
Abstract: In this paper, we propose an approach that can improve the quality of pedagogies based on Bloom's Taxonomy
(BT) cognitive theory. Theoretically, any domain knowledge can be learned and taught at multiple cognitive
domain levels. Moreover, other cognitive domain levels might be called, for learn specific domain knowledge.
If we know the dependencies between the domain knowledge, many interesting pedagogical applications are
possible. However, until now, the relationship levels between domain knowledge are highly sophisticated and
required tedious human judgment to be deduced. BT theory has been explored in the psychological sciences
paradigm, but has not been examined automatically. No comprehensive computer science map is currently
available. This paper, explores how the BT- relationships between various domain knowledge is automatically
extracted. A Bloom Topic Graph (BTG) that encodes concept space is extracted. BTG provides concept space
connected as BT cognitive relationships. Our approach utilizes verbs to discover the BT cognitive
relationships between computer sciences, domain knowledge. We evaluate the BT cognitive relationships
using ground truth, and our approach achieves an accuracy of average 65-75%, which is significantly high.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the most apparent problems that the common
faculty member must focus on includes which domain
concepts to teach, and how to rank each domain
concept or teaching method for the level of thinking
in terms of cognitive skills of those being taught
(Bloom and Krathwohl, 1956). One way to express
domain concepts, compatible with real thinking skills
of the learner, is Bloom Taxonomy cognitive skills.
Mechanisms for categorizing knowledge space into
Bloom Taxonomy cognitive skills will improve the
quality of curriculum structure, allowing appropriate
course and teaching plan development. Bloom
Taxonomy (BT), introduced in 1956 by Benjamin
Bloom, is an idea of classifying the learning
objectives in order to distinguish the fundamental
questions within the education system (Bloom and
Krathwohl, 1956). BT identifies three domains of
educational activities: Cognitive domain (mental
skills), Affective domain (growth in feelings or
emotional areas), and Psychomotor domain (physical
skills). Cognitive domain has come to our attention as
it closely relates to the real understanding of thinking.
The Cognitive domain is defined by Bloom into six
levels: 1) knowledge, 2) comprehension, 3)
application, 4) analysis, 5) synthesis, and 6)
evaluation.
In 2001, Anderson and a team of cognitive
psychologists made a significant change to Bloom's
Taxonomy, calling it the Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy
(Anderson et al. 2001). This change, in the Cognitive
domain’s levels, occurred by adding, ordering,
combining, and change level’s names, but keeping the
same number of six levels. The revised Cognitive
domain’s levels from simplest to most complex are:
1) remembering, 2) understanding, 3) applying, 4)
analyzing, 5) evaluating, and 6) creating. Despite the
significant changes made by Anderson, which may
work with some theoretical majors such as
psychology, scientific majors such as computer
science need specific Cognitive domain levels.
Therefore, we introduce a new Cognitive domain
named Computer-Science based Cognitive Domain
(CSCD), by modifying Anderson’s revised Cognitive
domain.
Based on CSCD, we built a model, called Bloom
Taxonomy Relational Model (BTRM), to facilitate
the classification of computer science, domain
concepts. Then, based on the BTRM model, we
design and develop a technique to generate the
relationships between computer sciences, domain
285
Nafa F. and Khan J..
Conceptualize the Domain Knowledge Space in the Light of Cognitive Skills.
DOI: 10.5220/0005441602850295
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2015), pages 285-295
ISBN: 978-989-758-107-6
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

concepts automatically. Our technique is based on the
use of Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) theory to find
verbs that use Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
(Landauer et al. 1998). A number of works have
explored how a range of taxonomies can be applied
in Computer Science (CS) to educate students more
effectively. In particular, there are three ways in
which such taxonomies have been applied to
Computer Science: 1) to design the courses at various
levels of granularity in time, 2) to design the teaching,
learning, and assessment materials, and 3) the
analysis of student responses to exercises in order to
validate the effectiveness of items 1 and 2 above. In
order to evaluate our model and technique, we used
an electronic book titled “Introduction to Algorithm”
to generate a knowledge map (a graph) which consists
of algorithmic concepts as nodes, and the
relationships between them as weighted directed
edges. The weights on the edges are names of the
relationships (BL1:1, BL2:2, BL3:3, BL4:4). To the
best of our knowledge, this is the best accurate
algorithmic map that reflects most algorithmic
concepts and their relationships. This map can be
used in Computer Science Departments by professors
who teach algorithm courses to better understand a
student’s educational needs.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows:
Section 2 provides an overview of the related work
for BT. Section 3 explains the Computer-Science
based Cognitive Domain (CSCD). Section 4 presents
the key model used. Section 5 contains a detailed
experiment that demonstrates a dramatic
improvement in observed accuracy of analyzing CS
domain knowledge.
2 RELATED WORK
Let us give an overview of various works that have
investigated how Bloom’s Taxonomy can pertain to
the field of Computer Science. Specifically, such
taxonomies have been used in four different ways: 1)
course design, 2) teaching methodology, 3) the
creation of learning and evaluative materials, and 4)
student responses to learning activity (Machanick,
2000). In this section, we appraise the work of a
number of research projects that applied Bloom’s
Taxonomy in the field of computer science by
Machanick. Machanick presents the idea of ordering
material according to the required cognitive skills
taught within three computer science courses
(Machanick, 2000). Bloom’s Taxonomy was used to
assign grades in an introductory programming course,
based on Bloom-level mastery of tiered curricular
components rather than grading on a curve by (Lister
and Leaney, 2003). In review of their work, the
taxonomy for computer science was questioned
(Johnson and Fuller, 2006). The problem is that
exams regularly fail to test the knowledge of students
for each level of mastery in Bloom’s Taxonomy
(Scott, 2003). Because of this, teachers cannot
accurately assess the depth of mastery for individual
students. A solution was to use Bloom’s Taxonomy
to assess the cognitive difficulty of computing
courses in an IT program by formulating and
calculating a Bloom Rating (Oliver et al 2004). A
Bloom level was assigned to each test question
according to the level of cognitive behaviour required
to properly answer it. Using a Bloom Rating, based
on the above work, a Bloom-based course assessment
tool could be constructed and deployed in a second-
level programming course (Burgess, 2005). The
result is the assignment of a grade, based on objective
measurements of learning outcomes. The paper
describes the cognitive tasks required at each of the
three grade tiers. Finally, Manaris et al. (Lister and
Leaney, 2003) applied BT within CS to specify
learning objectives of human-computer interaction
courses. They presented a collection of courses for
various target audiences, including freshman non-
majors, junior/senior majors, and graduate students.
For each course, they provided an outline containing
learning objectives using BT, the amount of time to
be spent on each topic, and related in-class activities.
A closely related research was also done by
Thompson et al. They focused on computer science
assessment (Thompson, 2007). Their main goal was
to use Bloom’s Taxonomy to assist in designing
introductory programming examinations. Research
that is more recent was done by Starr et al., which
focused on specifying assessable learning objectives
in computer science (Starr et al., 2008). They believed
that their idea of integrating Bloom’s Taxonomy with
computer science curriculum had made their faculty
communicate more effectively, and the department’s
assessment program stronger. Other research work
that was completed for specific computer science
areas of education using Bloom’s Taxonomy includes
a test-driven automatic grading approach for
programming (Hernán
-Losada et al., 2008), Bloom’s
Taxonomy levels for three software engineer profiles
(Borque et al. 2004), and Bloom’s Taxonomy for
system analysis workshops (Yadin,2007).
In addition, the use of existing taxonomies is not
as efficient for computer science. We address a novel
aspect of the problem. From Kolb (Kolb, 2005) we
know that different people can enter the learning
cycle at different points. We modify revised BT to
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
286

show how BT-cognitive thinking would be more
applicable for computer science than the existing
generic ones.
Let us explain an overview from “Conceptual
Knowledge Space,” Javed I. Khan, Yongbin Ma,
Manas Hardas (Khan, Ma, and Hardas, 2010). They
demonstrate how courses can be composed, based on
knowledge ontology.(Hardas,2011) present a novel
methodology to evaluate the bottom up technique for
teaching programming concepts, based on theory of
constructivism from educational psychology.
Educators in teaching employed their technique;
students do not employ or are not able to employ the
bottom up technique of constructing concepts in
learning. Most of the previous work does not focus on
building automatic models to assist in analyzing
domain concepts in level of cognitive skills. Our
automatic model builds the domain concepts as graph
and classifies cognitive skills between domain
concepts. The next section will explain Computer-
Science based Cognitive Domain (CSCD) by more
details.
3 COMPUTER SCIENCE BASED
COGNITIVE DOMAIN (CSCD)
Although we are using the basic Bloom Taxonomy
framework (CSCD) for this paper, CSCD was
introduced that provides a more flexible structure,
facilitating the classification of Knowledge domain.
The main goal for creating this new framework is to
provide an effective ordering of BT cognitive skills
for the computer sciences. CSCD introduces useful
specific-hierarchy to the existing Bloom Taxonomy.
BT of the cognitive skills has had a considerable
impact in the last fifty years. However, this does not
mean that their use is unproblematic. We create
CSCD to provide a more practicable framework for
assessing the domain knowledge within the CS realm.
Figure 1 illustrates CSCD. CSCD represents a new
understanding the at the “Understanding and
Remembering” level to explain the ability to
understand. The names of the levels are taken from
the revised version of Bloom’s, as we feel they are
sufficiently unambiguous. It is understood that the
learner must traverse each level in strict sequence. It
is not practical to begin the synthesis (Create) Level
first, because of the degree of competency required
through the Understanding and Applying Levels.
Before we proceed, it is useful to attempt to
understand and define what the plausible pieces of a
learning concept object (LeCon) are so that we can
proceed to model the requirements for achieving
Figure 1: Parts of a learning concept.
various learning skill levels, as defined by BT. A
learning concept is a unit of knowledge, which is the
target of learning. It can be a topic such as “insertion
sort,” “recursion”, “cache”, “disk scheduling,” etc.
LeCon objects have their parts and special
behaviours. A teacher would like to teach these
concepts via teaching various parts of the concept.
We define at least five generic parts for the LeCon
object:
(O) = {D, P, C, X, E } (1)
Question according to the level of cognitive
behaviour required to properly answer it. Using a D:
is the definition of the object O. Normally, it is a
formal statement of the meaning of the pertinent
concept. It is often a single sentence to a paragraph
description of the salient aspects of the concept.
Normally a LeCon will have a descriptive tile phrase.
The next important set of descriptions, are the
various properties, features, or aspects of the concept
taught. Each reinforces the understanding of the
learner about the core concept. We refer to these as
P= the set of properties of O. There are various ways
to classify the properties of a concept. We will
distinguish between functional/expressive properties
as (
) and the other internal properties as (
). The
functional or expressive properties of a concept are
those, which are related to the use or application of
the concept and must be understood by a learner to be
able to apply the concept. For example, a “car” will
have properties such as its maximum speed, color,
weight, seating capacity, fuel consumption, brand
name, etc. Depending on the goal of learning, certain
types of properties are more important than others. To
be able to use a car, it is important for the student to
know about its functional properties, such as a car
takes people from one place to another, it has seating
capacity, speed etc. Certain properties such as color,
brand, or type of break system may not be as
important to be able to use the car. To understand a
topic, often it is also important to understand its
composition. C is set of sub-components of the
ConceptualizetheDomainKnowledgeSpaceintheLightofCognitiveSkills
287

objects of O. Each member of C is also a learning
concept in itself. Knowing an object often requires
one to know what it is made of. The main object can
be more than the sum or union of the sub-objects, or
in other words, it is not necessary to have the equality:
C≥C
(2)
X = is the set of inter-relationships between sub
components. A deeper learning not only requires one
to know C, but also the relationships of Ci that
resulted in the C. We also clarify that that no
inheritance or preservation rule applies to LeCon
objects. Property set of the parent object O can be
different from the union (or some of the properties of
its components). For example, none of the
components of an aircraft can fly individually, but
together an airplane can fly. It is also possible that
properties of sub objects Ci will not be present at all
in the total object O. We further identify an
interesting quantity I, where I represents Innovation,
which refers to the emergent properties of an object:
=
−∪
)
(3)
Finally, to learn an object one also needs to know the
context of its functional property. We denote this by
E, where E is the environment in which the
subcomponents of O as well as O interact. For
example, for a car to transport a set of individuals
from one location to another it is not enough to know
that a car can transport people; you must know the
destination, the route, the number of people, the
capacity of the car, etc. Properties are meaningful in
a context. The context is defined by another set of
LeCons.
E=Everything-O
(4)
The above parts model now provides us the
opportunity to be more specific in defining the
cognitive skill levels. It is possible to organize the
skill level space in multiple ways and multiple
hierarchies. Below
Fig3.2 is one possible
arrangement.
Remembering (RM2): The minimum and lowest
level of learning is RECALL. In this skill level, the
learner is expected to know the definition (D) and the
properties (P) of the target concepts. This is a
minimum skill level. At the Recall level,
understanding means that student can memorize and
repeat the definition as well as properties and their
values. D+P = RM2 (O)
Knowing (KI2): In the second level of
understanding (which has been stated by Bloom as
the skill level UNDERSTAND or KNOW), we
Figure 2: Learning skill levels with model Element
Requirements.
require the learner to understand the meaning or
semantics of the named properties besides knowing
the values of the properties. For example, if a student
knows that a car has rear disk brakes, then she/he has
attained at least the RECALL level of understanding.
However, if the student understands what rear disk
brakes are, how they operate, and what the
implication of having such brakes are, that will
indicate the KNOW level of understanding. KI2
requires all of RM2, plus knowing the semantics.
Thus, K12 is a higher-level skill than RM2.
Consequently, D*+P* = KI2 (O).
For example if we have a car as an O at the RM2
skill level, one must be able to know the name,
manufacturer, model, color, shape of the car. It
represents memorizing basic information about the
car. One should also know the most important
properties of car such as movement, engine type, and
gas consumption, etc. However, at the higher KI2
level of understanding, one should also know the
function of each part such as the engine, which
converts the chemical energy into rotation energy to
move the car; or the brake system, which slows down
the car or stops it. After mastering all sub-levels of
Remembering and Understanding one will be able to
move to the next level of thinking, as in Figure 2.
There are some cases of not master all thinking skills
at the Remembering and Understanding levels, but
still moving to the next thinking level with a
knowledge gap.
Analysis level (AN2): The next higher level of skill is
the further ability to understand the composition of a
concept. This is the knowledge level at which one
knows the components of O. Mental ability is to
determine how the components relate to each other,
what the differences are between them, as well as
being able to distinguish between components. For
example, one can break a car into a number of C.
Chassis (C
) which holds everything on the car, body
(C
) which has the engine, passenger compartments,
the back seat, and transmission system (C
), which is
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
288

responsible to control the speed, etc. One must be able
to relate how these individual parts work together to
give rise to the key functional properties of a car. To
be able to attain this level he/she must master all
knowledge needed in the KI2 level. D*+P*+C =AN2
(O).
Applying level (AP2): The next level of a skill applies
the concept in various situations. To apply a concept
one must know the functional properties of the object.
However, it is not enough to know the functional
properties. As a requirement, one should know the
environment and real-world constraints (E). For
example, to be able to apply a certain type of car to
solve certain types of transportation problems, one
must know the factors such as road, distance, etc.
Depending on the object, O, E will normally require
a specific but wider set of other concepts to be known
at semantic depth. Thus, AP2 is a higher-level skill
than KI2. However, one can attain AP2 level without
learning the composition of O. Conversely, one might
know the composition of an object without knowing
how to apply it. Thus, AP2 is not necessarily a higher-
level skill than AN2 or vice versa. D*+P*+E*=AP2
(O).
Evaluating level (EV2): The next higher-level skill is
the ability to evaluate an object. So, what is needed to
be able to evaluate a concept? There can be at least
two types of evaluations; functional and
compositional. General evaluations will require all
the knowledge skill of AP2 and AN2. In additional, it
will require knowledge about multiple instances of
the object. Additionally, it will require a judgment
based on some form of measurement criteria and
standards through checking and analyzing. Thus,
concepts specific to the later must be known. For
example, to evaluate a car, one must know about
multiple instances of a car to compare their functional
properties such as speed, fuel consumption,
durability, etc. The learner may also be able to
compare the composite objects such as engine type,
break type etc. Finally, one must know associated
mathematical concepts to measure those.
Creating level (CR2): One of the highest levels of
skill is creating. So what is needed to create object O
(the subject or creation)? For most target driven
creations (regardless if it is of an engineering nature),
the specific application is the motivation. Thus, it is
essential for a creator to be at the AP2 level to start
with. In addition, the creator must also know about
the individual components (C), and how to combine
them. The creator must also know about the
properties of the components (C), and how the
properties of these components interact among
themselves (X). The creator is able to solve the puzzle
of creating the emergent property (I) from the
functional properties of the components.
Creation is such a high-level skill that one more
discussion in needed to illustrate the knowledge level
of this skill. Once an invention is made, if a student
knows D, P, C, X, E he has acquired the theoretical
minimum skills needed to create. However, the first
inventor normally would have to have much wider
knowledge. He or she is not given the answer. The
first inventor is required to experiment with a much
larger set of C* (and their properties) to invent which
specific combination of C will create the target I.
4 BLOOM TAXONOMY
RELATIONAL MODEL (BTRM)
In this section, we present a method to classify
domain knowledge into different BT-cognitive levels
Figure 4 illustrates the overall system architecture of
our BTRM model. Our model has two symmetrical
parts. One part is Semantic Analysis and the other is
BT-Relationship Extraction. Text in both stages goes
through various steps. The objective of part one is to
identify all the domain sentences within the text. The
process divided into different tasks, phrases
extraction, POS-tagging, stemming and stop-word
filtering. Algorithm 4.1 shows the functionality of
Semantic Analysis.
Figure 3: Overview of BTRM.
In the semantic analysis part, a pre-processing of
text should be applied using Algorithm4.1.
Input :( t: text as string)
Output: A= (A: as a 3D Matrix)
Def Extraction(S: text, alpha:
Integer, Type: string):
For each word w in text S
Set T=Type of w in S
Set p=position of w in S
Set Tag=Tagging of w in S
For w in S:
//Check word in the sentence
If w [1][0]= "V"or w[1][0]= "N"
Then:
ConceptualizetheDomainKnowledgeSpaceintheLightofCognitiveSkills
289

Count=count+1
Check[w].Type=w[1][0]="V":
Vlist[].append(w[0],count)
Else:
Nlist[].append(w[0],count)
End If
Def Check_Pos(Vlist,Nlist,p):
LNOUN=[] ,FNoun=[],VList=[]
For each Noun n in Nlist:
//Check the Leader noun and the Follower
noun for the verb in the sentence.
If n in Nlist < p:
LNOUN.append(n)
Else
FNOUN.append(n)
End if
End for
Return LNOUN,FNOUN
Def BuildMatrixA(LNoun,V,FNoun,W)
// based on Nouns AND Verbs
For each w in S:
A=NP.ZEROS([len(LNoun),len(V),len(FNoun
)])
For i in range(len(LNoun)):
i=LNoun.index(Pattrenlist[0])
For j in range(len(V)):
j=V.index(Pattrenlist[2])
For K in range(len(FNoun)):
K=FNoun.index(Pattrenlist[3])
End For
End For
End For
A[i][j][k]=A[i][j][k]+1
Return A
The algorithm4.1, shows the functions, which
includes reading the texts (textbook) to separate it
into sentences. In order to find out the boundaries of
the sentences. We use the period (.) in order to
determine the end and start point as in (Johnson and
Fuller 2006). The following is an example from the
textbook:
S1: {The heap sort algorithm starts by using build
max heap to build a max heap on the input array.} S2:
{The heap sort algorithm repeats that for the
maxheap.}.Then, Phrase-Extraction applies to
extract all domain-specific concepts by using N-gram
algorithm (Cavnar and Trenkle) an n-gram is a
sequence of n words in this paper n=1, 2, and 3 was
used. We say that an N-gram occurs in a text if these
domain concepts appear in the text in the same order
immediately one after another.
Next, the tokenization is used to tokenize each
sentence. Once the tokenization is complete,
PoSTagging procedure is used as a Parsing task. We
perform this in order to gain understanding of the
precise meaning of the sentence, using Stanford
parsing (De Marneffe el at. 2000).
Algorithm 4.1 is included three different parts:
Def Extraction, Def Check_Pos, and Def
BuildMatrixA for Extraction finds the type of the
word in the text where Type [Leader-Noun, Verb, and
Follower-Noun]. Def Check_Pos checks if the
position of the word in the sentence verb or noun and
if a noun check it if a leader-noun or Follower -noun
of the verb. If so save the word and the position of the
word in the text in checklist dictionary.
After the pre-processing step, we identify j as the
index of the verb in verb list, i as the index of the
leader concept and k is the index of the follower
concept in the concept list. We create a three
dimensional frequency matrix A
[LNoun][V][FNoun] = A(i,j,k) to capture the three
way associations between each leader concept, verb,
follower concept triple found in the text. Each cell of
the matrix A contains binary representations of the
noun as follows: zero (0) represents the noun
concepts that do not connect with other nouns in the
sentences by verb(s), and one (1) represents the noun
concepts that connected with verb. The output from
semantic analysis part is used as input to the next step.
The second part of our model is BT-Relationship
Extraction. Before starting the extraction part some
important steps is required algorithm 4.2 explains the
steps.
Input: A= [LNoun][V][FNoun]
//from the previous step and BT= []
//Bloom Taxonomy verbs list
Output: U matrix // Dimension Reduction
Matrix
A=NP.loadA (A= [LNoun] [V] [FNoun],
delimiter=",")
Def Calculation ( ):
U,S, VT = SVD(A)
// where U, S, VT are a matrixes
UR=U [: 0:3]
//The dimmintiaonl Reduction of U
VR=VT [0:3:]
//The dimmintiaonl Reduction of VT
Def verbClassify ():
L, V, F ← GetAll (SD)
//L:leader-noun,V:verb,F:follower-noun
A [L][F][V] =0
A [L][V][ F] ← SD
// SD: GenerateConceptLinkerCube.
For each sd ∈ SD Do
T<L, V, F> ← GetTuple (SD)
// Tuple data structure
For each t in T:
If (t not in A):
A [t(0)] [t(1)] [t(2)]=1
Else
A [t (0)] [t(1)] [t(2)]++
End For
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
290

U, D, VT ← SVD (A)
For all v ∈ V [ ] do:
Dicknown, dickunnown ← Checkclass
VCS, VBT)
V-Class ← ComputeNearstNighbor
(VCS)}
Def Checkclass (VCS, U [], VBT):
Dic-VBT= {}
//DICTIONARY TO SAVE BLOOM VERBS
V-Dimension= []
//Verb dimension from U matrix
Dicknown= {}
// LIST OF VERBS FOUND IN BLOOM LIST
Dickunnown= {}
//LIST OF VERBS NOT FOUND IN BLOOM
Key, value=line. Strip ().split ()
If key in dic-VBT.keys ():
Dic-VBT [key].append (value)
Else:
Dic-VBT [key] = [value]
V= dic-VBT
i=0
While (1):
i=i+1
For item in dic-VBT:
If item in dic-VBT.keys ():
Dicknown [item] =dic-VBT [item]
Else:
Dickunnown [item] = []
Return Dicknown, Dickunnown
In this part, verbs are classified based on Latent
Semantic Analysis (LSA). LSA is a theory and
method for extracting and representing the usage
meaning of domain concepts by statistical
computations (Landauer et al. 1998). The process is
divided into tasks; calculating SVD to divide the
matrix A into three matrixes, and finding verb level
in Bloom Taxonomy applying SVD to the matrix (A)
will break down each dimension in the matrix using
equation 5.
)
=
(5)
The final sentence of a caption must end with a
period.
As part of applying SVD (Landauer et al. 1998),
we utilize dimensionality reduction techniques in
Order to reduce the high dimensionality of Verbs
matrix (U). We consider only 2-dimensions. The
reason SVD is
useful, is that it finds a reduced
dimensional representation of our matrix that
emphasizes the strongest relationships and throws
away the noise. This is the key reason for using SVD
to transfer our problem into a mathematical-based
article.
Using Checkclass
function we will check each verb
in the verb list is in Bloom Taxonomy verbs or not. If
Figure 4: Matrix (A).
Figure 5: Matrix (U).
Figure 6: Matrix (S).
Figure 7: Matrix (V).
the verb found in Bloom list will return the verb level
(BL1, BL2, BL3, and BL4) as a verb class. Otherwise
will return not found as in Table 4.1.
Next, we classify verbs using a
Nearest-Neighbour
function, by computing the distance between each
two verbs after the two dimensions extracted from U
matrix. Equation 6 is used to calculate Euclidean
distance (d) between each two verbs.
d
)
=
∑
V
)
(6)
Table 1: Shows the verb dominations extracted from SVD.
Verb Returned-class Dimensions from U matrix
Use BL1 (-0.45,0.65)
Analyze BL3 (-0.86,-0.16)
Start BL3 (-10.-30)
Give BL3 (-0.01,-0.05)
Build Not found (-0.12,-0.39)
Repeat Not found (-0.14,-0.54)
−−−−
−−−−−
−−−−
−−−−−−
−−−−
−−−
=
18.010.069.039.054.014.0
49.032.065.024.039.012.0
17.090.016.036.005.001.0
83.004.0
27.037.030.010.0
03.017.001.044.016.086.0
07.019.004.056.065.045.0
U
=
55.000000
096.00000
0017.2000
00075.200
000007.70
0000054.22
S
−−−−−−−−−−−−
−−−−−−−−−−−−
−−−−−−−−−−−−
−−−−−−−−−−−−
−−−−−−−−−−−−
−−−−−−−−−−−−
=
43.001.022.
001.033.021.033.017.001.018.022.031.0
01.002.014.045.002.082.021.001.021.020.017.032.0
44.022.019.001.001.001.002.004.011.001.018.001.0
07
.019.033.076.021.038.030.016.023.011.001.017.0
01.012.022.086.042.011.026.002.017.018.029.018.0
18.016.002.018.017.018.010.001.018.001.0
64.001.0
T
V
ConceptualizetheDomainKnowledgeSpaceintheLightofCognitiveSkills
291
We need to compute distance between each two verbs
dimensions were normalized by scaling it between 0
and 1 as table 2 shows that and by using Equation 7.
The dimensions are scaled to fit into a specific range.
There are many types of normalization; we use Min-
Max Normalization. Min-Max Normalization
transforms a value D1 and D2 which fits in the range
[0, 1] as in Equation 7.
,01
=
−
−
(7)
Table 2: Normalized Dimensions for verbs.
Verb Dimensions from U
matrix
Normalized
dimension
Use (-0.45,0.65) (1,0.8)
Analyze (-0.86,-0.16) (0.6,1)
Start (-10.-30) (1,0.9)
Give (-0.01,-0.05) (1,0.7)
Build (-0.12,-0.39) (0.8,1)
Repeat (-0.14,-0.54) (0.4,1)
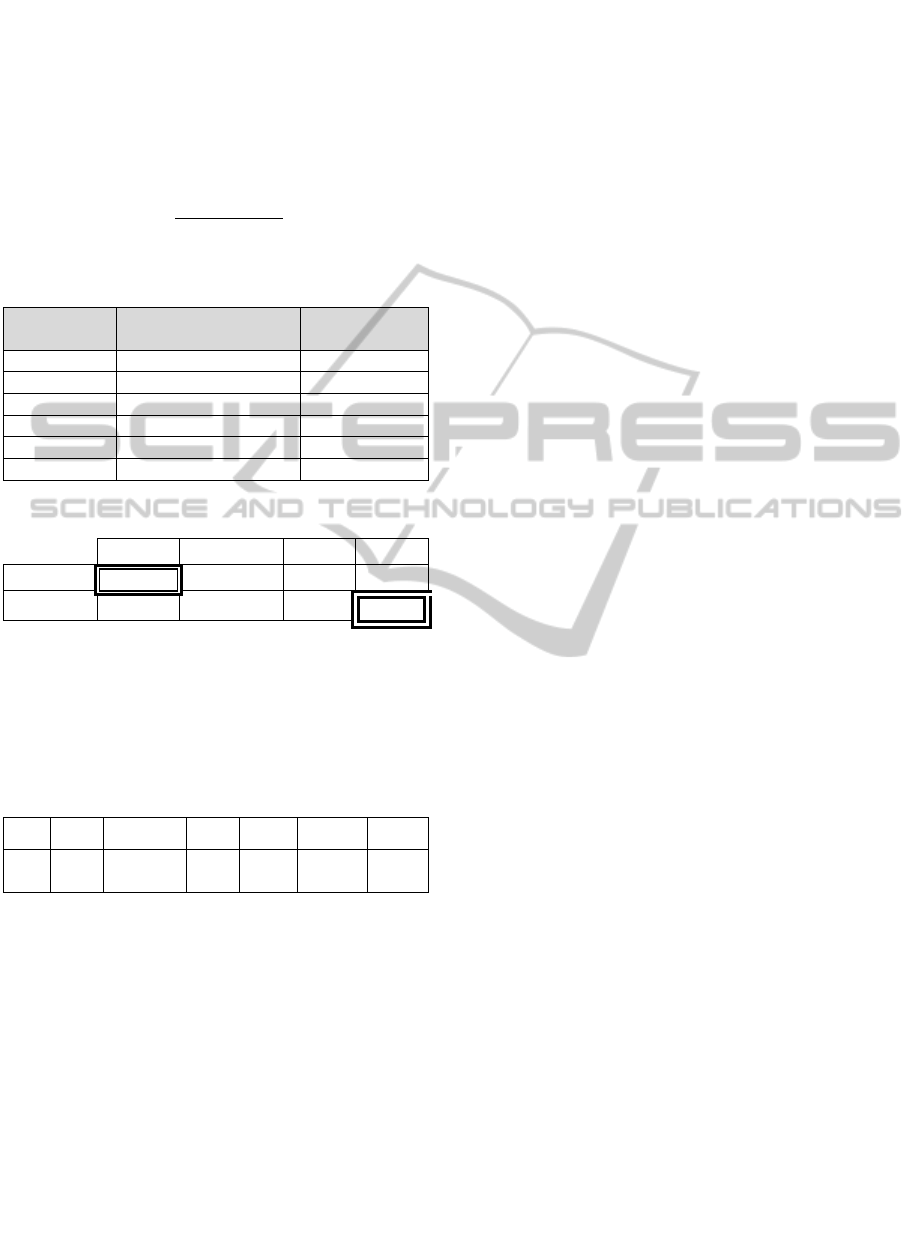
Table 3: Explaining the distances between verbs.
Use Analyze Start Give
Build 0.09 0.30 0.14 0.77
Repeat 1.23 0.90 1.012 0.43
Table 3. Explaining the distances between verbs. We
can see that closest distance for verb Build is Use, and
closest distance for verb Repeat is Give Finally, table
4 illustrates the BT-class for each verb with the name
code for the BT-class explained in section 3.
Table 4: BT-class label for verbs.
verb Use Analyze Start Give Build Repeat
BT-
class
REM ANE APP APP REM APP
After all verbs classified into Bloom Taxonomy we
will start extracting all BT- relations in the sentences
using algorithm 3.
Algorithm 3:
Def Distance (LNoun: list, FNoun: list,
Verb: list, alpha: integer):
Distance=999, alpha=0.5
If len (LNoun)>0 and len (FNoun)>0:
For NN1 in LNoun:
For NN2 in FNoun:
If NN1 [0]! =NN2 [0]:
d1=VV [1]-NN1 [1]
d2=VV [1]-NN2 [1]
D= ((d1+d2)-(2*(d1*d2)))
End If
If D > Alpha
D.remove
Else:
Pattrenlist. Append (NN1
[0], VV [1], NN2 [0], D))
End if
Return Pattrenlist
Three algorithms proposed to accomplish this are
identified as Sentence Co-occurrence of the
Collocation (SCC), Sentence Distance of the
Collocation (SDC) Algorithm, and Reverb algorithm.
In addition, three of them compared with Ground
Truth.
The Initial Algorithm (SCC) extracts all possible
BT relationships from the sentences when Alpha > =
zero. For example, in the triple (‘Heapsortalgorithm’,
‘start’, ‘Buildmaxheap’), verb start indicates the
relationship from Heapsortalgorithm to
Buildmaxheap, but not in reverse. Two domain
concepts, which occur together at least once in a
sentence are considered as valid pairs.
The Secondary Algorithm, (SCD), finds all
possible BT-relations, after filtering all verbs below a
specific Alpha threshold; where Alpha > = 0.5. We
accomplish this by measuring the distance between
the verbs and all possible nouns within the sentence
as in equation 8.
Finally, the ReVerbs algorithm takes a sentence as
input, identifies relation phrases that satisfy lexical
constraints, and then finds a pair of nouns from within
the sentence, and uses the extracted to label each
relation, without requiring any relation-specific
training data (Anthony et at. 2011). Small changes
modified this algorithm after the result was obtained
from the ReVerbs extraction. This is accomplished by
creating a two-dimension matrix just as the previous
two algorithms for comparing the BT relations
extraction.
5 EVALUATION AND RESULT
In order to evaluate the quality of the extracted BT-
relations, we are interested in two different measures.
The first one expresses the completeness of the set of
extracted BT-relations, that is, how many valid BT-
relations are found with respect to the total number of
BT-relations, which should have been found; this is
the recall rate. The second measure indicates the
reliability of the set of BT-relations, that is, how many
valid BT-relations are found with respect to the total
number of BT-relations; this is the precision rate.
These two rates were evaluated using a test sentences
containing all this information
.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
292

To construct this test sentences, we have focused our
attention on twenty-one sentences from introduction
to algorithm book it is contains 59 important concepts
from different topic from the book. In this
experiment, BT-relations between concepts were 40
relations
.
The concepts have been produced by our
methodology. For each of these 59 concepts, and 40
relations a ground-truth extraction of valid-BT and
candidate-BT-relations was carried out. PhD students
had background about the topic were asked to analyze
the sentences and decide what kind of BT-relations
are there. Finally, out of 136 BT-relations 52 of the
BT-relations examined are valid and 47 are
considered as candidate-BT- relations.
The results for each noun are detailed in Table 5.1.
The following table lists the statistics from our
experiments.
Table 5: Statistical of the sentences.
Algorithm Sentences Nouns Verbs BT relations
Ground Truth 21 59 27 39
SCC 21 59 27 15
SDC 21 59 27 40
Reverb 21 59 27 10
We compared the ground-truth data result with three
algorithms, as Figure 8 illustrates below. It is evident
from the chart that the (SDC) Algorithm is far higher
than the other two Algorithms over the valid and
invalid of the extraction of BT relationships.
Figure 8: Comparison of BT Relationships Estimation
Algorithm.
The line graph Figure 9 illustrates the behave of BT-
relations and BT-candidate-relations using an Alpha
(α) threshold that depends on measuring the distance
between verb and two nouns connecting by the verb .
Alpha (α) values is between 0-1 as the Figure shows
number of BT -candidate relations goes down and
number of BT -relation goes higher when (α) greater
than or equal to 0.5. Overall, the BT-relations and the
BT-candidate relations were far higher in the number
of extracted relations from SDC algorithm and less in
the candidate relations throughout the entire Alpha
threshold values.
Figure 9: Alpha threshold to control the extraction for BT
levels.
The line graph Figure 10 below illustrates the
false positive rate for discovering BT in different BT-
levels (REM, APP, ANE, EVA, and CRE) for three
algorithms.
Figure 10: False Positive Error Rate of BT- Relationships
Estimation Algorithm.
We conclude that the SDC algorithm using the
Alpha (α) threshold is greater than or equal to 0.5. In
reducing the false value, the false positive error rate
changed sharply through the levels depending on the
sentences that we have in each level.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This work provides various interesting aspects. First,
we introduce a technique is based on theory of BT-
cognitive skills from educational psychology.
Concepts are taught in an order of increasing
complexity so that complex concepts can be learnt
with the prior levels of simpler concepts that seems to
ConceptualizetheDomainKnowledgeSpaceintheLightofCognitiveSkills
293

dominate knowledge concepts. We test this technique
by students where are asked to analysis some topics
from introduction to algorithm book using Bloom
Taxonomy levels compared with automatic technique
to make operational conclusions though having many
benefits, its principal weakness is that the levels do
not appear to be well ordered when used to assess
practical subjects. Our recommended solution is to
use the new framework BT cognitive skills. This
removes the strict ordering, while retaining many of
the concepts of Bloom’s taxonomy. This generates a
way that can be used to identify a range of different
learning trajectories. In addition, for discovering BT-
relations, we obtain strong results on strength
relations; experimental results show an accuracy of
65.5%, which is significantly high.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We take this opportunity to thank all the reviewers for
this paper for the suggestions that provide helpful tips
to improve the paper.
REFERENCES
Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., Airasian, P. W.,
Cruikshank, K. A., Mayer, R. E., Pintrich, P. R., ... and
Wittrock, M. C. (2001). A taxonomy for learning,
teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom's
taxonomy of educational objectives, abridged edition.
White Plains, NY: Longman.
Bloom, B. S., and Krathwohl, D. R. (1956). Taxonomy of
educational objectives: The classification of
educational goals. Handbook I: Cognitive domain.
Bourque, P., Buglione, L., Abran, A., and April, A. (2003,
September). Bloom's taxonomy levels for three
software engineer profiles. In Software Technology and
Engineering Practice, 2003. Eleventh Annual
International Workshop on (pp. 123-129). IEEE.
Burgess, G. A. (2005). Introduction to programming:
blooming in America. Journal of Computing Sciences
in Colleges, 21(1), 19-28.
De Marneffe, M. C., MacCartney, B., and Manning, C. D.
(2006, May). Generating typed dependency parses from
phrase structure parses. In Proceedings of LREC (Vol.
6, pp. 449-454).
Doran, M. V., and Langan, D. D. (1995, March). A
cognitive-based approach to introductory computer
science courses: lesson learned. In ACM SIGCSE
Bulletin (Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 218-222). ACM.
Fader, A., Soderland, S., and Etzioni, O. (2011, July).
Identifying relations for open information extraction. In
Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods
in Natural Language Processing (pp. 1535-1545).
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Hernán-Losada, I., Pareja-Flores, C., and Velazquez-
Iturbide, A. J. (2008, July). Testing-Based Automatic
Grading: a proposal from Bloom's taxonomy. In
Advanced Learning Technologies, 2008. ICALT'08.
Eighth IEEE International Conference on (pp. 847-
849). IEEE.
Johnson, C. G., and Fuller, U. (2006, February). Is Bloom's
taxonomy appropriate for computer science?. In
Proceedings of the 6th Baltic Sea conference on
Computing education research: Koli Calling 2006 (pp.
120-123). ACM.
Jurafsky, D., and Martin, J. H. (2000). An introduction to
natural language processing, computational linguistics,
and speech recognition.
Kolb, A. Y. (2005). The Kolb learning style inventory–
version 3.1 2005 technical specifications. Boston, MA:
Hay Resource Direct, 200.
Landauer, T. K., Foltz, P. W., and Laham, D. (1998). An
introduction to latent semantic analysis. Discourse
processes, 25(2-3), 259-284.
Lister, R., and Leaney, J. (2003, February). Introductory
programming, criterion-referencing, and bloom. In
ACM SIGCSE Bulletin (Vol. 35, No. 1, pp. 143-147).
ACM.
Lister, R., and Leaney, J. (2003, January). First year
programming: let all the flowers bloom. In Proceedings
of the fifth Australasian conference on Computing
education-Volume 20 (pp. 221-230). Australian
Computer Society, Inc..
Machanick, P. (2000, May). Experience of applying
Bloom’s Taxonomy in three courses. In Proc. Southern
African Computer Lecturers’ Association Conference
(pp. 135-144).
Manaris, B. and McCauley, R. Incorporating HCI into the
undergraduate curriculum: Bloom's taxonomy meets
the CC'01 curricular guidelines. Frontiers in Education,
2004. FIE 34th Annual Meeting, 2004, T2H/10-
T2H/15.
Oliver, D., Dobele, T., Greber, M., and Roberts, T. (2004,
January). This course has a Bloom Rating of 3.9. In
Proceedings of the Sixth Australasian Conference on
Computing Education-Volume 30 (pp. 227-231).
Australian Computer Society, Inc.
Porter, M. F. (1980). An algorithm for suffix stripping.
Program: electronic library and information systems,
14(3), 130-137.
Scott, T. (2003). Bloom's taxonomy applied to testing in
computer science classes. Journal of Computing
Sciences in Colleges, 19(1), 267-274.
Starr, C. W., Manaris, B., and Stalvey, R. H. (2008).
Bloom's taxonomy revisited: specifying assessable
learning objectives in computer science. ACM SIGCSE
Bulletin, 40(1), 261-265.
Thompson, E. (2007, January). Holistic assessment criteria:
applying SOLO to programming projects. In
Proceedings of the ninth Australasian conference on
Computing education-Volume 66 (pp. 155-162).
Australian Computer Society, Inc..
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
294

Yadin, A. (2007). Implementation of Bloom’s Taxonomy
on Systems Analysis Workshops. In Proceedings of the
AIS SIG-ED IAIM 2007 Conference.
Khan, J. I., Ma, Y., and Hardas, M. (2006, December).
Course composition based on semantic topical
dependency. In Web Intelligence, 2006. WI 2006.
IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on (pp. 502-
505). IEEE.
Hardas, M. An Evaluation of the Constructive Teaching
Methodology of Programming Concepts.
ConceptualizetheDomainKnowledgeSpaceintheLightofCognitiveSkills
295
