
A Modular and Flexible Identity Management Architecture for National
eID Solutions
Thomas Lenz and Bernd Zwattendorfer
Egovnernment Innovation Center - Austria, Inffeldgasse 16a, Graz, Austria
Keywords:
Identification, Authentication, Identity Provider, Federation.
Abstract:
Identification and authentication are essential processes in various areas of application where access to sensi-
tive data needs to be protected and regulated. To achieve this, usually identity-management systems are put into
place, where an identity provider manages digital identities and handles the identification and authentication
process for a service provider, which hosts the protected data. Identity management is no new topic and hence
several identity management systems have evolved over time. However, new rising requirements also demand
modifications and improvements in the field of identity management. In particular, the need for exchanging or
federating identities across domains or even borders requires new interoperable solutions and flexible identity
management architectures. In this paper we present a flexible and modular identity management architecture
which focuses on federation and interoperability capabilities based on plug-able components. Due to that,
new arising requirements such as the support of different authentication protocols can be easily fulfilled by
implementing appropriate plug-ins. Hence, our proposed architecture is especially applicable for high quali-
fied identification systems such as national eIDs and their federation across borders. We further illustrate the
applicability of our architecture by implementing it to be used as an identity provider for Austrian eGovern-
ment applications, on the one side being applicable for national authentications and, on the other side, in a
cross-border context.
1 INTRODUCTION
Electronic identity (eID) is indispensable for a vari-
ety of Internet services and online applications. Once
the identity of communication entities is established
with a level of certainty matching the value associ-
ated with the service, the communication partners can
gain the confidence and trust needed for mutual trans-
actions. Such transactions can include social network
interactions, but also more security-sensitive services
such as a tax declaration or an eHealth application
that protects personal medical data. In each case, be-
sides using an electronic identity authentication is ad-
ditionally required to prove a claimed identity to be
authentic. Consequently, this authentication step link
the identity information to a person, which uses a PIN
or password to proved that he or she is the owner of
that identity information.
The more transactions are performed by using on-
line applications processing sensitive data, the higher
is the importance for a high level of assurance by
secure means of authentication linked to qualified
identity. eGovernment is such an area, where high
assurance in the citizen’s identity is needed. With
respect to eGovernement, several countries have al-
ready developed and deployed electronic identity sys-
tems since the beginning of the 21st century. Given
these identity systems were deployed about more than
a decade ago and since they are still in operation, it
is not too hard to guess that requirements on identity
management solutions have changed over time and
new technologies have emerged. Such technologies
and requirements are not only things like new authen-
tication protocols, which support a higher level of se-
curity, or new identification and authentication mech-
anisms, but moreover are requirements targeting us-
ability, interoperability, or identity-management fed-
erations.
Particularly, identity-management federations
such as nationally federated eID solutions or even
cross-boarder eID federations became more and more
important in the last couple of years. In the case of
cross-boarder eID, the European Commission has
recently published the EU regulation on Internal
Market electronic identification and trust services
(eIDAS)(European Union, 2014), which builds the
321
Lenz T. and Zwattendorfer B..
A Modular and Flexible Identity Management Architecture for National eID Solutions.
DOI: 10.5220/0005443103210331
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST-2015), pages 321-331
ISBN: 978-989-758-106-9
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

legal framework for cross-border eID acceptance
within the EU. However, the eIDAS regulation is
currently only the latest step towards the implemen-
tation of a pan-European eID federation. The aim on
cross-border eID recognition dates already back to
2005, as the aim was mentioned in the Manchester
Ministerial Declaration(European Union, 2005),
followed by the EU Service Directive (European
Union, 2006) in 2006 and the eID large scale pilot
projects STORK
1
and STORK 2.0
2
, which is still
running.
National eID systems have been deployed since
nearly a decade. In order to meet these new or
changed requirements on e.g. cross-border feder-
ation, an improved and enhanced architecture for
identity-management systems is inevitable for meet-
ing those requirements. Therefore, we present an im-
proved identity-management architecture in this pa-
per, which will meet current requirements and which
is open to future extensions.
This paper is structured as follows. In Section 2
general requirements for identity-management solu-
tions are defined. In Section 3, we describe related
work and discuss it with respect to the defined re-
quirements of Section 2. In Section 4, we propose an
enhanced architecture of an identity-management sys-
tem which is capable of meeting all the requirements.
Afterwards, in Section 5 we demonstrate the practical
applicability of our proposed identity-management
architecture by implementing an identity provider for
Austrian eGovernment applications supporting three
main identity-management use cases. Finally, con-
clusions are drawn in Section 6.
2 REQUIREMENTS
Identification and authentication are by far no new
issues, thus several different identity-management
systems have already evolved (Bauer et al., 2005).
In most of these identity-management systems, user
identification and authentication are handled by an
identity provider, which finally transfers the user
information and authentication data to the service
provider. Based on these information and data, the
service provider is able to decide whether to grant or
deny access to its protected resources. Consequently,
the identity provider constitutes a very important en-
tity within an identity-management system. Espe-
cially if the service provider is a public-sector applica-
tion providing eHealth or eGovernment services, the
1
https://www.eid-stork.eu/
2
https://www.eid-stork2.eu/
support of qualified citizen identification and secure
authentication by the identity provider is essential.
Hence, such an identity provider needs to fulfill cer-
tain requirements to meet the high level of assurance
and security required by public-sector applications.
For that reason, the following requirements should be
fulfilled and kept in mind, if an identity provider for
public-sector applications is designed.
• Security: An identity provider for public-sector
applications is typically used in a security-
sensitive area, which handles with highly personal
date, like medical information. Public-sector ap-
plications require a highly secure identification
and authentication process to protect these con-
fidential and sensitive data against unauthorized
access. Furthermore, a public-sector identity
provider needs to be resistant against attacks that
threaten to illegally influence the identification or
authentication result.
• Reliability and Testability: Service providers
that make use of the identity provider must be able
to rely on the results of the identification and au-
thentication processes carried out by the identity
provider. In addition, it should be possible for the
service provider to test and validate the authenti-
cation information to check if the information was
provided from a trusted identity provider and not
from a attacker.
• Flexibility: From a service provider’s point of
view, an identity provider should be able to pro-
vide different standardized interfaces for service-
provider communication, to offer a wide range of
possible connection scenarios. Therefore, flexi-
bility with respect to service providers can reduce
the deployment costs for them. From a citizen’s
point of view, an identity provider should provide
different identification and authentication meth-
ods, in order to being able to support a large num-
ber of users and to enable a simple usage of dif-
ferent secure tokens.
• Interoperability: An identity provider should
be work interoperable with other architectures,
e.g. if the communication with other identity-
management systems is necessary. The require-
ment of interoperability increases because the in-
terconnection of heterogeneous identity manage-
ment systems is important for identity federa-
tion. Especially, this requirement is important for
cross-border acceptance of identity-management
solutions and to interconnect national eID sys-
tems, like a pan-European eID federation.
• Adaptability: In many countries national legal
requirements or eID solutions serving domestic
WEBIST2015-11thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
322

needs exist, which an identity provider has to
comply with. Such solutions – which cannot be
implemented by generic standards – could be a
special secure token or a proprietary national in-
frastructure. Therefore, an identity provider sup-
porting public-sector applications needs to build
on an adaptable framework to fulfill national char-
acteristics and to support proprietary protocols or
architectures.
• Easy-to-Use Technology: The usage of an secure
identification and authentication process should
not impede usability and accessibility for both cit-
izens and service providers. Therefore, an identity
provider should provide a recognizable user inter-
face and enable a safe and known usage with this
security-relevant application. Furthermore, this
requirement covers several more aspects such as
hiding complexity for service providers or plat-
form independence to reduce deployment costs.
• Modularity: An identity provider should have
a modular architecture, because modularity is in
line with flexibility and interoperability. There-
fore, a modular architecture facilitates the imple-
mentation of new functionalities to meet new re-
quirements with respect to interoperability, stan-
dardized interfaces, or new identification or au-
thentication methods.
There exists some other works, which handles
with requirements for identity management systems
(K
¨
olsch et al., 2011; Ferdous and Poet, 2012). There-
fore, we use requirements of this related work in com-
bination with our own experience to defined a non-
exhaustive enumeration of requirements. This defined
requirements are rather generic to be not bound to a
special national identity-management system. In the
next section, available identity-management systems
are surveyed and their capabilities to meet the above
defined requirements are assessed.
3 RELATED WORK
Numerous identity-management initiatives and sys-
tems exist, therefore we will briefly introduce a cou-
ple of systems that gained importance either due to
their broad use, or as they established relevant stan-
dards.
First systems used simple directory based solu-
tions, like LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Pro-
tocol), to perform identity management for single
organisations. Since the borders between organi-
sations decrease, interoperable identity-management
becomes more and more important. In order to man-
age this, identity management has to be dynamic and
adaptable in different and more complex situations to
handle more then one specific context. This resulted
in more adaptable solutions, like Kerberos (Neuman
et al., 2005), which is one of the earliest systems that
allows secure authentication in unsecure TCP/IP net-
works.
With the increasing popularity of the World Wide
Web, more sophisticated identity-management solu-
tions, which allow secure authentication on applica-
tion level, became popular. Therefore, within the Web
new identity-management systems emerged, such as
Shibboleth
3
or the Kantara initiative
4
(formerly the
Liberty Alliance Project). Both projects influenced
the development of the current version of the Security
Assertion Markup Language (SAML 2.0) (Lockhart
and Campbell, 2008). SAML has been developed by
OASIS and defines one of the most important stan-
dards dealing with Single Sign-On or identity federa-
tion. A similar framework constitutes WS-Federation
(Kaler and McIntosh, 2009), being part of the WS-
Security (Nadalin et al., 2006) framework. Another
decentralized authentication system on the Web de-
fines OpenID
5
.
All above mentioned identity-management solu-
tions could be used to perform a secure identifica-
tion and authentication process, but most of them are
limited to a single or few authentication protocols or
standardized interfaces, which are used for service
provider communication. Another issue is that they
may not meet national legal requirements for qualified
identification or authentication in security-sensitive
areas of application as those identity-management
systems have been designed generic. For instance,
several countries use proprietary protocols or special
eID infrastructures, like electronic mandate services
for example, which can be used to add additional in-
formation to an authentication process. Furthermore,
interoperability and federation with other eID solu-
tions gains importance. While some of the previously
described identity-management systems support fed-
eration, this is only possible when interconnecting
systems with the same basic architecture or underly-
ing protocol. However, currently used national eID
systems have a heterogeneous structure, which means
that different communication and variegated imple-
mentations are in use which hinder interoperability
and identity federation.
In summary, there is currently no perfect solution
available, which directly is able to fulfill all require-
ments stated in Section 2. To overcome this problem,
3
http://shibboleth.net/
4
http://kantarainitiative.org/
5
http://openid.net/
AModularandFlexibleIdentityManagementArchitectureforNationaleIDSolutions
323

we propose an enhanced and flexible architecture for
identity-management systems using the example of
an Austrian identity provider. The architectural de-
sign of the proposed solution is presented in the next
section.
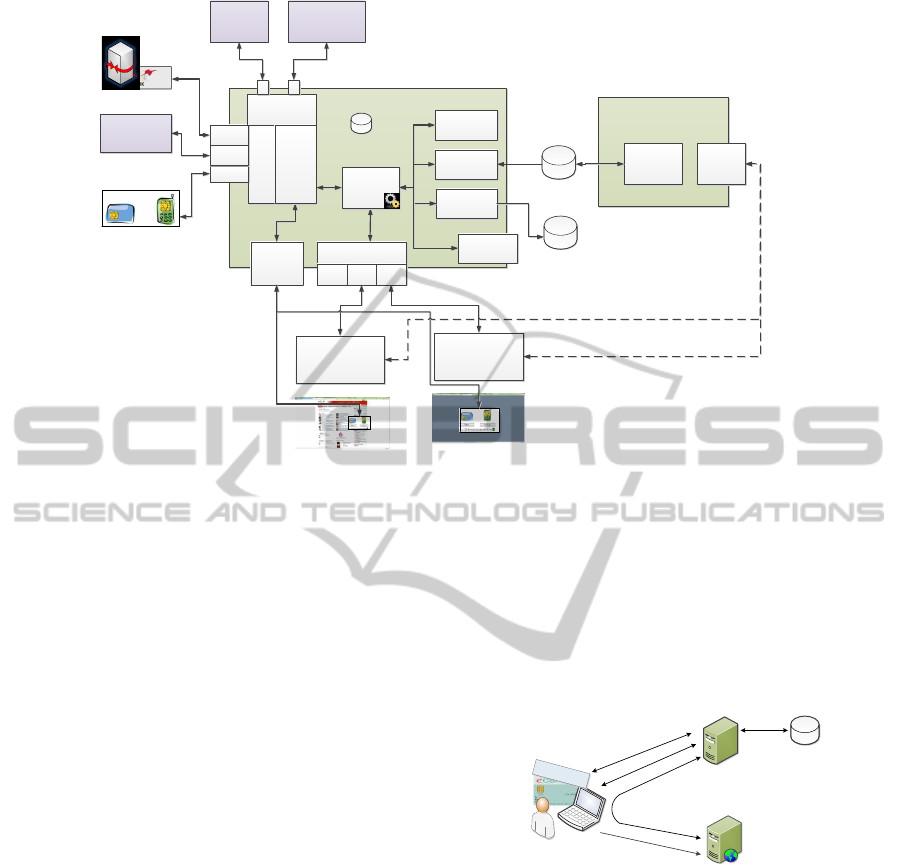
4 ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN
The proposed solution of an advanced identity
provider is based on a sophisticated modular archi-
tecture to satisfy the identified requirements. Figure
1 illustrates our proposal for a modular and adaptable
architecture for an Austrian identity provider, which
can be used for public and private sector applications
authentication. Therefore, our architectural solution
could not only be used in eGovernment applications
(public sector), but also are for a highly secure authen-
tication on commercial applications (private sector),
like a social network or an online shop.
The key component of the solution is the Core
Logic, which coordinates the different steps of an
identification and authentication process. An iden-
tification and authentication process can be divided
into different phases. To better illustrate the features
of the architecture, we will describe it using the ex-
ample of a generic identification and authentication
process. This generic identification and authentica-
tion process describes the components and modules of
our proposed solution on architecture level, but does
not include every single communication step between
the user’s browser and the identity provider, service
provider or other involved entities.
In the first phase, the authentication process is
initiated by a communication between the applica-
tion and the identity provider via a well defined au-
thentication protocol. This communication task is
accomplished by the Protocol Adapter Engine. For
each supported authentication protocol, an appropri-
ate Protocol Plug-in can be implemented. This mod-
ular Protocol Plug-in approach allows the usage of
protocols which are concerted to every single appli-
cation with respect to protocol security and the re-
quired scope of operation. Such protocols could be
SAML 2.0, which is widely in use, OpenID Con-
nect (Sakimura et al., 2014), SAML 1.1 (Maler et al.,
2003) or a national protocol, like the Austrian PVP
2.1 protocol (Rainer et al., 2014), for example.
In the second phase, a user could select the au-
thentication method, which he or she wants to use,
if the identity provider supports more the one iden-
tification and authentication solutions. This task is
carried out by a Template Generator, which gener-
ates a specific HTML Web interface providing the
appropriate user interface depending on the selected
authentication method. Every Web interface is gen-
erated dynamically depending on actually supported
Authentication Plug-ins and application-specific in-
formation. This dynamically generated Web interface
satisfies the requirement of an Easy-to-Use technol-
ogy, because it provides a uniform interface to enable
a safe and known usage of this security-relevant pro-
cess step.
The third phase performs the technical identifica-
tion and authentication operations. Our solution sup-
ports different high secure identification and authen-
tication methods, which are collected and handled by
an Authentication Source Engine. An identification
or authentication step is realized as a single Plug-in.
Such Plug-ins implement the communication with a
secure token, like a smart-card, a hardware security-
module (HSM), or the communication with another
identity-management system, by using a well-defined
interface, like STORK for example. A Process Flow
Engine combines the single Plug-ins and these func-
tionality to a well defined identification and authen-
tication process flow. Every process flow, which is
offered by the Process Flow Engine, is specified in
a XML based configuration file by using an expres-
sion language. This expression language can be used
to define single identification or authentication task,
transactions between single tasks, and conditions for
every transaction.
An additional Attribute Engine can be used in
a fourth phase. This Attribute Engine manages At-
tribute Provider Plug-ins, which can be used to col-
lect additional authentication attributes. Such at-
tributes could be an electronic mandate in case of
an authentication on behalf of somebody or other in-
formation collected from a national register, like the
Austrian Source-Pin Register, which could be used to
receive an additional unique identifier for this user.
In the last phase, the collected authentication in-
formation is processed to generate an authentication
protocol specific authentication token, which is trans-
mitted to the application by using a Protocol Plug-in.
This modular approach allows the definition of vari-
ous slightly different identification and authentication
processes which satisfy the requirement of every ap-
plication.
An additional feature of our architecture is a
generic interface, which can be used to add new func-
tionality to the Core Logic. The generic interface also
uses Plug-ins to add new features to the core func-
tionality. Such Plug-ins could implement features
like Single Sign-On methods, monitoring and testing
functionality, or a plug-in, which collects anonymised
statistics information for quality assurance. To ful-
WEBIST2015-11thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
324
Private Sector
Applications
Public Sector
Applications
Identity Provider
Auth
Sour
-ces
STORK
V-IDP
BKU
Protocol
Adapter Eninge
SAML PVP OpenID
Mandate
Service
Template
Generator
Citizen card
CORE
LOGIC
Source PIN
Register
Configuration
Configuration WEB-GUI
GUI
CORE
LOGIC
Session
Information
Statistics
Single Sign-On
&
Single LogOut
Statistic
Module
Monitoring &
Testing
Module
Configuration
Module
C-PEPS
Other
IDP
Interfederated
IDP
Attribut
Engine
Process
Flow
Engine
Figure 1: Enhanced architecture of the Austrian public sector identity provider.
fill the requirement of an Easy-to-Use technology, a
Web based management application, which provides
a graphical interface to application administrators,
can be used to configure the identity provider.
5 IMPLEMENTATION
The practical applicability of the proposed architec-
tural design has been evaluated by realizing and im-
plementing an identity provider in practice. To illus-
trate that, we have implemented an identity provider
for Austrian eGovernment applications. Our imple-
mentation is based on Java, thus achieving platform
independence and an easy deployment on heteroge-
neous server infrastructures. The next sub-sections
discuss three practical use cases and their implemen-
tation by using our architecture in more detail.
5.1 Use Case 1: Austrian Citizen
Authenticating at an Austrian
Service Provider
In Austria, unique citizen identification and secure au-
thentication is based on the technology-neutral con-
cept of the Austria citizen card (Leitold et al., 2002).
Currently, the Austrian citizen card is implemented
as a client-side approach using smart cards and as
a server-side approach involving the citizen’s cell
phone. Unique identification of a citizen is done by
using a special XML data structure which is stored
on the citizen card. Authentication is based by the
creation of a qualified electronic signature. Since the
Austrian citizen card is the official eID in Austria, a
basic functional requirement of an Austrian identity
provider is the support of the Austrian citizen card.
Figure 2 illustrates the involved entities and their in-
teractions in case of an identification and authentica-
tion process.
Service Provider
Service Provider
Identity Provider
Identity Provider
Citizen
Citizen
Browser
Browser
1
.)
,
7
.)
Client Middleware
2
.)
,
6
)
2
.)
,
6
.)
3
.)
4
a
.)
,
4
b
.)
Additional
Attributes
5.)
Figure 2: Involved entities in an identification and authenti-
cation process in Austria.
According to Figure 2, the process of identifica-
tion and authentication involves the following steps:
1. A citizen wants to access a protected area on a
service provider, by using a HTTP GET or HTTP
POST request. This area requires citizen card au-
thentication.
2. Therefore, the service provider starts an authenti-
cation process by triggering the identity provider.
The identity provider is triggered by the service
provider, which sending an authentication request
via a specified authentication protocol. Most
authentication protocols use HTTP POST or an
HTTP Redirect with GET parameters to send an
AModularandFlexibleIdentityManagementArchitectureforNationaleIDSolutions
325

authentication request from service provider to
identity provider via the user’s browser. To fulfill
the requirements of flexibility and interoperabil-
ity and to support service providers, which use a
diversified set of software implementations, our
practical solution implements different authenti-
cation protocol plug-ins and hence is able to re-
ceive authentication request using different pro-
tocol formats. Actually, we implemented four
protocol plug-ins to support SAML 2.0, OpenID
Connect (Sakimura et al., 2014), the Austrian-
specific PVP 2.1 S-Profile (Rainer et al., 2014)
and SAML 1.0
6
(Maler et al., 2003)
3. After the authentication request has been pro-
cessed by the identity provider, the identity
provider asks the citizen to select her preferred
authentication method. Therefore, the Template
Generator module, which is part of the identity
provider, generates a web form to illustrate the
different authentication solutions, which are sup-
ported by the identity provider. For Austria as ex-
ample, a smart card based solution and a mobile
phone based solution exists. After the citizen has
selected the preferred solution, the identification
and authentication process is started.
4. The proper identification and authentication pro-
cess is performed by the Process Flow Engine in
combination with the Authentication plug-ins. We
have implemented different Authentication plug-
ins to realize different processes for citizen iden-
tification and authentication. In the following two
sub-steps, we describe the process, which uses the
Austrian citizen card for this purpose, as an exam-
ple. Therefore, a client middleware, which is just
a piece of software (either installed on the citi-
zen’s PC or hosted on a server), facilitating access
to the underlying citizen card implementation. In
this example, a server hosted solution is used to
deploy a JAVA Applet based client middleware
in the citizens browser (Orthacker and Zefferer,
2011).
(a) First, the identity provider identifies the citizen
by using the XML data structure from the cit-
izen card through the client middleware. This
corresponds to the identification step. The cor-
responding plug-in implements the communi-
cation with the middleware and verification of
the XML data structure, which comprises citi-
zen identification information.
(b) Second, the identity provider requests the cit-
izen, via the client middleware, to create a
6
In Austria, SAML 1.0 is widely used as legacy protocol by
existing service providers.
qualified electronic signature for authentica-
tion. This task is also realized as a plug-in
which implements the task specific communi-
cation and validation operations. Especially,
validation is important to comply with the high
security requirements for eGovnernment appli-
cations. Therefore, the electronic signature
must be verified by the plug-in involving appro-
priate certificate revocation mechanisms, for
example.
5. After identification and authentication are com-
pleted, the identity provider could use the At-
tribute Engine to collect additional authentication
information of the citizen. Such additional in-
formation could be electronic mandates, for ex-
ample, which are often used in Austria (R
¨
ossler
et al., 2006). In our architecture, such additional
information can be easily added to the authentica-
tion process by realization of an Attribute Engine
plug-in. Therefore, we implement the communi-
cation with the Austrian electronic mandate ser-
vice by using the Attribute Engine functionality.
6. If all authentication information is collected prop-
erly, the identity provider generates a protocol
specific data structure. This data structure in-
cludes all authentication information that the ser-
vice provider has requested and is transferred to
the service provider.
7. Based on the received authentication information,
the service provider is able to provide the pro-
tected resource to the citizen.
5.2 Use Case 2: Identity Federation
This scenario covers the case, where authentication
information should be transferred from one identity
provider to another identity provider. Such function-
ality brings considerable advantages to heterogeneous
service models, in which service providers are linked
to differed identity providers. Such advantages, for
example are federated single sign-on (SSO) or inter-
action of identity providers which implements differ-
ent identification and authentication methods. Figure
3 illustrates the actors and their relations in a feder-
ated service model. In this use case, every service
provider is registered at a specific identity provider,
similar to Use Case 1 described in Section 5.1, but
in this use case there is the possibility of an authen-
tication data transfer between the individual identity
providers. To transfer the authentication data between
the concerned identity providers, a secure and trusted
communication channel has to be established. We
use the SAML 2.0 protocol to establish a trustworthy
WEBIST2015-11thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
326

communication channel by using the SAML2 Web-
SSO Profile (Hughes et al., 2005) and an exchange of
SAML2 metadata (Cantor et al., 2005). An advantage
of this solution is a high interoperability with other
identity-management systems or identity provider im-
plementations, because SAML2 is supported by al-
most all identity management solutions.
Service Provider 2
Service Provider 2
Identity Provider
1
Identity Provider
1
Service Provider 3
Service Provider 3
Service Provider 1
Service Provider 1
Trust relationship
Identity Provider
2
Identity Provider
2
Figure 3: Overview - Identity federation.
This functionality brings a lot of advantages for
citizens and service providers. In the Austrian eGov-
ernment, there actually exists practical applications
for such an identity federation. We will present two
of these applications next, one for citizens and one for
employees of a public authority.
5.2.1 Federated Single Sign-On (SSO)
eGovernment applications in Austria use a decen-
tralized identity management approach, which means
that service providers deploy there own identity
provider for authentication locally in their service
provider domain. This decentralized approach has ad-
vantages in case of availability and scalability but it is
difficult to provide modern user-friendly functional-
ity, like single sign-on for example. To overcome this
disadvantage, we implement a single sign-on federa-
tion mechanism. Figure 4 illustrates such an applica-
tion scenario graphically.
eHealth Service
eHealth Service
Identity Provider
Service Portal
Identity Provider
Service Portal
eGovernment
Service Portal
eGovernment
Service Portal
Identity Provider
eHealth
Identity Provider
eHealth
Citizen
Citizen
1.)
1.1.)
2.)
Citizen
Citizen
3.), 5.)
4.)
Single Sign-On
Figure 4: Federated Single Sign-On for citizens
According to Figure 4, the login process for fed-
erated single sign-on involves the following steps:
1. The citizen authenticates a single sign-on session
on an eGovernment Service Portal by using the
identity provider, which is dedicated to this appli-
cation. This service portal could be a One-Stop-
Shop for different eGovernmant applications, like
an eHealth Service for example.
2. Second, the citizen wants to use an eHealth Ser-
vice, which operates as a self-contained web ap-
plication. For this purpose, the citizen clicks a
link in the service portal which starts an identi-
fication and authentication process on the eHealth
Service. This link URL include the information of
a possible active SSO session on the service portal
IDP as a HTTP GET parameter, which contains a
unique identifier for the service provider IDP.
3. The eHealth Service requests authentication from
its dedicated identity provider, but in contrast to
Use Case 5.1 the information of an active SSO
session at the Service Portal identity provider is
provided.
4. If an active SSO session information is received,
the identity provider starts an authentication pro-
cess at the declared identity provider and requests
all information, which the eHealth service needs.
The SAML2 WebSSO Profile is used to transfer
authentication data between the identity providers
in an encrypted way. The encryption keys are
shared by using the information in SAML2 meta-
data, which are provided from each IDP. After
successful authentication at the declared identity
provider, the authentication information is trans-
mitted to the eHealth identity provider.
5. At last, the eHealth identity provider could gener-
ate an eHealth Service specific authentication pro-
tocol response and transmit it to the eHealth Ser-
vice.
By using our federated solution, it is possible to com-
bine the user-friendliness of single sign-on solutions
with the availability of decentralized services. Ad-
ditionally, this solution requires no service-provider
modifications because all functionality can be imple-
mented on identity provider side.
5.2.2 Public-Authority Network Gateway
eGovernment services are not only used by citizens,
they are also used by public officials during there oc-
cupation in public administrations. Such public ad-
ministrations are carried out from a private govern-
ment network on public eGovernment services. How-
ever, such administrative operations often require ex-
tensive privileges or additional attributes for security
reasons. Figure 5 shows this use case in a graphical
example. In this example, a public official would use
AModularandFlexibleIdentityManagementArchitectureforNationaleIDSolutions
327

an eHealth Service as part of his work as a civil ser-
vant. Here, the public official could be identified and
authenticated in the secure private network area and
maybe some additional information attributes could
be collected. After this, he could be authenticated
as a civil servant at the eHealth service without full
re-authentication on the eHealth identity provider, by
using identity federation. An advantage of this so-
lution is that there is no adjustment at the eHealth
service necessary because the functionality for pub-
lic officials is encapsulated in the identity provider
functionality and can be also used for other services
providers.
eHealth Service
eHealth Service
Identity Provider
eHealth
Identity Provider
eHealth
Identity Provider
Public authority
Identity Provider
Public authority
Public
Officials
Public
Officials
1
.)
Additional
Attributes
Public Network Area
Private Network Area
2.), 7.)
3
.)
,
6
.)
4.) 5.)
Figure 5: Authentication of public officials on public eGov-
ernment applications.
Both application scenarios can be implemented
easily by using our architectural design and actually
there is a trial period for establishment in Austrian
eGovernement applications.
5.3 Use Case 3: European Citizen with
European Service Provider
The third use case tackles the requirement of a se-
cure and seamless cross-border electronic identifica-
tion, which is part of the European eIDAS regulation
or the STORK 2.0 large scale pilot (Leitold et al.,
2014). Due the mobility of citizens, cross-border in-
teroperability of national electronic identity systems
in the European eID landscape has become more and
more important in the last couple of years. Actu-
ally, every EU member state has implemented its
own identity management service infrastructure. This
circumstance leads to a heterogeneous environment
when these individual solutions should be coupled to
a cross-border electronic identification solution. The
STORK large scale pilots treated with an interoper-
ability framework, which can be used to couple dif-
ferent national eID solutions.
The STORK interoperability framework defines
two different models, which can be used to build up
an interoperability layer between national eID solu-
tions. These models are the Pan European Proxy Ser-
vice (PEPS) model, which is shown in Figure 6(a) and
the middleware (MW) model illustrated in Figure 6(b)
(Zwattendorfer et al., 2013).
The PEPS model uses a proxy-based approach to
encapsulate specifics of the national eID infrastruc-
ture. In this model, a PEPS is a national gateway and
a single point of service for other countries, which im-
plements the cross-border authentication functional-
ity. In contrast to the PEPS model, in the middleware
model citizens are directly authenticated at the service
provider. Therefore, the service provider has to de-
ploy a so-called V-IDP in the service provider infras-
tructure. This V-IDP is the server-side middleware,
which provides all necessary functionality for citizen
identification and authentication. Actually, STORK
implements both models and all possible combina-
tions between them because there are advantages and
drawbacks in both interoperability framework mod-
els. (Zwattendorfer et al., 2013).
Therefore, we implement a solution for our Aus-
trian identity provider, which can be used in both
models in order to enable the widest possible utilisa-
tion. From a national point of view, the implemented
functionality can be separated into two process flows.
5.3.1 European eID to National Service Provider
Flow
This process flow covers the case in which a European
citizen, which does not have an Austrian eID, should
be identified and authenticated to use an Austrian ser-
vice provider. Therefore, we implement an authenti-
cation plug-in, which offers all functionality for PEPS
communication to support the PEPS model, and func-
tionality to identify and authenticate foreign citizens
directly, which is identical to the middleware model.
This direct identification and authentication is actu-
ally implemented for some European member states.
Additionally, a mapping from European authentica-
tion information to national authentication informa-
tion is required to fulfill Austrian legal requirements
and to provide all necessary information to Austrian
service providers (Stranacher, 2010).
eHealth Service
eHealth Service
Identity Provider
eHealth
Identity Provider
eHealth
PEPS
PEPS
Citizen
Citizen
1.)
2.), 5.)
3.2.)
3
.
2
.)
3
.
1
.)
Austria
Member State
ZOLL
DOUANE
Additional national
Attributes
4
.)
Additional national
Attributes
Figure 7: Process flow to authenticate an European citizen
at an Austrian service provider.
Figure 7 illustrates this inbound process flow.
WEBIST2015-11thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
328

Service Provider
Service Provider
C-PEPS
C-PEPS
Citizen
Citizen
Member State B
Member State A
ZOLL
DOUANE
S-PEPS
S-PEPS
Trust
Trust
Trust
(a) STORK - PEPS Model.
Service Provider
Service Provider
Citizen
Citizen
Member State B
Member State A
ZOLL
DOUANE
VIDP
VIDP
Trust
Trust
(b) STORK - Middleware Model.
Figure 6: STORK interoperability framework models
1. A citizen of a member state wants to access a pro-
tected area at an Austrian service provider.
2. The citizen is redirected to the identity provider
and there the citizen has to select the his or her
favourite identification and authentication model.
3. After selection, one of the following solutions is
performed.
(a) Middleware Model: In this case, the identifi-
cation and authentication process is performed
at the Austrian identity provider by using the
citizen’s secure token directly. Consequently,
only information that can be provided by the
secure token can be used for identification and
authentication.
(b) PEPS Model: In this case, the citizen is redi-
rected to the PEPS in the citizen’s member state
and there the identification and authentication
process is performed. By using this model,
some additional attributes could also be pro-
vided by using member state attribute infras-
tructure, which is connected to the PEPS. Af-
terwards, the authentication information is re-
turned by using the STORK communication
protocol.
4. To fulfill Austrian legal and technical require-
ments, the authentication data has to be processed
by the Austrian identity provider. Therefore, we
use the attribute plug-in functionality of our ar-
chitecture to implement a register query plug-in,
which uses the Austrian attribute mapping service
to fulfill these legal and technical requirements.
5. At last, the authentication information is transmit-
ted to the Austrian service provider and the citizen
can access the protected resource.
5.3.2 National eID to European Service Provider
Flow
The second process flow characterises the identifi-
cation and authentication of an Austrian citizen to
access protected resources at a European service
provider. To perform this assignment, we imple-
mented a new protocol plug-in, according to our ar-
chitecture, which implements the STORK communi-
cation protocol for service provider communication.
Therefore, this protocol plug-in can be used to authen-
ticate an Austrian citizen by using his secure token.
If our solution is deployed as a single point of
contact in Austria (C-PEPS) according to the PEPS
model (see 6(a)), then the member state service
provider and the intermediate service provider PEPS
(S-PEPS) can use the functionality of our identity
provider just like an Austrian service provider can do.
In this case all national legal requirements for addi-
tional attribute consuming, like the usage of electronic
mandates, can be easily fulfilled.
The situation is different if the middleware model
is used and our identity provider is deployed as a V-
IDP which operates in the service provider infrastruc-
ture outside of Austria, because some national legal
requirements cannot be achieved directly in this de-
ployment situation. This circumstances affect mainly
the attribute plug-ins, which are used to provide addi-
tional information after identification and authentica-
tion steps. In order to solve this problem, we benefit
from our modular architecture design because the af-
fected plug-ins can be easily replaced by a modified
implementation, which are used in case of V-IDP de-
ployment.
Figure 8 illustrates this deployment, in which a
modified attribute plug-in for electronic mandate col-
lection is used, as example. In contrast to the PEPS
AModularandFlexibleIdentityManagementArchitectureforNationaleIDSolutions
329

Service Provider
Service Provider
Austria
Member State
ZOLL
DOUANE
VIDP
VIDP
eMandate
IDP
eMandate
IDP
Mandate
Service
eMandate
Trust
Austrian
Citizen
Austrian
Citizen
Figure 8: Our IDP solution used as V-IDP with modified
attribute plug-in.
deployment, a request to the Austrian infrastructure
is only necessary if requested authentication informa-
tion cannot be provided by the V-IDP directly. The
advantage of this solution is obtained by combining
the benefits of the middleware model with the entire
functionality of an Austrian identity provider.
By combining the inbound and outbound process
flow, our solution can also be used to authenticate
an European citizen to an European service provider.
According to this, our implemented solution is also
directly usable in other European states and not only
in the Austrian national eID infrastructure.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Identification and authentication of citizens is an in-
tegral component for a variety of Internet services
and online applications. The capability for secure
and reliably identification and authentication accord-
ing to national legal requirements is important for ser-
vice providers, which process private and individual-
related data, like eGovernment applications. In
this paper, we have presented a new architecture
for identity-management systems, to provide a flex-
ible, interoperable and easy-to-use identity provider
for service provider identification and authentication.
Our solution relies on an adaptable and modular ar-
chitecture that facilitates future extensions. Although
the presented solution has been developed to meet
special requirements of the Austrian eID infrastruc-
ture and Austrian legal requirements, its general ar-
chitectural design and implementation is also appli-
cable in other contexts.
We have demonstrated the practical applicability
and flexibility of the architectural design by imple-
menting solutions for different use cases, which need
to be covered by an Austrian identity provider. These
use cases cover the use of the presented solution to
identify and authenticate Austrian citizens and pub-
lic officials in various ways and assure interoperabil-
ity of our solution in a European context. Actually,
the practical implementation of use case 1 is used for
productive applications in the Austrian eGovernment.
The implementation of the use cases 2 and 3 are actu-
ally evaluated in different national and European pilot
programs. The realization of further use cases or addi-
tional functionality, like two-factor authentication in
case of single sign-on, that make use of the presented
architecture is regarded as future work.
REFERENCES
Bauer, M., Meints, M., and Hansen, M. (2005). D3.1:
Structured overview on prototypes and concepts of
identity management systems.
Cantor, S., Moreh, J., Philpott, R., and Maler, E. (2005).
Metadata for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup
Language (SAML) V2.0. Technical report.
European Union (2005). Ministerial declaration, Manch-
ester, United Kingdom, on 24 november 2005. Euro-
pean Union.
European Union (2006). Directive 2006/123/ec of the euro-
pean parliament and of the council of 12 december
2006 on services in the internal market. European
Union.
European Union (2014). Regulation (eu) no 910/2014 of
the european parliament and of the council of 23 july
2014 on electronic identification and trust services for
electronic transactions in the internal market and re-
pealing directive 1999/93/ec. European Union.
Ferdous, M. S. and Poet, R. (2012). A comparative analysis
of identity management systems. In Smari, W. W. and
Zeljkovic, V., editors, HPCS, pages 454–461. IEEE.
Hughes, J., Cantor, S., Hodges, J., Hirsch, F., Mishra, P.,
Philpott, R., and Maler, E. (2005). Profiles for the OA-
SIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)
V2.0. Technical report.
Kaler, C. and McIntosh, M. (2009). Web Services Federa-
tion Language (WS-Federation) Version 1.2.
K
¨
olsch, T., Zibuschka, J., and Rannenberg, K. (2011). Pri-
vacy and identity management requirements: An ap-
plication prototype perspective. In Camenisch, J.,
Leenes, R., and Sommer, D., editors, Digital Privacy,
volume 6545 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 735–749. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Leitold, H., Hollosi, A., and Posch, R. (2002). Secu-
rity architecture of the austrian citizen card concept.
In Computer Security Applications Conference, 2002.
Proceedings. 18th Annual, pages 391–400.
Leitold, H., Lioy, A., and Ribeiro, C. (2014). Stork 2.0:
Breaking new grounds on eid and mandates. In
GmbH, M. M. F., editor, Proceedings of ID World In-
ternational Congress, pages 1 – 8.
Lockhart, H. and Campbell, B. (2008). Security As-
sertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0 Technical
Overview. Technical report.
WEBIST2015-11thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
330

Maler, E., Mishra, P., and Philpott, R. (2003). Asser-
tions and Protocol for the OASIS Security Assertion
Markup Language (SAML) V1.1. Technical report.
Nadalin, A., Kaler, C., Monzillo, R., and Hallam-Baker, P.
(2006). Web Services Security: SOAP Message Secu-
rity 1.1. Technical report.
Neuman, C., Yu, T., and Hartman, S und Raeburn, K.
(2005). The Kerberos Network Authentication Ser-
vice (V5).
Orthacker, C. and Zefferer, T. (2011). Accessibility chal-
lenges in e-government: an austrian experience. In
Stuart Cunningham, Vic Grout, N. H. D. O. R. P., edi-
tor, Proceedings of the Forth International Conference
on Internet Technologies and Applications (ITA 11),
pages 221 – 228.
Rainer, H., Pfl
¨
aging, P., Zwattendorfer, B., and Pichler, P.
(2014). Portalverbundprotokoll Version 2 S-Profil.
R
¨
ossler, T., Hollosi, A., Liehmann, M., and Schamberger,
R. (2006). Elektronische Vollmachten Spezifikation
1.0.0.
Sakimura, N., Bradley, J., Jones, M., de Medeiros, B., and
Mortimore, C. (2014). OpenID Connect Core 1.0.
Stranacher, K. (2010). Foreign identities in the austrian e-
government - an interoperable eid solution. In Cen-
ter, T. N. C., editor, IDMAN 2010 - 2nd IFIP WG-
11.6 International Conference on Identity Manage-
ment, pages 31 – 40.
Zwattendorfer, B., Sumelong, I., and Leitold, H. (2013).
Middleware architecture for cross-border identifica-
tion and authentication. Journal of information as-
surance and security, 8:107 – 118.
AModularandFlexibleIdentityManagementArchitectureforNationaleIDSolutions
331
