
A New Learning Platform using E-textbooks for Socially Networked
Online Learners
Masumi Hori
1
, Seishi Ono
2
, Kazutsuna Yamaji
3
, Shinzo Kobayashi
4
,
Toshihiro Kita
5
and Tsuneo Yamada
6
1
General Manager, Planning Office, NPO CCC-TIES, 7-1-1 Tezukayama, Nara-city, Nara, Japan
2
Vice President, NPO CCC-TIES, 7-1-1 Tezukayama, Nara-city, Nara, Japan
3
Associate Professor, Research and Development Centre for Academic Networks,
National Institute of Informatics, 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, Japan
4
CEO, SmileNC and Co., 2-3-20 Higashimizuhodai, Fujimi-city, Saitama, Japan
5
Professor, Kumamoto University, 2-40-1 Kurokami Chuo-ku, Kumamoto-city, Kumamoto, Japan
6
Professor, Open University Japan, 2-11 Wakaba, Mihama-ku, Chiba, Japan
Keywords: Open Education, Large-scale Online Course, E-Books, E-Learning.
Abstract: Conventional learning management systems that focus on traditional classrooms do not fit many-participant
online courses such as massive open online courses (MOOCs). A learning platform, Creative Higher
Education with Learning Objects (CHiLO) based on e-textbooks aims to develop a flexible learning
environment for large-scale online courses. CHiLO essentially has high portability in electronic publication
3.0 (EPUB3) format as well as a comprehensive open network learning system using various existing
technologies and learning resources, including open educational resources on open network communities,
such as social networking service. We produced a series of CHiLO Books called “Nihongo Starter A1” in
cooperation with the Open University of Japan (OUJ) and the Japan Foundation, and delivered them as a
learning course of OUJ MOOC in Japan MOOC. Our set of experimental outcomes shows that CHiLO
using not Web services but e-textbooks is available for large-scale online courses. The result reveals a
positive completion rate of 22% and active participants posting at 25%.
1 INTRODUCTION
A traditional learning management system (LMS) is
becoming outdated in large-scale online courses
(Sclater, 2008) because LMS provides support for
teaching and learning based on a conventional
classroom although it is an educational support
system at every level, for instance, managing
learning outcomes, learning progress, and
communication between learners. Therefore, a new
LMS with different concepts is required for large-
scale online courses (Mott, 2010).
Our learning platform, Creative Higher
Education with Learning Objects (CHiLO) consists
of components through e-textbooks developed with
a totally new design, considering large-scale online
courses such as massive open online courses
(MOOCs). In this paper, we report the possibilities
for CHiLO in our experiments on Japan massive
open online courses (JMOOCs).
The basic outline of this paper is as follows:
Section 2 provides a brief overview of the current
pedagogical situation. Section 3 presents the
architecture of CHiLO. Section 4 describes our
experimental results. Section 5 discusses some
challenges of CHiLO, and Section 6 is a summary.
2 PEDAGOGICAL SITUATION IN
RECENT YEARS
2.1 Traditional LMSs
In the early 2000s, LMSs became widely used in
higher education, along with the growth of the
Internet (Cross, 2004). Following this generation,
the LMSs we know today, e.g., Blackboard, Sakai,
Moodle, and Canvas, appeared. The typical LMS
comprises course creation and delivery, secure
authentication and enrolment, content management
and delivery, interaction between students, and
512
Hori M., Ono S., Yamaji K., Kobayashi S., Kita T. and Yamada T..
A New Learning Platform using E-textbooks for Socially Networked Online Learners.
DOI: 10.5220/0005444205120519
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2015), pages 512-519
ISBN: 978-989-758-108-3
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

methods of assessment and testing (see
https://docs.moodle.org/27/en/Features).
Such traditional LMSs are designed as course-
centric or time-based systems around content
delivery, course delivery, and mechanics of running
a course (Pitigala Liyanage, Lasith Gunawardena
and Hirakawa, 2013). The course-centric system
faces some challenges such as data analytics and
relationship management for new online educational
methods, including competency-based learning
(Irakliotis and Johnstone, 2014). The conventional
LMS focuses on a traditional classroom; it does not
fit the new educational method. The course-centric
system must be replaced with a learning-based or
competency-based system that is completely aligned
with students and what they need to progress
educationally (Sturgis, 2011).
2.2 Current Pedagogical Situation
As recent online educational trends, learning content
is split into smaller units, which are then
reassembled to allow self-paced and self-path
learning (Force, 2013).
2.2.1 Competency-based Education
Competency-based education (CBE) focuses on
effective short-time learning for adult learners, for
instance, working and self-supporting students, in a
short amount of time.
The following points define competency-based
learning approaches (Sturgis, 2011):
Students advance upon mastery.
Competencies include explicit, measurable,
transferable learning objectives that empower
students.
Assessment is a meaningful, positive learning
experience for students.
Students receive timely, differentiated support on
the basis of their individual learning needs.
Learning outcomes emphasize competencies that
include application and creation of knowledge,
along with the development of important skills
and dispositions.
Western Governors University (WGU) has used
CBE since 1997 (Morrison and Mendenhall, 2001).
In 2012, Southern New Hampshire University
(SNHU), seeing a market opening for an LMS
designed around CBE (Straumsheim, 2014), began
advertising its program nationwide. In the United
States, a number of community colleges provide
CBE (Irakliotis and Johnstone, 2014).
At the same time, CBE is criticized in that
colleges learn a great deal about their students’
competence from grades and test scores but have no
information about students’ creativity and character
(Grant, 2014).
2.2.2 Unbundling of Education
The Task Force on the Future of Massachusetts
Institute of Technology (MIT) Education provided
further insights into the unbundling of education,
deemed to take different roles—such as classrooms,
labs, and mentoring—as modules. A module is
defined by its corresponding outcomes such as the
instruction and assessment for the module. Each
module is re-bundled with competency-based
assessments or new assessment methods, which can
relate directly to measurable outcomes for a class or
module (Force, 2013). The Task Force considers
small private online courses (SPOCS), on edX
provided by MIT, to be nothing more than modules.
The unbundling of education is an innovative
method, and dozens of similar efforts are expected to
appear across the United States in the next 3 to 5
years (Bull, 2013).
2.2.3 NanoDegree
The NanoDegree rendered by Udacity, a for-profit
educational organization or a MOOC platform,
provides learners with a bite-sized bundle of
knowledge and immediate motivation for acquiring
a degree. Furthermore, its curriculum is designed for
acquiring specific business skills for 6–12 months
(10–20 hours/week), for $200 a month. Traditional
higher educational courses often do little to fill the
gap between education and business. Instead, the
evidence so far suggests that online education might
do better in motivating low-income students, unable
to invest time and money into liberal arts education,
if a program relates directly to work. Companies
might be best suited to shape such programs (Porter,
2014). However, the education favored by
companies is also criticized for its lack of emphasis
on liberal arts education (Belkin, 2014)
3 ARCHITECTURE OF CHILO
3.1 Implementation
An e-book has the advantage of being easily carried
in some device such as a mobile phone or tablet PC,
without a network. For learners, therefore, the e-
book provides a study environment—anywhere,
anytime.
ANewLearningPlatformusingE-textbooksforSociallyNetworkedOnlineLearners
513

An e-book standard format, EPUB, is the
distribution and interchange format standard for
digital publications and documents based on Web
standards. EPUB defines a means of representing,
packaging, and encoding structured and semantically
enhanced Web content—including XHTML, CSS,
SVG, images, and other resources—for distribution
in a single-file format (see IDPF
http://idpf.org/epub). EPUB can achieve economies
of scale in design, development, and distribution
(Belfanti, 2014).
The CHiLO, based on e-textbooks, aims to
develop a flexible learning environment for large-
scale online courses. It consists of the following four
components:
CHiLO Books using e-textbooks in EPUB3
format
CHiLO Lectures based on one-minute nano
lectures
CHiLO Badges providing authentication and
certification
CHiLO Communities such as social networking
services (SNS), bulletin boards, and chat rooms
(Figure 1).
Figure 1: Implementation of four CHiLOs.
3.1.1 CHiLO Book and CHiLO Lecture
The core component of CHiLOs is CHiLO Books,
which are created in EPUB3 format and have media-
rich content including graphics, animation, audio,
and embedded videos.
CHiLO Lectures comprise videos with scripts,
quizzes, and other learning materials. Videos are
one-minute nano lectures. This concept originated
from an experiment showing that the viewing time
of most online learners is approximately one minute.
A CHiLO Lecture is equivalent to one page in a
traditional textbook. A CHiLO Book includes
approximately 10 CHiLO Lectures and a link to a
comment box allowing the user to post to Facebook.
Furthermore, each page of the book has a link to
quizzes on the material presented. A standard
CHiLO course, comparable with a traditional
university course with one academic credit,
comprises 10 CHiLO Books.
3.1.2 CHiLO Badge
It is difficult to perform indirect assessments such as
those on learning time and academic workload in
large-scale online courses. Although CHiLOs
adopted a direct assessment approach for learning
outcomes, completion of a CHiLO course is
measured in standard course hours corresponding to
academic credits.
Whenever learners complete a CHiLO Book,
they receive a CHiLO Badge, which is a simple
mechanism of outcome assessment in CHiLOs.
When tutors wish to check a learner’s progress, they
simply ask the learner to present the CHiLO Badge.
They do not need to confirm with indirect
assessment tools such as grade books, tracking of
past results, and test scores. CHiLO Badges are
based on open Mozilla badges.
3.1.3 CHiLO Communities
Learning communities called CHiLO Communities
combine open SNS on the Web, such as Facebook
and Twitter, with a forum of LMS. Learners ask
questions, have discussions, and exchange
information about their CHiLO Book.
In a large-scale community, a tutor is incapable
of teaching many learners. A CHiLO Community
consists of many learners and a few tutors called
“connoisseurs” who act as substitutes for teachers. A
learner who studies and completes CHiLO Books in
a specific field can become a connoisseur. The
connoisseur and learner stand on equal ground so
that a connoisseur frequently exchanges information
with learners in their communities.
In a CHiLO Community, learners do not learn
from a tutor but on their own, with CHiLO Books as
the learning materials. In this way, learners are
constantly required to find suitable CHiLO Books in
the community. The CHiLO Community provides
functions of discovering, sharing, aggregating, and
repurposing CHiLO Books for learners using Open
Graph Protocol and Microdata.
4 RESULTS OF
DEMONSTRATION
EXPERIMENT
4.1 Experimental Methodology
We produced a series of CHiLO Books called
“Nihongo Starter A1 (NS A1)” in cooperation with
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
514
the Open University of Japan (OUJ) and the Japan
Foundation, and delivered them as a learning course
of OUJ MOOC in JMOOC: JMOOC “is an
organization that was formed in 2013 with the
cooperation of Japanese universities and businesses
that aims to spread and magnify Japanese MOOCs
throughout the country” (see
http://www.jmooc.jp/en/about/).
NS A1 comprises 10 e-textbooks for learners
who want to study Japanese. A single package of an
e-textbook is equivalent to one lesson. To improve
operability and accessibility for learners, we
developed and provided two types of CHiLO Books,
one an EPUB version and the other a Web version.
The Web versions were simply converted from the
EPUB versions of CHiLO Books.
In the demonstration experiment, learners were
allowed to download all the NS A1 CHiLO Books
(10 books) from August 4 to October 15, and to
participate in a learners group that was opened
on Facebook. In other words, without any particular
procedure of course registration, learners were free
to download the CHiLO Books from the Internet and
were able to learn at their own pace.
However, learners who participated in the
Facebook group were recommended to study these
10 books according to a predetermined or
standardized learning schedule, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Standardized Schedule.
Term Learning Objective
1st week Lessons 1 and 2
2nd week Lessons 3 and 4
3rd week Lessons 5 and 6
4th week Lessons 7 and 8
5th week Lessons 9 and 10
6th–10th week Supplementary classes
4.2 Experimental Results
The learners who downloaded or browsed NS A1
CHiLO Books had access from the United States,
Mexico, Colombia, Malaysia, Australia, Thailand,
and Vietnam—in all 94 countries. Table 2 shows the
number of people participating in the learners’
activities.
Table 2: Numbers of People participating in Each Learner
Activity.
Browsed at least 1 NS A1 CHiLO Book 2033
Participated in Facebook group 1491
Took at least one test 487
Were issued badges at least after one test 331
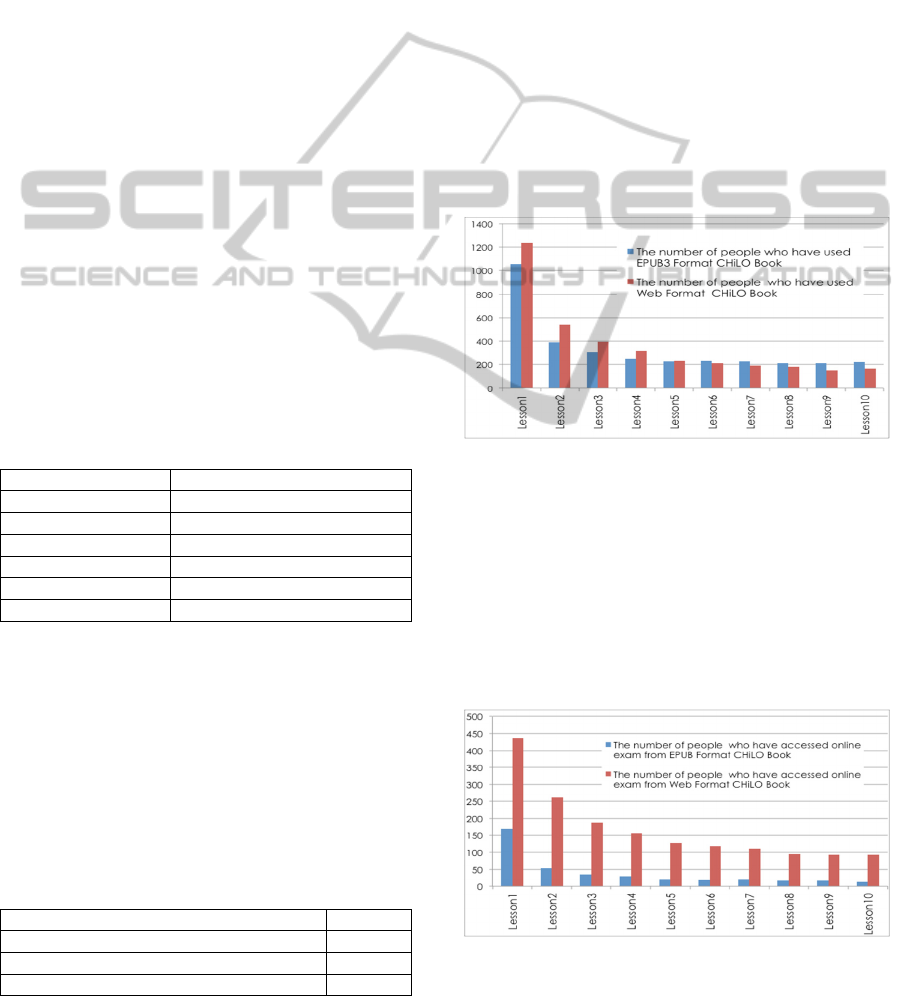
Figure 2 shows which type of format, EPUB3 or
Web CHiLO Books, the learners selected for each
lesson. For all the lessons, the Web format CHiLO
Books were used by 3,624 learners and EPUB
format CHiLO Books were used by 3,336 learners.
Although the number of Web format users was
slightly higher than that of EPUB3 format users, we
assume that the difference is not significant.
As the level of the lessons advanced, however,
the number of EPUB3 format users tended to
exceed that of Web format users. In comparison,
from Lesson 1 to Lesson 10, the number of Web
format users increased by 14% and that of EPUB3
format users increased by 21%.
Furthermore, the fact that the total number of
Web and EPUB format users for Lesson 1 exceeded
“the number of people who have browsed at least 1
NS A1 CHiLO Book: 2,033” as shown in Table 2,
suggests that some learners used both formats.
Figure 2: Number of learners who used EPUB3 format
CHiLO Books or/and Web format CHiLO Books for each
lesson.
Figure 3 shows the number of learners who had
access to online exams from EPUB3 format CHiLO
Books or/and Web format CHiLO Books for each
lesson. For all the lessons, online exams were
accessed by many more learners from Web format
CHiLO Books than from EPUB format CHiLO
Books.
Figure 3: Number of learners who accessed online exams
from EPUB3 format CHiLO Books or/and Web format
CHiLO Books on each lesson.
ANewLearningPlatformusingE-textbooksforSociallyNetworkedOnlineLearners
515

Figure 4 shows specific activities of 1,491
learners who joined the Facebook group. Of the
entire Facebook group, 336 learners, or over 20%,
posted messages. Moreover, 329 learners posted
certain comments responding to these
messages, and 709 learners, or 40% of the
participants in the Facebook group, sent Likes.
Considering that only 1% of users post messages
and only 9% post comments in general online
communities (Nielsen, 2006), learners in this
community were relatively active.
Figure 4: Activities of those who joined the Facebook
group.
Figure 5 shows the number of learners who took
online exams on each lesson and earned badges on
those exams. Of learners who took an online exam
on Lesson 1, 22% completed all 10 lessons and
earned 10 badges.
Figure 5: Number of learners who took online exams and
earned badges on each lesson.
Figure 6 shows the time period when learners
earned their first badges on Lesson 1. We divide the
learners into two groups: “group completed,” in
which learners finished all 10 lessons and earned 10
badges, and “group uncompleted,” in which learners
could not finish the entire course despite earning one
or more, but less than 10, badges. Additionally, we
observed that learners in “group completed” earned
their first badges earlier than those in “group
uncompleted.”
Figure 6: Time period when learners earned their first
badges on Lesson 1.
Furthermore, we compared the two groups in
terms of the time period for earning badges on each
lesson. Figure 7, presenting the result for “group
completed,” shows that learners earned badges
according to the recommended course schedule or
earlier. On the other hand, the result for “group
uncompleted” (Figure 8) shows that learners
increasingly delayed the recommended course
schedule for earning badges as the lessons
progressed.
Figure 7: Time period for earning badges on each lesson in
“group completed”.
Concerning the time period in which learners
completed the entire course and earned all 10
badges, Figure 9 shows that most learners in “group
completed” completed the course within 5 weeks or
according to the course schedule recommended. In
contrast, the other learners took 1 to 10 weeks to
complete the course.
Figure 8: Time period for earning badges on each lesson in
“group uncompleted”.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
516

5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Popularity of the Formats
As shown in Figure 2, the number of users of
EPUB3 format CHiLO Books was almost the same
as that of Web format CHiLO Books. However, the
online exams were mainly accessed by the users of
Web Format CHiLO Books, as indicated in Figure 3.
This is presumably because a high percentage of
learners had Internet connection at home and were
familiar with using Web browsers on PCs. Another
possible reason is that Web browsers are easier to
use than e-book readers for online quizzes.
Figure 9: Time period in which learners completed the
entire course.
Table 3: Which CHiLO Book did you use, the EPUB
version or the Web version? (n = 92).
Mostly used Web version 48%
63%
Mainly Web version, sometimes eBook
version
15%
Used both EPUB version and Web
version at the same rate
8%
37%
Mainly EPUB version, sometimes Web
version
14%
Mostly used the EPUB version 15%
Table 4: Why did you use the EPUB version? (Check all
that apply.).
Useful to have it downloaded to my device 32%
Wanted to use it in non-Internet-connected
environment
30%
Interested in the book 16%
Wanted to use the functions within the eBook,
such as bookmark, memo, etc.
9%
No specific reason 4%
Other 9%
According to the survey for learners who
completed all lessons, on the other hand, 37% of the
learners responded that they did use the EPUB
Format CHiLO Books because they could take the e-
books anywhere on their own devices and they could
read them even offline (Tables 3 and 4). From now
on, e-book-based learning will be more common and
useful as an increasing number of people will tend to
learn to use mobile devices. Additionally, highly
accessible EPUB3 e-book readers must be used
more widely for effective learning.
5.2 Learning Community
As indicated by the survey for those in the Facebook
group who completed all lessons, the Facebook-
based learning community was quite active (Tables
5 and 6).
Table 5: How often did you read the comments posted on
Facebook? (n = 92).
Every day 34%
More than 1 day, less than 3 days a week 37%
More than 3 days, less than 7 days a week 21%
Less than 1 day a week 9%
Table 6: Were you satisfied with the activities on
Facebook? (n = 92).
Very satisfied 45%
Somewhat satisfied 39%
Neither satisfied nor dissatisfied 14%
Somewhat dissatisfied 2%
Very dissatisfied 0%
There was a difference between learners in terms
of pace and assignment completion because no
explicit schedule for course enrollment or
assignment submission was announced.
Nevertheless, we observed that learning can occur
where learners with the same objective gather.
The learning community observed here consisted
of less than 1500 people—a small number compared
to a typical MOOC learning community. If a larger
number of people join the community, there will be
difficulties in group activities; therefore, there will
be some need to present an optimal grouping for
learners on the basis of the analysis of learners’
methods and objectives. This will be possible
through development of CHiLO Analytics.
5.3 Scheduling of Learning
Although we did not set deadlines for learners, those
who completed the course tended to progress
according to the standard schedule we presented. On
the other hand, only 30% of learners completed the
course in 5 weeks, as defined in the standard
schedule; the rest (70%) completed the course earlier
or later. In a conventional online course, these
ANewLearningPlatformusingE-textbooksforSociallyNetworkedOnlineLearners
517

learners would likely think that the materials’ levels
were too low, or they would drop out, failing to
complete the course by the deadline.
While there was no course as a learning
framework, indication of a recommended learning
schedule is an important factor for motivating
learners to continue learning, and it is also effective
to indicate the standard learning pace and learning
path. We should also indicate that many learners
who did not complete the course were delayed in
progress on the lessons, compared with the standard
schedule; this suggests that the standard schedule is
not suitable for them. We should manage to provide
learning schedules most suitable for individual
learners by implementing CHiLO Analytics tools.
5.4 CHiLO Analytics, CHiLO
Repository, and CHiLO Reader
We will launch a new component called the CHiLO
Reader. The CHiLO Reader, an e-textbook reader, is
easy to use while studying because it does not
require switching to a browser and supporting
media-rich functions. A Web format is currently
available for CHiLO Books; however, using only an
EPUB format that does not have to switch to the
browser would be better.
The International Digital Publishing Forum
(IDPF) has proposed the EDUPUB format to meet
the requirements of next-generation learning content
based on the e-book EPUB3 format (IDPF, 2014).
However, at present, most e-book readers do not
support the media-rich functions of the EDUPUB
format, for example, embedding videos, JavaScript
compliance, and JavaScript Object Notation (Figure
10).
6 CONCLUSIONS
In general, we obtained positive results in that 22%
of learners who attempted the Lesson 1 examination
completed their learning. The result is fairly good,
considering that the typical completion rate in
MOOCs is said to be less than 10%. However, rigid
comparison is not possible because learners did not
have to declare enrollment when they began learning
in this pilot study.
Furthermore, we observed an interesting
situation: a kind of mutual learning occurred in the
learning community. Learners who had completed
the course tended to provide helpful suggestions to
learners following them.
Figure 10: Developed CHiLO.
Additionally, Spanish-speaking learners
volunteered to form a learning group in which they
translated the NS A1 learning materials into
Spanish. Although the CHiLO project has shown
great development, several challenges persist. One is
that the files used in the e-textbooks are too large to
manage.
The embedded videos in CHiLO Books are small
nano lecture video clips; however, each CHiLO
Book typically includes a combination of graphics,
video clips, online exams, and other components,
which sometimes amount to over 200 files.
Managing individual components and keeping all
the parts up to date is a very complicated task.
Additionally, there is no editing software to create e-
textbooks; therefore, we had to code the sources
from scratch. Thus, creating CHiLO Books takes a
great deal of effort.
Finally, there is a need for an e-text reader that is
easier to use for learning. A Web-based format is
also available for CHiLO Books now, but it would
be better to use only an EPUB-based format that
does not require learners to switch to a Web browser
when they need to access online resources.
REFERENCES
Belfanti, P. (2014). What is EDUPUB. Retrieved August
1, 2014, from http://www.imsglobal.org/edupub/
WhatisEdupubBelfantiGylling.pdf.
Belkin, D. (2014). How to Sell a Liberal-Arts Education.
The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved from:
http://online.wsj.com/articles/how-a-college-president-
sells-a-liberal-arts-education-
1413751480?mod=rss_management.
Bull, B. (2013). Ongoing Unbundling of Higher Education
and the MOOC University. Etale - Life and Learning
in the Digital World. Retrieved from:
http://etale.org/main/2013/08/27/ongoing-unbundling-
of-higher-education-the-mooc-university/
Cross, J. (2004). An Informal History of eLearning. On the
Horizon, 12(3), 103-110.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
518

Force, M. T. (2013). Institute-wide Task Force on the
Future of MIT Education: Preliminary Report. Future
of MIT Education. Last accessed, 17, 02-14.
Grant, A. (2014). Throw Out the College Application
System. The New York Times Sunday Review.
Retrieved from: http://www.nytimes.com/2014/10/05/
opinion/sunday/throw-out-the-college-application-
system.html.
IDPF (2014). EPUB 3 EDUPUB Profile Draft
Specification. International Digital Publishing Forum.
Retrieved from: http://www.idpf.org/
epub/profiles/edu/spec/
Irakliotis, L. and Johnstone, S. (2014). Competency-based
Education Programs versus Traditional Data
Management. EDUCAUSE Review Online. Retrieved
from:
http://www.educause.edu/ero/article/competency-
based-education-programs-versus-traditional-data-
management.
Morrison, J. L., and Mendenhall., R. W. (2001).
Renaissance at Western Governors University: An
Interview with Robert W. Mendenhall. The Technology
Source. Retrieved March, 5, 2009.
Mott, J. (2010). Envisioning the Post-LMS Era: The Open
Learning Network. EDUCAUSE Quarterly, 33(1), 1-9.
Retrieved from: http://www.educause.edu/ero/
article/envisioning-post-lms-era-open-learning-
network.
Nielsen, J. (2006). The 90-9-1 Rule for Participation
Inequality in Social Media and Online Communities.
Retrieved from:
http://www.nngroup.com/articles/participation-
inequality/Pitigala Liyanage, M. P., Lasith
Gunawardena, K. S., and Hirakawa, M. (2013). A
framework for adaptive learning management systems
using learning styles. In Advances in ICT for Emerging
Regions (ICTer), 2013 International Conference on
(pp. 261-265). IEEE.
Porter, E. (2014). A Smart Way to Skip College in Pursuit
of a Job Udacity-ATandT ‘NanoDegree’ Offers an
Entry-Level Approach to College. The New York Times
Economy. Retrieved from:
http://www.nytimes.com/2014/06/18/business/economy
/udacity-att-nanodegree-offers-an-entry-level-
approach-to-college.html.
Sclater, N. (2008). Web 2.0, Personal Learning
Environments, and the Future of Learning
Management Systems. EDUCAUSE Center for
Applied Research Research Bulletin, 13(13), 1-13.
Straumsheim, C. (2014). Managing Competency-Based
Learning, Inside Higher Ed. Retrieved from:
https://www.insidehighered.com/news/2014/09/29/coll
ege-america-spins-its-custom-made-learning-
management-system.
Sturgis, C., Patrick, S. and Pittenger, L. (2011). It’s Not a
Matter of Time: Highlights from the 2011
Competency-Based Learning Summit. International
Association for K-12 Online Learning.
ANewLearningPlatformusingE-textbooksforSociallyNetworkedOnlineLearners
519
