
A Semi-Automatic Computer-Aided Assessment Approach for
Marking and Providing Feedback Comments
Adewale Adesina
1
, Roger Stone
1
, Firat Batmaz
1
and Ian Jones
2
1
Department of Computer Science, Loughborough University, Loughborough, U.K.
2
Mathematics Education Centre, Loughborough University, Loughborough, U.K.
Keywords: Marking & Feedback Support System, Computer-Aided Assessments, Analytical Assessment Rubrics,
Formative Assessment.
Abstract: Assessment is an essential part of the learning process. It is important for educators to provide detailed and
reliable evaluations to students so that they can be better prepared for future studies and the workplace.
Marking and providing formative feedback can be time-consuming and prone to errors especially when
detailed analyses of students’ problem-solving steps are considered. A computer-aided marking and
feedback support tool that aims at improving the efficiency and effectiveness of human marking may result
in reduced marking time, improved consistency in marking, and improved feedback capabilities. This paper
discusses a semi-automatic approach to marking problem-solving steps in the context of elementary school
mathematics using analytical assessment rubrics. A prototype tool which implements the approach is
described following recommendations based on research evidence in mathematics problem solving. The tool
was evaluated in an observational study which compared marking-time efficiencies obtained using the
technique with those obtained from marking done manually. The result suggests that the method has the
potentials to facilitate broad feedback delivery, improve marking consistency and may save on marking
time. The use of such marking and feedback support systems may contribute to the overall educational goal
of more accurate and consistent assessment procedures.
1 INTRODUCTION
Assessment is essential in teaching and learning. It
can provide information to help educators make
better educational decisions. Marking and providing
formative feedback on students’ performances are
essential activities in the educational process (Hattie
and Timperley, 2007; JISC, 2010). However the task
of providing quality feedback is challenging due to
the time and effort it takes to analyse students’
performance. Several studies have shown that the
most important in-school influence on student
learning and achievement is the teacher (Dinham,
2008; Hattie, 2008). Supporting the teacher in
classroom and feedback activities is likely to result
in better students’ performances.
Commonly tests used in classrooms concentrate
on the total or representative score for a task (Brown
et al., 2008). This information does not usually
contribute to quality feedback because it does not
help students to answer questions like “What was I
good at, and what was I weak at? What do I have to
do next (Brown et al., 2008; Mory, 2004)? Marking
and giving good feedback requires high quality
information. Collecting the data to inform teachers
of the process as well as the end product of a
problem-solving effort is likely to be valuable in
providing this information. A related challenge in
assessment practices is inconsistencies in human
marked assessments. For instance, Orrell, (2008)
showed that human markers are inherently
inconsistent and can be influenced by expectations
of individual students. Other studies have suggested
that inconsistences arise due to high classroom
workloads for teachers and the drudgery of marking.
Having teacher to assess detailed problem-solving
steps is likely to lead to even greater workloads.
Computer-Aided Assessment (CAA) is
increasingly being used to address these challenges.
The benefits of CAA have been widely reported.
These include, increased variety of assessed tasks,
the provision of instantaneous feedback, as well as
increased objectivity and resource saving (Bull and
McKenna, 2004; Conole and Warburton, 2005;
93
Adesina A., Stone R., Batmaz F. and Jones I..
A Semi-Automatic Computer-Aided Assessment Approach for Marking and Providing Feedback Comments.
DOI: 10.5220/0005447000930100
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2015), pages 93-100
ISBN: 978-989-758-108-3
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Hollingsworth, 1960). However the focus of many
CAA systems tends to be on providing fully
automatic assessment of student work. Fewer studies
have examined the combination of human and
computer in marking and provision of feedback
comments. Semi-automatic assessment is a term that
has been used to describe the cooperation between
human markers and the computer in assessment
(Herding and Schroeder, 2011; Bescherer et al.,
2011; Sargent, J et al., 2004).
This study describes a semi-automatic
assessment method for marking students’ work and
providing feedback comments in the context of
elementary school mathematics. The study further
evaluates the effectiveness of the approach in
reducing the time spent in marking. The core
research questions that guided the study can be
stated as follows:
How can semi-automatic CAA systems be
designed to assess problem-solving steps with
the aim or providing rich data for scoring and
feedback comments?
Does using this technique lead to reduced
marking time?
The significance of the research is two-fold.
First, results of this study may enable the assessment
of problem-solving processes for the purpose of
providing broad feedback. This may aid both
instructors and researchers to better understand
students' problem-solving steps and behaviour in
detail. Second, it may contribute to providing
empirical evidence on how the semi-automatic
approach may possibly reduce marking workloads.
This could be especially useful in situations where
there are large student populations.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows:
First a background to this work and the computer-
aided assessment is first outlined. This is followed
by a description of the semi-automatic assessment
approach adopted in the present study. After this, the
implementation of the approach on a prototype tool
is described in detail. Empirical evaluations of the
prototype tool with discussions are then presented.
2 EDUCATIONAL ASSESSMENT
2.1 Assessments and Feedback
Assessment has been defined as the practice of
systematically, gathering, analysing, and interpreting
evidence to determine how well students’ learning
matches the expectations and using the resulting
information to understand and improve student
learning (Suskie 2010). An essential purpose of
assessment is to improve learning. The empirical
research reviewed by Black and William (1998)
provides evidence that classroom assessment raises
students’ achievement when information gathered
about the processes and products of learning are
used to adapt teaching and formative feedback is
given to students to improve their learning. Also,
Hattie and Timperley (2008) showed that feedback
from teachers to students is important and has the
largest effect size in students achievement (Hattie
2009). An implication of this is that improving the
effectiveness of teachers will improve education
significantly.
2.2 Problem Solving in Elementary
Mathematics – an Illustration
Learning in mathematics involves students solving
problems in systematic ways (National Council of
Teachers in Mathematics (NCTM) 2000). When
problem solving is used, the emphasis is usually on
finding relevant and engaging tasks or problems that
help illustrate or assess a mathematical concept or
procedure. Many scholars hold the view that
effective assessment of problem solving should look
at more than the answers students give. For instance,
Szetela, (1992) argued that teachers should analyse
student processes and as much as possible help them
to communicate their thinking. This is commonly
because students make mental calculations without
explanations and only provide ending answers. This
often does not reveal sufficiently the student’s work
and thinking.
The Oregon mathematics scoring model (Arter
1993), NWREL Mathematics Problem-Solving
Model
TM
and the California Assessment Program
(Pandey 1990) draws our attention to at least four
distinctive categories that may be scored in problem-
solving performance assessment. These include
conceptual understanding, procedural understanding,
problem-solving strategies and communication.
Conceptual understanding is generally understood to
describe the ability to interpret the problem and
select appropriate information to apply a strategy for
a solution. Procedural knowledge refers to weather
students choose mathematical facts and operations to
help them solve a problem and how well they apply
those facts and operations (Rittle-Johnson and
Alibali 1999). Problem-solving strategies has been
described as the combination or sequence of skills
used in working toward the solution,` which is
demonstrated by good reasoning leading to a
successful resolution of a problem (Arter, 1993).
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
94
As an example, we consider the following
elementary mathematics problem.
Jason owned a factory that employs 53 workers. He hired
another 16 workers. He then hired another 7 workers. How
many workers are there at the factory altogether?
(Carpenter and Moser 1984).
The problem might typically be solved in two steps;
each step comprising pairing two numbers and
adding them. The way in which the numbers in the
problem are paired may reflect the strategy adopted
by the problem solver. For instance, the number may
paired in the order they appear in the question
((53+16) + 7) or the numbers may be paired using
the understating of numbers that bonds to multiples
of 10 i.e. ((53 + 7) + 16). This later approach
suggests a better conceptual understanding of
addition, and reduces the need to undertake
burdensome computation to obtain the result (Gray
and Tall, 1994).
Instead of scoring solutions only, assessors may
analyse the responses to the problems of the basis of
the different categories. One focus might be on
strategies used, another may be on answers or
procedures used. Feedback may be provided on each
of these categories separately or together. However,
such detailed assessment will add to the burden of
marking and feedback.
3 THE SEMI-AUTOMATIC
ASSESSMENT APPROACH
3.1 General Concept
Semi-automatic marking aims to reduce the effort an
assessor needs to put in to mark and provide
feedback comments on students’ work. Usually in
fully automatic assessment systems, the assessor
develops fair and consistent rules to handle different
answers and the exceptions (Bull and McKenna,
2004). These are usually prepared in advance to the
students answering the questions. The approach
adopted in this study does not attempt to consider all
possibilities of students’ responses, as these
sometimes may be unlimited. Instead of grading
submitted works in a black box, it relies on the
assessor to make judgments, assign scores and
provide feedback comments. These are then reused
in submissions with similar properties.
The approach considered in this work is a
combination of three techniques; the capture of
problem-solving steps from interaction traces,
assessment with analytic rubrics and re-use of
assessed items using the case-based reasoning
methodology (Aamodt and Plaza, (1994). This is
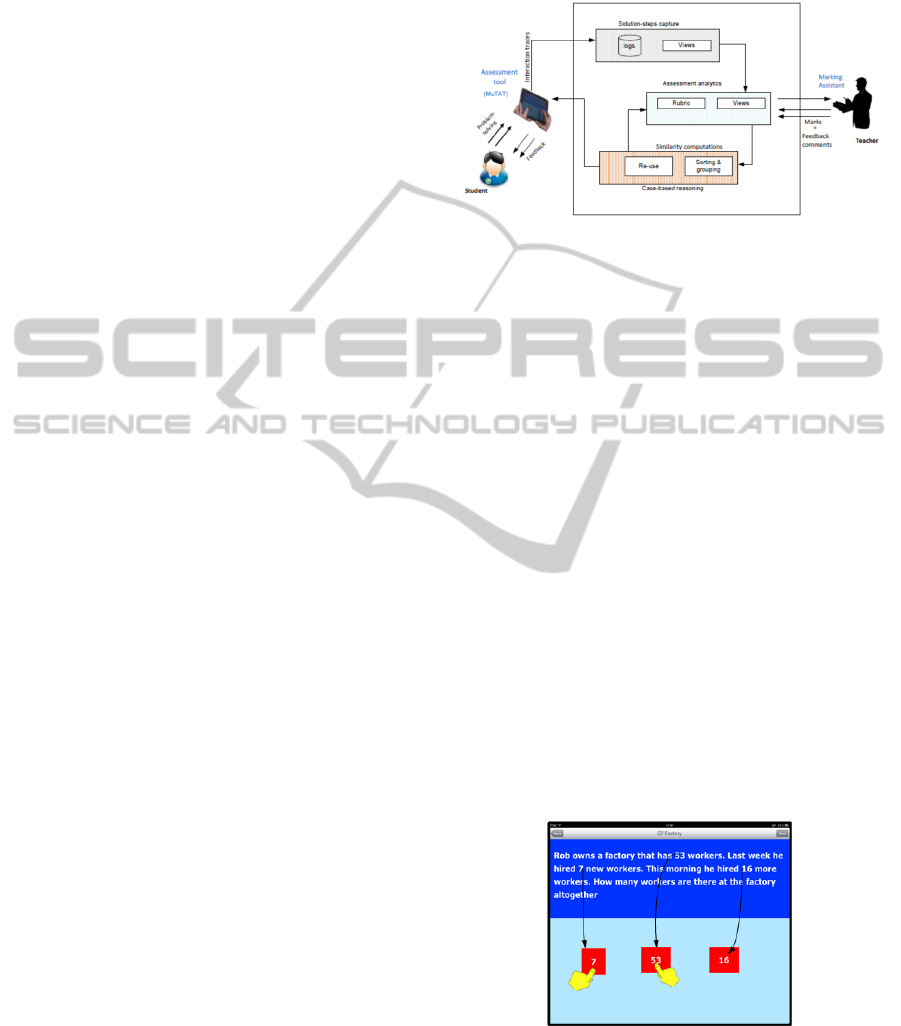
illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1:Semi-automatic assessment architecture.
The figure shows that the problem-solving steps are
captured from interactions on an assessment tool.
The steps are presented to the teacher who uses an
analytic rubric scheme to mark and make feedback
comments. The teacher’s effort is reused as
efficiently as possible. The results are then provided
to the student. The details of the techniques are
provided in the following sections.
3.2 The Capture of Problem-Solving
Steps
As mentioned in Section 2.2, detailed assessment
requires the consideration of steps used to solve
problems. This requires the use of an assessment
environment that captures and logs the actions of a
solution effort. A Multi-Arithmetic Tool (MuTAT)
allows this to be done. The tool, shown in Figure 2
and 3 provides an environment for rich interactions
between a problem text and solution items. It
explicitly allows the matching of key information in
the problem statement with the related component a
students’ response.
Figure 2: The Multi-Touch Arithmetic Tool (MuTAT).
The MuTAT provides several benefits; it compels
the student to break their problem-solving into small
steps while entering their solutions. This way the
thinking process is revealed as problems are being
ASemi-AutomaticComputer-AidedAssessmentApproachforMarkingandProvidingFeedbackComments
95
solved; here the reasoning behind a wrong (or right)
answer is not lost. Additionally, the software
provides visual representation of key elements in the
problem-solving process which may be used by
teachers and students themselves to understand how
the problem was approached. Because MuTAT
combines visual representations, with interactive
actions within a solution workspace, problem-
solving using different strategies are accommodated.
Details of the capture technique have been described
in a recent study (Adesina et al., 2014).
3.3 Assessment Analytics with Rubrics
For any type of assessment used to assign student
grades, it is recommended that scoring rubrics be
used (Garfield, 1994). Rubrics have been described
as a “scoring tool that lays out the specific
expectations for an assignment” (Stevens and Levi,
2011, p. 4), they are usually aligned along clearly
defined learning intentions or curriculum objectives,
and they simplify the grading process. Charles et al.,
(1987) referred to rubrics as a statement of
characteristics associated with different levels or
grades of performances by which a student work can
be understood. Rubrics can be applied in
assessments evaluating detailed solution steps. Two
types of rubrics which are commonly used are
holistic and analytic. While holistic rubrics provide a
single base or an overall impression of a student’s
performance on a task, analytic rubrics provide
specific feedback along several dimensions (Jonsson
and Svingby, 2007; Stevens and Levi, 2011).
The semi-automatic assessment will require
analytic rubrics to properly assess and provide
feedback comments on different categories of a
problem-solving effort. For example in the
arithmetic problem in Section 2.4, an assessor may
be able to separate what the student is trying to do
based on his understanding from his ability to
perform calculations. This way, the student can get
feedback on three categories i.e. calculation,
conceptual understanding, and strategy used. This is
in contrast to the assignment of single score as in
holistic rubrics. This technique provides the
opportunity for broad feedback. Other assessment
information such as time taken to complete a step,
overall time, and count of interactions can also be
obtained. Garfield, (1994) suggests that these types
of attributes need not be given a score or grade, but
they can inform the teacher about understanding,
feelings, and frustrations and can serve as inputs to
modifying instruction.
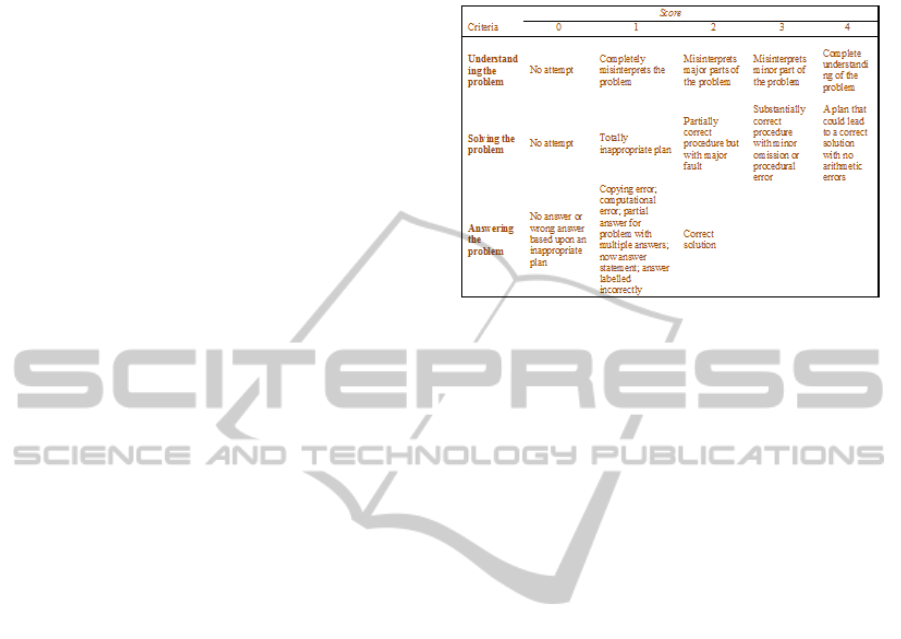
Table 1: Analytical rubric for mathematics problem
solving.
(Adapted from Charles et al., 1987 and Szetela, 1992)
Using a scoring rubric such as outlined in Table 1 to
assign points (such as 0, 1, 2 …) and provide
feedback comments to different components of the
assessment provides opportunities for richer
assessments and feedback.
3.4 Re-use of Assessed Items - Marks
and Feedback Comments
The semi-automatic method proposed in this work
aims to reuse the teachers’ feedback and marking
experiences. As discussed in Section 2.2, semi-
automatic assessment seeks to take advantage of the
strengths of human marking and computer-based
marking. This may be achieved by having the
decisions made by human-markers re-used in as
many scenarios as possible. The Case Based
Reasoning (CBR) methodology ones (Richter and
Rosina, O, 2013) provides a “reuse” stage where
matching cases are selected and reused. CBR
involves matching similar problems and their
solutions to new ones. Unlike in knowledge based
systems that relies on the use of rules to guide
decision process. CBR looks for similarities between
the current needs and previous examples of similar
problems and the attendant solutions. Reusing
information and knowledge in retrieved cases
reduces repetition which can be inefficient and
sometimes results in inconsistencies. Figure 3
shows a scenario where a solution to the example
problem in Section 2.2 is marked and comments
provided by an assessor.
In the figure, points are allotted to the assessable
pieces based on a pre-determined rubric. The
assigned marks and feedback for solution attributes
is reusable on different granular levels. The reuse of
assessed items enhances objectivity and consistency.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
96

Also, it makes it possible such that when moderation
is carried out the results are applied consistently
across all student submissions and is likely to bring
out savings of time and resources. In this paper, the
method of grouping by exact matches was adopted
for similar solutions.
Score: 75% (¾)
Feedback: The understanding of the
problem and use of the correct operators
is good. The strategy is also efficient, but
there is an inaccurate summing in one of
the steps.
+
6053 7
1660
+
66
Figure 3: Detailed marking and feedback comments.
4 IMPLEMENTATION ON
MARKING TOOL
The techniques outlined in the previous section have
been implemented in a prototype tool. This section
describes and discusses the implementation of the
assessment method on a prototype tool called
Marking Assistant (shown in Figure 1). The tool was
designed to ease the marking of the component parts
of students’ submitted work. The Marking Assistant
has five main functional requirements; first it should
be able to easily apply an analytic rubric scheme, it
should be able to re-use scores for similar solutions,
it should allow input of marks according to grouped
criteria, it should allow of entry of feedback
comments. Lastly, it should facilitate the generation
of feedback summaries and reports. The user
interface of the editor is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: The Marking Assistant user interface showing
marks assigned to “score-able” pieces.
The assessor simply taps on the score-able pieces to
assign scores and feedback comments. The
computer takes the marks and comments and applies
these to similar submissions on the same question.
As can be seen in the figure, when a score-able
component is assessed, other solutions with the same
properties are automatically assigned the same score
when they are encountered. During this process, the
examiner may enter feedback comments for the
actions and entered solution. Because similar
solutions have been grouped together for assessed
attributes, the same feedback is applied consistently
to all.
5 EVALUATION STUDY
The feedback support tool was evaluated regarding
the usability and time-saving potentials. The main
objective of the evaluation was to compare marking-
time on the application with that on paper.
Undergraduate students (N=8) in a university in
England were the participants in the study. The
evaluation was performed on a voluntary basis and
the student used the tool and paper independently
after being guided on general requirements. The
details of the study and results of the observational
study are described in this section.
5.1 Study Design
5.1.1 Participants
Eight participants were used in the study. They
were all required to mark the responses of 20
students on paper and the marking assistant tool. The
students’ solutions explicitly showed all the steps to
the answer.
5.1.2 Questions
The study used four arithmetic word problems which
commonly, solving the problem requires two steps
using two arithmetic operators.
Participants were required to mark four questions
– two on each media. The first question to be
marked on both media (tool and paper) requires the
use of addition operators in both steps. The second
question will require using both addition and
subtraction operators. The lists of both question
types are shown in Table 2.
A comparative cross-over experimental design
was used. To minimize ordering effects different
combinations of question type and marking media
were created as shown in Table 3. The participants
were randomly assigned into the four different
combination categories.
ASemi-AutomaticComputer-AidedAssessmentApproachforMarkingandProvidingFeedbackComments
97
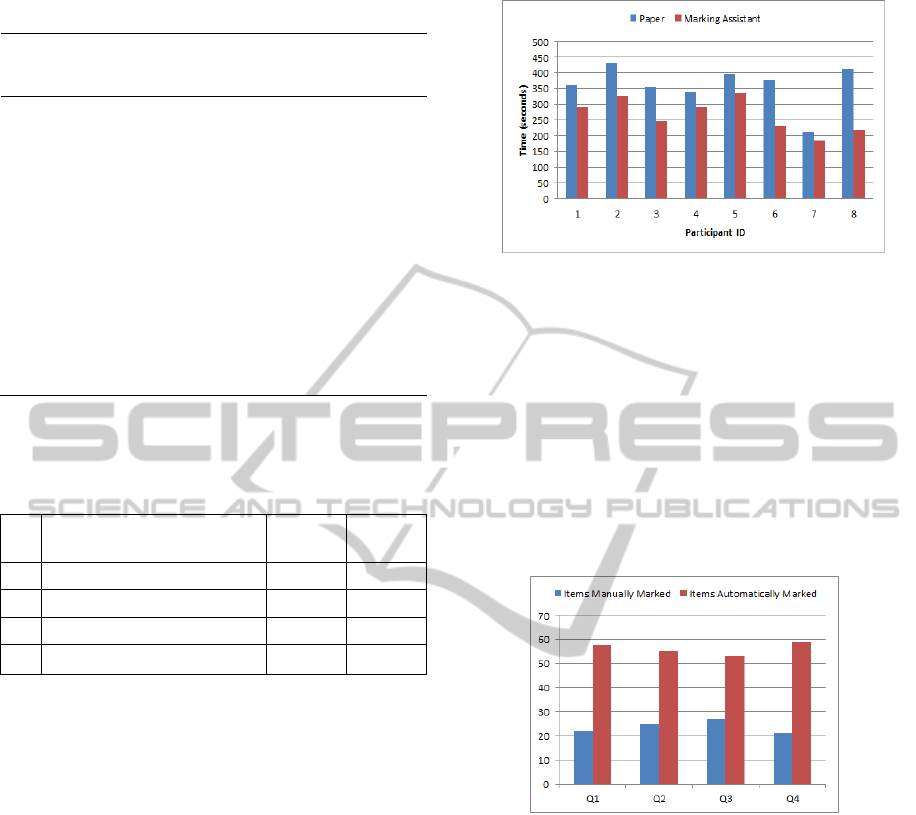
Table 2: Test questions.
Adapted from (Carpenter and Moser 1984)
a
and
(Gilmore and Bryant 2006)
b
Table 3: Order in which participants marked on paper and
the Marking Assistant.
No.
Marking order
Tablet
Question
Paper
Question
1
Tablet, Paper, Paper,
Tablet
1, 2
3, 4
2
Tablet, Paper, Paper,
Tablet
3, 4
1, 2
3
Paper, Tablet, Tablet,
Paper
1, 2
3, 4
4
Paper, Tablet, Tablet,
Paper
3, 4
1, 2
Each of the participants marked the four questions as
answered by 20 students. Two questions were
marked on each media.
5.1.3 Measures
The main measurement made was the time it took
the participants to complete the marking of the
questions on the two media used. On the Marking
Assistant the proportions of items marked manually
and automatically were recorded.
5.2 Results
Scoring on paper and the Marking Assistant tool
were successfully completed by all the participants.
The times it took the participants to complete the
marking on both media are shown in Figure 5.
Scoring on paper and the Marking Assistant tool
were successfully completed by all the participants.
The times it took the participants to complete the
marking of all the questions on both media are
shown in Figure 5.
As can be seen from the figure, all the
Figure 5: Marking time on paper and the Marking
Assistant.
participants spent less time on the tool compared to
paper. The mean time spent on the questions on the
Marking Assistant was 265.5 seconds while 360.9
seconds was spent marking on paper. This difference
was significant t(7) = 4.84, p = 0.00188.
The Marking Assistant therefore saved on
marking time. The relative proportion of items
manually marked and those marked automatically by
the computer re-using the manually marked results is
shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Proportion of marking done manually and
automatically.
From the figure above it can be seen that in all the
questions more items were marked automatically
(70%) than manually (30%). This is because the
computer handled all the repetitive marking which
evidently enabled time to be saved on the Marking
Assistant tool.
6 DISCUSSION
This study suggests a semi-automatic assessment
approach for CAA using the case-based reasoning
methodology. It explored how marking efficiency
and consistency may be improved while considering
detailed problem-solving steps.
Question with
addition only
Question requiring
both addition &
subtraction
Question 1: Jason
owned a factory that
employs 53 workers. He
hired another 7 workers.
He then hired another 16
workers. How many
workers are there at the
factory altogether?
a
Question 2: Sam has
21 books, he got 9 more
and gave 13 to Owen. At
the end, how many books
did Sam have?
a
Question 3: Sara has
8 sugar donuts. She also
has 15 plain donuts and
32 jam donuts. How many
donuts does Sara have
altogether?
b
Question 4: There
are 24 books on a shelf,
11 more where added and
then 6 taken away. At the
end, how many books
were there?
b
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
98

The first question in this study sought to determine
was how a semi-automatic assessment CAA may be
designed to help assess and score more than final
answers of a problem-solving effort. The approach
adopted combined three techniques; capture of
problem-solving steps, application of analytical
rubric and case-based reasoning. The
implementation of the assessment rubric and case-
based-reasoning techniques were successfully
carried out on the Marking Assistant tool described
in Section 4. A two-step elementary mathematics
problem was broken down into four assessable
components to increase the depth of what is
assessed. Because the tool automatically re-uses
judgment features of the marker, consistency in
application of the judgements to problems with
similar properties is ensured.
As regards the potential efficiency of the system,
the observational study provided useful insights. The
results show that the Marking Assistant enabled
significant time savings compared to marking done
entirely manually. For the four-components marking
examined, up to 70% of the required assessment was
done automatically. This suggests that the efficiency
of an assessor may be improved by using as cases
manually-assessed components. However, the
observational study has some limitations. Although
classroom test questions and solutions were used,
undergraduate students were the participants in the
marking exercises, rather than actual primary school
teachers. Since the study objective was to obtain
marking time from two mediums by the same
individual, results from students with fewer marking
experiences than actual classroom teachers helps
demonstrate the potentials of the approach.
The findings suggest several implications. The
improved efficiency in marking and feedback is
important to assessors such as teachers, because they
can reduce their marking workloads and devote
effort to other teaching activities. The improved
accuracy and consistency in marking ensures that
correct and fair marks are giving to all students
possibly resulting in more satisfied teaching staff,
students, and administrators. The system may assist
students in monitoring and reflecting on their
problem-solving processes and also to understand
how they were graded on a piece of work. The clear
rubrics may also be used to communicate to parents
the strengths and successes that students have
demonstrated.
All assessment procedures have strengths and
limitations. It is important to note that much work
has to be done before hand in design of questions
and software. Some authors have cautioned that the
less writing a student does in an assessment task, the
more work the assessor has do in creating the task
(Brown et al., 2008; Bull and Mckenna, 2004).
Sangwin (2013), also pointed out that a potential
limitation in emerging semi-automatic CAA systems
as the loss of immediate feedback. This is because
marking that requires the attention of a human
assessor comes with an inevitable delay. Instant
feedback is a big advantage of fully automatic
systems. However, the gains of detailed and
personalized feedback and the potential marking-
time savings gained from the re-use of assessed
items may allow assessors to respond quicker than
with manual scoring and feedback methods.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This study investigated a semi-automatic approach
to assessment and feedback. In the semi-automatic
approach used, the attributes of a student’s response
with the judgement (scores and feedback comments)
made by an assessor are carefully recorded and
linked together. The computer is then used to sort,
classify and re-apply these judgements and feedback
comments to similar students’ responses. The
findings suggest that in general, that process
evaluation using analytic rubrics and case-based
reasoning may enhance detailed marking and
feedback. The use of the case-based reasoning
methodology helps improve the consistency and
reliability in assessment and can potentially save in
marking time.
The semi-automatic approach was used in the
well-researched domain on elementary mathematics
allowing for prediction of distinct strategies to
obtain answers. The approach may be used beyond
basic arithmetic.
7.1 Further Work
The present study only considered exact matches of
the students work on which an assessor’s marking
and feedback experiences are reused as is. It may
be possible to increase the scope of similarity
assessments and adapt previous experiences to new
problems situations encountered. Further
investigations on this may be fruitful.
REFERENCES
Aamodt, A., & Plaza, E. (1994). Case-Based Reasoning:
ASemi-AutomaticComputer-AidedAssessmentApproachforMarkingandProvidingFeedbackComments
99

Foundational Issues, Methodological Variations, and
System Approaches. AI Communications, 7(1), 39–59.
Adesina, A., Stone, R., Batmaz, F., & Jones, I. (2014).
Touch Arithmetic: A process-based Computer-Aided
Assessment approach for capture of problem solving
steps in the context of elementary mathematics.
Computers & Education, 78, 333–343.
Bennett, R. E., Braswell, J., Oranje, A., Sandene, B.,
Kaplan, B., & Yan, F. (2008). Does it Matter if I Take
My Mathematics Test on Computer? A Second
Empirical Study of Mode Effects in NAEP. The
Journal of Technology, Learning and Assessment,
6(9).
Bescherer, Christine, Herding, Daniel, Kortenkamp,
Ulrich, Muller, Wolfgang, & Zimmermann, Marc.
(2011). E-Learning Tools with Intelligent Assessment
and Feedback for Mathematics Study. Idea Group Inc
(IGI).
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (1998). Assessment and
Classroom Learning. Assessment in Education:
Principles, Policy & Practice, 5(1), 7–74.
Brown, G., Irving, E., & Keegan, P. (2008). An
Introduction to Educational Assessment, Measurement
and Evaluation. Pearson Education New Zealand
Limited.
Bull, J., & McKenna, C. (2004). Blueprint for computer-
assisted assessment. London: RoutledgeFalmer.
Carpenter, T. P., & Moser, J. M. (1984). The Acquisition
of Addition and Subtraction Concepts in Grades One
through Three. Journal for Research in Mathematics
Education, 15(3), 179–202.
Charles, R., Lester, Frank, & O’Daffer, Phares. (1987).
How To Evaluate Progress in Problem Solving.
National Council of Teachers of Mathematics, 1906
Association Drive, Reston, VA 22901.
Conole, G., & Warburton, B. (2005). A review of
computerassisted assessment. ALT-J, 13(1), 17–31.
Dinham, S., 2008. How to Get Your School Moving and
Improving: An Evidence-based Approach. Aust
Council for Ed Research.
Garfield, J. . B. (1994). Beyond testing and grading: Using
assessment to improve student learning. Journal of
Statistics Education, 2(1), 1–11.
Gray, E.M., Tall, D.O., 1994. Duality, Ambiguity, and
Flexibility: A “Proceptual” View of Simple
Arithmetic. J. Res. Math. Educ. 25, 116–140.
Hattie, J. (2008). Visible Learning: A Synthesis of Over
800 Meta-Analyses Relating to Achievement.
Routledge.
Hattie, J., & Timperley, H. (2007). The Power of
Feedback. Review of Educational Research, 77(1),
81–112.
Herding, D., & Schroeder, U. (2011). Using Capture &
Replay for Semi-automatic Assessment. In CAA 2011
International Conference.
Hollingsworth, J. (1960). Automatic graders for
programming classes. Commun. ACM, 3(10), 528–
529.
JISC. (2010). Effective Assessment in a Digital Age: A
guide to technology-enhanced assessment and
feedback. Retrieved 2 February 2014, from http://
www.jisc.ac.uk/media/documents/programmes/elearni
ng/digiassass_eada.pdf.
Jonsson, A., & Svingby, G. (2007). The use of scoring
rubrics: Reliability, validity and educational
consequences. Educational Research Review, 2(2),
130–144.
Jordan, S. (2013). E-assessment: Past, present and future.
New Directions, 9(1), 87–106.
Mory, E. H. (2004). Feedback Research Revisited. In
Handbook of Research on Educational
Communications and Technology (2nd ed.) (pp. 745–
783). Mahwah, NJ, US: Lawrence Erlbaum
Associates Publishers.
National Council of Teachers in Mathematics (NCTM).
(2000). Principles and Standards for School
Mathematics. Reston, VA: NCTM.
Orrell, J. (2008). Assessment beyond belief: the cognitive
process of grading. Balancing Dilemmas in
Assessment and Learning in Contemporary Education,
251–263.
Richter, M. M., & Rosina, O. (2013). Case-based
reasoning: a textbook. London: Springer.
Rittle-Johnson, B., & Alibali, M. W. (1999). Conceptual
and procedural knowledge of mathematics: Does one
lead to the other? Journal of Educational Psychology,
91(1), 175–189.
Sangwin, C. (2013). Computer Aided Assessment of
Mathematics. Oxford University Press.
Sargent, J, Wood, M.M, & Aderson, S.M. (2004). A
human-computer collaborative approach to the
marking of free text answers. In 8th International
Computer Assisted Assessment Conference,.
Loughborough University.
Stevens, D. D., & Levi, A. J. (2011). Introduction to
Rubrics: An Assessment Tool to Save Grading Time,
Convey Effective Feedback, and Promote Student
Learning. Stylus Publishing, LLC.
Suskie, L. (2010). Assessing Student Learning: A
Common Sense Guide. John Wiley & Sons.
Szetela, W. (1992). Evaluating Problem Solving in
Mathematics. Educational Leadership, 49(8), 42–45.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
100
