
Tutoring and Assessment Through Games and Emotions
Sintija Petrovica
Department of Artificial Intelligence and Systems Engineering, Riga Technical University, 1/4 Meza Street, Riga, Latvia
Keywords: Tutoring, Affective Tutoring Systems, Emotions, Game-based Learning, Assessment.
Abstract: Research in psychology, neuroscience, pedagogy, and cognitive science has shown that emotions (or affect)
play a key role in the learning process, decision making, understanding of a problem domain and motivation
to learn. As a result, researchers have been working on the creation of affective tutoring systems.
Meanwhile, game-based learning is becoming more and more popular and it is considered as an emerging
technology that will have a large impact on education in the next 2-3 years. Therefore, there is no doubt that
researchers believe that the combination of educational games and affective tutoring systems may improve
students’ performance. The aim of this paper is to describe the current state of this research direction and to
identify gaps and possible opportunities for the future work. Research shows that the main emphasis is on
the adapted teaching/learning process that takes into account both student's knowledge and emotions but the
aspect of the assessment, which also is an integral part of this process, has been neglected in tutoring
systems that include emotions and game-based interactions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since 1970-ties the research is being carried out for
the development of intelligent tutoring systems
(ITS) that try to imitate human teachers and their
teaching methods. However, recent study in
psychology, neuroscience, pedagogy, and cognitive
science has shown that emotions play a key role in
the learning process, decision making, motivation,
and understanding (Ahn and Picard, 2005). As a
result, over the last decade researchers inspired by
the close relationship between emotions and learning
have been working on the integration of an affective
component into human-computer interaction. This
has led to creation of a new generation of ITSs –
affective tutoring systems (ATSs) that are capable
not only to act as traditional ITSs and to implement
all components of the tutoring process but also to
perform adaptation to an emotional state of the
student and to show system’s own emotions using
pedagogical agents.
In parallel to this research direction, another field
related to educational technologies is becoming
increasingly popular – game-based learning (GBL)
and digital educational games. GBL is considered as
an emerging technology that will have a large
impact on education in the next 2-3 years (Kerfoot
and Kissane, 2014). Therefore, there is no doubt that
researchers believe that the combination of
educational games and ATSs may improve students’
performance and attitude toward the learning
process (Novak and Johnson, 2012).
Despite the research carried out so far and the
already designed ATSs (including those few tutoring
systems that use game-like activities), the problem
of how to adapt tutoring not only to a student's
knowledge state but also to his/her emotional state
has received much less attention. Since this question
is mainly related to changes in ITS's pedagogical
actions then it is closely connected to the
implementation of the pedagogical module. This
component imitates the human teacher, determines
appropriate tutoring strategies, and manages the
entire teaching/learning process including tutoring of
the theory and practice, as well as assessment of
student's knowledge. In fact, the assessment process
is the one that mostly involves negative emotions
(e.g. anxiety or fear) that can inhibit learning and
negatively influence the reasoning and performance
of the student (Petrovica, 2014). Therefore, the aim
of this paper is to describe the current state of this
research direction and to identify gaps and possible
opportunities for the future work, as well as the
architecture of a game-based ATS focused on the
assessment of student's knowledge is proposed in
this paper.
The structure of the paper is as follows. Section 2
describes the concept of ATS and explains the role
539
Petrovica S..
Tutoring and Assessment Through Games and Emotions.
DOI: 10.5220/0005447605390544
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (AGEWELL-2015), pages 539-544
ISBN: 978-989-758-107-6
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

of emotions in the learning process. Section 3 is
devoted to the GBL and presents ATSs which use
game-like interactions in the tutoring process.
Section 4 introduces the current state in the game-
based assessment and discusses identified types of
the assessment used in games. Section 5 describes
the developed architecture of a game-based ATS
incorporating games as a tool for the assessment of
student's knowledge. Conclusions and planned
future work are presented in Section 6.
2 AFFECTIVE TUTORING
SYSTEMS
ITSs are a generation of computer systems which
aim to support and improve teaching and learning
process in certain knowledge domain, considering
individuality of a student like in traditional
one-to-one instructional process, which, according to
B. Bloom (1984), is an ideal condition for learning.
Thus, an effective ITS should simulate what good
human teachers do when carrying out individualized
tutoring process. Consequently, the development of
ITSs is related to a number of serious challenges
because appropriate implementation can be done
only having expertise in such fields as psychology,
computer science, and pedagogy (Stankov et al.,
2008). The traditional architecture of ITSs consists
of components that store three basic kinds of
knowledge (Figure 1): domain knowledge (Problem
domain module), pedagogical knowledge
(Pedagogical module), and knowledge about the
student (Student diagnosis module). Recently, a
fourth component was added to the architecture –
the Interface module that is responsible for the
interaction with students (Han et al., 2005).
Figure 1: The traditional architecture of ITSs.
Over the past few decades, research in
neuroscience and psychology has shown that
emotions are fundamental to learning because they
have an effect on perception, attention, decision
making, motivation to learn, understanding of a
problem domain, as well as acquisition, creation,
and retrieval of knowledge (Taylor, 2001;
Wilkinson, 2013). It has been shown that positive
emotions, such as engaged concentration, joy, and
excitement, can lead to increased learning, facilitate
long-term memory, retrieval, and working memory
processes and thereby can potentially improve
motivation, creativity, and problem-solving skills.
Alternatively, negative emotions, such as frustration,
boredom, and anger, may lead to decreased
motivation and desire to avoid the fulfilment of tasks
(Novak and Johnson, 2012).
As a result, the field of ATSs has started to
evolve by integrating into the traditional ITS the
ability to recognize student’s emotions and to
respond to them in an appropriate way in order to
enhance student’s performance (Ochs and Frasson,
2004; Li et al., 2014). In such a way, the system
becomes more flexible, adaptive, and natural in
terms of similarity to the traditional learning
environment, but in order to develop such a tutoring
system, special attention should be paid to the
pedagogical module and tutoring strategies that take
into account not only the student's current
knowledge state but also adapt tutoring to his/her
emotional state (Petrovica, 2013). In fact, there are
even more factors related to student himself/herself
and learning process that should be considered when
implementing the adaptation of the tutoring process,
e.g. personal needs and interests of a student, his/her
learning style and progress on the tutorial task,
tutor's domain knowledge, and pedagogical
objectives (Murray et al., 2004).
3 GAME-BASED LEARNING
AND EMOTIONS
GBL is the subject of increasing attention mostly
because it is thought that games increase motivation,
interest, and learning (Sabourin and Lester, 2014).
Educational games are games that are designed to
help people to learn about certain subjects, expand
concepts, understand an historical event or culture,
or assist them in acquiring skills as they play.
Realizing the psychological need and benefits of
gaming in the learning process, this educational tool
has become increasingly popular. Computer games
have now been accepted as a tool within academia
and even industry training. They are used for
teaching different problem domains, e.g. science,
education, mathematics, foreign languages, reading,
physics, health, etc. (Shute and Ventura 2013;
Kerfoot and Kissane, 2014).
Games are interactive and adaptive form of play
that includes goals, rules, outcomes, and feedback
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
540

(main elements of any teaching/learning process), as
well as develops problem solving skills, presents
challenge and competition and encourages social
interaction between multiple players (Kamenetz,
2014). They provide fundamental needs for learning
by giving enjoyment, encouraging involvement,
increasing motivation, doing, flow, learning,
adrenaline, creativity, social interaction, and
emotions (Prensky, 2001; Bonnycastle, 2009).
More than one learning style is also supported in
GBL because information is provided in various
formats, although the preference in most games is
for information to be visually presented. By
providing information in multiple formats (visual,
textual, auditory, etc.), students cannot only choose a
style that matches their own preference, but they can
also practice their skills in others (Becker, 2005).
Games are voluntary, internally motivating, and
involve active cognitive, physical, and/or affective
engagement that allows for the freedom to
experiment, fail, and recover from failures (Shute
and Ventura 2013). It has been shown that attention,
memory and motivation are main aspects affectively
influenced through GBL and that principles from
affective computing can assist in the development of
these areas (Wilkinson, 2013). Since student
engagement and motivation are critical aspects in
improving learning gains within educational learning
environments then the encouragement of positive
affect and engagement while students are learning
have become the main design goal of many learning
environments. GBL offer significant potential for
increasing student engagement and motivation
(Sabourin and Lester, 2014).
As a result, researchers believe that the
combination of educational games and ATSs may
improve students’ performance and attitude toward
learning and instructional tasks (Novak and Johnson,
2012). The research in emotion recognition domain
can also positively influence the field of educational
games, since the success of digital educational
games depends on the system ability to provide
gaming characteristics such as feedback and
challenge to student's cognitive and affective states
(Yannakakis and Paiva, 2015).
However, currently only a few ATSs are
developed as game-based environments. Prime
Climb (Conati et al., 2013) created for learning
number factorization skills, CRYSTAL ISLAND
(Sabourin and Lester, 2014) developed as 3D
narrative-centred learning environment for eighth-
grade microbiology, PlayPhysics (Munoz et al.,
2011) and Newton’s Playground (Andres and
Rodrigo, 2014) designed for tutoring basic physics
concepts and principles, can be mentioned as
examples of such kind of systems using embedded
pedagogical activities as engaging and game-like
interactions. Although emotional reactions are not
widely modelled in educational games and small
number of ATSs exploits GBL as main teaching
approach, the application of games for the
knowledge assessment is used even more rarely in
tutoring systems (Li et al., 2014).
4 ASSESSMENT OF
GAME-BASED LEARNING
Over the past several years, GBL and assessment
have emerged as a promising area of innovation in
education. Actually, the assessment of learning is
considered to have the greatest influence on the next
generation of educational games. It is well-suited to
measure new learning standards, can provide
authentic assessment activities and situations for
meaningful tasks, and can enhance the teaching and
learning process (Tucker, 2013). Therefore, many
educators and researchers see digital games as
potential learning and assessment environments for
the 21
st
century (Asbell-Clarke et al., 2013). In fact,
games are all about constant assessment. They do
not teach directly but rather provide constant
challenges and then give feedback on decisions
(Fujimoto, 2011).
In recent years, the research on the identification
of possible types of the game-based assessment
(GBA) has been carried out (Ifenthaler et al., 2012;
Asbell-Clarke et al., 2013; Shute and Ventura 2013).
Currently, it is possible to identify two most
commonly used assessment methods: external and
internal (embedded or in-game) assessment (Hainey
et at., 2012; Ifenthaler et al., 2012; Whitton, 2014).
External assessment is not a part of the game-
based environment. It is realized through reports,
interviews, knowledge maps or causal diagrams, and
test scores based on multiple-choice questions or
essays, therefore it is more time consuming and
labour intensive (Hainey et at., 2012; Whitton,
2014). Since this assessment type is usually
performed after tutoring process, it often focuses on
the outcome and does not allow conclusions on the
cause of a possible incorrect result. In addition, an
educational assessment after playing the game
cannot involve instant feedback while playing the
game (Eseryel et al., 2011; Ifenthaler et al., 2012).
Internal assessment is a part of the game and can
be carried out without interruption of the game
TutoringandAssessmentThroughGamesandEmotions
541

(Hainey et at., 2012; Whitton, 2014). This type is
also called "stealth assessment" because it is
integrated as a part of the game and aim to support
learning, maintain flow, and remove (or reduce) test
anxiety at the same time not losing the validity and
reliability of the assessment. Stealth assessments are
typically developed using the evidence-centred
design (ECD) framework that aims to establish a
logical alignment between the domain being
assessed (competency model), assessment task
design (task model), and interpretation (evidence
model) (Shute and Ventura 2013; Asbell-Clarke et
al., 2013). In contrast to previous assessment type,
the internal assessment mostly focuses on the
process. Also tracking of motivational, emotional,
and meta-cognitive characteristics during game-play
can help to better understand the specific behaviour
and final outcomes (Ifenthaler et al., 2012).
Currently, GBA and games designed particularly
for the assessment are only starting to evolve. The
first educational game SimCityEDU: Pollution
Challenge! intended for GBA was developed in
2014 by GlassLab (GlassLab, 2014). It incorporates
an assessment engine that is used to assess both
students’ individual knowledge and understanding.
As asserted by authors of the game, it aims to evoke
and measure real learning in real ways using both
summative and formative tests (Kamenetz, 2014).
However, it should be noted that this educational
game focuses only on the knowledge assessment and
disregards player’s emotions during the game-play.
Therefore, the consideration of students’ emotions in
the assessment of the learning effect and
combination of GBA and ATSs is encouraging area
for research positively influencing the development
of tutoring systems that are able to recognize
emotions and respond to them accordingly.
5 GAME-BASED AFFECTIVE
TUTORING SYSTEM
As it was mentioned at the beginning of paper, the
pedagogical module of ITSs is responsible for the
selection of tutoring strategies. Most strategies,
regardless of their complexity, are based on a
fundamental three-step process – teaching or
presentation of the theoretical material, practice
through exercises or applied scenarios, and
knowledge assessment by providing feedback to the
student after testing (Petrovica, 2014).
For limited or narrow problem domains (or
particular topics from wider problem domains like
mathematics or physics), the creation of an ATS as a
game-based environment that gives only
explanations about misunderstood concepts and is
intended mostly for developing practical skills, is
appropriate. But in case of more extensive problem
domains covering many topics, it will be almost
impossible to carry out teaching/learning process
without tutoring theory and training practical skills.
Therefore, GBL and GBA could be integrated in
ATSs tutoring wider problem domains as one of the
components to improve their adaptability, ability to
influence students’ emotions, to engage students in
the teaching/learning process, and to assess their
knowledge.
Keeping in the mind this idea, the architecture of
ATS has been developed to include traditional
architecture of the ITS, integrate the modelling of
the student’s emotional state and implement game-
based knowledge assessment as a part of the
pedagogical module (Figure 2). This figure shows
the general architecture of the planned system, the
main functions of each system’s module, as well as
presents the Pedagogical module in detail showing
how it will be divided in three main parts. Each of
the parts corresponds to one of the three previously
mentioned fundamental steps of tutoring strategies.
To create a more student-centred system (thus giving
the student more freedom) both the tutoring of the
theory and the practice is divided into two modes –
managed by the student and managed by the tutoring
system depending on the personality of the student.
Also the GBA is planned as a two-mode
implementation when the student can choose
between single-player and multi-player versions
because for some students the result will be
important only for them, while for others
competition with other players will be essential for
their personality.
In addition, the determination of the student’s
emotional state is intended during all three steps in
order to make changes in the tutoring process.
Changes can be applied in various forms – different
presentation way of the theoretical material can be
chosen to support the student’s learning style,
difficulty level of a practical task can be changed in
order to challenge student’s skills and abilities, or
the game can be paused to offer the additional
theoretical material or to provide assistance in case
of difficulties with the task solving.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
542
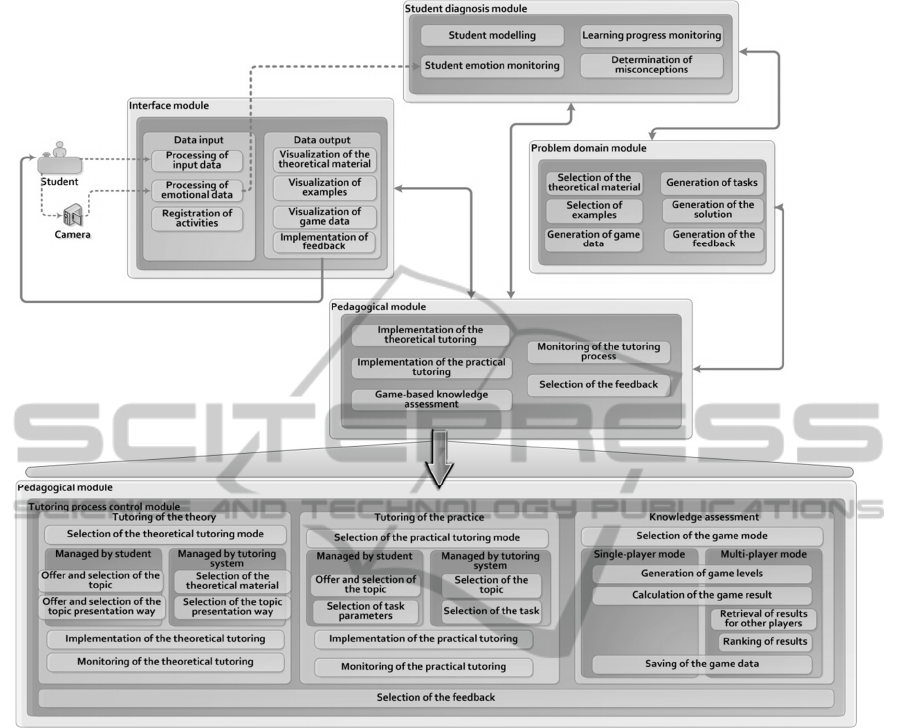
Figure 2: The architecture of ATS integrating game-based knowledge assessment.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The concepts of ITS and ATS are discussed in this
paper as well as the role of emotions in the learning
process is explained. Furthermore, GBL that is
becoming more and more popular is presented
describing also the influence of games on learning
process and student’s emotions. The application of
GBL in ATSs and examples of such kind of systems
are also given. However, it should be noted that
ATSs using game-like activities are not so common
and are mostly used to teach narrow problem
domains or particular topics from wider fields.
Moreover, games are used to provide knowledge to
students and to develop practical skills but not to
assess them in these systems. One of the possible
reasons for this can be the fact that the process of
design and implementation of assessment features
into GBL environments adds a very time-consuming
step to the design process, as well as this research
direction and development of such game-based
systems focused on the assessment are only at an
early stage. Therefore, research related to the
combination of game-based knowledge assessment
with ATSs is promising area for the development of
such tutoring systems.
The architecture of ATS incorporating game as
knowledge assessment tool in the pedagogical
module is designed in this paper. This work has been
carried out to supplement an existing theoretical
research on the GBA and to improve capabilities of
already developed ATSs in terms of the assessment
of student’s knowledge using game-based
interactions. The proposed architecture of ATS is
planned to be implemented as tutoring system for
the study course related to fundamentals of artificial
intelligence (AI), particularly for tutoring and
assessing knowledge of AI search algorithms.
TutoringandAssessmentThroughGamesandEmotions
543

REFERENCES
Ahn, H. and Picard, R.W. (2005). Affective-Cognitive
Learning and Decision Making: A Motivational
Reward Framework for Affective Agents. In First
International Conference on Affective Computing and
Intelligent Interaction, pages 866-873.
Andres, J.M.L. and Rodrigo, M.M.T. (2014). The
Incidence and Persistence of Affective States While
Playing Newton’s Playground. In 7th International
Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology,
Information Technology, Communication and Control,
Environment, and Management, Palawan, Philippines.
Asbell-Clarke, J., Rowe, E., and Sylvan, E. (2013).
Assessment design for emergent game-based learning.
In 2013 ACM SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors
in Computing Systems, pages 679-684.
Becker, K. (2005). Games and Learning Styles. In Special
Session on Computer Games for Learning and
Teaching at ICET 2005, Calgary, Canada.
Bloom, B.S. (1984). The 2 sigma problem: The Search for
Methods of Group Instruction as Effective as One-to-
one Tutoring. Educational Researcher, 13(6):4-16.
Bonnycastle, D. (2009). Promoting active learning using
games. Active learning series. www.slideshare.net/
DeirdreB/promoting-active-learning-using-games.
Conati, C., Jaques, N. and Muir, M. (2013). Understanding
attention to adaptive hints in educational games: an
eye-tracking study. International Journal of Artificial
Intelligence in Education, 23(1-4):136-161.
Eseryel, D., Ifenthaler, D., and Ge, X. (2011). Alternative
assessment strategies for complex problem solving in
game-based learning environments. In Multiple
perspectives on problem solving and learning in the
digital age, pages 159-178.
Fujimoto, R. (2011). Assessment in game-based learning.
http://shoyulearning.wordpress.com/2011/05/17/asses
sment-in-game-based-learning/
GlassLab. (2014). SimCityEDU: Pollution Challenge!
https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/playfully-
games/SC/brochures/SIMCITYbrochure_v3small.pdf.
Hainey, T., Connolly, T.M., Baxter, G.J., Boyle, L.,
Beeby, R. (2012). Assessment Integration in Games-
based Learning. In 6th European Conference on
Games-based Learning (ECGBL), pages 174-183.
Han, S.G., Lee, S.G., and Jo, G.S. (2005). Case-based
Tutoring Systems for Procedural Problem Solving on
the WWW. Expert Systems with Application,
29(3):573–582.
Ifenthaler, D., Eseryel, D., and Ge, X. (2012). Assessment
for game-based learning. In Assessment in game-based
learning. Foundations, innovations, and perspectives,
pages 3-10.
Kamenetz, A. (2014). Psychometric Considerations in
Game-based Assessment: Executive Summary.
GlassLab Research.
Kerfoot, B.P. and Kissane, N. (2014). The use of
gamification to boost residents' engagement in
simulation training. JAMA Surgery, 149(11):1208-
1209.
Li, J., Han, Y., and Liu, S. (2014). Physiological
Evaluation of the Players’ Emotions in Different
Educational Games. American Journal of Educational
Research, 2(9):735-739.
Munoz, K., McKevitt, P., Lunney, T., Noguez, J., and
Neri, L. (2011). Affective Educational Games and the
Evolving Teaching Experience. In Computer Games
as Educational and Management Tools: Uses and
Approaches, pages 206-228.
Murray, R.C., VanLehn, K., and Mostow, J. (2004).
Looking ahead to select tutorial actions: A decision-
theoretic approach. International Journal of Artificial
Intelligence in Education, 14(3-4):235–278.
Novak, E. and Johnson, T.E. (2012). Assessment of
student's emotions in game-based learning. In
Assessment in game based learning: Foundations,
innovations, and perspectives, pages 379-399.
Ochs, M. and Frasson, C. (2004). Emotionally Intelligent
Tutoring Systems (EITS). In 17th International
FLAIRS Conference, pages 251-256.
Petrovica, S. (2013). Adaptation of Tutoring to Students'
Emotions in Emotionally Intelligent Tutoring Systems.
In 2nd International Conference on e-Learning and e-
Technologies in Education, pages 131-136.
Petrovica, S. (2014). Tutoring Process in Emotionally
Intelligent Tutoring Systems. International Journal of
Technology and Educational Marketing, 4(1):72-85.
Prensky, M. (2001). Fun, play and games: What makes
games engaging? In Digital game-based learning,
pages 106-144.
Sabourin, J.L. and Lester, J.C. (2014). Affect and
Engagement in Game-Based Learning Environments.
IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 5(1):
45-56.
Shute, V.J. and Ventura, M. (2013). Digital Games,
Assessment, and Learning. In Measuring and
supporting learning in games: Stealth assessment,
pages 17-29.
Stankov, S., Rosić, M., Žitko, B., and Grubišić, A. (2008).
TEx-Sys Model for Building Intelligent Tutoring
Systems. Computers and Education, 51(3):1017–1036.
Taylor, W. (2001). Transformative Learning Theory: A
Neurobiological Perspective of the Role of Emotions
and Unconscious Ways of Knowing. International
Journal of Lifelong Education, 20(3):218-236.
Tucker, E. (2013). Designing the future of games,
learning, and assessment.
http://www.joanganzcooneycenter.org/2013/05/17/designi
ng-the-future-of-games-learning-and-assessment/
Whitton, N. (2014). Games as Reward Mechanisms. In
Digital Games and Learning: Research and Theory,
pages 99-108.
Wilkinson, P. (2013). Affective Educational Games:
Utilizing Emotions in Game-Based Learning. In 5th
International Conference on Games and Virtual
Worlds for Serious Applications, pages 1-8.
Yannakakis, G.N. and Paiva, A. (2015). Emotion in
Games. In The Oxford Handbook of Affective
Computing, pages 459-471.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
544
