
A Model Driven Approach for Design Flexible e-Assessment
Fahima Hajjej, Yousra Bendaly Hlaoui and Leila Jemni Ben Ayed
LaTICE, Tunis, Tunisia
Keywords: e-Assessment, MDA, LTSA, UML DA, Flexibility.
Abstract: Currently, there are many problems in the domain of the development of the e-Assessment process such as
the difficulty to use a same e-assessment process by different e-learning platforms, the low rate of the e-
assessment model reuse by various e-learning systems and the hardness to guarantee the consistency
between designs and codes. Therefore, to resolve these problems, we need an approach aiming to develop a
generic e-assessment process model which will be adapted automatically to any e-learning system. Hence,
we propose a model driven approach for design flexible E-assessment process. We use an abstract
description provided by UML activity diagram language and coupled with LTSA standards.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, universities and higher education
institutes have become more and more interested to
use computers to deliver their formative and
summative assessments. Hence, the e-assessment
plays a most important role as it constitutes an
appropriate technique to gather student feedback
relatively to provided course content.
However, the e-assessment strategy is not
defined as a similar and a unique e-assessment
strategy for different sections and departments of a
given education institute. This is because each of
these departments develops an e-assessment system
based on its specialization and courses. Therefore, at
a same university, we can have more than one e-
assessment system. While the usage different
systems gains recognition and acceptance amongst
institutions, there are new problems arising that need
to be solved. Because of multiplicity of platforms
and approaches used for various systems
implementation, it becomes increasingly difficult to
exchange pieces of information among these
systems. In fact, the variance of the e-assessment
strategy has a bad influence on the e-assessment
systems in the same university.
To solve such problems, we propose to develop a
generic e-assessment model able to support any kind
of assessment strategy.
Model Driven Architecture (MDA) (Kleppe et
al., 2003) has emerged as a software engineering
framework for dealing with the problem of system
interoperability across different execution platforms.
Then, MDA code generation mechanisms allow
generating code from developed models.
Actually, many teams have committed to resolve
e-learning problems by using MDA approach.
Authors in (Bizonova et al., 2007) have used a
Reversed MDA paradigm. Through the most popular
Learning Management Systems (LMS) Moodle and
OLAT, they have generated a Platform Independent
Model (PIM) suitable for a general learning
management system (LMS). Authors in (Bizonova
and Pilatova, 2010) focusing on interoperability of
two aspects of LMSs, such test question types and
assessments.
In summary, these approaches provide a solution
to the problem of LMS interoperability but they
present many limits and disadvantages. All the
suggested approaches do not follow a well defined
e-learning standard. Moreover, they do not have
specified the e-assessment process in their modelling
activity.
In parallel, it is necessary to guarantee the
interoperability across different LMSs to save
development effort, time and cost. The need for
interoperability of e-learning systems has been
intensively treated in recent years and several new
standards have been created such as SCORM
(Sharable Content Object Reference Model)
(Welsch, 2007) and IMS-LD and LTSA (Learning
Technology Systems Architecture) (Corbiere and
Choquet, 2004). However, these standards have
limits concerning personalization and contextual
expressiveness. In addition, most LMSs have been
364
Hajjej F., Bendaly Hlaoui Y. and Jemni Ben Ayed L..
A Model Driven Approach for Design Flexible e-Assessment.
DOI: 10.5220/0005453003640371
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2015), pages 364-371
ISBN: 978-989-758-107-6
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

created without regard to standards and therefore
cannot be considered as a part of an overall solution.
But is it possible to achieve the goal of
interoperability and data exchange even among
LMSs that are not based on standards?
In this paper, we suggest to solve the problems
mentioned above by proposing a common
framework that can be used to specify and classify
existing or future learning management systems
(LMS). We are interested to propose a model driven
approach (MDA) for e-assessment platform.
In this proposal, our objective is to give a high
level of abstraction to our model by coupling the
MDA and the LTSA. For the reason that, it has been
observed that LTSA is too abstract to be adapted in a
uniform way by LMS developers. A high level
design that satisfies the IEEE LTSA standard has
been proposed for future development of efficient
LMS software.
In the first level of our approach, we propose a
generic specification and design step for the e-
assessment process based on workflow technology
and learner profile adaptability.
As mentioned above, e-learning needs to be more
adaptive and flexible to support any kind of learner
according to his/her capability. In the e-learning
process, the e-assessment plays a most important
role not only to evaluate student knowledge but also
to gather student feedback relatively to a learning
content. An e-assessment is the fact that the learner
responds to question given by the tutor to evaluate
the learner knowledge. Therefore, in e-learning
environment, learning and assessment processes
must work together and in parallel as a complete
learning process.
Consequently, we need a solid e-assessment
approach to evaluate efficiently the learner
knowledge in one hand, and on the other hand to
allow tutor to regulate, update and improve his
teaching strategy. Such e-assessment approach could
not be suitable for all types of learners as they
present different knowledge profiles and learning
behaviours. Some of them need to be assessed on the
complete learning materials to evaluate their overall
knowledge. Others may only need to estimate their
knowledge at a particular stage of the learning
process in order to access to the suitable learning
material.
Hence, we need a flexible e-assessment approach
which evaluates each learner’s knowledge relatively
to its learning behaviour profile. To attempt this
objective, we propose an approach to specify a
generic e-assessment process. We use workflow
technology to coordinate different tasks and to
model e-assessment process. To specify this e-
assessment workflow process, we use UML activity
diagram language. Then, our approach is based on a
workflow composition by refinement to reduce
complexity. In addition, we define a set of
refinement rules to adapt the e-assessment process
for each learner.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. In
section 2 we present used technologies: explain the
benefits of MDA- based instructional design,
especially when compared to design based on
Technology Learning Standards. Section 3 discusses
scientific work related and presents MDA approach.
We end with a conclusion and an overview of future
possibilities.
2 USED TECHNOLOGIE
2.1 A Model Driven Architecture
Model-driven architecture (MDA) focuses on the
evolution and the integration of applications across
heterogeneous middleware platforms. It provides a
systematic framework using engineering methods
and tools to understand, design, operate, and evolve
enterprise systems. MDA promotes modelling
different aspects of software systems at levels of
abstraction, and exploiting interrelationships
between these models. In this paper, we propose a
model-driven approach to e-learning system
development based on core Object Management
Group (OMG) MDA standards.
Many researches on MDA in e-learning have
been conducted in recent years.
Zuzana bizonova Authors in (Bizonova et al.,
2007) have used a Reversed MDA paradigm. He
compares platform specific models of systems and
creates a platform independent model that covers
common functionalities of some learning
management systems. Authors in (Dehbi et al.,
2013) present LMSGENERATOR, a multi-target
Learning management system generator with a
model-driven methodology based on MDA approach
coupled with component approach. Nathalie Moreno
Authors in (Moreno and Romero, 2005) present a
framework model called e-MDA which is ideal for
the “4+1” view model, and equivalent to the
calculation of independent models (CIM) in MDA.
Authors in (Wei et al., 2006) proposed a model-
driven development approach for e-learning
platform. He establishes the domain model (CIM)
through the analysis of business logic, and then
AModelDrivenApproachforDesignFlexiblee-Assessment
365
stratified n the PIM under the J2EE framework, and
proposed the method of transformation from PIM to
PSM layer by layer.
Aimed at the problems that have been mentioned
above, we proposed a development approach which
is for developing e-learning platform with MDA.
We would like to use MDA (Soley et al., 2000)
principle as the background for solution of the
proposed problem with LMS integration. We can
compare platform independent models of different
systems and create a platform independent model
that covers common functionalities of all learning
management systems. Our goal is to define a
generalized model of LMS system consisting of
features of all other LMS systems that can be
mapped into it.
2.2 LTSA
The largest effort on developing Learning
Technology System architecture has been carried out
in the IEEE. The LTSA deals with the Learning
Technology System as a whole, encompassing
human resources, infrastructure and learning
resources as well as their interactions.
The LTSA describes high-level system
architecture and layering for learning technology
systems, and identifies the objectives of human
activities and computer processes and their involved
categories of knowledge. These are all incorporated
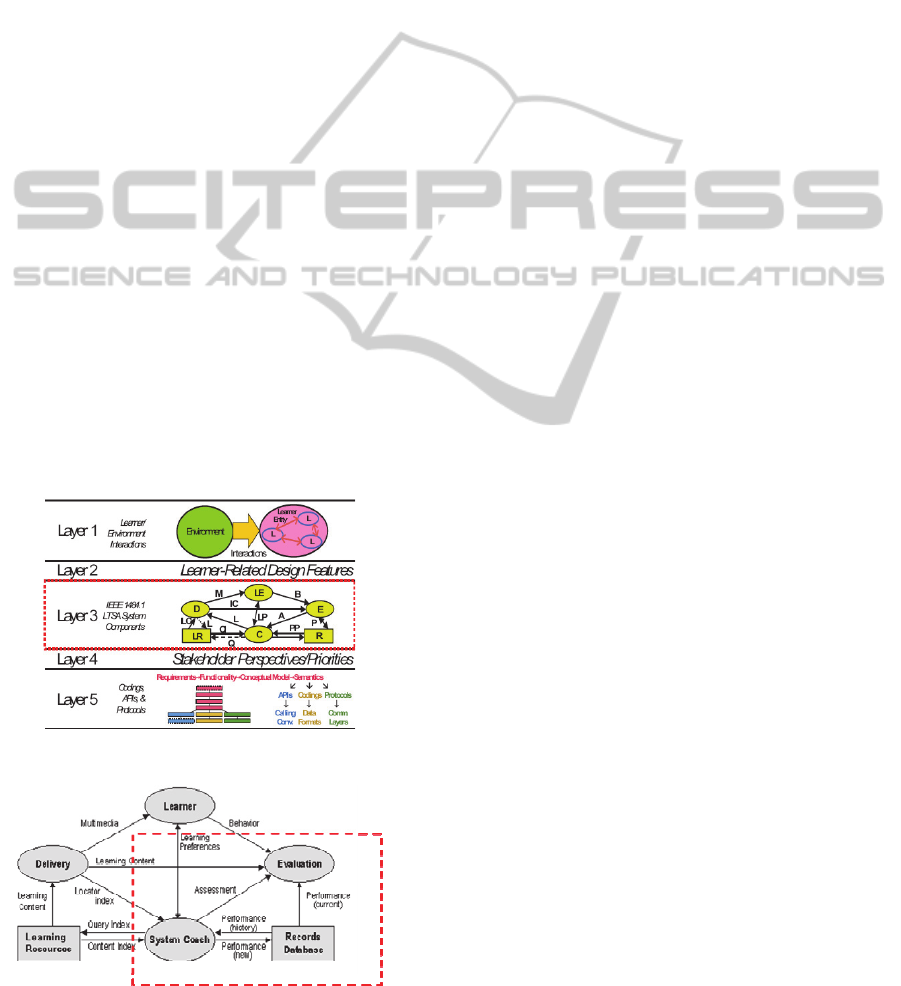
into the 5 layers, as presented in Figure1.
Figure 1: LTSA Layers.
Figure 2: LTSA processes.
Concretely, the LTSA identifies four processes:
learner entity, evaluation, coach, and delivery
process; as shown in Figure 2.
However, the use of this standard presents
certain disadvantages. Some of the functional areas
not included in LTSA are identified and a brief
report of the same is presented here.
a) The model does not regard the learning object
designer as an integrated component in the learning
process. b) The students evaluation records are
stored but how to use it is not specified. c) For a
distance mode learner, if the learner possess some
fundamental wrong/incomplete idea and the
feedback system fails to identify it, then the LTSA
layer II algorithm falls under a never ending iterative
cycle. d) Students counseling is not included in the
LTSA architecture. Students take on courses
generally by only the name of the course. Many a
times they overlook the prerequisites.
Considerable attention has been focused recently on
MDA (Model Driven Architecture) as an alternative
solution to systems that guarantees personalization
while ensuring interoperability based on software
engineering standards. Our current research focuses
on proposing coupling between MDA and LTSA.
This coupling aims to resolve limits of LTSA
standard and to improve the abstract view in our
approach. Then in our work, we propose a new
version learning application is totally independent of
any underlying platform. Therefore, it will follow
the guidelines proposed in MDA (OMG group).
Models of LTSA system will be structured explicitly
into Platform Independent Models (PIMs) and
Platform Specific Models (PSMs).
3 THE APPROACH OF
DEVELOPPING A GENERIC
E-ASSESSMENT PROCESS
MDA is a way to organize and manage system
architectures; it is supported by automated tools and
services for both defining the models and facilitating
model types. We would like to use MDA principle
as the background for solution of the proposed
problem with LMS integration. We can compare
platform independent models of different systems
and create a platform independent model that covers
common functionalities of all learning management
systems. Figure3 presents the three levels of model
driven approach for designing and integrating
flexible e-assessment process.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
366

3.1 Development of Generic
e-Assessment Process
In this section, we consider two subjects: flexible e-
assessment and the use of workflow in e-learning
environment.
Figure 3: MDA approach.
We present in this section the development of a
generic e-assessment process using the Learning
Management System (LMS) (Petrina, 2004)
(Aljenaa et al., 2011) and based on the Learning
Technology System Architecture (LTSA) (Corbiere
and Choquet, 2004) which we extend by some
features required to such development. The
generated e-assessment model is specified by UML
activity diagram language.
The advantages of using standards in learning
design have already been pointed out as Standards
are generally developed for use in systems design
and implementation for the purposes of ensuring
interoperability, portability and reusability.
It has been observed that LTSA (LTSC, 2002) is
too abstract to be adapted in a uniform way by LMS
developers. The LTSA describes high-level system
architecture and layering for learning technology
systems, and identifies the objectives of human
activities and computer processes and their involved
categories of knowledge.
In our work, we are interested in Evaluation
process that presents the processing of behaviour to
produce assessment and performance information.
But, some of the functional areas concerns e-
assessment are not included in LTSA. There are
identified as follow:
(a) The student’s evaluation records are stored but
are not useful in the system.
(b) For a distance mode learner, if the learner has
some fundamental wrong/incomplete idea and
the feedback system fails to identify it, then the
LTSA layer II algorithm falls under a never
ending iterative cycle.
To fulfil these limits, we propose in our approach to
adapt the developed generic e-assessment model to
the relative profile of each learner to avoid the
algorithm deadlock. To define the learner profile we
use the evaluation records stored in his\her log file
which are not useful in the LTSA.
To build this generic e-assessment process, we
are brought about following the next steps, as
presented in Fig. 3:
• Step1: Analyze and study the existing LMSs
functionality.
• Step2: create the generic e-assessment activities
from existing LMSs e-assessment tasks.
• Step3: create the generic e-assessment process.
3.1.1 Analyse and Study the Existing LMSs
Functionality
We have studied and analyzed a set of existing
LMSs (Learning Management System) such as
Moodle (Moodle Project), OLAT (OLAT Project)
and LAMS (LAMS Project)… These LMSs provide
several e-assessment tools and not a global e-
assessment process. In fact, we have explored the
functionalities that they offer to realize the e-
assessment.
3.1.2 Create the Generic e-Assessment
Activities from Existing LMSs
e-Assessment Tasks
Figure 4: Generic e-Assessment process activities.
AModelDrivenApproachforDesignFlexiblee-Assessment
367

In this step we have collected the e-assessment tasks
and concepts used by several LMSs to specify and
define generic e-assessment activities. A typical e-
learning system is represented by the following
important concepts: (Student, Teacher, Course
Administrator, Course, Content, Class, Goals, Test,
Assignment, Assessment…). We propose a set of
activities collected from the LMS specific e-
assessment tasks. These e-assessment activities,
corresponding to our generic e-assessment activities,
are presented in a user case, as shown in Figure4.
3.1.3 Create the Generic e-Assessment
Process
We have defined the e-assessment process by
coordinating the generic e-assessment activities,
generated from the previous step, in a workflow
structure. We use workflow technology to have
abstract, generic and flexible e- assessment process.
A workflow consists of a set of linked activities.
It represents an abstract and global view of the work
of a person or a group of persons. Therefore, with
workflows, we manage, in an abstract manner, the
synchronization of the e-learning and the e-
assessment activities between learners and tutors.
This e-assessment workflow model should be a
good communication axe between teachers, learners
and the e-assessment system. Due to the lake space,
we reduce our e-assessment process to a normal
scenario: we try to test learner on each level of
training to guarantee its comprehension and to help
him to reach a high level of knowledge. In fact our
e-assessment process is not independent from the e-
learning process.
In our work, we are interested in the formative e-
assessment because learners are more concerned in
how they have performed their activities more than
to compare their work to other learners.
Furthermore, we are interested in the two varieties of
question: objective and subjective tests. To design
our e-assessment process, we are based on the
learning cycle described in LTSA layer II by
combining two methods of evaluation: the e-
assessment part method and the e-assessment lesson
method.
Our e-assessment process scenario is defined as
follows:
a. The learning starts by choosing his studied
course. Then, the e-learning content is composed
into smaller parts to facilitate deployment and
execution assignment.
b. After the reading of each part, the learner carries
out a set of objective test activities. This satisfies
the LTSA layer III which describes the e-
learning components.
c. The e-assessment system corrects automatically
these activities and gives a score according to the
answers of the learner.
d. Learner passes to the following part only when
he\she reaches a score determined by the teacher.
This score and the interval time of the execution
activities are saved into her\his file log.
e. If the result is under the score given by e-
assessment system, the tutor gives additional
stages for the learner to help him to overcome
the crossed difficulty.
f. In fact, learners need regular feedback in order
to know how their performance was evaluated,
and how they can improve it, and also how their
grades are computed. Thus, at the end of the
lesson, tutor proposes a set of subjective
questions in order to observe the complete view
of what a student comprehend from the lesson. If
results are under the score given by e-assessment
system, the teacher would give more clarification
to learner. This, feedback could be presented
more frequently for the users who have started to
make more mistakes, and feedback can be
delayed to slow down students who are
answering too quickly and sloppily.
g. After correction of activities, system affects
score and updates a file log.
The above scenario is specified by the workflow
modelled by UML activity diagrams and presented
by Figure 5 and Figure 6.
Figure 5: Part test.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
368
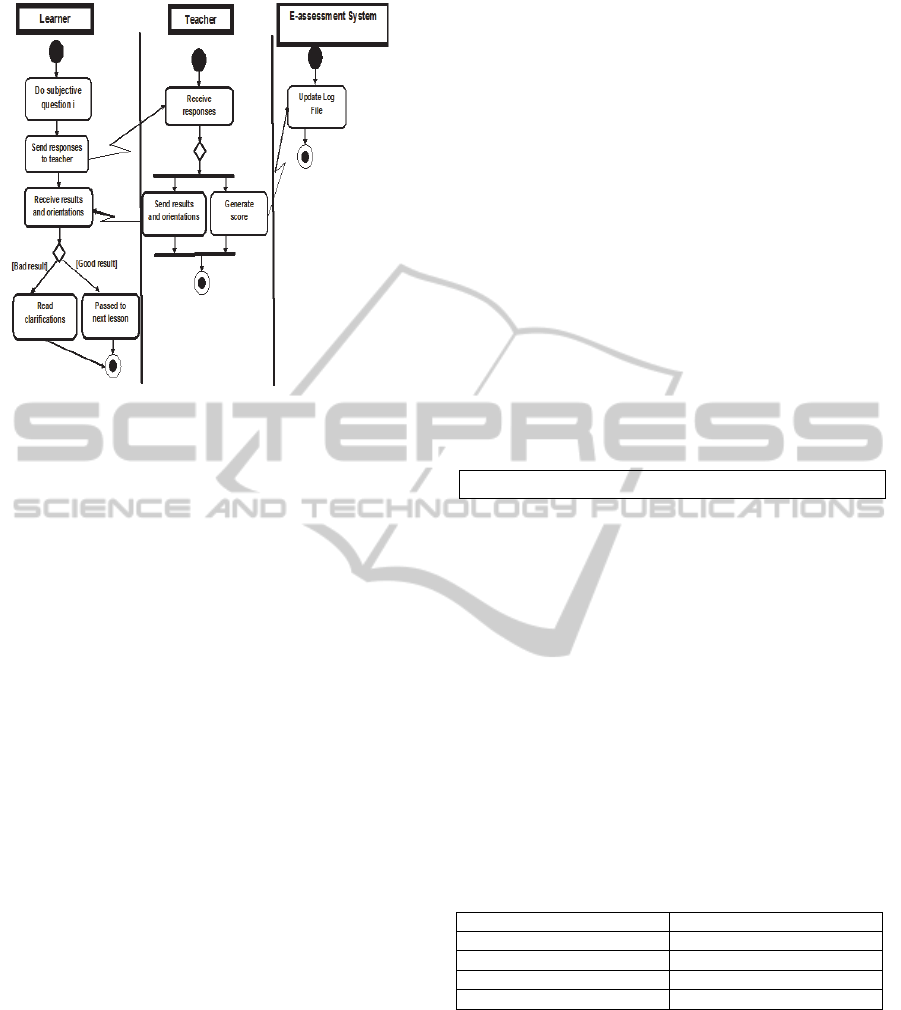
Figure 6: Lesson test.
3.2 Development of Adapted
e-Assessment Process
Once the generic e-assessment process is built, it
will be personalized according to a learner profile
defining her\his level of knowledge. In fact, learner
profiles consist of a set of attributes which describe
the personal data of learners, their formal education
and previous knowledge, their goals and their
evaluation data. In the adaptive e-assessment process
presented in this paper, learner profiles must
maintain information about the knowledge of the
learners on specific topics and data about their
testing activities. These data will be used to adapt
the evaluating and learning activity and could be
also presented at the end of a testing activity in order
to provide detailed descriptions of the progress of
the student.
Hence, we observe the user during a learning
process via her\his log file which contains the
learner behaviour. We use the different information
of the log file to establish and develop an ontology
describing user profile. Each user profile will be an
instance of the developed ontology. Using this
generated log file, the tutor will define and adapt the
learning and assessment material to the behaviour of
the learner. If the learner’s performance does not
meet the pre-defined expectations, the presentation
of the course content is adapted to his level of
knowledge and the selection of the appropriate
assessment content is then performed. Thus, each
learner will be able to get a highly personalized
course which will be appropriate to his level of
knowledge. Therefore, the number and the kind of e-
assessment activities are not similar to all kind of
learners. In fact, to specify an adaptive and flexible
e-assessment workflow, we propose to refine the
generic e-assessment workflow by adding, deleting
or editing specific e-assessment activities according
to each learner profile. Based on the level of
knowledge of a given learner, we define three
refinement rules: add activity (AddAC), delete
activity (DelAC) and edit activity (EditAC).
Applying these rules on a generic workflow, we
provide an adapted e-assessment workflow relatively
to the learner profile. The personalized refinement
is, in fact, the solution of the exception triggered by
the algorithm of the LTSA Layer II when the LMS
fails to identify to which learner belongs the current
assessment feedback.
Applying these functions on a generic e-
assessment process, we provide an adapted e-
assessment workflow relatively to the learner
profile. An adaptation rules is defined as follows:
if Condition then Action
Where Condition specifies a criteria choice of the
adapted rule and the Action represents the adapting
action based on the relative adaptation function.
3.3 Transformations
In this section, we define a set of rules to transform
generic activities to specific LMSs activities.
In this paper, Moodle serves as an example of an
open LMS. Moodle is implemented in PHP, uses a
traditional Apache server and a relational database
management system. Therefore the layout of the
web site is not separated from the logic of the
system. Table 1 is describing the mapping between
our Generic e-assessment actors and Moodle actors.
Table 1: Mapping actors.
Generic e-assessment actors Moodle e-assessment actors
Learner Student
Teacher Teacher
e-assessment system Teacher, administrators
Administrators Administrators
In the following, we present the set of the
elaborated transformations. The goal of the third
step is to create mappings between the PSM models
of candidate LMSs and our generic PIM. Practically
it means to create translation tables for data
structures of a LMS system to the generalized
system. Such relations or mapping rules can have
forms of 1 to1 (simple mapping), 1 to n (refining
mapping) or n to 1 (abstracting mapping). The set of
mapping rules is constructed by specifying the
AModelDrivenApproachforDesignFlexiblee-Assessment
369
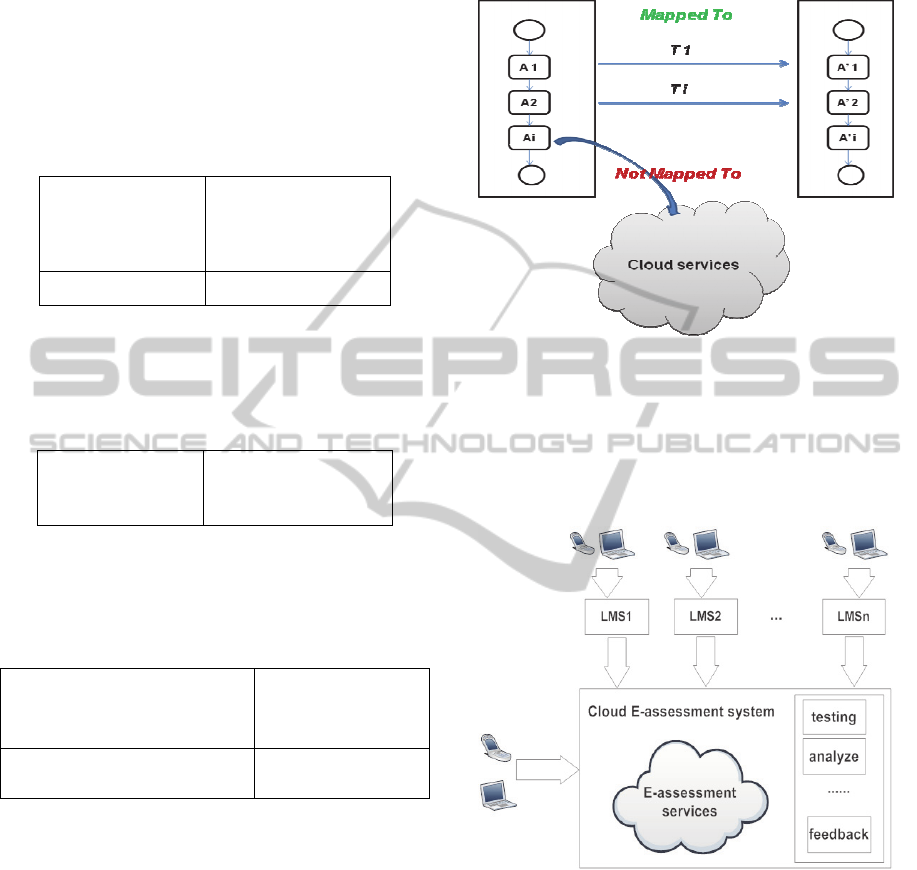
candidate LMS e-assessment activities and their
correspondent of our generic e-assessment process
model. The simple mapping case is trivial. We
simply translate one activity to another one. The
Table 2 shows an example of mapping the
G_SendTest activity of Moodle LMS to
C_SendActivity of our Generic E-assessment
process.
Table 2: Simple mapping.
General PIM activity
G_activity
PSM Candidate activity
Moodle C_activity
C_SendTest G_ SendActivity
There can also be a complex value consisting of
many activities that need to be combined. See an
example of 1 to n on the Table 3.
Table 3: Refining mapping.
General PIM activity
G_activity
PSM Candidate activity
C_activity i + C_activity j
We can also describe a candidate activity by a set
of general activities. See an example of 1 to n on the
Table 4.
Table 4: Abstracting mapping.
General PIM activity
G_activity i + G_activity j
PSM Candidate
activity
C_activity
Correct test-lesson + correct test-
part
Correct activity
As expected, these rules need some extensions to
cover other activities, such as their cognitive ability,
possible disabilities, learning style, computer
environment, etc. Also we would like to make the
existing rules more flexible. Therefore, we define a
cloud service implementing the adaptation process
based on the adaptation functions presented above,
as shown in Figure 7.
A cloud service can be specified and invoked
through as any web based application or service
offered via cloud computing. Cloud services can
include anything from spreadsheets to calendars and
appointment book (Masud and Huang, 2012). Cloud
services can be flexibly provisioned and released,
automatically, to scale and adjust to the levels of
demand. For the customer, the services available
usually appear to be unlimited and can be accessed
in any quantity at any time.
Figure 7: Activities transformation.
The innovation that this cloud e-assessment
system defines the resulting generic and adapted e-
assessment process as a composite cloud service
allowing flexibility and interoperability between any
LMS e-assessment, as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8: LMSs cloud interoperability.
4 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we have proposed a MDA approach
for developing generic e-assessment based on
flexible workflow for adaptation individual profile
learner. We have specified the workflow model by a
standard modeling language, the UML activity
diagram language. We have used in our approach an
UML-AD refinement technique for modeling and
describing workflow applications. Based on this
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
370

refinement, the first step of the approach provides an
UML-AD specification of a generic workflow. In
the second step, we have defined a set of adaptation
rules to achieve an adaptable workflow for each
learner. As future work, we plan to continue with the
implementation of our approach using the cloud
services.
REFERENCES
Bizonova, Z., Daniel Ranc, D., Drozdova, M., 2007.
Model Driven E-Learning Platform Integration,
Proceedings of the {EC-TEL} 2007, Doctoral
Consortium, Crete, Greece.
Bizonova, Z., Pilatova, K., 2010. Model-Driven Analysis
towards Interoperability of Assessments in LMS.
Journal of Information and Organizational Sciences.
Corbiere, A., Choquet, C., 2004. Designer integration in
training cycles: IEEE LTSA model adaptation.
International Conference on Computer Aided
Learning in Engineering Education, Grenoble, France.
12 p.
Lin, J., Ho, C., Sadiq, W., Orlowska, M., 2002. Using
workflow technology to manage flexible e-learning
services. International Forum of Educational
Technology & Society. vol. 5, pp. 116-123.
OLAT Project, University of Zurich, Switzerland,
http://www.olat.org, 1999.
Moodle project, Moodle Developper Documentation (Nov
2006), http://docs.moodle.org
Florian Gnägi: Olat 4.0 – Overview of functions,
University of Zurich (Nov 2005),
http://www.olat.org/downloads/material/OLAT_4_0_
Overview_of_functions_v15.pdf
LAMS Project, http://www.lamsinternational.com
IMS Global Learning Consortium Inc, 2004. IMS
Question and Test Interoperability Specification, V1.2.
Available at: www.imsglobal.org/question/index.cfm.
Chen, C. M., Lee, H. M., Chen, Y. H., 2005. Personalized
e-learning system using item response theory.
Computers & Education, vol. 44, pp. 237 – 255.
Petrina, S., 2004. Sidney Pressey and the automation of
education. 1924-1934. Technology and Culture. 45(2):
pp. 305-330.
Aljenaa, E., Al-Anzi, F., Alshayeji, M., 2011. Towards an
efficient e-learning system based on cloud computing.
In Proceedings of the Second Kuwait Conference on e-
Services and e-Systems. ACM.
Masud, M., and Huang, X., 2012. A novel approach for
adopting cloud based e-learning system. Computer
and Information Science (ICIS). 11th International
Conference on, pp. 37–42.
Dehbi, R., Talea, M., Tragha, A., 2013. MDA-Based
Transformation of LMS Business Components: The
Contribution of XML Technologies and Model
Transformations. International Journal Enterprise
Information System. Hershey, PA, USA.
Soley et al., 2000. MDA (Model-Driven Architecture),
White Paper, Draft 3.2, OMG Staff Strategy Group,
27.
Welsch, E., SCORM–Clarity or Calamity?,
http://www.allbusiness.com/services/educational-
services/4449495-1.html, downloaded: June, 10th
2007.
Kleppe, A., Warmer, J., Bast, W. MDA Explained The
Model Driven Architecture: Practice and Promise,
Addison Wesley, 2003.
Moreno, N., Romero, R. J., e-MDA Framework: Model
reuse in building e-learning systems, IADAT -e2005,
International conference on Education, Biarritz,
France, July 2005.
Wei, L., Junzhou, L., Jiuxin, C., 2006.
An Integrated
Framework for J2EE-Based E-Learning Systems and
Its Application. Journal of Computer Research and
Development.
AModelDrivenApproachforDesignFlexiblee-Assessment
371
