
CORE
A Context-based Approach for Rewriting User Queries
Antonio Mendonça¹, Paulo Maciel¹, Damires Souza² and Ana Carolina Salgado¹
1
Center for Informatics, Federal University of Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil
2
Academic Unit of Informatics, Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Paraiba, João Pessoa, Brazil
Keywords: Context, Query Personalization, Query Rewriting, SQL Queries.
Abstract: When users access data-oriented applications, they aim to obtain useful information. Sometimes, however,
the user needs to reformulate the submitted queries several times and go through many answers until a
satisfactory set of answers is achieved. In this scenario, the user may be in different contexts, and these
contexts may change frequently. For instance, the place where the user submits a given query may be taken
into account and thereby may change the query itself and its results. In this work, we address the issue of
personalizing query answers in data-oriented applications considering the context acquired at query
submission time. To this end, we propose a query rewriting approach, which makes use of context-based
rules to produce new related expanded or relaxed queries. In this paper, we present our approach and some
experimental results we have accomplished. These results show that, by considering the acquired user
context, it really enhances the precision and recall of the obtained answers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Data-oriented applications, i.e., applications which
make intensive use of data, have experienced a huge
growth in different settings, especially on the Web.
In these settings, the increasing amount of available
data has made it hard for users to find the
information they need in the way they consider
relevant. As a result, techniques which may assist
the users in these tasks have been a topic of research.
One of these topics regards query
personalization, which is mainly done by expanding
queries or by ranking query answers (Koutrika and
Ioannidis, 2005). In all of these possibilities, the
context surrounding the user, his task at hand, and
also the environment may be used to help providing
personalization. This occurs because, when
formulating queries or interacting with an
application, the user may be in different contexts,
and these contexts may change frequently.
The context may be understood as the
circumstantial elements that make a situation unique
and comprehensible (
Dey, 2001). We consider
context as a set of elements surrounding a domain
entity of interest, which are considered relevant in a
specific situation during some time interval (Vieira
et al., 2011). The domain entity of interest may be,
for instance, a person (e.g., a user) or a task (e.g., a
given query). In addition, we use the term
Contextual Element (CE) referring to pieces of data,
information or knowledge that can be used to
characterize the context of an entity in an application
domain (Vieira et al., 2011). The CE is the atomic
part of what composes the context. For instance,
regarding the user, his context (e.g., location) can be
exploited by a system either to answer queries or to
provide recommendations. Thus, users at different
locations may expect different results, even from a
same formulated query.
Particularly, sometimes, a user's query in a given
application may be an incomplete description of the
information he needs. Even when the information
needed is well described, a query engine may not be
able to return answers that match the user real
intention. In these cases, we argue that the involved
context might be used to provide query rewriting in
such a way that a new rewritten query would be able
to return more relevant answers to the user. With
this in mind, we propose a query rewriting approach,
named CORE – COntext-based Rules for rEwriting
queries, which provides query personalization
according to the acquired context. To this end, it
makes use of context-based rules, and contextual
elements (CEs) as components for these rules.
391
Mendonça A., Maciel P., Souza D. and Salgado A..
CORE - A Context-based Approach for Rewriting User Queries.
DOI: 10.5220/0005466503910398
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 391-398
ISBN: 978-989-758-096-3
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

In our approach, submitted queries (in SQL) are
expanded or relaxed according to the acquired
context. Each identified CE is likely to be used as a
condition for a rule, thus providing the means for the
inference of a fact. A fact may be thus a context
information or a rewriting directive. The former
regards the elements which have been inferred or
even acquired from the application. The latter are
excerpts from SQL standard clauses, including
specific operators developed as part of our approach.
These rewriting directives guide the generation of
new expanded or relaxed queries.
Our approach is indeed part of a system proposed
to provide context-sensitiveness features to DBMS
(Maciel and Mendonça, 2013). In this paper, we
focus on the rewriting approach, which has been
developed by means of some components of the
referenced system. We present our approach and
some obtained results. To clarify matters, we show
an example of use, where a front-end application has
been coupled to the developed service.
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2
introduces some concepts and defines the research
problem; Section 3 presents the CORE approach;
Section 4 describes some accomplished results.
Related work is discussed in Section 5. Section 6
draws our conclusions and points out future work.
2 BACKGROUND CONCEPTS
AND RESEARCH PROBLEM
The goal of query personalization is to assist users
when formulating queries in order to enable them to
receive relevant information, according to their
intentions (Kostadinov et al., 2007). The relevance
of the information is defined by a set of criteria and
preferences specific to each user. Godfrey and Gryz
(1996) define query rewriting as a technique that
uses some kind of semantic knowledge (e.g., from
the data domain) in order to generate a new query.
Query expansion is defined by Andreou (2005) as a
process of adding new terms to a query submitted by
the user, with the purpose of improving the
likelihood of retrieved answers. On the other hand,
query relaxation regards the process where the query
is simplified by weakening constraints from the
query expression that are responsible for a failure
(Lian et al., 2007; Stuckenschmidt et al., 2005).
Particularly, in this work, we focus on the
process of rewriting a query submitted by a user in a
given application. We consider query rewriting as a
technique which takes into account the context
surrounding the user and the queries at hand and use
this information to generate another query. This new
query may have been expanded or relaxed
depending on the acquired context, since this context
triggers specific defined rules.
The rules we use in our approach are based on
production rules (Newell, 1973) and are named as
context-based rules. As an illustration, we show a
rule which verifies if a body temperature of a given
person is higher than 37 degrees Celsius. If so, it
instantiates a CE establishing that this person has got
fever. The rule may be formulated as follows:
IF body temperature is above 37 degrees Celsius
THEN set fever context equals to true.
In this light, we define our research problem as
follows:
Given a user query Q, expressed through an
application, how can we generate a rewritten
query Q', which is semantically related to the
original query Q, but takes into account the
context surrounding the user and the query itself
at query submission time?
There are many ways in which the new query Q’
could be semantically related to the original query
Q. In our approach, we classify them into three basic
techniques which take into account the acquired
context, namely:
Query expansion, which is defined as the process
of adding terms to the original query Q, with the
purpose of expanding the set of relevant answers.
Query relaxation, which is a technique for
rewriting queries that aims to make changes on
the restrictions, by means of their removal or
softening.
Query formatting, which aims to provide the
query answers visualization in such a way that
they are easier and intuitive for users.
Based on that, we propose a query rewriting
approach, which is presented in the next section.
3 THE CORE APPROACH
In this section, we present the CORE approach.
Initially, we introduce the Texere system. Then, we
present the CORE rewriting process.
3.1 The Texere Architecture
The CORE approach is part of the Texere system
(Maciel and Mendonça, 2013). The main focus of
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
392
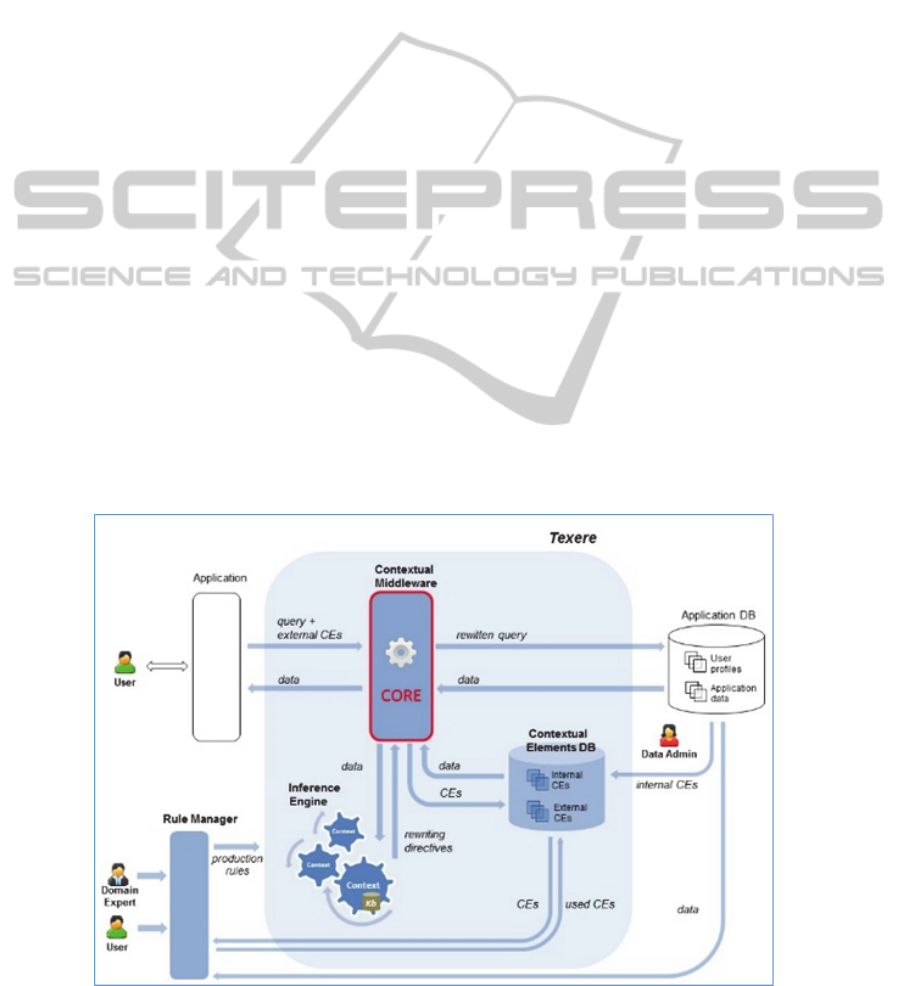
the Texere system is to provide context-
sensitiveness features to traditional DBMS by means
of query rewriting. Texere is able to acquire context
information from some sources, including external
ones and from data explicitly provided by the
application users. External sources may be, for
example, social networks, or sensors where
contextual elements may be acquired on the fly. The
main components of the Texere system are shown in
Figure 1, and are described shortly as follows.
Contextual Middleware: It corresponds to the
CORE approach and is responsible for the main
functionalities. It receives a given query from the
application and the set of CEs that has been
acquired. Then, it forwards the CEs to the
inference engine. After processing the rules, a set
of instructions called rewriting directives are
generated. Using these directives, it performs the
query rewriting process. Then, it executes the
rewritten query in the database application and
returns the obtained answers to the application.
Contextual Elements Database: it stores all
possible CEs which have been identified at
design time as important to be considered for the
application at hand. For example, if the context
of mobile devices is important, then a CE
“device” is stored into the CEs DB.
Application Database: it contains specific
application data, as well as some information
regarding the user profile. Information from the
user profile may also be used as CEs.
Rule Manager: The context-based rules creation
process is aided by an appropriate
application/interface. The DE uses the Rule
Manager component to create the rules to
compose conditions and actions. A rule element
is a piece of information, i.e., a CE or a context
assertion, used to form a rule sentence. A context
assertion is defined by an axiom or inferred by a
previous triggered rule. By considering only
effective rule elements mapped from the
Contextual DB and from the Application DB, the
Rule Manager ensures the rules validity.
Inference Engine: it is responsible for reasoning
mechanisms. It receives a set of CEs sent by the
middleware (CORE), which is used to process
the rules according to the acquired context. After
the rules processing, a set of rewriting
instructions is returned to the middleware, which
uses them to proceed with the query rewriting.
In our architecture, context-based rules are rather
important because they represent the knowledge
about a specific data domain, which will be used to
identify a given context on the fly. Thereby they
should be created by a domain expert (DE) in
accordance with what should be considered as
context information.
The integrity, expressiveness
and coverage of the created rules have a direct
influence not only in the context inference but also
in the returned directives that are used in the query
rewriting process.
Figure 1: The Texere Architecture.
CORE-AContext-basedApproachforRewritingUserQueries
393

At design time, the rules are identified and
created. Nevertheless, they can be changed anytime.
An important aspect of the system regards the
generation of rewriting directives. These directives
are generic instructions for rewriting queries. They
are generated after the context-based rules are
processed by the Inference Engine. The goal is using
these directives to rewrite the original query
according to the context that has been identified.
Rewriting directives are classified into four types, as
follows: Entity, Attribute, Grouping, and Ordering.
Each kind of directive is concerned with an
element that belongs to the original query. In this
sense, directives regarding the Entity type act on the
entities that are part of the query. This means that
they provide changes on the entities of the submitted
query. In the same way, the Attribute directives act
on the attributes (required properties) of the query.
The Grouping and Ordering directives are created
when the original query should be rewritten because
of presentation criteria. The former regards some
ways of combining the resulting data. The latter is
concerned with options of ranking the resulting data.
3.2 The CORE Approach
The CORE approach uses context-based rules to
perform the inference of the acquired context and
produce new facts. These new facts may be new CEs
or rewriting directives.
In this work, we consider queries submitted in
SQL language. Thereby, in order to create the
context-based rules, the DE uses some operators
which are then mapped to SQL clauses. In Table 1,
we present some examples of these operators.
Table 1: Some operators used in CORE.
Operator
SQL
Translation
Example
Trunk(attribute,
ini_posic,
qtde_char)
substring
(attribute,
arg1, arg2) as
alias
Trunk(review,1,200)
-> substring (review,
1, 200) As review
Constraint_order
(entity, attribute,
‘value’)
SELECT *
FROM table
WHERE
table.attribute
= ‘value’
UNION
SELECT *
FROM table
WHERE
table.attribute
!= ‘value’
Constraint_order(Bo
ok, language,
‘portuguese’)
-> SELECT *
FROM Book
WHERE
Book.language =
‘portuguese’
UNION
SELECT *
FROM Book
WHERE
book.language !=
‘portuguese’
Defined operators are used to compose rules. As
an illustration, consider the following rule which
makes use of the TRUNK operator:
IF the user is using a ‘mobile phone’
THEN TRUNK (attribute, 1, 200) and
location equals ‘Recife city’
In this example, the first consequence of the rule is
the generation of a formatting directive (the number
of characters belonging to “attribute” should be
truncated to 200); the second one is the instantiation
of a CE, i.e., location value becomes equal to
‘Recife city’. In this example, we consider that the
location has been captured by using a GPS. The
second consequence could possibly trigger another
rule, if the generated CE (fact) satisfied that.
Thereby, it is possible to infer some other new
knowledge, by starting with one context-based rule.
Regarding SQL and query rewriting, some
possible operations that should be dealt with are:
join, union, group by, order by, as well as the
addition or removal of specific constraints in the
Where clause. In the Select clause, it is possible to
define, add, modify and remove attributes.
A directive defined in the Texere system may
indeed make changes in more than one clause of a
SQL query. As a result, we have stated some SQL
clauses to be used for each defined Texere directive.
These clauses are based on the standard ANSI SQL
92 (ANSI, 2014). Table 2 presents the Texere
directives and their corresponding SQL clauses.
Table 2: Texere Directives and CORE Clauses.
Type of directive CORE Clause
Attribute
<select clause> :: = SELECT <list of
attributes [rewriting operators]>
<where clause> :: = WHERE <query
conditions [rewriting operators]>
Entity
<from clause> :: = FROM <reference
entity list>
Grouping
<group by clause> :: = GROUP BY
<list of grouping elements>
Ordering
<order by clause> :: = Order BY
<attribute list>
The idea is using these SQL clauses in order to
provide query rewriting by means of query
expansion, relaxation and/or formatting. Each clause
contemplates at least one of these three operations.
Thus, given an original query Q, and a rewritten
query Q’, each clause is defined as follows.
The <select clause> performs changes on the
attributes originally present in Q.
In this case, there are three possibilities: (i) query
expansion may occur by adding a new attribute,
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
394

(ii) relaxation can be executed by removing an
attribute, and (iii) formatting may be used to
change the way the required information will be
shown to users.
The <from clause> performs changes on the
FROM clause of Q.
In this case, it provides query expansion by
means of including entities in Q. It is also
possible to relax the query by removing some
entities.
The <where clause> performs changes on the
WHERE clause of Q.
This clause allows the use of relational operators,
e.g., “like”, “IN” in its composition. It executes
query expansion or relaxation operations by
adding or removing constraints on Q (in the
Where clause) and using that operators.
The <order by clause> performs changes on the
ORDER BY clause.
In this case, formatting operations are
accomplished. Particularly, changes are made on
Q so that the most relevant obtained data are
presented at first.
The <group by clause> performs changes on the
GROUP BY clause of Q.
This one also provides formatting operations. In
this case, resulting data are grouped.
To clarify matters, consider an example where a user
submits query Q, as follows.
Q = SELECT author.name as author
FROM book, author, author_book
WHERE author_book.id_book = book.id AND
author_book.id_author = author.id.
Consider that the user context C (with some CEs)
has been acquired, as follows:
C = {married = true,
literature_preference = ‘Brazilian’, language_preference =
‘Portuguese’, children = ‘no’, age = 26, scholarity =
‘graduate student’}.
The CORE approach considers these CEs and
triggers the rules associated to them. As an
illustration, suppose there is a rule which states that
if the user is older than 18 years, then do not return
books from child. Then, CORE generates a directive
that provides this restriction on Q, by including it in
Q’. The query is then rewritten as follows:
Q’ = SELECT author.name as author
FROM book, book_format, category, author,
author_book
WHERE book.language = 'Portuguese' AND
book.format = book_format.id AND
author_book.id_book = book.id AND
author_book.id_author = author.id AND
book_format.format Not In (‘Braille’, 'audio')
AND book.category_id = category.id AND
category.name Not In ('Child Story', 'Youth Story')
4 IMPLEMENTATION AND
EXPERIMENTS
The CORE approach has been implemented as a
Web service. We have used the JBoss Drools (2013)
to implement the inference engine. In this section,
we present some implementation issues and
experiments that have been accomplished.
4.1 Implementation and Example of
Use
In order to evaluate the CORE approach, we have
implemented a front-end application called
TexereLibrary to be coupled to the CORE service.
This application regards an online Library in which
users can submit queries about books. To this end,
users at first perform a registration providing some
basic data, such as education, age, physical
limitations, preferred language and profession.
These data will be used as CEs.
The application allows the submission of SQL
queries through two options: with or without
considering the use of context. If the context usage
option is enabled, a query rewriting request is
forwarded to the CORE service. Otherwise, the
query is directly executed on the DBMS.
As an illustration, consider a user Ana who is a
nine years old girl. Ana logs into the application and
receives an id (user_id=10), and her session is
identified (session_id=10). Ana uses a smartphone
(device=smartphone) as a device. Considering the
current data as ‘July, 1st’, the surrounding CEs are
gathered and persisted in the CEs Database. In
summary, the context C is then considered as
follows:
C = {user=10, device=’smartphone’,
season=’summer’, month=’July’}.
In this scenario, Ana submits the following SQL
query Q = Select name, review From book Where
book.title = ‘java’, as shown in Figure 2.
Once the Inference Engine is called, the rules
shown in Table 3, which were previously defined by
the DE, are triggered. After processing the related
rules and considering the generated rewriting
directives, a rewritten query Q’ is obtained, as
depicted in Table 4.
In this example, Q requires books whose title is
equal to ‘Java’. Q’ was generated by means of
expansion, formatting and relaxation operations. An
expansion operation regarding the inclusion of the
CORE-AContext-basedApproachforRewritingUserQueries
395

entity ‘Category’ was accomplished. This expansion
operation occurred because the DE created a rule
defining that when a person is a child, he should
receive books from child and youth categories. Thus,
a clause was generated with such condition. At
query rewriting time, CORE notices that the entity
‘Category’ was not present in the FROM clause. As
a result, the inclusion of that entity was done, what
characterizes an expansion operation.
Figure 2: TexereLibrary Query Interface.
Table 3: Context-based Rules for the Example.
Rule 1
IF device in (‘smartphone’, ‘cellphone’)
Then mobile_device is true;
Rule 2
IF mobile_device
Then trunk (review,1,30);
Rule 3
IF user_age < 12
Then show (book_category) in ( 'Children
Novel', 'Educational Middle School');
Rule 4
IF season in (‘summer’)
Then school_vacation is true;
Rule 5
IF school_vacation is true and user_age <= 12
Then constraint_order (Category, name,
‘Fairytale’);
Also, a formatting operation was applied
requesting that books belonging to the category
‘Fairytale’ were presented at first. This change was
also determined by a rule. To this end, it used the
operator ‘constraint_order’, which, when translated
to SQL, results in two queries. The answers of these
two queries are put together by a union clause. The
first query shows the books from the category
‘Fairytale’, and the second one shows the remaining
books from the other categories.
A relaxation operation was also performed. A
rule was created defining that when restrictions with
textual features and operators are too restrictive,
they can be relaxed by changing the restriction at
hand. In the example, the restriction book.title =
'java' was relaxed by replacing the "=" operator by
the operator 'like'. In addition, the character "%" was
included (book.title like ‘%java%).
Table 4: Log for rewritten query Q’.
Original
Query
Rewritten Query (Q') Used CEs
Rewriting
Operations
Select
name,
review
From book
Where
book.title
= ‘java’
SELECT book.name,
substring( review, 1,
30) As review
FROM book, category
WHERE
category.name =
'Fairytale' AND
book.title like
‘%java%’ AND
book.category_id =
category.id UNION
SELECT book.name,
substring( review ,1 ,30
) As review
FROM book, category
WHERE
category.name !=
'Fairytale' AND
book.category_id =
category.id AND
book.title like
‘%java%’ AND
category.name In (
'Children Novel',
'Educational Middle
School' )
Device, age,
school
vacation,
season
expansion,
relaxation,
formatting
4.2 Experiments
We have accomplished some experiments to
evaluate the CORE approach. The goal was to verify
whether the context-based query rewriting could
indeed produce answers with higher precision and
recall. We aim to verify if it is possible to reduce the
amount of irrelevant answers (high precision) and
ensure that relevant answers are not lost (high
recall). We used the TexereLibrary application and
data belonging to the “library” domain.
We consider the precision measure as the ratio of
the number of relevant answers over the total
number of returned answers (true positives)
(Rijsbergen, 1979). On the other hand, recall is the
ratio of the number of relevant answers over the total
of expected relevant answers (Rijsbergen, 1979).
The used formulas are shown in the following:
Recall=
#
#
Precision=
#
#
Where #RelevantAnswers is the number of answers that
are considered as relevant by users, #ExpectedAnswers is
the total of all possible answers that could be produced by
considering a gold standard, and #ReturnedAnswers is the
total number of all returned answers.
The experiment was accomplished with
Computer Science students. One of them was
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
396

defined as a domain expert, and he was asked to
define a “gold standard” regarding what would be
the ideal (expected) set of answers for each
submitted query. This ideal set was used to
determine the total number of expected answers and
calculate the recall measure. Then, users performed
the same queries and defined which of the obtained
answers were considered as relevant. This process
was done twice: (i) without considering the acquired
context, and (ii) with considering the context. Figure
3 shows the results obtained for the recall measure.
As shown in Figure 3, enabling the use of
context, i.e., the CORE service, we achieve better
results regarding recall. In some cases, however,
obtained results when considering context were
similar to what was obtained when no context was
taken into account. For example (select book.name,
language.name as language, category.name as
category from book, language, category where
book.language_id=language.id and
book.category_id =category.id and category.name
= ‘computer science’), this situation happened with
query number 11, where the recall measure was the
same. This is due to the fact that query 11 was very
restrictive, i.e., the selection conditions were very
strong and, thereby, the rewriting process could not
expand or relax that query. Nevertheless, in general,
most of the context-based rewritten queries obtained
higher recall than their versions which were
executed without context.
Figure 3: Recall of query results.
Results obtained with the precision measure are
shown in Figure 4. It is possible to observe that, in
general, queries rewritten by considering the context
obtained higher values of precision. This means that
rewritten queries acquired a higher number of
answers that were considered as relevant. There are
cases where the precision value of the original query
was higher than the one obtained by the context-
based rewritten query, e.g., in query 6. This happens
with queries which are very restrictive, what enables
a small number of answers. Thus, when a query is
rewritten by means of relaxing some restrictions, we
perceive that the number of answers returned is
usually larger. However, especially in query 6, the
returned answers were not considered as relevant.
In summary, we can observe that the CORE
approach is able to provide a higher number of
answers that are interesting to the users. This fact is
verified by the results obtained with the recall and
precision measures.
Figure 4: Precision of query results.
5 RELATED WORK
Query personalization techniques have been tackled
in diverse settings. Examples of query
personalization works using the user's preferences
are provided by Koutrika and Ioannidis (2005) and
Stefanidis et al., (2009). The first one provides query
personalization in databases using user profiles. The
second one provides a recommendation system that
expands query results according to user preferences
and considering the user history.
Regarding the use of context in query
personalization, Amo and Pereira (
2010) present an
extension to the SQL language, by means of
including user preferences in a new clause. To this
end, they define a language called CPrefSQL and
provide two operators (Select-Best and SelectK-
Best) that allow classifying the answers according to
the preferences and context.
The work of Ines and Habib (2012) helps the
user when a query does not return any answer,
usually due to a very restrictive formulation. This
approach also detects some conflicts, which may be
of aggregation and generalization types.
Levandoski et al., (2010) present a context and
preference-aware database system, implemented
inside the PostgreSQL DBMS. It provides
personalized location-based services to users based
on their preferences and current surrounding context.
Comparing these works with ours, we have some
key differences, as follows: we are concerned with
CORE-AContext-basedApproachforRewritingUserQueries
397

the process of handling context-based rules, and to
this end, we need a DE (domain expert) to define the
rules according to the application domain; we work
with standard SQL, so there is no need to change the
internal algorithm of the underlying relational
DBMS; we accomplish query rewriting by means of
query expansion, formatting and relaxation
according to specific acquired context on the fly.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In data-oriented applications, the context
surrounding queries and users are rather important to
produce answers with more relevance. In this work,
we have presented the CORE approach, which uses
context information to personalize user queries
submitted in data-oriented applications. The CORE
approach is accomplished by means of query
expansion, relaxation and formatting in accordance
with the acquired context. Directives and SQL
specific clauses are generated to this end.
Experiments carried out with real users have
shown that query answers have become more
relevant when the context has been considered to
rewrite the original query and produce another one.
Some limitations were observed in our approach,
namely: (i) The DE needs to be an experienced
person in the application domain in order to create
and maintain the context-based rules. If the rules are
poorly designed, the process of query rewriting
produces a query that may return less relevant
answers; (ii) The CORE approach is based on the
SQL 92 standard; (iii) Also, it does not perform
optimization operations on the original submitted
query nor on the rewritten query.
As further work, we intend to proceed with some
extensions in order to deal with these mentioned
limitations.
REFERENCES
Amo, S. and Pereira, F. Evaluation of conditional
preference queries. Journal of Information and Data
Management (JIDM). p. 521–536, 2010.
Andreou, A. Ontologies and query expansion. Master’s
thesis, University of Edin-burgh, 2005.
ANSI. Standard SQL 92 Available at:
<http://www.ansi.org/>. Accessed on: December, 15,
2014.
Dey, A. Understanding and Using Context. Personal and
Ubiquitous Computing Journal, p. 4-7, 2001.
Godfrey, P. Gryz, J. A framework for intensional query
optimization. Workshop on Deductive Databases and
Logic Programming, Germany, p. 57–68, 1996.
Ines, F. Habib, O. An ontological approach for SQL query
expansion. 2012 International Conference on
Information Technology and e-Services (ICITeS), p.
24-26, 2012.
JbossDrools. Available at <http://www.jboss.org/drools/>.
Accessed on December, 29, 2014.
Kostadinov, D., Bouzeghoub, M. e Lopes, S. Query
Rewriting Based on User's Profile Knowledge. In O.
Boucelma, M.-S. Hacid, T. Libourel & J. M. Petit
(eds.), BDA, 2007.
Koutrika, G. and Ioannidis, Y. Personalized Queries under
a Generalized Preference Model. 21st Intl. Conf. On
Data Engineering, Tokyo, p. 841-852, 2005.
Levandoski J. J., Mokbel M. F., and Khalefa M. E.
CareDB: A Context and Preference-Aware Location-
Based Database System. In Proceedings of the VLDB
Endowment, p. 1529-1532, 2010.
Lian, l. Ma, J. Lei, J. Song, L. Zhang, D. Query relaxing
based on ontology and users’ behavior in service
discovery. In Proceedings of the Fourth International
Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge
Discovery, 2007.
Maciel, P., Mendonça, A. Texere, a Context-aware System
for Improving Database Queries. Technical Report,
Federal University of Pernambuco, Brazil, 2013.
Newell A. In Visual Information Processing. Academic
Press. Chase E. (editor). 1973.
Rijsbergen, C. J., 1979. Inforamation Retrieval. London:
Butterworths.
Stefanidis, K. Drosou, M. and Pitoura, E. You May Also
Like Results in Relational Databases. Proc. 3rd
International Workshop on Personalized Access,
Profile Managementand Context Awareness in
Databases, Lyon, p. 37-42, 2009.
Stuckenschmidt H., Giunchiglia F., and van Harmelen F.
Query processing in ontology-based peer-to-peer
systems. In V. Tamma, S. Craneeld, T. Finin, and S.
Willmott, editors, Ontologies for Agents: Theory and
Experiences. Birkhuser, 2005.
Vieira, V., Tedesco, P., and Salgado A. C. Designing
Context-Sensitive Systems: An Integrated Approach.
Expert Systems with Applications 38. p. 1119-1138,
2011.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
398
