
A Review of Enterprise Modelling Studies
Lerina Aversano and Maria Tortorella
Department of Engineering, University of Sannio, Piazza Roma 21, 82100, Benevento, Italy
Keywords: Systematic Review, Enterprise Modelling, Modelling Language, Enterprise Assets, Research Methods.
Abstract: This paper aims to provide a basis for the improvement of enterprise modelling research through a review of
previous work published in literature. The review identifies 198 enterprise modelling papers in 49 journals
and classifies the papers according to: research topic, modelling approach, research approach, study context
and type of validation set. A database of these enterprise modelling papers is provided to ease the
identification of relevant research results. The review results are combined with other knowledge and
provide a support for modelling strategy recommendations for future enterprise modelling research,
including: identification of relevant papers within a carefully selected set of journals when completeness is
essential; need of conducting more studies on modelling methods commonly used from the software
industry; and increase the awareness of how the properties of the case studies impact on the results when
evaluating modelling methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Enterprise modelling is aimed to achieve a
comprehensive picture of an enterprise. The model
is a snapshot of the company at a particular moment
that incorporates all the knowledge regarding an
organization, including resources, products, and the
way the organization communicates.
Enterprise modelling is often used to create
representations applied in information technology
planning. In this case, the model looks at how
technology is being currently used in a company,
how the company structure supports the use of
information technology and the way in which
information technology can be integrated. For
example, the modelling is useful when an enterprise
evaluates the adoption of a new software system. In
this case, enterprise modelling determines whether
the acquisition of a new computer system is
compatible with the stated goals and needs of the
company.
Enterprise modelling is also used for improving
the business strategy and organization. By providing
a complete picture of the entire organization,
enterprise modelling allows companies to see how
their systems might be refined to better meet the
goals, counter external threats and eliminate internal
weakness (Ulrich 2002), (Gustas and Gustiene,
2003), (Dietz, 2006). This knowledge can be used to
improve management techniques, develop internal
procedures, and assume long term quality for the
business.
Business organizations also use enterprise
modelling for projecting the future, looking at the
changing relationships between a company and its
external environment. This type of enterprise
modelling considers what types of products the
company could develop to expand, how the market
is going to change, and how the expansion of the
company could be made smooth and efficient.
Enterprise modelling promotes and efficient,
well-run company by building a comprehensive and
integrated picture of it along its goals, resources, and
climate.
This paper proposes a literature review of
enterprise modelling research studies. The
performed review follow the guidelines defined in
literature (Petersen, 2008) (Kitchenham, 2007).
The main difference of the conducted review
respect to other reviews is the different goal. Indeed,
this paper reviews journal articles on enterprise
modelling with the goal of supporting and directing
future enterprise modelling research, differently
from traditional literature reviews that principally
aim at introducing novice researchers to the variety
of approaches, models, and tools. This difference in
goal leads to a different focus as this review focuses
on the research methods and does not include a
346
Aversano L. and Tortorella M..
A Review of Enterprise Modelling Studies.
DOI: 10.5220/0005468003460351
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 346-351
ISBN: 978-989-758-098-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

comprehensive description of the different enterprise
modelling approaches.
The analysis is mainly based on a systematic
search of journal papers. The study classifies the
enterprise modelling papers with respect to the
topics, research approaches, study contexts and used
data.
The following section described the issues that
have been identified as interesting. The motivation
for inserting the analysed questions was the
improvement of the enterprise modelling research.
The considered issues guided the design of the
review process. The remaining part of this paper is
organized as follows: Section 2 describes the review
process; Section 3 reports the review results; Section
4 summarizes the main threats to validity; Final
remarks are given in the last section.
2 REVIEW PROCESS
This section outlines the review steps that have been
followed for conducting the study.
2.1 Scope Definition
The first activity that has been performed is the
definition of the issues to be addressed. To this aim,
after a preliminary reading of the most relevant
papers, the following issues have been defined for
the analysis:
– Analysis of the paper distribution among
journals, proceedings and other type of
publications.
– Analysis of the main publication sources for the
Enterprise Modelling research studies.
– Quantification of the articles published over the
years by the most relevant authors.
– Analysis of the effort, measured as number of the
papers concerning this topic over the years.
– Classification of the papers based on the most
relevant research topics.
– Classification of the articles based of the
category they belong.
– Analysis of the used Modelling Languages.
– Analysing at which extent enterprise modelling
researches are applied
– Analysis of the used quantitative approaches.
2.2 Inclusion Criteria
The main criterion that was followed for including a
journal paper in the performed review was that it
described research on enterprise modelling. Papers
concerning software modelling, assessment of
enterprise complexity, or identification of factors
correlated with enterprise modelling, were only
included if the main purpose of the study was the
improvement of the enterprise modelling research.
Examples of papers basically describing a similar
study in more than one journal paper were found.
Fortunately, the number of such cases was small and
would not lead to important changes in the outcome
of the analysis. In any case, we decided, to exclude
these papers.
2.3 Identification of Papers
The proposed literature review was obtained by
analysing enterprise modelling papers selected from
the literature. In particular, a full investigation of the
research papers concerning this topic was performed
and the scientific databases were queried. Numerous
journal and conference papers were identified.
Therefore, it was decided to concentrate the
attention on journal papers as they should publish
more mature research results. With this in mind, the
Science Direct, IEEE and ACM database was taken
into consideration and queried.
The identification of relevant studies was based
on an examination of papers found through a manual
inspection of the papers resulting by querying the
database. The first query aimed to recover papers
including the term ‘enterprise modelling’. Then, the
selection was refined applying the ‘business
management’, ‘computer science’, and ‘modelling’
subject terms , from 2003 to present, and including
also journals. In total, 1483 paper were found, in the
first phase all papers was examined by using a
manual inspection of titles, and if unsure, the
abstracts. After this primary study, 198 papers
distributed within 49 peer-reviewed journals written
in English were selected as potentially relevant.
In spite of the high number of identified journals,
it was possible that there were, national or company-
specific journals with enterprise modelling papers
that have been missed. In any cases, following the
first analysis, the journal that was discovered to be
the most representative of the enterprise modelling,
topic was Computer in Industry from Elsevier. For
this reason, some of the analysis are mainly
concentrated on this journal.
2.4 Classification of Papers
For addressing the analysis, the identified papers
were classified according to their typology. Four
AReviewofEnterpriseModellingStudies
347

typologies were considered: Research papers,
proposing innovative strategies for enterprise
modelling; Practice papers, describing experiences
for experimenting defined strategies; Industrial
survey, those ones describing interviews performed
within operative organizations for understanding if
and how they were facing problems and/or adopting
approaches regarding the enterprise modelling; and
Reviews, describing literature studies, even if few
journals published this kind of study. The aim of this
classification was to understand the formalism and
practical aspects the papers analysed and their
maturity level. The considered papers were
distributed as it follows: 85 papers belonged to the
Practice category; 162 papers were classified as
Research; 11 papers were Review; and 13 papers
were Industrial survey. Some papers belonged to
more than one type.
A preliminary exploration of the papers allowed
the extraction of the properties and categories to be
considered in the analysis. They were based on
categories of research works commonly adopted in
journals and international conferences by IEEE, and
adapted to the needs of our analysis. Specifically
some categories were added with reference to
enterprise concepts. In the performed analysis the
classification was used to assess the interest of
authors for the different research topics. The chosen
research topics and categories addressed the purpose
of our review and do not have to be intended to
represent a general-purpose classification of
enterprise modelling studies. We also believe that
the classification may be useful for other researchers
while searching for relevant papers on, for example,
a particular modelling approach.
3 ANALYSIS
The classification of research papers provided a
general picture of the characteristics of the
Enterprise Modelling research. It represented for the
authors a starting point for a deeper investigation
and suggested important short comings in Enterprise
Modelling research and possibilities for
improvement. In the following, the considered issue,
listed in the scope definition section, will be
analysed and results will be described.
Analysis of the paper distribution among
journals, proceedings and other type of
publications
The aim of this analysis was to investigate the
editorial collocations where research papers
concerning the Enterprise Modelling topics are
mainly published. Specifically, journal papers and
book chapters were considered.
Table 1: Paper distribution among the work type and
publisher.
Type #Number Publisher
Book Chapter 12 ACM
Book Chapter 2 IEEE
Journal 162 Elsevier
Journal 1 IEEE
Journal 19 Springer
Table 1 shows that 198 research works concerning
the Enterprise Modelling were found. These works
were distributed in 14 book chapters and 182
journals. In particular, as regards the book chapters,
12 papers have been published by ACM while IEEE
published the remaining 2 papers. Concerning the
journals, Elsevier has published 162 papers, 1 paper
by the IEEE and 19 by Springer.
Analysis of the principal publication sources for
the Enterprise Modelling research studies
The goal of this analysis was to check which source
was predominant in the modelling studies on
Enterprise Modelling and in which venues they were
published. Specifically, it goes to consider the
placement of the items, the total number of items
according to the locations and how this affects the
percentage of the total number of articles. For
reasons of space, only the results greater than 1 are
reported in the results description.
Analysing the data reported in Table 2 it emerges
that the predominant journal publishing enterprise
modelling papers is Computer in Industry, published
by Elsevier, which comprises about 30% of the total
papers published in this area; followed by:
Information Systems with 6.3%; Expert Systems
with Applications with 5.7%, and Data &
Knowledge Engineering with 5.2%.
Quantification of the articles published over the
years by the most relevant authors
Table 3 shows the results of this analysis and
indicates that the researchers that have been
interested in enterprise modelling studies from 2004
to 2014. In particular, it emerged that Wil MP van
der Aalst is one of the most active researcher in this
area with five articles between 2007 and 2008;
followed by Jeongsoo Lee with 4 items between
2010 and 2014; and Kwangsoo Kim Lee with 4
items between 2010 and 2014.
Analysis of the effort measured as number of
paper dedicated on this topic over the years
The aim of this analysis was to observe how many
articles have been written in the different countries
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
348
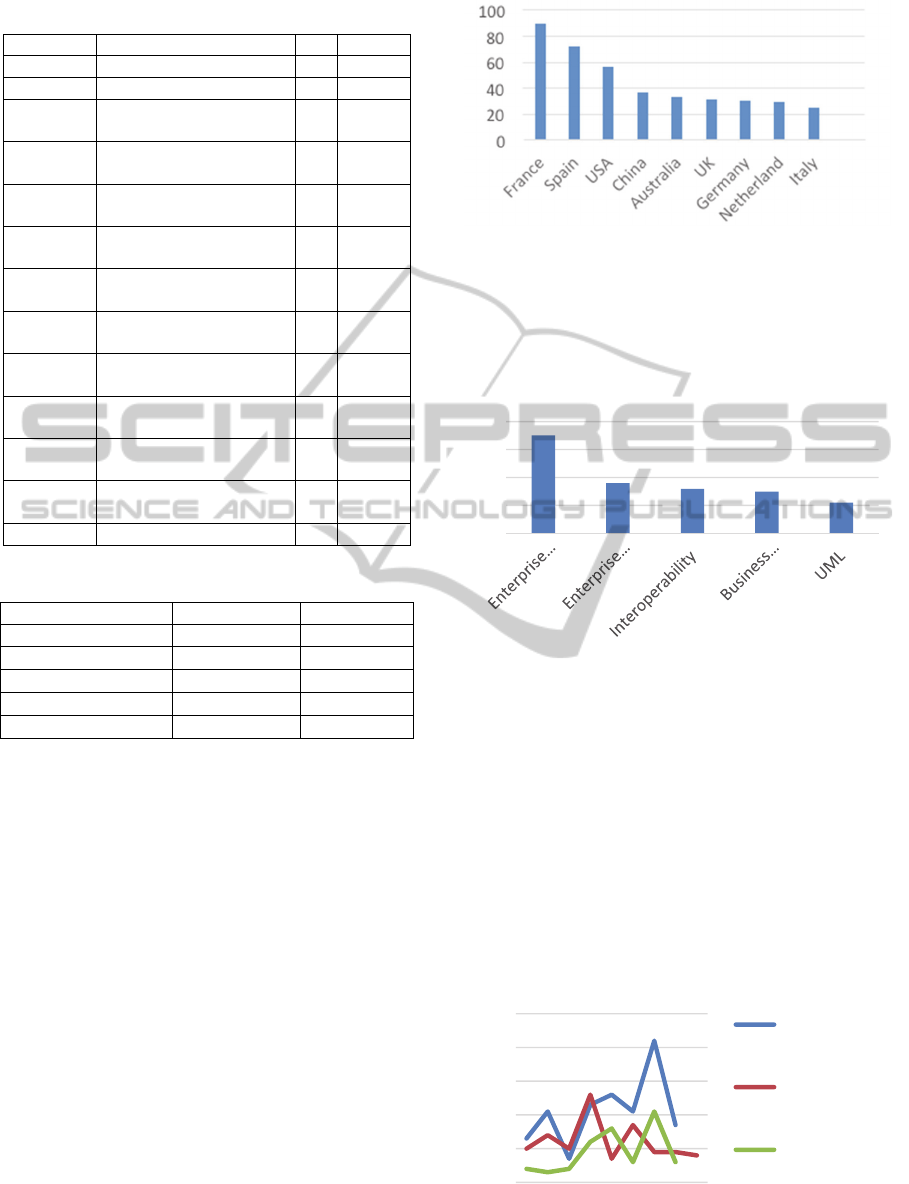
Table 2: Predominant Journal for Enterprise Modelling.
Publisher Collocazione # %
Elsevier Computers in Industry 54 27,22%
Elsevier Information Systems 12 6,28%
Elsevier Expert Systems with
Applications
11 5,75 %
Elsevier Data & Knowledge
Engineering
10 5,23 %
ACM ACM Computing
Surveys
8 4,18 %
Elsevier The Journal of Systems
and Software
8 4,18 %
Elsevier Information and Software
Technology
7 3,66 %
Elsevier Robotics and Computer-
Integrated Manufacturing
7 3,66 %
Elsevier Science of Computer
Programming
6 3,14 %
Elsevier Computers & Industrial
Engineering
5 2,61 %
Elsevier Procedia Computer
Science
4 2,09 %
Elsevier Advanced Engineering
Informatics
4 2,09 %
Springer Int J Adv Manuf Technol 4 2,09 %
Table 3: Authors more active over the years.
Authors Article number Years
Wil M.P. van der Aalst
5
2007, 2008
Jeongsoo Lee 4 2010, 2011
Kwangsoo Kim 4 2010, 2011
Marlon Dumas 2 2011
Guy Doumeingts 2 2008
over the years. Then, the papers were considered
with reference to the countries in which the
researches were conducted. For reasons of space, the
description of the results considers only results
greater than 1. The considered years go from 2004 to
2014.
Figure 1 shows the graphic distribution of
articles written during the considered period with
reference to countries. Results shows that European
countries, such as France and Spain, are the most
active in this research field and produced the higher
number of articles in the considered period. In
particular, a large part of the papers were published
by France Institutions (89) and Spain published 72
papers. Just 25 items were found for Italy.
Classification of the papers based on the most
relevant research topics
The goal of this analysis was to identify the
research topics regarding enterprise modelling
mainly investigated, and how they changed over
time. Figure 2 reports the number of papers
Figure 1: distribution of research paper for countries.
concerning the main research topics from 2004 to
2014. It is possible to observe that a large part of
papers discusses enterprise modelling with reference
to: Enterprise architecture; Interoperability; Business
process modelling and Unified Modelling Language.
Figure 2: Principal area investigating Enterprise
Modelling.
Classification of the articles based of the category
they belong
The goal was to analyse what are the research topics
of enterprise modelling more studied with reference
to the category they belonged and how these
changed over time. The categories were: Software
Engineering, Business Management and Artificial
Intelligence. Specifically, the categories were
analysed over the period going from 2004 to 2011,
sorted by ascending order. Figure 3 shows the results
of this analysis and indicates that Software
Engineering, with 175 papers, and Business
Figure 3: Main research categories investigating
Enterprise Modelling.
0
10
20
30
40
0
10
20
30
40
50
Software
Engineering
Business
management
Artificial
Intelligence
2004 2005 2013 2014
AReviewofEnterpriseModellingStudies
349

Management, with 119 papers are the most relevant
categories.
Figure 4: Modelling language mainly used.
Figure 5: Trend of the modelling language mainly used
over the years.
Analysis of the used Modelling Language
The goal of this analysis was to see what are the
modelling languages most studied and applied to
enterprise modelling, and how they changed over
time. Figure 4 shows the results of the analysis by
considering and indicates that the modelling
languages most studied and applied is UML (Unified
Modelling Language), followed form IDEF
(Integrated Definition for Function). In addition,
Figure 5 reports the trends of the modelling
language mainly used in the considered period of
time.
Analyse to what extent enterprise modelling
research are applied
The goal was to analyse at which extent the research
enterprise modelling techniques were applied and in
which context of study (e.g., case studies, on the
field, etc.). Then, the type of their application was
considered. The analysis showed that the
investigations of enterprise modelling techniques
was mainly performed through examples. In
particular, 105 articles concerned examples, 52
papers treated case studies, just 7 papers concerned
empirical studies, 2 articles regarded applications on
the fields, and 27 concerned other kind of
applications. Figure 6 shows graphically the count of
items in the various contexts of application.
Figure 6: Papers distribution for application type.
Analysis of the Quantitative approaches used
The goal of this analysis was to observe what were
the most studied and quantitative approaches used
and how this changed over time. Therefore, the
quantitative approaches were analysed in different
years. The analysis showed that few paper
considered quantitative approaches. In particular,
among the most studied and applied quantitative
approaches KPIs, Key performance indicators, were
used.
4 THREATS TO VALIDITY
The main threats to the validity of the proposed
review are described in the following.
The publication bias regards the exclusion of
conference papers and reports is based mainly on
practical concerns, including workload; e.g., the
problems of identifying all relevant conferences and
the amount of analysis needed to handle the fact that
many journal papers are improvements of previously
published conference papers. This exclusion of
conference papers would be more difficult to defend
if the study concerned a particular modelling
approach, such as UML Business Extensions. In that
type of studies, all relevant papers should be
identified and reviewed, regardless the type of
source. A small selection of Enterprise Modelling
papers published at conferences was analysed and it
was found that their research topics, methods, study
designs, and study contexts were similar to those of
the journal papers. However, the study concerned
executed research into Enterprise Modelling and the
journal papers are those ones with a high scientific
quality. An important difference between conference
and journal papers was that research scientists did
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
2004
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
UML(Unified
Modeling
Language)
IDEF
(Integrated
Definitionfor
Function)
BPMN,Busines
sprocess
modelling
notation
0
50
100
150
Example Case
study
Empirical
study
Onthe
Field
Other
ConteggioArticoli
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
350

not write modelling experience reports; that were
typically published at industry conferences.
Therefore, large part of the analysed papers was
written by academics. This means that probably
information about the software industry’s experience
has been excluded and needs to be further
investigated.
Another potential publication bias is that
significant enterprise modelling research results
have not been published, such as company-
confidential results, or results that did not yield the
desired outcomes or conducted on topics that did not
fit into the common enterprise modelling journals. It
could be interesting to study size and effect of the
potential publication biases, but this would require a
study design different from ours, and can fit our
research work.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Enterprise modelling is a growing relevant research
topic in the last years. This research issue was
addressed in several researches proposing numerous
methods, techniques and tools. This paper proposes
a literature review of different research studies with
the aim of discovering interests, limits, maturity,
models, and types in the performed researches. The
presented kind of investigation is aimed to support
and address future research concerning the
enterprise modelling topic.
Indeed, it is necessary to understand which are
the aspects considered in the literature of this area
with a quantitative approach. Because the field is
wide and concerns different aspects, the aim of the
presented study is to help practitioners, students and
researchers to focalize the attention on a particular
interested issue.
The proposed review was applied to the research
works regarding the enterprise modelling topics
published in primary international journals and the
results of the review are presented. The results for
this preliminary application emphasize that the
enterprise modelling approaches are not adequately
addressed.
Obviously, the results obtained in this
preliminary study need to be confirmed in a wider
investigation involving more and more research
approaches. This will be one of the main future work
involving the authors. As further future work, the
review proposed can be used to make a survey of the
studies presented in the literature, and understand
how to better address the research issues in the
enterprise modelling area. The aim will also regard
the classification of different modelling,
measurement, and quantitative approaches
addressing this issue at different abstraction level,
and the understanding of which of them better
address a specific problem.
REFERENCES
Petersen, K., Feldt, R., Mujtaba, S., Mattsson, M.,
Systematic Mapping Studies in Software Engineering,
In proceedings of the 12th international conference on
Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering,
British Computer Society Swinton, UK, 2008.
Kitchenham, B., Charters, S., Guidelines for performing
systematic literature reviews in software engineering,
Technical Report EBSE-2007-01, School of Computer
Science and Mathematics, Keele University, 2007.
Kitchenham, B., The current state of evidence-based
software engineering. keynote Interational Conference
on Evaluation and Assessment in Software
Engineering, 2007.
Gustas, R and Gustiene, P (2003) "Towards the Enterprise
engineering approach for Information system
modelling across organisational and technical
boundaries", in: Proceedings of the fifth International
Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, vol. 3,
Angers, France, 2003, pp. 77-88.
Dietz Jan (2006). Enterprise Ontology - Theory and
Methodology. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Ulrich Frank (2002). "Multi-Perspective Enterprise
Modeling (MEMO): Conceptual Framework and
Modeling Languages". In: Proceedings of the Hawaii
International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS-
35). Los Alamitos, CA. Ralph H. Sprague, Jr. (eds.).
IEEE Computer Society Press.
AReviewofEnterpriseModellingStudies
351
