
Enterprise Architecture Components for Cloud Service Consumers
Eapen George
1
and George Feuerlicht
1,2,3
1
Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology, University of Technology, Sydney, Australia
2
Unicorn College, V Kapslovně 2767/2,130 00 Prague 3, Czech Republic
3
Department of Information Technology, University of Economics, Prague, W. Churchill Sq. 4, Prague 3, Czech Republic
Keywords: Business-IT Alignment, Cloud Enterprise Architecture, Enterprise Architecture Components, Service
Oriented Architecture.
Abstract: Enterprise Architecture (EA) and appropriate governance enables cloud computing adoption by consumer
organisations. EA is gaining acceptability as an approach for strategic alignment of business and IT and as
key enabler for cloud computing. EA practices consist of a range of activities and covers many of the
elements necessary for enabling cloud computing. This paper discusses the key architectural components
necessary from the perspective of a consumer organization for the adoption of cloud computing and
discusses these elements in the context of EA frameworks and governance. The ability to use maturity
assessments on these architectural components to determine organizational readiness to achieve cloud
benefits is introduced.
1 INTRODUCTION
A number of innovative technology solutions are
driving changes in the nature of business and how
enterprises are addressing their market opportunity
and customer needs. Adapting to and leveraging the
opportunities that these new trends and emerging
technology capability bring is becoming an
important aspect of how business can get ahead of
the competition. The cloud paradigm is an
amalgamation of a number of proven and emerging
enterprise technologies, and enterprises are
leveraging the cloud paradigm to varying degrees.
A key aspect of cloud computing is that it has
brought about a cost model that leverages economies
of scale. By taking aspects of IT out of the enterprise
and into large scale utilities, the economies of scale
benefits are being accrued to enterprises (NIST,
2013). This has been especially true of IT hardware
infrastructure, but the benefits have not been equally
achieved for IT processes such as strategy, planning
and governance. Enterprises have attempted a trial
and error approach to adopting the suitable processes
that benefit from cloud computing. A Cloud Service
Consumer can be defined as an organisation or a
user or an IT system that consumes services
delivered by a cloud service provider (IBM CCRA,
2014).
Today, most business and IT leaders understand
the benefits of cloud computing but they need a
pragmatic, effective and transparent approach to
cloud adoption. Most existing methods tend to focus
on prioritization at a specific solution level and fail
to consider wider issues such as alignment of IT
strategy with overall business objectives (Feuerlicht,
George, 2013). Determining the business value is
important because it measures the potential for
realization of benefits directly related to the adoption
of cloud computing. Enterprise Architecture
provides a framework and models to assist IT
management with better utilization of IT, and
alignment of IT with business. Understanding the
challenges and operational constraints that the
organization faces helps to identify how cloud
computing can benefit the organization and what
business and IT capabilities will gain most from
cloud adoption. Enterprise architecture is a key
enabler for an effective adoption of SOA (Service-
Oriented Architecture) and hence cloud computing,
and this has been highlighted in the literature
(Ibrahim, 2007).
In this paper we firstly discuss the role of
Enterprise Architecture with specific focus on cloud
computing (section 2), and then consider the
problem of EA maturity assessment (section 3). In
section 4 we discuss our conclusions.
360
George E. and Feuerlicht G..
Enterprise Architecture Components for Cloud Service Consumers.
DOI: 10.5220/0005468303600365
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2015), pages 360-365
ISBN: 978-989-758-098-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 ROLE OF ENTERPRISE
ARCHITECTURE
As discussed in (George, 2013), Enterprise
Architecture is being used as an approach to
managing both business and IT at a strategic level
and forms the basis for achieving agile business-IT
environment enabling IT to respond to rapid changes
in business requirements as market conditions
change. At the same time, the building blocks of IT
(i.e. infrastructure components, business
applications, etc.) are becoming commoditized,
reducing the competitive advantage that
organizations gain directly from deploying
individual IT components. It is the combination of
various IT components and business functions in the
context of an EA framework that can deliver
business value and competitive advantage. SOA
architecture enables organizations to be more agile
and cost effective, and cloud computing delivers
similar benefits to IT.
2.1 Enterprise Architecture Functions
Enterprise Architecture in an organization is
achieved through the means of EA activities that
cover management activities and analysis and design
approaches. The activities carried out in the context
of EA can vary from organization to organization
depending on the scale, maturity and objectives of
the organization. However, it is possible to identify a
number of core activities that typically occur and
can be classified as EA activities. For example, in
one characterisation eight core activities that include
defining IT strategy, modelling EA component
architecture, facilitating IT transformation,
developing and enforcing standards and managing
IT risks have been identified (Bente, 2012).
In any organisation, the EA functions and
activities play a major role in the evaluation of new
technologies and in ensuring that any new IT
capability is delivering the planned business
benefits. In the context of cloud computing
evaluation and adoption it is possible to identify the
following key activities:
1) Creating the essential elements of the
Enterprise Architecture – the business architecture,
the applications architecture, data architecture and
technology architecture and evolving these
architectures to meet the changing business needs. In
the context of cloud computing adoption, it is critical
that all the architecture elements have been
adequately defined so that informed evaluation
choices can be made. Evolving the IT environment
to meet changing needs and adopting new
technology and computing models that will deliver
competitive advantage for the business is a key
activity.
2) Evaluating the business value of new
technologies and computing models such as cloud
computing.
3) Defining standards and policies for the
effective, secure and smooth running of the IT
environment.
4) Defining the maturity of the organisation with
respect to key skills and organisational capabilities
and preparing plans to address gaps.
5) Managing and mitigating risks. In the context
of cloud computing adoption, this involves defining
an acceptable level of risk for the available cloud
options and ensuring that the organisation has the
capability to deliver defined mitigation approaches.
IT departments in organisations have grown
large and complex providing multiple functions.
This has happened as the importance of IT to the
business grew which resulted in more IT solutions
being adopted and hence requiring a large and
complex IT organisation. The advent of cloud
computing promises to streamline and reduce IT
department growth since major functions that are
usually under the management of the IT department
are being provided by cloud service providers.
Figure 1 is a high-level illustration of key functions
that are relevant to cloud IT.
Figure 1: IT Functions for cloud IT.
As previously described Enterprise Architecture
covers a broad set of functions. IT Governance
incorporates IT Management and ensures that IT
structures and performance are supporting the
business objectives (ITGI, 2012), (Ross, 2006).
EnterpriseArchitectureComponentsforCloudServiceConsumers
361
IT Operations focuses on the operational support
requirements and works with IT Governance to
support the requirements and business goals (ISACA
2012). Development/QA is the solution development
function with QA (Quality Assurance) that provides
testing and quality assurance.
In this paper we present an approach that covers
the following two important elements:
1) Defining the foundational EA that will enable
cloud IT to leverage EA frameworks such as
TOGAF
2) Defining the governance structures for cloud
IT and defining the operations mechanisms
leveraging standards such as ITIL (ISACA, 2012).
2.2 Enterprise Architecture Layers
EA deals with all the main and relevant enterprise
elements, especially focusing on aligning IT
structures with the organisations objectives and
vision. As highlighted in (George 2013), an EA
helps IT functions to deliver business value
indirectly, for example by reducing complexity
through standardization of technology platforms,
and by improving governance through defining roles
and responsibilities.
An EA program in an organisation will deliver
intellectual property assets for an organisation that
include artefacts such as strategies, models,
methodologies, roadmaps and define technology
infrastructure and services, best practices and
metrics. An EA framework, e.g. TOGAF (TOGAF
2009) provides guidelines, methods and best
practices to help an organisation work through an
EA program. EA for a given organisation consists of
four layers as illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Enterprise Architecture Layers.
This layered approach is considered in the context of
cloud computing for the cloud service consumer in
the next section.
2.3 Enterprise Architecture
Components for Cloud Computing
The service-based paradigm is the approach through
which cloud computing is delivering value to
organisations. The service-based paradigm is
promoting improved agility and adaptability of
business process. The service centric business aims
to be agile enough to be able to support business,
process and technology changes. Business process
is the key element of how enterprises organise their
work and business processes are supported by
software capabilities. This service-based approach
when incorporated into the layered enterprise
architecture models has the service concept as the
main linking capability between the layers (Land
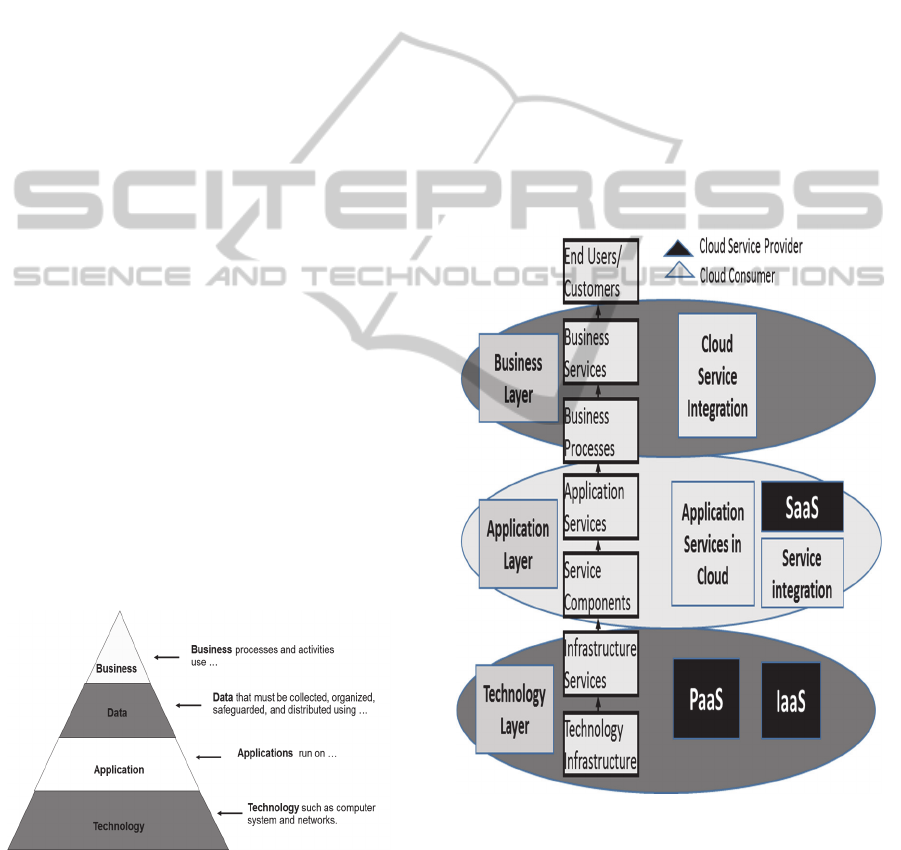
2009). This layered model is illustrated in Figure 3.
The way in which these layers exist in the cloud
environment is also illustrated in the diagram.
Figure 3: Service-based layered EA model and cloud
mapping.
Business Layer
The business layer models the organization structure
and the business services it produces, business roles
and business processes, and business objects.
Business services expose business functionality to
the environment and business processes deliver the
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
362

business behaviour of the organisation. Two
organisations in the same industry delivering the
same business service may appear different to the
customer if the business processes supporting the
business services exhibit different behaviours. Cloud
service integration tools provide business processes
with integration to application service components
in the cloud environment. These tools include cloud
brokers and cloud service integration capabilities.
Application Layer
The application layer describes application services
and their components and their interactions, logical
data entities and their relationships, and the resulting
services offered to the Business Layer. Services are
the building blocks of the application layer
architecture. The application service is available via
a web browser or web services API (Application
Programming Interfaces). Application components
and composite services enable the creation of
services dynamically improving business agility.
SaaS (Software as a Service) capability hosted by
the cloud service provider may be a part of the
services and applications portfolio available to
service consumers. Service Integration includes
Service Meshes and Service Mashups that enable
dynamic service assembly and service integration
(Raj, 2013). Service Components are a combination
of consumer application service components and
generic application support service components.
Technology Layer
Technology Layer models hardware, virtual
machines, application support software, networks
and storage showing how these components translate
into services provided to the Application Layer. The
Technology Layer in the cloud context consists of:
PaaS (Platform as a Service) and IaaS (Infrastructure
as a Service). Both PaaS and IaaS are cloud
capabilities provided by the cloud service provider
and hence the consumer organisation does not need
to provide the technology infrastructure. However,
governance structures including operational support
need to be adapted or enhanced to support the cloud
environment.
The EA model described above defines the
required elements for delivering cloud computing
services for the cloud service consumer.
2.4 Cloud Computing Governance
Cloud computing by divesting hardware and
software can reduce the size of the IT organisation.
Also, governance and management structures related
to hardware, networking and system software can be
reduced. However, some governance structures need
to be enhanced and new ones created to support
cloud computing.
IT governance and service management are
critical elements of IT and have been subject of
extensive research interest. Oragnizations have used
established frameworks such as COBIT (ITGI,
2012) and ITIL (ISACA, 2012) to address their
governance and service management requirements.
With respect to cloud computing, COBIT
provides support for the following three areas of
governance (Feuerlicht, 2012): 1) tools to manage
governance compliance, 2) best practice processes
to implement governance, and 3) governance
maturity model which help to determine the
readiness of the organisation for cloud computing
adoption. COBIT provides the necessary criteria to
ensure that the ITIL processes and functions are
performing to agreed to levels of quality. ITIL works
closely with COBIT and is responsible for ensuring
that ITIL best practices are in place to support and
maintain cloud services.
In a service-based environment such as the
cloud, SOA Governance and IT Governance aspects
are relevant (RAJ, 2013). Additional governance
activities for the cloud include activities related to
consumption and management of cloud services.
This includes IT Service management, Change
Management, Security management and Risk
management. Service Level Management includes
service level contracts and performance monitoring
for all entities participating the cloud supply chain.
Cloud governance needs to address design time
activities to support service development and run-
time activities to manage policy enforcement.
3 MATURITY ASSESSMENT
The EA components described as elements of EA
for cloud and the governance structures can be
evaluated to provide guidelines for organisations to
establish their readiness for various stages of cloud
computing. Maturity levels provide a mechanism for
assessing organisational or technical skill levels for a
particular capability (Ross, 2004). (Ross, Weil,
2006) have described a method for assessing
maturity levels of EA implementations.
IBM (IBM, 2015) has defined maturity levels for
cloud service providers as part of their cloud
computing reference architecture (CCRA). Using a
similar approach a set of maturity levels for the
cloud service consumer under the capability
Services Structure and Access can be defined as
follows:
EnterpriseArchitectureComponentsforCloudServiceConsumers
363

Maturity Level 1: basic IaaS capability for
hosting applications as services
Maturity Level 2: use of individual cloud
services
Maturity Level 3: EA enables catalog of cloud
services and static access to the catalog
Maturity Level 4: EA enables a fully capable
cloud environment and enables integration
Maturity Level 5: EA design and implementation
enable seamless integration of application services
transparently regardless of location of the underlying
service
The application architecture component of the
EA can be assessed to determine the maturity level
the current service structure capability for a
particular business scenario or business service. The
target maturity level to address a specific business
need such as agility can be determined for the
business scenario. This allows the organisation to
determine the gap and the steps that need to be taken
to bridge the gap. It is not always necessary to be at
the highest maturity level to achieve a particular
business outcome. This enables focused allocation of
resources based on the business requirements.
(George, 2013) has discussed this assessment
approach in the context of how EA can be evaluated
against business goals and objectives.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Cloud Computing Reference Models (NIST 2013)
provide a reference architecture and a reference
implementation approach for planning and
implementing cloud computing. These reference
models give greater detail from the cloud service
provider viewpoint than from the cloud consumer
organisation viewpoint. The NIST Reference
Architecture defines the various cloud services in the
context of an overall cloud computing model and
provides a reference for cloud consumers to
understand, categorise and compare cloud services.
The IBM CCRA (IBM 2015) shows at a high level
the cloud components from both the consumer and
service provider perspective, and describes the cloud
management platform in line with ITIL definitions.
However a detailed discussion of the architecture
and governance from a consumer organisation
perspective has not been adequately covered. In this
paper the perspective of the consumer organisation
and the main architectural elements that are critical
for adopting cloud computing in this context have
been presented. Details of the architectural elements
presented will need to be further studied in ongoing
research. Further research into the relationship
between the proposed approach in this paper and the
cloud computing reference models like the NIST
model needs to be conducted. Maturity models have
been used to develop understandings of
organisational readiness for adoption of new
technologies and capabilities. The idea of using
maturity models and assessment approaches to gain
understanding of organisational ability to achieve
planned cloud benefits has been introduced in this
paper. Further research defining maturity levels and
maturity assessment approaches of capabilities
associated with Enterprise Architecture components
proposed needs to be conducted.
REFERENCES
Bente, S., Bombosch, U., Langade, S. 2012. Collaborative
Enterprise Architecture. Morgan Kaufmann.
Feuerlicht, G. and George E., 2013, Enterprise
Architecture Value Model, Proceedings of
International Conference on Enterprise Information
Systems, pages 376 – 381, July 4-7, 2013, Angers,
France, Lecture Notes in Business Information
Processing.
Feuerlicht, G. and George E., 2013, Cloud Computing
Adoption Framework, Proceedings of CONFENIS-
2013, 7th International Conference on Research and
Practical Issues of Enterprise Information Systems,
September 11-13, 2013, Prague, Czech Republic,
ISBN: 978-3-990033-081-4, Trauner Verlag, 2013,
pages 320-327.
Feuerlicht, G., Schneider, S. and Tranter
,
L., 2012,
Enterprise Architecture for Cloud Computing
Environments, accepted for publication in the
proceedings of The Eleventh Workshop on e-Business,
December 15, 2012, Orlando, FL, USA, published
online: http://infosys.uncc.edu/web2012/Proceedings.
aspx.
IBM 2015. Enterprise Architecture in the age of Cloud
Services”. Retrieved January, 2015 from
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/library/e
nterprise-architecture-cloud/
IBM Cloud Computing Reference Architecture 4.0
2014. http://ibm.co/1xnmKwQ.
Ibrahim, M. and Long G. 2007. Service-Oriented
Architecture and Enterprise Architecture, a three-
article series. IBM DeveloperWorks (April 2007).
ISACA.2012. ITIL Retrieved from http://www.isaca.org/
Groups/Professional-English/itil/Pages/Overview.aspx.
ITGI. 2012 “COBIT Framework for IT Governance and
Control.”.Retrieved from
http://www.isaca.org/Knowledge-Center/cobit/Pages/
Overview.aspx.
Landhorst, M. 2009. Enterprise Architecture at Work.
Springer.
ICEIS2015-17thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
364

NIST 2013, NIST Cloud Computing Standards Roadmap.
Retrieved Jan 2015 from http://www.nist.gov/itl/
cloud/ upload/NIST_SP-500-291_Version-2_2013_
June18_FINAL.pdf.
TOGAF 2009, The OpenGroup TOGAF version 9.
http://www.opengroup.org/togaf.
Raj, P. 2013. Cloud Enterprise Architecture. CRC Press.
Ross, J. W., Weill, P., & Robertson, D. 2006. Enterprise
architecture as strategy: Creating a foundation for
business execution. Harvard Business Press.
Ross, J. W., & Beath, C. M. 2006. Sustainable IT
outsourcing success: Let enterprise architecture be
your guide. MIS Quarterly Executive, 5(4), 181-192.
Ross, J. 2004. Maturity Matters: How Firms Generate
Value From Enterprise Architecture. Research
Briefing, CISR, Sloan School of Management, MIT,
4(2B).
EnterpriseArchitectureComponentsforCloudServiceConsumers
365
