
Post Processing Method that Acts on Two-dimensional Clusters of
User Data to Produce Dead Bands and Improve Classification
David Adrian Sanders
1
and Alexander Gegov
2
1
School of Engineering, University of Portsmouth, Anglesea Road Building, Portsmouth, U.K.
2
School of Computing, University of Portsmouth, Buckingham Building, Lion Terrace, Portsmouth, U.K.
Keywords: User Information, Post Processing, 2-D Clusters, Data, Mining, Dead Bands, Set.
Abstract: A post processing method is described that acts on two-dimensional clusters of data produced from a data
mining system. Dead bands are automatically created that further define the clusters. This was achieved by
defining data within the dead bands as NOT belonging to either cluster. The three clusters produced were
definitely YES, definitely NO and a new set of DON’T KNOW. The creation of the new set improved the
accuracy of decisions made about the data remaining in YES and NO clusters. The introduction of the dead
bands was achieved by either setting a radius during the learning process or by setting a straight line
boundary. Each radius (or line) was calculated during the learning process by considering the two-
dimensional position of each of the users within each cluster of dimensions. A radius line (or straight line)
was then introduced so that the 80% of users within a particular dimension who were nearest to the origin
(or edge) were placed into a set. The other 20% were outside the radius line (or straight line) and not
recorded as being part of the set. If the two lines did not overlap, then this sometimes created a dead-band
that contained users with less certain results and that in turn increased the accuracy of the other sets. Two
case studies are presented as examples of that improvement.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper describes recent advances in improving
the identification of accurate sub-sets by post
processing outputs from data mining systems. The
data mining identifies rules for separating data. The
new methods then improve on those results by
automatically creating dead bands that further define
clusters of data. This was achieved by defining data
within the dead bands as NOT belonging to either
cluster. The three clusters that were produced were
then definitely YES, definitely NO and a new set of
DON’T KNOW. The creation of the new set
improved the accuracy of decisions made about the
data remaining in the YES and NO clusters. Two
case studies are presented as examples of that
improvement:
CASE STUDY ONE - Inferring Learning Style
from the Way Users Interact with a Computer User
Interface and the WWW.
CASE STUDY TWO - Predicting whether a
visitor to a WWW Site will convert to a potential
customer by monitoring their user behaviour.
2 CASE STUDY ONE
Some systems have considered perception (Sanders,
1999) and intelligent Web-based and other software
systems have attempted to adapt in order to match
user learning styles (Bergasa-Suso et al, 2005). That
adaption has depended on identifying learning
style(s). They have tended to assess learning styles
through questionnaires, and systems like iWeaver
dynamically adapted to preferences by monitoring
user feedback and navigation patterns. None of the
systems managed to successfully infer learning
styles by analyzing the way people interacted with a
computer and navigated the WWW.
Learning styles of volunteers were initially
determined by questionnaire so that they could be
tested against styles automatically calculated using a
software agent that analyzed interaction with a User
Interface (UI). A user activity analyzer detected
whether a user was participating or not by timing the
UI.
To determine the learning style of a user
automatically, patterns needed to be found in the
way users with different learning styles made use of
the Internet. Patterns also had to be found in the
267
Adrian Sanders D. and Gegov A..
Post Processing Method that Acts on Two-dimensional Clusters of User Data to Produce Dead Bands and Improve Classification.
DOI: 10.5220/0005473202670272
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST-2015), pages 267-272
ISBN: 978-989-758-106-9
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

layout and elements of Web pages that were more
easily understood by users, depending on their
learning style. Various models of learning style were
considered (Litzinger et al, 2007; Felder & Soloman,
2009). The Felder-Silverman dimensions of
learning style was selected for further study before
fully coding the new systems because it provided
four dimensions of learning style that might be
measured from data obtained from computer
systems: timings, actions, locations, etc.
The Active / Reflective Dimension is used as an
example in this paper. Active learners tend to retain
and understand information best by doing something
active, such as discussing it, applying it or
explaining it to others. Reflective learners prefer to
think about it quietly first.
3 CREATION AND TESTING OF
PATTERNS
An experiment was conducted to find rules in UI
activity and in the characteristics of Web pages that
would predict learning style based on behaviour
while browsing the Internet. An agent registered UI
interaction while a user was engaged. User activity
and page structure were analyzed and recorded each
time a page was visited. User data was stored in a
database tagged with a user’s dimensions of learning
style questionnaire results, so that it could be
processed by a data mining engine along with data
from other users. The parameters recorded by the
agent were: time in a page; mouse speed, total
mouse distance, mouse distance in X and Y axis;
scroll speed, scroll distance, changes in scroll
direction; use of back and forward buttons; data
copied and data dragged. The page structure
parameters recorded were: length of page text;
number and area of images; ratio of text to images,
presence, and location of tables, bulleted and
numbered lists, presence of sound files, video files,
animations and ActiveX components; presence and
location of question marks, and keywords, such as:
“example,” “figure,” “question” and “diagram.”
A group of 24 users (with different learning
styles) from the initial group volunteered to
investigate a subject for 20 minutes using Internet
Explorer while the agent monitored their activity,
and to rate each page depending on how easy that
page was to understand. Once information had been
gathered from the group of users, the data was
analyzed to find correlations between: dimensions of
learning style, UI usage, and the way information
was presented in useful pages. Correlations were
found between each of the dimensions of learning
style and the UI activity and page content
parameters monitored by the agent. The 20
parameters monitored by the agent that were most
significant in predicting each dimension were
extracted from Data Mining software (called
PolyAnalyst). As an example, the five most
significant parameters to predict whether a user is
Active or Reflective were:
These parameters and the values recorded for
each user were used to create a probability model for
each learning style dimension that could predict the
learning style dimensions of new users based on the
value of each selected parameter as recorded by the
agent. This model returned a percentage of certainty
that a user belonged to one of the extremes of each
learning style dimension.
To test the effectiveness of the model, a group of
seven users (with various different learning styles)
were given the same research task as the initial
group. The agent monitored their activity and the
data recorded by the agent was fed into the model,
which returned the predicted dimensions of each
user. The users then completed ILS Questionnaires,
and the questionnaire results were compared with
those predicted by the models for each user.
When a similar method was used by Bergasa-
Suso (2005), the model to predict a user as being
active or reflective was only slightly more accurate
than the naive prediction calculated from a sample
population. That work was a first success even
though the results were relatively naïve.
In this work, prior to the experiment, a group of
67 users completed the ILS Questionnaire and the
results were entered into a database. In this way, the
preferred learning style of each user was known
before the experiments, along with the distribution
of the different dimensions of learning style over the
sample population, see Table I.
The percentage of users belonging to each
dimension determined the minimum accuracy
required for the rules. For example, a naive
WEBIST2015-11thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
268
prediction that considered every user as Active
would have an accuracy of 57% according to Table
I.
Table 1: Distribution of dimensions of learning style over
sample population.
Dimension
Number of
people
%
Actives
38 57%
Reflectives
29 43%
Any rule found to predict a user’s dimension of
learning style must be more accurate than the naive
prediction.
In the initial tests for Sensing/Intuitive,
Visual/Verbal and Sequential/Global, the results
were only equivalent to guessing. The new methods
described in this paper improved on the results by
introducing a new unknown set for pairs of
significant parameters.
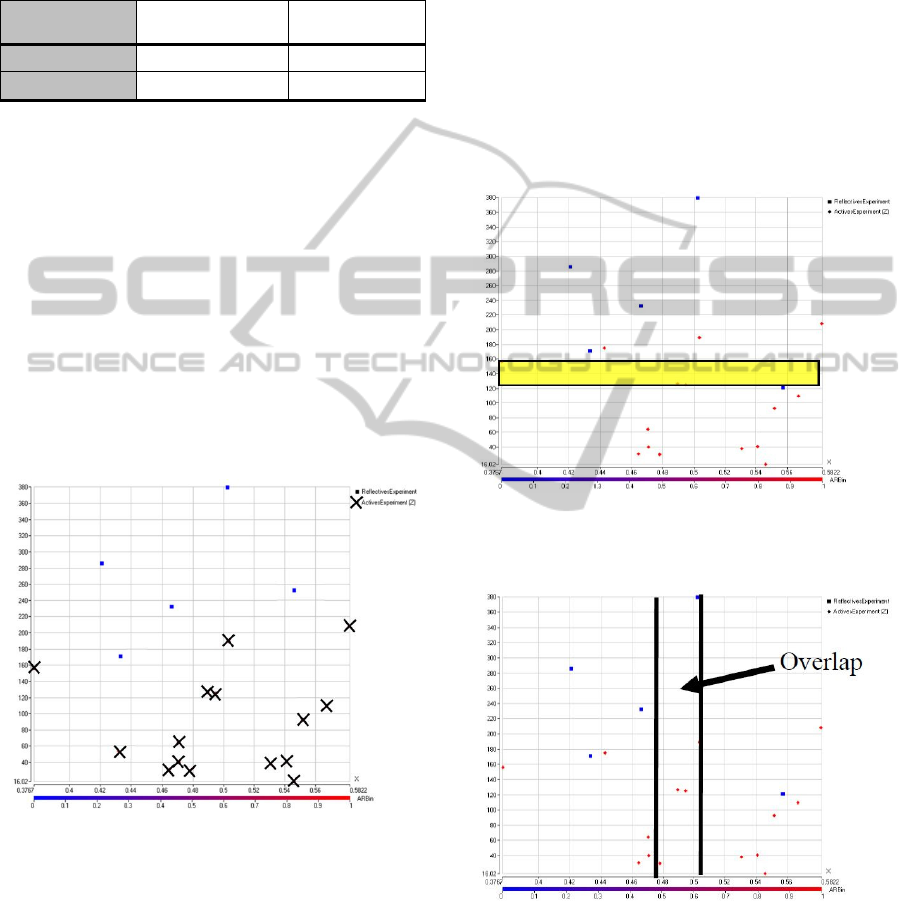
As an example, a scatter graph showing some
results from twenty users is shown in Fig. 1. Three
or four dimensional scatter graphs were generally
used but for ease of representation, Fig. 1 just shows
the clusters of Active (cross) and Reflective (square)
users in two dimensions.
Figure 1: Clusters of Active (crosses) and Reflective
(square) users visualized by plotting data points against
“Amount of mouse movement in the Y axis” (X) and
“ratio of images area to document length and scroll
distance” (Y).
The clusters overlap in Fig. 1 and it would be
difficult to draw a meaningful line to separate the
data into two clusters. That was a problem with the
work in Sanders & Bergasa-Suso (2010). Users
were always considered to belong either to the set of
Active Users or to the set of Reflective Users. Each
of the twenty most useful sets of parameters made a
decision about each dimension, and the probability
of a user being one or other dimension was then
calculated from the twenty decisions. This was
satisfactory for users who clearly fell into a single
category virtually all the time, but most people only
tended towards a particular dimension, and even that
might change depending on circumstances or mood.
Each two-dimensional
cluster was further
defined by creating some dead bands within which a
user was not defined as belonging to either
dimension. This was achieved by either setting
straight line boundaries, as shown Fig. 2 and Fig 3
or by setting a radius during the learning process as
shown in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5.
Figure 2: A dead band created with straight lines for two
sets of attributes in two dimensions that could be used to
classify a user.
Figure 3: An overlap shown for two sets of attributes in
two dimensions that could be used to classify a user.
Each radius (or line) was calculated during the
learning process by considering the two-dimensional
position of each of the users within each cluster of
dimensions. A radius line (or straight line) was then
introduced so that the 80% of users within a
PostProcessingMethodthatActsonTwo-dimensionalClustersofUserDatatoProduceDeadBandsandImprove
Classification
269

particular dimension who were nearest to the origin
(or edge) were placed into a set. The other 20% were
outside the radius line (or straight line) and not
recorded as being part of the set. If the two lines did
not overlap, then this sometimes created a dead-band
that contained users with less certain results.
Fig. 2 and Fig. 4 have dead bands shown by the
shaded area. The dead bands represented new
unknown sets of results so that users could be
considered as Active, Reflective or Unknown. Fig.
3 and Fig. 5 do not have dead bands, because in both
cases the 80% lines overlapped each other.
Figure 4: A dead band created with curves for two sets of
attributes in two dimensions that could be used to classify
a user.
Figure 5: A curved overlap shown for two sets of
attributes in two dimensions that could be used to classify
a user.
If there was a choice between sets of data with a
dead band then the widest dead band would be
selected. So in this case, Fig. 4 shows the shape of
the sets selected for Reflective / Active dimensions
using the “Amount of mouse movement in the Y
axis” (plotted on the X axis) and “ratio of images
area to document length and scroll distance” (plotted
on the Y axis). That was because the distance
between the curved lines was greater in that graph
than the straight lines in other graphs. The
algorithm to calculate the dead band during the
learning shown in Sanders & Bergasa-Suso (2010).
The sets produced for the parameters used in this
work were: Active, Reflective and a new set
“Unknown”. Users were only classified as probably
Active or Reflective for each pair of parameters if
they were outside the dead band and therefore
clearly within one of the two sets bounded by the
established lines.
That effectively removed less certain cases from
individual pairs of results so that when all the results
were collated, the final results were more certain and
less naïve.
A significant advance occurred when the
additional programming was incorporated to add in
the unknown set for each pair of sets of results from
the data-mining.
4 TESTING FOR CASE STUDY 1
The new method had a significant effect on the
Active/Reflective set of results as shown in Table II.
Using this new method, some users were sometimes
not defined by the system, because they always fell
into the unknown set for every pair of useful
parameters (less than 10%).
Table 2: Accuracy achieved by the new system after dead
bands were introduced, and naïve predicted accuracy that
needed to be reached before results could be considered
significant.
Accuracy with
Dead Bands
Naïve pred.
Accuracy
Active/Reflective
81% 58%
Table II shows an improvement over Bergasa-
Suso et al (2005) which had 71% and 57%. The
accuracy in determining whether a user was Active
or Reflective increased significantly and correctly
classified Active / Reflective users increased from
71% to 81%.
5 CASE STUDY 2
A second case study attempted to predict whether a
visitor to a WWW Site would convert to a potential
customer by monitoring their user behaviour.
WEBIST2015-11thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
270

An experiment was conducted to find rules in
activity on test WWW Sites and in the
characteristics of Web pages that would predict
whether a visitor would become a potential
customer.
A potential customer was defined as a visitor
who contacted the company hosting the WWW site
by email from the site in order to ask for more
information or to purchase a service or product.
An experimental system was created to record
and analyze data.
An agent registered WWW usage while the user
was investigating test sites.
User activity and page structure were analyzed
and recorded each time a page was visited. User
data was stored in a database.
These could then be replayed while tagged with
the user’s result (left the site or became a potential
customer), so that it could be processed by a data
mining engine along with data from other users.
Parameters recorded by the agent were: time in a
page; use of back and forward buttons etc.
The page structure parameters recorded were:
length of page text; number and area of images; ratio
of text to images, presence, and location of tables,
bulleted and numbered lists, presence of sound files,
video files, animations and ActiveX components.
Once information had been gathered from site
users, the data was analysed to find correlations
between: customer conversion, UI usage, and the
way information was presented in useful pages.
Correlations were found between whether a
customer converted and the UI activity and page
content parameters monitored by the agent.
The 20 parameters monitored by the agent that
were most significant in predicting each dimension
were extracted from the Data Mining software.
Unfortunately the significant parameters are
commercial in confidence at the time of writing and
cannot be reproduced here.
These parameters and the values recorded for
each user were used to create a probability model for
each result (leaving or converting to a potential
customer) that could predict the likely conversion of
new users based on the value of each selected
parameter as recorded by the agent.
This model returned a percentage of certainty
that a user belonged to one of the extremes of each
possible result.
To test the effectiveness of the model, a group of
320 users (with various results) were tested. The
agent monitored their activity and the data recorded
by the agent was fed into the model, which returned
the predicted result of each user.
Actual results were compared with those predicted
by the models for each user.
6 TESTING OF PATTERNS AND
THE RESULTS FOR CASE
STUDY 2
A significant advance occurred when the additional
programming was incorporated to add in the
unknown set for each pair of sets of results from the
data-mining.
This had a significant effect as shown in Table
III.
Using this new method, a very small number of
users were sometimes not defined by the system,
because they always fell into the unknown set for
every pair of useful parameters (less than 2%).
In the initial tests for convert/leave the results
were only equivalent to guessing, see Table IV.
The new methods described in this paper
significantly improved on these results by
introducing a new unknown set for pairs of
significant parameters.
Table 3: Distribution of dimensions of learning style over
sample population.
Dimension Number of users %
Convert
3800 57%
Leave
34 43%
Table 4: Accuracy of models without dead bands.
Accuracy
Naïve pred.
Accuracy
Convert/Leave
59% 56%
Table 5: Left = Accuracy achieved by the new system
after dead bands were introduced, and Right = naïve
predicted accuracy that needed to be reached before results
could be considered significant.
Accuracy with
Dead Bands
Naïve pred.
Accuracy
Convert/Leave
69% 58%
Table V shows a significant improvement over the
initial results in Table IV.
7 DISCUSSION / FUTURE WORK
Introducing a new unknown set for pairs of useful
PostProcessingMethodthatActsonTwo-dimensionalClustersofUserDatatoProduceDeadBandsandImprove
Classification
271

parameters produced more accurate rules.
Current work used a keyboard and mouse but on-
going research is experimenting with different
sensors and UIs (Sanders, 2007, 2008a, 2008b,
2009a; Stott & Sanders 2000), including touch
screens (Chester et al, 2006 & 2007; Sanders et al,
2005), pointer devices (Sanders et al 2009; Sanders
and Tewkesbury, 2009), and joysticks (Stott et al,
1997; Sanders & Stott, 1999), and Blackboard
systems ( Sanders & Husdon, 2000) and ANNs
(Sanders et al 1996; Sanders 2009b) are being
considered to identify correlations between the
relevance rating of Web pages and their usefulness.
The more accurate classification rules might
improve effectiveness and efficiency of software
systems by automatically modifying them to better
support users with a particular learning style (active
or reflective) or to convert more customers.
The work so far has assumed that learning styles
and buyer intentions are relatively static, but these
styles may not be completely distinctive and the
validity of models for both has been questioned.
Research is on-going to consider that as well as to
investigate some new applications for the work but
for the moment is concentrating on improving
models for the other dimensions of learning style.
At the time of writing, some research is just
beginning to investigate the effect of adjusting the
threshold settings on the algorithms for calculating
learning styles in real time and to compare data and
results for customers who revisit www sites. Future
work will test more users to further verify the
measurements and effectiveness of the adaptation.
REFERENCES
Bergasa-Suso, J., Sanders, d., Tewkesbury, G., 2005.
Intelligent browser-based systems to assist Internet
users. IEEE T EDUC 48 (4), pp. 580-585.
Chester, S., Tewkesbury, G., Sanders, D., et al 2006. New
electronic multi-media assessment system. 2nd Int
Conf on Web Info Sys and Tech, pp: 424 Year.
Chester, S., Tewkesbury, G., Sanders, D., et al 2007. New
electronic multi-media assessment system. Web Info
Systems and Technologies 1, pp 414-420.
Felder, R., Soloman, B., 2009. Index of Learning Styles
Questionnaire [Online] Available:
http://www.engr.ncsu.edu/learningstyles/ilsWeb.html.
Litzinger, T., Lee, S., Wise, J., et al. 2007. A
psychometric study of the Index of Learning Styles. J.
Eng Ed vol. 96, no. 4, pp 309-319.
Sanders, D. A., 1999. Perception in robotics IND ROBOT
26 (2), pp: 90-92.
Sanders, D. A., 2007. Viewpoint - Force sensing IND
ROBOT 34 (4), pp: 268.
Sanders, D. A., 2008a. Controlling the direction of
"walkie" type forklifts and pallet jacks on sloping
ground. ASSEMBLY AUTOM 28 (4), pp 317-324.
Sanders, D. A., 2008b. Progress in machine intelligence.
IND ROBOT 35 (6), pp: 485-487.
Sanders, D. A., 2008c. Environmental sensors and
networks of sensor. SENSOR REV 28 (4), pp: 273-
274.
Sanders, D. A., 2009a. Introducing AI into MEMS can
lead us to brain-computer interfaces and super-human
intelligence. ASSEMBLY AUTOM 29 (4), pp: 309-
312.
Sanders, D. A., 2009b. Recognizing shipbuilding parts
using artificial neural networks and Fourier
descriptors. P I MECH ENG B-J ENG 223 (3), pp:
337-342.
Sanders, D. A., Bergasa-Suso, J., 2010 Inferring Learning
Style From the Way Students Interact With a
Computer User Interface and the WWW. IEEE T
EDUC 53(4), pp: 613-620.
Sanders, D. A., Haynes, B. P., Tewkesbury, G. E., 1996.
The addition of neural networks to the inner feedback
path in order to improve on the use of pre-trained feed
forward estimators. MATH COMPUT SIMULAT 41
(5-6), pp: 461-472.
Sanders, D. A., Hudson, A. D., 1999. A specific
blackboard expert system to simulate and automate
the design of high recirculation airlift reactors MATH
COMPUT SIMULAT 53 (1-2), pp: 41-65.
Sanders, D., Stott, I., 1999. A new prototype intelligent
mobility system to assist powered wheelchair users
IND ROBOT 26 (6), pp: 466-475.
Sanders, D., Tan, Y. C., Rogers, I., et al 2009. An expert
system for automatic design-for-assembly.
ASSEMBLY AUTOM 29 (4), Pages: 378-388.
Sanders, D., Tewkesbury, G., 2009. A pointer device for
TFT display screens that determines position by
detecting colours on the display using a colour sensor
and an Artificial Neural Network. DISPLAYS 30 (2),
pp 84-96.
Sanders, D., Urwin-Wright, S., Tewkesbury, G., et al
2005. Pointer device for thin-film transistor and
cathode ray tube computer screens. ELECTRON
LETT 41 (16), pp 894-896.
Stott, I., Sanders, D., 2000. New powered wheelchair
systems for the rehabilitation of some severely
disabled users. INT J REHABIL RES 23 (3), pp 149-
153.
Stott I., Sanders, D., Goodwin, M., 1997. A software
algorithm for the intelligent mixing of inputs to a tele-
operated vehicle. Euromicro Conference 95 in J
SYST ARCHITECT 43 (1-5), pp 67-72.
Tewkesbury, G. E., Sanders, D., 1999. A new simulation
based robot command library applied to three robots J
ROBOTIC SYST 16 (8), pp: 461-469.
WEBIST2015-11thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
272
