
Computational Neuroscience
Challenges and Implications for Brazilian Education
Raimundo José Macário Costa
1
, Luís Alfredo Vidal de Carvalho
2
, Emilio Sánchez Miguel
3
,
Renata Mousinho
2
, Renato Cerceau
2,5
, Lizete Pontes Macário Costa
4
, Jorge Zavaleta
2
,
Laci Mary Barbosa Manhães
2
and Sérgio Manuel Serra da Cruz
1,6,7
1
Universidade Federal Rural do Rio de Janeiro (UFRRJ), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
2
Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
3
Salamanca University (U.S.A.L), Salamanca, Spain
4
Rio de Janeiro State University (UERJ), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
5
National Regulatory Agency for Private Health Insurance and Plans (ANS), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
6
Programa de Educação Tutorial (PET-SI/UFRRJ), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
7
Programa de Pós- Graduação em Modelagem Matemática e Computacional (PPGMMC/UFRRJ), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Keywords: Education, Neuroscience, Computer Science, Databases, Artificial Intelligence, Cognitive Science.
Abstract: Understanding the core function of the brain is one the major challenges of our times. In the areas of
neuroscience and education, several new studies try to correlate the learning difficulties faced by children
and youth with behavioral and social problems. This work aims to present the challenges and opportunities
of computational neuroscience research, with the aim of detecting people with learning disorders. We
present a line of investigation based on the key areas: neuroscience, cognitive sciences and computer
science, which considers young people between nine and eighteen years of age, with or without a learning
disorder. The adoption of neural networks reveals consistency in dealing with pattern recognition problems
and they are shown to be effective for early detection in patients with these disorders. We argue that
computational neuroscience can be used for identifying and analyzing young Brazilian people with several
cognitive disorders.
1 INTRODUCTION
Understanding brain function remains one of the
major challenges in the scientific community for the
twenty-first century (Abbot 2013). Research on the
subject has been growing exponentially since the
1960s. Neuroscience is a research field that has also
been growing significantly, beginning from the
1980s (Figure 1). Neuroscience aims to study and
analyze the central nervous system (CNS) of humans
and animals, their functions, particular format,
physiology, and injuries or pathologies. This area
has achieved important advances that have been
responsible for positive effects on the quality of life
of patients suffering from, for example, multiple
sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease,
and other diseases related to the CNS (Lent 2001).
However, despite extensive investment in the area,
much remains to be done, especially in relation to
understanding the binding mechanisms between
brain structures and functions at a microscopic level
for cognitive and behavioral processes (Markram
2013).
In the scientific area, the early 90s was
announced as the "decade of the brain". This
denomination originated in the U.S.A. and sought to
encourage the identification of normal
neuropsycobiological processes and related
disorders. Thus, together with significant advances
in computer science and the spread of the Internet,
the area of computational neuroscience flourished
(Schwartz 1990). Since then, works have been
developed and new strategies have been sought for
the development of realistic mathematical and
computer models to simulate the brain.
Most recently in April 2013, major investigative
projects the BRAIN Initiative (NIH 2014) and the
Human Brain Project (HBP 2014) were presented
again, in the U.S.A. and Europe, respectively. These
initiatives presented demands that propose to
revolutionize the understanding of the functioning of
the mysteries of the human brain. Thus, in order to
436
José Macário Costa R., Alfredo Vidal de Carvalho L., Sánchez Miguel E., Mousinho R., Cerceau R., Macário Costa L., Zavaleta J., Manhães L. and
Serra da Cruz S..
Computational Neuroscience - Challenges and Implications for Brazilian Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0005481004360441
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2015), pages 436-441
ISBN: 978-989-758-107-6
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
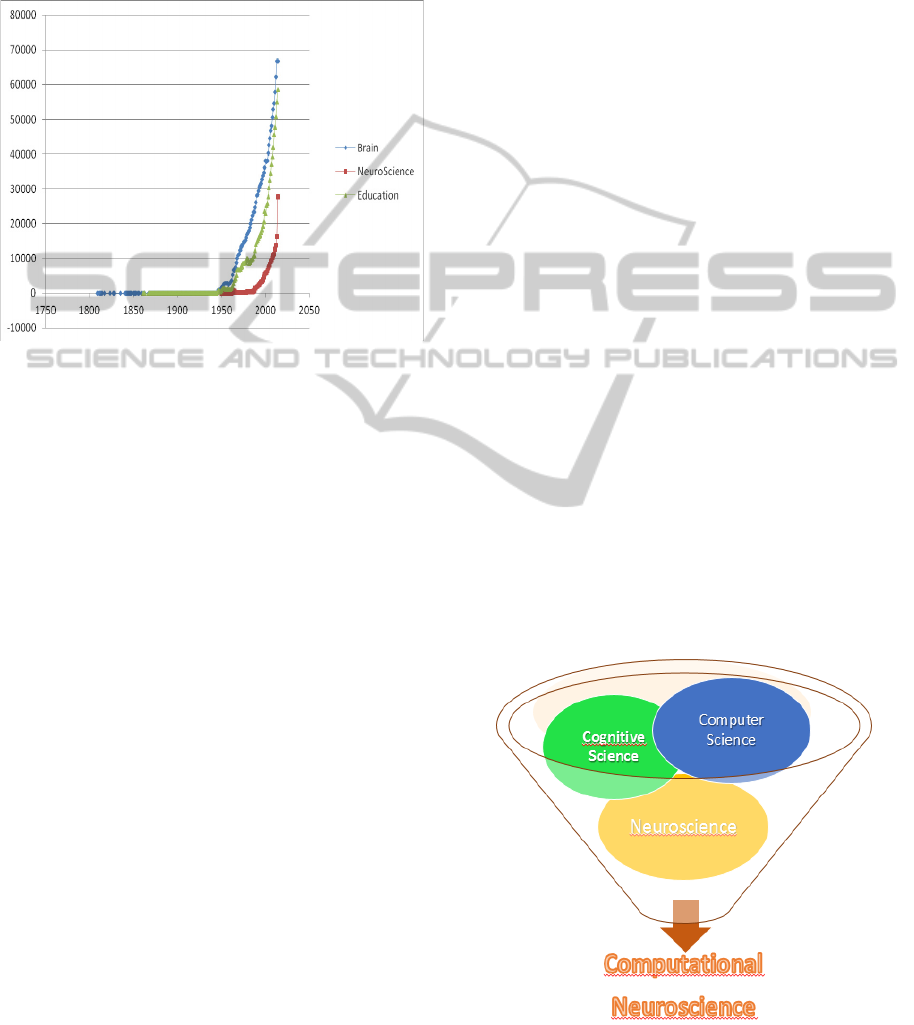
accelerate the development of new technologies that
will allow researchers and scientists to obtain
dynamic images of the brain in action, showing how
brain cells and complex neural circuits interact at the
speed of thought, thereby expanding knowledge
about how we think, learn, and remember.
Figure 1: Quantitative comparison of articles, published in
the PubMed database, that include the terms "brain",
"education" and "neuroscience" in the title (January,
2015). (Y-axis: Number of published articles X-axis: Year
of publication).
The structure to accomplish the BRAIN Initiative
includes private companies, research centers, and
government agencies, as well as a wide range of
experts ranging from physicians, neuroscientists,
nanoscientists to engineers and computer scientists
as well. The last ones working in the fields of
artificial intelligence, databases, high performance
computing, big data, e-science, games, robotics,
sensors, and social networks, among other (Zhong
2012; NIH 2014; HBP 2014).
In Brazil, significant efforts developed by
neuroscientists is recorded for the development of
knowledge related to the brain and the "Brazilian
Brain Industry". Among the various research
centers, we can mention the work developed at the
International Neuroscience Institute of Natal
Edmond and Lily Safra (IINN-ELS) and the Institute
of Biomedical Sciences of UFRJ (ICB-UFRJ).
Despite these great efforts and the synergy between
computational neuroscience and education still
needs to go further. Novel studies that correlate the
learning disorders faced by children and young
people with various computational techniques ought
to be developed. Such disorders have deep social
relevance in the educational area, for example,
where they may have an effect on truancy,
functional illiteracy, and repeated failures, as well as
the self-esteem of individuals.
The goal of this paper is to report research
directions and highlight the challenges related to the
adoption of computational neuroscience to enhance
the quality Brazilian education. This work also
presents our ongoing computational approaches
related to the classification of patients with dyslexia,
one of the learning disorders that has aroused
interest among Brazilian researchers, health
professionals, and schools teachers.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2
persent the current challenges of Computational
neuroscience. Section 3 present the researche
opportunities. Section 4 present the researches that
are being conducted by our research team. Finally,
section 5 concludes the paper.
2 CHALLENGES
Computational neuroscience can be used as a toolset
for building intelligent computational systems that
are capable of processing and analyzing large
volumes of (structured and semi-structured)
educational data. Computational neuroscience can
be used to elaborate educational games, or even
developing mobile applications targeted at
diagnostic support and tracking of learning disorders
(Zavaleta et al., 2012).
Computational neuroscience is essentially
interdisciplinary and rests on key three pillars:
neuroscience (the areas of medicine and biological
sciences); cognitive science (psychology); and
Figure 2: Three pillars in computational neuroscience and
prospects for technological investigations supported by
computer science.
ComputationalNeuroscience-ChallengesandImplicationsforBrazilianEducation
437

computer science (artificial intelligence, databases,
e-science, provenance, big data, high performance
computing (HPC), cloud computing, internet of
things, etc.) (Figure 2). However, one of the major
difficulties of computational neuroscience is to
model (mathematically and computationally) a
learning disorder, identify the most relevant
variables and data, transcribe them for technological
solutions, and determine if the computational results
are significant and valid according to medical,
ethical, and educational aspects.
To achieve a technological level compatible with
the multifaceted demands of brain studies in the
twenty-first century, we must consider the structure
of a research agenda that is focused on new models
and the incorporation of (data intensive)
computational techniques traditional to e-science
(Hey et al. 2009) for the development of applications
in computational neuroscience. In this case, it is
possible to advance in the following areas:
a) Development of intelligent and predictive
systems based on artificial intelligence
techniques (Macário Costa et al. 2007, 2008,
2009, 2010, 2011, 2013; Zavaleta et al. 2012)
capable of handling large volumes of data;
b) Use of distributed computational environ-ments
for high-performance processing of
intelligent systems, to support in silico
simulations and experiments based on
scientific workflows (Deelman et al. 2009) of
simulations of brain models (Abbot 2013;
Kubilius, 2014; NIH 2014; HBP 2014).
c) Adoption of management techniques for large
volumes of semi-structured biological data
and processing typically used for big data
(Davison 2010; Berman 2011; Abbott 2013)
— computational neuroscience projects are
gravitating towards mapping increasingly
larger and more complex brain models that
use sensors and data in different formats
(Zhong et al. 2011; Zhong 2012);
d) Incorporation of provenance descriptors (Cruz
et al. 2009, 2012) and data management and
techniques to increase the reproducibility and
reliability of studies in computational
neuroscience (Chen, Zhong, and Liang 2012;
Ciccarese et al. 2013) — these activities tend
to be conducted by interdisciplinary research
teams that are geographically and temporally
dispersed (Chen and Zhong 2013);
The knowledge acquired in the area of
neuroscience can be associated with novel tools and
computational techniques for improving the
opportunities to act on learning disorders.
Dyslexia can be characterized by a failure in the
acquisition and/or development of scholastic skills.
Dyslexia is a learning disorder that affects 3–7% of
the school-age population, and it highlights other
disorders including severe delays in reading, writing,
and spelling, as well as inversion of symbols. This
work is focused in dyslexia due to its singularity and
limited nature of the phonological deficit (Shaywitz
and Shaywitz 1999; Mousinho 2003). Detailed
understanding of the correlations between genetic
variations, brain dysfunction, and cognitive
difficulties is a great challenge in dyslexia research
(Giraud and Ramus 2013) such investigation require
large computing efforts due to the large amount of
data. Currently, an evaluation of a dyslexic
individual takes on average two months until the
establishment of a diagnosis by a qualified team.
Usually, the students referred to the health service
do not have dyslexia, but learning problems of
different orders. Here it we state that the
establishment of new tracking systems, based on
computational neuroscience, will possibly reduce the
queues and speed up access to diagnosis, thus
offering chances of intervention to more children
and young people in a short time period, in a more
opportune, efficient, and socially just manner.
3 IMPLICATIONS
Investigations directed at the tracking of children
and young people with dyslexia at school age will
contribute to establishing evaluations related to the
timely identification and referral of people with
learning disorders in schools, whether public or
private.
Mousinho (2011) states that it is almost a routine
situation to find students with reading problems. In
most schools, classes are composed of children who
are more or less adept at reading. Among the less
skilled children, there are still those that stand out.
Despite their efforts, reading tasks for these children
becomes a laborious and even painful activity. The
effort put into this action is so big that it may even
hinder the pleasure of reading.
Children with more impaired reading tend to
increase the gap between themselves and their peers,
which may increase the incidence of undesirable
consequences such as the loss of enjoyment of
reading, low performance in other disciplines that
depend on reading, and the development of low self-
esteem by the child (Mousinho 2011).
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
438

Early identification of children with reading and
learning difficulties has become a priority due to the
possibility of eliminating or reducing the detriment
to the children’s scholastic and social progress.
Thus, the adoption of disruptive computational
strategies based on computational neuroscience can
make all the difference in this identification.
One of the most common computational
strategies of computational neuroscience is the use
of neural networks. Neural networks are
mathematical models that simulate biological neural
structures and have computing ability acquired
through learning and generalization. We believe that
the biggest challenge is in gathering all the different
kinds of information (variables) into databases and
developing new mechanisms for analysis and
detection of dyslexic patients.
Therefore, our research efforts were developed
in order to detect which children and adolescents
were at risk of dyslexia. The prior versions of the
intelligent system developed by Macário Costa et al.
(2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2013) is expanding
its database in order to further consolidate the
accuracy of the algorithms. The algorithms were
used to extract the useful patterns from the data
collected during interviews done with the person
responsible for the child who is enrolled in the
school, in the search for a desired pattern to identify
individuals who have the learning difficulties.
In order to support the diagnosis of specific
learning disorders, Macário Costa et al. (2011, 2012,
2013) resent the implementation of a multi-layer
perceptron neural network to probabilistically
classify youth and adult patients with dyslexia.
4 RESEARCH GOALS
This paper aims to discuss the challenges and open
opportunities to develop novel computational
solutions that can contribute as support tools for
specialists to detect and diagnose, in advance,
individuals with learning disorders in our country.
The computational solutions we highlight can be
applied directly by teachers in elementary and
primary schools. We advocate that there is a need to
establish partnerships with public and private
institutions, governments, and research groups, that
can cooperate and provide computational
infrastructure capable of storing and processing, in a
distributed manner, large amounts of semi-structured
data. Besides, it is also important to offer a
commitment to involve their teams in the schools in
order to track the individuals who have learning
difficulties and/or are at risk of dyslexia or other
learning disorders.
The goals of our research is inherently
multidisciplinary and should be performed by people
with different skills (Macário Costa et al, 2014). It is
divided into three phases. The first phase, which has
already been performed, consisted of outlining the
problem and designing the tools and the neural
networks, followed by the construction of the
intelligent system and its database, and then
performing the testing and evaluation of the models.
The second phase, which is in progress, consists
of the survey of new demands necessary for the
scalability of the solution, enabling it to incorporate
the new technological artifacts (discussed above)
that can process large volumes of data in high-
performance distributed environments. In this phase
there is also the mapping of new collaborators and
schools. Without a combination of technologies, we
cannot answer the basic questions such as: How do
we detect — at an early stage, at a low operating
cost, and at high effectiveness — young people at
risk of dyslexia or other learning disorders? In a
country like Brazil, with its continental dimensions
and its historical social inequalities, obtaining
answers to questions of this nature could be a
strategic advantage for the country's future.
The third and final phase is crucial for the
project’s success. It will be more widespread and
will be operational. It will be directed toward the
massive and early detection approaches in the school
environment in order to detect the children with
reading and learning difficulties. This phase requires
accurate, reliable, and quick analysis and processing
of data to assist in the medical diagnosis, and to
establish early referral of these individuals to
specialists.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This research allowed us to develop an intelligent
computational system, using artificial intelligence
techniques for the detection of individuals between 9
and 18 years of age who have learning difficulties
(dyslexia). The intelligent computational system is
composed of several modules, some are completed
and the others are being developed.
The neural network (NN) module allowed the
development of a method to support the process for
identifying people and children with dyslexia and
other learning difficulties. A database was developed
for the collection of data used by the NN module.
This module has been completed and the others are
ComputationalNeuroscience-ChallengesandImplicationsforBrazilianEducation
439

in the development and testing phase.
The individuals identified in the NN module pass
to the Response to Intervention (RTI) pyramidal
module which consists of three layers of evidence-
based interventions for promoting the social,
emotional, and behavioral development of children.
Each layer uses fuzzy logic to assign degrees of
learning difficulty to the individuals and determine
the most appropriate computational intervention for
each layer of the RTI model. Each layer of the RTI
model will consist of a set of computational
intervention methodologies (e.g., games) activated
by the degree of difficulty for each individual.
The proposed approach can be used innovatively
as a support tool for the diagnosis of dyslexia and
other learning difficulties. Further details and
detailed descriptions can be found at our previous
work (Macário Costa et al., 2014).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors R.J.M. Costa and R. Mousinho thank
the team of the ELO Project (Department of Speech
Pathology, and Faculty of Medicine at UFRJ) and
the Delindo Couto Neurology Institute of UFRJ and
USAL. J. Zavaleta thanks CAPES for the financial
support received. S.M.S. Cruz thanks CNPq,
CYTED (Programa Iberoamericano De Ciencia Y
Tecnologia Para El Desarrollo - grant P514RT0013),
FAPERJ (grants E-26/112.588/2012 and E-
26/110.928/2013), MEC/SeSU and PET-SI/UFRRJ
for the financial support of the research.
REFERENCES
Abbott, A. (2013) “Neuroscience: Solving the brain”, In:
Nature 499, pages. 272–274.
Berman JJ, (2009) “Principles of Big Data: Preparing,
Sharing, and Analyzing Complex Information”
Morgan Kaufmann; 1st Edition.
Ciccarese, P., Soiland-Reyes, S., Belhajjame, K., Gray,
A.J.G, Goble, C., Clark, T. (2013) “PAV ontology:
provenance, authoring and versioning”, Journal of
Biomedical Semantics 2013, 4:37.
Chen J. H., Zhong, N. (2013) “Toward the Data-Brain
driven systematic brain data analysis”. IEEE
Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:
Systems, 43(1), pages. 222-228.
Chen J. H., Zhong, N., Liang, P. P. (2012) “Data-Brain
driven systematic human brain data analysis: A case
study in numerical inductive reasoning centric
investigation” Cognitive Systems Research, Elsevier,
vol. 15-16, pages. 17-32.
Cruz, S.M.S, Campos, M. L M., Mattoso, M. (2009)
“Towards a Taxonomy of Provenance in Scientific
Workflow Management Systems”. SERVICES I 2009:
259-266.
Cruz, S.M.S, Campos, M. L M., Mattoso, M. (2012) “A
Foundational Ontology to Support Scientific
Experiments”. ONTOBRAS-MOST 2012: 144-155.
Davison, A.P. (2010) “Challenges and solutions in
replicability and provenance tracking for simulation
projects”. BMC Neuroscience 2010, 11(Suppl 1):P76.
Deelman E, Gannon D, Shields M, Taylor I (2009)
“Workflows and e-Science: An overview of workflow
system features and capabilities”, Future Generation
Computer Systems 25(5):528–540.
Giraud A.L., Ramus, F. (2013) “Neurogenetics and
auditory processing in developmental dyslexia”. Curr.
Opin. Neurobiol. 23:37–42.
HBP (2014) “Human Brain Project”.
https://www.humanbrainproject.eu/
Hey, T., Tansley, S., Tolle, K (2009) “The Fourth
Paradigm: Data-Intensive Scientific Discovery”
Microsoft Press. 1st Edition.
Kubilius, J. (2013) “A framework for streamlining
research workflow in neuroscience and psychology”.
Front. Neuroinform. 7: 52.
Lent, R. (2001) “Cem Bilhões de Neurônios – Conceitos
Fundamentais de Neurociência”. SP. Ed. Atheneu.
Macário Costa, R. J., Pará, T. S., Caloba, L. P., Carvalho,
L. A. V. (2007) “Classificação de pacientes com
transtorno de dislexia usando redes neurais artificiais”.
In: XXX CNMAC, Florianópolis.
Macário Costa, R. J., Mousinho, R., Carvalho, L. A. V.
(2008) “Redes Neuronais: um instrumento no rastreio
(screening) de pessoas com risco de transtorno
específico de leitura”. In: I Congresso Ibro/Larc de
Neurociências da América Latina, Caribe e Península
Ibérica, 2008, Búzios, RJ.
Macário Costa, R. J., Mousinho, R., Vidal, L. A. (2009)
“Abordagem Computacional no Screening da Dislexia
e do TDAH”. In: XXXII CNMAC, Cuiabá.
Macário Costa, R. J., Cruz, S. M. S., Vidal, L. A.,
Mousinho, R, Tosta, F. O. (2009) “Redes neuronais e
transtornos de aprendizagem: rastreio de pessoas com
dislexia”. In: SBIE. v. 20. p. 1-10. Florianopólis.
Macário Costa, R. J., Mousinho, R.; Vidal, L. A. (2009)
“Dislexia e Inteligência Computacional: Um sistema
para rastrear (Screening) pessoas com sinais de
transtorno de leitura”. In: 2o. Congresso Internacional
de Dislexia, São Paulo.
Macário Costa, R. J. (2011) “Uma Estratégia
computacional na detecção da dislexia”. Rio de
Janeiro: Tese – UFRJ/COPPE.
Macário Costa, R. J. Cruz, S. M. S., Zavaleta, J, Carvalho,
L. A. V.; Mousinho, Renata (2011) “Abordagem
tecnológica para rastreio de pessoas com dislexia”.
Tecer (Belo Horizonte), v. 4, p. 41-53.
Macário Costa, R. J., Zavaleta, J., Cruz, S. M. S., Cerceau,
R., Mousinho, R., Carvalho, L. A. V. (2013) “A
Computational Approach for Screening Dyslexia”. In:
CBMS 2013, 2013, Porto. 26
th
IEEE International
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
440

Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems.
Macário Costa, R. J., Carvalho, L. A. V, Miguel, E.
Mousinho, R S., Cerceau, R., Macario Costa L. P.,
Cruz, S. M. S. (2014) “Desafios e Oportunidades em
Neurociência Computacional na Educação Brasileira”.
In: Grandes Desafios da Computação no Brasil 3a
Edição. Porto Alegre. Sociedade Brasileira da
Computação. SBC. (to be published).
Markram, H. (2013) “Seven Challenges in Neuroscience”,
In: Functional Neurobiology 28(3) 145-151.
Mousinho, R. (2003) “Desenvolvimento da Leitura,
Escrita e seus Transtornos. In: Goldfeld, M. Fund. em
Fonoaudiologia”. Guanabara Koogan. 2a edição.
Mousinho, R. et al. (2011) “Dislexia – Novos temas,
novas perspectivas. Wak Editora. Rio de Janeiro.
NIH (2014) “BRAIN 2025: A Scientific Vision”,
http://www.nih.gov/science/brain/2025/.
Schwartz, E. (1990) “Computational Neuroscience”, MIT
Press, 1st edition.
Shaywitz, S.E. Shaywitz, B.A. (1999) “Dyslexia In:
Swaiman KF, Ashwal S. Pediatric Neurology -
Principal e Practice”, Connecticut. Ed. Mosby.
Zavaleta, J. et al. (2012) “DysDTool: Uma Ferramenta
Inteligente para Avaliação e Intervenção no Apoio ao
Diagnóstico da Dislexia”. In: CSBC- XII Workshop
de Informática Médica.
Zhong, N. et al. (2011) “Brain Informatics”. IEEE
Intelligent Systems. September, pages 16-20.
Zhong, N (2012) “Research Issues and Challenges on
Brain Informatics Towards Computing & Intelligence
in the Big Data Era”.
pakdd2014.pakdd.org/tutorial3.pdf.
ComputationalNeuroscience-ChallengesandImplicationsforBrazilianEducation
441
