
Unobtrusive Monitoring of Physical Activity in AAL
A Simple Wearable Device Designed for Older Adults
Adelmo De Santis, Antonio Del Campo, Ennio Gambi, Laura Montanini, Giovanni Pelliccioni,
Davide Perla and Susanna Spinsante
Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell’Informazione, Universita’ Politecnica delle Marche, Via Brecce Bianche 12, 60131
Ancona, Italy
Keywords:
Smart Insole, Wearable Sensor, Activity Monitoring, Ambient Assisted Living.
Abstract:
Many solutions and projects proposed within the Ambient Assisted Living research area, aim at monitoring
the degree of vitality of elderly users in their daily activities, and in their home environment, to possibly
avoid or strongly limit the need for clinical evaluations. In fact, the information on the subject’s vitality,
manifested through his/her activity profile, may be used to evaluate possible anomalous trends, related to cog-
nitive or physical decay. For such a kind of analysis to be realistically affordable, the monitoring device shall
be unobtrusive, and transparent to the user. With the aim of striving for the simplest and most reliable design
compatible with the aforementioned requirements, this paper presents a wearable device equipped with a sens-
ing insole hosting force sensors, and the related electronics for signal processing and data transmission. The
device locally classifies different dynamic states (sitting, walking, standing) and transmits the correspond-
ing information to a supervising system. Preliminary experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the
approach, in correctly detecting and classifying the user’s activities.
1 INTRODUCTION
The monitoring of physical activity has a very impor-
tant role in Ambient Assisted Living (AAL) related
scenarios, systems, and applications. In fact, one of
the aims of AAL is to reduce risk factors for chronic
disease and improve quality of life for older adults.
This can be obtained by building awareness about the
importance of physical activity and by assisting with
the development and implementation of appropriate
and effective interventions that reduce risk factors and
improve quality of life (Wojtek, 2014). Behavioral
analysis, to provide feedback for correcting erroneous
habits, relies on the availability of data about the sub-
ject’s physical activity. They have to be collected in
unobtrusive way, without affecting the daily life activ-
ities performed by the subject, possibly within his/her
usual home environment, and for a sufficiently long
time (Sazonov et al., 2011). A shoe-mounted wear-
able device can be used to generate the requested
data, and to comply with the aforementioned require-
ments. The device is composed by a sensing element,
the so-called smart insole (DeSantis et al., 2014), and
the associated electronics, in charge of collecting the
sensor-generated data, performing a preliminary pro-
cessing of them, and transmitting them to a receiving
node, on a wireless channel. With respect to a solu-
tion providing the electronics fully embedded into a
generic insole (Nagaraj and Sazonov, 2014), the pro-
posed approach requires the modification of the shoe,
which may be potentially seen as an obstacle to its ef-
fective adoption by an older user. Preliminary investi-
gations were performed to clarify this issue, with the
help of a shoe manufacturer specialized in the produc-
tion of instrumented shoes for elderly, people with di-
abetes, or affected by stroke and motor impairments.
The outcomes of such an analysis suggested that it is
possible to limit the impact of the modification, both
on the shoe manufacturing process and on the final
product, so that the sensor and its electronics may be
safely hosted in the shoe, and even easily moved from
one shoe to another, if both of them were designed
to be equipped by the wearable device. Based on the
above premises, this paper presents a simple wearable
device designed to keep complexity as low as possi-
ble, in any aspect, ranging from the manufacturing-
related issues, to the data processing and transmis-
sion, to the usability constraints, in a real life sce-
nario. Many proposals of smart insoles or wearable
sensors for physical activity monitoring have been
200
De Santis A., Del Campo A., Gambi E., Montanini L., Pelliccioni G., Perla D. and Spinsante S..
Unobtrusive Monitoring of Physical Activity in AAL - A Simple Wearable Device Designed for Older Adults.
DOI: 10.5220/0005497102000205
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AgeingWell-
2015), pages 200-205
ISBN: 978-989-758-102-1
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

presented in the literature (Liu et al., 2009; Bamberg
et al., 2008; Sazonov et al., 2011; Jarchi et al., 2014).
Most of them aim at providing a gait analysis tool,
or a tool that can make it possible to move a typical
diagnostic process out to a home environment. For
example, a sophisticated solution allowing to moni-
tor the position of the foot in order to detect incorrect
positions and send vibration feedback has been exten-
sively tested, demonstrating a reduction from 30% to
50% of the over-pronation of the foot (Berengueres
et al., 2014). Another solution exploits eight pressure
sensors to assess the body balance in order to identify
the pathomechanical dysfunction and evaluate an ap-
propriate medical treatment (Manupibul et al., 2014).
The device here presented, on the contrary, is con-
ceived to ensure a reliable classification of the phys-
ical activity performed by the subject, striving for a
simple design and use. Activity classification pro-
vides a basic information on the health status of the
monitored subject, and its evolution along time may
be observed to detect possible anomalies or alarming
trends (Lester et al., 2006). The paper is organized as
follows: Section 2 presents the main components of
the system, from the design requirements to the hard-
ware elements; Section 3 discusses the operations per-
formed to process the signals generated by the sens-
ing elements of the wearable device. In Section 4, the
experimental activities performed to test the wearable
device are discussed, and the results obtained are an-
alyzed. Finally, Section 5 draws the main conclusion
of the work.
2 SYSTEM
2.1 Design Requirements
The main requirements to account for in designing the
wearable device for physical activity monitoring, deal
with reduced obtrusiveness, limited power consump-
tion (to avoid the need of frequently replacing the bat-
tery), and adequate precision and reliability in classi-
fying the detected activity. The aim of the project is to
get a device that can effectively discriminate among
three main activity-related states: sitting (sedentary
behaviours), standing, and walking. Further, it is ex-
pected to be able to detect the condition ”the subject
is not wearing the shoe”, and to get information about
the step cycle, for example to evaluate the step fre-
quency and understand how fast the subject can move.
2.2 Sensing Component
The wearable device includes a sensing component,
given by a smart insole equipped with Force Sensing
Resistors (FSRs), and its electronic board. FSRs pro-
vide an output resistance that varies according to the
pressure applied on the active area of the transducer.
The output voltage generated by the transducer and
depending on the applied force may be expressed as:
V
out
=
R
M
·V
+
R
M
+ R
FSR
(1)
The value of R
M
is chosen to maximize the desired
force sensitivity range, and to limit the electric cur-
rent, V
+
is the polarization voltage, and R
FSR
is the
electric resistance of the transducer that varies with
the applied force. A family of V
out
vs. force curves
for the specific transducer used in the design of the
wearable device, and for different values of the R
M
resistor, is shown in Figure 1. According to the value
of R
M
, the sensor may get more or less sensitive to the
applied force.
Figure 1: FSR sensor V
out
vs. force curves.
The specific transducer model employed is the FSR
402 Short, manufactured by Interlink Electronics (In-
terlinkElectronics, 2014), and shown in Figure 2. It is
a two-wire device, a robust polymer thick film (PTF)
sensor that exhibits a decrease in resistance for an in-
crease in the force applied to its surface.
Figure 2: FSR@ 402 Short sensor.
The selected transducer is 25 mm long, and the diam-
eter of the active area is 13 mm: the reduced physical
dimensions make the transducer suitable for applica-
tion to a shoe insole, and the very limited thickness
UnobtrusiveMonitoringofPhysicalActivityinAAL-ASimpleWearableDeviceDesignedforOlderAdults
201

makes it not detectable by the subject, when he/she
wears the shoe. These are important features in the
perspective of a unobtrusive design.
The optimal positioning of the transducers on the in-
sole is a crucial aspect to consider, because it affects
the clear and reliable detection of the subject’s phys-
ical activity or gait analysis, traded off by the limited
acceptable complexity, set as a design requirement.
For this reason, several tests have been conducted,
considering different amounts of sensors and locating
them in different positions on the insole. The out-
come of this preliminary investigation suggested the
possibility to employ only three FSR sensors, placed
in two different configuration sets. In the first one the
FSRs are placed in correspondence to the heel, the
1st metatarsal head and the toe, as shown in Figure
3(a), while in the second configuration the FSRs are
placed in correspondence to the heel, the 1st and the
5th metatarsal heads, as shown in Figure 3(b).
(a) (b)
Figure 3: a) 1st configuration: FSR1 - heel, FSR2 1st
metatarsal head, FSR3 - toe; b) 2nd configuration: FSR1
- heel, FSR2 - 1st metatarsal head, FSR3 - 5th metatarsal
head.
The location chosen for the three sensors in the 1st
configuration provides a high level of availability and
allows to recognize the activity performed by the user.
However, when dealing with the “walking” activity
the choice of the second configuration allows to bet-
ter analyse each step, identifying the different gait
phases. Such an identification allows to isolate the
individual steps, count them and, in the future, to ex-
tract information for gait analysis.
2.3 Electronics and Data Transmission
The signal acquisition and processing, and the data
transmission procedures, are implemented by an elec-
tronic board developed ad hoc, and shown in Figure
4. Power is supplied by a Lithium battery, featuring a
nominal capacity of 0.95 Ah @0.5 mA to 2V.
The following operations are performed by the micro-
controller on the board:
• reading signals generated by the FSRs;
• processing the acquired signals and generating the
corresponding data;
• transmitting the data to a control station.
Figure 4: Electronic board for acquisition and processing
of the signals generated by the FSRs, and wireless trans-
mission of the data.
In the first version of the prototype device, a se-
rial data transmission via USB cable was adopted, to
rapidly check the feasibility of the design and the cor-
rect data transfer (DeSantis et al., 2014). In order to
attain a really usable device, a wireless communica-
tion interface has finally been implemented, operat-
ing at a frequency of 868 MHz (ISM band). The use
of such a frequency band is not licensed, however it
is necessary to limit the occupancy of the channel to
1%-10% of the time. This constraint motivates the
need for an onboard processing of the signals col-
lected from the FSRs, aimed at generating a mini-
mum amount of data to transmit. The choice of the
868 MHz operating frequency allows to use an an-
tenna of reduced dimensions, that is compatible with
the need of limiting as much as possible the impact
of the wearable device on the shoe structure. Figure
5 shows the slot that has been manufactured within
the shoe to host the wearable electronics, in the least
obtrusive way possible.
Figure 5: The shoe modified to host the wearable device: in
evidence, the slot to accommodate the electronic board.
3 DATA PROCESSING
As previously stated the FSRs sensors have been ap-
plied to the insole in two different ways, aimed re-
spectively at activity recognition and steps detection.
During the step movement, the increase of the force
ICT4AgeingWell2015-InternationalConferenceonInformationandCommunicationTechnologiesforAgeingWelland
e-Health
202
applied on each individual transducer produces a de-
crease of the resistance at each sensor connector, and,
consequently, an increase in the measured voltage.
For every configuration, the analog voltage signals
measured at each resistance divider are processed by
a different algorithm running on the electronic board.
The first one allows to identify the activity performed
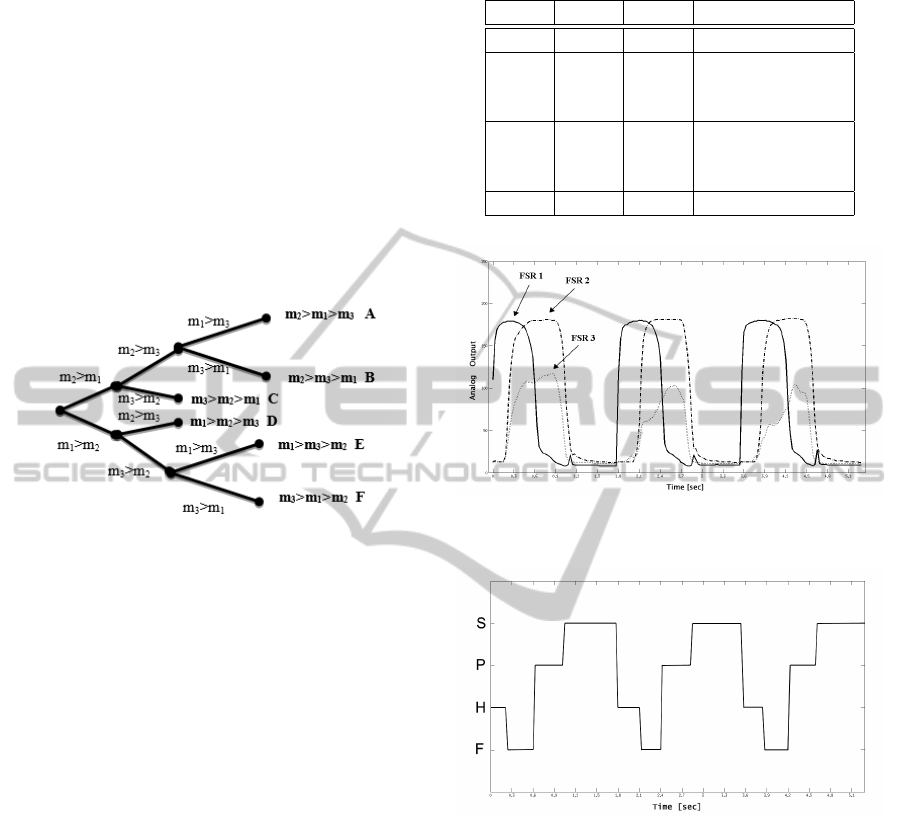
by the user. Figure 6 shows the binary tree allowing
to identify all possible 3! = 6 permutations of the sub-
ject weight distribution associated to each sensor. The
value m
i
, with i from 1 to 3, is the average of ten con-
secutive samples associated with the i-th FSR. From
Figure 6: The binary tree allowing to identify all possible
3! = 6 permutations of the subject weight distribution.
the six possible branches (through appropriate thresh-
olds) a decision on the user’s physical activity (sitting,
standing, walking or not wearing the shoes) is made.
As previously stated, the second configuration allows
to recognize the various phases of the step during
walking , i.e. heel contact (H), flat foot contact (F),
push off (or heel off) (P) and limb swing (S). In this
case, by combining the binary information on the state
of each transducer (active = 1, non active = 0), it is
possible to encode up to 2
3
= 8 different foot-support
conditions (eight step phases). Actually, not all the
possible combinations correspond to a different state;
some of them are related to the same state, as detailed
in Table 1. The binarization of the information gen-
erated by each transducer is performed through the
definition of a proper threshold, against which each
output voltage level is compared, to discriminate be-
tween activation and non activation of the transducer.
Using such a sensor configuration, the time variation
of the analog voltage signal measured at each resis-
tance divider is shown in Figure 7, where three step
cycles are considered in time, along the horizontal
axis. According to the association between the com-
binations of active and non active transducers, and the
step phases detailed in Table 1, the sequence of step
phases corresponding to these voltage outputs is pro-
vided in Figure 8.
Table 1: Step phases identification by transducer activation.
FSR1 FSR2 FSR3 Step Phase
1 0 0 Heel Contact (H)
1 0 1
1 1 0 Foot Contact (F)
1 1 1
0 0 1
0 1 0 Push Off (P)
0 1 1
0 0 0 Limb Swing (S)
Figure 7: Time variation of the analog voltage signal mea-
sured at each transducer during the step movement.
Figure 8: Time sequence of the step phases (heel contact
(H), flat foot contact (F), push off (or heel off) (P) and limb
swing (S)) corresponding to the time variation of the ana-
log voltage signal measured at each transducer, according
to Table 1.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The hardware and software components of the wear-
able device have been designed to address the afore-
mentioned aims of the project, namely to discrimi-
nate among three main activities, i.e. sitting (seden-
tary behaviour), standing, and walking, and to be able
to detect the condition of the subject not wearing the
shoe. Both the two algorithms described in the pre-
vious section run on the electronic board of the wear-
able device. The first one is able to identify the weight
UnobtrusiveMonitoringofPhysicalActivityinAAL-ASimpleWearableDeviceDesignedforOlderAdults
203
distribution, and to exploit this information in order to
determine the type of activity performed by the sub-
ject. The second one allows to perform a more ac-
curate analysis of the step, distinguishing the various
phases that characterize it and counting the walking
steps. This way, the two software output a numerical
value that identifies respectively the type of activity
and the step frequency, which is wireless transmitted
to a central unit.
This choice complies with the requirements on the use
of the 868 MHz ISM bandwidth, and also allows sav-
ing on energy consumption, because the device trans-
mits a small amount of data, less frequently than what
required by a continuous transmission of each sensor
signal.
Static activities concern whether the user stands still,
either sitting or standing. In this case, the analysis is
based on the fact that, when the user is in the upright
position, the weight is almost uniformly distributed
on the foot sole, while, when sitting, the weight is
more distributed on the chair. So, in the former case,
the average pressure on the sensors will be close to
the maximum value they are able to pick up, while
in the latter case, the average pressure will be much
lower. Analyzing the duty cycle of the step wave-
forms allows to differentiate static and dynamic activ-
ities, and to discriminate the dynamic ones, according
to the step frequency. The information transmitted by
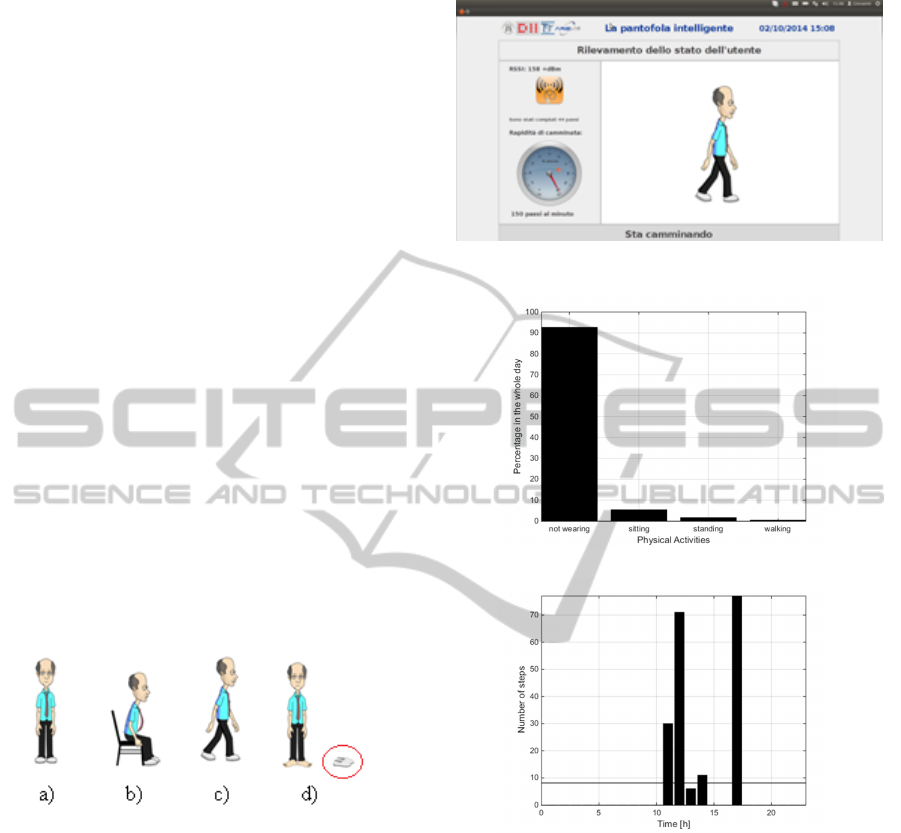
Figure 9: Physical activities visualized through the avatar:
a) standing, b) sitting, c) walking, d) not wearing the shoes.
the board on the wireless link is collected from a soft-
ware application running on a desktop system, that is
used to visualize the activity performed by the subject
through an avatar. The avatar may be standing, sitting,
walking, or may be not wearing the shoes, as graphi-
cally shown in Figure 9. The desktop application (the
interface of which is presented in Figure 10) could
be running on a machine remotely connected to the
wearable device, by means of an internet connection,
thus enabling an unobtrusive and remote monitoring
of the subject. The same information pictorially rep-
resented by the application graphic interface is also
collected and stored in a database, to populate a suit-
able dataset for further analyses of the subject’s health
status and its time evolution.
The saved data are used to derive user’s daily activ-
Figure 10: Desktop application interface.
(a) ADL Daily Monitoring
(b) Daily step frequency per hour
Figure 11: a) Daily percentage of each physical activity ob-
tained using the configuration depicted in Figure 3(a); b)
Daily step frequency per hour obtained using the configu-
ration depicted in Figure 3(b). The horizontal black line
represents the average of number steps on 24 hours.
ity reports, for example in Figures 11(a) and 11(b) the
daily reports of the activities performed in a labora-
tory environment are shown. The upper one shows the
daily percentage for each activity, instead the lower
one shows the number of steps recorded at each hour
of the day.
ICT4AgeingWell2015-InternationalConferenceonInformationandCommunicationTechnologiesforAgeingWelland
e-Health
204

5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presented a simple wearable device de-
signed to enable unobtrusive physical activity mon-
itoring of ageing people. Despite the availabil-
ity of more sophisticated solutions proposed in the
literature, the proposed device can attain the ex-
pected outcomes, without affecting the user’s daily
life habits. The development activities performed
up to this point are being completed and validated
through an adequate test campaign involving users,
possibly the older adults addressed by the proposed
technology. Future work include implementation of
a more widespread and energy-attentive communica-
tion technology (BLE). Furthermore, the configura-
tions used in the prototyping stage could be combined
in a single solution that allows, through a suitable
decision algorithm, to recognize both activities and
step phases. This solution, in addition to evaluating
the vitality level of the user, should also contribute to
perform a gait analysis, in order to diagnose possible
pathologies or recognize incorrect postures.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Regione Marche -
INRCA project “Casa intelligente per una longevit
`
a
attiva ed indipendente dell’anziano” (DGR 1464,
7/11/2011).
REFERENCES
Bamberg, S. J. M., Benbasat, A. Y., Scarborough, D. M.,
Krebs, D. E., and Paradiso, J. A. (2008). Gait analy-
sis using a shoe-integrated wireless sensor system. In
IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed, pages 413–423.
Berengueres, J., Fritschi, M., and McClanahan, R. (2014).
A smart pressure-sensitive insole that reminds you to
walk correctly: An orthotic-less treatment for over
pronation. In Engineering in Medicine and Biol-
ogy Society (EMBC), 2014 36th Annual International
Conference of the IEEE, pages 2488–2491. IEEE.
DeSantis, A., Gambi, E., Montanini, L., Raffaeli, L., Spin-
sante, S., and Rascioni, G. (2014). A simple ob-
ject for elderly vitality monitoring: The smart insole.
In 2014 IEEE/ASME, 10th International Conference
on Mechatronic and Embedded Systems and Applica-
tions. IEEE.
InterlinkElectronics (2014). Product data sheet
http://www.interlinkelectronics.com/fsr402.php.
Jarchi, D., Lo, B., Ieong, E., Nathwani, D., and Yang, G.-
Z. (2014). Validation of the e-ar sensor for gait event
detection using the parotec foot insole with applica-
tion to post-operative recovery monitoring. In Wear-
able and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN),
2014 11th International Conference on, pages 127–
131. IEEE.
Lester, J., Choudhury, T., and Borriello, G. (2006). A prac-
tical approach to recognizing physical activities. In
Pervasive Computing 2006.
Liu, T., Inoue, Y., and Shibata, K. (2009). Development of a
wearable sensor system for quantitative gait analysis.
In Measurement, pages 978–988.
Manupibul, U., Charoensuk, W., and Kaimuk, P. (2014).
Design and development of smart insole system for
plantar pressure measurement in imbalance human
body and heavy activities. In Biomedical Engineer-
ing International Conference (BMEiCON), 2014 7th,
pages 1–5. IEEE.
Nagaraj, H. and Sazonov, E. (2014). Smartstep: A fully
integrated, low-power insole monitor. In Electronics,
volume 3, pages 381–397. MDPI.
Sazonov, E., Fulk, G., Hill, J., Schutz, Y., and Browning, R.
(2011). Monitoring of posture allocations and activi-
ties by a shoe-based wearable sensor. In Biomedical
Engineering, IEEE Transactions on, volume 58, pages
983–990.
Wojtek, J. C.-Z. (2014). Exercise and physical activity for
older adults. In Kinesiology Review, volume 3, pages
101–106.
UnobtrusiveMonitoringofPhysicalActivityinAAL-ASimpleWearableDeviceDesignedforOlderAdults
205
