
Scalable QoE Prediction for Service Composition
Natalia Kushik and Nina
Yevtushenko
Department of Information Technologies, Tomsk State University, Tomsk, Russia
Keywords: Service (Composition), QoE Estimation/Prediction, Logic Network/Circuit.
Abstract: In this paper, we present an approach for scalable QoE estimation/prediction of a composition of given
services. The approach relies on using logic circuits/networks for the QoE prediction. Given two logic
circuits that predict the QoE values of two service components, we propose a method for synthesizing the
resulting logic circuit that predicts the QoE of the overall service composition. As the complexity of this
resulting circuit significantly depends on the complexity of an implementation of a MIN function, we
present an experimental evaluation of the complexity of the corresponding circuit.
1 INTRODUCTION
The number of services designed for various
purposes increases rapidly, and almost all of them
are developed for improving or simplifying human
life. As an example of the service one can consider a
multimedia service, that delivers some video/audio
traffic to an end-user, or a web service that allows to
book a hotel or to buy some products online, etc. As
all these services are developed “for people”, the
Quality of Experience metrics (QoE) remains the
most common metrics to evaluate their quality.
The QoE is used to measure the end-user
satisfaction with a given service and thus, the
problem of its evaluation remains one of the most
challenging problems in the artificial intelligence
area. The reason is that in order to evaluate the QoE,
it is necessary to ‘guess’ how much an end-user
would like or dislike a given service. This problem
is often solved with the use of various self-adaptive
models that can accept service parameter values as
inputs and return the QoE value as an output. If a
model behaves in a wrong way for some newly
emerged input/output pairs, the model can be trained
by itself or by an external ‘teacher’ that could be a
service provider. Most popular self-adaptive models
are decision trees (see, for example, Mitchell, 1997;
Pokhrel, J., Mallouli, W., and Montes de Oca, E.,
2013), neural networks (Ahmed et al., 2012; Al-
Masri and Mahmoud Qusay, 2009), fuzzy logic
formulae (Lin et al., 2005; Torres et al., 2011), and
logic circuits (Kushik et al., 2014). All these models
have their own advantages, as well as the known
drawbacks. Most common criteria that a researcher
or a service provider should take into account are the
QoE prediction ability of the model and the
scalability of the “teaching” process. It has been
previously shown that the approach proposed by
Kushik et al. in 2014 allows to adequately predict
the end-user satisfaction with a given service, and, at
the same time, to perform the model adaptation in a
scalable way (Kushik et al., 2014). This approach is
based on logic networks, in particular,
combinational circuits, for the QoE prediction. The
initial logic network is derived based on statistical
data that are gathered from experts, developers
and/or end-users who agreed to provide a feedback
about the service quality. The circuit accepts the
service parameter values encoded as Boolean
vectors and outputs the Boolean vector that
corresponds to the encoded QoE value. The circuit is
a self-learning machine, i.e., when new statistical
data appear the circuit is checked for having the
corresponding behaviour and if the behaviour does
not correspond to newly emerged data the circuit is
resynthesized. Such resynthesis can be efficiently
performed using various tools (see, for example,
Berkeley Logic Synthesis and Verification Group,
ABC).
Once the QoE of a given circuit is carefully
estimated, one can use this service not only as a
single self-sufficient entity, but also as a part of a
‘big’ service composition. In this case, the problem
arises of predicting the QoE of this composition. It is
well known, that even if the service components
have the high QoE value for a given statistical
16
Kushik N. and Yevtushenko N..
Scalable QoE Prediction for Service Composition.
DOI: 10.5220/0005524600160026
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Emerging Software as a Service and Analytics (ESaaSA-2015), pages 16-26
ISBN: 978-989-758-110-6
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

pattern, the QoE of the composition is not
necessarily high for this pattern. Therefore, the
composition QoE value has to be effectively
predicted. Given two service components, and two
logic circuits for predicting component QoE values,
we propose a technique how to synthesize the
resulting logic circuit that predicts the QoE of the
service composition. The technique relies on
scalable operations over logic networks, such as
introducing additional inputs and connecting nodes
in the circuit to combine particular circuit parts. We
introduce a special circuit implementation of the
minimum function that outputs a minimal integer of
two integers. This circuit is further used as a part of
the resulting logic network that predicts the QoE
value of the service composition. The algorithm
provided in the paper takes into account the fact that
the user satisfaction can be only decreased in the
service composition. The reason is that if a user is
not satisfied with a given service component, his/her
satisfaction cannot be increased with the use of the
other components, i.e., our approach assumes the
worst-case scenario. We notice, that this scenario
supports the scalability of the approach, since we are
not interested in the composition details, i.e.,
compositional patterns, differently from predicting
some objective service parameter values (see for
example, Zheng et al., 2013). Furthermore, we
discuss how the proposed QoE estimation technique
can be adapted to the case when the composition
QoE is calculated not as the minimum function but
as more complex mathematical formula.
Therefore, the main contribution of this paper is
an approach for estimating the QoE of the service
composition, when the QoE of each service
component is calculated by a corresponding logic
circuit. We also provide the preliminary
experimental evaluation for a proposed approach
addressing the complexity of parts of the resulting
circuit. These experimental results clearly show the
approach scalability.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 contains the preliminaries. A running
example for a service composition and its QoE
prediction is given in Section 3. A scalable approach
for estimating the QoE of the service composition as
well as the experimental evaluation of the
complexity of the overall circuit are given in Section
4. A discussion on possible extensions of the
proposed approach is presented in Section 5. Section
6 concludes the paper.
2 PRELIMINARIES
In our normal human life, we are surrounded by
services. Those can be web services that represent
specific software designed to support interoperable
machine-to-machine interaction over a network
(Booth et al., 2004) or multimedia services that are
used to deliver a multimedia traffic to an end-user
(Pokhrel, J., Wehbi, B., Morais, A., Cavalli, A., and
Allilaire, E., 2013). One can consider other types of
services, not directly related to Computer Sciences
area, such as cleaning service, delivery service,
booking service, etc. Anyway, all these services are
developed to improve or to simplify the human life
quality and thus, not a single service is left without
evaluating the quality of this service. There exist
various metrics to evaluate the service quality where
the most known seems to be the Quality of Service
(QoS) metrics. The QoS can be defined as a vector
with components which are values of given
attributes (parameters) that can be objectively
measured (Kondratyeva et al. 2013). We mention
that there have been performed a lot of research and
some interesting contributions have been made
regarding the estimation of the QoS for a composite
service (El Hadad et al., 2010; Zheng et al., 2013).
However, the most interesting metrics to
estimate the service quality is the Quality of
Experience (QoE) that represents a user satisfaction
(see, for example, Winckler et al., 2013). In spite of
the fact that the QoE is more difficult to evaluate,
this metrics is more close to the adequate description
of the service quality, since the main purpose of
each service is to satisfy an end-user. In other words,
the algorithm for the QoE evaluation has to be
adapted to a human’s brain in order to ‘predict’ what
a user likes/dislikes. That is the reason why different
self-adaptive models and algorithms are now used
for this purpose. The advantage of a self-adaptive
model is that it can be learnt or trained by a ‘teacher’
or by itself according to the feedback from people
who use the service. As usual, an initial
model/machine is derived based on some statistical
data that contain a number of user/expert opinions
about the service. Afterwards, the model can
‘predict’ the user satisfaction of the service for the
given values of service parameters. The more
statistical data are gathered the better is the
‘prediction’. Moreover, as the model is self-
adaptive, when new statistical data appear for which
the model does not behave in an appropriate way,
the model is adjusted to these new data and this
process is the model training.
Various self-adaptive models can be used for the
ScalableQoEPredictionforServiceComposition
17

QoE prediction of the service. One of short surveys
of these models can be found in (Kondratyeva et al.
2013). In particular, Kondratyeva et al. discuss three
most popular self-adaptive models that are used to
predict the QoE value for web services. We briefly
sketch this survey to provide an overview of the use
of self-adaptive models for the QoE prediction.
Almost all self-adaptive models rely on pre/post
conditions that can be expressed in terms of IF-
THEN operator. The first group of machine learning
algorithms is based on a Decision Tree (Mitchell,
1997; Pokhrel, J., Mallouli, W., and Montes de Oca,
E., 2013) that can be described for a web service as a
tree which nodes correspond to service parameters
(attributes) while edges are marked with different
parameter values (scores). Each tree level
corresponds to a single service parameter which can
be evaluated by scores that label outgoing edges.
The leaves of the tree correspond to different values
of the user satisfaction. The decision tree can be
derived based on IF-THEN conditions where a path
labelling each branch of the tree to a node with a
given QoE value corresponds to the conjunction of
conditions under IF operator. The decision tree can
be learnt based on deriving IF-THEN conditions by
adding additional paths. As usual, such pre/post
conditions are derived based on experimental results
or following some expert opinions. The decision tree
provides an algorithm for evaluating the user
satisfaction if and only if it is completely specified.
Those paths in the tree that are not specified by the
conditions have to be somehow augmented in order
to predict the user satisfaction in this undefined
situation. Thus, the purpose of specifying undefined
paths is to “guess” what a user would like or dislike
under appropriate conditions. The complexity of the
completely specified tree is exponential w.r.t. the
number of quality parameters. Other self-adaptive
models, such as neural networks and fuzzy logic
formulae are known to be more compact. Neural
networks are widely used for solving various
problems in the artificial intelligent area. Such
networks are used in the “machine learning sense”
and all the neurons of the network are assumed to be
artificial and can be modified by a “teacher” in a
given way. Neurons are connected to each other and
these connections also can be trained. Usually neural
networks without feedbacks are considered and in
this case, the network can be divided into levels.
Usually, for each neuron there exists a formula that
calculates its output according to weighted inputs
that is used when coming to the next level via
weighted edges. A neural network can accept values
of input (QoS/QoE) parameters and depending on
the neuron definition and on the weight of
distributed connections the network produces the
output (the QoE value) (Al-Masri and Mahmoud
Qusay, 2009) by changing states from level to level.
At the initial step, the network connections are set
based on the initial statistical data, i.e., on the set of
given input/output pairs. A network learning process
consists of modifying weighted connections (or a set
of nodes) of the network based on new knowledge
(more statistical data, for example). In other words,
when new statistical data appear the network can be
learnt how to modify its connections and possibly,
nodes in order to have the correct behaviour. A good
alternative to artificial neural networks is a fuzzy
logic that was introduced by Lotfi A. Zadeh (Zadeh,
1965) in 1965 and can be also considered for
modelling a human behaviour. Similar to a decision
tree, a fuzzy model can be built based on a set of IF-
THEN conditions that can be combined taking into
account how disjunction and conjunction are defined
for fuzzy sets. The fuzzy logic model can be learnt
by changing membership degree of each parameter
to the service, i.e., the weight of linguistic values for
quality parameters in the resulting fuzzy formula, as
well as by changing the relative importance of each
quality parameter.
In 2014, Kushik et al. have proposed another
self-adaptive model that can be used to predict the
QoE value with a given service. Moreover, the
proposed approach has been compared with the one,
based on using fuzzy logic formulae, and the former
has shown the higher scalability (Kushik et al.,
2014). This approach is based on analyzing and
training of logic networks/circuits that can be
effectively performed using the tools developed for
logic synthesis and verification. In this paper, we
extend the approach proposed by Kushik et al. to the
case when a service under investigation is a
composition of ‘smaller’ services, such that the
corresponding logic circuits for the service
components are known in advance. Furthermore, we
address the methods for deriving such logic circuits
for various service types and propose a technique for
the efficient QoE estimation for a composite service
using the same logic synthesis ‘apparatus’. That is
the reason why we further briefly sketch the
necessary definitions related to the logic synthesis.
We mention that these definitions are mostly taken
from (Kushik et al., 2014).
Definition 1. A logic network (circuit) consists
of logic gates. Each logic gate has input (-s) and a
single output. Outputs of some gates are connected
to inputs of the others. The inputs of some gates that
are not connected to any other gate output are
ESaaSA2015-WorkshoponEmergingSoftwareasaServiceandAnalytics
18
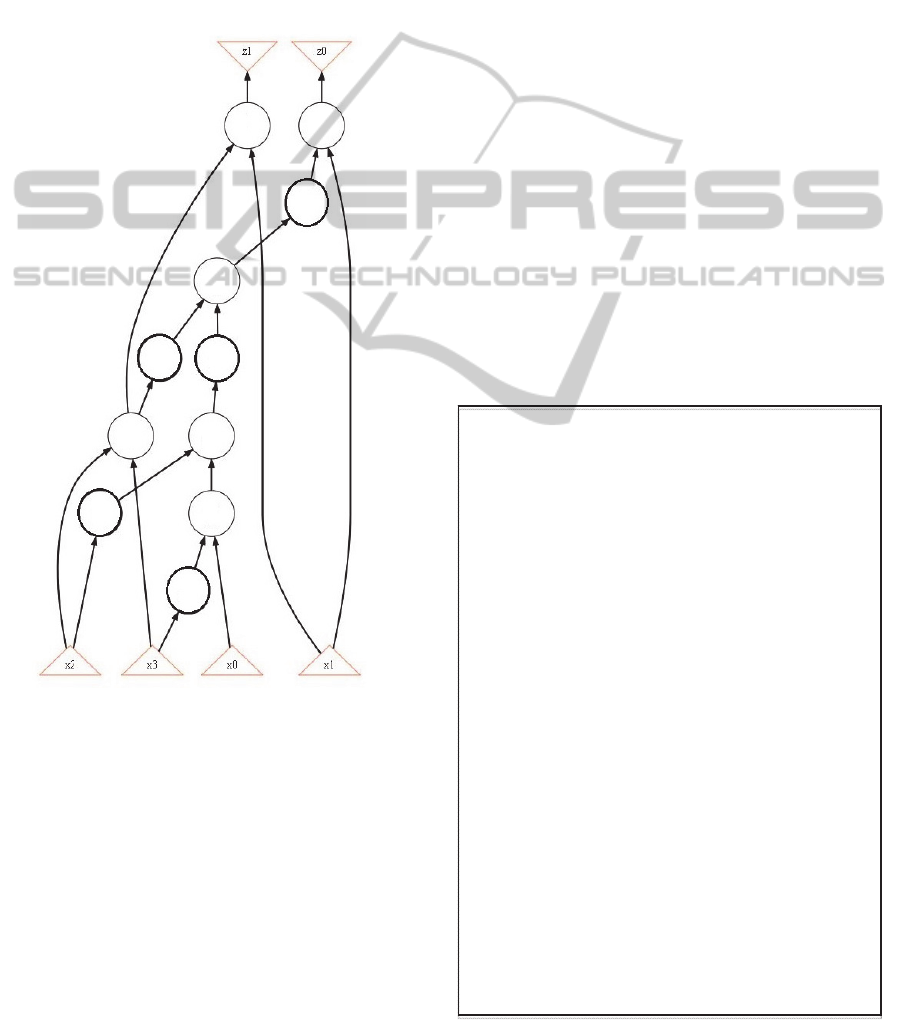
claimed to be primary inputs while the outputs of
some gates are claimed as primary outputs. In this
paper, we consider combinational circuits, i.e.,
feedback-free circuits which have no latches.
Each gate implements a Boolean function. Most
common 2-input gates are
AND/OR/XOR/NAND/NOR/XNOR that implement
conjunction/disjunction/xor and their inversions.
There are also 1-input gates such as NOT/BUFF that
implement the inversion and the equality function,
correspondingly.
Figure 1: A circuit S.
As an example, consider a combinational circuit in
Fig. 1 with a set X = {x
0
, x
1
, x
2
, x
3
} of inputs, a set Z
= {z
0
, z
1
} of outputs and 11 AND and NOT gates
(AIG nodes); the latter are taken in bold.
Definition 2. By definition, a logic circuit
implements or represents a system of Boolean
functions. A circuit accepts a Boolean vector as an
input and produces a Boolean vector as an output
according to the corresponding system of Boolean
functions. Each logic circuit can be described by a
Look-up-Table (LUT). A LUT contains a set of
input/output pairs of a given circuit: if for the input i
the circuit produces an output o, then the pair i/o is
included into the LUT.
A LUT can be used as the specification when
deriving a logic network that implements the system
of Boolean functions, and there exist a number of
methods how to synthesize a logic network that
implements a given system of functions. In this
paper, we use the ABC tool (Berkeley Logic
Synthesis and Verification Group, ABC) to design a
circuit for a given LUT. For this purpose, such LUT
is described in a special form; in this paper, we use
the PLA format.
As in this paper we focus on using logic
networks to evaluate/predict the QoE of a given
service, we further briefly sketch the algorithms
proposed in (Kushik et al., 2014) for deriving and
training these circuits. In order to derive the initial
circuit С, one uses statistical data gathered from
service experts, from the automatic evaluation of
service parameters and/or from end-users, who have
experience of using the service. These statistical data
are encoded as Boolean vectors of appropriate
length, and this set of input/output vectors is written
in the PLA format. The circuit C that evaluates the
QoE value is then designed from a system of
partially specified Boolean functions. The
corresponding procedure is given as Algorithm 1.
Algorithm 1 for deriving an initial logic
circuit to evaluate the QoE value
Inputs: Service parameters p
1
, p
2
, …, p
k
with
nonnegative (unsigned) integer values bounded
by
1
p
M ,
2
p
M , …,
k
p
M ; maximal value of the
QoE
QoE
M ;
Statistical data, i.e., feedbacks from users U
1
,
…, U
r
represented as a list of patterns p
1
_value,
p
2
_value, …, p
k
_value, UserSatisfaction_value.
Output: a logic circuit C
1. Determine the number of primary inputs
and primary outputs of C:
The number of primary inputs equals
k
i
p
i
M
1
2
[log] while the number of primary
outputs equals ]log
2
QoE
M [.
2. Derive a LUT
2.1 For each user U
i
, i {1, …, r}, convert
his/her statistic scores p
1
_value, p
2
_value, …,
p
k
_value, UserSatisfaction_value into Boolean
vectors and add the corresponding lines to the
LUT.
3. Synthesize the circuit C from a system of
partial Boolean functions and Return C.
ScalableQoEPredictionforServiceComposition
19

The circuit C has to be self-adaptive, i.e., when a
new end-user agrees to leave his/her feedback about
the service quality the circuit behavior has to be
modeled under a corresponding input i and if the
result produced by the circuit differs significantly
from the expected then the circuit has to be
resynthesized. To evaluate the difference between
the circuit output and the user satisfaction value
Kushik et al. introduced some value that represents
a confidence interval, i.e., the QoE(W) produced by
the circuit C has to belong to the interval
[UserSatisfaction_value – , UserSatisfaction_value
+ ]. If this fact does not hold, i.e., |QoE(W) –
UserSatisfaction_value| > then the circuit C is
resynthesized. The corresponding procedure taken
from (Kushik et al., 2014), is presented as Algorithm
2.
Algorithm 2 for learning / training the logic
circuit that evaluates / ‘predicts’ the QoE
value for a service
Inputs: QoE parameters p
1
, p
2
, …, p
k
with
nonnegative values bounded by
1
p
M ,
2
p
M , …,
k
p
M ; maximal value of the QoE
QoE
M ;
The circuit C that evaluates the QoE value for a
service W;
A new user feedback p
1
_value, p
2
_value, …,
p
k
_value, UserSatisfaction_value;
Maximal difference for corresponding
confidence interval.
Output: a modified logic circuit C
1. Integers p
1
_value, p
2
_value, …, p
k
_value,
UserSatisfaction_value are converted into
Boolean vectors v_p1, v_p2, …, v_pk, v_us.
2. The output QoE(W) of the circuit C is
computed for the input v_p1, v_p2, …, v_pk.
3. If | QoE(W) - UserSatisfaction_value | > then
3.1 If the line v_p1, v_p2, …, v_pk is
specified as input in the LUT, then change the
corresponding output into v_us,
Otherwise
Add the new line v_p1, v_p2, …, v_pk, v_us
to the LUT.
3.2 Synthesize the new circuit C; assign C =
C and Return C.
In this paper, we propose an approach how a circuit
that predicts the QoE of a composite service can be
derived under the assumption that the QoE of the
service components are given. These circuits can be
derived using Algorithm 1 and effectively trained by
applying Algorithm 2. The approach proposed in the
paper is illustrated by a running example.
3 A RUNNING EXAMPLE
In this paper, we consider a given web service as a
running example. In particular, we rely on the
example of vacation planner service that is taken
from (Kondratyeva et al., 2013). This service offers
a user an opportunity to purchase flight tickets and
to book an accommodation at the destination point.
A user submits traveling dates and the planner
proposes a number of available options for flight
tickets and hotel rooms. If the user and the planner
agree on the flight ticket and the hotel room then the
vacation is successfully booked. Otherwise, the
vacation is not reserved. The list of crucial service
parameters that significantly affect the QoE is as
follows: the execution time, service availability and
service popularity. In other words, the QoE of the
vacation planner significantly depends on the
component values of the vector t, a, p, where t
denotes the execution time, a – the availability and p
– the popularity.
As the vacation planner is designed as a
composition of a flight booking and a hotel booking
services, the QoE of this composite service can be
calculated based on the QoE of the flight booking
and the QoE of the hotel booking services. Given the
flight booking service, in the running example, we
consider that the execution time t and its popularity
p are the crucial parameters for most users. Let
Table 1 contain the statistical data gathered from the
users and/or experts A, B, C, and D.
Table 1: Statistical data gathered for the flight booking
service.
User identifier t p QoE
A 3 0.3 3
B 1 0.9 5
C 3 0.2 1
D 2 0.5 4
Similar to the flight booking service, in this paper,
we consider the availability a to be a crucial
parameter for the second component of the vacation
planner. In other words, once a user has agreed on
all the flights details, he/she is redirected to a hotel
booking service that has to be necessarily available
at the moment. If this service is not available the
user’s QoE goes immediately down. The
corresponding statistical data left by experts and/or
some users E and F of the hotel booking service are
shown in Table 2.
Given the statistical data for the service
components, we consider that the QoE of the
composite service is always the minimal value for
ESaaSA2015-WorkshoponEmergingSoftwareasaServiceandAnalytics
20
Table 2: Statistical data gathered for the hotel booking
service.
User identifier a QoE
E 0.9 5
F 0.6 4
all possible values of the vector t, a, p. The latter
means, that in order to predict the QoE of the
vacation planner, one should consider the worst
users’ opinions. The reason is that if a user is not
satisfied with a given service component, he/her
satisfaction cannot be increased with the use of other
components. In the running example, in order to
consider the statistical data for the vacation planner
one should concatenate the data given in Tables 1
and 2, correspondingly. The resulting statistical data
are given in Table 3.
Table 3: Statistical data for the vacation planner.
t p a QoE
3 0.3 0.9 3
1 0.9 0.9 5
3 0.2 0.9 1
2 0.5 0.9 4
3 0.3 0.6 3
1 0.9 0.6 4
3 0.2 0.6 1
2 0.5 0.6 4
Table 3 contains eight lines; each line represents a
vector t, a, p, QoE where the QoE is the minimal
value taken from the vectors t, a, QoE (Table 1)
and p, QoE (Table 2).
Consider two logic circuits C
1
and C
2
designed
for predicting the QoE of the flight booking and the
hotel booking services, correspondingly. We further
discuss how one can build a logic circuit that
predicts the QoE value of the vacation planner.
4 SCALABLE APPROACH FOR
ESTIMATING THE QoE OF A
COMPOSITE SERVICE
In this section, an approach for automatic
evaluation/‘prediction’ of the QoE value for a
composite service is proposed. Without loss of
generality, we consider two service components S
1
and S
2
that are somehow combined when designing
the composite service S
1
@ S
2
, where @ is a
composition operator. If the number k of service
components is greater than two, this approach can be
applied iteratively, i.e. first, the QoE of the service
S
1
@ S
2
is estimated, then, the QoE of the service (S
1
@ S
2
) @ S
3
is estimated, etc. At the final step, the
QoE is predicted for the service (S
1
@ … @ S
k - 1
) @
S
k
. The question about communicative and
associative properties of the composition operator is
out of the scope of this paper.
Given two composite services S
1
and S
2
, consider
two logic circuits C
1
and C
2
that predict their QoE
values, correspondingly. These circuits can be
derived as proposed in (Kushik et al., 2014). We
provide an algorithm for designing a logic circuit C
1
@ C
2
that predicts the QoE value of the composition
S
1
@ S
2
.
4.1 Deriving a Logic Circuit for
Predicting the QoE of a Composite
Service
In this section, we provide an algorithm (Algorithm
3) for designing a logic circuit C
1
@ C
2
. At the first
step, the set of inputs of this circuit is determined. In
fact, this set contains all the inputs that correspond
to S
1
service parameters and S
2
service parameters.
In other words, the set of inputs for C
1
@ C
2
is the
union of the sets of inputs for C
1
and C
2
, If the sets
of S
1
and S
2
parameters do not intersect, the set of
inputs for C
1
@ C
2
is the set of inputs for C
1
plus
inputs of C
2
.
At the second step, the special circuit C
min
for
implementing a minimum function is designed. This
circuit will be used to choose between two QoE
values produced by the circuits C
1
and C
2
. As
mentioned above, we always rely on the minimal
value of the two QoE values, considering that the
user satisfaction can be only decreased for a
composite service. Each circuit C
1
or C
2
produces
the Boolean vector of corresponding length. These
vectors correspond to integers I
1
and I
2
that
represent the QoE values for the service components
S
1
and S
2
. The MIN function is used to choose the
minimum value of I
1
and I
2
; if these values coincide
then the QoE of the composite service equals I
1
= I
2
.
The corresponding circuit that implements this
function has the number of inputs that is the sum of
outputs of circuits C
1
and C
2
. Hereafter, in the paper,
we consider that the QoE is measured within the
Mean Opinion Score (MOS) scale (ITU-T, 2006)
and thus, outputs of each circuit encode integers of
the set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, i.e., the number of outputs of
each circuit C
1
and C
2
equals three.
At the final step of the algorithm, the outputs of
the circuits C
1
and C
2
are connected to the inputs of
the circuit C
min
, and the resulting circuit is returned.
A scheme that illustrates the procedure for
ScalableQoEPredictionforServiceComposition
21
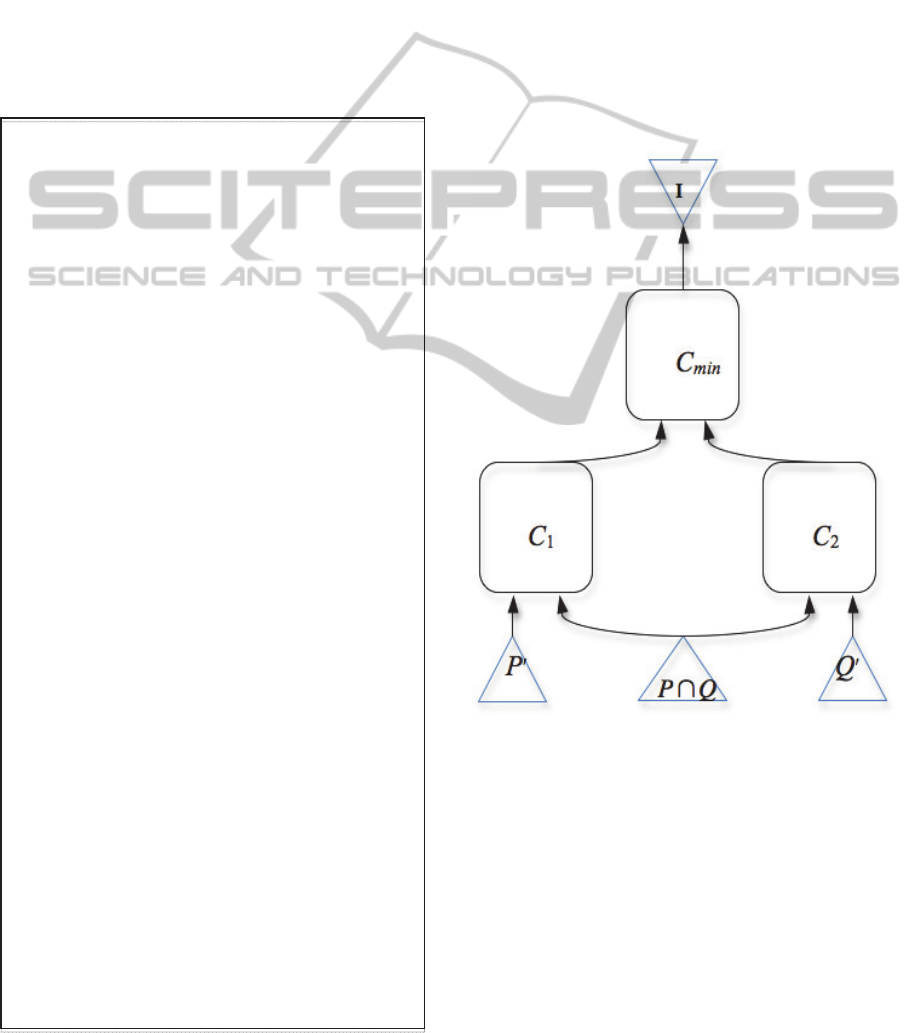
deriving the circuit C
1
@ C
2
for evaluating the QoE
of the composed service is shown in Fig. 2. The
items of the set P correspond to Boolean vectors
which represent the values of parameters p
1
, p
2
, …,
p
k
of the service S
1
whereas the items of the set Q
correspond to Boolean vectors which represent the
values of parameters q
1
, q
2
, …, q
l
of the service S
2
.
The set
P
Q
corresponds to the Boolean vectors,
which represent the same parameters of services S
1
and S
2
. Therefore, the set
P P \ PQ
denotes the
set of Boolean vectors for parameters of S
1
that are
not shared with S
2
while the set
Q Q \ P
Q
denotes the set of Boolean vectors for parameters of
S
2
that are not shared with S
1
.
Algorithm 3 for deriving a circuit C
1
@ C
2
Inputs: Service components S
1
and S
2
.
S
1
has the set P = {p
1
, p
2
, …, p
k
}of parameters;
each p
i
parameter value is bounded an integer
M
p
i
.
S
2
has the set Q = {q
1
, q
2
, …, q
l
} of parameters;
each q
i
parameter value is bounded an integer
M
q
i
.
The circuit C
1
has
]log
2
M
p
i
[
i1
k
inputs and
three outputs; the circuit C
2
has
]log
2
M
q
i
[
i1
l
inputs and three outputs.
Output: a logic circuit C
1
@ C
2
.
1. Determine the number of primary inputs of
C
1
@ C
2
:
The number of primary inputs equals
(
]log
2
M
p
i
[
i1
k
+
]log
2
M
q
i
[
i1
l
) –
]log
2
M
g
i
[
i1
t
for all g
i
that belong to the
P
Q
, where |
P
Q
| = t. The number of
primary outputs of the circuit of C
1
@ C
2
equals
three.
2. Design the circuit C
min
. This circuit has six
inputs i
1
, i
2
, … i
6
, and returns the minimal value
of two integers I(i
1
i
2
i
3
) and I(i
4
i
5
i
6
).
3. Synthesize the circuit C = C
1
@ C
2
identifying inputs which correspond to the same
parameters of services S
1
and S
2
; the outputs of
C
1
are connected to inputs i
1
, i
2
, i
3
of C
min
while
the outputs of C
2
being connected to the inputs i
4
,
i
5
, i
6
of C
min
,
Return C.
The circuit C
min
in Fig. 2 is used to compute the
minimal value of the two QoE values computed by
the circuits C
1
and C
2
for the services S
1
and S
2
,
correspondingly. The set I of C
min
denotes the set of
Boolean vectors representing the QoE of the
composite service of S
1
and S
2
.
By construction of the circuit C
1
@ C
2
using
Algorithm 3, the following proposition holds.
Proposition 1. Given a composite service S
1
@
S
2
and two statistical patterns p
1
_value, p
2
_value, …,
p
k
_value, S
1
_UserSatisfaction_value, and q
1
_value,
p
2
_value, …, q
l
_value, S
2
_UserSatisfaction_value.
Algorithm 3 produces the output C = C
1
@ C
2
such
that the output o of the circuit C corresponds to the
minimum of the integers S
1
_UserSatisfaction_value
and S
2
_UserSatisfaction_value.
Figure 2: A scheme to derive the circuit C
1
@ C
2
, where
P
P \ P
Q
and.
Q
Q \ P
Q
.
We notice that the complexity of Algorithm 3 is
polynomial as it is mostly ‘hidden’ in Step 3. The
arithmetic evaluation of the number of primary
inputs and outputs (Step 1) of the circuit C
1
@ C
2
can be performed in ‘no time’ while the circuit C
min
can be derived just once for various service
components S
1
and S
2
. Therefore, the complexity of
Algorithm 3 can be estimated as the number of
operations required to connect each output of circuit
ESaaSA2015-WorkshoponEmergingSoftwareasaServiceandAnalytics
22
C
1
(or C
2
) to a corresponding input of the circuit
C
min
, and these operations are very scalable. The
latter proves the scalability of the overall approach.
As mentioned above, the proposed approach to
estimate the QoE of a composite service can be also
applied when there exist more than two component
services. For example, when evaluating the QoE of
the service S that is represented as composition (S
1
@ S
2
) @ S
3
of three services, one can apply the
proposed approach iteratively. At the first step, the
QoE of the composition S
1
@ S
2
is predicted by the
circuit C
1
@ C
2
. At the second step, the circuit C =
(C
1
@ C
2
) is combined with the circuit C
3
using
again Algorithm 3. Let the set R correspond to
Boolean vectors which represent the values of
parameters r
1
, r
2
, …, r
m
of the service S
3
. In this
case, the set of inputs of the circuit (C
1
@ C
2
) @ C
3
is the union of the sets P, Q, and R of the circuit
components. After the first application of Algorithm
3, the union W of the sets P and Q is obtained, i.e.,
W P
Q
. After the second Algorithm 3
application, the circuit C = (C
1
@ C
2
) @ C
3
is
obtained, and the set of its inputs is
W
R
. A
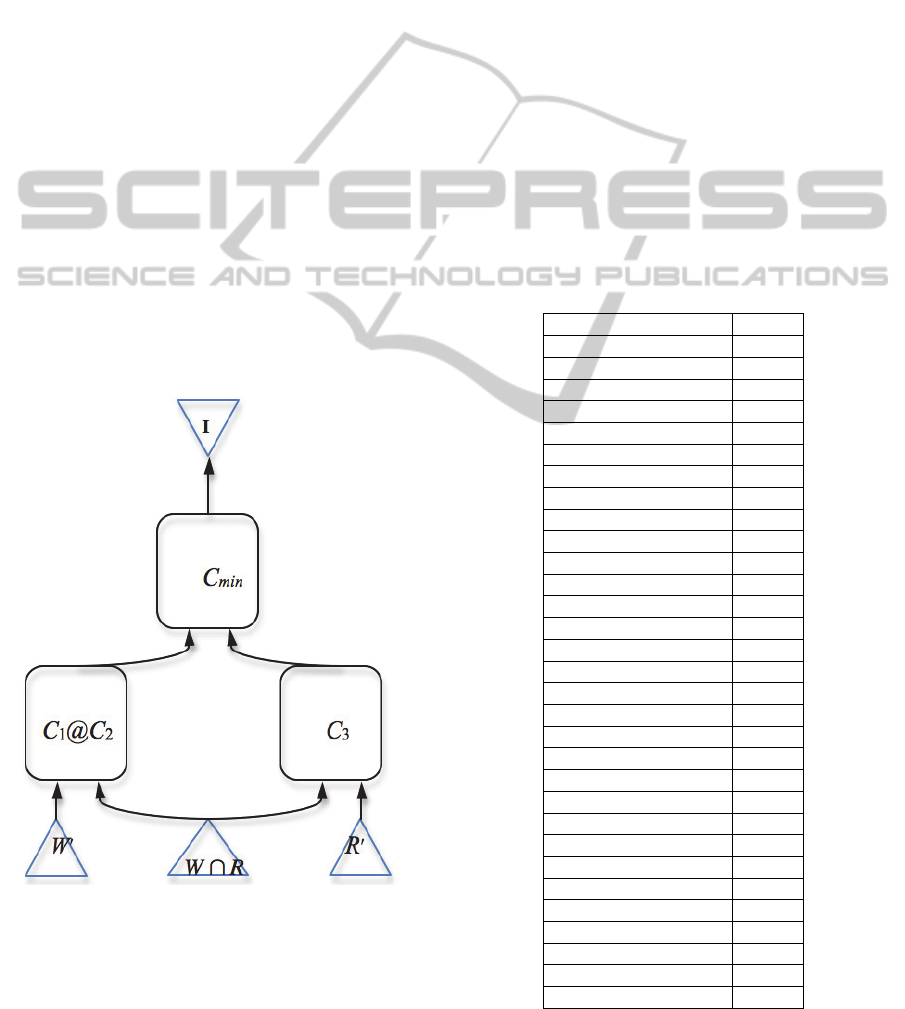
scheme that illustrates the procedure for deriving the
circuit (C
1
@ C
2
) @ C
3
when evaluating the QoE of
the composed service is shown in Fig. 3.
Figure 3: A scheme to derive the circuit (C
1
@ C
2
) @ C
3
,
where
W W
\
W
R
and.
R
R
\
W R
.
4.2 Designing a Logic Circuit C
min
by
ABC
The complexity of the circuit C = C
1
@ C
2
significantly depends on the complexity of the
circuit C
min
. We have derived this logic network
using the software tool ABC (Berkeley Logic
Synthesis and Verification Group, ABC). For this
purpose, we have derived a LUT for a corresponding
MIN function. This LUT contains 64 lines, as the
circuit has 6 inputs. The corresponding LUT is
partially presented in Table 4. The circuit C
min
has
significant input values that correspond to pairs (j, k)
of integers, j, k {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}. Other pairs with
integers 0, 6, 7 are so-called Don’t Care (DNC)
inputs, and as the circuit is used to compute the
minimum of two integers, for these pairs, we define
the output as the corresponding minimal value,
extending the input domain of the corresponding
MIN function.
We have run the ABC tool against the LUT that
Table 4: A LUT for the circuit Cmin.
x
1
x
2
x
3
x
4
x
5
x
6
MIN
000 000 000
000 001 000
000 010 000
000 011 000
… …
001 110 001
001 111 001
010 000 000
010 001 001
010 010 010
010 011 010
010 100 010
010 101 010
010 110 010
… …
100 000 000
100 001 001
100 010 010
100 011 011
100 100 100
100 101 100
100 110 100
… …
110 100 100
110 101 101
110 110 110
… …
111 100 100
111 101 101
111 110 110
111 111 111
ScalableQoEPredictionforServiceComposition
23
is partially represented in Table 4. For this purpose,
we have presented the set on input/output vectors in
the PLA format. The resulting circuit C
min
designed
by the ABC has 40 AIG nodes (gates).
We mention that the size of the circuit C
min
is
essentially related to the scalability of the proposed
approach and the circuit C
min
came out to be very
compact and thus, can be effectively combined with
the circuits C
1
and C
2
. Moreover, the size of C
min
is
very close to the size of the circuits that can be
obtained when predicting the quality of some ‘real
life’ services. As an example, the reader can address
the experimental results for multimedia services
presented in (Kushik et al., 2014), where the size of
the circuit with two service parameters, namely jitter
and packet loss, was 154 AIG nodes.
Nevertheless, as various services are designed
for different purposes and, therefore, have different
crucial parameters, we note that further experimental
research is needed to estimate the efficiency of the
proposed approach.
6 DISCUSSION ON
APPLICABILITY OF THE
APPROACH
In this section, we briefly discuss how the proposed
approach for the composite service QoE evaluation
can be more rigorously implemented. In the previous
sections, we considered the worst case scenario
when the QoE value is the minimal value of QoE
over all component services. However, this
assumption is very strict and not realistic in many
cases. More often, the QoE of the composite service
significantly depends on the structure of the
composite service and can be estimated as a special
formula taken into consideration the service
composition pattern. As usual, a linear combination
of the two variables QoE
1
and QoE
2
(or more if there
are more component services) that represent the QoE
values of the services C
1
and C
2
can be considered as
the simplest case. In this case, following the
technique proposed in the paper, one should derive a
logic circuit C
formula
that substitutes the C
min
one and
implements a corresponding linear combination.
Consider a circuit C
formula
that returns the Boolean
vector o = (o
1
o
2
o
3
) that corresponds to the integer
that is calculated with a formula (α
1
I(i
1
i
2
i
3
) + α
2
I(i
4
i
5
i
6
)). The coefficients α
1
and α
2
can been taken
from various domains, however, in order to simplify
the logic synthesis procedure they should be
normalized as integer values. A modified scheme
that illustrates the procedure for deriving the circuit
C
1
@ C
2
such that the QoE of the overall circuit is
computed as the linear combination (α
1
I(i
1
i
2
i
3
) + α
2
I(i
4
i
5
i
6
)), is shown in Fig. 4.
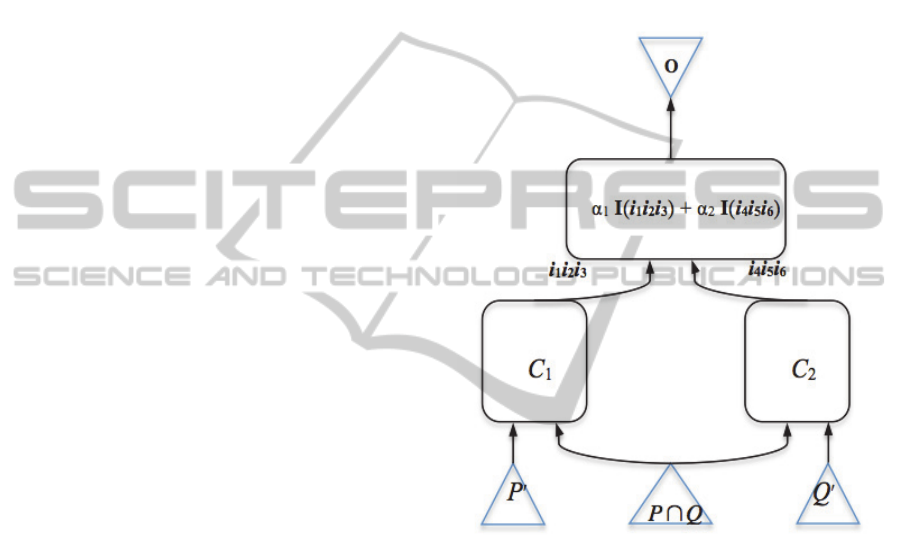
The circuit C
formula
that computes the linear
combination (α
1
I(i
1
i
2
i
3
) + α
2
I(i
4
i
5
i
6
)) in the circuit
C
1
@ C
2
, can be implemented in different ways.
Nevertheless, this implementation is reduced to
implementing two arithmetical multiplications and
one addition.
Figure 4: A modified scheme to derive the circuit C
1
@
C
2
, where
P
P \ P
Q
and.
Q Q \ PQ
.
In this case, the most scalable implementation can be
achieved when the coefficients α
1
and α
2
are integers
that represent the powers of two, namely, there exist
x > 0 and y > 0, such that α
1
= 2
x
and α
2
= 2
y
. This
fact simplifies the multiplication procedure. Indeed,
the circuit that performs such multiplication can be
implemented as a shift register that shifts the inputs
i
1
i
2
i
3
and i
4
i
5
i
6
by x and y bits, correspondingly.
Therefore, such linear combinations preserve the
scalability of the proposed approach. However, the
use of different coefficients can reduce the approach
scalability. This drawback can be overcome by
considering α
1
and α
2
as external inputs of the
C
formula
. Similar to Section 4, the circuits can be
constructed not for two but for bigger number of
service components. More general types of the
circuit C
formula
that implement some specific
ESaaSA2015-WorkshoponEmergingSoftwareasaServiceandAnalytics
24

functions that compute the QoE value of the
composite service and take into account the
compositional pattern as well as the component QoE
values need additional research and are left as future
work.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have proposed an approach for
scalable QoE prediction of a composite service. The
approach relies on logic circuits that are designed to
predict the QoE values of the service components.
The algorithm provided in the paper returns the logic
circuit that predicts the QoE value of a composite
service taking into account the fact that the user
satisfaction can be only decreased in the service
composition. Therefore, a MIN function can be
effectively used to decide between the two QoE
values of the service components. We have
estimated the complexity of the resulting circuit that
predicts the QoE of the composite service.
Preliminary experimental results show the scalability
of the proposed approach. More experiments with
different services considering different service
parameters are planned as a future work.
We also notice that despite the fact that using the
worst-case scenario provides a scalable approach for
the QoE composition estimation, in many realistic
cases, the internal composition structure, i.e.,
compositional patterns have to be taken into
account. The reason is that the degradation of the
QoE in one component can affect the QoE of other
components in different ways. On the other hand, a
user satisfaction within a composite service cannot
rely only of the values of the service component
parameters, it also depends on the network traffic,
the properties of the computer of the user, additional
user parameters such as his/her mood, etc. The
approach proposed in the paper does not take into
account the above issues, and this study is also
remained for the future work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the scientific
support of the research group lead by Prof. Ana
Cavalli (TELECOM SudParis, France) that initiated
the study of the QoE estimation and was
significantly involved in the first steps of using the
logic synthesis techniques for the service analysis
issues. The authors are pleased to provide novel
contributions to this area based on these first steps
that have been made together.
The authors also mention that this work is
partially supported by RFBR grant № 14-08-31640
мол_а (Russia).
REFERENCES
Ahmed, S., Begum, M., Hasan Siddiqui, F., Abul Kashem,
M., 2012. Dynamic Web Service Discovery Model
Basedon Artificial Neural Network with QoS Support.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering
Research Volume 3, Issue 3, pp. 1-7.
Al-Masri, E., Mahmoud Qusay, H., 2009. Discovering the
Best Web Service: A Neural Network-based Solution.
SMC 2009, pp. 4250-4255.
Berkeley Logic Synthesis and Verification Group, ABC:
A System for Sequential Synthesis and Verification,
url: http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~alanmi/abc/.
Booth, D., Haas, H., McCabe, F., Newcomer, E.,
Champion, M., Ferris, C., Orchard, D., 2004. Web
services architecture. W3C Working Group Note, W3C
Technical Reports and Publications, url:
http://www.w3.org/TR/ws-arch/.
El Hadad, J., Manouvrier, M., Rukoz, M., 2010. TQoS:
Transactional and QoS-Aware Selection Algorithm for
Automatic Web Service Composition. IEEE
Transactions on Services Computing, vol. 3, issue. 1,
pp. 73-85.
Kondratyeva, O., Kushik, N., Cavalli, A., Yevtushenko N.,
2013. Evaluating Web Service Quality using Finite
State Models. In Proc. of QSIC 2013.
Kushik, N., Pokhrel J., Yevtushenko N., Cavalli A.R.,
Mallouli W., 2014. QoE Prediction for Multimedia
Services: Comparing Fuzzy and Logic Network
Approaches. International Journal of Organizational
and Collective Intelligence, 4(3), pp. 44-65.
Lin, M., Xie, J., Guo, H., Wang, H., 2005. Solving QoS-
driven web service dynamic composition as fuzzy
constraint satisfaction. EEE 2005, pp. 9-14.
Mitchell, T.M., 1997. Machine learning. McGraw Hill
series in computer science, McGraw-Hill.
Pokhrel, J., Mallouli, W., Montes de Oca, E., 2013. QoE
Prediction and Self-Learning Mechanisms. Technical
report on the PIMI Project.
Pokhrel, J., Wehbi, B., Morais, A., Cavalli, A., Allilaire,
E., 2013. Estimation of QoE of video traffic using a
fuzzy expert system. In Proc. of CCNC, pp. 224-229.
Torres, R., Astudillo, H., Salas, R., 2011. Self-Adaptive
Fuzzy QoS-Driven Web Service Discovery. In IEEE
SCC 2011, pp. 64-71.
ITU-T, 2006. Mean opinion Score (MOS) terminology.
Recommendation P.800.1.
Winckler, M.A., Bach, C., Bernhaupt, R., 2013.
Identifying user experience dimensions for mobile
incident reporting in urban contexts. IEEE
Transactions on Communications, vol. 56, no. 2, pp.
40-82.
ScalableQoEPredictionforServiceComposition
25

Zadeh, L.A., 1965. Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, 8
(3), pp. 338–353.
Zheng, H., Zhao, W., Yang, J., Bouguettaya, A., 2013.
QoS analysis for web service compositions with
complex structures. IEEE Transactions on Services
Computing, vol. 6, issue. 3, pp. 373 - 386.
ESaaSA2015-WorkshoponEmergingSoftwareasaServiceandAnalytics
26
