
Cognitive Assessment through “Casual Video Games” and Machine
Learning
Doctoral Consortium Contributions
Sonia M. Valladares Rodríguez, Roberto Pérez Rodríguez, Luis E. Anido Rifón
and Manuel J. Fernández Iglesias
School of Telecommunication Engineering, University of Vigo, Vigo, Spain
1 RESEARCH PROBLEM
Cognitive evaluation aims to the examination of
higher cortical functions like memory, attention,
orientation, language, or executive functions (e.g.,
activity planning and sequencing) (Howieson and
Lezak 2010) to discard anomalies in cognitive
capabilities that may led to attention deficit disorder,
depression, delirium, dementia, and other conditions.
Cognitive capabilities manifest in all daily
activities and are essential to autonomous
development. As a consequence, the ability to
develop and use them constitutes one of the main
indicators of the degree of autonomy and cognitive
ability of an individual, which in turn justifies
cognitive evaluation.
Cognitive impairments are typically associated to
senior citizens, whose cognitive capacity is gradually
limited with age, and could be dramatically
compromised due to dementia and other related
processes. Therefore, one of the main applications of
cognitive evaluation is MCI screening to detect
cognitive anomalies in adults (Xu et al., 2002;
Ashford et al., 2007).
Another population group where cognitive
evaluations are typically performed are students.
Through these evaluations study methodologies and
cognitive strategies applied to understand texts or
face problematic situations can be discovered and
analysed. In other words, with the information
provided by analysing common tasks in the learning
process it could be possible to recommend activities
and / or interventions to increase academic
performance. Therefore, a key application of
cognitive evaluation is to obtain student profiles when
facing conditions like dyslexia, attention deficit
disorder or hyperactivity.(Letteri, 1980; Watkins,
2000; Hatcher et al., 2002).
Currently, cognitive assessments take place in a
controlled environment, usually in a clinical setting,
conducted by health professionals (e.g., neurologists,
psychologists, etc.) The main diagnostic tools used
are a number of validated neuro-psychological tests
or scales colloquially known as "classic tests" (Spreen
1998; Bermejo et al., 2008). These tests provide
results in the form of a scale evaluation of the
cognitive state of a person. Besides, the usual format
of the cognitive evaluation process is a face-to-face
interview of variable duration, depending on the
complexity and variability of the selected test suite,
along with a data collection process performed
typically using pen and paper.
A cognitive or neuropsychological examination
should include the evaluation of the several processes
or cognitive domains that comprise the cognitive
spectrum of each individual. This spectrum consists
of the following areas: alert level; general intellectual
ability; counselling and care; linguistic, spatial and
visual functions; visuo-constructive abilities;
memory; executive functions (i.e., formulating goals,
and their planning and execution, reasoning,
abstraction ability, etc.) and finally, the affective
state. In clinical practice, many classic tests are used
to assess the areas just mentioned, such as:
Alert: Glasgow Coma Scale (Teasdale and
Jennett, 1974).
Motor functions: Strength (Reitan and Wolfson,
2009).
Orientation: Wechsler Memory Scale III (Scale-
Third, 1997).
Attention and concentration: Trail Making Test
(Tombaugh, 2004).
General cognitive level: MMSE (Cockrell and
Folstein, 1987).
Memory: King’s figure; Wechsler Memory Scale
III (Scale-Third, 1997); WAIS-III (Wechsler,
1997).
Language: Token test (Swihart et al., 1989);
Verbal fluency (Gourovitch et al., 2000;
Herrmann et al., 2005).
Executive function: Stroop test (Stroop, 1935);
Hanoi towers (Dehaene and Changeux, 1997).
3
M. Valladares Rodríguez S., Pérez Rodríguez R., E. Anido Rifón L. and J. Fernández Iglesias M..
Cognitive Assessment through “Casual Video Games” and Machine Learning - Doctoral Consortium Contributions.
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Affective areas: Geriatric Depression Scale
(GDS) (Brink et al., 1982).
On the other hand, these classic tools suffer several
limitations that have to be taken into account so that
the results of cognitive evaluation are not biased.
Firstly, the personalized attention of health
professionals is required, and the total time needed
cannot be foreseen, but depends on the complexity of
the test suite and the test subjects. Besides, their
application is usually performed retrospectively, that
is, once the individuals concerned, their families or
their educational environment detect or become
aware of the cognitive impairment. This delay
dramatically limits the intervention and treatment
options (Holtzman et al., 2011).
Another relevant limitations are the confounding
factors (Pearl, 2014). In fact, the scores on
neuropsychological tests will vary depending on
these variables or conditions. Among the main ones
we can identify the educational level as the variable
that most affects the scores in existing psychological
and neuropsychological tests (Ardila et al., 2000).
More specifically, the skills included in these
cognitive evaluations are typically skills acquired at
school time, which makes them not suitable for
people with a low educational level.
Age is another factor to consider, since
intellectual abilities vary over time, which introduces
a relevant degree of variability in the results obtained
with classical neuropsychological evaluations.
Overall, age makes scores in cognitive tests to
improve during the first decades of life; then they
have a tendency to stabilize, and after a certain age
results start to worsen (Strauss et al., 2006).
Regarding the influence of gender, no consensus
has been reached so far. It has been traditionally
accepted that there are differences in cognitive
abilities between men and women as men outperform
women on tests that require greater spatial ability and
/ or mathematics, while women outperform men in
tests in which verbal skills predominate. On the other
side, in relation to mathematical skills several studies
conclude that this difference is limited to the
adolescence and to complex mathematical tasks
(Rosselli et al., 2009). Besides, as to the alleged better
language skills of women, there are studies that do not
support classical evidence (Wallentin, 2009). In short,
presently it is fairly unusual to find
neuropsychological evaluation tests including
separate standards for men and women.
Another factor to consider in cognitive
evaluations is the set of characteristics or behavioural
traits that define people from a particular location,
like the culture or idiosyncrasy of the place. Note that
most of classic test suites have been developed in a
very specific cultural environment, namely the
Western society. Therefore, these tests will be
influenced by the values of Western culture and its
application in other geographical or cultural areas
may not be entirely appropriate or could be
extrapolated (Ardila et al., 2007).
To complete the enumeration of the limitations of
the classic mechanisms of cognitive evaluation, it is
important to note that testing sessions are seen as
intrusive and unnatural by many subjects. Indeed,
new approaches are being developed, like the
introduction of virtual reality. As a consequence, the
concept of ecological cognitive evaluation (i.e.,
ecological validity) is starting to develop (Chaytor
and Schmitter-Edgecombe, 2003).
Among the new trends to overcome the
limitations identified above, some researchers have
raised the possibility of using video games in order to
perform cognitive evaluation. Most of the references
found are characterized by studying the correlation
between a classic test and the results of the interaction
with a series of "casual games", to assess the
reliability and efficiency of such games as
instruments for cognitive evaluation. In relation to the
classic tests that have been used as a reference,
(Baniqued et al., 2013) studied, among others,
Raven's Advanced Progressive Matrices and WAIS-
III - Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale; (Aalbers et
al., 2013) used Kings Figure, Cambridge
Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery, among
others; and (Zygouris et al., 2014; Zucchella et al.,
2014; Pazzi et al., 2014; Hagler et al., 2014; Tarnanas
et al., 2013; Aalbers et al., 2013; Jimison et al., 2008;
Jimison et al., 2006), targeted Mini Mental State
Examination as a general cognitive validation
element.
With respect to the video games employed, most
studies are based on the design and development of
an ad hoc game or video game suite as a replica of the
classic test used as the initial validation model.
(Zygouris et al., 2014; Lamb et al., 2014; Tong and
Chignell, 2014; Tenorio Delgado et al., 2014; Nolin
et al., 2013). However, it is possible to find case
studies based on generic video games that, besides
providing the intrinsic motivation of games, are
perceived as everyday elements (Baniqued et al.,
2013) (e.g. Memotri, Simons Says, Blobs, etc.);
(Thompson et al., 2012) (e.g. sudoku, etc.) y (Jimison
et al., 2008; Jimison et al., 2006) (e.g. solitary game,
etc.).
Finally, in relation to the data analysis techniques
applied, most of the studies carry out a statistical
analysis of the correlation between the classic tests
and the results of the interaction with video games. In
ICT4AgeingWell2015-DoctoralConsortium
4

a lesser extent, some studies use more advanced,
analysis and prediction mechanisms such us machine
learning, neural networks and the Theory of Response
Items (Lamb et al., 2014; Sternberg et al., 2013).
2 STATE OF THE ART
The authors carried out a review of the literature on
the use of video games to perform cognitive
evaluation in relation to classical methods currently
used in clinical practice. The main outcomes from this
process are summarized below.
All studies reviewed establish as a reference the
classical evaluation mechanisms, that is, the so-called
neuropsychological tests, as they are validated
solutions presently used to perform cognitive
evaluation and diagnosis. According to the
recommendations to conduct a neuropsychological
evaluation (Allegri et al., 2000; Groth-Marnat, 2000;
of Neurology & others, 1996; Hodges, 2007), we
adopted a classification of the main cognitive areas to
be evaluated (cf. Table 1 in Appendix). This
classification is what we named in our research as the
cognitive spectrum. Based on this classification, we
found that none of the studies consulted has sought
base truth on the entire spectrum, which is an initial
limitation, since not covering the entire spectrum of
areas that make up the cognitive capabilities of an
individual will most likely limit the outcomes of an
evaluation process.
On the other side, according to the design
paradigm in this type of research (i.e., existing games,
and new games), we found that most studies have
opted for games designed ad hoc (Zygouris et al.,
2014; Lamb et al., 2014; Tong and Chignell, 2014;
Tenorio Delgado et al., 2014; Zucchella et al., 2014;
Hagler et al., 2014; Atkins et al., 2014; Nolin et al.,
2013; Tarnanas et al., 2013; Aalbers et al., 2013;
Koenig and Krch, 2012; Jimison et al., 2008; Jimison
et al., 2006). Note that no study has used as a
paradigm for designing their games both options
above, which would have served to compare and
assess the effectiveness of a model over the other. In
our opinion, the introduction of existing popular
games should not be discarded, since this would
simplify the implementation process and also would
provide greater confidence and user-friendliness to
cognitive monitoring, as it would be performed using
games and / or activities already known by target
users.
We have also performed an analysis of the games
used by different studies. From this analysis the facts
below were identified.
The vast majority relied on a collection of games
to cover the cognitive spectrum targeted in each
research. However, some studies (Zygouris et al.,
2014; Lamb et al., 2014; Zucchella et al., 2014;
Hagler et al., 2014; Nolin et al., 2013; Tarnanas et
al., 2013; Koenig and Krch, 2012) selected a
single game including several phases and/or tasks.
No evidence has been found to support one option
versus the other, so additional research is needed.
All studies present some methodological
inconsistencies in some scenarios, as they rely on
classic tests to capture information that is not
further evaluated through the game(s) selected.
The opposite situation has also been detected, that
is, the use of games to evaluate areas that are not
supported by data from any classical evaluation
mechanism.
To sum up, after analysing the video games used, we
found that the entire cognitive spectrum is not
addressed, either through classical testing or video
game playing. As a consequence, recent research
denotes a lack of completeness and rigor.
In relation to the variables taken from game
interaction (i.e., granularity), we identified many
different approaches encompassed according to the
following classification: high (i.e., a limited amount
of higher level variables); average, and low (i.e.,
many lower-level variables). For example, some
relevant variables are:
High: scores, reliability, difficulty, etc.
Medium: total number of movements, total
number of levels completed, time to complete a
task, etc.
Low: answers, speed, precision, motor
coordination level, total number of interactions,
total number of completed actions, total number
of errors, total number of omissions, distance
covered with the mouse, etc.
As a general remark, we could infer that the best
combination would be lower granularity and having
more analysis elements available, always keeping a
balance from the point of view of computational cost.
Considering the analysis model applied in the
studies surveyed, most rely on statistical techniques
to both reduce the sampling space and to facilitate
correlation with respect to classic tests. Evidence of
this is that these studies are limited to establish
similarities or correlations with the results of those
tests, allowing them to perform cognitive evaluations
but being unable to detach from the classic model.
This is the situation of most studies in this area (Lamb
et al., 2014; Hagler et al., 2014; Baniqued et al.,
2013; Aalbers et al., 2013; Carvalho et al., 2014;
CognitiveAssessmentthrough"CasualVideoGames"andMachineLearning-DoctoralConsortiumContributions
5

Tong and Chignell, 2014; Tenorio Delgado et al.,
2014; Zygouris et al., 2014; Zucchella et al., 2014;
Atkins et al., 2014; Nolin et al., 2013; Thompson et
al., 2012).
When we analysed the introduction of advanced
predictive algorithms based on machine learning,
artificial intelligence or neural networks, the number
of relevant contributions in the literature is rather
limited (Lamb et al., 2014; Jimison et al., 2008;
Jimison et al., 2006). In these cases, the authors claim
to have used these novel approaches, but no
information is provided to be able to study and assess
them.
With respect to the devices used to play video
games to perform cognitive evaluation, we found that
the most used graphical interface is the personal
computer (Zygouris et al., 2014; Lamb et al., 2014;
Tenorio Delgado et al., 2014; Zucchella et al., 2014;
Hagler et al., 2014; Atkins et al., 2014; Nolin et al.,
2013; Tarnanas et al., 2013; Baniqued et al., 2013;
Aalbers et al., 2013; Koenig and Krch, 2012; Jimison
et al., 2008; Jimison et al., 2006). However, the
introduction of mobile and touch devices like tablet
computers or smartphones is becoming more and
more popular (Tong and Chignell, 2014; Tenorio
Delgado et al., 2014; Thompson et al., 2012; Zygouris
et al., 2014). No study provides detailed usability
results focused on the device used, although some
mention the digital literacy of participating users as a
relevant aspect, as a low technological level may
disturb the cognitive evaluation process in these cases
leading to false positives.
Finally, we performed an analysis of the different
processes conducted to validate the research
performed in the works surveyed. In general,
validation is based on real users that fit the target
profile (e.g., male / female, students, seniors, etc.).
Most studies take into account a number of variables
when defining its population sample for validation.
Typical variables considered are:
Number of users.
Age.
Gender: all contributions have been validated by
a greater number of women than men, but no
reason or justification is provided for that. It
should be noted that cognitive problems in older
people are more prevalent in the female
population, although primarily due to greater
longevity rates, so in our opinion this population
bias should not be translated to population
sampling for cognitive evaluation. As pointed out
above, no justification is provided about this.
Socio-educational variables. As discussed in the
introduction of this paper, these variables are
especially relevant as many classic tests depend
on the educational level of the subject.
Place and duration of video game sessions.
In some cases, cross-sectional population studies
were performed instead of longitudinal ones
(Zygouris et al., 2014; Zucchella et al., 2014; Nolin et
al., 2013; Tarnanas et al., 2013; Jimison et al., 2006).
In these cases, the system proposed is validated with
healthy users and users suffering from dementia or
other mild conditions as a mechanism to train and
refine the cognitive evaluation system under study.
3 THESIS STATEMENT
After the thorough revision of the state of the art on
existing mechanisms for cognitive evaluation
discussed above, we found a candidate research gap
based on the absence of relevant literature providing
reliable knowledge about the cognitive evaluation of
individuals through a collection of generic video
games and machine learning techniques.
Therefore, we intend to tackle the following
research challenge or working hypothesis: is it
possible to create a device to estimate the cognitive
status of a person, from their interaction with casual
games, using machine learning techniques?
To address this hypothesis we will relay on the
following knowledge elements:
Gamification: cognitive evaluation will be
performed through the interaction with video
games, and more specifically popular, unspecific
video games like Tetris, puzzles, word quizzes,
etc.
Machine Learning: cognitive evaluation will
make use of multi-variable regression techniques
to infer cognitive capabilities from video game
interactions.
Information and communication tools: cognitive
evaluation will use accessible devices and
software, in a way that these technological tools
will not hinder interaction, and therefore distort
evaluation results.
Ecological validity: cognitive evaluation will be
continuing and non-intrusive.
4 OBJECTIVES
To address the working hypothesis raised in the
previous section, we have identified the following
objectives whose achievement will allow us to cover
the scope of this research:
ICT4AgeingWell2015-DoctoralConsortium
6
A) General Objective:
To develop an artefact or system to perform
non-intrusive cognitive evaluation through
casual video games, machine learning
techniques and information tools.
B) Specific Objectives:
O1. To identify and select a suite of digital
applications or video games to be developed or
adapted according to accessibility criteria.
O2. To define a cognitive profile model
reflecting the cognitive areas to be evaluated,
that is, to define the cognitive spectrum.
O3. To identify the classic neuro-psychological
tests for cognitive scanning that will be used to
obtain validated back-up data on the cognitive
spectrum.
O4. To perform scanning tests on a statistically
significant number of subjects.
O5. To design and implement an accessible
prototype integrating the selected video games
to perform cognitive evaluation.
O6. To perform the validation of the artefact or
system designed with real users matching the
profile under study.
O7. To design and implement a prediction
model to infer the cognitive level and profile of
individuals from their interaction with video
games only. This algorithm will be trained with
the results obtained from video game interaction
and from classic tests performed to the users in
the control group. Thus algorithm will be based
on machine learning techniques.
O8. To validate the results obtained by peer
researchers, through their publication in
scientific journals and contributing to relevant
conferences in the field.
5 METHODOLOGY
In order to carry out the research presented in this
article, we have opted to follow the next methodology
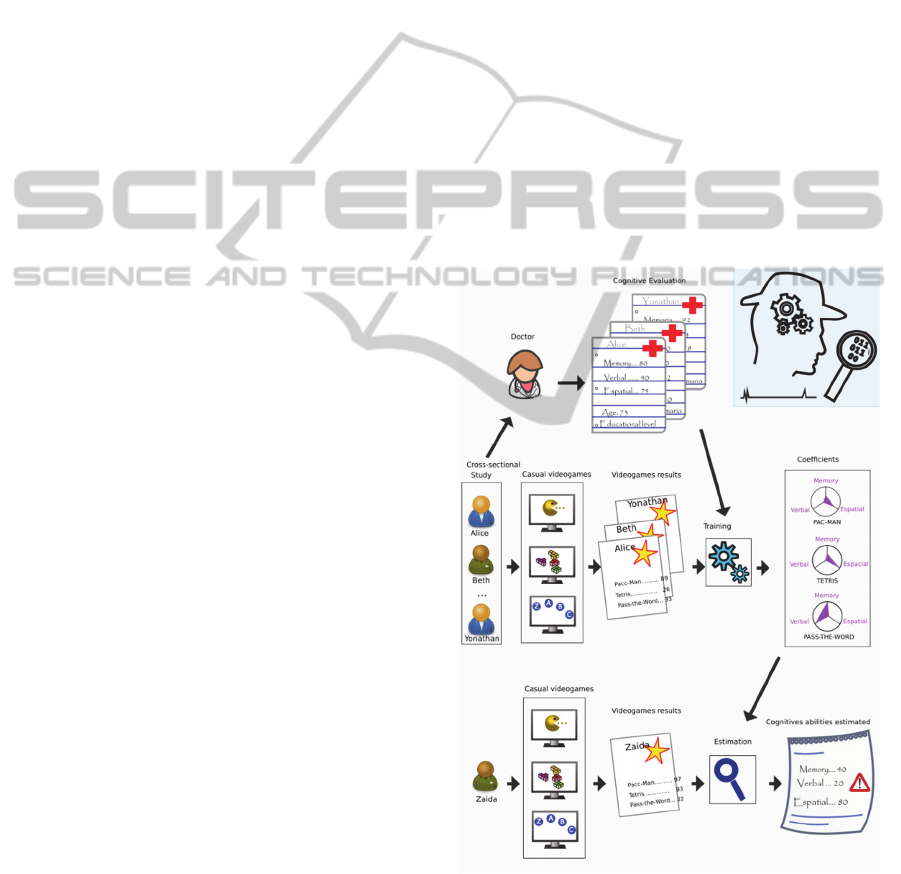
described through Figure 1:
Firstly, we will define the entire cognitive spectrum,
so that it will be identified clearly cognitive areas that
make it up (e.g. memory, attention, verbal fluency,
visuospatial ability, etc).
Secondly, a cross-sectional population group will be
selected, over which it is going to conduct the study.
We have opted for a cross-sectional or prevalence
study (Barnett et al., 2012; Rosenbaum, 2002; Kelsey,
1996), instead of longitudinal one, because we want
design and validate a device to perform the cognitive
evaluation of its users in a given moment, so it should
have training data to discriminate between healthy
people and people with a deficit in their areas
cognitive.
Then, to this group except one (i.e. one-left-out
methodology (Kearns and Ron, 1999; Cawley and
Talbot, 2003)), will spend classical mechanisms or
tests, for being these tools that currently offer a
validated outcome about cognitive state of a person.
This same control group will interact with video
games that cover the entire cognitive spectrum, in the
same line as the classic tests selected should do, too.
Once we have validated data from the tests and
data sets resulting from the interaction of the games,
these are used as input variables for the designed
algorithm based on machine learning techniques. As
a result of this training period, the algorithm will
extract coefficients able to correlate the measured
variables of video games with cognitive areas
evaluated.
Figure 1: Methodology Cross-sectional & one-left-out.
For example as shown in Figure 1, the “pass-the-
word” videogame will have greater weight
coefficients with working memory and verbal fluency
that spatial ability. After a suitable period of training,
CognitiveAssessmentthrough"CasualVideoGames"andMachineLearning-DoctoralConsortiumContributions
7

the algorithm will be able to estimate the cognitive
abilities of a person (i.e. Zaida in Figure 1) only with
his/her interaction with video games. For this,
algorithm will use the obtained coefficients in the
training phase and multivariable regression advanced
techniques.
6 EXPECTED OUTCOME
In relation to possible impact that the proposed
research will provide, we can highlight the following:
Under a scientific and/or technological
perspective, this research will generate knowledge in
the use of video games in order to detect cognitive
impairment, especially when games are used for
continuous and non-intrusive monitoring of cognitive
abilities. It is at that point where the use of
conventional-games—unlike other approaches using
games created specifically for evaluating cognitive—
offer promising possibilities, as they were designed
for the sole purpose of being entertained.
In addition, we will gain the necessary knowledge
of machine learning, especially its application in
detection and estimation of patterns, thus it will be
possible to infer the cognitive state of a person from
their interaction with "casual video games".
Therefore, it is within the scope of the use of machine
learning where this research hopes to have a greater
scientific impact, both nationally and internationally.
From a social and/or individual level, this research
will have a positive impact in the different groups of
end-users of it:
Primary users. People object of cognitive
assessment (e.g. elders, students, etc.) will be the
main beneficiaries of this research, since it will
enable to them a transparent, non-intrusive and
continuous cognitive screening, so that it could
detect early signs of cognitive problems.
Secondary users. Family members, educators and
the circle next to people under evaluation, will
also benefit from this research. This will enable to
receive evaluations and alerts, if problems are
detected in any cognitive domain. Therefore, the
pressure of these users will decrease because they
will have a cognitive assessment tool that it helps
them to detect anomalies without falling over
them all responsibility for issuing early warnings.
Tertiary users. Those in charge of the social,
health and education policies, will also benefit
from this research, to provide a non-intrusive,
sustainable and effective mechanism for cognitive
assessment of people. That is, it allows them to
incorporate more agile technology solutions that
traditional mechanisms (e.g. scales or
neurological & classic tests), which usually apply
a posteriori, after the detection of cognitive
problems’ signs.
Finally, in economic terms this research will
contribute to the sustainable maintenance of health
and education systems, since early detection of
possible cognitive problems, enables to increase the
success of crash interventions. In this way, we could
address the problem before it goes to most severe
stages (e.g. attention deficit disorder, depression,
delirium, dementia, etc.) and therefore, it would
require greater professional assistance, with the
consequent economic expenditure for public funds.
7 STAGE OF THE RESEARCH
To conclude the discussion of this article, we are
going to indicate the current state of this research.
To date we have conducted a detailed study of the
state of the art regarding this matter. As a result
thereof, it has allowed us to propose a methodology
or taxonomy that includes the needed requirements to
address a research and/or development about of
effective systems of cognitive assessment.
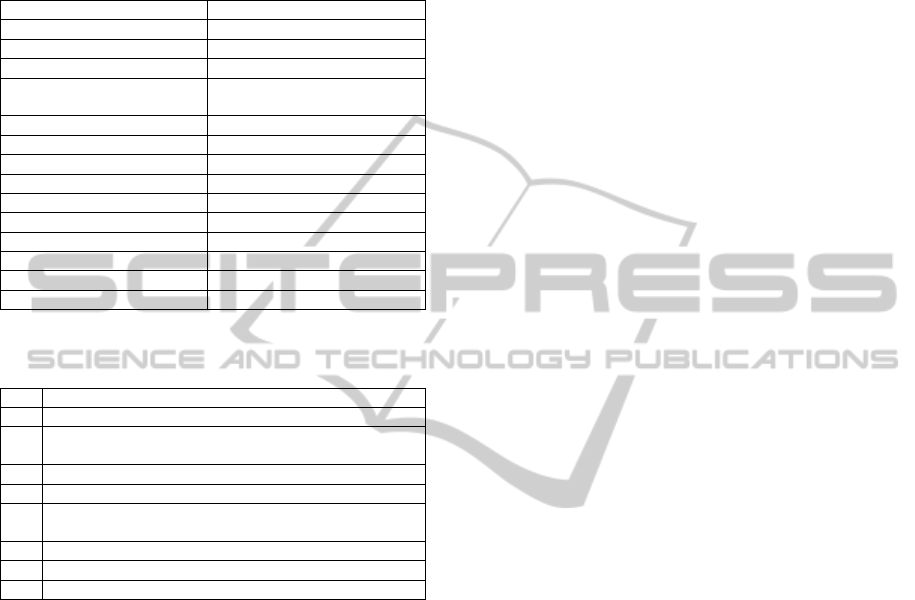
This classification (c.f. Table 2 in Appendix)
includes the following sections:
T1) Classic tests categorized by cognitive areas,
which should cover the entire cognitive spectrum.
T2) Best design paradigm: using existing games
or games designed from the ground up.
T3) Casual video games, which should cover the
entire spectrum cognitive.
T4) Most appropriate variables to collect the most
representative data sets.
T5) Most appropriate tools of data analysis (e.g.
statistical, machine learning, neural networks,
etc.).
T6) Most appropriate devices or interfaces to
access to games.
T7) Methodology to allow to define the user
profile and most appropriate N for validation.
At the present time, we have begun to define a
cognitive profile, indicating the cognitive areas that
should be evaluated, namely, in order to define the
entire cognitive spectrum. At the same time, we are
going to proceed to identify and select a battery of
digital applications or casual video games, covering
also the entire cognitive spectrum. Finally this
research is expected to close along the 2016.
ICT4AgeingWell2015-DoctoralConsortium
8

REFERENCES
Aalbers, T. et al., 2013. Puzzling With Online Games
(BAM-COG): Reliability, Validity, and Feasibility of
an Online Self-Monitor for Cognitive Performance in
Aging Adults. Journal of medical Internet research,
15(12). Available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC38689
77/.
Allegri, R., Harris, P. & Drake, M., 2000. La evaluaci{ó}n
neuropsicol{ó}gica en la enfermedad de Alzheimer.
Rev Neurol Arg, 25(supl 1), pp.11–15.
Ardila, A. et al., 2000. Age-related cognitive decline during
normal aging: the complex effect of education.
Archives of clinical neuropsychology, 15(6), pp.495–
513.
Ardila, A. et al., 2007. The impact of culture on
neuropsychological test performance. International
handbook of cross-cultural neuropsychology, pp.23–
44.
Ashford, J.W. et al., 2007. Should older adults be screened
for dementia? It is important to screen for evidence of
dementia! Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 3(2), pp.75–80.
Atkins, S.M. et al., 2014. Measuring working memory is all
fun and games: A four-dimensional spatial game
predicts cognitive task performance. Experimental
Psychology (formerly Zeitschrift für Experimentelle
Psychologie). Available at:
http://psycontent.metapress.com/content/v8813723327
73455/?referencesMode=Show.
Baniqued, P.L. et al., 2013. Selling points: What cognitive
abilities are tapped by casual video games? Acta
psychologica, 142(1), pp.74–86. Available at:
http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?a
rtid=3679476&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
[Accessed September 1, 2014].
Barnett, K. et al., 2012. Epidemiology of multimorbidity
and implications for health care, research, and medical
education: a cross-sectional study. The Lancet,
380(9836), pp.37–43.
Brink, T.L. et al., 1982. The geriatric depression scale.
Measuring health: A guide to rating scales and
questionnaires, pp.259–263.
Carvalho, A. et al., 2014. Physical activity and cognitive
function in individuals over 60 years of age: a
systematic review. Clinical interventions in aging, 9,
p.661.
Cawley, G.C. & Talbot, N.L.C., 2003. Efficient leave-one-
out cross-validation of kernel Fisher discriminant
classifiers. Pattern Recognition, 36(11), pp.2585–2592.
Chaytor, N. & Schmitter-Edgecombe, M., 2003. The
ecological validity of neuropsychological tests: A
review of the literature on everyday cognitive skills.
Neuropsychology review, 13(4), pp.181–197.
Cockrell, J.R. & Folstein, M.F., 1987. Mini-Mental State
Examination (MMSE). Psychopharmacology bulletin,
24(4), pp.689–692.
Dehaene, S. & Changeux, J.-P., 1997. A hierarchical
neuronal network for planning behavior. Proceedings
of the National Academy of Sciences, 94(24),
pp.13293–13298.
F. Bermejo, Pareja J. Porta-Etessam, J. Díaz Guzmán, P.M.-
M., 2008. Más de CIEN ESCALAS en NEUROLOGÍA,
Gourovitch, M.L. et al., 2000. A comparison of rCBF
patterns during letter and semantic fluency.
Neuropsychology, 14(3), p.353.
Groth-Marnat, G.E., 2000. Neuropsychological assessment
in clinical practice: A guide to test interpretation and
integration., John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Hagler, S., Jimison, H.B. & Pavel, M., 2014. Assessing
executive function using a computer game:
Computational modeling of cognitive processes. IEEE
Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 18(4),
pp.1442–1452. Available at:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnum
ber=6732879.
Hatcher, J., Snowling, M.J. & Griffiths, Y.M., 2002.
Cognitive assessment of dyslexic students in higher
education. British Journal of Educational Psychology,
72(1), pp.119–133.
Herrmann, M.J. et al., 2005. Optical topography with near-
infrared spectroscopy during a verbal-fluency task.
Journal of Psychophysiology, 19(2), pp.100–105.
Hodges, J.R., 2007. Cognitive assessment for clinicians,
Oxford University Press.
Holtzman, D.M., Morris, J.C. & Goate, A.M., 2011.
Alzheimer’s disease: the challenge of the second
century. Science translational medicine, 3(77),
pp.77sr1–77sr1.
Howieson, D.B. & Lezak, M.D., 2010. The
neuropsychological evaluation. Essentials of
Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Neurosciences,
pp.29–46.
Jimison, H., Pavel, M. & Le, T., 2008. Home-based
cognitive monitoring using embedded measures of
verbal fluency in a computer word game. In
Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2008.
EMBS 2008. 30th Annual International Conference of
the IEEE. pp. 3312–3315. Available at:
http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-
61849185753&partnerID=40&md5=d64b42435084eb
11eaa24a9a8be838cf.
Jimison, H.B. et al., 2006. A framework for cognitive
monitoring using computer game interactions. In
Medinfo 2007: Proceedings of the 12th World Congress
on Health (Medical) Informatics; Building Sustainable
Health Systems. p. 1073.
Kaye, J. et al., 2014. Unobtrusive measurement of daily
computer use to detect mild cognitive impairment.
Alzheimer’s & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's
Association, 10(1), pp.10–7. Available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23688576
[Accessed January 5, 2015].
Kearns, M. & Ron, D., 1999. Algorithmic stability and
sanity-check bounds for leave-one-out cross-validation.
Neural Computation, 11(6), pp.1427–1453.
Kelsey, J.L., 1996. Methods in observational epidemiology,
Oxford University Press.
CognitiveAssessmentthrough"CasualVideoGames"andMachineLearning-DoctoralConsortiumContributions
9

Koenig, S. & Krch, D., 2012. User-centered development
of a virtual reality cognitive assessment. In Proceedings
of International Conference on Disability, Virtual
Reality and Associated Technologies. pp. 10–12.
Available at:
http://www.icdvrat.reading.ac.uk/2012/papers/ICDVR
AT2012_S08N2_Koenig_etal.pdf [Accessed
November 22, 2014].
Lamb, R.L. et al., 2014. Cognitive diagnostic like
approaches using neural-network analysis of serious
educational videogames. Computers & Education, 70,
pp.92–104. Available at:
http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S03601315
13002303 [Accessed November 10, 2014].
Letteri, C.A., 1980. Cognitive profile: Basic determinant of
academic achievement. The Journal of Educational
Research, 73(4), pp.195–199.
Nolin, P. et al., 2013. Virtual Reality as a New Approach to
Assess Cognitive Decline in the Elderly. Academic
Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 2(8), p.612.
of Neurology, A.A. & others, 1996. Assessment:
Neuropsychological testing of adults. Considerations
for neurologists. Neurology, 47(2), pp.592–599.
Pazzi, S. et al., 2014. A Serious Games platform for early
diagnosis of mild cognitive impairments. In Games for
Health 2014. Springer, pp. 110–113.
Pearl, J., 2014. Comment: Understanding Simpson’s
Paradox. The American Statistician, 68(1), pp.8–13.
Reitan, R.M. & Wolfson, D., 2009. The Halstead--Reitan
Neuropsychological Test Battery for Adults—
Theoretical, Methodological, and Validational Bases.
Neuropsychological assessment of neuropsychiatric
and neuromedical disorders, 1.
Rosenbaum, P.R., 2002. Observational studies, Springer.
Rosselli, M. et al., 2009. Gender differences and cognitive
correlates of mathematical skills in school-aged
children. Child Neuropsychology, 15(3), pp.216–231.
Scale-Third, W.D.W.M., 1997. Edition (WMS-III). San
Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation.
Spreen, O., 1998. A compendium of neuropsychological
tests: Administration, norms, and commentary, Oxford
University Press.
Sternberg, D.A. et al., 2013. The largest human cognitive
performance dataset reveals insights into the effects of
lifestyle factors and aging. Frontiers in human
neuroscience, 7.
Strauss, E., Sherman, E.M.S. & Spreen, O., 2006. A
compendium of neuropsychological tests:
Administration, norms, and commentary, Oxford
University Press.
Stroop, J.R., 1935. Studies of interference in serial verbal
reactions. Journal of experimental psychology, 18(6),
p.643.
Swihart, A.A. et al., 1989. The Token Test: Validity and
diagnostic power in Alzheimer’s disease.
Developmental Neuropsychology, 5(1), pp.69–78.
Tarnanas, I. et al., 2013. Ecological validity of virtual
reality daily living activities screening for early
dementia: longitudinal study. JMIR Serious Games,
1(1), p.e1.
Teasdale, G. & Jennett, B., 1974. Assessment of coma and
impaired consciousness: a practical scale. The Lancet,
304(7872), pp.81–84.
Tenorio Delgado, M. et al., 2014. TENI: A comprehensive
battery for cognitive assessment based on games and
technology. Child Neuropsychology, (ahead-of-print),
pp.1–16.
Thompson, O. et al., 2012. Examining the neurocognitive
validity of commercially available, smartphone-based
puzzle games. Psychology, 3, p.525.
Tombaugh, T.N., 2004. Trail Making Test A and B:
normative data stratified by age and education.
Archives of clinical neuropsychology, 19(2), pp.203–
214.
Tong, T. & Chignell, M., 2014. Developing a serious game
for cognitive assessment: choosing settings and
measuring performance. In Proceedings of the Second
International Symposium of Chinese CHI. pp. 70–79.
Wallentin, M., 2009. Putative sex differences in verbal
abilities and language cortex: A critical review. Brain
and language, 108(3), pp.175–183.
Watkins, M.W., 2000. Cognitive profile analysis: A shared
professional myth.
Wechsler, D., 1997. WAIS-III, Wechsler Adult Intelligence
Scale: Administration and Scoring Manual,
Psychological Corporation.
Xu, G. et al., 2002. Screening for mild cognitive
impairment (MCI) utilizing combined mini-mental-
cognitive capacity examinations for identifying
dementia prodromes. International journal of geriatric
psychiatry, 17(11), pp.1027–1033.
Zucchella, C. et al., 2014. Serious games for screening pre-
dementia conditions: From virtuality to reality? a pilot
project. Functional Neurology, 29(3), pp.153–158.
Available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC42647
81/.
Zygouris, S. et al., 2014. Can a Virtual Reality Cognitive
Training Application Fulfill a Dual Role? Using the
Virtual Supermarket Cognitive Training Application as
a Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment.
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
ICT4AgeingWell2015-DoctoralConsortium
10
APPENDIX
Table 1: Categorization of the areas that make the cognitive
spectrum of a person (e.g. Allegri et al. (2000), Groth-
Marnat (2000), Hodges (2007) y of Neurology and Others
(1996)).
Cognitive area Cognitive sub-area
General General
Intellectual performance Intelligence
Attention Attention
Spatial distribution of
attention
Memory Global
Verbal episodic memory
Visual episodic memory
Working memory
Semantic memory
Procedural memory
Language Language
Visuospatial abilities Visuospatial ability
Executive functions Mental flexibility
Reasoning and abstraction Reasoning and abstraction
Table 2: Categorization or taxonomy designed to analyse
the state of the art of this research. Own development.
T
i
Field or assessment criteria
T1 Ground truth/Classic Tests
T2
Design paradigm (e.g. 1. Using existing games or 2.
Games designed from the ground up)
T3 Video games/Cognitive areas
T4 Granularity (e.g. HIGH, MEDIUM or LOW)
T5
Data Analytics (e.g. statistical, machine learning, neural
networks, etc.)
T6 Device or user interface
T7 Pilot and N (i.e. end users)
T8 Results
CognitiveAssessmentthrough"CasualVideoGames"andMachineLearning-DoctoralConsortiumContributions
11
