
Adaptive Decision-level Fusion for Fongbe Phoneme Classification using
Fuzzy Logic and Deep Belief Networks
Fr
´
ejus A. A. Laleye
1,2
, Eug
`
ene C. Ezin
1
and Cina Motamed
2
1
Unit
´
e de Recherche en Informatique et Sciences Appliqu
´
ees, Institut de Math
´
ematiques et de Sciences Physiques,
Universit
´
e d’Abomey-Calavi, BP 613, Porto-Novo, B
´
enin
2
Laboratoire d’Informatique Signal et Image de la C
ˆ
ote d’Opale, Universit
´
e du Littoral C
ˆ
ote d’Opale, 50 rue F. Buisson,
BP 719, 62228 Calais Cedex, France
Keywords:
Decision Fusion, Fuzzy Logic, Deep Belief Networks, Phoneme Classification, Naive Bayes, LVQ, Fongbe
Language.
Abstract:
In this paper, we compare three approaches for decision fusion in a phoneme classification problem. We
especially deal with decision-level fusion from Naive Bayes and Learning Vector Quantization (LVQ) clas-
sifiers that were trained and tested by three speech analysis techniques: Mel-frequency Cepstral Coefficients
(MFCC), Relative Spectral Transform - Perceptual Linear Prediction (Rasta-PLP) and Perceptual Linear Pre-
diction (PLP). Optimal decision making is performed with the non-parametric and parametric methods. We
investigated the performance of both decision methods with a third proposed approach using fuzzy logic. The
work discusses the classification of an African language phoneme namely Fongbe language and all experi-
ments were performed on its dataset. After classification and the decision fusion, the overall decision fusion
performance is obtained on test data with the proposed approach using fuzzy logic whose classification ac-
curacies are 95, 54% for consonants and 83, 97% for vowels despite the lower execution time of Deep Belief
Networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the most exciting and difficult open problem of
automatic speech recognition is enabling a recognizer
machine to perform the phoneme classification task
and to recognize the phoneme segments in a speech
signal. Phoneme classification is an integrated pro-
cess to the phoneme recognition and the first and im-
portant step in automatic speech recognition. Since
the 60s, very significant research progress and related
to the development of statistical methods and artificial
intelligence techniques, tried to overcome the prob-
lems of analysis and characterization of the speech
signal. Among the problems, there is still the acoustic
and linguistic specificity of each language. Consider-
ing the number of languages that exists, there were
some good reasons to approach the phoneme recogni-
tion problems.
The aim of the speech recognition is to convert
the acoustic signal to generate a set of words from
a phonemic or syllabic segmentation of the sentence
contained in the signal. Phoneme classification is the
process of finding the phonetic identity of a short sec-
tion of a spoken signal (Genussov et al., 2010). To
obtain good recognition, phoneme classification step
must be well achieved in order to provide acoustic
knowledge of phonemes of the given language. Like
this, phoneme classification is applied in various ap-
plications such as speech and speaker recognition,
speaker indexing, synthesis etc. and it is a difficult
and challenging problem.
In this paper, we placed the phoneme recogni-
tion problems in a classification context from multi-
ple classifiers. We have dealt with the decision-level
fusion from two different classifiers namely: Naive
Bayes and Learning Vector Quantization (LVQ).
Since the 90s, the combination of classifiers has been
one of the most sustained research directions in the
area of pattern recognition. Methods of decision-
level fusion have been successfully applied in vari-
ous areas as the recognition and verification of sig-
natures, identification and recognition of faces or the
medical image analysis. In automatic speech recog-
nition, decision-level fusion was introduced to recog-
nize phoneme, speech, speaker age and gender and
to identify language with the best performance. The
work we present in this paper deals with the phoneme
15
Laleye F., Ezin E. and Motamed C..
Adaptive Decision-level Fusion for Fongbe Phoneme Classification using Fuzzy Logic and Deep Belief Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0005536100150024
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2015), pages 15-24
ISBN: 978-989-758-122-9
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

recognition of Fongbe language which is an unres-
sourced language. Fongbe is an African language
spoken especially in Benin, Togo and Nigeria. It is a
poorly endowed language which is characterized by
a series of vowels (oral and nasal) and consonants
(oral and nasal). Its writing recently created consists
of a number of Latin characters and the International
Phonetic Alphabet. Scientific studies on the Fongbe
started in 1963. In 2010, there was the first publi-
cation of Fongbe-French dictionary (Akoha., 2010).
Since 1976, several linguists have worked on the lan-
guage and many papers are published on the linguistic
aspects of Fongbe. Until today, these works have been
aimed at the linguistic description of the language, but
less work has approached the automatic processing
with a computing perspective.
The idea behind this work is to build a ro-
bust discriminatory system of consonants and vow-
els based on decision-level fusion from independent
decisions of two classifiers. To do this, we inves-
tigated both methods of decision fusion namely the
non-parametric method using weighted combination
and parametric method using deep neural networks
and a proposed adaptive approach based on fuzzy
logic. To perform classification, we extracted from
the speech signals the popular speech features as
Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficents (MFCCs), Per-
ceptual linear prediction coefficients (PLP) and Rel-
ative Spectral Transform - Perceptual Linear Predic-
tion Coefficients (RASTA-PLP). These speech analy-
sis techniques were combined to produce coefficients
as input variables to the classifiers. Experiments
were performed on our Fongbe phoneme dataset and
showed better performance with the proposed fuzzy
logic approach. The rest of the paper is organized
as follows. In section 2, we briefly present the re-
lated work in phoneme recognition and decision fu-
sion. Section 3 presents an overview of our classifica-
tion system. In section 4, we describe the classifiers
methods and their algorithms. In section 5, the pro-
posed Fongbe phoneme classification is detailed and
explained. Experimental results are reported in sec-
tion 6. In the same section we show a detailed anal-
ysis of the used performance parameters to evaluate
the decision fusion methods. We conclude in section
7.
2 RELATED WORK
This work deals with two different issues: decision-
level fusion from multiple classifiers and phoneme
classification of a West Africa local language
(Fongbe).
2.1 Phoneme Classification
Some of the recent research works related to phoneme
classification applied to the world’s languages is dis-
cussed as follows.
In (Lung et al., 2014), the authors have proposed
an approach of phoneme classification which per-
formed better on TIMIT speech corpus, with warp
factor value greater than 1. They have worked on
compensating inter-speaker variability through Vocal
tract length normalization multi-speaker frequency
warping alternative approach. Finally, they compare
each phoneme recognition results from warping fac-
tor between 0.74 and 1.54 with 0.02 increments on
nine different ranges of frequency warping bound-
ary. Their results obtained show that performance
in phoneme recognition and spoken word recogni-
tion have been respectively improved by 0.7% and
0.5% using warp factor of 1.40 on frequency range
of 300 − 5000 Hz.
Phoneme classification is investigated for linear
feature domains with the aim of improving robust-
ness to additive noise (Ager et al., 2013). In this pa-
per, the authors performed their experiments on all
phonemes from the TIMIT database in order to study
some of the potential benefits of phoneme classifica-
tion in linear feature domains directly related to the
acoustic waveform, with the aim of implementing ex-
act noise adaptation of the resulting density model.
Their conclusion was that they obtain the best prac-
tical classifiers paper by using the combination of
acoustic waveforms with PLP+M + M + M.
In (Genussov et al., 2010), the authors integrated
into the phoneme classification a non-linear manifold
learning technique, namely ”Diffusion maps” that is
to build a graph from the feature vectors and maps
the connections in the graph to Euclidean distances,
so using Euclidean distances for classification after
the non-linear mapping is optimal. The experiments
performed on more than 1100 isolated phonemes, ex-
cerpted from the TIMIT speech database, of both
male and female speakers show that Diffusion maps
allows dimensionality reduction and improves the
classification results.
The work presented in (Palaz et al., 2013) suc-
cessfully investigates a convolutional neural network
approach for raw speech signal with the experiments
performed on the TIMIT and Wall Street Journal cor-
pus datasets. Always on the TIMIT datasets, the au-
thors in (Yousafzai et al., 2009) focused their work
on the robustness of phoneme classification to addi-
tive noise in the acoustic waveform domain using sup-
port vector machines (SVMs). The authors in (Es-
posito et al., 1998) used a preprocessing technique
ICINCO2015-12thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
16

based on a modified Rasta-plp algorithm and a clas-
sification algorithm based on a simplified Time De-
lay Neural Network (TDNN) architecture to propose
an automatic system for classifying the English stops
[b,d,g,p,t,k]. And in (Esposito et al., 1996), they
proposed an artificial Neural Network architecture to
detect and classify correctly the acoustic features in
speech signals.
Several works have been achieved on the TIMIT
dataset which is the reference speech dataset but other
works were performed on other languages than those
included in the TIMIT dataset. We can cite, for ex-
ample the following papers (Le and L, 2009; Niesler
and Louw, 2004; Schlippe and Edy Guevara Kom-
gang Djomgang, 2012; Mugler et al., 2014), where
the authors have worked respectively on Vietnamese,
Afrikaans, English, Xhosa, Hausa language and all
American English phonemes.
A state of the art on the works related to Fongbe
language present the work that has been done in the
linguistic area as most Gbe dialects. In (Agoli-Agbo
and Bernard, 2009), the authors have studied how six
Fon enunciative particles work : the six emphatic par-
ticles h...n ”hence”, sin ”but”, m ”in”, l ”I insist”, lo ”I
am warning you”, and n ”there”. Their work aimed at
showing the various and specific of these enunciative
particles. In these works (Lefebvre and Brousseau.,
2001; Akoha., 2010) listed in the Fongbe language
processing, the authors introduced and studied gram-
mar, syntax and lexicology of Fongbe.
In (LALEYE et al., 2014), the authors addressed
the Fongbe automatic processing by proposing a clas-
sification system based on a weighted combination of
two different classifiers. Because of the uncertainty
of obtained opinions of each classifier due to the im-
balance per class of training data, the authors used
the weighted voting to recognize the consonants and
vowels.
2.2 Decision-level Fusion Methods
The second issue dealt with in this work is the deci-
sion fusion for optimal Fongbe phoneme classifica-
tion. Combining decisions from classifiers to achieve
an optimal decision and higher accuracy became an
important research topic. In the literature, there are
researchers who decided to combine multiple clas-
sifiers (Rogova., 1994; Cho and Kim., 1995; Kittler
et al., 1998). Some researchers worked on mixture of
experts (Jacobs., 1995; Jacobs et al., 1991)
In decision fusion methods, there are so-called
non-parametric methods (classifiers outputs are com-
bined in a scheme whose parameters are invariant)
and the methods with learning that seek to learn and
adapt on the available data, the necessary parame-
ters to the fusion. In speech recognition, several re-
searchers have successfully adopted the decision level
fusion to recognize phoneme, speech, speaker age and
gender and to identify language. For example, the au-
thors in (A. Metallinou and Narayanan., 2010) per-
formed decision level combination of multiple modal-
ities for the recognition and the analysis of emo-
tional expression. Some authors have adopted non-
parametric methods as weighted mean (Lewis and
Powers., 2001; Iyengar et al., 2003; Neti et al., 2000)
and majority voting (Corradini et al., 2003; Pfleger.,
2004). Others have adopted parametric methods as
Bayesian inference (Pitsikalis et al., 2006; Meyer
et al., 2004; Xu and Chua., 2006) and Dempster-
Shafer method (Foucher et al., 2006).
In this work we adopted both methods to com-
pare their performance in decision fusion of classifiers
for an optimal phoneme classification of Fongbe lan-
guage. First, we performed a weighted mean, which is
a non-parametric method, to combine decisions. This
method needs a threshold value chosen judiciously
by experiment in the training stage. The second
method we used is a parametric method with learn-
ing based on deep belief networks. Deep Belief Net-
works (DBNs) have recently shown impressive per-
formance in decision fusion and classification prob-
lems (O’Connor et al., 2013). Other than these both
methods we also used an adaptive approach based on
fuzzy logic. Fuzzy logic is often used for classifica-
tion problems and recently has shown a good perfor-
mance in speech recognition (Malcangi et al., 2013).
Indeed, the limitations of the use of threshold value
that requires weighted mean is that the value is fixed
and does not provide flexibility to counter any varia-
tions in the input data. In order to overcome the lim-
itations of the threshold based weighted mean which
gives a hard output decision of which either “True” or
“false” and the time that can be taken a training pro-
cess of deep belief networks, we proposed a third ap-
proach based on fuzzy logic which can imitate the de-
cision of humans by encoding their knowledge in the
form of linguistic rules. Fuzzy logic requires the use
of expert knowledge and it is able to emulate human
thinking capabilities in dealing with uncertainties.
3 OVERVIEW OF OUR
PHONEME CLASSIFICATION
SYSTEM
The phoneme classification system consist of three
modules which are each subdivided into submodules.
AdaptiveDecision-levelFusionforFongbePhonemeClassificationusingFuzzyLogicandDeepBeliefNetworks
17
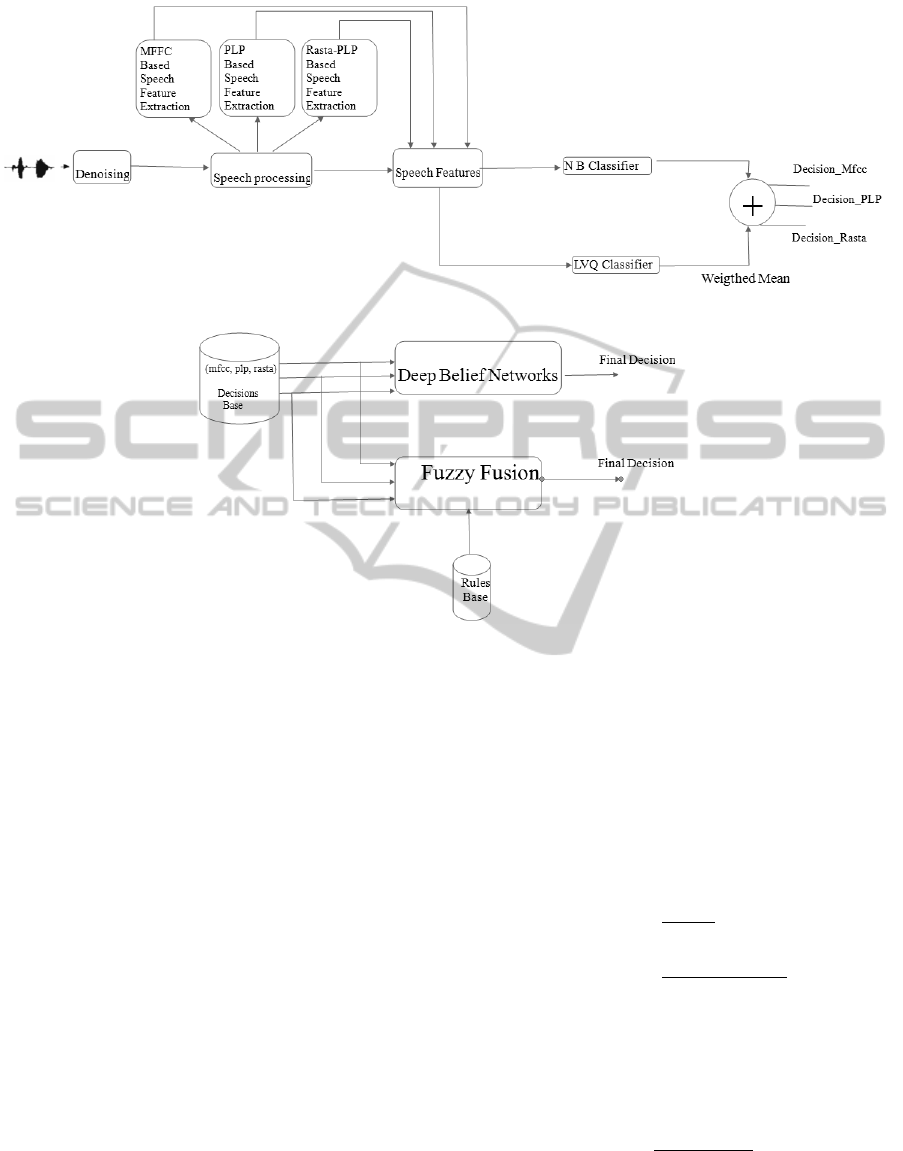
(a) Classification and standardization.
(b) Decision fusion using fuzzy logic and Deep Belief Networks.
Figure 1: Paradigm of our classification system.
The first module performs classification with Naive
Bayes and LVQ classifier and produces outputs with
the coefficients applied as input. It contains the sub-
modules which are (i) signal denoising, (ii) feature
extraction (MFCC, PLP, and Rasta-PLP), (iii) classi-
fication with Naive Bayes and LVQ. The second mod-
ule performs weighted mean calculation of classifiers
outputs and contains the submodule which is (iv) stan-
dardization for classifiers decisions database. The last
module performs in parallel the decisions fusion with
fuzzy approach that we proposed and the method with
learning based on Deep Belief Networks. Figure 1
shows the various steps of classification.
4 CLASSIFICATION METHODS
AND ALGORITHMS
4.1 Naive Bayes Classifier
Naive Bayes is a probabilistic learning method based
on the Bayes theorem of Thomas Bayes with indepen-
dence assumptions between predictors. It appeared in
the speech recognition to solve the multi-class classi-
fication problems. It calculates explicitly the proba-
bilities for hypothesis and it is robust to noise in input
data. Despite its simplicity, the Naive Bayesian clas-
sifier often does surprisingly well and is widely used
because it often outperforms more sophisticated clas-
sification methods. The Bayes classifier decides the
class c(x) of the input data x based on the Bayes rule:
p(c|x) =
p(c, x)
p(x)
(1)
=
p(c)p(x|c)
∑
c
0
p(c
0
)p(x|c
0
)
(2)
where p(c) is the prior probability of class c, and
p(x|c) is the class c-conditional probability of x.
Consider an example X = {x
1
, x
2
, ..., x
n
}
X is classified as the class C = + if and only if,
F(X) =
p(C = +|X)
p(C = −|X)
≥ 1 (3)
F(X) is a Bayesian classifier.
Naive Bayes is the simplest form of Bayesian net-
work, in which we assume that all attributes are inde-
ICINCO2015-12thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
18

pendent given the class (Zhang., 2005).
p(X|c) = p(x
1
, x
2
, ..., x
n
|c) =
n
∏
i=1
p(x
i
|c) (4)
The naive Bayesian classifier is obtained by :
F
nb
(X) =
p(C = +|X)
p(C = −|X)
n
∏
i=1
p(x
i
|C = +)
p(x
i
|C = −)
(5)
4.2 Learning Vector Quantization
Classifier
Learning Vector Quantization (LVQ) is a supervised
version of vector quantization. Networks LVQ were
proposed by Kohonen (Kohonen., 1988) and are hy-
brid networks which use a partially supervised learn-
ing (Borne et al., 2007). Figure 2 shows a representa-
tion of LVQ network which presents two layers.
Algorithm:
LVQ method algorithm can be summarized as fol-
lows:
1. Initialize the weights w
(1)
i j
to random values be-
tween 0 and 1.
2. Adjust the learning coefficient η(t)
3. For each prototype p
i
, find the neuron of the index
i
∗
which has the weight vector w
(1)
i
∗
closest to the
p
i
.
4. If the specified class at the network output for the
neuron of the index i
∗
corresponds to the proto-
type of the index i, then do:
w
(1)
i
∗
(t + 1) = w
(1)
i
∗
(t) + η(t)(p(t) − w
(1)
i
∗
(t)) (6)
else
w
(1)
i
∗
(t + 1) = w
(1)
i
∗
(t) − η(k)(p(t) − w
(1)
i
∗
(t)) (7)
5. If the algorithm has converged with the desired
accuracy, then stop otherwise go to the step 2 by
changing the prototype.
Figure 2: Representation of a network LVQ.
5 OUR FONGBE PHONEME
CLASSIFICATION
To compare the optimal decisions obtained with each
fusion approach, in a first step, we extract speech sig-
nals that are then classified into two classes (conso-
nants and vowels) by the Naive Bayes and LVQ clas-
sifiers. The outputs are then combined in the second
step to produce a single decision that is applied to the
modules of fuzzy fusion and neuronal fusion.
5.1 Speech Feature Extraction
From phoneme signals we extracted MFCC, PLP and
Rasta-PLP coefficients to perform the proposed adap-
tive decision fusion using Fuzzy approach and deep
belief networks. The benefit of using these three
types of coefficients is to expand the variation scale
from input data of classification system. This enabled
to our system to learn more acoustic information of
Fongbe phonemes. These three speech analysis tech-
niques were initially allowed to train two classifiers
and then put together to build the set of input vari-
ables to the decision fusion. Phoneme signals were
split into frame segments of length 32ms and the first
13 cepstral values were taken.
5.2 Decision Fusion using Simple
Weighted Mean
An intermediate step between the two steps was the
normalization of output data of the first step. First, we
calculated the weighted mean value of the two classi-
fier outputs for each coefficient using the expression
(8).
input
1
=
S
naivebayes
× τ
naivebayes
+ S
lvq
× τ
lvq
τ
naivebayes
+ τ
lvq
(8)
S
A
represents the output of classifier A whereas τ
A
represents the recognition rate of classifier A. Before
applying fuzzy logic and neuronal technique to fuse
the decisions of each classifier, we performed the out-
put combination based on the simple weighted sums
method using the threshold value obtained and given
by the equation 9.
τ = −1, 2
∑
i
C
i
+ 2, 75(
∑
k
w
1
k
λ
1
+
∑
k
w
2
k
λ
2
) (9)
C
i
: is the number of class i, w
1
k
: weight of classifier
k related to the class 1, w
2
k
: weight of classifier k re-
lated to the class 2, λ
1
and λ
2
are values that are 0 or
1 depending on the class. For example, for the conso-
nant class: λ
1
= 1 and λ
2
= 0. The results are com-
pared with fuzzy logic method and neuronal method
AdaptiveDecision-levelFusionforFongbePhonemeClassificationusingFuzzyLogicandDeepBeliefNetworks
19
to evaluate the performance of our phoneme classifi-
cation system.
5.3 Fuzzy Logic Based Fusion
5.3.1 Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy logic is a mathematical-linguistic approach
introduced by L.A. Zadeh in 1965 to generalize
Boolean logic which has some drawbacks. Fuzzy
logic provides a simple way to arrive at a definite con-
clusion based upon vagueness, ambiguous, imprecise,
noisy, or missing input information. Fuzzy logic mod-
els consist of a number of conditional ”if-then” rules.
The fuzzy systems convert these rules to their mathe-
matical equivalents.
5.3.2 Decision of Fuzzy Fusion
Nature of the results obtained in the first step allows
us to apply fuzzy logic on four membership functions.
The inputs to our fuzzy logic system are MFCC, PLP
and Rasta-PLP and the output obtained is the mem-
bership degree of a phoneme to consonant or vowel
class. The input variables are fuzzified into four com-
plementary sets namely: low, medium, high and very
high and the output variable is fuzzified into two sets
namely: consonant and vowel. Table 1 shows the
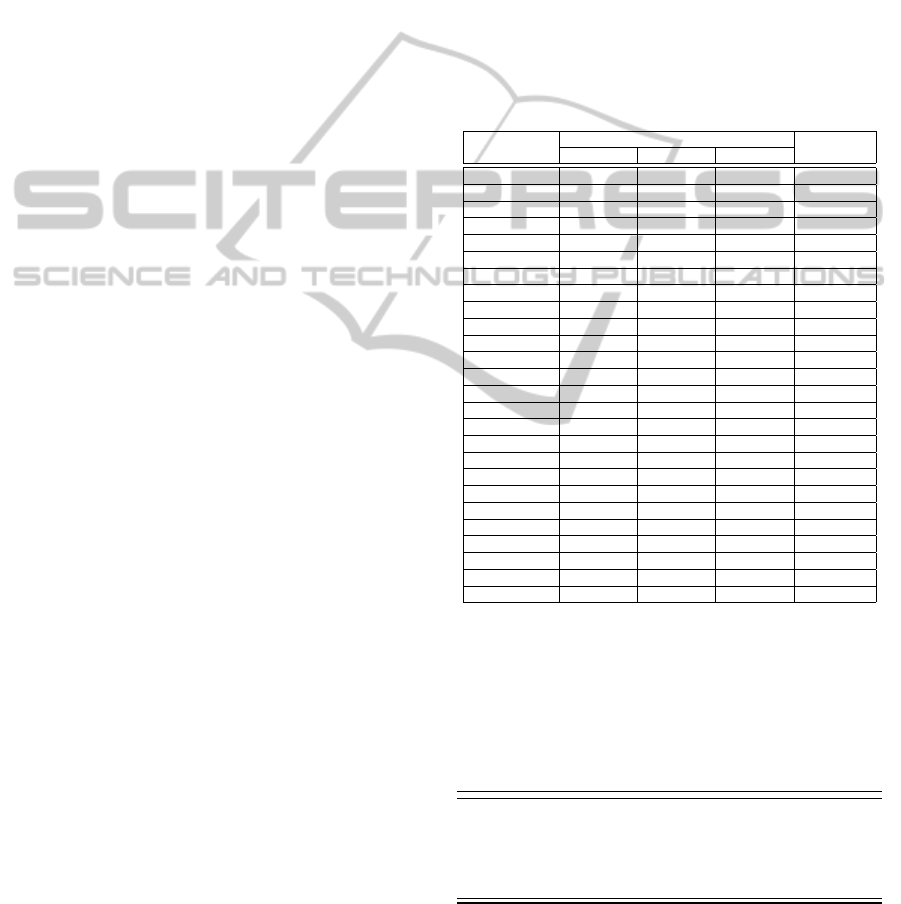
fuzzy rules which were generated after fuzzification.
First, the input data is arranged in an interval as [Xmin
.. Xmax]. The different membership functions were
obtained by examining the local distribution of sam-
ples of both classes. Local distribution has induced
four subsets according to the variation of the input
data and the output is obtained depending on the na-
ture of the data. For example, if we give MFCC, PLP
and Rasta as input to the system, the consonant or
vowel output is obtained according to the subsets of
the input data. Because of the linearity of values in
the subsets, a simple triangle curve (trimf ) is used for
low and medium membership functions and a trapeze
curve (trapmf ) is used for high and very high mem-
bership functions.
5.4 DBN Based Fusion
In this section, we describe the second method used
for decision fusion to adapt the final classification de-
cision. This method based on the use of deep belief
networks requires a learning step for a good adapta-
tion of the decisions to the system input.
5.4.1 Deep Belief Networks
DBNs are multilayered probabilistic generative mod-
els which are constructed as hierarchies of recurrently
connected simpler probabilistic graphical models, so
called Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) (Ben-
gio et al., 2006; Hinton et al., 2006). Every RBM
consists of two layers of neurons, a hidden and a vis-
ible layer. Using unsupervised learning, each RBM
is trained to encode in its weight matrix a probabil-
ity distribution that predicts the activity of the visible
layer from the activity of the hidden layer (O’Connor
et al., 2013).
Table 1: Generated fuzzy rules.
Rules No
Input Output
mfcc rasta plp
1 low low low consonant
2 low low medium vowel
3 low low high consonant
4 low medium low vowel
5 low high low consonant
6 low high high consonant
7 low very high low vowel
8 low very high very high vowel
9 medium low low vowel
10 medium low very high vowel
11 medium very high low vowel
12 medium very high very high vowel
13 high low low consonant
14 high low high consonant
15 high high low consonant
16 high high high consonant
17 very high low low vowel
18 very high low medium vowel
19 very high low high consonant
20 very high low very high vowel
21 very high medium low vowel
22 very high medium very high vowel
23 very high high high consonant
24 very high very high low vowel
25 very high very high medium vowel
26 very high very high very high vowel
5.4.2 Decision of Deep Belief Networks
To perform the classifier for making of decision we
used the DBN parameters showed in Table 2.
Table 2: DBN parameters.
RBM Layer 1 200 units
RBM Layer 2 200 units
Learning rate 0.01
Training Epochs 100
Batch size 8
5.5 Classification Algorithms
Algorithms 1 and 2 summarize the different parts of
our classifier implemented with Matlab.
ICINCO2015-12thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
20

In the algorithms description, function names give
the idea about the operation they perform and sen-
tences beginning with // represent comments. For
example, final decision 2 ← dbn f usion(all input)
means that the optimal decision given by DBN fusion
is stored in final decision 2.
Algorithm 1: Classification with Naive Bayes and
LVQ.
Data: Phoneme signals
Result: Decision of each classifier for each
extraction technique.
signal denoising;
for signal ∈ phoneme
d
atabase do
signal←denoising(signal);
base←put(signal)
end
Feature extraction;
for signal ∈ base do
m←mfcc calculation(signal);
p←plp calculation(signal);
r←rasta calculation(signal);
base mfcc←put(m);
base plp←put(p);
base rasta←put(r);
end
training←put(m,p,r);
//Classification with Naive Bayes and LVQ;
for i ← 1 to size(training) do
if i <= size(base m f cc) then
bayes m f cc decision←bayes(training(i));
lvq mfcc decision←lvq(training(i));
end
if i > size(base m f cc) and
i <= size(base m f cc)+ size(base pl p)
then
bayes pl p decision←bayes(training(i));
lvq plp decision←lvq(training(i));
end
if i > size(base m f cc)+ size(base pl p)
and i <= size(base m f cc)+
size(base pl p)+ size(base rasta) then
bayes rasta decision←bayes(training(i));
lvq rasta decision←lvq(training(i));
end
end
Algorithm 2: Decision fusion with Fuzzy logic and
Deep belief networks.
Data: Decision of each classifier for each
extraction technique.
Result: Final Decision
//calculation of recognition rate;
for j ← 1 to size(classes) and k ← 1 to
size(classi f iers) do
τ ← −1, 2
∑
i
C
i
+ 2, 75(
∑
k
w
1
k
λ
1
+
∑
k
w
2
k
λ
2
);
end
//calculation of weighted mean values as input
of fuzzy system;
for l ← 1 to 3 do
input
i
←
S
naivebayes
∗τ
naivebayes
+S
lvq
∗τ
lvq
τ
naivebayes
+τ
lvq
;
all input ← put(input
i
);
end
final decision 1
← f uzzylogicsystem(all input);
final decision 2 ← dbn f usion(all input);
6 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
AND ANALYSIS
we present different results obtained after training and
testing with two classifiers and results of decision fu-
sion with fuzzy logic approach and deep belief net-
works. Experiments were performed on phonemes
of the Fongbe language that we describe in the next
subsection. Programming was done with Matlab in
an environment which is Intel Core i7 CPU L 640 @
2.13GHz × 4 processor with 4GB memory.
6.1 Speech Data Structure
The used speech dataset were obtained by recording
different phonemes pronounced by foreigners and na-
tives speakers with a recorder in various environments
of real life. It contains 174 speakers whose ages are
between 9 and 45 years, including 53 women (chil-
dren and adults) and 119 men (children and adults). It
is an audio corpus of around 4 hours of pronounced
phonemes which includes 4929 speech signals for all
32 phonemes. 80% of speech signals in dataset is used
to construct the training data and 20% for the testing
data.
6.2 Experimental Results
6.2.1 Classification Results
LVQ parameters:
AdaptiveDecision-levelFusionforFongbePhonemeClassificationusingFuzzyLogicandDeepBeliefNetworks
21

• number of hidden neurons: 60
• first class and second class percentage: 0.6 and
0.4
• learning rate: 0.005
• number of epochs: 750
Normal distribution is used for Naive Bayes classi-
fication. Table 3 shows the training results and the
testing recognition rate..
Table 3: Training and Testing results. Values are estimated
in percentage.
Classifier MFCC RASTA-PLP PLP
C
1
C
2
C
1
C
2
C
1
C
2
Training results
Naive Bayes 88,66 51,53 90,43 59,17 88,2 68,25
LVQ 98,09 47,44 97,32 40,65 97,35 51,53
Testing results
Naive Bayes 92,29 38,34 91,48 46,04 93,10 60,24
LVQ 98,78 24,95 98,58 21,70 97,97 20,89
6.2.2 Decision Fusion Results of Classifiers
We presented in Table 4 the fusion results of used
methods.
Table 4: Results of decision fusion using fuzzy logic.
Fusion methods Consonant Vowel
Weighted mean 99,73% 54,02%
Fuzzy logic 95,54% 83,97%
Deep Belief Networks 88,84% 84,79
6.3 Performance Analysis
Several measures have been developed to deal with
the classification problem (Wang and Yao., 2009).
The values of True Positive (TP), True Negative (TN),
False Positive and False Negative were calculated af-
ter decision fusion with the different used methods.
These values are used to compute performance pa-
rameters like sensitivity (SE), specificity (SP), Likeli-
hood Ratio Positive (LRP), Accuracy (Ac) and Preci-
sion (Pr). Three other important measures are used
as evaluation metrics: F-measure, G-measure and
execution time. F-mesure considers both the preci-
sion Pr and the sensitivity SE to compute the score
which represents the weighted harmonic mean (pre-
cision&sensitivity). G-mean is defined by sensitiv-
ity and specificity and measures the balanced perfor-
mance of a learning between the positive class and the
negative class. Execution time measures the compu-
tation time of each fusion methods in the testing step.
We used the same dataset to evaluate the perfor-
mance of Naive Bayes, LVQ and the decision fu-
sion methods on consonants and vowels of Fongbe
phoneme. Table 4 shows that by considering the bal-
ance of phoneme classes, decision fusion of classi-
fiers based on fuzzy logic has achieved better perfor-
mance even if the approaches based on the weighted
mean and deep belief networks classify respectively
consonants and vowels better than fuzzy logic. We
find that fuzzy logic approach combines efficiently
the decisions and gets the optimal decision but with
an execution time increased by sixty percent com-
pared to DBN. The results in Table 5 show the highest
performances of Fuzzy logic approach on Accuracy,
F-measure and G-measure parameters which are the
chosen metrics to evaluate the performance of com-
pared methods. The best performances obtained with
fuzzy logic confirm that adding extra expert knowl-
edge improves decision making after decision combi-
nation made by multiple classifiers.
Table 5: Performance analysis. Values in bold are empha-
sized for the performance comparison.
Parameters Naive
Bayes
LVQ Using
weighted
mean
Using
Fuzzy
logic
Using
Deep
Belief
Nets
SE 0.93 0.99 0.99 0.95 0.88
SP 0.60 0.25 0.38 0.84 0.86
LRP 2.36 1.32 1.60 5.94 6.28
LRN 0.12 0.04 0.03 0.06 0.14
Ac 0.77 0.62 0.69 0.90 0.87
Pr 0.70 0.57 0.62 0.86 0.88
F-measure 0.80 0.72 0.76 0.90 0.88
G-measure 0.75 0.50 0.61 0.89 0.87
Execution
time (sec-
onds)
- - 0.10 0.7 0.04
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have compared three decision-level
fusion methods in a classification problem with mul-
tiple classifiers. The performance evaluation of deci-
sion fusion module has been achieved with the meth-
ods as weighted mean, deep belief networks and fuzzy
logic. After classification with the classifiers namely
Naive Bayes and LVQ, we combined their outputs for
making an optimal decision. The results of the accu-
racy, F-measure and G-measure parameters achieved
in Table 5, show the best performance with the pro-
posed decision fusion using fuzzy logic which uses
human reasoning. So, this paper highlights two main
results which are performance comparison of three
decisions fusion methods in a phoneme classification
ICINCO2015-12thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
22

problem with multiple classifiers and the proposal of
a robust Fongbe phoneme classification system which
incorporates a fusion of Naive Bayes and LVQ classi-
fiers using fuzzy logic approach. This proposal builds
on the performance achieved by our fuzzy logic based
approach compared to DBN based approach and es-
pecially because of the limitations of the fixed thresh-
old value in weighted combination. The future of this
work is an automatic continuous speech recognition
from phonetic segmentation in Fongbe language.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is partially supported by Association AS2V
and the Fondation Jacques De Rette, France. The
authors appreciate the help of Jonas DOUMATE for
proof-reading the paper. Fr
´
ejus A. A. LALEYE is
also grateful to Agence Universitaire de la Franco-
phonie (AUF).
REFERENCES
A. Metallinou, S. L. and Narayanan., S. (2010). Decision
level combination of multiple modalities for recogni-
tion and analysis of emotional expression. In IEEE In-
ternational Conference on Acoustics Speech and Sig-
nal Processing (ICASSP), pages 2462–24665.
Ager, M., Cvetkovic, Z., and Sollich, P. (2013). Phoneme
Classification in High-Dimensional Linear Feature
Domains. Computing Research Repository.
Agoli-Agbo, E. O. and Bernard, C. (2009). Les particules
nonciatives du fon. Institut national des langues et
civilisations orientales, Paris, 1st edition.
Akoha., A. B. (2010). Syntaxe et lexicologie du fon-gbe:
B
´
enin. Ed. L’harmattan, page 368.
Bengio, Y., P., L., D., P., and H., L. (2006). Greedy layer-
wise training of deep networks. In Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems.
Borne, P., Benrejeb, M., and Haggege., J. (2007). Les
rseaux de neurones, pr
´
esentation et applications.
TECHNIP Editions, page 90.
Cho, S.-B. and Kim., J. (1995). Combining multiple neural
networks by fuzzy integral and robust classification.
IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernet-
ics, pages 380–384.
Corradini, A., Mehta, M., Bernsen, N., Martin, J., and
Abrilian., S. (2003). Multimodal input fusion in hu-
mancomputer interaction. In NATO-ASI Conference
on Data Fusion for Situation Monitoring, Incident De-
tection, Alert and Response Management.
Esposito, A., Ezin, E., and Ceccarelli, M. (1996). Prepro-
cessing and neural classification of english stop con-
sonants [b, d, g, p, t, k]. In The 4th International Con-
ference on Spoken Language Processing, pages 1249–
1252, Philadelphia.
Esposito, A., Ezin, E., and Ceccarelli, M. (1998). Phoneme
classification using a rasta-plp preprocessing algo-
rithm and a time delay neural network : Performance
studies. In Proceedings of the 10th Italian Workshop
on Neural Nets, pages 207–217, Salerno,.
Foucher, S., Laliberte, F., Boulianne, G., and Gagnon., L.
(2006). A dempster-shafer based fusion approach for
audio-visual speech recognition with application to
large vocabulary french speech. In IEEE International
Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Process-
ing, volume 1.
Genussov, M., Lavner, Y., and Cohen, I. (2010). Classifica-
tion of unvoiced fricative phonemes using geometric
methods. In 12th International Workshop on Acoustic
Echo and Noise Control. Tel-Aviv, Israel.
Hinton, G., S., O., and Teh, Y. (2006). A fast learning algo-
rithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput, 18:1527–
1554.
Iyengar, G., Nock, H., and Neti., C. (2003). Audio-
visual synchrony for detection of monologue in video
archives. In IEEE International Conference on Multi-
media and Expo, volume 1, pages 329–332.
Jacobs., R. (1995). Methods for combining experts’s prob-
ability assessments. Neural Computation, pages 867–
888.
Jacobs, R., Jordan, M., Nowlan, S., and Hinton., G. (1991).
Adaptive mixture of local experts. Neural Computa-
tion, pages 79–87.
Kittler, J., Hatef, M., Duin, R., and Matas., J. (1998). On
combining classifiers. IEEE Transactions on Patterns
Analysis and Machine Intelligence, pages 226–239.
Kohonen., T. (1988). An introduction to neural computing.
Neural Networks, 1:3–16.
LALEYE, F. A. A., EZIN, E. C., and MOTAMED, C.
(2014). Weighted combination of naive bayes and lvq
classifier for fongbe phoneme classification. In Tenth
International Conference on Signal-Image Technol-
ogy & Internet-Based Systems, pages 7 – 13, Mar-
rakech. IEEE.
Le, V.-B. and L, B. (2009). Automatic speech recognition
for under-resourced languages: Application to viet-
namese language. In IEEE Transactions on Audio,
Speech, and Language Processing, pages 1471–1482.
IEEE.
Lefebvre, C. and Brousseau., A. (2001). A grammar of
fonge, de gruyter mouton. page 608.
Lewis, T. W. and Powers., D. M. (2001). Improved speech
recognition using adaptive audio-visual fusion via a
stochastic secondary classifier. International Sym-
posium on Intelligent Multimedia, Video and Speech
Processing, 1:551–554.
Lung, J. W. J., Salam, M. S. H., Amjad Rehman, M. S.
M. R., and Saba, T. (2014). Fuzzy Phoneme Classi-
fication Using Multi-speaker Vocal Tract Length Nor-
malization. IETE Technical Review, London, 2nd edi-
tion.
Malcangi, M., Ouazzane, K., and Patel, K. (2013). Audio-
visual fuzzy fusion for robust speech recognition. In
The 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural
Networks (IJCNN), pages 1 – 8, Dallas. IEEE.
AdaptiveDecision-levelFusionforFongbePhonemeClassificationusingFuzzyLogicandDeepBeliefNetworks
23

Meyer, G., Mulligan, J., and Wuerger., S. (2004). Contin-
uous audio-visual digit recognition using n-best deci-
sion fusion. Information Fusion, 5:91–101.
Mugler, E. M., Patton, J. L., Flint, R. D., Wright, Z. A.,
Schuele, S. U., Rosenow, J., Shih, J. J., Krusienski,
D. J., and Slutzky, M. W. (2014). Direct classification
of all american english phonemes using signals from
functional speech motor cortex. J. Neural Eng.
Neti, C., Maison, B., Senior, A., Iyengar, G., Decuetos, P.,
Basu, S., and Verma., A. (2000). Joint processing of
audio and visual information for multimedia index-
ing and human-computer interaction. In Sixth Inter-
national Conference RIAO. Paris, France, pages 294–
301.
Niesler, T. and Louw, P. H. (2004). Comparative phonetic
analysis and phoneme recognition for afrikaans, en-
glish and xhosa using the african speech technology
telephone speech database. In South African Com-
puter Journal, pages 3–12.
O’Connor, P., Neil, D., SC, L., Delbruck, T., and Pfeiffer,
M. (2013). Real-time classification and sensor fusion
with a spiking deep belief network. Front. Neurosci.
Palaz, D., Collobert, R., and Magimai.-Doss, M. (2013).
End-to-end phoneme sequence recognition using con-
volutional neural networks. Idiap-RR.
Pfleger., N. (2004). Context based multimodal fusion. In
ACM International Conference on Multimodal Inter-
faces, pages 265–272.
Pitsikalis, V., Katsamanis, A., G.Papandreou, and Mara-
gos., P. (2006). Adaptive multimodal fusion by un-
certainty compensation. In Ninth International Con-
ference on Spoken Language Processing. Pittsburgh,
volume 7, pages 423–435.
Rogova., G. (1994). Combining the results of several neu-
ral networks classifiers. Neural Networks, pages 777–
781.
Schlippe, T. and Edy Guevara Komgang Djomgang, Ngoc
Thang Vu, S. O. T. S. (2012). Hausa large vocabulary
continuous speech recognition. In The third Interna-
tional Workshop on Spoken Languages Technologies
for Under-resourced Languages, Cape-Town.
Wang, S. and Yao., X. (2009). Diversity analysis on im-
balanced data sets by using ensemble models. IEEE
Symp.Comput. Intell. Data Mining, pages 324–331.
Xu, H. and Chua., T. (2006). Fusion of av features and ex-
ternal information sources for event detection in team
sports video. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Com-
mun. Appl., 2:44–67.
Yousafzai, J., Cvetkovic, Z., and Sollich, P. (2009). Tun-
ing support vector machines for robust phoneme clas-
sification with acoustic waveforms. In 10th Annual
conference of the International Speech communica-
tion association, pages 2359 – 2362, England. ISCA-
INST SPEECH COMMUNICATION ASSOC.
Zhang., H. (2005). Exploring conditions for the optimality
of nave bayes. IJPRAI, 19:183–198.
ICINCO2015-12thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
24
