
Multiple Model SPGPC for Blood Pressure Control
Humberto A. Silva
1
, André L. Maitelli
2
, Celina P. Leão
3
and Eurico A. Seabra
4
1
Instituto Federal de Ciencia e Tecnologia do Rio Grande do Norte, Natal, RN, Brazil
2
Departamento de Engenharia de Computação e Automação,
Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Natal, RN, Brazil
3
Departamento de Produção e Sistemas, Escola de Engenharia da Universidade do Minho, Guimarães, Portugal
4
Departamento de Engenharia Mecânica, Escola de Engenharia da Universidade do Minho, Guimarães, Portugal
Keywords: Blood Pressure Control, Predictive Control, Multi-Model, Smith Predictor.
Abstract: Multiple model adaptive control procedures have been considered for a computer-based feedback system,
which regulates the infusion rate of a drug (nitroprusside) in order to maintain the blood pressure as close as
possible to the desirable value. Transfer function parameters can differ significantly between patients, and
also time-dependent, so the development of a suitable algorithm becomes required not only for maintaining
steady-state but also the transient specifications. In this paper, based on computer simulations, a multiple
model adaptive control procedures show to be successfully applied to blood pressure control, despite the
uncertainty related with delays, time constant and gains associated.
1 INTRODUCTION
Arterial hypertension is an important risk factor
responsible to cause cardiovascular diseases, begin
responsible for 40% of the deaths caused by
coronary arterial disease. Twenty-nine percent
(29%) of the world’s population has arterial
hypertension with Brazil contributing to 22% to
44%, depending on the region (Mion et al., 2010).
These numbers become very important as high blood
pressure is directly associated to cerebrovascular
events, coronary arterial disease and mortality
(Kochar and Woods, 1990).
Postsurgical complications of hypertension can
occur, or to be aggravated, in cardiac patients. To
decrease the probability of complications it is
necessary to reduce, at the earliest stage possible, the
elevated blood pressure. A way to reach this
objective is to use a continuous infusion of
vasodilator drugs, such as sodium nitroprusside
(SNP), that can quickly lower the blood pressure in
most patients, bearing in mind that an overdose of
nitride could cause toxic side effects.
It is known that each patient has a different SNP
sensibility, and therefore it can also be time-
dependent. So, it is necessary to establish an
appropriate control of the infusion rate of SNP to
accomplish the desired blood pressure. To maintain
the desired blood pressure, a constant monitoring of
arterial blood pressure is required and a frequently
adjust on drug infusion rate. Manual control of
arterial blood pressure by clinical personnel it is
very demanding and time consuming, usually
leading to a poor control quality of the hypertension.
The objective of this paper is to develop an
adaptive method control for a blood pressure
management for any patient without changing the
controller. Blood pressure control of a patient under
the influence of SNP, that is a vasodilator, is
modelled through an uncertain model (Slate, 1980;
Maitelli and Yoneyama, 1997). A multi-model
approach is used in order to control the blood
pressure under the influence of this drug. Multi-
model approaches are commonly applied to control
non-linear systems that operates in long ranges
(Cavalcanti et al., 2007; Cavalcanti et al., 2009;
Silva et al. 2010; Silva, 2010). The basic idea of
multi-model approach consists in decompose the
system’s operating range into a number of operating
regimes that completely cover the chosen trajectory
(Cavalcanti et al., 2009). There are, basically, two
approaches for multi-model. The first one consists of
designing a set of suitable controllers (one for each
operating regime) and to calculate weighting factors
to them as showed by the study by Cavalcanti et al.
(2009). The global control signal is a weighting sum
of the contributions of each controller. The second
563
Silva H., Maitelli A., Leão C. and Seabra E..
Multiple Model SPGPC for Blood Pressure Control.
DOI: 10.5220/0005540805630568
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2015), pages 563-568
ISBN: 978-989-758-122-9
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

one consists of building a global model as a
weighting sum of each local model as showed in
(Cavalcanti et al., 2009). In both cases, a way to
measure distances between models is defined.
In this work, a multi-model is used to control the
blood pressure control. A set of models is chosen
and a Smith Predictor Generalized based Predictive
Control (SPGPC) is designed for each chosen
model. A validity function is defined in order to
calculate the weight of each controller. The weight
factor selected considers the residual error between
the output of a given model and the plant (patient)
output.
2 PROBLEM FORMULATION
A model of the mean arterial pressure (MAP) of a
patient under the influence of sodium nitroprusside
can be represented, as in Slate (1980), by:
0
() () ()
M
AP t P P t v t
(1)
where MAP is the mean arterial pressure, P
o
is the
initial blood pressure, also called a background
pressure, ∆P(t) is the pressure differential due to
infusion of Nipride, and v(t) is a stochastic
background noise. In this paper it is assumed that P
o
is constant. A continuous-time deterministic model
describing the relationship between the change in the
blood pressure and drug infusion rate (Slate, 1980) is
as follows:
(1 )
() ()
1
ic
Ts T s
Ke e
P
sIs
s
(2)
where ∆P(s) is the blood pressure variation, I(s) is
the infusion rate, K is drug sensitivity, α is the
recirculation constant, T
i
is the initial transport
delay, T
c
is the recirculation time delay, and τ is a
time constant.
The corresponding discrete-time deterministic
model for this process can be given as follows:
1
1
()
() (); 0
1
dm
om
o
qbbq
Pt It b
aq
(3)
where
1
q
denotes a unit delay operator. The
parameters b
o
, b
m
, a
1
, d, and m are obtained from the
sampled version of the continuous-time model given
in (2).
A range of typical values for the parameters of
the model (2) for different patients is given by Slate
(1980). Values for the parameters in the model (3)
for the case with the sampling time 15 s are found in
Table 1.
Table 1: Range of values for parameters of the discrete-
time deterministic plant model for sampling time of 15 s.
Parameter Minimum Maximum Nominal
b
o
0.053 3.546 0.187
b
m
0 1.418 0.075
a
1
0.606 0.779 0.741
d 2 5 3
m 2 5 3
It can be seen that there is a considerable
difference in the parameter values, including the
pure time delay, for different patients. For a given
patient, time delays are unknown, but are assumed to
be constant over a long period of time. The
parameters b
0
, b
m
and a
1
, however, change during
the infusion procedure. In this work, it is assumed
that the parameters change in an exponential
manner. The change of parameters is modeled as
follows (Pajunen et al., 1990):
)2)(0()(
/
t
epartpar
(4)
for increase and decrease in the parameter value,
respectively, where par(t) represents the parameter
of the continuous-time model and
is the change
time constant. Thus, the controller when turned for a
particular patient, should be able to handle time-
varying parameters and initially unknown time
delays. An automated drug SNP infusion system for
blood pressure control should produce good
response characteristics, such as pressure undershoot
(i.e., maximum excursion below commanded level)
less than 10 mmHg, 20 percent settling time of 5-10
min, steady-state error within +5 mmHg, and also
satisfy the following clinical conditions (Slate,
1980), where:
U
M
= maximum infusion rate (ml/hr);
W
p
= patient weight (kg);
i
M
= maximum recommended dose (
11
10 . mingkg
);
C
S
= drug concentration (
/
g
ml
).
For patient safety, the infusion rate should be
reduced under hypotension, i.e., when there is a drop
in excess of 20 mmHg from the set point.
3 SMITH PREDICTOR BASED
GENERALIZED PREDICTIVE
CONTROL (SPGPC)
The Smith Predictor (SP) was the first control
system proposed in the literature that introduces a
ICINCO2015-12thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
564

delay compensator (Smith, 1957). The SP improves
the performance of a system with a delay compared
to other techniques, such as PID, especially when
the delay is dominant (greater than twice the
dominant time constant of the system).
The idea of using a Smith predictor instead of an
optimal predictor in generalized predictive
controllers for stable plants was presented in
Normey-Rico and Camacho (1996). The advantages
in the use of this control strategy instead of the
standard Generalized Predictive Control (GPC) in
real applications was also shown in Normey-Rico et
al. (1998). This has great interest in the case of time-
delay systems. These authors have shown that, by
modifying the GPC algorithm, it is possible to
improve the robustness of the closed-loop system
while maintaining the nominal performance. The
basic idea of the Smith predictor based generalized
predictive control (SPGPC) is to use a Smith
predictor structure to compute the predictions of the
output of the plant and to calculate a sequence of
future control signals in order to minimize a
multistage cost function defined over a control
horizon, as follows:
dN
j
N
Nj
jtuj
jtwtjtyjNNJ
2
2
1
1
2
2
21
)]1()[(
)]()|(
ˆ
)[(),(
(5)
where N
1
and N
2
are the minimum and maximum
costing horizons, respectively, d is the delay of the
process model, δ(j) and λ(j) are weighting sequences,
w(t+j) is a future set-point or reference sequence,
∆u(t) is the incremental control action (∆u(t) = u(t)-
u(t - 1)) and
y
ˆ
(t+j|t) is the j-step ahead prediction
of the system output on data up to time t computed
using the following model of the plant:
)1()()()(
11
tuzBztyzA
d
(6)
where
nb
nb
na
na
zbzbzbbzB
zazazazA
2
2
1
10
1
2
2
1
1
1
)(
1)(
(7)
Using this procedure, the final control law can be
written as:
(8)
where ly
i,
lu
i
and f
i
are constants and the prediction of
the output of the plant is computed using the
prediction of the output using the open loop model
of the plant given in (6). Moreover, a correct
prediction in each open loop can be used, by adding
the mismatch between the output and the prediction:
)(
ˆ
)(
)|(
ˆ
)|(
ˆ
ityity
tidtytidty
(9)
To compute the coefficients of the control law in (8),
the same procedure as in the GPC is used. First,
consider that the horizons N
1
and N
2
are computed as
N
1
=d+1 and N
2
=N+d where d is the dead time of
the plant model. Then, using these horizons, the
prediction of the output of the plant is computed
using an incremental model of the process
(Camacho, 2003).
4 MULTIPLE MODEL SPGPC
METHOD
The Multiple Model SPGPC (MMSPGPC)
procedure, shown in Figure 1, is based upon the
assumption that the plant can be represented by a
finite number of models and, for each model a
controller can be priori designed.
An adaptive mechanism is then need to decide
which controller should be dominant for a given
plant. One procedure for solving this problem is to
considered a weighted sum of all the controller
outputs, where the weighting factors are determined
by the relative residuals between the plant response
and the model responses (Silva et al., 2010).
In Figure 1, since the plant gain is negative, the
system error is expressed as:
(10)
where k is the sampling time and p
c
, is the
commanded or set-point pressure level.
4.1 Model Bank Design
The model bank consists of a number of models with
constant parameters characterizing the individual
plant subspace (He et al., 1986). Since these models
should have the same structure as the plant, the
following discrete model will describe them:
(j=1, ..., N)
(11)
where the output pressure from model j is:
c
pkpke
)()(
0);(
1
)(
)(
1
1
0
oj
j
m
mjj
d
mj
bku
qa
qbbq
kP
MultipleModelSPGPCforBloodPressureControl
565

Figure 1: Multi-model SPGPC schema.
0
)()( PkPkP
mjmj
(j=1,…,N)
(12)
where ∆P
mj
(k)is the change in the jth model output,
u(k) is the model input, P
0
is the initial value of each
model’s output and equals the initial plant output.
The relative residual R
j
2
(k) will be defined as the
normalized squared error between plant and model,
i.e., as follows:
22
0
() {[ () ()]/( )}
jmj c
Rk Pk Pk P P
(j=1,…,N)
(13)
At each sample time k, the model that has the
smallest residual is defined as the matching model,
which is used to represent the plant characteristics.
4.2 Control Algorithm
To reach desirable system performance and to
guarantee patient safety, the control algorithm
should converge quickly to the optimal values and
should react to time varying plant characteristics, as
well as ensure a reasonable rate of blood pressure
change. Thus, the control was computed as a
weighted sum of controller bank signals, and
represented by the following equation:
1
() () ()
N
cij
j
uk Wkuk
(14)
where N is the number of models, u
c
(k) is the control
variable, u
j
(k) are the individual controller outputs
and W
j
(k) are the weighting factors. The weights
were selected as follows:
1. Recursive update
22
'
22
1
exp[ / 2 ] ( 1)
()
exp[ / 2 ] ( 1)
jj
j
N
ii
i
RVWk
Wk
RVWk
(15)
2. Bounding away from zero
''
'
() ()
()
()
jj
j
j
Wk Wk
Wk
Wk
(16)
3. Normalization
2
2
1
[()]
()
[()]
j
j
N
i
i
Wk
Wk
Wk
(17)
where R
j
(k) are the residuals and defined in (13), V is
a parameter controlling the convergence rate of
W'j(k) with R
j
(k) and δ is a threshold to limit the
importance of past information.
Equations (14) and (15) express the basic
relationship between the control, the weighting
factors, and the relative residuals. Equation (16) is
used to delimit the importance of past information
enabling the adaptive mechanism quickly react to
the new information about the plant characteristics.
ICINCO2015-12thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
566
Equation (17) is used to normalize the weighting
factors so that their square sum is equal to unity.
5 SIMULATION RESULTS
Computer simulations were used to evaluate the
response of the system design (Section 4) over a
representative plant parameter envelope. Of interest
were the response to step command in the presence
of plant background noise, the adaptation of the
algorithm to time-varying plant parameter.
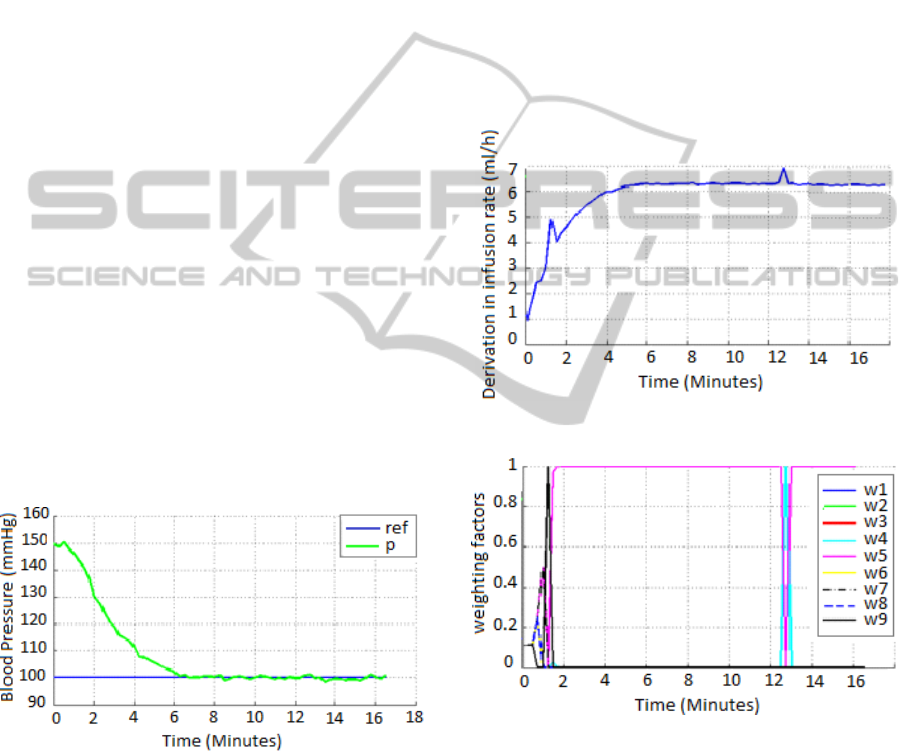
The regime blood pressure considered was 150
mmHg and the multi-model controller deviation
reference of -50 mmHg. The plant background noise
v(t) was simulated as a white Gaussian noise
sequence with standard deviation of 2 mmHg. Figure
2 shows the blood pressure of a given simulated
patient, with time varying parameters, calculated by
the Equation (4). Figure 3 shows the deviation in
infusion rate.
Simulations results have shown the convergence
process of the weighting factors W
j
(k), in Figure 4,
such as the global control effort is calculated to the
closest model (less residual error). Figure 2 shows
that the schema leads the blood pressure of the
chosen patient to the given reference. Thus, the drug
infusion rate and the blood pressure both change in a
smooth manner. These responses also show that the
MMSPGPC algorithm is robust even in the presence
of the plant background noise.
Figure 2: blood pressure (mmHg).
6 FINAL REMARKS
The results showed that this multi-model schema
MMSPGPC presented has a great potential of
application in uncertain systems. Even in presence
of representative noise background, the presented
approach has shown a reasonable result and could be
applied, as first approach, in tests with animals.
Others basic controllers, in order to attenuate the
delay effect, may be considered.
The results also show that the controller using
GPCs with Smith predictor, in the controllers bank,
provides a faster control (in the order of 6 min) and
with a reasonable rate of infusion, compared to the
results obtained in Cavalcanti et al. (2009), that used
only GPCs in the controllers bank, with an obtained
response times of 20 min.
In the future, robustness tests can be
implemented with the submission of the system to a
larger range of disturbances and parameters.
Comparative studies with other control algorithms,
as adaptive control, they would also be important to
accomplish.
Figure 3: deviation in infusion rate.
Figure 4: weighting factors.
REFERENCES
Camacho, E. F., Bordons, C., 2003. Model Predictive
Control, (2ª Ed., Chap. 4, pp. 47-77), Spain: Springer.
Cavalcanti, A. L., Fontes, A. B., Maitelli, A. L., 2007.
Generalized Predictive Control Based in Multivariable
Bilinear Multimodel. Proceedings of 8th International
IFAC Symposium on Dynamics and Control of
Process Systems, pp. 91-96, Cancún.
MultipleModelSPGPCforBloodPressureControl
567

Cavalcanti, A. L., Silva, H. A., Maitelli, A. L., 2009.
Multiple Model GPC for Blood Pressure Control. XVI
Congresso Internacional De Ingenieria Eletrónica,
Eléctrica Y Computación, INTERCON, Arequipa,
Peru.
He, W. G., Kaufman, H., Roy, R., 1986. Multiple Model
Adaptive Control Procedure for Blood Pressure
Control. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical
Engineering, vol. BME 33, no. 1.
Kochar, M. S.,Woods, K. D., 1990. Controle da
hipertensão: para enfermeiras e demais profissionais
da saúde.. 2. ed. São Paulo: Andrei, 317 pp.
Maitelli, A. L.,Yoneyama, T., 1997.Suboptimal Dual
Adaptive Control for blood pressure management.
IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol.
44, no. 6.
Mion, Jr. D., CA. Machado, M. Gomes et al., 2010. VI
diretrizes brasileiras de hipertensão arterial. Brazilian
Journal of Hypertension, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 2-19.
Normey-Rico, J. E., Camacho, E. F., 1996. A Smith
Predictor Based Generalized Predictive Controller.
Technical Report GAR 02-96, University of Seville.
Normey-Rico, J. E., Camacho, E. F., Gomez-Ortega, J.,
1998. A Smith Prediction Based Generalized
Predictive Controller for Mobile Robot Path Tracking.
III IFAC Symposium on Intelligent Autonomous
Vehicles, Madri, Spain, pp. 471-476.
Pajunen, G. A., M. Steinmetz, R. Shankar, 1990. Model
Reference Adaptive Control with Constraints for
Postoperative Blood Pressure Management, IEEE
Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 37, no.
7, pp. 679-687.
Silva, H. A., Cavalcanti A. L. O., Maitelli, A. L., 2010.
SPGPC Multi-Modelo para controle de Pressão
Arterial. XVIII Congresso Brasileiro de Automática,
CBA, Bonito, MS, Brazil.
Silva, H. A., 2010. Multi-Model Generalized Predictive
Controller Applied to Blood Pressure Control (in
portuguese). Master's Thesis, Department of Electrical
and Computer Engineering, Universidade Federal do
Rio Grande do Norte, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil.
Slate, J. B., 1980. Model-based design of a controller for
infusing nitroprusside during postsurgical
hypertension. PhD thesis, University of Wisconsin-
Madison.
Smith, O. J. M., 1957. Closed control of loops with dead-
time. Chemical Engineering Process, 53: 217-219.
ICINCO2015-12thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
568
