
Computational Correction for Imaging through Single Fresnel Lenses
Artem Nikonorov
1,2
, Sergey Bibikov
1,2
, Maksim Petrov
1
, Yuriy Yuzifovich
1
and Vladimir Fursov
1,2
1
Samara State Aerospace University, 34 Moskovskoe shosse, Samara, Russian Federation
2
Image Processing Systems Institute of the RAS, 151 Molodogvardeyskaya str., Samara, Russian Federation
Keywords: Fresnel Lens Imaging, Chromatic Aberration, Deconvolution, Deblur, Sharping, Color Correction, Total
Variance Deblur.
Abstract: The lenses of modern single lens reflex (SLR) cameras may contain a dozen or more individual lens elements
to correct aberrations. With processing power more readily available, the modern trend in computational
photography is to develop techniques for simple lens aberration correction in post-processing. We propose a
similar approach to remove aberrations from images captured by a single imaging Fresnel lens. The image is
restored using three-stage deblurring of the base color channel, sharpening other and then applying color
correction. The first two steps are based on the combination of restoration techniques used for restoring images
obtained from simple refraction lenses. Color correction stage is necessary to remove strong color shift caused
by chromatic aberrations of simple Fresnel lens. This technique was tested on real images captured by a simple
lens, which was made as a three-step approximation of the Fresnel lens. Promising results open up new
opportunities in using lightweight Fresnel lenses in miniature computer vision devices.
1 INTRODUCTION
Modern camera lenses have become very complex.
They typically consist of a dozen elements or more
necessary to remove optical aberrations (Meyer-
Arendt, 1995). Recently, simple lenses with one or
two optical elements were proposed (Heide et al.,
2013). These lenses are similar to lenses used
hundreds years ago, and chromatic aberration is still
an issue for images captured using simple lenses
(Heide et al., 2013). This aberration can now be
corrected with digital processing.
A chromatic aberration is a correlation between
optical system characteristics and a wavelength of the
registered light. Chromatic aberrations result in a
chroma in achromatic objects and/or in coloring the
contours.
Lens producers use special arrays of low-
dispersing elements to negate aberrations in imaging
elements. The weight of these complex lenses may
vary from 400 to 800 grams, sometimes as much as
1500 grams. Algorithmic solutions for the aberration
problem were proposed (Powell, 1981; Farrar et al.,
2000; Millan et al., 2006; Fang et al., 2006).
Chromatic aberrations in distorted images can be
computationally corrected with two methods: with
the blind or semi-blind deconvolution using PSF
estimation, and with a contour analysis in different
color channels (Chung et al., 2010). In (Kang, 2007),
a combination of these two is used.
Aberration model in this case is derived as a
generalization of an optical system defocus model.
Well known Richardson and Lucy proposed an
iteration deconvolution method for optical defocus
compensation in astronomical observations. In recent
years, a modified approach was used to correct
chromatic aberration (Kang, 2007; Cho et al., 2010;
Cho et al., 2012).
We use both correction methods to improve
images obtained with Fresnel lenses. This type of lens
(Soifer, 2012) can be defined as a stepped
approximation of the Fresnel lens (Fig. 1), when a
Fresnel lens is created by consecutive etching with
different binary masks.
Fresnel lenses have advantages over refractive
lenses in weight and linear size, especially
pronounced for long focal lengths, where a single
Fresnel lens can replace a complex set of refractive
lenses. However, this comes at a cost: resulting
images are blurred depending on the light wavelength
and have multiple distortions such as moiré. As a
result, Fresnel lenses are typically used as optical
collimators or concentrators but not as imaging lens
(Davis and Kuhnlenz, 2007).
Fresnel lenses have much stronger chromatic
aberrations than simple refractive lenses do, which
68
Nikonorov A., Bibikov S., Petrov M., Yuzifovich Y. and Fursov V..
Computational Correction for Imaging through Single Fresnel Lenses.
DOI: 10.5220/0005543300680075
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications (SIGMAP-2015), pages 68-75
ISBN: 978-989-758-118-2
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

need to be corrected in post-processing. One of the
color channels (in this paper we use the green
channel) has less blurring and can be used as a
reference to correct the other two channels.
If color aberrations can be corrected, Fresnel
lenses can be used as imaging lenses. In this paper we
propose the model for correcting chromatic
aberrations in the images obtained with Fresnel
lenses, followed by the deconvolution, edge analysis
and color correction. Finally, we present correction
results for images captured using lens manufactured
as a three-step approximation of Fresnel surface.
Figure 1: Conceptual illustration of collapsing aspheric
refraction lens into Fresnel lens.
2 IMAGE CORRECTION FOR
FRESNEL LENSES
A Fresnel lens typically adds a strong chromatic
distortion in the non-monochromatic light. For any
wavelength further away from the base wavelength
λ
0
, diffraction efficiency of the zero order decreases.
The light focused in the zero order creates an
additional chromatic highlight. This highlight
becomes stronger as the wavelength deviates from λ
0
.
Diffraction efficiency of zero order can be expressed
as:
21
0
cos 1 ,nh
(1)
where
is transmittance coefficient in the zero order
direction,
0
total lens transmittance coefficient,
h
-
height of Fresnel lens microrelief,
n – refraction
index. We will call the color highlights caused by the
energy focused in non-working diffraction orders as
chromatic shift, in addition to the chromatic
aberration. Chromatic aberration leads to color fringe
along the edges and the color shift distorts colors of
uniform colored areas of the image.
Chromatic aberration in refraction lenses is
described by the general defocus model (Heide et al.,
2013). In this model, the point spread function (PSF)
is supposed to be linear, at least in the local spatial
area, as shown in:
0
n,
B
RGB RGB
pp
xB x
(2)
where
B
RGB
p x
is the one of color channels of the
blurred image, and
0
RGB
p x
is the corresponding
channel of the underlying sharp image,
B
is a blur
kernel, or PSF,
n
is additive image noise,
2
x
is
a point in image spatial domain.
Paper (Shih et al., 2012) shows that the lens PSF
varies substantially being a function of the aperture,
the focal length, the focusing distance, and the
illuminant spectrum. So, a blur kernel
B
in (2) being
a constant is not accurate enough, especially for
Fresnel lenses with strong chromatic aberration.
For this strong aberration, a kernel
B
is space-
varying. There are two distortion types in the image:
a space-varying blur along the edges and a color shift
in the regions with plain colors. Therefore, to handle
these distortions, we use the following modification
of (2):
,
n,
DB D
RGB RGB RGB
pp
xB x
(3)
0
.
D
RGB RGB RGB
pDpxx
(4)
Here
,DB
RGB
p x
are color channels of the image
captured with Fresnel lens;
0
RGB RGB
Dpx
is a
component characterizing the color shift, caused by
the energy redistribution between diffraction orders.
Blurring kernels
R
GB
B in (3) are different for different
color channels; let us call these kernels the chromatic
blur.
According to (3), the correction consists of two
stages – removing the chromatic blur and the
correction of the color shift. To correct chromatic blur
we will use both deconvolution and sharpening. At
first, we obtain a deblurred green channel, the
sharpest one, by a deconvolution:
1,DDB
GGG
pp
xB x
(5)
Here operation
1
G
B
is a deconvolution for the
chromatic deblurring, with an intermediate image
D
G
p
x
as a result.
Then we apply sharpening to red and blue
channels using the deblurred green channel as the
guidance image:
,
,.
DDBD
RB RB G
pSppxxx
(6)
Finally, we apply color correction to the obtained
image:
,.
DD
RGB RB G
pFppxxx
(7)
ComputationalCorrectionforImagingthroughSingleFresnelLenses
69

,
DD
RB G
Fp pxx
is a color correction
transformation. Similar to sharpening, we use
information available in the green channel to correct
color shift in red and blue channels.
Combining the above steps, we propose the
following technique based on model (3)-(4):
1) the chromatic deblurring (5) of the green
channel based on the deconvolution, described in
Section 3);
2) the chromatic sharpening (6) of the blue and red
channels using the contours analysis (this approach is
described in Section 4);
3) the color correction (7) to remove color shift,
which is described in Section 5.
3 DECONVOLUTION BASED
CHROMATIC DEBLURRING
To solve the image deconvolution problem (6), we
base our optimization method on the optimal first-
order primal-dual framework by Chambolle and Pock
(Chambolle and Pock, 2011), whose original paper
we recommend for an in-depth description. In this
section, we present a short overview of this
optimization.
Let X and Y be finite-dimensional real vector
spaces for the primal and dual space, respectively.
Consider the following operators and functions:
:X YK is a linear operator from X to Y;
:X [0, )G is a proper, convex, (l.s.c.)
function;
:Y [0, )F is a proper, convex, (l.s.c.)
function, where l.s.c. stands for lower-
semicontinuous.
The optimization framework considers general
problems of the form
ˆ
arg min
x
xFKxGx
(8)
To solve the problem in the form (8), the
following algorithm is proposed in the paper
(Chambolle and Pock, 2011).
Initialization step: choose -
, R
,
[0,1]
,
00
,XYxy
– some initial approximation,
00
xx.
Iteration step:
0n , iteratively update ,,
nnn
xyx
as follows:
1*nFnn
prox
yy
Kx
(9)
*
11nnn
prox
G
xxKy
(10)
11 1nn nn
xx xx
(11)
Following paper (Chung et al., 2010), a proximal
operator with respect to G in (8), is:
1
2
2
ˆˆ
1
ˆ
arg min ,
2
prox
G
x
xEGx
xx Gx
(12)
where E is identity matrix. The proximal operator in
(9)
*
F
prox
is the same.
In order to apply the described algorithm to the
deconvolution model, we follow (Chambolle, 2011):
1
F ii
(13)
2
2
Gi i jB
(14)
Using (13) and (14), it is possible to obtain the
proximal operators for steps (9) and (10) of the
algorithm. Further details are available in
(Chambolle, 2011). The deconvolution algorithm
based on the total variance can preserve sharp edges.
This deconvolution step is applied to the sharpest
channel of the distorted image. The other two
channels are restored using an edge processing
procedure described in the next section.
4 COLOR CONTOURS
PROCESSING
We propose a modification of the algorithm (Chung
et al., 2010) to sharpen red and blue channels based
on the deblurred green channel. This algorithm makes
transition areas along the edges in red and blue
channels look similar to transition areas in the green
channel. An example of this area is shown in Fig. 2.
For this algorithm to work properly, edges must be
achromatic. While this is not always the case, we
must rely on this assumption because we need to get
strong chromatic blur removed in red and blue
channels.
The original algorithm is based on the contour
analysis. One of the color channels is used as a
reference channel, a green channel in our case. Here
we will consider one row of the image pixels with
fixed
2
x
. Below in this section we will use one-
dimensional indexing for clarity.
We will search for the edges in the green channel.
Let
c
x
be the first detected transition point in the
green channel, such as
Gc
p
xT
, where
T
– a
threshold value. Let us consider a neighborhood of
c
x
– N :
SIGMAP2015-InternationalConferenceonSignalProcessingandMultimediaApplications
70

max .
Gc RGB
xN
Bx sign p x p x
(15)
The required transition zone
()
Cc
Nx is defined as
follows:
:T,.
Cc c
Nx xBx xx
(16)
Let
C
l be the left border, and
C
r be the right
border of this area.
In the transition area, an abrupt change of values
in red or blue or both color channels occurs. The
algorithm transforms signals in red and blue channels
to match the signal in the green channel in the
transition area
Cc
Nx
as closely as possible.
To do this, we define differences between signals:
.
RB RB G
dxpxpx
(17)
For each pixel
C
x
N , these differences must be
smaller than the differences on the border of the
transition area. If this is not the case, red and blue
components of these pixels need to be corrected in
one of the following ways.
(a)
(b)
Figure 2: Algorithm output results: (a) an original image (b)
an image after color contour processing.
The signal
RB
Sx
depends on the color
difference between channels (17) at a pixel
C
x
N
:
max , ,
if max , ;
min , ,
if min , ;
0, else.
RB C RB C G
RB RB C RB C
RB C RB C G
RB RB C RB C
dldr px
dx dldr
dldr px
dx dldr
(18)
Therefore, color differences
R
B
d decrease, and
the red and blue signals in the transition area look
more similar to the green signal. An example of the
algorithm output is shown in Fig. 2(b).
The energy of the red and blue channels can be
low or high compared to the green channel. We can
define normalization constants
R
B
c to reduce this
imbalance.
R
B
c are defined as a ratio of per pixel
energy in the red and blue channels to the energy in
the green channel. So, (17) takes the following form:
() ( () ()) .
n
R
BRBGRB
dx pxpxc
(19)
After replacing
R
B
d with
n
R
B
d
()
RB
Sx takes the
following form:
min ( ), ( ) ( ),
if ( ) min ( ), ( ) ;
max ( ), ( ) ( ),
if ( ) max ( ), ( ) .
nn
RB C RB C G
nnn
RB RB C RB C
nn
RB C RB C G
nnn
RB RB C RB C
dldr px
dx dldr
dldr px
dx dldr
(20)
If pixel luminosity in the red and blue channels in
transition regions is close to zero, we replace it with
the middle value in a neighboring window.
There are several pixels with close to zero values
in the green channel, pixels #16-19 in Fig. 2(a). This
means that there is no significant information in the
green channel for pixel correction in the red and blue
channels in this part of the transition area. We
propose the following algorithm to solve this
problem:
1) We use a median filter to preprocess the green
channel in order to handle close to zero values. We
replace a pixel with a close to zero value to the middle
value in a neighboring window. If the new value is
also close to zero, the window size of the median filter
increases.
2) We compute the matrix of the correction
coefficients
RB
R x
for the whole image. Then we
apply the post processing steps 3) and 4) to the
RB
R x
values.
3) We apply grayscale dilation (Gonzalez and
Woods, 2001) to matrices of sharpening values
RB
S x
.
4) We limit excessively bright pixels to values
allowed inside the transition area.
Finally we sharpen red and green channels using
the following rule:
,
,0;
,0.
RB RB
D
RB
DB
RB RB
SS
p
pS
xx
x
xx
(21)
Pixel position
Intensit
y
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
0
50
100
150
200
250
r
N (x)
l
C
C
C
Pixel position
Intesit
y
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
0
50
100
150
200
250
r
l
N
(x)
c
c
c
ComputationalCorrectionforImagingthroughSingleFresnelLenses
71

After deblurring of the green channel and
sharpening of the red and blue channels, we use color
correction, described in the following section, to
remove the strong color shift caused by the energy
redistribution between diffraction orders.
5 COLOR SHIFT CORRECTION
The proposed chromatic aberration correction
includes color correction in its final stage. A detailed
description of the color correction approach is
provided in (Nikonorov et al., 2014). This correction
problem consists of correcting non-isoplanatic
deviation in illumination
,I
x
and restoring an
image with the given illumination
0
I
:
00
,, ,
,,
RI d
RI d
px x xT x
px x T
(22)
where
R
and
I
are
2
[0,1]R functions of the
wavelength
.
R
is the spectral reflectance of the
scene surfaces.
I
is the spectral irradiance that is
incident at each scene point.
1
,...,
T
K
TT
T
is the spectral
transmittance distribution of color sensors. In
(Nikonorov et al., 2014) it was shown that the task
(22) could be solved by finding the correction
function.
We propose using prior knowledge of the colors
of small isolated patches in the image in the same way
as any color correction specialist would do. These
small neighborhoods, limited in color and space, are
defined in (Nikonorov et al., 2014) as color shape
elements, CSE. This model was useful for both, color
correction and artefact removing problems
(Nikonorov et al., 2010).
Using CSE, the task of the correction function
identification takes the following form:
0
*argmin (,),
ii
F
a
auau
(23)
where
i
u
is a set of distorted CSE, and
0
i
u
is a
set of distortion-free CSE. Hausdorff-like measure
between CSEs in three dimensional color space is
used as a metric
,
in (23). A general form for this
metric is:
max min (x), (y) ,
,max ,
max min (x), (y)
j
i
i
j
ij
yu
xu
xu
yu
pp
uu
pp
(24)
where
,
is a distance in color space. We use a
separate parameter estimation (23) for each color
channel.
Since we use a channel-wise correction
procedure, the metric (19) can be calculated using
only two values for each color channel independently,
and (18) takes the following form for each color
channel
p :
0
1
000 0
1
*argmin ,, ,
p
min , p max ,
p
min , p max .
kk
kik i
kik i
Fp p
pp
pp
a
aa
uu
uu
(25)
Here we assume that the distortions are described
by a modified dichromatic model (Maxwell et al.,
2008) of the following form:
,
() (,) ,
RGB B
AB RGB
pHIR
IR D d
xx x
xT
(26)
where
,IR
x
is the diffuse reflection,
(,) (,)
S
IR
xx is the specular reflection, and the
ambient light is
()
A
I
, ()H x is the attenuation
factor, and
RGB
D
is added to describe the color
shift caused by energy redistribution between
diffraction orders. We use this model for correction
identification using calibration tables so specular
reflection is ignored in our case
.
For the distortions described by this model, the
CSE matching condition theorem from (Nikonorov et
al., 2014) could be proven with constraints on the
ambient light. Using necessary condition from this
theorem, the identification problem of the correction
function takes the following form:
2
0
'
*argmin , ,
,0.
kk
k
Fp p
Fp
a
aa
a
(27)
In the problem of color correction for Fresnel
lenses, we use a color checker scale, shown in
Fig. 4(c, f), for correction identification of each color
channel. The original colors of the scale are used as
distortion-free CSE,
0
i
u
. The same scale captured
using a Fresnel lens is used for getting distorted
CSEs,
i
u
.
SIGMAP2015-InternationalConferenceonSignalProcessingandMultimediaApplications
72

As shown in (Nikonorov et al., 2014), the problem
(27) could be solved for polynomial representation of
F
. However, the distortions caused by the
aberrations in the simple Fresnel lens are too strong.
To improve color correction quality, we apply
additional conditions.
First, we add two boundary conditions for
F
:
setting it to zero at the starting point, while setting it
to one at the end:
0, 0, 1, 1.FFaa
(28)
Because these conditions cannot be applied to a
polynomial representation of
F
, we use cubic
smoothed splines with boundary conditions (28).
Second, as shown in Fig. 3, an initial SSEs set is
too noisy, and some data points must be dropped. A
classic algorithm for noisy data selection with
dropping outliers is RANSAC algorithm. We use a
slightly modified RANSAC-based scheme:
1) Select a subset of the initial set.
2) Using this subset, estimate cubic smoothing
spline parameters for
F
according to (26)-(27).
3) For each pair of SSEs, the following
inequality can be computed:
0
,, ,
ii
F
tua u
(29)
where t is a threshold. Inequality (29) is true for
inlayer CSEs pairs and false for outliers.
Figure 3: Chromatic shift correction curve for the green
channel, solid points for inlayers CSEs, pitted – for outliers.
After identifying color correction transform
parameters we apply this transform to the image as
the final step of the technique based on model (3)-(4).
To check correction quality we use the following
measure:
0
2
max max , ,
ji
jj
i
q
xu
px px (30)
where
2
,
is Euclidian distance between colors of
corresponding points of two CSEs – source
0
j
px
and corrected
j
p
x
. We know the matching
between the source and the corrected point for color
checker tables. This usually unavailable knowledge
allows us to estimate the value of quality measure
(30), and we will use this measure to evaluate
correction quality.
6 RESULTS
The results of the correction are shown in Fig. 4. The
original picture was captured using a simple, wich
was made as three-step approximation of the Fresnel
lens. First we removed the blur from the green
channel using deconvolution, and then we used edge
analysis for the red and blue channels. Color
correction transform was identified using color
checker table (Fig. 4(c, f)), and finally color
correction was applied to the image.
As shown in Fig. 4, the proposed correction
technique restores both colors and edge information
from distorted images, captured by a simple Fresnel
lens. We compared our color correction technique
with an implementation of Retinex approach from
(Limare et al., 2011). Results for Retinex-based
correction are shown in Fig. 4(e). Visual quality of
color correction exceeds the quality of the Retinex-
based correction. The value of the quality measure
(30) for Retinex is 113 versus 14 for our method.
7 CONCLUSIONS
We show that a simple Fresnel lens can be used for
imaging. Strong aberrations inherent in this optical
system can be restored by digital image processing.
Images captured with a simple Fresnel lens are
corrected with deconvolution and contour analysis
with good results. After we applied deconvolution for
deblurring of the typically less blurred green channel,
we then sharpened the image for other color channels
taking green channel as the guidance image.
After deblurring and sharpening we applied color
correction to remove strong chromatic shift.
Correction transformation was identified using color
checker tables. These tables help to quantify
correction quality, and the proposed correction
technique shows a better quality than the well-known
Retinex method of color correction.
For further research, we see two main directions
ComputationalCorrectionforImagingthroughSingleFresnelLenses
73
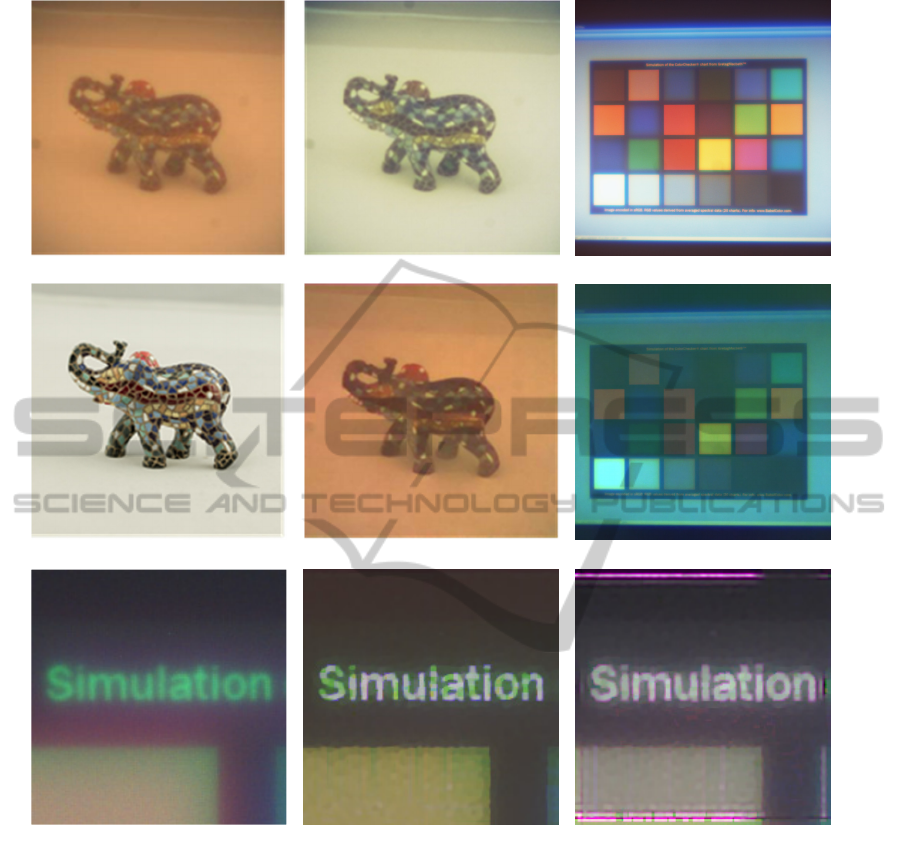
Figure 4: Example of chromatic aberration correction: (a) - image captured by four-step Fresnel lens, (b) - image after color
correction, (d) - image captured by refraction lens, (e) - image after Retinex-based color correction; (c) - color checker image
for correction identification, and (f) - color checker image after correction; (g) - part of color chart, captured by four-step
Fresnel lens, (h) - same part after computational correction, (i) – after final color sharpening.
that may yield additional quality improvements: 1)
increasing the quality of deconvolution, taking into
account the estimation of space-varying PSF and 2)
combining edge analysis and color correction to a
single filter.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by project
#RFMEFI57514X0083 by the Ministry of Education
and Science of the Russian Federation.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) (e)
(f)
(g) (h)
(i)
SIGMAP2015-InternationalConferenceonSignalProcessingandMultimediaApplications
74

REFERENCES
Chambolle, A., & Pock, T., 2011. A first-order primal-dual
algorithm for convex problems with applications to
imaging. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision,
vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 120–145.
Cho, T. S., Joshi, N., Zitnick, C. L., Sing Bing Kang,
Szeliski, R., & Freeman, W.T., 2010. A content-aware
image prior IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pp. 169-176.
Cho, T. S., Zitnick, C. L., Joshi, N., Sing Bing Kang,
Szeliski, R., & Freeman, W.T., 2012. Image restoration
by matching gradient distributions. IEEE Transactions
on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 34,
no. 4, pp. 683-694.
Chung, S.-W., Kim, B.-K., & Song, W.-J., 2010. Removing
chromatic aberration by digital image processing.
Optical Engineering, vol. 49, no. 6, 067002.
Davis, A., & Kuhnlenz, F., 2007. Optical design using
Fresnel lenses - basic principles and some practical
examples. Optik & Photonik, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 52–55.
Fang, Y. C., Liu, T. K., MacDonald, J., Chou, J. H., Wu, B.
W., Tsai, H. L., & Chang, E. H., 2006. Optimizing
chromatic aberration calibration using a novel genetic
algorithm. Modern Optics, v. 53, no. 10, pp. 1411-1427.
Farrar, N. R., Smith, A. H., Busath, D. R., & Taitano, D.,
2000. In situ measurement of lens aberration. Proc.
SPIE, vol. 4000, March, pp. 18-29.
Gonzalez, R. C., & Woods, R. E., 2001. Digital Image
Processing, Second Edition, Prentice Hall, 2001.
Heide, F., Rouf, M., Hullin, M. B., Labitzke, B., Heidrich,
W., & Kolb, A., 2013. High-quality computational
Imaging Through Simple Lenses. ACM Transactions
on Graphics, vol. 32, no. 5, article No. 149.
Kang, S. B., 2007. Automatic removal of chromatic
aberration from a single image. Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, 2007, pp. 1-8.
Limare, N., Petro, A. B., Sbert, C., & Morel, J. M., 2011.
Retinex Poisson equation: a model for color perception.
Image Processing On Line.
Maxwell, B. A., Friedhoff, R. M., & Smith, C. A., 2008. A
bi-illuminant dichromatic reflection model for
understanding images. Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, IEEE Conference on, pp. 1–8.
Meyer-Arendt, J. R., 1995. Introduction to Classical and
Modern Optics. Prentice Hall.
Millan, M. S., Oton, J., & Perez-Cabre, E., 2006. Chromatic
compensation of programmable Fresnel lenses. Opics
Express, vol. 14, no. 13, pp. 6226-6242.
Nikonorov, A., Bibikov, S., & Fursov V., 2010. Desktop
supercomputing technology for shadow correction of
color images. Proceedings of the 2010 International
Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia
Applications (SIGMAP), pp. 124-140.
Nikonorov, A., Bibikov, S., Yakimov, P., & Fursov, V.,
2014. Spectrum shape elements model to correct color
and hyperspectral images. 8th IEEE IAPR Workshop on
Pattern Recognition in Remote Sensing, 2014, pp. 1-4.
Powell, I., 1981. Lenses for correcting chromatic aberration
of the eye. Applied Optics, v. 20, no. 24, pp. 4152–4155.
Shih, Y., Guenter, B., & Joshi N., 2012. Image
enhancement using calibrated lens simulations.
Computer Vision – ECCV 2012, pp. 42-56.
Soifer, V. A. (ed.), 2012. Computer Design of Diffractive
Optics. Woodhead Publishing.
ComputationalCorrectionforImagingthroughSingleFresnelLenses
75
