
Parametric Study of Liquid Flow in Five- and Six-stage Centrifugal
Pumps
Lahbib Kerbouci and Guyh Dituba Ngoma
University of Quebec in Abitibi-Témiscamingue, School of Engineering’s Department, 445, Boulevard de l’Université,
Rouyn-Noranda, Quebec, J9X 5E4, Canada
Keywords: Multistage Centrifugal Pump, Impeller, Diffuser, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), Modeling and
Simulation.
Abstract: Two models of a multistage centrifugal pump using a five- and six-stage centrifugal pumps were developed
and numerically investigated. The continuity and Navier-Stokes equations with the k- turbulence model
and standard wall functions were used by means of the ANSYS-CFX code. To enhance the design of the
multistage pump, the concept consisting of varying three parameters at a time was used. Thus, the combined
effects of the impeller blade angle, the impeller blade number and the impeller blade width on the
performance of the five- and six-stage centrifugal pumps was analyzed. The results obtained reveal, among
other things, that the highest pump efficiency was reached for the outlet impeller blade angle of 25.38°, the
number of impeller blades of 7, and the impeller blade width of 7 mm.
1 INTRODUCTION
Multistage centrifugal pumps are widely used in
industrial and mining enterprises (Gülich, 2010). For
a more performing multistage pump, its design
parameters, such as the number of stages, impeller
blades, diffuser vanes and diffuser return vanes,
angle of the impeller blade, height of the impeller
blade and diffuser vane, the width of the impeller
blade and diffuser vane, the impeller and diffuser
diameter, the rotating speed of the impeller and the
casing geometry must be determined accurately.
Many experimental and numerical studies have been
conducted on the liquid flow through a multistage
centrifugal pump varying one key parameter at a
time (Among other things, La Roche-Carrier et al.,
2013; Miyano et al., 2008; Kawashima et al., 2008,
Gantar et al., 2002). In this study, a concept
consisting of varying three key parameters of
multistage centrifugal pumps at a time was used to
identify parameters to lead to the best design and
performances of multistage centrifugal pumps. Thus,
the following parameters were varied at a time for
the five- and six-stage centrifugal pumps: a) the
numbers of impeller blades (6, 7 and 8), b) the outlet
angle of the impeller blade (19.81°, 21.24° et
25.38°), and c) the impeller width blade (4 mm, 5
mm and 7 mm).
2 GOVERNING EQUATIONS
Fig. 1 shows the domain fluids of five- and six-stage
centrifugal pumps considered in this research work
to run the numerical simulations.
Figure 1: Domain fluids of five- and six-stage pumps.
The following assumptions were made for the
governing equations for liquid flow in the five- and
six-stage centrifugal pumps: (i) a steady state, three-
dimensional and turbulence flow using the k-
model was assumed; (ii) it was an incompressible
liquid; (iii) it was a Newtonian liquid; and (iv) the
liquid’s thermophysical properties were constant
with the temperature.
To account for these assumptions, the theoretical
analysis of the liquid flow in the impeller passages,
diffuser vane passages and diffuser return vane
passages was based on the continuity and
Navier-Stokes equations (Ansys inc., 2011). For the
three-dimensional liquid flow through these five-
and six-stage centrifugal pumps as shown in Fig. 1,
178
Kerbouci L. and Dituba Ngoma G..
Parametric Study of Liquid Flow in Five- and Six-stage Centrifugal Pumps.
DOI: 10.5220/0005543601780182
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH-2015),
pages 178-182
ISBN: 978-989-758-120-5
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

the continuity equations are expressed by:
0
z
w
y
v
x
u
(1)
and the Navier–Stokes equations are given by:
z
2
2
2
2
2
2
eff
y
2
2
2
2
2
2
eff
x
2
2
2
2
2
2
eff
B
z
p
z
w
y
w
x
w
z
w
w
y
w
v
x
w
u
B
y
p
z
v
y
v
x
v
z
v
w
y
v
v
x
v
u
B
x
p
z
u
y
u
x
u
z
u
w
y
u
v
x
u
u
(2)
where p is the pressure, is the density,
eff
is the
effective viscosity accounting for turbulence, and
B
x
, B
y
and B
z
are the source terms. They can be
expressed by:
.0B and u2rB ,v2rB
zzy
2
zyzx
2
zx
(3)
Furthermore,
eff
is defined as
teff
, where
is the dynamic viscosity and
t
is the turbulence
viscosity, it
is linked to turbulence kinetic energy k
and dissipation ε via the relationship:
12
t
kC
,
where C
is a constant. The values of k and tem
directly from the differential transport equations for
turbulence kinetic energy and turbulence dissipation
(Ansys inc., 2011). Additionnally, for the flow
modeling near the wall, the logarithme wall function
is used to model the viscous sub-layer (Ansys inc.,
2011).
To solve equations 1 and 2 numerically while
accounting for the boundary conditions and
turbulence model k-, the computational fluid
dynamics ANSYS-CFX code, based on the finite
volume method, was used to obtain the liquid flow
velocity and pressure distributions. Pressure velocity
coupling is calculated in ANSYS-CFX code using
the Rhie Chow algorithm (Ansys inc., 2011).
In the cases examined involving the five- and
six-stage centrifugal pumps, the boundary conditions
were formulated as follows (figure 2): the static
pressure provided was given at the pump inlet, while
the flow rate provided was specified at the pump
outlet. The frozen rotor condition was used for the
impeller-diffuser interfaces. A no-slip condition was
set for the flow at the wall boundaries.
Figure 2: Boundary conditions.
The pump head is determined as follows:
g
pp
H
tito
(4)
where p
ti
is the total pressure at the pump inlet and
p
to
the total pressure at the pump outlet. They are
expressed as:
2
vel
iti
i
V
2
pp
and
2
vel
oto
o
V
2
pp
(5)
Moreover, the hydraulic power of the pump is given
by
QgHP
h
, where Q is the flow rate and H is the
pump head.
Furthermore, the brake horsepower of the pump
stage is expressed as
CP
s
, where is the angular
velocity and C is the impeller torque.
From the hydraulic power and the brake
horsepower, the efficiency of the pump can be
written as
s
h
P
P
(6)
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The main reference data used for the impeller were
89 mm for the inner diameter, 175 mm for the outer
diameter and 2800 rpm for the rotating speed. For
the diffuser, the main reference data were 176 mm
for the inner diameter, 234 mm for the outer
diameter, 6 for the number of vanes and 8 for the
number of return vanes. The numerical simulation
results presented in this work were obtained with the
highest accuracy by conducting mesh-independent
solution tests in each case study using different
numbers of mesh elements.
ParametricStudyofLiquidFlowinFive-andSix-stageCentrifugalPumps
179

3.1 Combined Effect of the Impeller
Blade Angle, Impeller Blade
Number and Impeller Blade Width
To investigate the influence of the combined effect
of the impeller blade angle, the impeller blade
number and the impeller blade width on the pump
head, brake horsepower and efficiency, the values of
the blade angle, the blade number and the blade
width were varied at a time while the other
parameters were kept constant, as indicated in Tab. 1
for the five- and six-stage centrifugal pumps.
Table 1: Selected parameters for simulations.
Impeller blade number; Impeller blade angle [°];
Impeller blade witdh [mm]
Case 1 6; 21.24; 7
Case 2 7; 19.81; 4
Case 3 8;25.38°;5
Figs. 3 and 4 represent the variation of the head
as a function of the flow rate for the five- and six-
stage centrifugal pumps respectively. There, it is
observed that the lowest head was achieved with the
combined of the values of the blade number of 6, the
blade angle of 25.34° and the blade width of 4 mm.
Figure 3: Head versus volume flow rate (five-stage pump).
Figure 4: Head versus volume flow rate (six-stage pump).
Additionally, as shown in Figs. 5 and 6, the
lowest brake horsepower was reached using the
blade number of 7, the blade angle of 25.38° and the
blade width of 7 mm for the five- and six-stage
centrifugal pumps.
Figure 5: Brake horsepower versus volume flow rate (five-
stage pump).
Figure 6: Brake horsepower versus volume flow rate (six-
stage pump).
Furthermore, Figs. 7 and 8 represent the
efficiency curves, showing that the highest
efficiency was achieved for the flow rate about of 33
m³/h.
Figure 7: Efficiency versus volume flow rate (five-stage
pump).
SIMULTECH2015-5thInternationalConferenceonSimulationandModelingMethodologies,Technologiesand
Applications
180
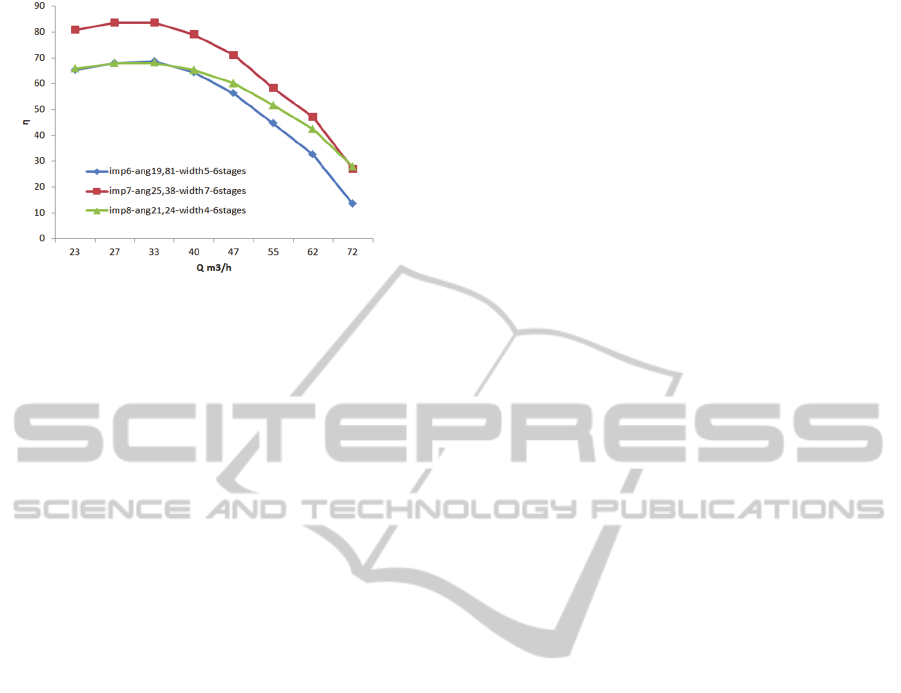
Figure 8: Efficiency versus volume flow rate (six-stage
pump).
3.2 Parameters of Improved Five- and
Six-centrifugal Pumps
Taking account of the accomplished simulations in
section 3.1, an analysis was performed to identify
the parameters which improve the efficiency of the
five- and six-centrifugal pumps. Thus, the following
values were found for the five- and the six-stage
centrifugal pumps:
Impeller blade number: 7
Impeller blade angle: 25.38°
Impeller blade width: 7 mm
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, a liquid flow in a five- and six- stage
centrifugal pumps was umerically investigated using
a ANSYS- CFX code. The combined effects of the
outlet blade angle, the impeller blade number and
impeller width on the on the five- and –six
centrifugal pump head, efficiency and the brake
horsepower were performed. The results obtained
demonstrate, among other things, that a multistage
centrifugal pump can be improved selecting
adequately three key parameters. Further research
work is planned to complete this study finding a
general appropriated to enhance the performances of
a multistage centrifugal pump of any size.
NOMENCLATURE
B source term (Nm
-3
)
C torque (Nm)
g acceleration of gravity (ms
-2
)
H head (m)
P power (W)
p pressure (Nm
-2
)
p
turbulence production due to viscous and
buoyancy forces
Q flow rate (m
3
s
-1
)
r radial coordinate (m)
V velocity (ms
-1
)
u flow velocity in x direction (ms
-1
)
v flow velocity in y direction (ms
-1
)
w flow velocity in z direction (ms
-1
)
x x-coordinate (m)
y y-coordinate (m)
z z-coordinate (m)
Greek symbols
difference
turbulence dissipation (m
2
s
-3
),
efficiency
turbulence kinetic energy (kg m
-2
s
-2
)
fluid density (kg m
-3
)
dynamic viscosity (Pa s)
eff
effective viscosity (Pa s)
t
turbulence viscosity (Pa s)
ω angular velocity (rad s
-1
)
Subscripts
1 inlet
2 outlet
h hydraulic
i inlet
m mechanical
o outlet
s shaft
t total
v volumetric
vel velocity
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are grateful to the Foundation of
University of Quebec in Abitibi-Temiscamingue
(FUQAT) and the Company Technosub inc.
REFERENCES
Gülich, J. F., 2010. Centrifugal Pumps, second Edition,
Springer.
Miyano M., Kanemoto T., Kawashima D., Wada A., Hara
T., Sakoda K., 2008. Return Vane Installed in
Multistage Centrifugal Pump. International Journal of
Fluid Machinery and Systems, Vol. 1, No. 1.
ParametricStudyofLiquidFlowinFive-andSix-stageCentrifugalPumps
181

Kawashima D., Kanemoto T., Sakoda K., Wada A., Hara
T., 2008. Matching Diffuser Vane with Return Vane
Installed in Multistage Centrifugal Pump.
International Journal of Fluid Machinery and
Systems, Vol. 1, No. 1.
Gantar M., Florjancic D., and Sirok B., 2002. Hydraulic
Axial Thrust in Multistage Pumps - Origins and
Solutions. Journal Fluids Engineering, Vol. 124, Issue
2, 336-341.
La Roche-Carrier N., Dituba Ngoma G., and Ghie W.,
2013. Numerical investigation of a first stage of a
multistage centrifugal pump: impeller, diffuser with
return vanes, and casing. ISRN Mechanical
Engineering, Volume 2013, Article ID 578072, 15
pages.
Ansys inc. 2011. ANSYS-CFX (CFX Introduction, CFX
Reference Guide, CFX Tutorials, CFX-Pre User's
Guide, CFX-Solver Manager User's Guide, CFX-
Solver Modeling Guide, CFX-Solver Theory Guide),
release 14.0, USA.
SIMULTECH2015-5thInternationalConferenceonSimulationandModelingMethodologies,Technologiesand
Applications
182
