
An Investigation of Customers’ Loyalty to Social Commerce Websites
Hilal Alhulail, Martin Dick and Ahmad Abareshi
School of Business IT and Logistics, RMIT University, 445 Swanston Street, Melbourne, Australia
Keywords: Social Commerce, Customer Loyalty, Social Presence, Trust, Information Systems Success, Australia.
Abstract: The emergence of web 2.0 has brought new applications which have played a significant role in extending
e-commerce websites with social commerce (S-Commerce) functionality. S-Commerce is a new extension
of B2C e-commerce where customers purchase products/services online with the existence of social cues in
the websites (such as reviews, recommendations and sharing). There has been little research in the area of
customer loyalty to S-Commerce websites. Drawing upon theories of social presence and trust; and the
Delone and McLean model of information systems success, this study aims to determine what factors affect
customer loyalty to S-Commerce websites and to develop a framework that helps in investigating those
factors. In order to achieve this objective, a quantitative approach will be employed. Data will be collected
from S-Commerce users in Australia via survey. Analysis will be performed using Structural Equation
Modeling (SEM). This study will contribute to the S-Commerce literature through a theoretical framework
that shows how the loyalty of customers can be generated in S-Commerce websites. In addition, it is
expected that this study will help businesses to have understanding of how to retain their customers which
will result in higher profits.
1 INTRODUCTION
The emergence of web 2.0 has brought with it new
applications that have played a significant role in
developing e-commerce sites which enhanced with
social features. Social media sites have offered users
the opportunity to communicate with each other,
exchange opinions, post comments, photos, and
videos, as well as give recommendations and
referrals. The dynamic nature of social interaction
via social media sites and the potential financial
benefits of these sites have been recognized by e-
commerce businesses and social networks
throughout the world as part of what is known today
as “social-commerce” (s-commerce), which also can
be defined as the usage of social media in e-
commerce. This initial research in progress aims to
examine the aspect of customer loyalty in relation to
social commerce
The term “s-commerce” was introduced by
Yahoo in 2005 (Wang and Zhang, 2012). According
to (Shen and Eder, 2009), s-commerce is an
extension of business-to-consumer e-commerce in
which consumers interact with each other while
conducting online shopping activities, such as
discovering products, aggregating and sharing
product information, and collaboratively making
shopping decisions. For the purposes of our study,
we have chosen to follow Shen and Eder's definition
of s-commerce. Researchers have predominantly
discussed s-commerce in two different ways: first, in
terms of commercial features added to social
networking sites (SNS) that allow people to make
purchases, such as Facebook (Liang et al., 2011).
Second, in terms of traditional e-commerce sites that
add social features and content to allow people to
socialize while making purchases, such as Amazon
and eBay (Shen and Eder, 2009). This study will
focus on the second form, as the majority of s-
commerce transactions currently being made
throughout the world are of this type.
Many studies have been published that have
sought to investigate various aspects of s-commerce
(see Table 1), yet there currently exists a gap in the
literature in terms of customer loyalty. The
exception are Liang et al., (2011) who have
conducted an empirical study on a Social Network
Site (SNS) to investigate how social factors such as
social support and relationship quality affect the
user’s intention of future participation in social
commerce. However, in this study we will study
customer loyalty from different angle. Therefore, the
researcher seeks to conduct a survey to investigate s-
88
Alhulail H., Dick M. and Abareshi A..
An Investigation of Customers’ Loyalty to Social Commerce Websites.
DOI: 10.5220/0005562000880093
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on e-Business (ICE-B-2015), pages 88-93
ISBN: 978-989-758-113-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
commerce customer loyalty in Australia. The
following factors of customer loyalty in the s-
commerce context will be considered in this study:
satisfaction, trust, social presence, service quality,
system quality, information quality, reputation,
online shopping experience, word-of-mouth, and
communication. Of these, little research has been
done to investigate the influence of social presence
(SP) on customer attitudes in the s-commerce
context (see Table 1), as well as the influence of SP
on customer loyalty. Lu and Fan, (2014) argue that
the multidimensional nature of SP should be taken
into consideration when studying SP because people
in virtual communities do not deal only with the
computer medium; however, they interact with other
people in such a medium. They propose three
dimensions of SP in the s-commerce context: the SP
of a website (i.e., websites that are rich in
information and have social cues, such as images,
audio, and videos), the perception of other users on
the web (i.e., websites that allow for the social cues
of users, such as recommendations, reviews, and
rankings), and the SP of customers interactions with
sellers. This study will focus on customer loyalty
from a buyer perspective, examining the impact of
SP on customer loyalty in the s-commerce context
from two perspectives: the SP of a website and the
perception of other users on the web.
The current study seeks to develop a framework
to assist businesses using s-commerce to improve
customers’ loyalty to their websites. To achieve this
objective, this primary question is formulated:
What are the key factors that influence customer
loyalty to s-commerce websites?.
Sub-questions are:
1. What are the dimensions of customer loyalty to
s-commerce websites since it is different from
customer’s loyalty to e-commerce websites?
2. How do the key factors interact to influence
customer loyalty to s-commerce websites?
3. What are the factors that affect trust in s-
commerce websites?,
4. How does SP in its two dimensions affect
customer loyalty to s-commerce websites?
5. How does customer satisfaction have an impact
on customer loyalty to s-commerce websites?
This paper will be organized as follows: first, a
literature review will be presented. Second, the
study’s theoretical framework and research
hypotheses will be given. Third, the study’s
methodology will be presented, followed by its data
collection, data analysis, study outcomes, ethical
considerations, and time schedules.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
This section reviews prior literature on s-commerce
and customer loyalty. Table 1 shows a summary of
this literature review.
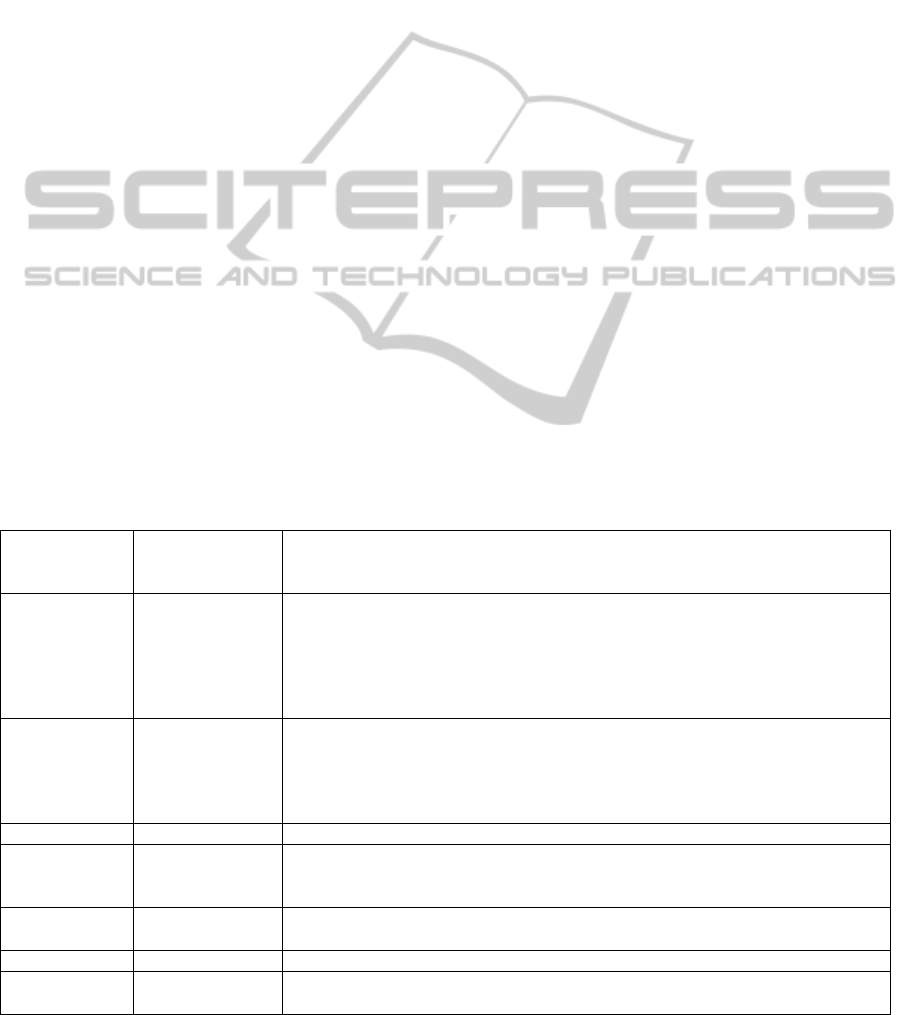
Table 1: A Summary of Previous Literature on s-commerce.
Dependant
Variable/
Outcome
Author(s)/
Year
Theory Used
Purchase
Intention
(Hajli, 2013, Ng,
2013, Kim and
Park, 2013, Hajli,
2012b, Ng, 2012,
Mikalef et al.,
2013)
Social support, Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB), Technology Acceptance
Model (TAM), Social Influence, Social Impact, Theory of Reasoned Action
(TRA), Trust Transference Theory, Social Interactions, and Hofstede’s Cultural
Dimensions.
Behavioural
Intention
(Shen, 2012,
Gatautis and
Medziausiene,
2014, Tan et al.,
2012)
Social Comparison Theory, Social Presence, Flow theory, TAM, , technology
Acceptance and Technology Resistance Theories, SoloMo Theory, TAM, and
TRA
Behaviour (Shin, 2013) TPB and TAM
Word-Of-
Mouth
Intention
(Kim and Park,
2013, Mikalef et
al., 2013)
TRA and TPB
S-commerce
Intention
(Zhang et al.,
2014)
Stimulus-Organism-Response (S-O-R) Model
Use Intention (Hajli, 2012a) TAM
Continuance
Intention
(Liang et al.,
2011)
TRA, TAM and Social Support
AnInvestigationofCustomers'LoyaltytoSocialCommerceWebsites
89

2.1 Attitudinal and Behavioural
Customer’s Loyalty
According to the literature, there are two kinds of
customer loyalty: behavioural customer loyalty and
attitudinal customer loyalty. The former is past-
focused (i.e., retrospective) and refers to loyalty
obtained through repeated purchasing behaviours
and engaging in recommendations over time,
whereas the latter is future-focused (i.e.,
prospective) and refers to a loyalty of intention to
engage in certain purchasing behaviours in the future
(Allagui and Temessek, 2004, Jang et al., 2008,
Kandampully and Suhartanto, 2003, Toufaily et al.,
2013).
Many researchers have argued that customer
loyalty to a website cannot be measured simply by
observing repeat purchases, which is the method of
the behavioural approach (Shankar et al., 2003,
Currás-Pérez et al., 2013). Instead, an understanding
of customer loyalty to s-commerce websites should
take into consideration customers’ intentions to
continue using a website, including their browsing,
purchasing, and sharing of purchases with friends on
a particular social networking site, as well as
recommending such sites to other users through
various social media features, such as comments,
recommendations, and rankings. Given this
recognition, this study will adopt an attitudinal
approach to customer loyalty.
2.2 Customer’s Loyalty in
s-Commerce
The difference between traditional customer loyalty
and e-loyalty is that the former represents a
customer's attitudinal preference toward a particular
product or service, whereas the latter refers to a
customer's attitude or behaviour toward revisiting a
particular website (Anderson and Srinivasan, 2003).
Cyr et al., (2008) define e-loyalty as the perceived
intention to visit a website and purchase and
repurchase from it in the future. Currás-Pérez et al.,
(2013) define customer loyalty to a social
networking site as "a favourable attitude towards
that social networking site expressed by the intention
to continue using it in the future and recommend that
other users use it." In line with this definition, and
based on the s-commerce definitions of prior
mention in this study (Afrasiabi Rad and Benyoucef,
2011, Zhong, 2012, Leitner and Grechenig, 2007,
Wang, 2009, Shen and Eder, 2009), we define
customer loyalty toward s-commerce websites as a
favourable attitude toward a particular s-commerce
site expressed by the intention to continue using it.
Here, usage includes the following: browsing the
site, purchasing from the site, creating content,
sharing a purchase with other friends on a particular
social networking site, and recommending the site to
other users through integrated social features, such
as comments, recommendations, and rankings.
Usage is more complex in s-commerce than in e-
commerce. On a traditional e-commerce website,
there are only two possible actions: browsing and
purchasing. On an s-commerce website, however,
there are an additional three possible actions:
creating content, sharing, and recommendations.
These are major differences between customers’
loyalty to the two kinds of websites, each of which
are related to customer loyalty.
3 THE THEORETICAL
FRAMEWORK AND
RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS
This section summarize the theoretical background,
research model, and hypotheses development of the
study.
3.1 Theoretical Background
The conceptual model, in Figure 1 draws on
customer loyalty, SP and trust theories detailed in
the literature review as well as the updated IS
success model of Delone and McLean (2003) review
to identify both possible factors and their
relationships. These theories were used for the
following reasons: first, these theoretical approaches
and this model will help to investigate customer
loyalty in s-commerce as other studies focus on
customers’ intentions to use s-commerce websites in
a variety of ways. Second, many studies have
utilized various theoretical approaches to study
consumer attitudes in the e-commerce and e-service
contexts (Gefen and Straub, 2004, Hassanein and
Head, 2007, Cyr et al., 2007), yet social presence
theory has yet to be used to study customer loyalty
in the s-commerce context. These theoretical
approaches have assisted to identify twelve possible
factors and their relationships that influence
customer loyalty in s-commerce.
3.2 Research Model and Development
of Hypothesis
The proposed research model is depicted in Figure 1.
ICE-B2015-InternationalConferenceone-Business
90
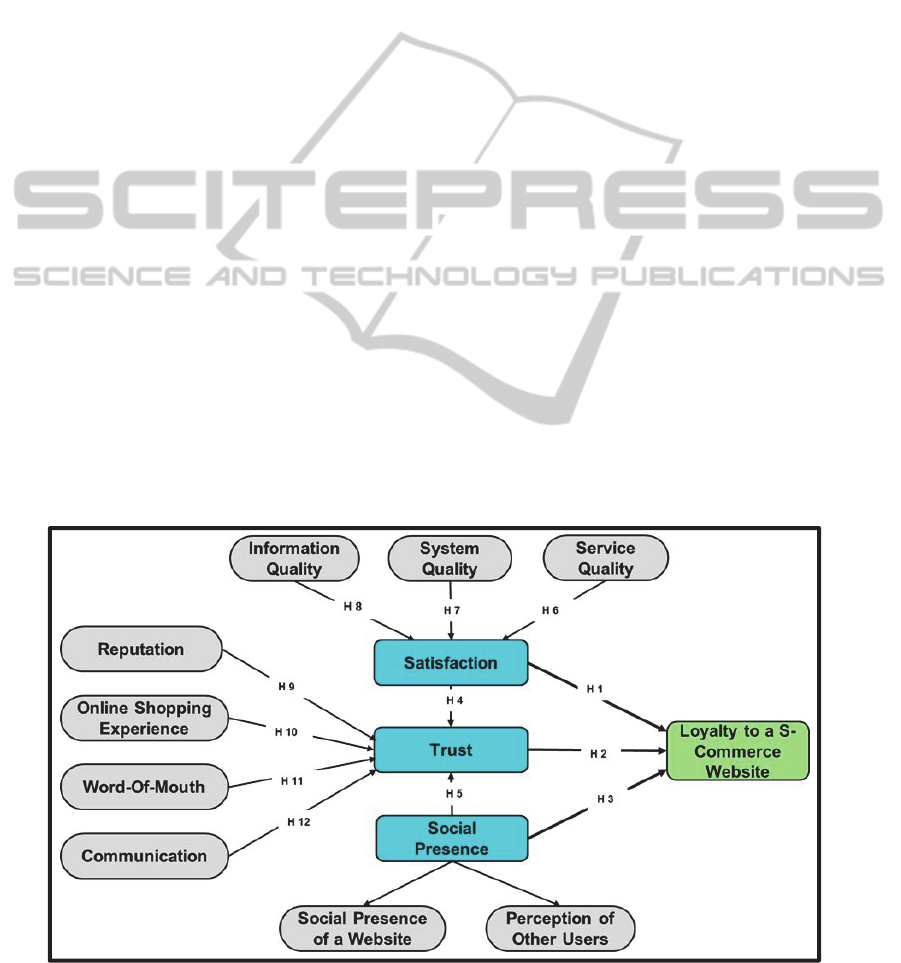
There is a positive relationship between the
factors. The first two hypotheses are examples, as
there is insufficient space to provide all the
hypotheses in detail:
Hypothesis 1. There is a positive association
between customers’ levels of satisfaction and
customer loyalty to an s-commerce website.
Hypothesis 2. There is a positive association
between customers’ levels of trust and customer
loyalty to an s-commerce website.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
AND DESIGN
Given the objectivity of the data in this research, a
quantitative approach was deemed appropriate for
the current study. The benefits of quantitative
research include the strong validity and reliability
that come with utilizing only observable facts. This
study aims to involve 1,000 s-commerce customers.
Therefore, the study’s survey will be web-based.
The study will employ a cross-sectional method for
the survey and use a structured questionnaire to
collect data. The population of the study will consist
of male and female customers of multiple s-
commerce websites (e.g., Kogan, eBay, Amazon,
Target, Big W, Harvey Norman, Dick Smith, Etsy,
OO, Booktopia, Shopping.com Network, Deals
Direct, and Gumtree) who live in Australia and is
sourced from a research panel. The survey questions
are based on a range of existing surveys that address
the relevant factors.
4.1 Data Analysis
The research model of this study will be tested using
structural equation modelling (SEM). SEM is a
statistical technique for testing and estimating causal
relations via the use of qualitative causal
assumptions and statistical data. The use of SEM
will allow the researcher to compare the study’s
empirical data and model. SEM will then be used to
test the hypothesized relationships among the
study’s constructs.
5 OUTCOMES OF THE STUDY
The conceptual model generated by this study,
especially when tested and refined by the future
work will be useful for businesses using or
considering the use of s-commerce, customers of s-
commerce websites, and other academics studying
this topic. From the academic perspective, it will add
a framework that details the factors influencing
customers’ loyalty to the body of s-commerce
research, will contribute to an in-depth
understanding of the impacts of social presence
(especially the social presence of other users),
satisfaction, trust, and loyalty of customers in s-
commerce, it will give more understanding of
Figure 1: Research Model.
AnInvestigationofCustomers'LoyaltytoSocialCommerceWebsites
91

dimensions of customers’ loyalty to s-commerce
websites since it is different from customers’ loyalty
to e-commerce websites. From the business
perspective, it will provide businesses a framework
that will allow them to improve their s-commerce
websites to increase customer loyalty. Finally, from
the customer perspective, if businesses implement
the framework, customers will receive better s-
commerce website services.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Drawing upon SP and trust theories as well as the
updated IS success model of Delone and McLean
(2003), this paper presents a conceptual model to
studying the impact of social presence, trust and the
three web qualities (information, system, service) on
customers’ loyalty to s-commerce websites. In future
work, a survey of 1,000 s-commerce customers will
be conducted and the conceptual model tested and
refined using a SEM approach.
REFERENCES
Afrasiabi Rad, A. & Benyoucef, M. 2011. A Model for
Understanding Social Commerce. Journal of
Information Systems Applied Research, 4, 63.
Allagui, A. & Temessek, A. 2004. Testing an E-Loyalty
Conceptual Framework. Journal of e-Business, 4, 1-6.
Anderson, R. E. & Srinivasan, S. S. 2003. ESatisfaction
and ELoyalty: A Contingency Framework.
Psychology & Marketing, 20, 123-138.
Currás-Pérez, R., Ruiz-Mafé, C. & Sanz-Blas, S. 2013.
Social Network Loyalty: Evaluating the Role of
Attitude, Perceived Risk and Satisfaction. Online
Information Review, 37, 61-82.
Cyr, D., Hassanein, K., Head, M. & Ivanov, A. 2007. The
Role of Social Presence in Establishing Loyalty in E-
Service Environments. Interacting With Computers,
19, 43-56.
Cyr, D., Kindra, G. & Dash, S. 2008. Web Site Design,
Trust, Satisfaction and E-Loyalty: The Indian
Experience. Online Information Review, 32, 773-790.
Delone, W. H. & Mclean, E. R. 2003. The Delone and
Mclean Model of Information Systems Success: A
Ten-Year Update. Journal of Management
Information Systems, 19, 9-30.
Gatautis, R. & Medziausiene, A. 2014. Factors Affecting
Social Commerce Acceptance in Lithuania. Procedia-
Social and Behavioral Sciences, 110, 1235-1242.
Gefen, D. & Straub, D. W. 2004. Consumer Trust in B2c
E-Commerce and the Importance of Social Presence:
Experiments in E-Products and E-Services. Omega,
32, 407-424.
Hajli, M. 2012a. An Integrated Model for E-Commerce
Adoption at the Customer Level with the Impact of
Social Commerce. International Journal of
Information Science and Management (IJISM), 77-97.
Hajli, M. 2012b. Social Commerce: The Role of Trust.
(July 29, 2012). AMCIS 2012 Proceedings. Paper 9.
Http://Aisel.Aisnet.Org/Amcis2012/Proceedings/Issecurity
/9.
Hajli, M. 2013. A Research Framework for Social
Commerce Adoption. Information Management and
Computer Security, 21, 144-154.
Hassanein, K. & Head, M. 2007. Manipulating Perceived
Social Presence Through The Web Interface And Its
Impact On Attitude Towards Online Shopping.
International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,
65, 689-708.
Jang, H., Olfman, L., Ko, I., Koh, J. & Kim, K. 2008. The
Influence of On-Line Brand Community
Characteristics on Community Commitment and
Brand Loyalty. International Journal of Electronic
Commerce, 12, 57-80.
Kandampully, J. & Suhartanto, D. 2003. The Role of
Customer Satisfaction and Image in Gaining Customer
Loyalty in the Hotel Industry. Journal of Hospitality &
Leisure Marketing, 10, 3-25.
Kim, S. & Park, H. 2013. Effects of Various
Characteristics of Social Commerce (S-Commerce)
On Consumers’ Trust and Trust Performance.
International Journal of Information Management, 33,
318-332.
Leitner, P. & Grechenig, T. Community Driven
Commerce: Design of an Integrated Framework for
Social Shopping. Iadis International Conference E-
Commerce, 2007. 4.
Liang, T.-P., Ho, Y.-T., Li, Y.-W. & Turban, E. 2011.
What Drives Social Commerce: The Role of Social
Support and Relationship Quality. International
Journal of Electronic Commerce, 16, 69-90.
Lu, B. & Fan, W. 2014. Social Presence, Trust, and Social
Commerce Purchase Intention: An Empirical
Research.
Mikalef, P., Giannakos, M. & Pateli, A. 2013. Shopping
and Word-Of-Mouth Intentions on Social Media.
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic
Commerce Research, 8, 17-34.
Ng, C. S.-P. 2012. Examining the Cultural Difference in
the Intention to Purchase in Social Commerce.
Ng, C. S.-P. 2013. Intention to Purchase on Social
Commerce Websites Across Cultures: A Cross-
Regional Study. Information & Management, 50, 609-
620.
Shankar, V., Smith, A. K. & Rangaswamy, A. 2003.
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty In Online and
Offline Environments. International Journal of
Research in Marketing, 20, 153-175.
Shen, J. 2012. Social Comparison, Social Presence, and
Enjoyment in the Acceptance of Social Shopping
ICE-B2015-InternationalConferenceone-Business
92

Websites. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research,
13, 198-212.
Shen, J. & Eder, L. 2009. Determining Factors in the
Acceptance of Social Shopping Websites. AMCIS
2009 Proceedings, 290.
Shin, D.-H. 2013. User Experience In Social Commerce:
In Friends We Trust. Behaviour & Information
Technology, 32, 52-67.
Tan, X., Qin, L., Kim, Y. & Hsu, J. 2012. Impact of
Privacy Concern in Social Networking Web Sites.
Internet Research, 22, 211-233.
Toufaily, E., Ricard, L. & Perrien, J. 2013. Customer
Loyalty to a Commercial Website: Descriptive Meta-
Analysis of the Empirical Literature and Proposal of
an Integrative Model. Journal of Business Research,
66, 1436-1447.
Wang, C. 2009. Linking Shopping and Social Networking:
Approaches to Social Shopping.
Wang, C. & Zhang, P. 2012. The Evolution of Social
Commerce: The People, Management, Technology,
and Information Dimensions. Communications of the
Association for Information Systems, 31, 105.
Zhang, H., Lu, Y., Gupta, S. & Zhao, L. 2014. What
Motivates Customers To Participate In Social
Commerce? The Impact of Technological
Environments and Virtual Customer Experiences.
Information & Management, 51, 1017-1030.
Zhong, Y. 2012. Social Commerce: A New Electronic
Commerce. Eleventh Wuhan International Conference
on E-Business. Paper 49.
AnInvestigationofCustomers'LoyaltytoSocialCommerceWebsites
93
