
Probability-based Controlled Flooding in Opportunistic Networks
Sanjay K. Dhurandher
1
, Satya Jyoti Borah
1
, Mohammad S. Obaidat
2
, Deepak Kr. Sharma
1
,
Sahil Gupta
1
and Bikash Baruah
3
1
CAITFS, Divison of Information Technology, Netaji Subash Institute of Technology, University of Delhi, New Delhi, India
2
Dept. of Comp. Sc. and Eng., Monmouth University Monmouth, NJ, U.S.A.
3
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, North Eastern Regional Institute of Science and Technology, Deemed
University, Itanagar, India
Keywords: Opportunistic Networks, Opportunistic Network Simulator (ONE) Environment, Epidemic, Spray and Wait,
Prophet, Routing Protocol.
Abstract: Opportunistic networks (Oppnet) are challenged networks in present wireless communication scenario. These
networks are mainly applied to situations where a persistent end–to-end path between the source and the
destination does not exist. Delay/Disruption Tolerant Networking (DTN) is mostly used to solve this end-to-
end path problem in such networks. Many routing protocols have been proposed in literature that consider
various performance metrics such as delivery delay, packet delivery rate, hop count, among others. In this
paper, a new routing protocol named as PRoWait has been designed which can overcome the shortcomings
of the already existing protocols in Oppnets. The proposed protocol also incorporates the merits of existing
protocol so that it can be reliable and efficient for the communication of pedestrians with handheld devices.
Simulation results obtained for the proposed scheme show better performance as compared to the Porphet,
Spray and Wait and Epidemic routing protocols in terms of packets delivery probability, overhead ratio, and
hop count performance metrics.
1 INTRODUCTION
An Ad hoc network (Royer, 1999) is a peer to peer
communication network. It uses wireless/Wi-Fi tech-
nology and the communication takes place without
any access point. It is an infrastructure less, cost effi-
cient, quicker to setup, and works as an extension to
existing networks. In this chain, there is one more
specific network where the nodes are mobile in na-
ture. This network is called as mobile Ad hoc network
[MANET] (Toh, 2002). The main aim of MANETs is
to establish a synchronous communication between
two or more nodes. In a multi-hop communication en-
vironment for MANET, every node is assumed to be
helpful to each other. They agree to contribute and
route any traffic within the network. However, they
have some limitations such as minimal security
against unwanted incoming connections, which
makes it easy for attackers.
Opportunistic networks (Pelusi et all, 2006) are
the recent evaluations of MANETs. They have many
similarities and differences to the MANETs. MA-
NETs follow the synchronous mode of communica-
tion while Oppnets follow the asynchronous mode of
communication. In MANETs first a fixed path is es-
tablished between the source and destination and then
the message passing takes place. But, in Oppnets no
previous assumption is made regarding the existence
of a complete path between the two nodes that wish
to communicate with each other (Huang et al., 2008).
Source and destination nodes might not be in the same
network or within range of each other at the same
time. However, Oppnet provides a platform for nodes
to communicate in the aforementioned type of chal-
lenged network scenarios. Packets are often buffered
in the network waiting for a path towards the destina-
tion to be available. Due to this, additional delay gets
incorporated in message delivery. However, there are
various applications which can tolerate longer delays
such as e-mailing. Again frequent connections and
disconnections between nodes may degrade the per-
formance of a number of applications in Oppnets.
3
K. Dhurandher S., Jyoti Borah S., S. Obaidat M., Sharma D., Gupta S. and Baruah B..
Probability-based Controlled Flooding in Opportunistic Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0005580300030008
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems (WINSYS-2015), pages 3-8
ISBN: 978-989-758-119-9
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Routing and forwarding of packets in Opnets is a
very difficult task. It is completely different from tra-
ditional network routing techniques. Here, the main
objectives are to expect a reliable delivery of packets
even in the absence of permanent path between the
sender and the receiver. As the nodes are mobile in
nature in this kind of network, one cannot predict to-
tally about the routes for packets transmission. Hence,
conventional routing protocols do not have any role
to play in these networks (Pelusi et all, 2006).
Routing is mainly based upon three things
(Dhurandher et al., 2008). The first is a node’s coop-
eration that is its willingness in the routing and for-
warding. The second is nodes mobility which can be
utilized to forward a packet from one portion of the
network to the other. The third is store-carry-forward
method. This method ensures that the packet copy re-
mains saved in the buffer of the nodes until it meets
the next forwarding node or the destination node. It
also requires proper buffer management when buffer
gets full. Hence, there is always a need for proper
routing protocol that minimizes the delivery delay,
buffering space and maximize delivery ratio.
In this work, a new protocol named as PRoWait
has been proposed which is based on the concept of
earlier work of Spray and Wait and Prophet routing
protocols. It integrates the working principle of the
two aforementioned protocols together in order to
achieve a better packet delivery ratio, latency and hop
count. This paper does not address the acknowledge-
ment of packets and security issues in Oppnets. The
overall scenario is simulated with the help of ONE
simulator (Keranen, 2008) and respective results were
recorded.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section II gives a brief overview of existing protocols
that have been used in this work. Section III presents
the proposed protocol in detail. Section IV describes
the simulation scenarios and Simulation results with
various graphs. Section V summarizes this work.
2 RELATED WORK
So far many routing protocols have been designed in
the past in Oppnets such as Epidemic (Vahdat, 2000),
Spray and Wait (Spyropoulos et al., 2005), Binary
Spray and Wait (Spyropoulos et al., 2005), Prophet
(Lindgren et al., 2003), HBPR (Dhurandher et al.,
2013) (Dhurandher et al, 2014), GAER (Dhurandher
et al, 2014), among others. The main objective of these
protocols is to achieve maximum successful delivery
of packets and minimize the delay. In this section, a
brief discussion of some of these routing protocols is
presented.
A. Epidemic Routing Protocol
The Epidemic routing protocol, as its name suggests is
similar to spreading/flooding like infectious diseases
in nature. It is a simple protocol which delivers most
of the packets successfully to its destination, but
requires large amount of bandwidth and buffer size.
When a pair of nodes that want to communicate come
into a communication range, the first node sends the
second node, a summary vector containing
information that uniquely identifies the packets it has
in its buffer. The second node also transfers to the first
node any packets it has which are not available with
the first node. Hence transmission of packets takes
place in both directions whenever two nodes meet
each other. In this way all the packets will ultimately
be distributed to every node, and finally every packet
will reach its destination as quickly as possible with a
very high probability.
The main approach of this protocol is to distribute
and deliver application packets to hosts, called
carriers, within connected portion of Oppnets. By
using this scheme, packets are spread quickly within
the connected portion of the network through node
mobility. At this point, the packets get spread to an
additional group of nodes. Through such transitive
transmission of data, packets have a high probability
of eventually reaching their destination. This scheme
requires large amount of bandwidth and buffer space.
Moreover, a large number of multiple copies of the
same packets get generated throughout the network
which leads to network congestion.
B. Spray and Wait Routing Protocol
This scheme consists of the following two phases
(Spyropoulos et al., 2005):
Spray phase: The packet originating at the
source node having X copies initially spread/for-
warded the copies by source or possibly other
intermediate nodes receiving a copy of X dis-
tinct relays.
Wait phase: During spraying phase if no desti-
nation is found then each of the X nodes carrying
packets performs direct transmission.
This protocol uses the concept of Epidemic routing
due to its speediness and simplicity for packets
spreading and direct transmission. The scheme starts
by spreading numbers of packets in a manner that is
similar to the routing. By doing so, enough copies of
the same packet get generated in the network and
eventually at least one of them will find the
WINSYS2015-InternationalConferenceonWirelessInformationNetworksandSystems
4

destination as quickly as possible (with high
probability). In this scheme, the node stops spreading
packets when it has only one copy with it. The node
which is carrying a single copy performs the direct
transmission. Due to this mechanism Spray and Wait
could be viewed as single and multi-copy schemes.
Hence, its performance is quite better as compared to
Epidemic routing and other single and multi-copy
schemes in terms of number of transmissions and
delivery delay.
C. Prophet Routing Protocol
In the Probabilistic Routing Protocol using History of
Encounters and Transitivity) [10], if a node visited a
location many times in the past then the chance of
visiting same location by the same node is more. In
this scheme before sending packets a probabilistic
metric called delivery predictability is created, say P
(a;b)
ϵ [0 ; 1], at every source node “a” for each known
destination “b”. This delivery predictability reflects
how likely a node will be able to deliver a message to
the destination. When a node “a” comes in contact
with node “b” then node “a” will transfer the packet
to node “b” if and only if the delivery predictability
of the node “b” is higher than that of node “a”.
3 PROPOSED SCHEME:
PRoWAIT
In this section, the PRoWait protocol is discussed in
detail. It is a hybrid forwarding strategy that combines
the advantages of Prophet and Spray and Wait proto-
cols.
A. Forwarding Strategies
Most of the routing protocols designed so far forward
a packet from one node to its neighbor based upon
lowest cost of the path towards the destination. Also,
the packet is sent to a single node instead of multiple
nodes due to high reliability of multipath
communication. However, in Oppnets things are
completely different. When a packet arrives at a node,
there might not be any available path to the
destination and the node has to buffer it in its storage
space. When the source node encounters another
node, a decision has to be made whether a particular
packet is to be transferred or not. To increase the
delivery probability it may also be required to
forward a packet to multiple nodes. But, these types
of decisions are not trivial to make.
When a node encounters another node with low
value of delivery predictability, one cannot predict
whether this node will encounter another node with
higher probability within a reasonable period of time.
Furthermore, selecting a particular node out of many
available nodes for transmitting a certain packet is
another problem. However, with distribution of large
number of packets to a large number of nodes, the
probability of delivering a packet to its destination
will increase. As a result more resources are required
which results in wasting system resources. Thus,
instead of giving a packet to many nodes, if only a
few nodes are selected, then lesser number of system
resources will get utilized. This will lower the
probability of delivering a packet and incur high
delay.
In PRoWait, we have chosen a rather simple
forwarding strategy–when two nodes meet each
other, a packet is transferred to the other node if the
delivery predictability of the destination of the packet
is higher at that node. The delivery predictability of
PRoWait is calculated from Prophet routing protocol.
Spraying the packets to the neighboring nodes is done
with the Spray and Wait protocol’s technique, while
Prophet’s delivery predictability is used in the
selection of a node as a next hop.
Figure 1: Algorithm with an illustrative example.
The source node initially has x copies of packet to be
sent. Any node A that has (x >1) copies of the packet
(source or relay) and encounters another node B (with
no copies), hands over to B [x/2] copies and keeps
[x/2] copies for itself. When B encounters another
node C (with no copies), it hands over to C [x/4]
copies and keeps [x/4] copies for itself. This process
Probability-basedControlledFloodinginOpportunisticNetworks
5

will continue until a node is left with only one copy
or reach the destination. If the destination is not
found, then each of the nodes carrying a single copy
of the packet performs direct transmission. Here
every node is provided with two variables: hop count
and probability. When two nodes come within the
range of each other, then a packet is passed from a
node having lower probability to a node having
higher probability, else no transmission occurs.
PRoWait creates neither too less nor too much copies
of the packets in the network. It tries to maintain
enough copies of the packets that ensure its successful
delivery with lesser delay to the destination. It also
tries to reduce the resource consumption by limiting
the amount of flooding done in comparison to the
Epidemic routing protocol.
B. Algorithm
The algorithm used in PRoWait is also depicted in
Fig.1. In this figure, node A is the source node that
has x copies of message M1 with it. It has two neigh-
bors, node B and node C. Both nodes do not have
message M1 with them. The value of delivery predict-
ability at node A, B, and C are 0.2, 0.3, and 0.1, re-
spectively. Thus, according to PRoWait, node B is se-
lected and node C is rejected as it has higher value of
delivery predictability than node A. Node A then
transfers the [x/2] copies of the message to node B
and keeps [x/2] copies with itself. This process of
message copy transfer goes on from one node to an-
other node until x becomes equal to 1 or the message
TTL expires. All nodes that have x = 1transfer the
message to the destination on having direct contact
with it.
4 SIMULATION AND RESULTS
We evaluated the performance of the proposed
scheme using simulation analysis. Simulation for the
PRoWait has been done on the Opportunistic
Network Environment (ONE) simulator. It is a Java
based simulation environment that is capable of:
• Generating node movement using different
movement models.
• Routing packets between nodes with various
Oppnet routing algorithms.
• Visualizing real time mobility and packets pass-
ing in its graphical user interface.
For Simulation analysis, we consider six groups
of mobile node. The pedestrian groups have 40 nodes
and one group (term) has 2 nodes each. Out of six
groups three groups are of pedestrian type with a
walking speed of 0.5 – 1.5 m/s. Another group,
term/period group, has a speed of 2.7 – 13.9 m/s and
final group is of city bus with a moving speed of 10 –
30 m/s. A TTL of 300 minutes is assigned to each
group for their messages. Group of pedestrians has a
buffer size of 50M each while the group of term has
50M buffer size. Transmission speed for pedestrians
is 2Mbps with a transmission range of 10m each and
for term it is 10Mbps with 1000m transmission range.
Each simulation is run for 20,000 second. A new mes-
sage of size 500Kb – 1Mb is created after every 25–
35 seconds. For movement of nodes Shortest path
map based movement model [14] is used with world
size of 4500 m x 3400 m.
The performance of PRoWait was evaluated and
compared to the Epidemic, Prophet, Spray and Wait
protocols by varying the buffer size and TTL. The
buffer size of each node in the scenario was changed
from 2MB to 15 MB and the resultant outputs were
observed. Further, evaluation was carried out by var-
ying the TTL of each message from 90 minutes to 210
minutes. The corresponding results were recorded,
analyzed, and discussed next.
Fig.2 shows the relation between the buffer size
and delivery probability. It can be observed from
Fig.2 that the delivery probability of packets for PRo-
Wait is found to be 0.4436 which is the second highest
among the four protocols plotted (Prophet = 0.2955,
Spray and Wait = 0.4522 and 0.2855 is for Epidemic).
Fig.3 shows the relation between buffer size and
mean overhead ratio. It is found that the mean average
overhead ratio for the proposed protocol is 8.703
which is the least among the four protocols plotted
(Spray and Wait = 11.65, Prophet = 52.136, Epidemic
= 78.021). Fig.4 depicts the relation between buffer
size and hop count. It can be observed from Fig.4 that
the mean value of hop count in PRoWait is 2.245,
which is lower than other three protocols (Prophet =
2.93, Spray and Wait = 2.35 and 3.86 is for Epidemic).
Figure 2: Comparison graph between Buffer size and De-
livery Probability.
WINSYS2015-InternationalConferenceonWirelessInformationNetworksandSystems
6
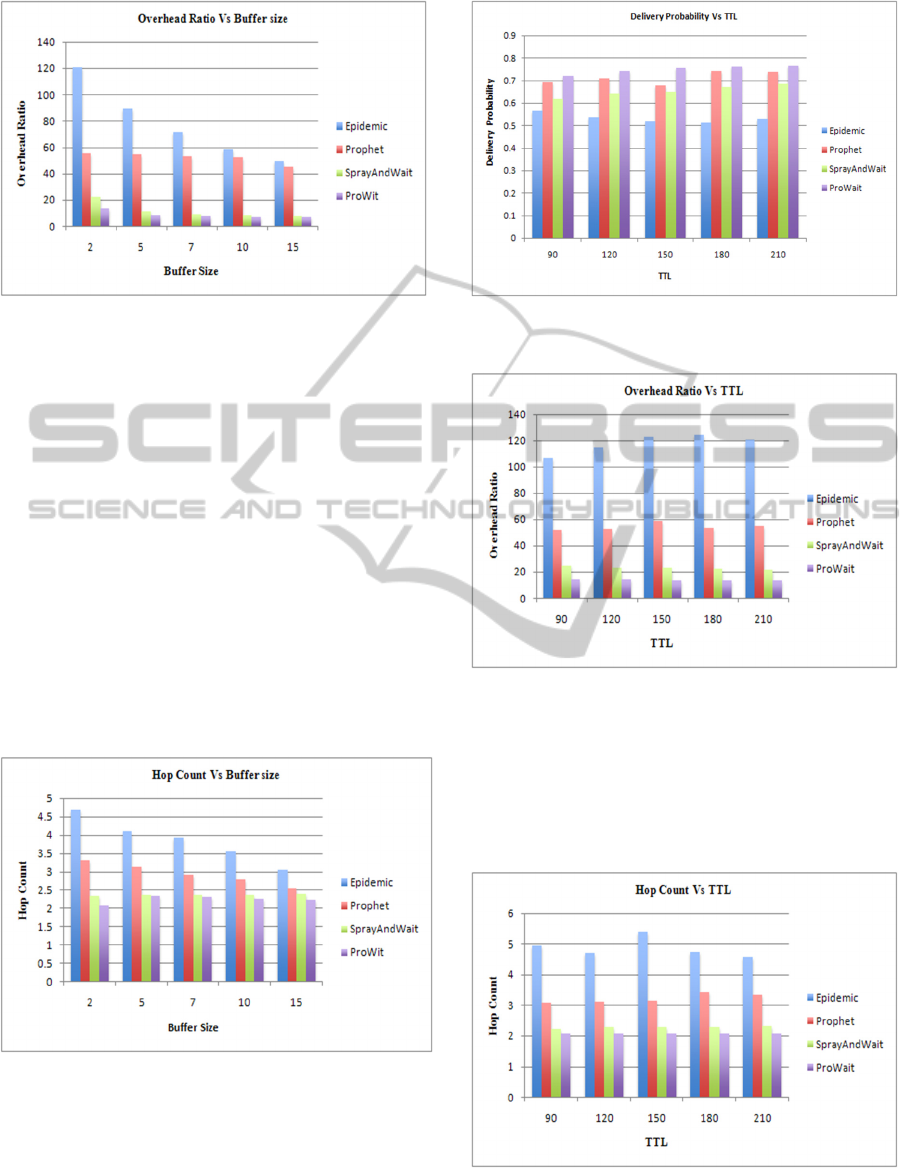
Figure 3: Comparison graph between Buffer size and Aver-
age Latency.
Fig.5 illustrates the relation between TTL and de-
livery probability of the four protocols. It is observed
that the mean delivery probability of packets for PRo-
Wait is 0.7492 which is the clear highest among the
four protocols plotted (Spray and Wait = 0.6536,
Prophet = 0.7115, and 0.5332 is for Epidemic). Due
to this, the number of packets successfully delivered
is quite high in PRoWait. Fig.6 is depicts the relation
between TTL and overhead ratio. It has been observed
that the mean overhead ratio for PRoWait is 14.05,
which is the lowest among the four protocol plotted
(Prophet = 45.42, Spray and Wait = 23.07 Sec, Epi-
demic = 181.133). Further, the ProWait performance
is 61.57% better than the Epidemic, 68.25% better
than Spray and Wait and Prophet, respectively in
terms of mean overhead ratio.
Figure 4: Comparison graph between Buffer size and Hop
count.
Figure 5: Comparison graph between TTL and Delivery
Probability.
Figure 6: Comparison graph between TTL and Average La-
tency.
Fig.7. shows the relation between TTL and hop count.
It is found that the mean value of hop count in
PRoWait is 2.07 which is again the lowest when
compared to the other three protocols (Spray and Wait
= 2.28, Prophet = 3.222 and 4.88 is for Epidemic).
Figure 7: Comparison graph between TTL and Hop Count.
Probability-basedControlledFloodinginOpportunisticNetworks
7

5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, a new routing protocol named as
PRoWait is designed to overcome some of the
shortcomings of the existing protocols in Oppnet. As
the area of routing in Oppnets is still under research
and much work is to be done in different aspects, the
main focus in this work is mainly to increase the
packet delivery ratio and lower delay and hop count.
The PRoWait is designed to overcome some of the
shortcomings of the existing protocols in Oppnet.
Through simulation analysis the performance of
PRoWait is evaluated and compared with Epidemic,
Spray and Wait, and Prophet protocols in terms of
delivery probability, overhead ratio, and average hop
count performance metrics. It has been observed that
PRoWait outperforms these protocols on the basis of
aforementioned performance metrics.
In future, efforts will be focused on increasing the
packet delivery ratio by adding some more
parameters and functions to the PRoWait scheme.
Performance of PRoWait on different mobility
models will also be explored in the future.
REFERENCES
Elizabeth M. Royer and Chai-Keong Toh, 1999, “A review
of current routing protocols for ad hoc wireless net-
works”, IEEE Personal Communication Magazine, vol.
6, no. 2, pp. 46-55.
C.-K. Toh, 2002, “Ad Hoc Mobile Wireless Networks: Pro-
tocols and Systems”, Prentice Hall PTR, Englewood
Cliffs, NJ.
L. Pelusi, A. Passarella, and M. Conti, 2006, “Opportunistic
networking: data forwarding in disconnected mobile ad
hoc networks”, IEEE Communications Magazine, vol.
44, Issue 11, pp. 134-141.
C.-M. Huang, K.-C. Lan, C.-Z, and Tsai, 2008, “A survey
of opportunistic networks”, in proceedings of the 22
nd
Intl. Conference on Advanced Information Networking
and Applications- workshops, 2008 (AINAW 2008),
Okinawa, Japan, pp. 1672-1677.
S. K. Dhurandher, Deepak Kr. Sharma, I. Woungang, and
H.C. Chao, 2011, “Performance Evaluation of Various
Routing Protocols in Opportunistic Networks”, in Pro-
ceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM Workshop 2011, Hou-
ston, Texas, USA , pp. 1067-1071.
A. Keranen, 2008, “Opportunistic Network Environment
Simulator”, Special Assignment Report, Helsinki Uni-
versity of Technology, Dept. of Communications and
Networking.
A. Vahdat, and D. Becker, 2000, “Epidemic routing for par-
tially connected ad hoc networks”, Technical Report
CS-2000-06, Dept. of Computer Science, Duke Univer-
sity, Durham, NC.
T. Spyropoulos, K. Psounis and C. S. Raghavendra, 2005,
“Spray and Wait: An Efficient Routing Scheme for In-
termittently Connected Mobile Networks”, in proceed-
ings of SIGCOMM Workshop on Delay-Tolerant Net-
working, Philadelphia, USA, pp. 252-259.
A. Lindgren, A. Doria, and O. Schelen, 2003, “Probabilistic
routing in intermittently connected networks”, ACM
SIGMOBILE, Mobile Computing and Communica-
tions Review, vol. 7, Issue 3, pp. 19–20.
S. K. Dhurandher, Deepak Kr. Sharma, I. Woungang , and S.
Bhati, 2013, “HBPR: History Based Prediction for Rout-
ing in Infrastructure-less Opportunistic Networks”, in
Proceedings of 27
th
IEEE International Conference on
Advanced Information Networking and Applications
(AINA-2013), Barcelona, Spain, pp. 931-936.
S. K. Dhurandher, Deepak Kr. Sharma, I. Woungang, A.
Saini, 2014, “Efficient Routing based on Past Infor-
mation to Predict the Future Location for Message Pass-
ing in Infrastructure-less Opportunistic Networks”, in
the Special Issue Support Technology and Architecture
for Networked and Distributed Systems, Journal of Su-
percomputing, Springer, DOI: 10.1007/s11227-014-
1243-5, Online, June 28, 2014 (Impact Factor: 0.917).
S. K. Dhurandher, Deepak Kr. Sharma, I. Woungang, R.
Gupta, S. Garg, 2014, “GAER: Genetic Algorithm based
Energy-efficient Routing Protocol for Infrastructure-less
Opportunistic Networks”, Journal of Supercomputing,
Springer, DOI: 10.1007/s11227-014-1195-9, Online,
May 3, 2014 (Impact Factor: 0.917).
A. Keranen, J. Andott, 2007, “Opportunistic increasing re-
ality for DTN protocol simulations”, Special Technical
Report, Helsinki University of Technology, Networking
Laboratory.
WINSYS2015-InternationalConferenceonWirelessInformationNetworksandSystems
8
