Chinese-keyword Fuzzy Search and Extraction over Encrypted
Patent Documents
Wei Ding
1
, Yongji Liu
1
and Jianfeng Zhang
2
1
China Defense Science and Technology Information Center, 100036, Beijing, China
2
National University of Defense Technology, 410073, Changsha, China
Keywords: Chinese Keywords, Fuzzy Search, Extraction, Encrypted Documents.
Abstract: Cloud storage for information sharing is likely indispensable to the future national defence library in China
e.g., for searching national defence patent documents, while security risks need to be maximally avoided
using data encryption. Patent keywords are the high-level summary of the patent document, and it is
significant in practice to efficiently extract and search the key words in the patent documents. Due to the
particularity of Chinese keywords, most existing algorithms in English language environment become
ineffective in Chinese scenarios. For extracting the keywords from patent documents, the manual keyword
extraction is inappropriate when the amount of files is large. An improved method based on the term
frequency–inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) is proposed to auto-extract the keywords in the patent
literature. The extracted keyword sets also help to accelerate the keyword search by linking finite keywords
with a large amount of documents. Fuzzy keyword search is introduced to further increase the search
efficiency in the cloud computing scenarios compared to exact keyword search methods. Based on the
Chinese Pinyin similarity, a Pinyin-Gram-based algorithm is proposed for fuzzy search in encrypted
Chinese environment, and a keyword trapdoor search index structure based on the n-ary tree is designed.
Both the search efficiency and accuracy of the proposed scheme are verified through computer experiments.
1 INTRODUCTION
Along with the development strategy of civil-
military integration in China, the sharing and remote
acquisition of Chinese defence information becomes
increasingly desirable. Cloud storage (Weiss, 2007)
is likely inevitable to the future national defence
library in China, but the sensitive data have to be
encrypted before outsourcing. Data encryption
makes effective data utilization more challenging,
since there could be a large amount of outsourced
data files when data owners in cloud computing can
share their outsourced data with many users (Li,
2010). When one user might only want certain
specific data files, keyword-based search technique
is suitable for selectively retrieving files of interest.
Exact keyword search greatly enhances system
usability by returning the matching files when users’
searching inputs exactly match the predefined
keywords or the closest possible matching files,
when exact match fails. Various keyword search
protocols for encrypted data were proposed (Liu,
2009; Liu, 2012; Boneh, 2004; Chang, 2005), and
(Song, 2000) designed a double-encryption structure
based on a searchable encryption model used in
(Goh, 2003) to guarantee the data privacy. The
aforementioned exact-keyword search method
enjoys higher security but its fatal drawback of little
tolerance about keyword typos and format
inconsistencies makes the search experience very
frustrating (Chor, 1995). For retrieving the data in a
privacy preserving manner but more efficiently, the
fuzzy keyword search is introduced, e.g., in (Ji,
2009), where fuzzy sets based on wild card
technique and gram based technique are constructed
and a symbol-based trie-traverse search scheme is
adopted. However, these methods are adapted to
English language, and thus turned to be invalid for
Chinese keywords because of their diverse semantic
analysis philosophy. In order to utilizing fuzzy
search engine for Chinese keywords, a pre-process
procedure on the initial Chinese characters is
necessary (Cao, 2009). Keyword extraction is also
helpful to accelerate the keyword search progress
since it links finite keywords with a far more number
of files. The drawbacks of the traditional method of
168
Ding, W., Liu, Y. and Zhang, J..
Chinese-keyword Fuzzy Search and Extraction over Encrypted Patent Documents.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2015) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 168-176
ISBN: 978-989-758-158-8
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
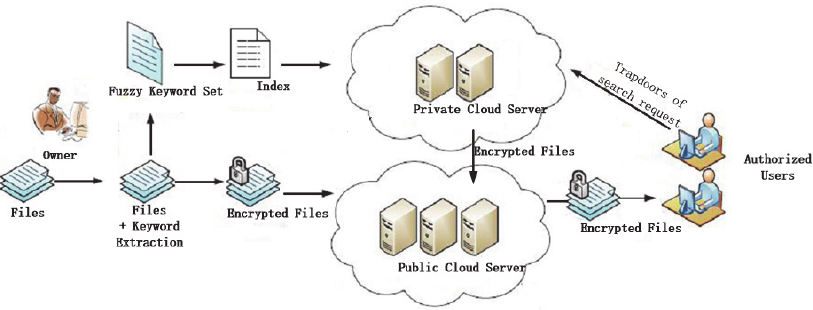
Figure 1: Adopted architecture of the fuzzy keyword search.
manual keyword extraction are obvious, e.g.,
including the inconformity of keyword combination
and low efficacy, especially in the scenarios of cloud
computing. Many research can be found for the
automatic keyword extraction, e.g., (Witten, 2009)
adopts statistical methods based on English
dictionary to build a KEA system for automatic
keyword extraction, and (Yang, 2002) uses PAT-tree
structure to auto-collect keywords, while an
improved scheme based on the co-occurrence
frequency of Chinese phases is reported in (Du,
2011). However, few studies are done particularly
for automatic keyword extraction over Chinese
patent documents.
In this paper, for increasing the accuracy of
keyword extraction, we overall consider the
influence of the word frequency in the special
regions, the penalty function of parallel structure and
the weighted lexical morphemes upon the subjects of
Chinese patent literature. After removing the
common words, Chinese keywords are automatically
extracted based on an improved method of the term
frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF)
algorithm. To efficiently search Chinese keywords, a
Pinyin-Gram-based algorithm is proposed to build
the fuzzy keyword set, since Chinese Pinyin offers a
unique method to study the Chinese word similarity,
which is substantially different from English.
Encrypted Files and keyword sets are transferred to
the private cloud server. From the side of authorized
users, a keyword trapdoor search index structure
based on the n-ary tree is designed, and the searched
encrypted files are outsourced by the public server,
which usually has much more memories than the
private server. The efficiency of the proposed
scheme is verified through computer experiments,
which is significantly higher than the traditional
methods.
2 SYSTEM DESIGN AND TASK
2.1 System Description
In this paper, the adopted system architecture is
consist of four components, i.e., the owner, the
private cloud server, the public cloud server and the
authorized users as indicated in Fig. 1. The
difference compared to general system architecture,
e.g., in (Li, 2010), lies in that a private cloud server
is introduced. The advantages of such arrangement is
to doubly enhance the security of sensitive files,
since information leakage may happen through the
index analysis if all the data are stored together in
the public server.
The flow of the fuzzy keyword search is depicted
as the follows. The keywords are extracted
automatically from the patent files, and then the
fuzzy keyword sets and search index are constructed.
Patent files are encrypted and transferred to the
private server by the owner. These encrypted files
are uploaded to the public cloud server with
necessary remarks or extra encryption. The
authorized users deliver the search request and the
responding trapdoor functions are processed at the
private server. The file indexes and the found
encrypted files are outsourced to the user. Besides
these features, the encryption of certain patent
literature, e.g., the national defense patents, are
desired for cloud computing. As implied by (Li,
2010), the cloud server cannot be fully trusted. On
one hand, it does not delete the encrypted files and
the index, and only response to the query requests
from authorized authors with unchanged search
results. On the other hand, it may analyze the data
stored in the server for certain purposes and sell the
analyzed results as additional information to
Chinese-keyword Fuzzy Search and Extraction over Encrypted Patent Documents
169
opponents. Inspirited by (Shi, 2007), the following
two models are considered to protect the data
security.
1) Cipher-text Model. With this model, the cloud
server only knows the encrypted files without the
secret key. Hence, the data information would be
safe and the query request is conceal.
2) Trapdoor Model. In this model, the cloud server is
potential to perform additional operations on stored
data, e.g., attaining static data and extra analysis
information according to the utilization frequency of
certain keyword strings or outsourcing files (Zerr,
2008). Using the trapdoors of keyword fuzzy set,
exact keywords are hidden and thus it is unlike that
the cloud server learns the specific information about
keywords.
It is noteworthy that Chinese characters have a
different formation philosophy compared with
English language, and Chinese-Pinyin plays an
essences role in constructing fuzzy set (Cao, 2009)
which is adopted in this paper.
2.2 Design Target
Our purpose is to design an efficient and safety
Chinese-keyword fuzzy search system based on
cloud storage. More specifically, the design tasks
include:
1) Automatic Chinese keyword extraction;
2) Constructing the keyword fuzzy set, which should
be of small size and fast building period.
3) Keyword fuzzy search, which supports a rapid
encrypted file searching using an efficient trapdoor
index structure;
4) Data security, which prevent the leakage of
sensitive files and keyword information;
5) System usability, which costs low level
communication bandwidth and computation
complexity to complete all the above tasks.
2.3 Notation Definition
Herein we define the notations used in the following
sections. Let
1)
{}
12
,,,
K
DW DW DW DW¼=
denotes the
collect of the specialty domains, with K as the
number of all concerned specialties.
2)
{
}
12
,,,WD wd wd wd
À
¼=
denotes the collection
of all the Chinese words or phrases in the dictionary
of science and technology, where
À
is the total
number of Chinese words;
3)
{
}
12
,,,WS ws ws ws
Á
¼=
denotes the collection of
all the initial keywords contained in outsourcing files,
where
Á
is the total number of initial keywords;
4)
{}
12
,,,
M
wWww=¼
denotes the collections of
all the pre-processed keywords
l
w
where M is their
total number;
5)
{}
12
,,,
N
FFFF=¼
denotes the collection of the
outsourcing files with N as the file number;
6)
{
}
'' '
12
,,,
N
CFFF¼=
denotes the collection of the
encrypted files of the outsourcing files with N as the
file number;
7)
(, )
l
wl
THwSk=
denotes the trapdoor of length
τ according to the keyword
l
w
, where H(·)
represents the keyed-Hass message authentication
code, e.g., HMAC-MD5, and Sk is the shared key
between the owner and the authorized users;
7)
FID
l
denotes the sole label of the encrypted file;
8)
{
}
'
,
'
|(,)
l
llwd l
Swedwwd=£
denotes the collection
of the keywords whose edit-distance with the
keyword
l
w
is no more than d, where
'
(, )
ll
ed w w
is
the edit distance between the keywords
l
w
and
'
l
w
;
9)
12
l
wK
AIII= “”
denotes the adapted Pinyin
syllable string according to the keyword
W
l
w Î
,
where K is the number of Chinese characters in this
keyword
l
w
and
j
I
represents the j-th syllable
according the j-th Chinese character in the keyword;
10)
{}
'
,
,
'
|'
l
w
l
Ad
wd
ASdd=£
denotes the collection
of the adapted Pinyin syllable strings according to
the keyword collection
,
l
wd
S
, with
,
l
dw
A
=
{}
''
|(, )
l
ll
w
ww
AAAed d=
.
12
l
wK
AIII= “”
denotes the fuzzy counterpart
of
12
l
wK
AIII= “”
, where
j
I
may lack no more
than a final compound, an initial consonant or a
KDIR 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
170

Pinyin tone compared with
j
I
in this paper, and
{}
,,'
|'
wl
l
Ad wd
dASd=£
collects all the fuzzy strings
whose edit-distance with the keyword
l
w
A
is no more
than d, with
{
}
,
|(, )
llll
wwwwd
edAAAAd==
.
It is noteworthy that each syllable
j
I
contains
three parts, i.e., the Pinyin spelling, the Pinyin tone
and an underline symbol “_”, where the Pinyin tone
ranges from 1 to 4, and the Pinyin spelling contains
at most two parts, which are the final compound and
the initial consonant picked from a pre-fixed Pinyin
spelling combination table while a small number of
Pinyin syllables only contain the final compound in
the spelling. For example,
j
I
=“zhong1_” according
to the Chinese character “中” with “zhong” being its
Pinyin spelling and “1” being its Pinyin tone as well
as an underline symbol “_” for separating adjacent
syllables, where “zh” is the initial consonant and
“ong” is the final compound.
3 KEYWORD EXTRACTION
3.1 Common Word Removal
The common words are defined in this paper as
those words which have a high word frequency in
most patent documents. These words are known to
strongly affect the keyword extraction based on the
TF-IDF algorithm (Yang, 2002). We collect the
common words according to the following criterion
(, )
(, )
1, min ( , )
(, )
(, )
(, )
0, min( , )
TF i p
TF i k
pk
cw i
TF i p
TF i k
pk
fwdDW
fwdDW
NN
fwdDW
fwdDW
fwdDW
NN
d
d
ì
ï
ï
ï
>
ï
ï
ï
=
í
ï
ï
ï
£
ï
ï
ï
î
(1)
which indicates that the word
i
wd
shall be seen as a
common word if
(, )1
cw i
f
wd DW =
when its
occurrence frequency in any two specialty domains
(e.g.,
p
DW DWÎ
and
k
DW DWÎ
) is more than
the threshold number
d
, with
p
N
and
k
N
being the
patent document number in these two corresponding
domains.
(, ) (,, )
TF i p TF ID
k
Fik p
f
wd DW f wd F DW
-
=
å
summarizing the TF-IDF value of the word
i
wd
in
all the files (i.e.,
k
F
) which belongs to the domain
p
DW
, while
(,, )
TF IDF i k p
f
wd F DW
-
returns the TF
value of
i
wd
in the file
k
F
.
3.2 Keyword Weighted Function
Traditional methods based on TF-IDF usually take
the influence of the word frequency in the special
regions of the literature (e.g., the title) into account
in order to accelerate the extraction speed (Witten,
1999). Different from other literature, patent
literature also characteristics of particular features,
which can help a fast and accurate keyword auto-
extraction. The following two features are
considered in this paper for Chinese patent literature:
1) Combined phrases or words probably contains
the keyword. In Chinese literature, there are
many combined phrases which usually share the
same lexical morphemes, and it is likely that
keywords lie in these phrases. For instance, two
Chinese phrases
1
wd =
“ 战术电台” and
2
wd =
“ 背负电台” share the same lexical
morpheme
3
wd =
“电台”,which is likely one
of the keywords in that document.
2) Words in the parallel structure are not the
keywords. The words or phrases in the parallel
structure in Chinese literature, which are
normally remarked by Chinese conjunction
words (e.g., “ 和 ”, “ 与 ” and “ 或 ”) and
punctuation mark (i.e., ”、”), usually have a high
word frequency, but do not be considered as the
keywords.
The weighted function used for extracting the
keywords in a document is defined as follows
wei 1 reg 2 3 pemor n
() () () ()
ii ii
f wd W wd W wd f wdll l=+ -
(2)
where
reg
()
i
Wwd
reflects the weight of the word
occurrence frequency given by
reg title other
() () () ()
iTFi i i
W wd f wd f wd f wd=+ +
(3)
with
()
TF i
fwd
denoting the word frequency of
i
wd
in this document while
title
()
i
fwd
and
Chinese-keyword Fuzzy Search and Extraction over Encrypted Patent Documents
171
other
()
i
fwd
denoting the weights if the word lies in
the title and other special regions respectively;
mor
()
i
Wwd
on behalf of the weight of the lexical
morphemes described in details by (Du, 2011),
which responds to the first aforementioned feature of
the patent literature;
pen
()
i
fwd
representatives of the penalty function
when the word lies in a parallel structure as
described in the second aforementioned feature of
the patent literature. More specifically,
mpen 1 par o2ra
() () (, )
ii ij
ij
fwd f wd fwdwdaa
¹
=+
å
(4)
given that
para
()
i
fwd
counts the total number of the
word
i
wd
appearing in the parallel structure and
mor
(, )
ij
fwdwd
counts the number of the same
lexical morphemes shared by
i
wd
with other words
(i.e.,
j
wd
’s) in the parallel structure, while
1
a
and
2
a
are the responding weight parameters. For
instance, two Chinese phrases
1
wd =
“战术电台”
and
2
wd =
“背负电台” show in a parallel structure,
and then
1mor 2
(, )1fwdwd=
by knowing the they
share one lexical morpheme “电台”.
Plus,
1
l
,
2
l
and
3
l
represents the weight of the
word appearance frequency, the weight of the lexical
morphemes and the penalty of the parallel structure,
respectively.
To this end, we define the keyword as
wei
{|() ,(, )0}
li icwi
ws wd f wd f wd DW=>G =
(5)
which means that the extracted keyword
l
ws
is the
word whose weighted function value is higher than
the threshold
G
as well as outside the common
word collection.
4 KEYWORD FUZZY SEARCH
The extracted keywords form a pre-defined keyword
set by the owner, which offers to the keyword search
engine as the reference. However, in order to
facilitate the search experience of the user, the fuzzy
search scheme over the encrypted data is introduced.
4.1 Pinyin-Gram-based Algorithm
In the informatics and computer science, the edit
distance between two strings are counted by the
number of the letter replacement to convert one
string into the other. The Gram of a string is defined
as the core sub-string utilized for an efficient fuzzy
search, and a Gram-based keyword fuzzy set was
introduced to build fuzzy search schemes over
encrypted data. One of its basic hypotheses is that all
original operations by users only make changes on a
single word within the keyword, and do not
disorganize the positions of all the letters within
such keyword. Such condition is usually true in
reality and thus the Gram-based algorithm to
construct keyword fuzzy sets is widely adopted, e.g.,
in (Li, 2010). However, Chinese keywords are no
like English keywords whose adjacent words are
separated by a space symbol, while Chinese
characters are connected with each other. Hence a
pre-process operation is first needed to isolate all the
characters, where Pinyin syllable strings are
introduced (Cao, 2009). In additions, the traditional
method used in English scenarios treats one
replacement of a letter as the edit distance of 1, and
such idea shall results in a hug fuzzy set not only
because Chinese Pinyin contains both spelling and
tone, but also since the same Pinyin syllable string
can represent various characters. It is also vain to
consider Pinyin string as a generalized English letter
strings since deleting, inserting or replacing a letter
of Pinyin spelling may introduce an illegal Pinyin
string. In (Wang, 2007; Bellare, 1997), Pinyin
strings are used for matching approximate Chinese
strings in plaintext scenarios. For a Chinese Pinyin
syllable, the difference between other syllables can
be classified into 3 aspects: the initial consonant, the
final compound and the tone. Based on this fact, we
define the edit distance used in this paper as follows:
Definition 1: Edit Distance for Pinyin Syllable
1) When the tone varies, the edit distance increases
by 0.5;
2) When either the initial or the final varies but the
changed notes belong to the prefixed collection of
Pinyin similar pairs, the edit distance increases by
0.5;
3) When either the initial or the final varies but the
changed notes do not belong to the prefixed
KDIR 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
172
collection of Pinyin similar pairs, the edit distance
increases by 1;
4) When both the initial and the final vary, the edit
distance increases by 4.
In this definition, note that the prefixed collection of
Pinyin similar pairs have finite options (Cao, 2009),
e.g., ’z’ and ‘zh’ form a pair of similar initial
consonants while ‘en’ and ‘eng’ form a pair of
similar final compounds.
Definition 2: Edit Distance between Pinyin Syllable
and Its Fuzzy String
1) When an initial or a final is deleted, the edit
distance increases by 1;
2) When both the initial and the final vary, the edit
distance increases by 4;
3) When the tone varies, the edit distance increases
by 0.5.
Based on the above definitions, we introduce the
Pinyin-Gram-based algorithm for constructing
Chinese keyword fuzzy set as Algorithm 1:
Algorithm 1: Constructing Chinese-keyword Fuzzy
Set
1) Build the Pinyin syllable table and the collection
of Pinyin similar pairs;
2) Let
l
w
A
=
''
'
,0
,0
| and ASCII ASCII
l
ll
w
l
Aw
ww
AS
ìü
ïï
ïï
íý
ïï
ïï
îþ
=
distinguish two different keywords
l
w
and
'
l
w
when
'
l
l
w
w
AA=
, e.g.,
l
w
=“ 意义” and
'
l
w
=“ 异议”,
where
ASCII
l
w
denotes the ASCII code of
l
w
.
3) Traverse
,
w
l
Ad
S
and
,
w
l
Ad
S
recursively from
,0.5
w
l
dA
S
-
and
,0.5
w
l
Ad
S
-
by varying and deleting
only one parameter
Y
, respectively, with the initial
condition of
{}
,0 ,0
ww l
ll
AwA
SS A==
and with
Y
representing an initial consonant, a final compound
or the tone symbol;
4) Let
,,,
Fuzzyword
www
lll
Ad Ad Ad
SS=È
, where
,
Fuzzyword
w
l
Ad
collects all the fuzzy set of the
keyword
l
w
with an edit distance threshold of d.
Based on Algorithm 1, an example would be that
according to the keyword
l
w
=“法制”, the fuzzy set
with the edit distance threshold of 1 shall be
,1
Fuzzyword
w
l
A
=
(
)
,0.5 ,0.5
ll l
ww w
AA AÈÈÈ
(
)
,1 ,1
ll
ww
AAÈ
= {fa2_zhi4_
ASCII
|
w
l
} ∪ {fa_zhi4_,
fa2_zhi_, fa2_zi4_} ∪ {a2_zhi4_, f2_zhi4_,
fa_zhi_, fa2_i4_, fa2_zh4_, fa_zi4_, fa2_zi_}, by
noticing that ’z’ and ‘zh’ belong to the collection of
Pinyin similar pairs while
l
w
=“法制” varies from
'
l
w
=“ 法治” although they share the same
pronunciations.
4.2 Multi-node Search Tree Structure
The balanced binary search tree is widely adopted to
build keyword index and several improvements were
proposed, e.g., in (Li, 2010) by using symbol-based
tire-traverse search scheme and in (Li, 2012) by
using binary sort search tree. It is known that HMAC
is featured to be unidirectional and collision resistant,
and its output string has the same length. We divide
(, )
l
wl
THwSk=
into
p
l
segments (Li, 2010), with
p
being the length of this trapdoor and
l
being the
length of each segment. For example, for
{
}
i
Aa=
as a full permutation sequence of length
l
in the
binary sense, where
1
1
ii
aa
-
=+
with
0
0a =
,
hence each divided segment can be represented by a
parameter
i
a
. According to (Li, 2010), we introduce
the adopted keyword trapdoor search index structure
as Algorithm 2:
Algorithm 2: Balanced Multi-node Search Tree
1)The data owner outsources the encrypted files
and the trapdoors
(
)
||
ll
ww
FID T
of all keywords in
the fuzzy set to the private cloud server;
2)Let Gw be the index root node at the private
cloud server and each node can have
2
l
sub nodes
with
Node
i
as the i-th sub node as indicated in Fig.
2, performing the following operations:
Chinese-keyword Fuzzy Search and Extraction over Encrypted Patent Documents
173

3)For a segment of
l
w
T
with
,
l
j
w
T
as the value of
the j-th segment at a node denoted as
,
Node
wj
l
T
, with
the initial father node as Gw.
Gw
0
Node
1
Node
2
Node
l
2
Node
l
0
Node
2
Node
l
0
Node
0
Node
2
Node
l
0
Node
0
Node
2
Node
l
0
Node
FID
index
FID
index
FID
index
FID
index
Figure 2: Adopted balanced multi-node search tree.
4 ) Process
,
l
jw
T
from j=1 to j=
2
l
, and judge
whether the last segment of
l
w
T
has been treated or
not; If yes, the index
l
w
FID
is added to the index
table of the sub node (i.e.,
,
Node
wj
l
T
) and terminate
the search; If not, when the sub node
,
Node
wj
l
T
is
null, then fill this node with
2
l
empty sub nodes
and consider
,
Node
wj
l
T
as the new father, otherwise
directly consider
,
Node
wj
l
T
as the new father, iterating
the step (1). Using Algorithm 2, the update
operations like inserting or deleting can be
performed too by similarly updating the file
identification, i.e.,
l
w
FID
in the index table, after
finding the leaf node.
5 PERFORMANCE VALIDATION
We randomly choose 800 documents from the patent
reports stored in China Defence Science and
Technology Information Centre from their titles. The
test environment is 3.3GHz CPU, 4G DRR3-
1333MHz RAM and 32bit Windows 7 operating
system.
To remove the common words from these
documents, we first let the threshold
0.4d =
and
recall
()
TF IDF
f
-
from (Yang, 2002) in (1). To extract
keywords, we use
0.7G=
in (3), given that
312
1/3lll===
in (2) where
reg
()
i
Wwd
and
mor
()
i
Wwd
are recalled from (Du, 2011) while
1
5a =
and
2
2a =
is used for
pen
()
i
f
wd
. We note
that the optimal combination of these parameters is
beyond the range of this paper. To depict the
performance the proposed method of keyword
extraction, we choose the F-measure defined as
2 PR
F
PR
´´
=
+
(6)
where the precision value P gives the percentage of
the correctly extracted keywords versus all the
extracted keywords, while the recall value R is the
percentage of the correctly extracted keywords
versus all the true keywords. Fig. 3 depicts the
comparison of several keyword extraction methods,
which indicates the proposed method in this paper is
much more effective than the traditional TF-IDF
method. Compared with (Du, 2011), similar
performance is witnessed, however, when the
number of the keywords is large as the case in cloud
computing, our method shows performance
superiority.
0 500 1000 1500 2000
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
Keyword Number
F Measure
Proposed
Traditional TF-IDF
[14]
Figure 3: Automatic Keyword Extraction Performances.
From the extracted keywords, we choose 1800
keywords for testing our fuzzy search scheme. Fig. 4
shows the comparison of the proposed Pinyin-Gram-
based algorithm and the wild-card-based method
used in (Li, 2010) for constructing Chinese keyword
fuzzy set, which indicates that the proposed scheme
KDIR 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
174

is more efficient. In additions, it also shows that the
construction time increases linearly along the
keyword number while a dramatic increase is
witnessed when the edit distance threshold d of the
fuzzy set is raised.
Fig. 5 shows the comparison of the proposed
multi-node search tree and symbol-based trie-
traverse search scheme used in (Li, 2010) for
constructing Chinese keyword search tree, which
indicates that the proposed scheme is faster. In
additions, it also shows that the construction time
increases linearly along the number of the keyword
trapdoors.
0 500 1000 1500 2000
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
Number of Keywords
Time (ms)
d=0.5, proposed
d=0.5, [2]
d=1, proposed
d=1, [2]
Figure 4: Consumed Time for constructing fuzzy set.
0 2000 4000 6000 8000
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Num of trapdoors
Time (ms)
d=1, proposed
d=1, [2]
Figure 5: Consumed Time for constructing search tree.
Fig. 6 shows the comparison of the proposed
scheme, the methods used respectively in (Li, 2010),
(Li, 2012) and a basic method for searching Chinese
keywords. The basic method means to use a standard
wild-card-based method for constructing the fuzzy
set as used in (Li, 2010) combined with the standard
balanced binary search tree. It indicates that the
proposed scheme is faster than all other methods.
0 2000 4000 6000 8000
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
Num of trapdoors
Time (ms)
Proposed
[17]
[2]
Basic
Figure 6: Consumed Time for searching keywords.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The Chinese Pinyin string construction is purposely
tailored for Chinese keyword scenarios. The Pinyin-
Gram-based algorithm and a balanced multi-node
search tree are proposed for Chinese keyword fuzzy
search over encrypted data. In the system design, a
private cloud is introduced isolated from public
cloud servers for higher security purpose. The
complexity of our scheme is shown to increase
linearly along the keyword number and the proposed
search method shows a more efficient performance
than existing methods.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Dr. Tao Xu for his invaluable advice and
suggestions, who is in part supported by China
Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M570230)
and Tianjin Enterprise-Postdoctoral Fund for
Selected Innovation Program, at University-
Enterprise joint postdoctoral station between
Tsinghua University and Tianjin Zhonghuan
Electronic & Information (Group) Co., Ltd.
REFERENCES
Weiss, A., 2007. Computing in the Clouds. netWorker.
Li, J., et al, 2010. Fuzzy keyword search over encrypted
data in cloud computing, Proceedings of IEEE.
Liu, Q., et al, 2009. An Efficient Privacy Preserving
Keyword Search Scheme in Cloud Computing, IEEE
Int. Sym. on Trusted Computing and Communications.
Liu, Q., et al, 2012. Secure and Privacy Preserving
Keyword Search for Cloud Storage, Journal of
Network and Computer Applications.
Chinese-keyword Fuzzy Search and Extraction over Encrypted Patent Documents
175
Boneh, D., et al, 2004. Public Key Encryption with
Keyword Search, Int. Conf. on Theory and
Applications of Crypto-graphic Technique.
Chang, Y., et al, 2005. Privacy Preserving Keyword
Searches on Remote Encrypted Data, Applied
Cryptography and Network Security.
Song, D., et al, 2000. Practical techniques for searches on
encrypted data, IEEE Sym. on Security and Privacy.
Goh, E.-J., 2003. Secure indexes, Cryptology ePrint
Archive Report.
Chor, B., et al, 1995. Private information retrieval, Annual
Sym. on Foundations of Computer Science.
Ji, S., et al, 2009. Efficient interactive fuzzy keyword
search, VLDB Journal.
Cao, J., et al, 2009. A Pinyin indexed method for
approximate matching in Chinese, CMMSC'2009.
Witten, I., et al, 1999. KEA: Practical Automatic
Keyphrase Extraction, ACM Confrence on Digital
Libraries.
Yang, W., et al, 2002. Chinese Keyword Extraction based
on Max-duplicated Strings of the Document, ACM
SIGIR Conf. on Research and Development in
Information Retrieval.
Du, Y., et al, 2011. Automatic extraction of keyword
based on word co-occurrence frequency, Journal of
Beijing Institute of Machinery.
Shi, E., et al, 2007. Multidimensional range query for
encrypted data, IEEE Symposium on Security and
Privacy.
Zerr, S., et al, 2008. r-Confidential indexing for distributed
documents, IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy.
Wang, J., et al, 2007. An Approximate String Matching
Algorithm for Chinese Information Retrieval Systems,
Journal of Chinese Information Processing.
Bellare, M., et al, 1997. HMAC: Keyed-hashing for
message authentication, Internet Request for Comment
RFC.
Ma, X., 2005. Analysis of Chinese homonym, Contents of
Major Papers.
Li, Q., et al, 2012. Efficient Multi-keyword research over
Secure Cloud Storage, Computer Science.
KDIR 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
176
