A Semantic Web Service Description of Learning Object
Chaker Ben Mahmoud
1
, Ikbel Azaiez
1
, Fathia Bettahar
1
and Faïez Gargouri
2
1
IResCoMath, University of Gabès, Gabès, Tunisia
2
ISIMS, University of Sfax, Sfax, Tunisia
Keywords: e-Learning, Learning Paths, Learning Service, Ontology, Semantic Web Services, OWLS, Web Services.
Abstract: How to find and identify learning objects according with the learner profile represents a main interest in the
quality of learning process. Thus, using the paradigm of Semantic Web Services ensure the independence
and reusability of learning object in a different context. In this paper, we propose an extension of OWLS
that encompass the description of the learning intention and the context of use that characterize a learning
object. We also describe the generic scenario of the publication and discovery process.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recent years, several works have dealt on adaptation
and personalization of learning content. In this
context, the learning objects became a fundamental
element to develop educational contents.
In fact, learning objects include several
problems. First, they cannot be effectively reused
because they are distributed between several places
and depends on the learning system. Besides, the
learning objects have a limit of cooperation which
presents a low probability of binding between
objects.
Therefore, many rules and metadata standards
have been proposed as a solution to overcome the
problem of accessibility and interoperability of
learning objects, and a lot of norms and standards
were created to achieve this. In this stage, several
standardization efforts have been launched including
LOM and SCORM (Lee et al., 2006). These
standard descriptions of learning resources focus on
the characterization of content rather than on its use.
In fact, the above standards have limitations in
the context of heterogeneous learning objects. In
addition, the definition of specialized courses
according to desired skills requires a composition of
learning objects to provide the learner with a
personalized learning course. The problems of
interoperability, reusability and composition of
learning content can be solved by using the
principles of Web service paradigm. Web services
are defined as open standards that provide a flexible
solution for integrating heterogeneous and dynamic
applications that enable interoperability between
different systems.
In this paper, we propose a semantic description
of learning services that encompasses the description
of the learning intention and the use of context that
characterizes a learning object. Then, we propose a
semantic service descriptor, based on our OWLS
extension, to enrich service registry.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: In
Section II we present some related works. Then, we
give an overview of our approach in section III. We
describe, in section IV, the learner profile in the
form of ontology where it specifies four basic
concepts. In Section V we propose an extension of
OWLS to support learning object. In Section VI we
present the principle of learning semantic web
service publication and discovery. Finally, we finish
with a conclusion and some remarks/hints about
future work.
2 RELATED WORKS
(Padron et al., 2004) present a learning web services
framework to support the integration of newer,
complex learning processes and the dynamic
generation of content based communities of interest.
This framework is based on two elements of
construction: the first is The Learning Web Services,
supported by a basic Web Service architecture,
which allows to create, define and publish learning
objects that encapsulate different learning processes;
and the second is Learning Web Services
Mahmoud, C., Azaiez, I., Bettahar, F. and Gargouri, F..
A Semantic Web Service Description of Learning Object.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2015) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 195-201
ISBN: 978-989-758-158-8
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
195

Composition, supported by an architecture for
services composition that allows to look for,
integrate, execute and redefine the learning
processes.
(Gutiérrez-Carreón et al., 2009) is interested to
the semantic description of services to ease the
discovery learning services based on semantic
matching process between educational service
features and user needs. To do this, each device is
controlled by a computer with internet connection.
The user can control the devices that are connected
to computers and the acquisition of data stored in
databases. The implementation of these features is
based on the semantic web, particularly on the use of
ontologies and metadata to annotate learning
services. Indeed, this system uses three types of
ontology domain ontology, an ontology representing
the goals and an ontology describing the learning
services. Ontology learning services is described
using the terms in WSMO (Web Service Modelling
Ontology). The ontology of the objectives described
aspects related to user needs. The domain ontology
defines the terminology and concepts of the subject
area that are used to describe the relevant aspects of
the objectives.
(Cho et al., 2008) focus on the description of the
context of services to adapt learning services to the
user. Moreover, taking into account the context of
the adaptation of services is based on a set of rules.
These are predicates that combine contextual
information and service descriptions to check their
relevance to a particular situation.
(Zniber et al., 2010) presented an approach to
build personalized pathways called POPS (Process-
Oriented Pedagogic Service) by composing services
dynamically. This approach is a conceptual
framework that defines a model for describing the
pedagogical services. This model of Pedagogical
Service provides a set of concepts to describe the
services. According to Zniber, a pedagogical service
is composed of three parts: "profile”, "structure" and
"behavior". The "Profile" describes the general
appearance of the pedagogical service. It
corresponds to the service interface and will be used
when searching for a match between the available
services and the learners’ intentions. The "structure"
part describes the organization of the process to
achieve the pedagogical objective. It is defined by a
process, an initial position and a final position. The
"behavior" element is the "executable" level of
service. It describes the use of the service by a
learner and it takes the form of an implementation
plan with activities and resources to be mobilized.
3 PROPOSED APPROACH
3.1 Motivation
The development of learning systems aims to
provide learners with courses adapted to their needs
and their profile. The challenge therefore is to make
the system more responsive to the request of the
student is based on learning object scattered on
several platforms.
In this context, we consider a learning system as
a set of Learning Semantic Web services where each
service represents a learning object that describes an
intention and context of use. It’s by composing
dynamically services learning that possible to build
custom course adapted to a given profile. The
description of these services and the formulation of
the request of learner are made by two ontologies:
objectives ontology and ontology of the domain
learning.
3.2 Overview of Our Approach
The architecture, shown in Figure 1, represents our
e-learning approach to provide learners with
learning paths adapted to their requests (Ben
Mahmoud et al., 2015), (Ben Mahmoud et al., 2014).
This approach consisted of three components:
Learning data representation component of
learning in order to achieve the learner's learning
objectives.
Formulation component of the learner Query
The building component of the learning path that
satisfied a particular objective set by the learner.
Figure 1: Components of the learning approach
architecture.
In our proposed approach, we use ontologies
both for a semantic description of learning services
and to make easy their research and composition to
generate personalized learning paths. They are also
KEOD 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
196

used for sharing and reuse of learning objects.
Indeed, the same ontologies are used to semantically
describe the learning services (point of view of the
course designer) and to define the learning
requirement (point of view of the learner). Thus, we
have used a domain ontology and objectives
ontology. The first is used to represent knowledge
about the domain of education and the second is to
provide knowledge about the learning objectives.
4 LEARNER PROFILE
In the learning systems, the learner model is
essential for the generation of personalized paths. It
is to take into consideration the concepts of learning
which the system must adapt. These concepts can be
different from one learner to another. At this stage,
there are an adaptable model and an adaptive model.
The adaptable model is modified only by the learner,
while the adaptive model is changed by the system
according to the learner's paths.
The term "model" is used to describe
informations related to learners. The authors use this
term to express the way to represent learners'
knowledge in a given system that to describe
knowledge of a particular learner in this system.
However, in our work, we are interested only to the
data of a learner and not their construction process.
For this reason, we prefer to use the term "profile" of
the learner, in order to separate this object of how to
create it.
Several standards describe the model of the
learner such as PAPI, IMS-LIP. Our learner profile
is based on the IMS-LIP standard (IMS-LIP, 2001),
which is a proposal of the consortium "IMS Global
Learning" made primarily to meet the need for
standardization of data relating to the description of
learners different learning systems. As the majority
of learning systems, knowledge learning expresses
the competence, educational goals, history learning
and preferences.
We describe the learner profile in the form of
ontology where it specifies four basic concepts
(existing in the IMS-LIP): Identification, Affiliation,
Accessibility and Competence (Figure 2).
Accessibility: describes the general accessibility
such as: language skills, disabilities, eligibility
requirements and learning preferences.
Competence: describes the Competence,
experience and knowledge.
Affiliation: provides information on membership
in professional organizations.
Identification: describes the demographic and
geographic data on the learner (name, age,
address, email, etc.)
Figure 2: Learner Profile.
5 OWLS-LO EXTENSION
In this section, we describe our proposed extension
to the OWLS recommended (Wang et al., 2013).
This extension allows the description of the
educational aspect of service learning in ontology
"ServiceLearning". It corresponds to the service
interface and is used when searching for a match
between the semantic learning services available on
the one hand, and the requests expressed by the
learners, on the other hand.
Figure 3: The ServiceLearning Ontology.
The Figure 3 illustrates our Learning extension
of OWLS. The proposed property “provide” is a
property of Service. The class "ServiceLearning"
corresponds to the respective range of this property.
Each instance of Service will provide a
ServiceLearning description. The ServiceLearning
represents the information needed to discover the
A Semantic Web Service Description of Learning Object
197

appropriate service in order to satisfy a specific
learning need.
This extension is composed of three basic
concepts: Leaning intention, context of use, and
required services (see Figure 4).
Figure 4: OWLS extension to represent LO.
5.1 The Intention
The intentional vision places the concept of service
to a higher level of abstraction where the service is
designed to lead to the satisfaction of a user’s
intention. This intention is what the user awaits in
performing a service (Jackson, 1995). Our
description of a service is as the learning intention
allowed defining the finality of service, without
going into the details of its use. It expressed an
intention that the learner sought to achieve. In this
context, Prat (Prat, 1997) have proposed a model for
the concept of intention which is derived from the
linguistic approach and inspired by the case
grammar of Fillmore (Fillmore, 1968) and
extensions of Dik (Dik et al., 1989).
The intention, in this model, is represented by a
verb, targets and different parameters that play
specific roles in relation to the verb. The verb
describes the action of the realization of the
intention, while the target is affected by the object
embodiment of the intention. The parameters (way,
direction, quantity and quality) are used to clarify
and express additional information.
In our approach, the intention was defined by a
learning objective (verb) and a concept of learning
domain (Target). The concept learning objective
depicted the types of learning objectives in
accordance with Bloom's taxonomy [bloom]. They
are expressed in terms of goals and organized in
levels. The definition of the objective falls within the
ontology of learning objectives. The learning
concept domain indicated the target of the learning
intention. The specification of the concept used the
terminology defined in the ontology of the
educational domain (Figure 5).
Figure 5: Intention Code.
For example, for the OWLS-LO (01) Service
("Define Class"), was characterized by the learning
objective "Define" defined in the ontology of
learning objectives and the concept of learning
"class" defined in the ontology of the educational
domain "Java".
5.2 The Context
The context provides a description of the
pedagogical aspect of the learning object as well as
the learning situation in which the service can be
used. To describe this aspect, we based on the
descriptions of the IEEE LOM (IEEE, 2007). Thus,
this context was a selection of properties of the
LOM allowing indexing learning objects
semantically and describing mainly the container but
not its contents.
It's represented by three types of knowledge:
affiliation, accessibility and competence. First, the
Affiliation describes the level of targeted studies for
learning object. Secondly, the accessibility mainly
describes the language in which the resource was
presented. Finally, the competence presents the level
of difficulty of this Learning Object relative to the
target audience: easy, medium, or difficult as it is
illustrated in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Context Code.
KEOD 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
198
For example, for the OWLS-LO (01) Service
("Define Class"), referred to a learning object
whose context was characterized by a "University"
affiliation, language was "Fr" and competence
"Easy."
5.3 The Required Services
The required services are all the knowledge required
so that the learner can use the learning object. This
notion can describe a navigation strategy among the
reused learning objects. Indeed, for a learner, to
access the contents of an object check that it has a
body of knowledge needed to tackle it. Therefore,
the requirement for each service must be satisfied. In
our extension, we define the services required as the
set of coupled {Concept learning domain and
Concept learning objective} needed to use the
service learning during any one specifying the
weighting of each. (Figure 7)
Figure 7: Required service code.
For example, for the OWLS-LO (01) Service
("Define Class"), we could define two required
services: {Define, Attribute} with a weighting of 0.5
and {Define, Method} with a weighting of 0.5.
6 OWLS-LO EXTENSION
IMPLEMENTATION
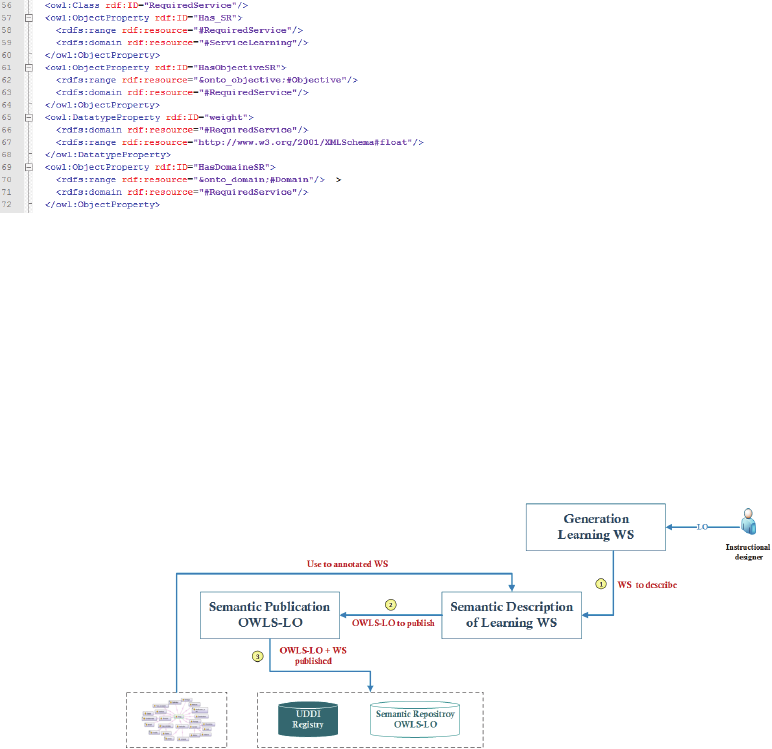
6.1 Process of Publishing
In this section, we present the generic scenario of the
publication process (Figure 8). The instruction
designer presents the learning object to be
interoperable.
After the generation of the learning Web service,
appropriate to learning object, we passed to semantic
description of learning web service by using existing
ontologies. Finally, the learning Web service and
OWLS-LO were published in UDDI registry and
OWLS-LO repository, respectively.
6.2 Process of Discovery
After publishing the learning semantic Web services
both in OWLS-LO repository and in UDDI registry,
we proceeded to discover them. Thus, we present the
generic scenario of the discovery process (Figure 9).
The learner used Semantic Description Query to
describe their intention (Semantic Request) of
learning through browsing ontologies (Domain
ontology, Ontology of objective).
Once the request is submitted, the building path
module (Step of Construction of Learning Path)
extracts the intention and profile of learner and
proceeds, thereafter, to seek (step of Semantic
Matching) appropriate services allowing the
generation of a learning path. Indeed, this semantic
matching similarity proceed to match the intention
of learner with the intention learning of OWLS-LO,
on the one hand, and to match the use of context of
OWLS-LO with learner’s current profile, on the
other hand. After that, we calculate the importance
factor of all required services. Therefore, we select
the OWLS-LO having the highest score.
Finally, we presented a learning path to the
learner according to their goal.
Figure 8: Process of publishing.
A Semantic Web Service Description of Learning Object
199
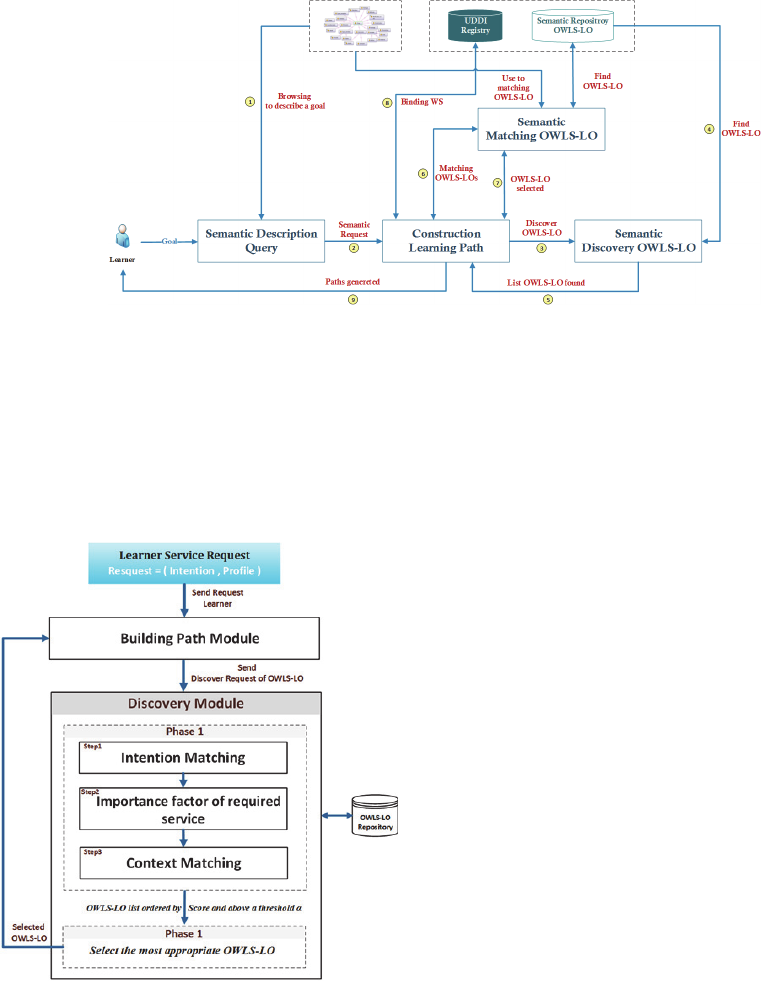
Figure 9: Process of discovery.
6.3 Semantic Matching OWLS-LO
This section gives a global description of the
discovery process (Figure 10), starting from the
query submission to the OWLS-LO replies, by
emphasizing the main steps related to this
matchmaking.
Figure 10: OWLS-LO Discover Mechanism.
When the learner presented their request based
on an intention to be satisfied, the discovery process
was started. The discovery mechanism loaded all
OWLS-LO semantic description of the services and
launched the matching. In a first step, we proceeded
to match the learner’s intention with the intention
that the OWLS-LO service satisfied. Then we
calculated the importance factor of each service
required for this selected OWLS-LO. In the end, we
matched the educational context services with
learner’s current context. After getting a list of the
most appropriate OWLS-LO, we selected the service
having the highest score matching.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we proposed an approach defined a
learning Web service for each learning object to
overcome the problems of interoperability and
accessibility of learning objects. This web service is
represented by an extension of OWLS composed of
three basic concepts: learning intention, use of
context and required services. This extension will be
used when searching for a match between the
semantic learning services available on the one
hand, and the requests expressed by the learners
according on her profile, on the other hand.
In order to appreciate the usefulness and the
efficiency of our approach, we intend to make the
description more meaningful and the service
discovery more precise and appropriate to the
learner‘s needs. Also, we expect to evaluate our
service discovery mechanism in a more interesting
scenario in future work.
REFERENCES
Lee, M., Tsai, J., Wang, T., 2006. An Ontological
Approach for Semantic-Aware Learning Object
Retrieval. In Sixth International Conference on
Advanced Learning Technologies, pp.208-210.
Padron, C. L., Torres, J., Dodero, J. M., Diaz, P., Aedo, I.,
2004. Learning Web services composition and learner
communities support for the deployment of complex
learning processes. In IEEE International Conference
on Advanced Learning Technologies. pp. 390-394.
KEOD 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
200
Gutiérrez-Carreón, G., Daradoumis, T., Jorba, J., 2009.
Automatic composition of Learning Grid Portlets: a
comparison of syntactic and semantic approaches. In
International Journal of Grid and Utility Computing
(IJGUC), vol.1, no.4, pp.308-315.
Cho, D. J., Woo Hong, M. W., 2008. A Design of
Ontology Context Model in Ubiquitous Learning. In
12th WSEAS International Conference on
COMPUTERS, pp.844-848.
Zniber, N., 2010. Service-Oriented Model for Personalized
Learning Process Desig. These, Université Paul
Cézanne - Aix-Marseille III.
Ben Mahmoud, C., Azaiez, I., Bettahar, F., Abel, M.,
Gargouri, F., 2015. A Learning Semantic Web Service
for Generating Learning Paths. 14th IEEE/ACIS
International Conference on Computer and
Information Science, ICIS 2015, Las Vegas, NV, USA,
June 28 - July 1, 2015, pp 627—631.
Ben Mahmoud, C., Bettahar, F., Abel, M., Gargouri, F.,
2014. A New Approach Based on Learning Services to
Generate Appropriate Learning Paths", In 16th
International Conference on Enterprise Information
Systems, Portugal, pp.643-646.
IMS-LIP. (2001). IMS Learner Information Packaging
Information Model Specification, Retrieved 24 June,
2014,
http://www.imsglobal.org/profiles/lipinfo01.html.
Wang, H., Gibbins, N., Payne, T., Patelli, A., 2013. A
Survey of Semantic Web Services Formalisms. In
Ninth International Conference on Semantics,
Knowledge and Grids, pp.135–142.
Jackson, M., 1995. Software requirements specifications: a
lexicon of practice, principles and prejudices. ACM
Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing. New York, NY,
USA, 228 p.
Prat, N., 1997. Goal Formalisation and Classification for
Requirements Engineering. In third International
Workshop on Requirements Engineering: Foundation
for Software Quality.
Fillmore, C. J., 1968. The case for case. In Bach et
Harms", eds. (New York: Holt, Rinehart, and
Winston), Universals in Linguistic Theory, 88 p.
Dik, S. C., 1989. The theory of functional grammar. (Foris
Publications). Dordrecht, Holland ; Providence, RI,
U.S.A.: Foris Publications, p. 497.
IEEE, 2007. Draft standard for Learning Object Metadata
(LOM) (IEEE 1484.12.1-2002), IEEE Learning
Technology Standards Committee (LTSC).
A Semantic Web Service Description of Learning Object
201
