Predicting the Empirical Robustness of the Ontology Reasoners based on
Machine Learning Techniques
Nourh
`
ene Alaya
1,2
, Sadok Ben Yahia
2
and Myriam Lamolle
1
1
LIASD, IUT of Montreuil, University of Paris 8, Montreuil, France
2
LIPAH, Faculty of Sciences of Tunis, University of Tunis, Tunis, Tunisia
Keywords:
Ontology, OWL, Reasoner, Robustness, Supervised Machine Learning, Prediction.
Abstract:
Reasoning with ontologies is one of the core tasks of research in Description Logics. A variety of reason-
ers with highly optimized algorithms have been developed to allow inference tasks on expressive ontology
languages such as OWL (DL). However, unexpected behaviours of reasoner engines is often observed in prac-
tice. Both reasoner time efficiency and result correctness would vary across input ontologies, which is hardly
predictable even for experienced reasoner designers. Seeking for better understanding of reasoner empirical
behaviours, we propose to use supervised machine learning techniques to automatically predict reasoner ro-
bustness from its previous running. For this purpose, we introduced a set of comprehensive ontology features.
We conducted huge body of experiments for 6 well known reasoners and using over 1000 ontologies from the
ORE’2014 corpus. Our learning results show that we could build highly accuracy reasoner robustness pre-
dictive models. Moreover, by interpreting these models, it would be possible to gain insights about particular
ontology features likely to be reasoner robustness degrading factors.
1 INTRODUCTION
The key component for working with OWL ontolo-
gies is the Reasoner. This is because knowledge in an
ontology might not be explicit, then a reasoner is re-
quired to deduce its implicit knowledge. However, the
high expressivity of OWL has increased the compu-
tational complexity of inference tasks. For instance,
it has been shown that the complexity of the consis-
tency checking of SR OI Q ontologies, the descrip-
tion logic (DL) underlying OWL 2, is of worst-case
2NExpTime-complete (Horrocks et al., 2006). There-
fore, a number of highly-optimized reasoners have
been developed, which support reasoning about ex-
pressive ontologies (Sirin et al., 2007; Glimm et al.,
2012; Steigmiller et al., 2014).
Despite the remarkable progress in optimizing
reasoning algorithms, unpredictable behaviours of
reasoner engines is often observed in practice, partic-
ularly when dealing with real world ontologies. Two
main aspects would depict this phenomena. On the
one hand, the respective authors of (Weith
¨
oner et al.,
2007; Gonc¸alves et al., 2012) have outlined the vari-
ability of reasoner’s time efficiency across OWL on-
tologies. Roughly speaking, the reasoner optimiza-
tion tricks, set up by designers to overcome particu-
lar DL complexity sources, would lead to enormous
scatter in computational runtime across the ontolo-
gies, which is still hardly predictable a priori. These
findings have motivated various attempts of reasoner
runtime prediction using machine learning techniques
(Kang et al., 2012; Sazonau et al., 2014; Kang et al.,
2014). On the other hand, results reported from
the latest Ontology Reasoner Evaluation Workshops,
ORE (Gonc¸alves et al., 2013; Bail et al., 2014) have
revealed another aspect of reasoner behaviours vari-
ability, namely the correctness of the reasoning re-
sults. In fact, the evaluations were surprising as rea-
soners would derive different inferences for the same
input ontology. Therefore, an empirical correctness
checking method was established to examine reasoner
results. Actually in both ORE 2013 and 2014 com-
petitions, there were no single reasoner, which cor-
rectly processed and outperformed on all given inputs.
Even the fastest reasoner have failed to derive accu-
rate results for some ontologies, while others less per-
forming engines, have succeeded to correctly process
them. Thus, we would admit that the most desired
qualities, i.e. result correctness and time efficiency,
are not empirically guaranteed by all the reasoners
and for every ontology. These observations pinpoints
the hardness of understanding reasoner empirical be-
Alaya, N., Yahia, S. and Lamolle, M..
Predicting the Empirical Robustness of the Ontology Reasoners based on Machine Learning Techniques.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2015) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 61-73
ISBN: 978-989-758-158-8
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
61
haviours even for experienced and skilled reasoner
designers. Thus, it would be worthwhile to be able to
automatically predict both correctness and efficiency
of reasoners against given ontologies. More invalu-
able would be gaining insights about which particular
aspects in the ontology are lowering these qualities.
Obviously, learning such aspects would further im-
prove reasoner optimizations and enhance ontology
design by avoiding reasoner performances degrading
factors.
In this paper, we introduce a new approach aim-
ing to predict an ontology classification quality that
a particular reasoner would be able to achieve by
a specific cutoff time. To the best of our knowl-
edge, no prior work tackled such an issue. We de-
signed by robustness, the required reasoner quality.
We rely on supervised machine learning techniques
in order to learn models of reasoner robustness from
their previous running. To achieve our purpose, we
proposed a set of valuable ontology features, likely
to be good indicators of ontologies’ hardness level
against reasoning tasks. Then, we carried out a huge
body of experiments using the widely recognized
ORE’2014 Framework (Bail et al., 2014). Over 1000
ontologies were processed by 6 well known reason-
ers. Given these evaluation data, reasoner predictive
models were trained by 5 of the most effective super-
vised learning algorithms. We have further improved
the accuracy of our models by employing a set of fea-
ture selection techniques. Worth of cite, no prior work
made use of the discretization to identify ontology rel-
evant features. Then, we discussed and employed a
variety of prediction assessment measures, well suited
in the case of imbalanced datasets. Thanks to our es-
tablished study, we unveiled a set of local and global
ontology key features, likely to alter the reasoner ro-
bustness. In overall, our trained reasoner robustness
predictive models have shown to be highly accurate,
which witness the worthiness of our learning process.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Sec-
tion 2 briefly recalls basic notions that will be of use
throughout the paper. Section 3 scrutinizes the related
work approaches. Our reasoner robustness learning
process as well as the achieved results are, respec-
tively, detailed in Sections 4 - 9. Concluding remarks
as well as our future works are given in Section 10.
2 BACKGROUND
In this paper, we focus on OWL 2 (OWL Work-
ing Group, 2009) ontologies. Recommended by the
W3C, OWL 2 is based on the highly expressive De-
scription Logics SR OI Q (Horrocks et al., 2006).
This logical provides a precisely defined meaning for
statements made in OWL and thus, makes it pos-
sible to automatically reason over OWL ontologies.
Among the reasoning tasks, classification is consid-
ered as the key one. It computes the full concept
and role hierarchies in the ontology (Baader et al.,
2003). Explicit and implicit subsumption will be de-
rived to help users navigating through the ontology
towards mainly explanation and/or query answering
respective tasks. Thus, it’s supported by all modern
DL reasoners and its duration is often used as a per-
formance indicator to benchmark reasoning engines
(Abburu, 2012). From an application point of view,
an ontology should be classified regularly during its
development and maintenance in order to detect un-
desired subsumptions as soon as possible.
We recall some basic concepts of machine learn-
ing (ML) (Kotsiantis, 2007) for a better understanding
of our study. In any dataset used by machine learn-
ing algorithms, every instance is represented using the
same set of features. In our case, the instances are on-
tologies belonging to some corpus and the features
are metrics characterizing the ontology content and
design. Thus, each ontology is represented by a d-
dimensional vector x
(i)
= [x
1
(i)
, x
2
(i)
, . . . , x
d
(i)
] called
a feature vector, where i refers to the i-th ontology in
the dataset, i ∈ [1, N], with N denoting the total num-
ber of ontologies and d standing for the total number
of features. The latter ones may be continuous, cat-
egorical or binary. The learning is called supervised
when the dataset ontologies are given with known la-
bels. In our context, a label would describe a given
reasoner performances when processing the consid-
ered ontology, for instance a time-bin. The vector of
all labels is specific to one reasoner and denoted Y ,
where y
i
is the label of the i-th ontology. Thus, for
each under study reasoner a dataset is built in and de-
signed by D = [X
N,M
| Y
T
]. Later, the dataset is pro-
vided to a supervised learning algorithm in order to
train its data and establish a predictive model for its
corresponding reasoner. Roughly speaking, a model
is a mapping function from a set of features, to a spe-
cific label. It would be a mathematical function, a
graph or a probability distribution, etc. When a new
ontology, which does not belong to the dataset is in-
troduced, then the task is to predict its exact label,
using a reasoner predictive model.
3 RELATED WORKS
Works that attempted to predict reasoner’s runtime us-
ing supervised machine learning techniques are the
closest to our context. Authors of (Kang et al., 2012)
KEOD 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
62
were the first to apply supervised machine learning
techniques (Kotsiantis, 2007) to predict the ontology
classification computational time, carried by a spe-
cific reasoner. 27 ontology metrics were computed for
each ontology. These metrics were previously pro-
posed by a work stressing on ontology design com-
plexity (Zhang et al., 2010). The labels to be predicted
were time bins specified by the authors. They learned
Random Forest based models for 4 state of art rea-
soners and obtained high prediction accuracy. More-
over, they proposed an algorithm to compute the im-
pact factors of ontology metrics according to their ef-
fectiveness in predicting classification performances
for the different reasoners. Kang et al. have fur-
ther improved their approach, in a more recent work
(Kang et al., 2014). They replaced time bin labels by
concrete values of reasoner’s runtime and proposed
more ontology metrics. They learned regression mod-
els for 6 widely known reasoners. In addition, they
demonstrated the strengths of their predictive models
by applying them to the problem of identifying ontol-
ogy performance Hotspots (Gonc¸alves et al., 2012).
On the other hand, in (Sazonau et al., 2014), authors
claimed that Kang’s et al. metrics based on graph
translation of OWL ontologies are not effective. Thus,
they proposed another set of metrics and deployed a
dimensionality reduction method to remove the inter-
correlations between ontology features. They further
proposed a new approach to build predictive models
based on examining single ontologies rather than the
whole corpus.
In all these previous works, machine learning
techniques were set up to estimate the amount of time
a given reasoner would spend to process any input
ontology. However, no attention was paid to assess
the correctness of the reasoner derived results. In
our opinion, a reasoner that quickly but incorrectly
process an ontology is of little use. Therefore, we
believe that the effectiveness and the utility of these
approaches are still limited in meeting the need of
predicting reasoner empirical behaviours. Neverthe-
less, these works have succeeded to establish highly
accurate reasoner performances models, which is a
promising advance towards the practical understand-
ing of reasoners. Thus, we are convinced that em-
ploying machine learning techniques would be the ul-
timate approach to gain insights about the reasoner ro-
bustness facing real world ontologies. Certainly, pre-
viously deployed ML techniques need to be reviewed
and improved for a better fit to our learning context.
4 PREDICTING THE
ROBUSTNESS OF THE
ONTOLOGY REASONERS
In this section, we specify, at first, the notion of rea-
soner robustness and then, the main steps to automat-
ically learn it from empirical data.
4.1 Why Robustness?
The research question of this paper is whether it is
possible to predict the robustness of modern reason-
ers using the results of their previous running. Worth
of mention, the notion of robustness differs by the
field of research. For software developer, (Mikol
`
a
˜
sek,
2009) defined the robustness as the capability of
the system to deliver its functions and to avoid ser-
vice failures under unforeseen conditions. Recently,
(Gonc¸alves et al., 2013) bought forward this defini-
tion in order to conduct an empirical study about the
robustness of DL reasoners. Authors underlined the
need to specify the robustness judgement constrains
before assessing the reasoners. These constrains are:
1) the range of the input ontologies, 2) the reasoner
functional and non functional properties of interest,
and 3) the definition of the failure state. The instanti-
ation of the constrains would describe some reasoner
usage scenario. Thus, a reasoner may be considered
as robust under a certain scenario and non-robust un-
der another.
Given these findings, we started by setting our
proper constrains in order to describe an online ex-
ecution scenario of reasoners. In addition to the com-
putational time which should be maintained as short
as possible, we focused on assessing the correctness
of the reasoner computed results. Reasoning engines
can load and process an ontology to achieve some
reasoning task, but they can also deliver quite dis-
tinct results. Disagreement over inferences or query
answers, computed over one input ontology, would
make it hard to provide interoperability in the Se-
mantic Web. Therefore, we consider the reasoner ro-
bustness as its ability to correctly achieve a reason-
ing task for a given ontology within a fixed cut-off
time. Consequently, the most robust reasoner over an
ontology corpus would be the one satisfying the cor-
rectness requirement for the greatest number of on-
tologies while maintaining the shortest computational
time. Based on this specification, we tried to conduct
a new reasoner robustness empirical study. One ma-
jor obstacle we faced was about whether it is possi-
ble to automatically check the correctness of the rea-
soning results. In fact, little works have addressed
the issue. As previously outlined by (Gardiner et al.,
Predicting the Empirical Robustness of the Ontology Reasoners based on Machine Learning Techniques
63
2006), manually testing the correctness of reasoner
inferences would be relatively easy for small ontolo-
gies, but usually infeasible for real world ontologies.
Authors claimed that the most straightforward way to
automatically determine the correctness is by com-
paring answers derived by different reasoners for the
same ontology. Consistency across multiple answers
would imply a high probability of correctness, since
the reasoners have been designed and implemented
independently and using different algorithms. Luck-
ily, this testing approach was implemented in the ORE
evaluation Framework (Gonc¸alves et al., 2013). The
reasoner output was checked for correctness by a ma-
jority vote, i.e. the result returned by the most reason-
ers was considered to be correct. Certainly, this is not
a faultless method. Improving it would be advanta-
geous for our study, however it is out of the scope of
this paper.
Afterwards, we designed four labels that would
describe the termination state of a reasoning task. The
first label describes the state of success and the others
distinguish three types of failure. These labels are: 1)
Correct (C) standing for an execution achieved within
the time limit and delivered expected results; 2) Unex-
pected (U) in the case of termination within the time
limit but delivered results that are not expected, other-
wise incorrect; 3) Timeout (T) in the case of violating
the time limit; and 4) Halt (H) describing a sudden
stop of the reasoning process owing to some execu-
tion error. Thus, the set {C, U, T, H} designs our label
space L admitted for the learning process. Intuitively,
the reasoner robustness is close to the reasoning task
to be processed. In our study, we focus on the ontol-
ogy classification task (Section 2).
4.2 The Learning Steps
We propose the following steps for predicting the ro-
bustness of a given reasoner on individual ontologies.
Our learning steps are partially inspired by the earlier
work (Kang et al., 2012).
Step 1. Features Identification. We carried a rigor-
ous investigation on the most valuable ontology fea-
tures, likely to have an impact on the reasoner ro-
bustness. The results of this investigation is detailed
in Section 5, where we introduced a rich set of fea-
tures covering a wide range of ontology characteris-
tics. The latter ones depict our features space F
d
,
where d stands for the space dimension.
Step 2. Ontologies Selection. An ontology corpus
C (O) should be provided to carry out the reasoner
evaluations. This corpus should be highly diversified
in terms of ontology characteristics, in order to reduce
the probability for a given reasoner to encounter only
problems it is particularly optimized for. Features,
identified in the previous step, will be computed for
each ontology O
i
∈ C (O), to obtain its corresponding
d-dimensional feature vector X
(O
i
)
∈ F
d
.
Step 3. Reasoner Selection. Any reasoner would
be enough for the study; no knowledge about its algo-
rithm neither details about its internal working mech-
anism are needed for the training process. Thus, given
a set of reasoners S(R ), a reasoner R
k
∈ S(R ) will be
iteratively picked to carry on the process.
Step 4. Dataset Building. At this step, each on-
tology belonging to the corpus O
i
∈ C (O) will be
processed by the previously selected reasoner R
k
to
achieve the classification task. Then, the termi-
nation state of this task will be retained l
R
k
(O
i
) ∈
{C, U, T, H}. Thus, the final training dataset of the
selected reasoner R
k
, designed by D
R
k
, is built in by
gathering the pairs (feature vector, label), i.e. D
R
k
=
{(X
(O
i
)
, l
R
k
(X
(O
i
)
)), i = 1 ···N}, where N = |C (O)|.
Step 5. Feature Selection. A huge amount of fea-
tures does not necessarily improve the accuracy of
the prediction model. Commonly, feature selection
or dimensionality reduction techniques are applied to
identify the relevant features. In our study, we will
compare three different methods of feature selection,
described in Section 7. Consequently, three variants
of the initial reasoner dataset are established, called
featured datasets, each with a different and eventu-
ally reduced subset of ontology features. The initial
dataset is also maintained and called ”RAWD”.
Step 6. Learning and Assessing the Models. Each
reasoner dataset D
( j)
R
k
established in the Step 5 is pro-
vided to a supervised machine learning algorithm.
The latter train the data and build a reasoner predic-
tive model, M
R
k
(section 2):
M
R
: X ∈ F
d
7→
ˆ
l
R
(X) ∈ Y (1)
Worth to cite, we investigated 5 well known super-
vised machine learning algorithms. Therefore, this
step will be repeated as far as the number of algo-
rithms and the number of datasets for a given rea-
soner. Then, the established models will be evaluated
against a bunch of assessment measures. Further, we
introduced a method to compare these models and fig-
ure out their ”best” one. Details about the learning al-
gorithms, the assessment measures and the selection
procedure are given in Section 8.
Step 7. Unveil the Key Features. Steps 3-6 are re-
peated K times to cover all reasoners in the set S(R ),
with K = |S (R )|. As a result, K best predictive mod-
els are identified each for a reasoner, and each having
its own most relevant feature subset. Accordingly, we
KEOD 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
64

believe that the key ontology features likely to have
impact on reasoner robustness are those the most in-
volved across the whole set of best models. We denote
this subset as the Global Key Features, in contrast to
Local Key Features, which designs features employed
in one given reasoner best predictive model.
5 ONTOLOGY FEATURES
(STEP 1)
When reviewing the state of art, we noticed that there
is no known, automatic way of constructing ”good”
ontology feature sets. Instead, distinct domain knowl-
edge should be used to identify properties of ontolo-
gies that appear likely to provide useful informations.
To accomplish our study, we reused some of previ-
ously proposed ontology features and defined new
ones. Mainly, we discarded those computed based
on specific graph translation of the OWL ontology, as
there is no agreement of the way an ontology should
be translated into a graph (Kang et al., 2014). We split
the ontology features into 4 categories: (i) size de-
scription; (ii) expressivity description; (iii) structural
features; and (iv) syntactic features. Within these cat-
egories, features are intended to characterize specific
aspect of an OWL ontology. Some of the categories
are further split up. In overall, 101 ontology features
were characterized. Figure 1 lists the main ones. In
the following, we will shortly depict our feature cate-
gories. We give a more detailed description in (Alaya
et al., 2015).
Ontology Size Description. The purpose of this fea-
ture category is to characterize the size of the ontol-
ogy considering both the amount of its terms and ax-
ioms. Therefore, we designed 5 features, each records
the names of a particular OWL entity. In addition, we
computed the number of its axioms (SA) and more
particularly the logical ones (SLA).
Ontology Expressivity Description. We retained
two main features to identify the expressivity of the
ontology language, namely the OWL profile
1
(OPR)
and the DL family name (DFN).
Ontology Structural Description. We paid a special
attention to characterize the taxonomic structure of
an ontology, i.e. its inheritance hierarchy. The lat-
ter sketches the tree like structure of subsumption re-
lationships between named classes A v B or named
properties R v S. In this category, we gathered vari-
ous features that have been defined in literature to de-
scribe the ontology hierarchies. These are, basically,
1
For further details about OWL 2 profiles, the reader is
kindly referred to http://www.w3.org/TR/owl2-profiles/.
metrics widely used by the ontology quality evalua-
tion community (Gangemi et al., 2006; Tartir et al.,
2005; LePendu et al., 2010). The following subcat-
egories describe the essence of the retained features.
• Class and Property Hierarchical Features: five
features were specified to outline the design of the
class hierarchy (CHierarchy). They consider the
depth of this tree like structure and the distribu-
tion of the subclasses as well as the super-classes.
These features were also used to characterize the
design of the property hierarchy (PHierarchy).
• Cohesion Features: the literature provides a
plethora of various metrics to design the Cohesion
of the ontology, otherwise the degree of relatedness
of its entities. We retained the ones introduced by
(Faezeh and Weichang, 2010). Roughly speaking,
the ontology cohesion (OCOH) is a weighted ag-
gregation of the class cohesion (CCOH), the prop-
erty cohesion (PCOH) and the object property co-
hesion (OPCOH).
• Schema Richness Features: we enriched the on-
tology structural category by two additional fea-
tures proposed by (Tartir et al., 2005): the schema
relationship richness (RRichness), and the schema
attribute richness (AttrRichness). These features
are well known for ontology evaluation community
as they are part of the OntoQA tool.
Ontology Syntactic Features. When collecting fea-
tures for this category, we conducted an investigation
about the main reasoning algorithms (Baader and Sat-
tler, 2000; Motik et al., 2009). Our main purpose was
to quantify some of the general theoretical knowledge
about DL complexity sources. Thus, we gathered rel-
evant ontology features, that have inspired the imple-
mentation of well known reasoning optimization tech-
niques (Horrocks, 2003; Tsarkov et al., 2007). Fea-
tures of the current group are divided in 6 subcate-
gories, each specific to a particular ontology syntactic
component. This organization was inspired by the one
introduced by (Kang et al., 2012).
• Axioms Level: reasoners process differently each
type of axiom with different computational cost
(Baader et al., 2003). We introduced two sets of
features, (KBF) and (ATF), in order to character-
ize the different types of OWL axioms as well as
their respective relevance in the ontology. Further,
we computed the maximal and the average parsing
depth of axioms (AMP, AAP).
• Constructors Level: these concern particularly
DL class constructors
2
(Baader et al., 2003). In
previous reasoner prediction works (Kang et al.,
2
By DL class constructor, we refer to conjunction (∪),
disjunction (∩), negation (¬), quantification (∃, ∀), etc.
Predicting the Empirical Robustness of the Ontology Reasoners based on Machine Learning Techniques
65
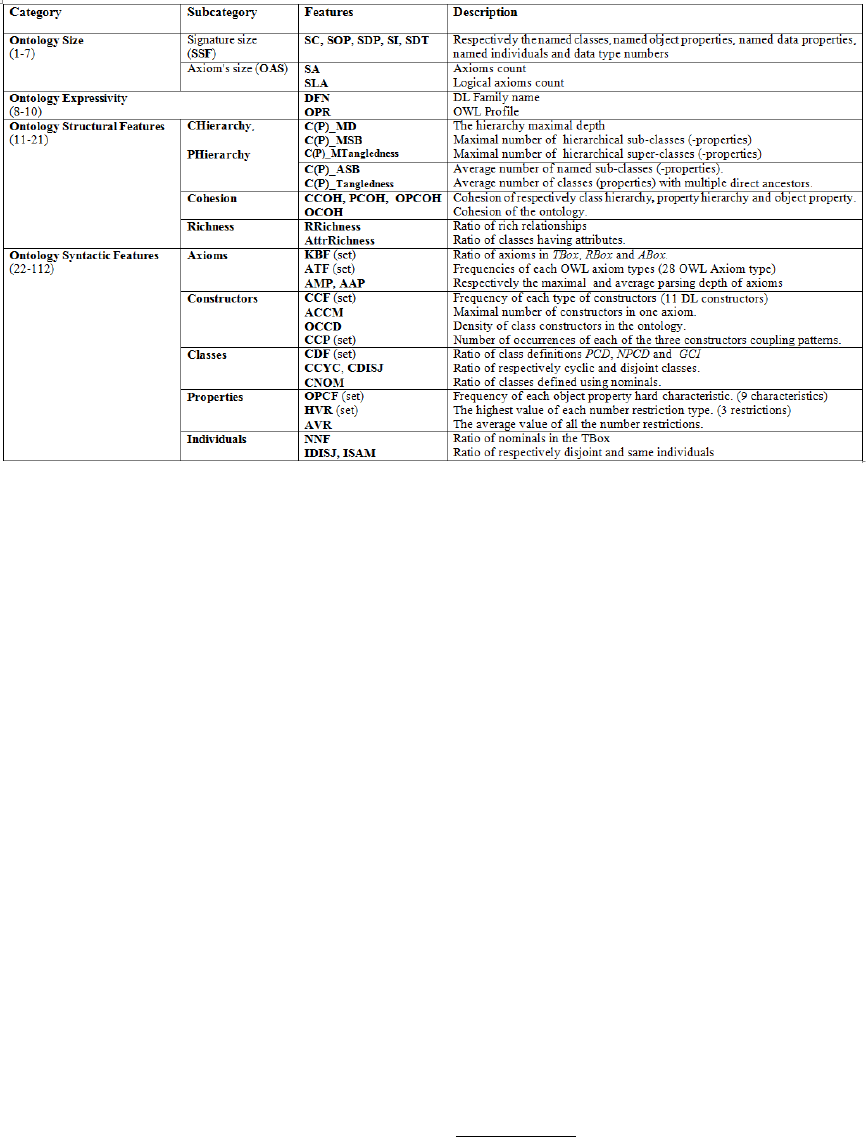
Figure 1: Ontology Features Catalog.
2012; Kang et al., 2014), authors simply counted
axioms that involve potentially hard constructors.
However, they missed that one constructor could be
invoked more than once in the same axiom. Con-
sidering this fact, we proposed a metric to com-
pute a class constructor frequency in the ontology
(CCF). Moreover, we defined the density of the
overall constructors (OCCD). We also introduced
three modelling patterns of particular combinations
of constructors. We believe that these combina-
tions, whenever used in an axiom, would increase
the inference computational cost.
• Classes Level: classes in the ontology could be
named ones or complex expressions. They would
be cyclic or disjoin ones. In this subcategory, we
introduced features that pinpoint different methods
to define a class and track their impact in the ontol-
ogy TBox part.
• Properties Level: we were interested in capturing
two aspects of the ontology properties syntactic de-
scription. First, we tried to outline the relevance
of specific object property characteristics, such as
transitivity, symmetry, reflexivity, etc. Thus, we in-
troduced a metric, (OPCF), that measures their re-
spective frequencies in the ontology. Then, we pro-
posed two further metrics (HVC, AVC) aiming at
examining the impact of using high values in num-
ber restrictions.
• Individuals Level: we specify some of the in-
teresting characteristics of named individuals that
would be declared in the ontology. We examined
the ratio of nominals in the TBox (NNF) and com-
puted the number of individuals declared as equal
ones (ISAM) or disjoint ones (IDISJ).
6 DATA COLLECTION (STEPS
2-4)
To ensure the reliability of reasoner evaluation results,
we have chosen to reuse the ORE’2014 evaluation
Framework
3
, as well as, its test set ontologies. Under
this experimental environment, we conducted new DL
and EL classification evaluations, for 6 reasoners and
using over 1000 ontologies. The motivation behind
our choice is multi-fold: first, the event is widely rec-
ognized by the Semantic Web community; the ontol-
ogy corpus is well established and balanced through-
out easy and hard cases; and finally the description
of reasoner results is consistent with the specification
of the robustness criterion, designed in the previous
Section 4.1.
Ontologies. In overall, we retained 1087 ontologies
from the ORE’2014 corpora
4
. The testing ontolo-
gies fall into both the OWL 2 DL and the OWL 2
EL profiles. For each profile, the ontologies were fur-
ther binned according to their sizes
5
. The latter varies
3
The ORE’2014 Framework is available at
https://github.com/andreas-steigmiller/ore-2014-
competition-framework/
4
The whole corpus of ontologies is available for down-
load at http://zenodo.org/record/10791
5
The size corresponds to the number of logical axioms.
KEOD 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
66

from small ([100,1000[), going to very large one ( ≥
100 000). In addition, the set covers more than 100
distinct DL families. Table 1 describes the distribu-
tion of ontology size bins over the OWL profiles. #O
stands for the number of ontologies.
Table 1: Ontology Test Set Description Summary.
Profile #O #O per Size Bin
Small Medium Large V-Large
DL 487 125 124 124 113
EL 600 173 150 150 127
Reasoners. We investigated the 6 best ranked rea-
soners
6
in both the DL and EL classification chal-
lenges of the ORE’2014 competition. These rea-
soners are included in our study set S(R ). They
are namely Konclude, MORe, HermiT, TrOWL,
FaCT++ and JFact. We excluded ELK despite its
good results and high rank, as it doesn’t support the
classification of DL ontologies. We run the ORE
Framework in the sequential mode on one machine
equipped with an Intel Core I7-4470 CPU running at
3.4GHz and having 32GB RAM, where 12GB were
made available for each reasoner. We set the condi-
tion of 3 minutes time limit to classify an ontology by
a reasoner. This tight schedule would be consistent
with the chosen scenario, i.e. the online classification
of the ontology.
Table 2 summarizes the new classification chal-
lenge results
7
. We did not distinguish between re-
sults of DL and EL ontology classification. Reasoners
are listed based on their robustness rank, that is the
number of correctly processed ontologies within the
fixed cutoff time. For each reasoner, Table 2 shows
the number of ontologies within a specific robustness
bin (Section 4.1) and the range of processing time of
the correct cases.
Building the Reasoner Datasets. Each testing on-
tology was examined to compute and to record its fea-
tures. Having the evaluation results and the ontology
feature vectors, 6 datasets were established each for a
specific reasoner. It’s important to notice that our rea-
soner datasets are imbalanced. Based on the descrip-
tion made by (Hu and Dong, 2014), a dataset is con-
sidered as imbalanced, if one of the classes (minor-
ity class) contains much smaller number of examples
than the remaining classes (majority classes). In our
context, the classes are reasoner robustness labels. We
take as an example the Konclude’s dataset described
in the table 2, we can easily notice the huge difference
6
All ORE’2014 reasoners are available for download at
https://zenodo.org/record/11145/
7
All the results of our experiments are available at https://
github.com/PhdStudent2015/Classification Results 2015.
Table 2: Ontology classification results. The time is given in
seconds. #C, #U, #T and #H stand respectively for the num-
ber of ontologies labelled by Correct, Unexpected, Timeout
or Halt after the classification.
Reasoner #C #U #T #H Runtime (correct)
Min Max Mean
Konclude 1030 22 27 8 0.001 54.73 1.48
MORe 971 3 110 3 0.259 144.56 3.77
HermiT 954 29 102 2 0.082 144.12 9.59
TrOWL 927 106 52 2 0.027 109.95 3.36
FaCT++ 821 13 205 48 0.019 141.87 4.88
JFact 683 13 323 68 0.019 138.34 9.68
between the number of ontologies labelled as Correct
#C(the majority) and those labelled as Unexpected #U
or Timeout #T (the minority). However, its obvious
that predicting the minor cases is much more interest-
ing for both ontology and reasoner designers, since
they describe a failure situation in processing the on-
tology. In fact, a user would probably want to know,
if it would be safe to choose Konclude to classify its
ontology. The learning from imbalanced datasets is
considered as one of the most challenging issue in the
data mining (Hu and Dong, 2014). We will be consid-
ering this aspect when training the predictive models.
7 FEATURE SELECTION (STEP 5)
We started by performing some preprocessing steps
on the reasoner datasets. Mainly, we applied feature
selection methods. The latter ones were designed to
recognize the most relevant features, by weeding out
the useless ones. In our study, we tried to track down
the subset of features, which correlate the most with
the robustness of a given reasoner. Thus, we chose
to investigate the utility of employing discretization
(Garcia et al., 2013), as a feature selection technique.
Basically, discretization stands for the transforma-
tion task of continuous data into discrete bins. More
specifically, we opted for the well known Fayyad &
Irani’s supervised discretization method (MDL). This
technique makes use of the ontology label to achieve
the transformation. If the continuous values of an on-
tology feature are discretized to a single value, then
it means the feature is useless for the learning. Con-
sequently, it can be safely removed from the dataset.
Seeking of more validity, we decided to compare the
discretization results to further feature selection tech-
niques. Thus, we carefully chose two well known
methods representative of two distinct categories of
feature selection algorithms: first, the Relief method
(RLF), which finds relevant features based on a rank-
ing mechanism; then, the CfsSubset method (CFS),
Predicting the Empirical Robustness of the Ontology Reasoners based on Machine Learning Techniques
67

Table 3: Summary of feature selection results. (∩) stands
for the intersection of feature subsets.
Dataset MDL RLF CFS (∩)
D
Konclude
53 64 8 4
D
MORe
74 61 12 8
D
HermiT
85 61 15 10
D
TrOW L
81 51 13 10
D
FaCT ++
79 58 16 12
D
JFact
86 56 19 15
(∩) 50 49 1 1
which selects subsets of features that are highly cor-
related with the target label while having low inter-
correlations. All of aforementioned feature selec-
tion methods are available in the machine learning
working environment, Weka (Hall et al., 2009). Ta-
ble 3 summarizes the feature selection results when
applied to the feature space, F
d
, of each of the rea-
soner datasets. The reported values are the sizes of the
reduced feature subsets
8
computed by the respective
method. We further investigated the possible presence
of common features across these subsets, by com-
puted the size of their respective intersections.
Interestingly enough, in the all cases, we observe
that the initial feature dimension was reduced. This
would confirm that there are some particular features,
which are more correlated to the reasoner robust-
ness bins. However, the reduction level of the fea-
ture selection methods varies even for the same rea-
soner dataset. Nevertheless, it would be noticed that,
for each reasoner dataset, feature selection methods
agreed on the predictive power of some number of on-
tology features. Moreover, given a selection method,
common features were identified across the datasets
of the different reasoners, particularly when using
MDL and RLF. However, the CFS method delivered
just one shared feature, this is the frequency value
(CCF) of the OWL constructor hasSelf. Worth of
cite, this feature also figures in the intersection set of
MDL’s feature subsets. Certainly, at this stage, it is
hard to decide which feature subset is having the most
relevant features for a given reasoner. This would be
concluded only after training predictive models from
these featured datasets. We believe that the subset
leading to the most accurate predictive model, is the
one having the key ontology features, likely to impact
the reasoner robustness. As mentioned in the Section
4.2, we will conduct a comparison between predictive
models derived from reasoner initial datasets, RAWD,
and those trained form the featured ones respectively
by i.e. MDL, RLF and CFS.
8
The initial dimension of our feature space is 101.
8 LEARNING METHODS OF
REASONER ROBUSTNESS
(STEP 6)
In this paragraph, different learning algorithms and
assessment measures will be shortly described.
Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms. Seek-
ing for diversity in the learning process, we selected
5 candidate algorithms, each one is representative of
a distinct and widely recognized category of machine
learning algorithms (Kotsiantis, 2007). All the used
implementations are available in the Weka framework,
and was applied with the default parameters of this
tool. They are namely: 1) Random Forest (RF) a com-
bination of C4.5 decision tree classifiers; 2) Simple
Logistic (SL) a linear logistic regression algorithm;
3) Multilayer Percetron (MP) a back propagation al-
gorithm used to build an Artificial Neural Network
model; 4) SMO a Support Vector Machine learner
with a sequential minimal optimization; and finally 5)
IBk a K-Nearest-Neighbour algorithm with normal-
ized euclidean distance.
Prediction Accuracy Measures. In previous works
(Kang et al., 2012), the accuracy standing for the frac-
tion of the correct predicted labels out of the total
number of the dataset samples, was adopted as main
evaluation metric of the predictive models. How-
ever, accuracy would be misleading in the case of
imbalanced datasets as it places more weight on the
majority class(es) than the minority one(s). Conse-
quently, high accuracy rates would be reported, even
if the predictive model is not necessarily a good one.
Thus, we looked for assessment measures known for
their appropriateness in the case of imbalanced data.
Based on the comparative study conducted by (Hu
and Dong, 2014), we retained the following ones.
Worth to cite, all of these measures are computed
based on the confusion matrix, that we describe in
what follows.
• Confusion Matrix it is a square matrix, L×L, where
L is the number of labels to be predicted. It shows
how the predictions are made by the model. The
rows correspond to the known labels of the data, i.e.
in our case {C, U, T, H}. The columns correspond to
the predictions made by the model. Each cell (i, j)
of the matrix contains the number of ontologies from
the dataset that actually have the label i and were
predicted as with label j. A perfect prediction model
would have its confusion matrix with all elements on
the diagonal.
• Precision (PR), Recall (RC), and F-Measure
(FM): these are common measures of model effec-
tiveness. Precision is a measure of how many er-
KEOD 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
68

rors we make in predicting ontologies as being of
some label l. On the other hand, Recall assesses
how good we are in not leaving out ontologies that
should have been predicted with the label l. How-
ever, both measures are misleading when consid-
ered separated. Usually, we rather employ the F-
Measure (FM) to assess the model. This measure
combines both Precision and Recall into a single
value: FM =
2×RC×PR
RC+PR
.
• Kappa Coefficient (κ): it is used to measure the
agreement between the predicted labels and the real
ones. The value of Kappa lies between −1 and 1,
where 0 represents agreement due to chance. The
value 1 represents a complete agreement between
both values. In rare cases, Kappa can be negative.
• Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC): it is per-
formance measure barely influenced by imbalanced
test sets since it considers mutually accuracies and
error rates on all labels. So, it involves all values
of the confusion matrix. MCC ranges from 1 for a
perfect prediction to −1 for the worst possible pre-
diction. A MCC value close to 0 indicate a model
that performs randomly.
Training and Selecting the Best Predictive Mod-
els. A reasoner dataset, D
R
, is trained by each of
the above-mentioned supervised machine learning al-
gorithms. Thus, five distinct predictive models are
learned. We made use of the standard cross-validation
technique for evaluating these models. We applied a
stratified 10-fold cross-validation to ensure the ”gen-
eralizability” of the results. For the sake of sim-
plicity, we only retained the average values of the
computed assessment measures over all the cross-
validation steps.
We recall, our study covers 6 reasoners, for each 4
datasets were built in and then provided to 5 super-
vised learning algorithms, each of which have trained
it separately and produced its corresponding predic-
tive model.To sum up, 20 models were learned for ev-
ery reasoner, and assessed using 3 distinct evaluation
measures. All these steps were put forward to reveal
the reasoner best predictive model, according to the
aforementioned assessment measures. Being aware
of the amount of data to analyse, we propose to com-
pute a score index per model. By referring to it, we
will be able to establish a total order of the reasoner’s
predictive models. We called it, the Matthews Kappa
Score (MKS). As the acronym would suggest, MKS
is a weighted aggregation of the MCC and the Kappa
values computed to assess a reasoner model M
R
.
MKS(M
R
) =
α ∗ MCC(M
R
) + β ∗ Kappa(M
R
)
α + β
(2)
,where (α + β) = 1. Thus, the best predictive model
for a given reasoner is the one having the maximal
value of the MKS score:
M
RBest
= arg max
M
i
R
∈M R
( MKS(M
i
R
)) (3)
,where M R denotes the set of predictive models
learned for a reasoner R. In the case where multi-
ple maximal models are identified, the model with
the highest F-Measure (FM) is selected. We believe
that using MKS is the straightforward way to automat-
ically determine the best robustness predictive model
for a given reasoner. The rational behind this proposal
is twofold: first, MCC and Kappa are widely recog-
nized as powerful assessment measures, even more
effective that FM, in the case of imbalanced datasets;
second both measures are ranging in [−1, 1], which
makes the aggregation coherent.
9 RESULTS OF REASONER
ROBUSTNESS PREDICTIVE
MODELS
The selection of a reasoner best predictive model is
achieved within two stages: the best model given a
specific reasoner dataset variant; then the best model
across all the datasets. Results of each stage will be
discussed in the following:
9.1 Best Models from RAWD Datasets
For the sake of brevity, we only report the assessment
results of the predictive models learned from reasoner
RAWD datasets. Indeed in this type of datasets, on-
tology feature vectors are full ones, counting 101 dis-
tinct features. Table 4 shows the distributions of F-
Measures (FM), MCC and Kappa (κ) across the 5
learned models and for every reasoner. The end-
ing line of table 4 displays the name of the reasoner
best predictive model, denoted by M
d
RBest
, under the
RAWD datasets. The selection was made according
to the MKS values
9
. The assessment results of M
d
RBest
are denoted in boldface.
A number of important observations can be made
from this table. Obviously, the RF algorithm is the
most performing learning algorithm in training the
RAWD datasets, since it derived the best predictive
models for all the 6 reasoners. Moreover, it would
be noticed that the maximal reported value of the F-
Measure (FM) for the 6 reasoner ranges from 0.86 by
RF in the case of TrOWL, going to 0.96 also by RF
in the case of Konclude. These close to optimum FM
9
In our experimentations, we set up α = β = 0.5.
Predicting the Empirical Robustness of the Ontology Reasoners based on Machine Learning Techniques
69

Table 4: Assessment summary of the reasoners’ models learned from RAWD datasets.
Konclude MORe HermiT TrOWL FaCT++ JFact
M
R
FM MCC κ FM MCC κ FM MCC κ FM MCC κ FM MCC κ FM MCC κ
RF 0.96 0.66 0.57 0.95 0.79 0.77 0.89 0.66 0.65 0.86 0.51 0.48 0.91 0.75 0.74 0.92 0.86 0.86
SL 0.94 0.40 0.33 0.94 0.74 0.72 0.88 0.62 0.62 0.82 0.34 0.27 0.87 0.66 0.64 0.90 0.80 0.80
MP 0.95 0.53 0.47 0.94 0.68 0.64 0.83 0.48 0.43 0.79 0.24 0.18 0.81 0.50 0.44 0.75 0.51 0.50
IBk 0.95 0.56 0.48 0.94 0.73 0.72 0.87 0.61 0.60 0.84 0.45 0.43 0.88 0.68 0.67 0.90 0.81 0.80
SMO 0.94 0.43 0.36 0.93 0.69 0.68 0.83 0.57 0.57 0.83 0.40 0.33 0.85 0.61 0.57 0.87 0.75 0.75
M
d
RBest
RF (MKS: 0.62) RF (MKS: 0.78) RF(MKS: 0.66) RF (MKS: 0.50) RF (MKS: 0.75) RF (MKS: 0.86)
Table 5: Best reasoner models across the different types of datasets.
Dataset Konclude MORe HermiT TrOWL FaCT++ JFact
variant M
d
best
MKS FM M
d
best
MKS FM M
d
best
MKS FM M
d
best
MKS FM M
d
best
MKS FM M
d
best
MKS FM
RAWD RF 0.62 0.96 RF 0.78 0.95 RF 0.66 0.89 RF 0.50 0.86 RF 0.75 0.91 RF 0.86 0.92
MDL RF 0.65 0.96 SL 0.80 0.96 SL 0.71 0.91 MP 0.61 0.89 RF 0.77 0.92 SMO 0.89 0.92
RLF RF 0.62 0.96 RF 0.77 0.95 RF 0.67 0.89 RF 0.50 0.87 RF 0.75 0.91 RF 0.86 0.92
CFS RF 0.65 0.96 RF 0.74 0.95 RF 0.70 0.90 RF 0.58 0.88 RF 0.74 0.90 RF 0.87 0.90
M
RBest
RF+CSF(8f) SL+MDL(74f) SL+MDL(85f) MP+MDL(81f) RF+MDL(79f) SMO+MDL(86f)
values indicate that our proposed set of ontology fea-
tures entails highly accurate predictive models, even
when no feature selection or dimensionality reduction
techniques are deployed a priori. Thereby, the rela-
tively high correlation between our ontology features
and the reasoners’ robustness is confirmed. In overall,
the reasoner best models have achieved good MCC
and Kappa values, as their MKS scores vary between
0.5 (by RF for TrOWL) and 0.86 (by RF for JFact).
This finding proves the ability of the learned mod-
els to predict the minor classes (Timeout, Unexpected
and Halt). Nevertheless, TrOWL’s and Konclude’s
predictive models are less effective than the other rea-
soner models. At this stage, we can not conclude,
which precise aspect is lowering the MKS scores of
both models. It would be either the biased nature of
the datasets, or probably some noisy features, which
should be removed.
9.2 Best Models Across the Dataset
Types
In the table 5, each reasoner best model given a
dataset type is reported as well as its assessment val-
ues of MKS and FM. The last line of the table sum
ups the comparison by revealing, the across datasets,
reasoner best robustness predictive model, denoted by
M
RBest
. The dataset type and the dimension of the fea-
ture space of the M
RBest
are also indicated.
Not once the RAWD dataset, with its entire set of
101 ontology features, was listed in the final selec-
tion of the reasoners’ best models. In most cases, the
MKS and FM values of reasoner predictive models
derived from featured datasets exceed the ones com-
puted from RAWD models. Therefore, it is quite cer-
tain, that restricting the full initial set of ontology fea-
tures to some particular subsets would improve pre-
dictive power of the reasoner robustness models. It
would also observed that the size of feature vectors of
the M
RBest
models varies from 8 in the case of Kon-
clude going to 86 in the case of JFact. This observa-
tion pinpoints that key ontology features, are close to
the reasoner under study. Reasoners implement dif-
ferent optimization techniques to overcome particular
complexity sources in the ontology and thus, indica-
tors of their robustness would also vary. Nevertheless,
we are not sure which feature selection method would
be the most suited in discovering key features for all
the reasoners. In fact, the MDL method have outper-
formed in major cases, but beaten by the CFS’s tech-
nique in one reasoner instance, i.e. Konclude. For this
reasoner, the assessment measures of the MDL’s and
CFS’s predictive models were equal. However, the
CFS method have delivered a more compact feature
set fully included in the one identified by MDL. Given
this fact, we chose the CFS’ model as the best one for
the reasoner Konclude, since it is much easier to inter-
pret. On the other hand, SL, SMO, MP and RF have
shared the podium of the most performing supervised
learning algorithms. Considering these findings, we
would confirm that there is no ultimate best combi-
nation, i.e. feature selection technique and learning
algorithm, that suits all the reasoners. Accordingly,
we admit that even if the learning process may be
maintained the same, the learning techniques must
be diversified to grasp, in a better way, the reasoner-
specific empirical behaviours. In overall, the learned
reasoners’ best predictive models showed to be highly
accurate, achieving in the most cases, an over to 0.90
FM value. In addition, they are well resisting to the
KEOD 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
70

problem of minor classes, as in all cases, their MKS
scores were over 0.60. In particular, the MKS of the
JFact best predictive model was 0.89, indicating al-
most a perfect predictive model. All of these findings
witness the high generalizability of the learned model
and their effectiveness in predicting reasoner robust-
ness for the ontology classification task.
9.3 Unveil the Key Features
The high accuracy of the reasoner robustness predic-
tive models trained from featured datasets confirmed
the validity of our assumption that particular ontol-
ogy features would help tracking down the reasoner
empirical behaviours. Henceforth, the robustness
of reasoners would be explained in terms of the
reduced set of ontology features, involved in their
respective best predictive models. We have called
these subsets, a reasoner local key features. We
have also investigated possible presence of shared
features across the different reasoners’ best predictive
models, i.e. global key features. We pinpointed their
contribution to the reasoner robustness prediction, by
computing their occurrences in the best models. A
group of 8 features were recognized to be the most
relevant indicators as they were involved in each of
the 6 best predictive models. Namely, these are: the
number of named object property (SOP), the highest
value of the max and the exact number restrictions,
i.e. HVC(max) and HVC(exact), as well as the
average value of numbers used in the different car-
dinality restrictions (AVR), two members of the set
of class constructors frequency CCF(owl:hasSelf)
and CCF(owl:maxCardinality), the ob-
ject property hard characteristics frequency
OPCF(owl:symmetricObjectProperty),
and finally the ratio
ATF(owl:functionalDataProperty). Worth
of mention, these features are the local key ones
of Konclude, but also good indicators for the other
reasoners. To have further insights about the contri-
bution of the remaining features, we distinguished
four levels of frequencies. Given O
f
the number of
occurrences of the feature f in the set of the 6 best
models, f has high frequency if O
f
≥ 5, medium one
if 3 ≤ O
f
≤ 4, low in case 1 ≤ O
f
≤ 2 and eventually
the feature could be NotUsed having O
f
= 0. In
overall, 69 features were found to be highly frequent,
10 were medium ones, 9 had low frequencies and
13 never been involved in the set of reasoners’ best
predictive models. The important number of highly
frequent features indicates the worthiness of our
conducted investigation about the most valuable on-
tology features. As we can not detail the frequencies
Figure 2: Frequency levels of ontology feature sets.
of each of the 101 features, we choose to report
the distribution of feature subcategories, over the
frequency levels. Figure 2 illustrates the results.
According to the established inspections, we
would assume that the highly frequent features among
best reasoner predictive models form a core group
of good indicators of reasoner robustness considering
the ontology classification task. These features would
be recommended as starting points to conduct further
improvement in ontology modelling as well as rea-
soning optimization. We must stress that we are not
concluding that the low frequent features are unim-
portant for the reasoners. Quite the contrary, these
features could be very specific to a particular reasoner
behaviour.
10 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we conducted a rigorous investigation
about empirically predicting reasoner robustness. Our
main purpose was to be able to explain the empirical
behaviour of reasoners when inferring particular on-
tologies. To fulfill this purpose, we learned predictive
models of the robustness of 6 well known reasoners.
We put into comparison various supervised learning
algorithms and feature selection techniques in order
to train best reasoner predictive models. Thanks to
this predictive study, we unveiled sets of local and
global ontology key features likely to give insights of
ontology hardness level against reasoners. We want
to stress that these features are key ones under the se-
lected reasoner quality criterion, i.e. the robustness.
However, we cannot confirm that the same features
would be always key ones when moving to different
criteria. Investigating this point would be interesting,
as to gain more insights about the most relevant fea-
tures across different reasoning quality criteria. In our
case, this purpose would be easily established, since
the whole learning steps described in this paper were
implemented in one single prototype. Our implemen-
Predicting the Empirical Robustness of the Ontology Reasoners based on Machine Learning Techniques
71
tation is generic enough, that it would be applied to
any reasoner, with the only requirement of provid-
ing enough amount of its running results. Our present
work could open further research perspectives. We as-
sume that the most important one would be extending
our learning steps by a ranking stage, where reasoners
could be compared based on their predicted robust-
ness for a given ontology. Such ranking would made
it possible to automatically recommend the most ro-
bust reasoner for any input ontology.
REFERENCES
Abburu, S. (2012). A survey on ontology reasoners and
comparison. International Journal of Computer Ap-
plications, 57(17):33–39.
Alaya, N., Lamolle, M., and Yahia, S. B. (2015). Towards
unveiling the ontology key features altering reasoner
performances. Technical report, IUT of Montreuil,
http://arxiv.org/abs/1509.08717, France.
Baader, F., Calvanese, D., McGuinness, D. L., Nardi, D.,
and Patel-Schneider, P. F., editors (2003). The De-
scription Logic Handbook: Theory, Implementation,
and Applications. Cambridge University Press, USA.
Baader, F. and Sattler, U. (2000). Tableau algorithms for
description logics. In Proceedings of the Interna-
tional Conference on Automated Reasoning with Ana-
lytic Tableaux and Related Methods (TABLEAUX).
Bail, S., Glimm, B., Jimnez-Ruiz, E., Matentzoglu, N., Par-
sia, B., and Steigmiller, A. (2014). Summary ore 2014
competition. In the 3rd Int. Workshop on OWL Rea-
soner Evaluation (ORE 2014), Vienna, Austria.
Faezeh, E. and Weichang, D. (2010). Canadian semantic
web. chapter A Modular Approach to Scalable Ontol-
ogy Development, pages 79–103.
Gangemi, A., Catenacci, C., Ciaramita, M., and Lehmann,
J. (2006). Modelling ontology evaluation and valida-
tion. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Semantic
Web Conference.
Garcia, S., Luengo, J., Saez, J., Lopez, V., and Herrera, F.
(2013). A survey of discretization techniques: Tax-
onomy and empirical analysis in supervised learning.
IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineer-
ing, 25:734–750.
Gardiner, T., Tsarkov, D., and Horrocks, I. (2006). Frame-
work for an automated comparison of description
logic reasoners. In Proceedings of the International
Semantic Web Conference, USA, pages 654–667.
Glimm, B., Horrocks, I., Motik, B., Shearer, R., and Stoi-
los, G. (2012). A novel approach to ontology classifi-
cation. Web Semant., 14:84–101.
Gonc¸alves, R. S., Matentzoglu, N., Parsia, B., and Sattler,
U. (2013). The empirical robustness of description
logic classification. In Informal Proceedings of the
26th International Workshop on Description Logics,
Ulm, Germany, pages 197–208.
Gonc¸alves, R. S., Bail, S., Jim
´
enez-Ruiz, E., Matentzoglu,
N., Parsia, B., Glimm, B., and Kazakov, Y. (2013).
Owl reasoner evaluation (ore) workshop 2013 results:
Short report. In ORE, pages 1–18.
Gonc¸alves, R. S., Parsia, B., and Sattler, U. (2012). Per-
formance heterogeneity and approximate reasoning in
description logic ontologies. In Proceedings of the
11th International Conference on The Semantic Web,
pages 82–98.
Hall, M., Frank, E., Holmes, G., Pfahringer, B., and Reute-
mann, P. (2009). The weka data mining software: An
update. SIGKDD Explor. Newsl., 11:10–18.
Horrocks, I. (2003). Implementation and optimisation tech-
niques. In The Description Logic Handbook: Theory,
Implementation, and Applications, chapter 9, pages
306–346. Cambridge University Press.
Horrocks, I., Kutz, O., and Sattler, U. (2006). The even
more irresistible S R OI Q . In Proceedings of the 23rd
Benelux Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pages
57–67.
Hu, B. and Dong, W. (2014). A study on cost behaviors
of binary classification measures in class-imbalanced
problems. CoRR, abs/1403.7100.
Kang, Y.-B., Li, Y.-F., and Krishnaswamy, S. (2012). Pre-
dicting reasoning performance using ontology met-
rics. In Proceedings of the 11th International Con-
ference on The Semantic Web, pages 198–214.
Kang, Y.-B., Li, Y.-F., and Krishnaswamy, S. (2014). How
long will it take? accurate prediction of ontology rea-
soning performance. In Proceedings of the 28th AAAI
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pages 80–86.
Kotsiantis, S. B. (2007). Supervised machine learning: A
review of classification techniques. In Proceedings
of the Emerging Artificial Intelligence Applications in
Computer Engineering Conference., pages 3–24, The
Netherlands. IOS Press.
LePendu, P., Noy, N., Jonquet, C., Alexander, P., Shah,
N., and Musen, M. (2010). Optimize first, buy later:
Analyzing metrics to ramp-up very large knowledge
bases. In Proceedings of The International Semantic
Web Conference, pages 486–501.
Mikol
`
a
˜
sek, V. (2009). Dependability and robustness: State
of the art and challenges. In Software Technologies for
Future Dependable Distributed Systems, pages 25–31.
Motik, B., Shearer, R., and Horrocks, I. (2009). Hyper-
tableau reasoning for description logics. Journal of
Artificial Intelligence Research, 36:165–228.
OWL Working Group, W. (27 October 2009). OWL 2 Web
Ontology Language: Document Overview. W3C Rec-
ommendation. Available at http://www.w3.org/TR/
owl2-overview/.
Sazonau, V., Sattler, U., and Brown, G. (2014). Predicting
performance of owl reasoners: Locally or globally? In
Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Confer-
ence on Principles of Knowledge Representation and
Reasoning.
Sirin, E., Parsia, B., Grau, B. C., Kalyanpur, A., and Katz,
Y. (2007). Pellet: A practical owl-dl reasoner. Web
Semant., 5:51–53.
KEOD 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
72
Steigmiller, A., Liebig, T., and Glimm, B. (2014). Kon-
clude: System description. Web Semantics: Science,
Services and Agents on the World Wide Web, 27(1).
Tartir, S., Arpinar, I. B., Moore, M., Sheth, A. P., and
Aleman-Meza, B. (2005). OntoQA: Metric-based on-
tology quality analysis. In Proceedings of IEEE Work-
shop on Knowledge Acquisition from Distributed,
Autonomous, Semantically Heterogeneous Data and
Knowledge Sources.
Tsarkov, D., Horrocks, I., and Patel-Schneider, P. F.
(2007). Optimizing terminological reasoning for ex-
pressive description logics. J. of Automated Reason-
ing, 39(3):277–316.
Weith
¨
oner, T., Liebig, T., Luther, M., B
¨
ohm, S., Henke, F.,
and Noppens, O. (2007). Real-world reasoning with
owl. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference
on The Semantic Web, pages 296–310.
Zhang, H., Li, Y.-F., and Tan, H. B. K. (2010). Measuring
design complexity of semantic web ontologies. J. Syst.
Softw., 83(5):803–814.
Predicting the Empirical Robustness of the Ontology Reasoners based on Machine Learning Techniques
73
