Construction and Implementation of Games Information System in
Aid Program for the 27th SEA Games Myanmar
Yang Linyun, Zhang Chao and Cheng Xiudong
China Sport Information Center, Tiyuguan Road 11#, Beijing, China
Keywords: Multi-sport Games, Games Information System, Timing & Scoring System, on-Venue Result System.
Abstract: Multi-sport Games is one of the important social and cultural activities all over the world. It is a necessity to
establish the information system for the multi-sport Games, along with the increase in the social concern
and participation, and the development of computer and information technology. Games Information
System provides complex, accurate and prompt on-site services of all kinds of Games information and
results during the competition, and provides more detailed and convenient information services for athletes,
coaches, competition officials, OC staff, audiences, media & the public. In this way, the Games Information
System ensures the efficient running of the on-site game management and game organization. The 27th
SEA Games were held in Myanmar in 2013. As an important part of Aid Program which China gave to
Myanmar for supporting the SEA Games, the Games Information System was constructed and implemented
by China Sport Information Center. This paper studied and discussed the construction and implementation
of Games Information System for the SEA Games. The system went well during the Games, and was highly
praised by Myanmar side and different fields related to the Games.
1 INTRODUCTION
Multi-sport Games is one of the important social and
cultural activities all over the world. It is a necessity
to establish the information system for the multi-
sport Games, along with the increase in the social
concern and participation, and the development of
computer and information technology (Liu et al.,
2012). Information technologies were widely
applied in Olympic Games, Continental Games,
National Games, and various sport events with the
rapid development of modern science and
technology(Han et al., 2013). The construction and
implementation of information system was a
substantial part during the performance of Games.
Compared with “higher, faster and stronger” in
competition, information systems were expected to
be “more accurate, more rapid and more stable”.
Games Information System provides complex,
accurate and prompt on-site services of all kinds of
Games information and results during the
competition, and provides more detailed and
convenient information services for athletes,
coaches, competition officials, OC staff, audiences,
media & the public. Through all kinds of
information distribution methods, Games
Information system could display the eye-catching
competitions and their results, which would make
the possibility to interact between athletes and media
& the public, to display the athletic elegancy, to
exert the media’s power in publicity, and to let the
public enjoy the competitions, and thus make more
people participate in the Games. Under the support
of information service system, the Games create
enormous commercial opportunities, which attract
more enterprises, and promote the development of
the sports industry. There is no doubt that the
modern Games will not thrive and develop without
the comprehensive Games information systems. It is
hard to imagine that successful multi-sport Games
will be held without the support of information
system.
China sport information center is responsible for
Games Information System. This paper was
completed during the construction and
implementation of the system, and discussed about
the top-level design of the system. The system
focused both on the environment in Myanmar and
modern trends of development of information
system. The system offered services in various
aspects, including competition support for 33 events,
integrated result process, TV graphics display, result
232
Linyun, Y., Chao, Z. and Xiudong, C..
Construction and Implementation of Games Information System in Aid Program for the 27th SEA Games Myanmar.
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support (icSPORTS 2015), pages 232-238
ISBN: 978-989-758-159-5
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
and information distribution, accreditation, arrival
and departure management, etc. The system went
well during the Games, and was highly praised by
Myanmar side and different fields related to the
Games.
2 REQUIREMENTS AND
ORIENTATION OF SYSTEM
The 27th SEA Games was held from December 11th
to 22th, 2013 in Myanmar. 33 sport events, 406
disciplines were set in the Games. Competition
venues were distributed mainly at Nay Pyi Taw and
Yangon, besides one football venue at Mandalay and
sailing venue at Ngwe Saung beach (People.cn,
2013). All 11 countries and regions took part in the
Games. Around 5000 athletes and delegate officials
participated in the Games, and 40,000 staff served
for the Games.
It was the third time that Myanmar held SEA
Games, after 44 years since last time. According to
the agreement between China and Myanmar
government, China would offer help to Myanmar for
holding the SEA Games. The aid program included
the training of Myanmar athletes, the show of
opening and closing ceremonies, and the
construction and implementation of Games
Information system. It was the first time that
software systems were included in aid program of
China. The aid program would enhance the level of
cooperation with China and Myanmar, expand new
areas of cooperation, and increase the friendship
between China and Myanmar (Liu, 2013).
In 2012, Myanmar government asked China for
help including Games Information system. China
working group investigated Myanmar twice in May
and August 2012, and determine the aid program for
the SEA Games. And the agreement was signed in
September 2012.
Myanmar raised requirements for Games
Information system as follows:
In accreditation, the system was expected to
manage the information for all participators,
including athletes, officials, VIPs, volunteers and
working staffs. Moreover, the system was expected
to make ID cards and car passing cards.
The arrival and departure management module was
expected to manage information of arrival and
departure of athletes and officials, so the relative
department could pick up and send them
conveniently.
In competition support, timing & scoring system and
on-venue result system for 33 events, result display
on public scoreboard, TV graphics display were
expected.
In information distribution, result website was
expected to publish individual event results,
integrated result, gold medals ranking, medals
ranking, etc.
SEA Games was a regional multi-sport, in which
only 11 countries and regions took part. The
competitive level was limited, and the international
attention was not very high. The economic level of
Myanmar was limited and basic environment such as
electric power, network, transportation,
accommodation was not good. Myanmar
government put more money and resource to
improve basic environment for holding the SEA
Games, however those were not enough. It was a big
challenge to implement Games Information system
under such basic environment.
According to the requirements of Myanmar, and
compared with information systems applied in
similar level multi-sport Games, the service level of
Games Information system was oriented to be
medium, slightly better than which was applied in
SEA Games 2011 in Indonesia. The system would
focus the service on field of play in venue. The
construction and implementation of the system
would meet the requirements of Myanmar side under
the consideration of actual local environment.
3 DESIGN OF GAMES
INFORMATION SYSTEM
3.1 Overview
According to the requirements, Games Information
System was designed as a high-efficient, complete,
open and advanced competition information
processing system, which integrates all kinds of
resources such as hardware platform, net
communication platform, tools platform and
application software platform etc. The system is
applied to provide services for the Games to
guarantee its high-efficient and faultless operation,
which include athlete entry by name and by event,
competition organization and management, timing
and scoring, results processing, information
distribution and results inquiry and so on.
Games Information System is mainly responsible
for processing competition results information,
including sports entry, defining the scale of the
Construction and Implementation of Games Information System in Aid Program for the 27th SEA Games Myanmar
233
Games, defining competition events, arranging
competition schedule and program, getting and
processing results, generating and printing various
competition reports.
The construction and implementation of Games
Information System involves not only its own
construction but also basic environment such as
venue, electric power, network, communications,
volunteer which would guarantee smooth operation
of the whole system.
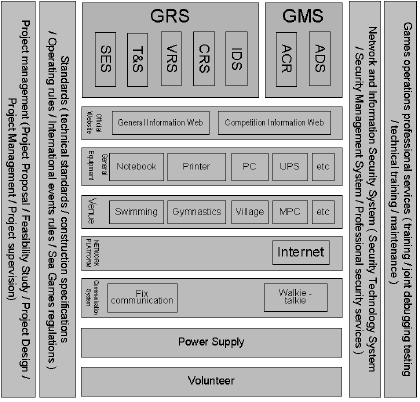
The architecture of the system is shown as follow:
Figure 1: Architecture of Games Information System.
There are 2 main parts of Games Information
System: Games Result System (GRS) and Games
Management System (GMS). GRS offer direct
service for competition which contains 5 parts: Sport
Entries System (SES), Timing & Scoring System
(T&S), Venue Result System (VRS), Central Result
System (CRS) and Information Diffusion System
(IDS). GMS offer service for Games management
which contains 2 parts: Accreditation System (ACR)
and Arrive and Departure System (ADS).
3.2 Games Result System (GRS)
3.2.1 Sport Entries System (SES)
SES operates before competition and is the only
entrance system for athlete competition entry.
Registration via SES involves two parts: Entry by
name and Entry by Event. Entry by name indicates
athlete registration information by ACR; Entry by
Event refers to the information of the specific events
which athletes participate in.
The function of SES is:
- Delegation Management: Delegation Management
refers to the management of delegation roster
including delegation code, name of delegation in
both abbreviated and full form, and the management
of whether delegations participate in the
competition.
- Athletes Management: every country / region
submits athlete information to OC via internet.
Athlete Roster information refers to the registration
of athlete’s personal information.
- Event Management: Athlete’s entry by event is
very complicated. Event management refers to the
management of information of what event will every
athlete participate.
3.2.2 Timing & Scoring System (T&S)
A data acquisition system is needed for a high-level
competition to provide a high-demanding live
operating service under a series of technical work
such as data capturing, processing and distributing
and so on.
Timing & Scoring System is an aggregated
system customized according to rules and
regulations of each discipline, which involves
various equipments or devices operating
simultaneously with diverse technology aggregates
at different operating places. The combined system
operates flexibly in a variety of complex working
conditions. T&S is applied to the core part of
competitions, namely, generating competition results
and records as the only criteria for athlete results.
Besides, Timing and Scoring System, as a front
basic system of Games Result System, is responsible
for providing the raw competition data for the other
sub-systems of Venue Results System (VRS) and its
operation decides the success or failure of
competitions and, sequentially, decides whether the
whole system can operate faultlessly.
The main functions of T&S can be defined as the
following:
- Provide equipment and service for operation
- Provide service for the special display equipment
in competition
- Exchange real time data.
- Offer analysis report to referees.
3.2.3 Venue Result System (VRS)
A modern Games makes high requirement of
competition organization and management
(including arranging competition program and
management of athlete entry by name and by event),
results capturing and processing (such as acquiring
icSPORTS 2015 - International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
234
the results from Timing and Scoring System or the
results by manual entry, ranking and qualification
processing etc.) and on-venue data exchange and
data distribution (including data exchange and real-
time data service).
Venue Result System is deployed at each venue
to provide the service for competition management
and competitions for each event. The system is
directly engaged in competition commanding
management and referees’ work, which is an
inseparable part of competition organizing
management. As a result, the operating conditions of
Venue Result System directly influence whether
competition events can go smoothly.
Being unique and special, each event is
configured with a specified venue result system
compliant with its rules and regulations.
The main modules of VRS are:
- Result Data Entry: Result Data Entry (RDE) is the
data inputting system of VRS. RDE stores data
into the database of OVR by acquiring data from
external systems (e.g. T&S) or generating
technical statistics, manual result.
- On-Venue Result system: On-Venue Result system
(OVR) is the core module of VRS. Its main
function is to assist sport-event departments in
organizing, managing and arranging the events and
dealing with results. OVR handles the result for an
on-going competition. It acquires data through
automatic collecting or manual inputting.
Meanwhile, it processes ranking & ordering,
promotion, record-breaking and penalty.
- Local Result Print: Local Result Print (LRP) runs
offers the functions of result report design,
management and print. It is allocated to the entire
workflow of VRS, capable of printing competition
result report.
- Public Scoreboard display: Public Scoreboard
display (PSCB) is a monitor system which
coordinates with competition control, then display
results on venue scoreboard. During the
competition, PSCB acquires real-time data from
OVR and display the data acquired in prescribed
templates on the venue scoreboard.
- TV Graphics system: TV Graphics system (TVG)
is a system equipped in each competition venue,
capable of transmitting high or standard definition
TV signals and running independently. Through
network, TVG promptly and accurately transmits
real-time information on timing & scoring,
competition schedules, and result processing in the
form of TV pictures to television viewers.
3.2.4 Central Result System (CRS)
The difference between multi-sport Games and
individual event is the capability of processing the
integrated results. Multi-sport Games require a
capable system to provide integrated competition
information service by collecting and processing all
venue competition information (mainly results
information).
Central Results System is the core of Games
Results System (GRS), and also the center of
integrated transaction system and data base of GRS.
Its function is setting up the parameters of Games
such as the scale of Games, competition event,
record-breaking, arranging competition schedule,
monitoring and collecting the results and reports for
each event, dealing with the communication and
data exchanges between VRS and IDS.
The main modules of CRS are:
- Data exchange Management system: Data
exchange management system (DXM) provides
basic-level service to control and manage the data
communication. It’s mainly responsible for the
management of message distribution route and the
data exchange taking place between CRS and VRS
as well as between CRS and IDS.
- Central Management System: Central Management
System (CMS) is mainly responsible for the
management and configuration of CRS, including
coding management, application safety
management and the management of Games
configuration.
- Central Process System: Central Process System
(CPS) is mainly in charge of set the plans, making
the arrangements and handling the concerning
work, including the sports plan management,
ranking management, broken records management,
medals management, and central monitoring
console management and so on.
3.2.5 Information Diffusion System (IDS)
The display of competition process and results is an
important means to show the unique charm of high-
level competitions in international multi-sport
Games. Modern multi-sport Games require a variety
of channels or means to provide press and media and
the public with the competition information.
As an important component of GRS, IDS support
the multi-user information generation in various
formats and the information distribution to the
official website. It is the main channel for the
competition participants, media and the public to
acquire the competition information. The list of
contents to be distributed includes: athletes’
Construction and Implementation of Games Information System in Aid Program for the 27th SEA Games Myanmar
235
information, game results, competition schedules,
reports, competition progress, medals, rankings, etc.
The main channel of distributing information is
website and APP for smartphone.
3.3 Games Management System (GMS)
3.3.1 Accreditation System (ACR)
The function of Accreditation system is to collect
personal information for all participators, including
athletes, officials, working staff, volunteers, etc.
ACR will design ID cards which contain all
necessary information of participators.
The function of ACR is:
- Data interface: Define data interface between ACR
and other systems.
- Query and modification: After the participator
applies registration, he or she can query on the
website, and revise if there are any changes.
- Data input: Input personal information.
- Data audit: OC can audit the participator whether
he or she can participate in the Games.
- Access permission management: Define the access
permission to determine which venue the
participator can enter.
- ID cards design: Design ID cards which contain all
necessary information of participators.
3.3.2 Arrive and Departure Management
System (ADS)
The function of ADS is to manage information of
arrive and departure of athletes and officials, so that
the relative department could pick up and send them
conveniently.
The function of ADS is:
- Data interface: Define data interface between ADS
and other systems (mainly ACR).
- Data input: Input arrival and departure information
of participators.
- Data query: Query arrival and departure
information on the website.
3.4 Local Environment Requirements
For the smooth performance of the Games
Information System, Myanmar should offer local
environment such as:
- Venue environment: Functional rooms, desks,
chairs, etc.
- Network: A network is necessary to connect all
competition venues and main data center. Internet
access is required on every spot where the devices
are deployed.
- Communication: Cellphones and walkie-talkies.
- Electric power: To provide electric power and UPS
at each venue.
- Volunteers: A number of local volunteers are
required to assist the system operation.
4 IMPLEMENTATION OF
GAMES INFORMATION
SYSTEM
The implementation of Games information system is
illustrated briefly as following:
Table 1: Implementation schedule.
Work content Time
Preparation September, 2012
Venue inspection October, 2012
Requirement investigation of
GRS
October, 2012
Requirement investigation of
GMS
October, 2012
Development of GMS
November, 2012
to July, 2013
Development of GRS
November, 2012
to August, 2013
Delivery of requirements of
venue environment
December, 2012
Venue environment
construction
June, 2013
Venue inspection (second time) July, 2013
Training staff for ACR August, 2013
Trail operation of ACR 8, August, 2013
Operation of ACR 8, September, 2013
Venue inspection (third time) November, 2013
End of Sport entry 8, November, 2013
Training staff for ADS November, 2013
Trial operation of ADS 8, November, 2013
Devices and equipment arrival November, 2013
Training volunteer
18, November to 27,
November, 2013
Operation team ready 28, November, 2013
Rehearsal
1, December to 5,
December, 2013
System ready 5, December, 2013
Training referee to use the
system
Before competition
System operation of SEA
Games
4, December to 22,
December, 2013
Tail-in work End of 2013
The SEA Games was started on 4, December 2013
and ended on 22, December 2013. There were 19
icSPORTS 2015 - International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
236

match days and thousands of matches. 461 gold
medals, 459 silver medals, 611 bronze medals,
totally 1531 medals were produced (Wikipedia,
2013).
To complete the Games Information System in
aid program, China sport information center have
organized a specialized team which have 222
members. The ACR has produced 40763 ID cards.
The SES has completed works for 4906 delegation
members. Much data have been generated by Games
Information System including reports of start list,
result, statistics, real-time information, etc. 1090
start list reports, 1388 result reports, 460 medal list
reports and 24 record-breaking reports were
generated.
Some screenshots and pictures were shown as
following:
Figure 2: Website of Information Diffusion System.
Figure 3: Competition Report – Athletics.
Figure 4: App for smartphone.
Figure 5: System Operation - Swimming.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORKS
Games Information System provides complex,
accurate and prompt on-site services of all kinds of
Games information and results during the
competition, and provides more detailed and
convenient information services for athletes,
coaches, competition officials, OC staff, audiences,
and for media & the public. In this way, the Games
Information System ensures the efficient running of
the on-site game management and game
organization. With the help of China’s aid program,
Myanmar has held a successful SEA Games.
This paper was completed during the
construction and implementation of the system, and
discussed the top-level design of the system. The
system focused both on the environment in
Myanmar and on the modern trends of development
of information system. The system offered services
in various aspects, including competition support for
33 events, integrated result process, TV graphics
display, result and information distribution,
accreditation, arrival and departure management,
etc.
The whole system went well during the Games,
and was highly praised by Myanmar side and
different fields related to the Games.
In the future works, we will make more effort on the
expansion and integration of the Games Information
System.
REFERENCES
Liu, Guangxian, Wang Ping, Wang Feng, 2012. Establish
of Networking mode of Competition Information
Acquisition System. In Microprocessors 1002-2279
Construction and Implementation of Games Information System in Aid Program for the 27th SEA Games Myanmar
237
(2012) 05-0085-05.
Han, Jian, Zhong Yaping, Wang Jinyu, Lei Zhao, 2013.
The Prospect and Application of Sports Computer
(Information Technology). In National Sport Sciences
Conference (China).
People.cn, 2013. Website, http://sports.people.com.cn/n/
2013/1212/c22155-23820727.html.
Liu, Hongshu, 2013. Website, http://gb.cri.cn/42071/2013/
11/06/5931s4312331.htm.
Wikipedia, 2013. Website, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
2013_Southeast_Asian_Games.
icSPORTS 2015 - International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
238
