An Extended Q Learning System with Emotion State to Make Up an
Agent with Individuality
Masanao Obayashi
1
, Shunsuke Uto
1
, Takashi Kuremoto
1
, Shingo Mabu
1
and Kunikazu Kobayashi
2
1
Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Yamaguchi University, Ube Yamaguchi, Japan
2
School of Information Science and Technology, Aichi Prefectural University, Nagakute, Aichi, Japan
Keywords: Reinforcement Learning, Amygdala, Emotional Model, Q Learning, Individuality.
Abstract: Recently, researches for the intelligent robots incorporating knowledge of neuroscience have been actively
carried out. In particular, a lot of researchers making use of reinforcement learning have been seen,
especially, "Reinforcement learning methods with emotions", that has already proposed so far, is very
attractive method because it made us possible to achieve the complicated object, which could not be
achieved by the conventional reinforcement learning method, taking into account of emotions. In this paper,
we propose an extended reinforcement (Q) learning system with amygdala (emotion) models to make up
individual emotions for each agent. In addition, through computer simulations that the proposed method is
applied to the goal search problem including a variety of distinctive solutions, it finds that each agent is able
to have each individual solution.
1 INTRODUCTION
Reinforcement learning (RL) for the behavior
selection of agents/robots has been proposed since
1950’s. As a machine learning method, it uses trial-
and-error search, and rewards are given by the
environment as the results of exploration
/exploitation behaviors of the agent to improve its
policy of the action selection (Sutton et al., 1998).
The architecture of RL system is shown in Fig.1.
However, when human makes a decision, he finally
does it using the various functions in the brain, e.g.,
emotion. Even the environmental state is the same;
many different selections of the behavior may be
done depending on his emotional state then.
A computational emotion model has been
proposed by J. Moren and C. Balkenius (Moren et
al., 2001). Their emotion model consists of four
parts of the brain: “thalamus, sensory cortex,
orbitofrontal cortex and amygdala” as shown in
Fig.2. Fig.2 represents the flow from receptors of
sensory stimuli to assessing the value of it. So far,
the emotion model has been applied to various fields,
especially, the control field of something. For
example, H. Rouhani, et al. applied it to speed and
position control of the switched reluctance motor
(Rouhani, et al., 2007) and micro heat exchanger
control (Rouhani, et al., 2007). N. Goerke applied it
to the robot control (Nils, 2006), E. Daglari, et al.
applied it to behavioral task processing for cognitive
robot (Daglari, et al., 2009). On the other hand,
Obayashi et al. combined emotion model with
reinforcement Q learning to realize the agent with
individuality (Obayashi, et al., 2012). F. Yang et al.
also proposed the agent’s behaviour decision-
making system based on artificial emotion using
cerebellar model arithmetic computer (CMAC)
network (Fuping, et al., 2014). H. Xue et al.
proposed emotion expression method of robot with
personality to enable robots have different
personalities (Xue, et al., 2013). Kuremoto et al.
applied it to a dynamic associative memory system
(Kuremoto, et al., 2009). All of these applications
have good results.
In this paper, we propose an interesting
reinforcement learning system equipping with
emotional models to make up “individuality” for the
agent.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2, a computational emotion model we used
is provided. Our proposed hierarchical Q learning
system with emotions is given in Section 3.
70
Obayashi, M., Uto, S., Kuremoto, T., Mabu, S. and Kobayashi, K..
An Extended Q Learning System with Emotion State to Make Up an Agent with Individuality.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2015) - Volume 3: NCTA, pages 70-78
ISBN: 978-989-758-157-1
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
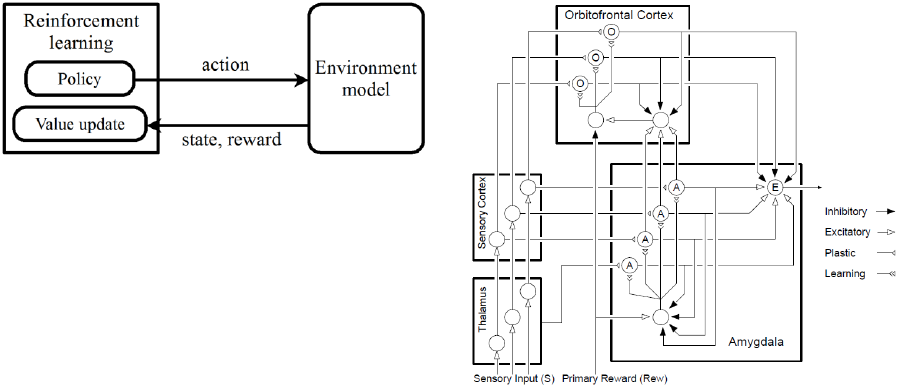
Figure 1: A reinforcement learning system (Sutton, et al.,
1998).
A computer simulation using a grid world
environment is carried out to evaluate the proposed
system in Section 4. This paper is concluded in
Section 5.
2 COMPUTATIONAL EMOTION
MODEL
The computational emotional model is proposed by J.
Moren and C. Balkenius (Moren, et al., 2001)
consists of 4 parts of the brain, “thalamus, sensory
cortex, orbitofrontal cortex and amygdala” as shown
in Fig.2, it represents the flow from receptors of
sensory stimuli to assessing the value of it. The
dynamics of the computational emotional model are
described as follows;
iii
SVA
(1)
iii
SWO
(2)
i i
ii
OAE
(3)
))Re,0max((
amy
j
jii
AwSV
(4)
)Re(
amy
wESW
ii
, (5)
here, S
i
denotes input stimuli from the sensory cortex
and thalamus to the ith neuron in the amygdala, i = 1,
2, ….. , N
amy
, where N
amy
corresponds to the number
of neurons in the amygdala and A
i
denotes the output
of the ith neuron in the amygdala. Likewise, O
i
denotes the output of ith neuron in the orbitofrontal
cortex. E is the output of the amygdala after
subtracting the input from the orbitofrontal cortex.
amyamy
,
are learning rates, V
i
, W
i
are synaptic
weights of connections between the sensory cortex
and amygdala, as well as the sensory cortex and
orbitofrontal cortex, respectively. Primary reward
Rew is the reinforcing signal.
Figure 2: A computational emotional model proposed by J.
Moren, et al. (Moren, et al., 2001).
3 HIERARCHICAL Q LEARNING
SYSTEM WITH EMOTIONS
When a person saw an exciting landscape, he feels it
pleasant or unpleasant. In this paper, we introduce
the degree of - (pleasant-displeasant) impression of
the image using the colour characteristics of the
image as one of the emotional state to be defined in
the internal robot. Figure 3 shows the proposed
extended reinforcement learning system with
emotional models and integrated emotional state
model. It has a hierarchical structure, the first layer
is an image processing model, the second layer is a
fuzzy inference model, the third layer is emotional
models by Moren, the fourth layer is the integrated
emotional state model by Russel and the fifth layer
is the proposed extended reinforcement Q learning
system (Obayashi, et al., 2012). In the next
subsections short contents of them are described.
3.1 Image Processing Model: First
Layer
In the first layer, RGB values of each pixel of the
image acquired from the environment is converted to
the HSV (Hue, Saturation and Value) values, using
the following (6). These are transmitted to Fuzzy
inference model of the second layer,
An Extended Q Learning System with Emotion State to Make Up an Agent with Individuality
71

Figure 3: The proposed hierarchical reinforcement (Q)
learning system with emotional models.
(6)
where Max = max{R, G, B}, MIN = min{R, G, B}.
3.2 Fuzzy Inference Model: Second
Layer
In the second layer, the colour features (Saturation,
Value which represent modifier: dull thin, dark-
bright-dark, and Hue which represents basic colour
name: red, blue and green) provided from the first
layer is converted to a degree of pleasure-displeasure
using Mamdani type simplified singleton fuzzy
inference.
The membership functions of Saturation, Value
and Hue used in this paper are shown in Fig. 6, 7
and 8, respectively. They are set corresponding to
their values. The fuzzy rules of Saturation and Value,
Hue are shown in Table 1 and 2. The impressions
sv
I
and
H
I
in these Tables are decided according to
our human impression. In Table 2, the Impression
(
H
I
) of red is set to high and that of blue is set to
low. This represents to express the vitality
impression with the colour.
Concretely, we inference the impression (
SV
I
)
from the Saturation and Value, taking the minimum
value between the grade of S and V for each rule,
and then taking fuzzy singleton inference for
defuzzification. The impression (
H
I
) from the Hue
are calculated as same as
SV
I
. Then, it is integrated
to obtain an impression value (
HSV
I
) for a pixel by
(7). This operation is applied to all the pixels. Then
the emotion of the entire image (Image impression:
Imi) is obtained by taking the average of all of the
impression values (8). Calculating Imi for each
direction of the image, sum of them is input to
emotion model 1 (the third layer) which is
responsible for pleasure-displeasure as Rew.
Impression (
HSV
I
) =
Impression (
H
I
)
Impression (
SV
I
) (7)
length pixel
)(IImression
(Imi) impression Image
pixel
HSV
(8)
Figure 4: Impression (
SV
) fuzzy inference model.
Figure 5: Impression (
H
) fuzzy inference model.
Figure 6: Membership function for Saturation (S).
Figure 7: Membership function for Value (V).
First layer
Second layer
Third layer
Fourth layer
Fifth layer
Agent
action
environment
state, reward
Extended
reinforcement Q
learning model
emotion state
Integrated emotion
state model
Emotion
model 1
Emotion
model 2
Fuzzy inference model
H
S, V
Image processing
model
H, S, V
emotion 1
emotion 2
Rew
Image data(R.G.B)
Rew
Environment
model
.MIN-MAXS
.MAXV
.
G MIN if5)
MIN-MAX
R-G
(60
R MIN if3)
MIN-MAX
R-G
(60
B MIN if1)
MIN-MAX
R-G
(60
MAX MIN ifundefined
H
Fuzzy inference
SV model
S
V
(0.0~1.0)
(0.0~1.0)
SV
I
Fuzzy inference
H model
H
(0.0~1.0)
H
I
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
0.55
0.6
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
Value
1
2
3
4
Grade
NCTA 2015 - 7th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
72
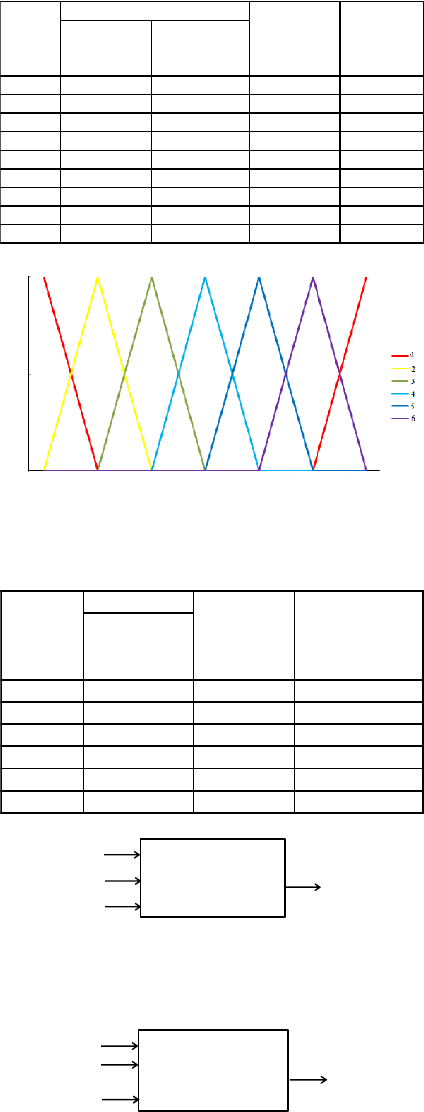
Table 1: Fuzzy rule table for Saturation and Value.
Figure 8: Membership function for Hue (H).
Table 2: Fuzzy rule table for Hue.
Figure 9: Emotion pleasure-displeasure model.
Figure 10: Emotion activity-disactivity model.
3.3 Emotion Model: Third Layer
Figure 9, 10 show the input and output for the
pleasure-displeasure and activity-disactivity emotion
models respectively. The structures of them are
same and their learning method is explained in
Section 2. The output of the emotion model for
pleasure-displeasure is
1
E
, and
2
E
is output of the
activity-disactivity emotion model. These
1
E
and
2
E
are used for two axis for the integrated emotion
state model in the fourth layer.
3.3.1 Emotion Model 1
The function of the emotion model 1 whose
structure is same as the computational emotion
model in Section 2 is to produce the emotion of
pleasure-displeasure by making use of
characteristics of the image. Its input and output
components are shown in Fig.9.
3.3.2 Emotion Model 2
The function of the emotion model 2 whose
structure is same as emotion model 1 is to produce
the emotion of activity-disactivity by making use of
the primary reward given by the environment. Its
input and output components are shown in Fig. 10.
3.4 Integrated Emotion State Model:
Fourth Layer
In this paper we use the circumplex emotion model
(Russel, 1980) as the integrated emotion state model.
The circumplex emotional model proposed by J.A
Russel consists of two axes that are pleasure-
displeasure (horizontal axis) and activity-disactivity
(vertical axis); it is shown in Fig. 11. The figure
shows unidimensional scaling of 28 emotion words
on the plane. Russel said that all the emotions of the
living body can be dealt by this circumplex model.
This model decides the current two dimensional
emotional states of the agent using two inputs
1
E
(displeasure–displeasure value) and
2
E
(activity–
disactivity value) from the third layer as shown in
Fig. 3.
3.5 Extended Q Learning with Emotion
State
The Emotion extended Q learning (Obayashi, et al.,
2012) is almost all of commonly used standard Q
learning. The extended Q learning with emotion
Rule
Number
If
Then Impression
(I
SV
)
Number of
membership
func. of S
Number of
membership
func. of V
1 3 1
Very
Dark 0
2 3 2
Dark Grayish
0.3
3 4 2
Dark
0.6
4 1 3
Grayish
0.9
5 5 3
Deep
1.2
6 1 4
Very
Pale 1.5
7 2 4
Pale
1.8
8 3 4
Light
2.1
9 5 4
Vivid
2.4
Grade
0.00
1.00
0.17
0.23
0.33
0.42
0.50
0.92
0.83
0.75
0.67
0.58
0.08
Hue
Rule
Number
If
Then Impression
(I
H
)
Number of
membership
func. of H
1 1
Red
2.0
2 2
Yellow
1.5
3 3
Green
1.0
4 4
Light Blue
-1
5 5
Blue
1.0
6 6
Purple
1.5
Emotion
pleasure-displeasure
model
Pleasure - displeasure
value (0.0 ~ 1.0)
Primary reward
(Image impression) from
2th layer ( 0.0 ~ 5.0)
Stimulus
from sensors
( s
1
~s
4
)
E
1
}1,0{
Emotion
activity-disactivity
model
Primary reward
(Prize) from environment
( -0.05 ~ 0.6)
Activity - disactivity
value (0.0 ~ 1.0)
E
2
Stimulus
from sensors
( s
1
~s
2
)
}1,0{
An Extended Q Learning System with Emotion State to Make Up an Agent with Individuality
73

state has the emotion state of the agent in addition to
environment state of standard Q learning. The value
function of the state, emotion and action in the
extended Q learning is represented as
),,( assQ
e
. The
update equation of
),,( assQ
e
is as follows;
,),,(),,(max
),,(),,(
'''
'
assQassQr
assQassQ
ee
a
ee
(9)
where
s
: current environment state,
e
s
: current
emotion state with two dimensions from the fourth
layer.
a
: current action,
r
: reward,
'
s
: next current
environment state,
'
e
s
: next current emotion state,
: learning rate,
: discount rate. We use the
greedy method as selection policy of behaviors of
the agent.
Figure 11: The circumplex emotional model by J.A.
Russel (Russel, 1980).
4 COMPUTER SIMULATION
4.1 Preparation
4.1.1 Problem Description
To evaluate our proposed method, we carried out a
computer simulation using a grid world environment
as shown in Fig. 12. The wall surrounds around it.
There are meaningful plural paths from start to goal.
We found that each agent learned the different path
from start to goal, forming the different emotions by
use of the different parameter for learning of the
emotion model.
4.1.2 Assumptions
In these simulations, next followings are assumed,
1) The agent knows his own position.
2) The action which the agent can take is “to move
one cell to one direction among up, down, left
and right”.
3) If the agent collides with the wall, the agent
stays at the position before collision.
4.1.3 Environment Used in the Simulation
In the simulation with environment shown in Fig.12,
there are the cell which is locked and the switch cell
to release the lock. It is necessary for the agent to
visit the switch cell once to release the lock to get
the goal. The agent has to take a circuitous route to
get the red and blue foods and also has to take a
hazard route to take the shortest path to the goal. So
the agent has the dilemma, which route should be
selected. It is verified the dilemma is solved by the
individuality of the agent.
4.1.4 Emotion Formation in the Simulation
In this simulation, the number
n
of the sensory
inputs
n
s
is 4 in the computational emotion model
shown in Fig. 2, toward the information about up,
down, right and left. If there is a food within 5 cells
from the agent,
i
s
is set to 1, otherwise 0 (see Fig.
14). According to the distance between the food and
the agent, Rew is set as following equations;
Figure 12: The environment used in the simulation.
Figure 13: The image used as input to Image processing
model in the simulation.
Excited
Astonished
Delighted
Glad
Pleased
Happy
Satisfied
Content
Serene
Calm
Relaxed
At ease
Sleepy
Tired
Miserable
Droopy
Aroused
Alarmed
Afraid
Angry
Tense
Distressed
Annoyed
Frustrated
Sad
Depressed
Gloomy
Bored
pleasure - displeasure
activity
-nonactivity
(a) Image given as the red
big food
(b) Image given as the blue
small food
NCTA 2015 - 7th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
74

Figure 14: Example of the sensory input s and primary
reward input (Rew) of the emotion model for making the
pleasure-displeasure value (E
1
).
(Imi) impression Image0.9 Prize
distance
(10)
,PrizeRe
mage
i
w
(11)
The images used as input to Image processing model
in the simulation are shown in Fig. 13. A calculation
example of values is shown in Fig. 14. The emotion
model of activity-disactivity is as to “activity of the
agent itself”. The number of sensory inputs S is 2, as
to the information, one is always S = 1, the other is S
= 1 if the agent is in hazardous yellow area, or pink
area, S =0 for otherwise. The value of Rew changes
step by step according to the rules of Table 3.
Parameters used in the learning of the emotion
Table 3: Primary rewards (Rew) for the emotion model 2
with activity-disactivity.
Initial value
0.4
when after 1 step
- 0.005
blue food acquisition
+0.2
hazardous area :
yellow
-0.02
red food acquisition
+0.6
hazardous area :
purple
-0.05
when release the
yellow switch
+0.4
Table 4: Parameters used in the learning of the two
emotion models.
models are shown in Table 4. In Table 4, the method
“Q + AE” is our proposed extended Q learning with
emotion state, however, the parameters used in the
learning of the emotion model are fixed while in the
simulations. The method “Q+AE+S” is also our
proposed method. The bigger the learning
coefficient parameter
amy
is, the bigger the output
of the emotion model is. In reverse, the bigger the
learning coefficient parameter
amy
is, the smaller the
output of the emotion model is. In the emotional
model 1, the learning parameters
amy
and
amy
are
changed in order to reduce the level of the pleasure
when the level is over 0.3. The emotion model 2
about the activity is almost same as the emotion
model 1.
4.1.5 Integrated Emotion State Model
The object of the integrated emotion state model in
the fourth layer is to decide the two dimensional
emotion states
))4,,1(),( iiS
e
, using the output
21
E and E
of the emotion models 1 and 2,
respectively in the third layer and to transmit the
state to the extended Q learning system in the fifth
layer.
Figure 15: The circumplex emotion model used in the
simulation.
4.1.6 Parameters and Rewards Used in the
Extended Q Learning
Rewards given by the environment are shown at Table 5.
The parameters used in the extended Q learning are given
at Table 6.
Table 5: Reward r given by the environment for the
extended Q learning in simulation 1 or 2.
arrival to the goal
10.0
red food acquisition (Given as
image of Fig. 14(a))
4.0
collision to the
wall
-2.0
blue small food acquisition
(Given as image of Fig. 14(b))
1.5
hazardous area :
yellow
-0.5
when release the blue switch
5.0
hazardous area :
pink
-2.0
others (when move 1 step)
-0.1
amy
amy
pleasure
- displeasure activity
-
disactivity
learning
rate
learning
rate
learning
rate
learning
rate
Q+AE
0.4 0.3 0.2
0.5
Q+AE +S
0.4
0.01
0.3
0.8
0.2
0.01
0.5
0.8
)5.0(E
2
)5.0(E
2
)5.0(E
2
)5.0(E
2
)3.0(E
1
)3.0(E
1
)3.0(E
1
)3.0(E
1
amy
amy
pleasure
E
1
activity
E
2
( 0.0 , 0.0) ( 1.0 , 0.0)
( 0.0 , 1.0)
( 1.0 , 1.0)
0.3
0.5
)1(
e
s
)2(
e
s
)3(
e
s
)4(
e
s
An Extended Q Learning System with Emotion State to Make Up an Agent with Individuality
75
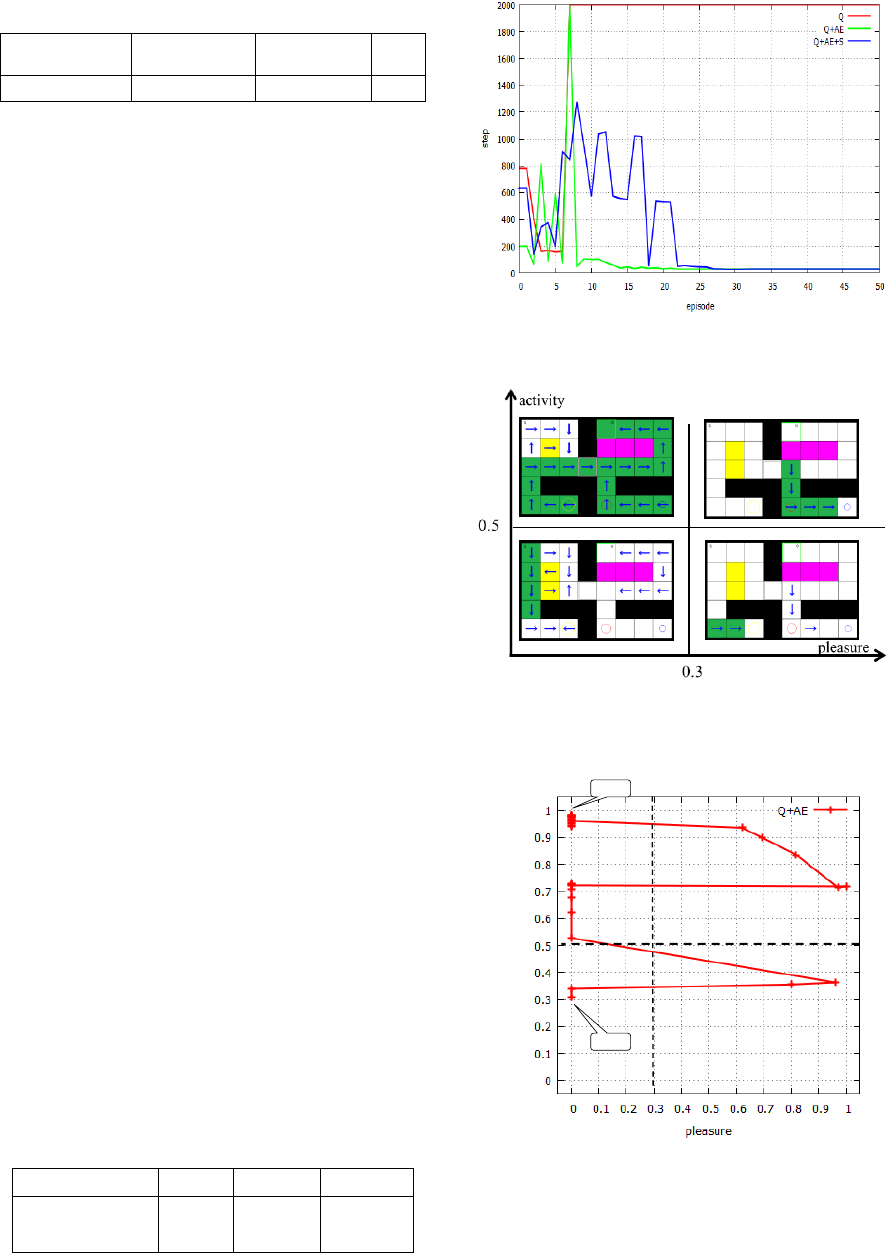
Table 6: Parameters used in the extended Q learning.
learning rate
0.5
discount rate
0.95
policy
greedy method
4.2 Simulation and Its Result
To confirm the performance of the proposed method,
we compared with three methods: 1) the
conventional Q learning method named “Q”, the
other two methods are our proposed methods, that is,
2) the method using extended Q learning with the
learning parameter fixed emotional model named
“Q+AE”, 3) the method using extended Q learning
with the learning parameter changed emotional
model named “Q+AE+S”.
The results of these three methods are shown at
Table 7 and in Figs. 16~20. Table 7 shows average
convergence steps to the goal of 100 times in each
method. Fig.16 shows the number of steps to the
goal for each method and episode. From these
results, the conventional Q learning method could
not get the goal at all. Our two proposed methods
succeeded to get the goal. However, from Fig. 16
our two methods with success have a peak, after that
the number of steps to the goal are decreasing
according to progress of episodes. This means that
the agent takes a lot of steps until the agent find that
he has to proceed to the goal after pressing the
switch. The reason why this could be achieved is
that the emotion comes to be different from before
and after the agent push the switch due to the
emotional learning as shown in Figs. 17~20. The
difference between the Q+AE method and the
Q+AE+S method is their convergence steps, that is,
in the Q+AE method the agent got the two foods
although in the Q+AE+S method the agent got only
the red food to be discovered firstly.
Fig. 17 and 18 show the simulation results of the
Q+AE method. Fig.17 shows the convergence path
along green cells in the four emotion states for the
method. Fig 18 shows changes of the emotion state
of the robot corresponding to the behaviour of the
robot for the method. From Fig. 18, we can find that
the agent starts with the emotion
)3(
e
S
, passing
through
)4(
e
S
,
)2(
e
S
and
)1(
e
S
, finally it got the
goal with
)2(
e
S
.
Table 7: Average convergence steps to the goal of 100
times in each method.
Q
Q+AE
Q+AE+S
convergence
step to the goal
---
32
28
Figure 16: The number of steps to the goal for each
method (average of 100 times).
Figure 17: The convergence path (arrow direction with
green) in the each emotion state for the proposed method
named “Q+AE”.
Figure 18: The change of emotions from start to the goal
for the proposed method named “Q +A E”.
0
activity
Goal
Start
NCTA 2015 - 7th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
76

Figure 19: The convergence path (arrow direction with
green) in the each emotion state for the proposed method
named “Q+AE+S”.
Figure 20: The change of emotions from start to the goal
for the proposed method “Q +AE+S”.
Fig. 19 and 20 show the simulation results of the
Q+AE+S method. How to see both Figures is as
same as Fig.17 and 18. Comparing Figs. 17 and18
with Figs. 19 and 20, it is found that although the
result of the Q+AE+S method is the same as in the
Q+AE method until the agent gets the red food to be
firstly discovered on the path, the robot in Q+AE
method, besides, gets the blue food, although it in
Q+AE+S method moves to the goal, by changing the
learning coefficients
amyamy
,
of the emotion
model to reduce the reaction for the emotion. This is
the reason why the agent didn’t visit the cell the blue
food is placed in the Q+AE+S method.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we proposed an extended
reinforcement Q hierarchical learning system with
emotion state to make up an agent with individuality.
We generated the emotions in the robot using the
emotion models. In the computer simulation for a
path-finding problem with plural meaning paths, that
is, having a dilemma, it was verified that the agent
could get a variety of behavior patterns by setting
the different learning parameters in emotional model
learning. This means that by giving the different
learning parameters mentioned above to each agent,
it is able to make each agent give different
individuality, i.e., each agent get the goal achieving
any different and meaningful things.
In this study, we considered the single agent case.
In the future, we would like to try to the multi agent
case, i.e., to problems to be solved by multi-agents.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
A part of this work was supported by Grant-in-Aid
for Scientific Research (JSPS 25330287, and
26330254).
REFERENCES
Sutton R, Barto A, 1998. Reinforcement learning: an
introduction. Bradford Book. The MIT Press,
Cambridge.
J.Moren, C.Balkenius, 2001. A Computational Model of
Emotional Learning in the Amygdala. Cybernetics and
Systems 32(6), pp.611-636 .
H. Rouhani, A. Sadeghzadeh, C. Lucas, B. N. Araabi,
2007. Emotional learning based intelligent speed and
position control applied to neurofazzy model of
switched reluctance motor. Control and Cybernetics,
Vol.36, No.1, pp.75-95.
H.Rouhani, M.Jalili, B.N.Araabi, W.Eppler and C.Lucas,
2007. Brain Emotional Learning Based Intelligent
Controller Applied to Neurofuzzy Model of Micro
Heat Exchanger. Expert Systems with Applications,
Vol.32, No.3, pp.911-918.
Nils Goerke, 2006. EMOBOT:A Robot control
architecture based on emotional-like internal values.
Mobile Robotics, Moving Intelligence, J. Buchli ed.,
Chp. 4, intechopen.com.
E. Daglari, H. Temeltas, M. Yesiloglu, 2009. Behavioral
task processing for cognitive robots using artificial
emotions. Neurocomputing, 72, pp.2835-2844..
Obayashi, M.,Takuno, T, Kuremoto, T., and Kobayashi, K,
2012. An Emotional Model Embedded Reinforcement
Learning System. Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on System, Man, and
Cybernetics (IEEE SMC 2012), pp. 1058-1063.
Fuping Yang, Xuewen Zhen, 2014. Research on the
Agent’s Behavior Decision-making Based on
Artificial Emotion. Journal of Information &
computational science, vol.11, No.8, pp.2723-2733.
0
pleasure
Start
Goal
activity
An Extended Q Learning System with Emotion State to Make Up an Agent with Individuality
77
Xue Hu, Ln Xie, Xin Lin, Zhiliang Wang, 2013. Emotion
Expression of Robot with Personality. Mathematical
Problems in Engineering.
Kuremoto, T., Ohta, T., Kobayashi, K., and Obayashi, M.,
2009. A Dynamic Associative Memory System
Adopting Amygdala Model. Artificial Life and
Robotics, Vol.13, No.2, pp.478-482.
Rusell, James A, 1980. A circumplex model of affect.
Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,
Vol.39(6), pp.1161-1178.
NCTA 2015 - 7th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
78
