Individual and Contextual Antecedents of Knowledge Acquisition
Capability in Joint ICT Project Teams in Malaysia
Adedapo Oluwaseyi Ojo and Murali Raman
Faculty of Management, Multimedia University, Cyberjaya, Selangor, Malaysia
Keywords: Absorptive Capacity, Individual Differences, Knowledge Acquisition Capability, Joint ICT Project Team,
Partner’s Support, Malaysia, Micro Antecedents.
Abstract: This study investigates the significance of joint ICT projects with foreign partners in the acquisition of
knowledge by local personnel in an emerging economy, based on the perspective of individual’s absorptive
capacity (i.e., ACAP). The model conceptualizes knowledge acquisition capability as the individual
dimension of ACAP and posits differences in prior experience and learning orientation as well as
individual’s perception of partner’s support as antecedents to local employees’ abilities to (i) recognize the
value of and (ii) assimilate foreign partners’ embedded knowledge. This model was validated by the results
of the structural equation modelling, conducted on a cross sectional survey of 205 local team members of
joint ICT projects in Malaysia. All the hypothesized relationships were supported, with the exception of that
between prior experience and ability to recognize the value of knowledge as well as learning orientation and
ability to assimilate knowledge. Accordingly, the theoretical and practical implications of the findings were
expatiated, with suggestions offered on the areas for future research.
1 INTRODUCTION
In support of the national drive towards attaining the
knowledge based economy, the Malaysian
Government has acknowledged technology parks as
platform to facilitate the engagement of world’s
leading firms in the local economy. One of the major
milestones was the establishment of the multimedia
super corridor (MSC) in 1996. The MSC was
inaugurated in order to advance the country to the
cutting-edge of the bourgeoning information and
communications technology (ICT) industry. The
MSC has succeeded in attracting multinational
corporations (MNCs) and international joint
ventures, thereby facilitating the growth of local ICT
talents and firms, through access to foreign
knowledge and expertise. The knowledge inflow has
been associated with institutional and policy
intervention (Ramasamy et al., 2004), inter-firm
interaction (Richardson et al., 2012; Malairaja and
Zawdie, 2004), as well as firm and employees
characteristics (Awang et al., 2013).
Absorptive capacity (ACAP) is one of the most
significant characteristics of a firm with a
constraining impact on the acquisition of external
knowledge (Lyles and Salk, 1996; Lane et al., 2001;
Raman et al., 2014). Based on R&D activities, an
organisation builds internal capability, as the
employees gain exposure and insight to new
concepts, and incorporate the learning into the firm’s
activities, thereby expanding the knowledge bases
(Cohen & Levinthal, 1990). In essence, by sharing
experience and learning, the personnel facilitates
both the individual and collective capacity to
respond to changes. Therefore, both the individual
members and the context of their engagement are
critical to the firm’s ACAP. However, extant studies
have overlooked the underlying role of individuals,
but ACAP has repeatedly been associated with the
organisational and dyadic antecedents (Lane and
Lubatkin, 1998; Jansen et al., 2005). Consequently
firm’s heterogeneity have been isolated from
differences at the individual level, thereby
dissociating organisational level outcome from the
underlying choice and actions of the members
(Volberda et al., 2010; Felin et al., 2012).
Despite the recent studies hypothesizing
individual level antecedents as prior experience
(Lane et al., 2006; Minbaeva et al., 2003; Zhao and
Anand, 2009), cognition (Zahra and George, 2002),
and task motivation (Silva and Davis, 2011; Ojo and
Raman, 2015), limited attempts have been offered to
70
Ojo, A. and Raman, M..
Individual and Contextual Antecedents of Knowledge Acquisition Capability in Joint ICT Project Teams in Malaysia.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2015) - Volume 3: KMIS, pages 70-78
ISBN: 978-989-758-158-8
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
empirically clarify these antecedents. Specifically,
the effects of individual differences on the
associated dimensions of ACAP have been
overlooked, while data have mostly originated from
single respondent or proxy measures used to infer
individual differences. Consistent with the dynamic
capability perspective, clear delineation of the
individual characteristics and interaction pertinent to
learning capabilities could offer clarification on the
path to strategic renewal (Teece, 2012). Therefore,
further to the extant emphasis on organisational
mechanisms, individual difference is another
important building block to organisational change.
Given the above, the present study investigates
the underlying differences and the implication of the
context of engagement on individual’s ACAP. The
context is the asymmetrical joint project teams, set
up to facilitate the transfer of knowledge from
expatriate to local employees in the Malaysian ICT
industry. In line with recent conceptualization on
micro-antecedents, we argued that the local team
members of the joint project teams must demonstrate
the right aptitude and disposition, in order to acquire
the foreign knowledge. The next section presents the
theoretical background for our propositions, after
which the research method is explained. This
encompasses sub-sections on the sample and
procedure, measurements, as well as analysis and
results. Furthermore, we discuss the theoretical and
practical implications of our findings. Thereafter the
concluding section considers the limitations of the
present study and offers relevant suggestions for
future research.
2 THEORETICAL
BACKGROUND
From the individual level perspective, ACAP can be
considered as the capacity to learn or acquire
knowledge (van den Bosch et al., 2003). Thus, an
organisation learns through the individual members,
who acquire knowledge by interacting and sharing
experience with others (von Krogh et al., 1994;
Crossan et al., 1999). Organisational knowledge can
be embedded in people, routines, processes, tasks or
tools, nevertheless, people’s ability in adapting
knowledge across different context is exceptional
and unique (Argote et al., 2003). Although, the
management can coordinate knowledge transfer by
motivating the local personnel, and also facilitate the
organisational processes to support strategic renewal
(Lyles and Salk, 1996), nevertheless, without the
personnel demonstrating the learning capability, the
acquisition of partner’s knowledge is unrealistic. To
this end, the learner’s knowledge receptive
capability, i.e. ACAP has been established as the key
determinant to learning in joint project teams
(Inkpen, 2008).
The present study explicates the role of
individuals in ACAP, in particular, within the
context asymmetric project team, set up to facilitate
knowledge transfer. The external knowledge is the
expertise possessed by the expatriate, but accessible
to the local employees through their engagement in
the joint project teams. Theorists have mainly
ascribed individual differences to dispositions
towards thinking, goals, values or beliefs (Lubinski,
2000; Schmitt et al., 2003). Therefore, we posit that
the knowledge acquisition capability, i.e. ACAP is a
function of the variation in individual’s experience,
disposition to learning. Furthermore, we hypothesize
the effect of the context of their engagement in terms
of partner support on the local personnel’s ACAP.
The above proposition is premised on the notion
that individual ACAP constitutes one of the building
blocks to organisational ACAP (Zahra and George,
2002; Raman et al., 2014). Thus, consistent with
Zahra and George’s (2002) theoretical exposition of
potential ACAP as an individual level capability, we
consider the two associated dimensions. First is the
ability to recognize the value of partner knowledge,
which is operationalized as the individual capability
to search, identify, and accurately evaluate the worth
of the knowledge (Ojo et al., 2014). The second
dimension is the ability to assimilate knowledge,
which is the individual capability to learn, interpret
and develop a deep understanding on valuable
knowledge (Nemanich et al., 2010). The subsequent
subsections examine the underlying hypotheses for
the above proposition.
2.1 Prior Experience
Cohen and Levinthal (1990) emphasize the
cumulative impact of learning, whereby individual’s
earlier learning influences the ability to learn new
things. Prior experience has corresponding effect on
the locus and extent of search for external
knowledge (Lane et al., 2006). Seeley and Targett
(1999) found that individual’s knowledge in a given
task diminishes as he/she engages less in updating
his/her knowledge about the task. Van Riel and
Lievens (2004) found that experienced marketing
researchers possess higher capability to interpret and
assimilate emerging market trend and incorporate
such into the design of new offerings. Based on a
Individual and Contextual Antecedents of Knowledge Acquisition Capability in Joint ICT Project Teams in Malaysia
71
sample of 208 engineers, Deng et al. (2008)
established the positive impact of prior engagement
in problem solving on innovative capability. Based
on prior experience, individuals accumulate
knowledge in the memory, which enable them to
recognize and assimilate related external knowledge.
Thus, employees with related knowledge as that
embedded in foreign partner are hypothesized to
possess the ability to access the partner’s valuable
knowledge as well as target it for assimilation. To
this end, the following hypotheses are put forward:
H1a. Prior experience in related knowledge is
positively associated with the ability of an
individual to recognize the value of foreign
partner knowledge in a joint project team.
H1b. Prior experience in related knowledge is
positively associated with the ability of an
individual to assimilate foreign partner
knowledge in a joint project team.
2.2. Learning Orientation
This is the strong disposition towards improving
competence by developing new skills and taking up
challenging tasks (Bell and Kozlowski, 2002). By
taking learning as personal responsibility, an
individual inclination is towards acquiring new
knowledge underlying the development of
competence (Hansen, 1999). Proactive minded
individuals are well disposed and attentive to others’
experience, as well as understanding and
interpretation on given concept (Ayas, 1998;
Hansen, 1999). Thereby strong orientation towards
learning could impact on the willingness to put in
the extra effort needed to acquire complex skills and
improve the knowledge based (Bell and Kozlowski,
2002; Laursen and Salter, 2006). Empirical research
on absorptive capacity within the R&D domain
(Howell and Shea, 2001) found the positive impact
of individual search effort on the identification of
valuable external knowledge. Also, Yeh (2008)
investigation on middle level engineers, confirmed
self-initiated learning as antecedent for performance.
Thus, the following hypotheses are suggested.
H2a. Learning orientation is positively
associated with the ability of an individual
to recognize the value of foreign partner’s
knowledge in a joint project team.
H2b. Learning orientation is positively
associated with the ability of an individual
to assimilate foreign partner’s knowledge
in a joint project team.
2.3 Partner’s Support
Given the competence gap between the partners, the
acquisition of knowledge by the local personnel
could be facilitated through the technical support
provided by the foreign partners. Scholars (Lane et
al., 2001; Lyles and Salk, 1996) have demonstrated
the provision of training and technological
assistance, as the support mechanisms relevant in
enabling technological acquisition in joint ventures.
The acquired knowledge is easily institutionalized,
when the transferor becomes actively engaged in
supporting the acquirer to adapt it within the specific
context (Steensma and Lyles, 2000; Kasuga, 2003).
For instance, the expatriate could support the local
employees to acquire related understanding on the
specific practices, thereby enabling the latter to
assimilate the knowledge (Inkpen, 2008; Dyer and
Nobeoka, 2000). Dhanaraj et al. (2004) assert that as
interactions deepen between partners the
collaboration becomes seamless. This is consistent
with Inkpen’s (2008) findings on the strategic
alliance between GM and Toyota. The lack of
support by the grafted managers, contributed in
GM’s initial inability to appreciate the value of
Toyota Production Systems (TPS). In addition, the
empirical significance of organisational support has
been demonstrated in the transfer knowledge to new
hires or trainee employees (Simosi, 2012). Thus, in
line with the above, we hypothesize that;
H3a. Individual’s perception of foreign partner
support is positively associated with the
ability of an individual to recognize the
value of partner’s knowledge in a joint
project team.
H3b. Individual’s perception of foreign partner
support is positively associated with the
ability of an individual to assimilate
partner’s knowledge in a joint project team.
2.4 Individual Absorptive Capacity
The individual members of the firm play the
significant role of absorbing knowledge from the
external sources. Zahra and George (2002) argued
that an organisation needs to first acquire and
assimilate external knowledge before effort could be
concentrated towards the exploitation of such
knowledge. To this end, they delineate ACAP into
potential and realized components corresponding to
individual and collective levels, respectively. The
latter is dominant at the individual level and
expressed as the abilities to (i) recognize the value of
and (ii) assimilate external knowledge. Thus,
KMIS 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
72
individuals are not just resources possessed by the
firm, but enabler of the process for the firm’s
transformation, i.e., through the acquisition of
external knowledge. Proponents of innovation
theory have acknowledged the significant role of
individuals in learning from firm activities (Nelson
and Winter, 1977; Allen, 1977). For instance R&D
activities can be considered as firm’s investment in
building employees’ capability to search for internal
technological and organisational knowledge.
An individual’s ability to assimilate external
knowledge is conditioned on his/her ability to
recognize how such knowledge relates to the
cognitive map already stored in the memory
(Todorova and Durisin, 2007). The cognitive map is
the pattern of association that impacts an
individual’s search for and categorization of new
information (Tripsas and Gavetti, 2000). This map
enables an individual to exert the knowledge search
effort on an area with the most significant value to
the assigned task. Thus, the aptitude of an individual
in recognizing the value of knowledge can be
associated with efficient search effort, which in turn
can facilitate his/her commitment to understand the
specific valuable knowledge (Lettl et al., 2008). The
investigation of Nemanich et al. (2010) on U.S.-
based research teams supported the positive
relationship between the ability of the team member
to evaluate external knowledge and the ability to
assimilate the knowledge.
H4. Individual’s ability to recognize the value
of foreign partner’s knowledge is positively
associated with the ability to assimilate the
knowledge in a joint project team.
3 METHOD
3.1 Sample and Procedure
A random sample of local ICT professionals
engaged in joint projects with expatriates was
selected across 62 joint ventures on the list of active
MSC-status companies. To facilitate the data
collection, human resource (HR) personnel in each
firm was designated as contact persons. The contact
persons were requested to randomly select ICT
project teams constituted by the local personnel and
expatriates in their respective firms, and to
administer the questionnaires on the former. They
were specifically instructed to select two to three
local personnel who were directly attached with the
expatriates from each of the identified project team.
Out of a total of 390 questionnaires sent out, 205
valid responses were returned, corresponding to an
overall response rate of 52.6 percent. In order to
ascertain the absence of non-response bias, we
obtained the demographic profiles for the non-
respondents from the contact person. Accordingly,
series of χ2 and t test were computed to compare the
respondents (n= 205) with those who had not
completed the questionnaires (n= 185). Based on the
outcomes, responses were found not to be selective
for age, education level, work experience, joint team
tenure, as well as job position (p > 0.05).
The demographic profiles of the respondents are
presented as follow. More than 81 percent of the
respondents were above the age of 26 years, and
73.1 percent had at least a bachelor degree.
Moreover, 67.8 per cent of the respondents had
acquired professional experience of at least four
years, while two-thirds of the respondents had been
engaged in at least two joint project teams. In terms
of job positions, almost half of the respondents (49.8
percent) were system analysts, while 17.5 per cent
were project managers. Programmers and system
designers made up 16.2 and 12.4 percent of the total
respondents, respectively, and the remaining 4.1
percent accounted for other positions, such as testers
and technical support.
3.2 Measurements
All the constructs were measured with scales
adapted from extant literature, and the assessment
based on the five-point Likert scale (ranging from 1
= strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree). We
conducted the pilot testing for the initial
questionnaire, with a sample of 35 respondents
selected from across the joint ventures ICT firms on
the list of active MCS-status companies. These
respondents were excluded from the final survey.
The majority of the respondents (i.e. 55%) are
within the age group of 26 – 35 years, followed by
those within 36 – 45 years (i.e.19%). More than 68%
had at least a bachelor degree and about 70% had
acquired professional experience of at least four
years. Moreover, 75% of the respondents have been
engaged in at least 2 joint project teams and 55% of
them are system analyst. Based on their comments
and statistical assessment, some of the questions
were rephrased to improve clarity and content
validity. In addition, we ensured that the anonymity
of the respondents were preserved, as promised in
the enclosed cover letter, thereby minimizing the
effects of social desirability and biasness associated
with self-reported survey.
Individual and Contextual Antecedents of Knowledge Acquisition Capability in Joint ICT Project Teams in Malaysia
73

Prior experience was operationalized as the
quantity of the accumulated knowledge that is
related to the new external knowledge (Cohen and
Levinthal, 1990). Thus, respondents were asked to
assess the extent to which they agree with five (5)
statements describing the level of their possessed
general and theoretical knowledge (Gimeno et al.,
1997), training, work experience and expertise
(Cooper et al., 1994; Huber, 1991) on the project.
The Cronbach’s alpha for this construct was 0.91.
Learning orientation was operationalized as the
disposition to ask mastery and measured with five
adopted from VandeWalle (1997). The Cronbach’s
alpha for the constructs was 0.92.
The measurement scale for partner’s support
consists of three items obtained from inter-firm
knowledge transfer literature (Lyles and Salk, 1996;
Lane et al., 2001; Minbaeva et al., 2003). These
items assess the extent to which the foreign
employees are accessible and helpful, and actively
participated in the joint project.
The ability to recognize the value of partner’s
knowledge was operationalized as the capability to
accurately evaluate the worth of knowledge and the
ability to assimilate partner’s knowledge was
operationalized as the capability to learn, interpret,
and develop a deep understanding of valuable
knowledge (Nemanich et al., 2010; Ojo et al., 2014).
Both were measured by two different sets of four
items. Specifically, the respondents were asked to
assess the extent to which they agree with certain
statements that describe their engagement in joint
project teams. The Cronbach’s alpha was 0.89 and
0.88 for the ability to recognize and the ability to
assimilate partner’s knowledge, respectively.
3.3 Analysis and Results
In order to ascertain the non-significance of common
method variance, the Harman’s one-factor test was
conducted (Podsakoff and Organ, 1986). The
outcome from the single un-rotated EFA on all the
constructs revealed the absence of common factor.
The largest factor accounted for 32.71% of the total
74.70% variance explained by all the five factors,
with eigenvalues greater than 1.00. Consequently,
the overall measurement model for the five
constructs was evaluated in a single CFA procedure
(Anderson and Gerbing, 1988). All the items loaded
on their specified factors. The composite reliability
(CR) and average variance extracted (AVE) values
were computed from the CFA loadings. As shown in
Table 1, the AVE and CR values are above the cut-
off criterion of 0.50 (Fornell and Larcker, 1981) and
0.7 (Hair et al., 2010), respectively. Thus,
convergent validity was demonstrated for all of the
constructs.
Table 1: Measurement Scales and Standardized CFA
Estimates.
Constructs and items Std. Est
.
Prior Experience (CR = 0.91; AVE = 0.68)
I had the required general knowledge on the
project.
.806
I had acquired substantial theoretical knowledge. .852
I had attended extensive training in related area. .811
I had substantial working experience in related
area.
.847
I had acquired some level of ex
p
ertise in related
area.
.731
Learning Orientation (CR = 0.92, AVE=0.69)
I am willing to pursue challenging tasks from
which I can learn new things.
.756
I often look for opportunities to develop new
skills and knowledge.
.797
I prefer taking up challenging and difficult tasks
at work from which I can learn new skills.
.913
I am willing to put in extra effort where
necessary to develop new skills and enhance my
knowledge.
.872
I prefer to work in environments that require a
high level of ability and talent.
.796
Partner’s Support (CR=0.87, AVE=0.69)
I received adequate technical support from the
foreign partner
.654
I received relevant training from the foreign
partner
.745
I received timely and helpful assistance from
foreign partner
.895
Ability to Recognize (CR = 0.88, AVE=0.64)
I was able to develop awareness on partner’s
knowledge.
.842
I was able to keep track of partner’s knowledge,
by consulting other sources of information.
.833
I was able to identify partner’s knowledge with
the most significant value to the project
performance.
.827
I was capable at accurately evaluating the worth
of partner’s knowledge in the project.
.691
Ability to Assimilate (CR = 0.89, AVE=0.66)
I was able to learn the use of partner’s
knowledge.
.801
I was capable at understanding the knowledge
associated with project.
.850
I was adept at interpreting the use of the
knowledge associated with the project.
.845
I tried to experiment with the knowledge
associated with the project.
.748
KMIS 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
74
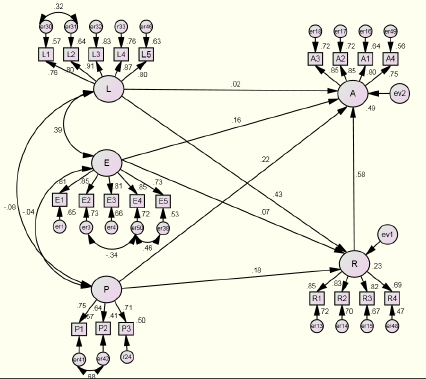
Sequel to the above, the structural model was
evaluated by replacing the covariance paths (i.e.
double edged arrows) associated with the
endogenous variable with the hypothesized
structural paths (i.e. single edged arrows). The
selected goodness-of-fit indices from the AMOS 18
package revealed a good fit to data (i.e. χ2 = 127.765
/ p=.390; RMSEA = .011 / p-close = 1.000; CFI =
.997, TLI = .997). Specifically, the value of p for the
χ2 was not significant, i.e., > 0.05, thus the model
can be regarded as acceptable (Bagozzi and Yi,
2012). As a result, the model was employed in
testing the hypothesized effects.
As shown in Figure 1, the relationship between
prior experience (E) and the ability to assimilate
knowledge (A) was significant (β= .16, p < .05),
however, the relationship between the former and
ability to recognize the value of knowledge (R) was
not significant. Thus, H1b was supported, but H1a
was not supported. The path from learning
orientation (L) to ability to recognize the value of
knowledge was significant (β= .43, p < .001), but the
path to ability to assimilate knowledge was not.
Thus, H2a was supported, but H2b was not
supported. Furthermore, both H3a and H3b were
supported, with a significant path obtained from
partner’s support (P) to ability to recognize the value
of knowledge (β= .18, p < .05) and ability to
assimilate knowledge (β= .22, p < .01), respectively.
Finally, the individual’s ability to recognize the
value of knowledge was determined to be
significantly related to the ability to assimilate
knowledge (β= .58, p < .001). Thus, H4 was
supported.
Figure 1: Standardized Path Estimates.
4 DISCUSSION
The present study advances the dynamic capability
perspective to develop a model which demonstrates
the role of team members and the context of their
engagement in strategic renewal, thereby suggesting
individual differences as another antecedent of
learning, in addition to the widely acknowledged
organisational and environment factors (Teece,
2012). Specifically, the current study investigates
the pertinent antecedents of the individual ACAP,
thus contributing to extant literature in several
aspects.
Further to the theoretical notion on the existence
of potential ACAP at the individual level (Zahra and
George, 2002) this study empirically validates its
pertinent dimensions, i.e. ability to recognize the
value of and ability to assimilate foreign partner’s
knowledge. As revealed in this study, individuals
that have recognized the value of foreign partner’s
knowledge in their assigned task are able to develop
better understanding on the relevance of such
knowledge in the joint project team. Thus, the
recognition of the value of knowledge can facilitate
deeper assimilation, in that the effort could be fully
channelled toward uncovering the underlying
knowledge bases.
Our findings corroborate the varying effect of
prior experience on ACAP (Cohen and Levinthal,
1990; Minbaeva et al., 2003). We found that the
prior experience acquired by an individual in an area
related to the joint ICT project could impact on his /
her ability to assimilate the partner’s knowledge (i.e.
H1b). Surprisingly, the former was determined not
to be associated with the ability to recognize the
value of partner’s knowledge (i.e. H1a). Even
though this challenges the theoretical notion on
ACAP, yet, it conforms to Lane and Lubatkin’s
(1998) findings – firm’s engagement in R&D (i.e.,
knowledge acquisition) was not related to the
variance of ACAP. This outcome is also in line with
the path dependence nature of learning. Individual’s
understanding could deepen with the possession of
prior related knowledge, but this might have little or
no appreciable impact on his/her ability to recognize
the value of knowledge. According to Cohen and
Levinthal (1990) an individual’s mental model
accumulated in the memory evolves along the path
of his/her exposure. Therefore, unless concerted
effort is channelled toward exploring new things, an
individual’s interpretation of future phenomena
could be limited by the mental model.
Moreover, individual’s learning orientation was
significantly associated with the ability to recognize
Individual and Contextual Antecedents of Knowledge Acquisition Capability in Joint ICT Project Teams in Malaysia
75
the value of knowledge, i.e., H2a, but not ability to
assimilate knowledge, i.e. H2b. This reinforces the
complementary nature of prior related knowledge
and learning disposition (Cohen and Levinthal
1990). Except concerted effort is exerted to
exploring new things, individual’s interpretation of
new concept could be limited by the mental model
already registered in the memory. Crossan et al.
(1999) revealed that the ability to recognize new
knowledge is conditioned on the recognition of a
similar pattern in the memory. Learning-oriented
people are opened to experiencing new things (Brett
and VandeWalle, 1999) and self-directed (Yeh,
2008). Thus, they are more likely to break barriers
and cross boundaries in their drive towards task
mastery, especially when they perceive their skill set
as inadequate. As a result, their disposition is suited
to putting in the necessary effort towards uncovering
patterns related to that already stored in the memory,
thereby facilitating the recognition of the value of
new knowledge.
As hypothesized, foreign partner’s support was
determined to be associated with both ability to
recognize the value of knowledge and ability to
assimilate knowledge. Given the asymmetric nature
of the joint project, knowledge acquisition by the
local team members could be fast tracked when the
foreign partners facilitate the adaption and
dissemination of the embedded knowledge to the
former. The target knowledge is tacit and embedded
in practice so that team member interactions can
enable stronger ties and the sharing of experience
and perspective. By providing adequate support to
and engaging actively with the local partner, the
foreign partner can deepen the strength of social ties
within the joint project team (Uzzi & Lancaster,
2003). Thus, the extent of support provided by the
expatriates grafted into the joint project team, as
perceived by the local members, could impact the
acquisition of knowledge.
Our findings have implications for the
management of joint ICT project teams in Malaysia.
It is essential that the managerial and leadership
drive for the upgrade of local capability through the
acquisition of competent partners’ knowledge be
supported with the engagement of personnel with the
underlying learning capabilities. In addition to the
organisational norm of recruiting experienced
personnel, the management should also consider
their disposition to learning. The ability to
recognize the value of new knowledge requires the
commitment of effort towards uncovering patterns
related to that already stored in the memory.
Therefore, individual learning disposition
complements prior related experience in order to
facilitate the recognition and assimilation of new
knowledge. With respect to the significance of
foreign partner’s support, the local partner should
ensure that the contractual agreement with the
former explicitly state the level of support to be
provided to the local team members. By ensuring
supportive collaboration, the local team members of
the joint project teams could be enabled to identify
and assimilate the knowledge embedded in the
foreign partner. This could enable them to develop
close relationship with and be connected enough to
the expatriates to seek clarification, when relevant,
without fear of rejection. Basically, when the
expatriates are perceived as helpful, the local
members are better disposed to approach them for
assistance. Likewise, the former will take proactive
measures to facilitate problem resolution.
Furthermore, the ability to assimilate knowledge
requires the development of deeper insight, which is
evident in the mastery of procedures / methods
underlying the task.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study advances the micro-level perspective of
ACAP, by demonstrating the effects of individual
differences and the context of their engagement on
knowledge acquisition capability. Thus, further to
the clarification of the role of individuals in the
acquisition of knowledge from joint project teams,
this study also offers opportunities for further
research. Future studies should attempt to clarify the
effects of other antecedents on both the individual
and collective components of ACAP. There is also
need for study to investigate the mechanisms
through which individual components are linked to
the collective components. The impact of cultural
differences on ACAP within joint project is another
important area for future studies. Furthermore,
subsequent studies are expected to address some of
the limitations of this study. The use of longitudinal
design is recommended, so as to capture the
underlying temporal and causal effects of ACAP.
Also, the attendant weakness of the self-reported
survey could be minimized by incorporating data
from other sources. For example, future studies
should consider the perspective of the foreign team
members on the ACAP dimensions. Finally, the
validated model should be extended to other
contexts, in order to ascertain the generalization of
the findings.
KMIS 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
76
REFERENCES
Allen, T. J. (1977). Managing the Flow of Technology.
Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Argote, L., McEvily, B. and Reagans, R. (2003).
Managing knowledge in organisations: an integrative
framework and review of emerging themes.
Management Science, 49(4), 571-582.
Anderson, J. C. and Gerbing, D. W. (1988). Structural
equation modeling in practice: A review and
recommended two stage approach. Psychological
Bulletin 27(1), 5-24.
Awang, A. H., Hussain, M. Y. and Malek, J. A. (2013).
Knowledge transfer and the role of local absorptive
capability at science and technology parks. The
Learning Organisation, 20(4/5), 291-307.
Ayas, K. (1998). Learning through projects: meeting the
implementation challenge. In R., Lundin and C.
Midler (Eds.), Projects as arenas for renewal and
learning processes (pp. 89-98). USA: Kluwer
Academic Publishers.
Bagozzi, R. P. and Yi, Y. (2012). Specification,
evaluation, and interpretation of structural equation
models. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science,
40(1), 8-34.
Bell, B. S., and Kozlowski, S. W. J. (2002). Goal
orientation and ability: Interactive effects on self-
efficacy, performance, and knowledge. Journal of
Applied Psychology, 87(3), 497–505.
Brett, J. F. and VandeWalle, D. (1999). Goal orientation
and specific goal content as predictors of performance
in a training program. Journal of Applied Psychology,
84(6), 863–873.
Cohen, W. M., and Levinthal, D. A. (1990). Absorptive
Capacity: A new perspective on learning and
innovation. Administrative Science Quarterly, 35(1)
128-152.
Cooper, A. C., Gimeno-Gascon, F. J., and Woo, C. Y.
(1994). Initial human and financial capital as
predictors of new venture performance. Journal of
Business Venturing, 9(5), 371-395.
Crossan, M., Lane, H., and White, R. (1999). An
organisational learning framework: From intuition to
institution. Academy of Management Review, 24, 522-
538.
Deng, X., Doll, W. J., and Cao, M. (2008). Exploring the
absorptive capacity to innovation/ productivity link for
individual engineers engaged in IT enabled work.
Information and Management, 45, 75-87.
Dhanaraj, C., Lyles, M. A., Steensma, H. K., & Tihanyi,
L. (2004). Managing tacit and explicit knowledge
transfer in IJVs: The role of relational embeddedness
and the impact on performance. Journal of
International Business Studies, 35(5), 428-442.
Dyer, J.H. and Nobeoka, K. (2000), “Creating and
managing a high-performance knowledge-sharing
network: The Toyota case”, Strategic Management
Journal, 21(3), 345-367.
Felin, T., Foss, N.J., Heimeriks, K.H. and Madsen, T.L.
(2012). Microfoundations of routines and capabilities:
individual processes and structure. Journal of
Management Studies, 49(8), 1351-1374.
Fornell, C. and Larcker, D.F. (1981). Evaluating structural
equation models with unobservable variables and
measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research,
18, 39-50.
Gimeno, J., Folta, T. B., Cooper, A. C., and Woo, C. Y.
(1997). Survival of the fittest? Entrepreneurial human
capital and the persistence of underperforming firms.
Administrative Science Quarterly, 42, 750-783.
Hair, J. F. Jr., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., and Anderson, R.
E. (2010). Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global
Perspective (7th ed.). New Jersey: Pearson Education
Inc.
Hansen, M. (1999). The search-transfer problem: The role
of weak ties in sharing knowledge across organisation
subunits. Administrative Science Quarterly, 44(1), 82–
111. 178).
Howell, J. M. and Shea, C. M. (2001). Individual
differences, environmental scanning, innovation
framing, and champion behaviour: Key predictors of
project performance. The Journal of Product
Innovation Management, 18, 15–27.
Huber, G. P. (1991). Organisational learning: The
contributing processes and the literature. Organisation
Science, 2, 88–115.
Inkpen, A. C. (2008). Knowledge transfer and internatio-nal
joint ventures: The case of NUMMI and General
Motors. Strategic Management Journal, 29(4), 447-453.
Jansen, J. J. P., Van Den Bosch, F. A. J., and Volberda, H.
W. (2005). Managing potential and realized absorptive
capacity: How do organisational antecedents matter?
Academy of Management Journal, 48(6), 999-1015.
Kasuga, H. (2003). Capital market imperfections and
forms of foreign operations, International Journal of
Industrial Organization, 21, 1043–1064.
Lane, P. J., and Lubatkin, M. (1998). Relative absorptive
capacity and interorganisational learning. Strategic
Management Journal, 19(5), 461-77.
Lane, P. J., Koka, B. R., and Pathak, S. (2006). The
reification of absorptive capacity: A critical review
and rejuvenation of the construct. Academy of
Management Review, 31(4), 833-863.
Lane, P. J., Salk, J. E. and Lyles, M. A. (2001). Absorptive
capacity, learning, and performance in international
joint ventures. Strategic Management Journal, 22(12),
1139-1161.
Laursen, K., and Salter, A. (2006). Open for innovation:
The role of openness in explaining innovation
performance among U.K. manufacturing firms.
Strategic Management Journal, 27, 131-150.
Lettl, C., Hienerth, C., and Gemuenden, H. G. (2008).
Exploring how lead users develop radical innovations;
Opportunity recognition and exploitation in the field
of medical equipment technology. IEEE Transaction
on Engineering Management, 55,
219–233.
Lubinski, D. (2000). Scientific and social significance of
assessing individual differences: Sinking shafts at a
few critical points. Annual Review of Psychology,
51(1), 405–444.
Individual and Contextual Antecedents of Knowledge Acquisition Capability in Joint ICT Project Teams in Malaysia
77
Lyles, M.A. and Salk, J.E. (1996). Knowledge acquisition
from foreign parents in international joint ventures: an
empirical examination in the Hungarian context.
Journal of International Business Studies, 27(5), 877-
903.
Malairaja, C. and Zawdie, G. (2004). The ‘black box’
syndrome in technology transfer and the challenge of
innovation in developing countries. International
Journal of Technology Management and Sustainable
Development, 3(3), 233-251.
Minbaeva, D., Pedersen, T., Björkman, I., Fey, C. and
Park, H. J. (2003). MNC knowledge transfer,
subsidiary absorptive capacity, and HRM. Journal of
International Business Studies, 34(6), 586-599.
Nelson, R. R., and Winter, S. G. (1977). In search of
useful theory of innovation. Research Policy, 6(1), 36-
76.
Nemanich, L. A., Keller, R. T., Vera, D. and Chin, W. W.
(2010). Absorptive capacity in RandD project teams:
A conceptualization and empirical test. IEEE
Transactions on Engineering Management, 57(4),
674-688.
Ojo, A. O. and Raman, M. (2015). Micro perceptive on
absorptive capacity in joint ICT project teams in MSC
Malaysia status companies. Library Review, 64(1/2),
162 – 178.
Ojo, A. O., Raman, M., Chong, S. C., and Chong, C. W.
(2014). Individual antecedents of ACAP and
implications of social context in joint engineering
project teams: A conceptual model. Journal of
Knowledge Management, 18(1), 173-197.
Podsakoff, P. M., and Organ, D. W. (1986). Self-reports in
organisational research: Problems and prospects.
Journal of Management, 12(4), 531-544.
Raman, M., Ojo, A. O., and Chong, C. W. (2014),
“Absorptive Capacity in joint project teams: Evidence
from Nigerian upstream oil industry”, Proceedings of
the 6th International Conference on Knowledge
Management and Information Sharing, Rome; Italy;
21-24 October 2014, pp.140-145.
Ramasamy, B., Chakrabarty, A. and Cheah, M. (2004).
Malaysia’s leap into the future: an evaluation of the
multimedia super corridor. Technovation, 24, 871-883.
Richardson, C., Yamin, M., and Sinkovics, R. R. (2012).
Policy-driven clusters, interfirm interactions and firm
internationalization: Some insights from Malaysia’s
multimedia super corridor. International Business
Review, 21, 794-805.
Schmitt, N., Cortina, J. M., Ingerick, M. J., and
Wiechmann, D. (2003). Personnel selection and
employee performance. In W. C. Borman, D. R. Ilgen,
and R. J. Klimoski (Eds.), Handbook of psychology
(pp. 77–105). London: Wiley.
Seeley, M., and Targett, D. (1999). Patterns of senior
executives’ personal use of computers. Information
and Management 35(6), 315–330.
Silva, N. D. and Davis, A. R. (2011). Absorptive capacity
at the individual level: Linking creativity to innovation
in academia. The Review of Higher Education, 34(3),
355-379.
Simosi, M. (2012), “Disentangling organizational support
construct: The role of different sources of support to
newcomers’ training transfer and organizational
commitment”,
Personnel Review, 41(3), 301-320.
Steensma, K. and Lyles, M.A. (2000), “Explaining IJV
survival in a transitional economy through social
exchange and knowledge-based perspectives”,
Strategic Management Journal, (21)8, 831–852.
Teece, D.J. (2012). Dynamic capabilities: Routines versus
entrepreneurial action. Journal of Management
Studies, 49(8), 1395 - 1401.
Todorova, G. and Durisin, B. (2007). Absorptive capacity:
valuing a reconceptualization. Academy of
Management Review, 32(3), 774–786.
Tripsas, M., and Gavetti, G. (2000). Capabilities,
cognition, and inertia: Evidence from digital imaging.
Strategic Management Journal, 21, 1147–1161.
Uzzi, B. and Lancaster, R. (2003), “Relational
embeddedness and learning: the case of bank loan
managers and their clients”, Management Science,
49(4), 383–399.
Van den Bosch, F. A. J., Van Wijk, R., and Volberda. H.
W. (2003). Absorptive capacity: Antecedents, models
and outcomes. In M. Easterby–Smith and M.A. Lyles
(Eds.), The Blackwell Handbook of Organisational
Learning and Knowledge Management (pp.278-301),
Oxford, UK: Blackwell.
Van Riel, A. C. R. and Lievens, A. (2004). New service
development in high tech sectors: A decision making
perspective. International Journal of Service Industry
Management, 15(1), 72–101.
VandeWalle, D. (1997). Development and validation of a
work domain goal orientation instrument. Educational
and Psychological Measurement, 57(6), 995-1015.
Volberda, H. W., Foss, N. J., and Lyles, M. A. (2010).
Absorbing the concept of absorptive capacity: How to
realize its potential in the organisation field.
Organisation Science, 21(4), 931-951.
von Krogh, G., Ross, J. and Slocum, K. (1994). An easy
on corporate epistemology. Strategic Management
Journal, 15(Special Issue): 53-71.
Zahra, S. A., and George, G. (2002). Absorptive capacity:
A review, reconceptualization, and extension.
Academy of Management Review, 27(2), 185-203.
Zhao, Z. J., and Anand, J. (2009). A multilevel perspective
on knowledge transfer: Evidence from the Chinese
automotive industry. Strategic Management Journal,
30, 959-983.
Yeh, Q. J. (2008). Exploring career stages of midcareer
and older engineers: When managerial transition
matters. IEEE Transaction on Engineering
Management, 55(1), 82–93.
KMIS 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
78
